Kinesiology (PSK4U)
1/265
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
266 Terms
closes eyelid
obicularis oculi
flares nostrils
nasalis

lip muscle
obicularis oris
raises eyebrows
frontalis
rotation and lateral flexion of cervical vertebrae
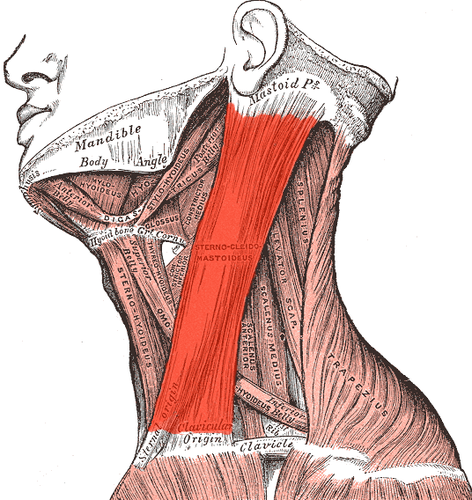
Sternocleidomastoid
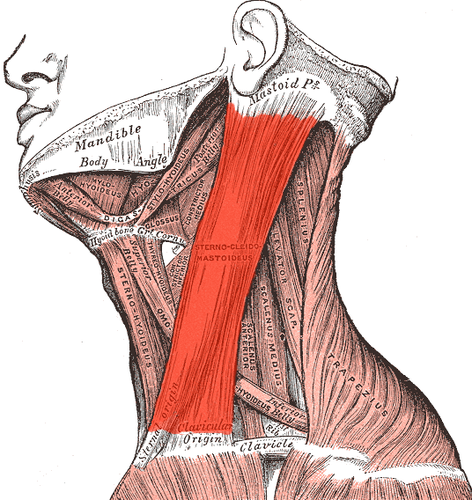
origin - manubrium and clavicle (medial portion)
insertion - masteiod process of temporal bone
Sternocleidomastoid origin & insertion
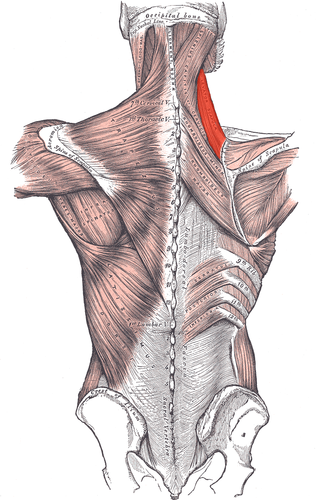
elevates scapula
levator scapulae
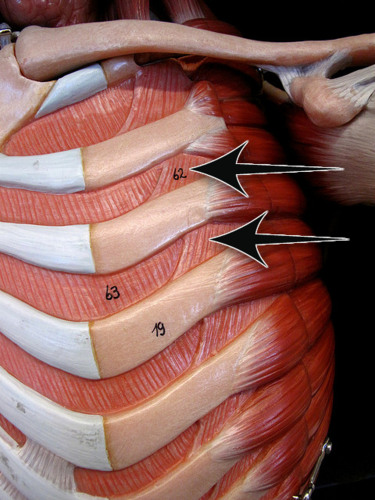
elevation and depression of ribs, used for breathing
intercostal muscles
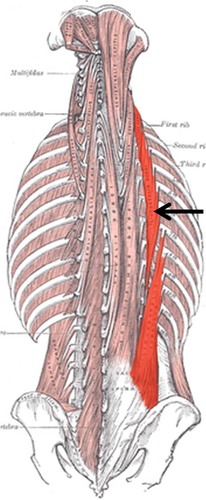
extends vertebral column
erector spinae
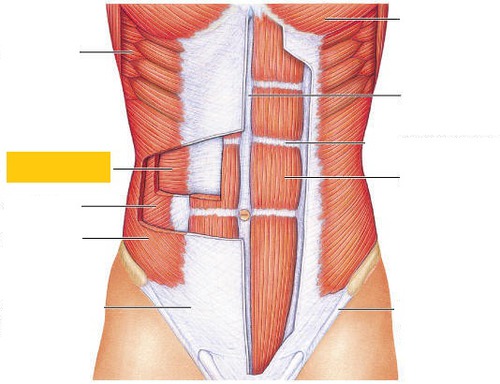
compresses abdomen and stabilizes trunk
transverse abdominis
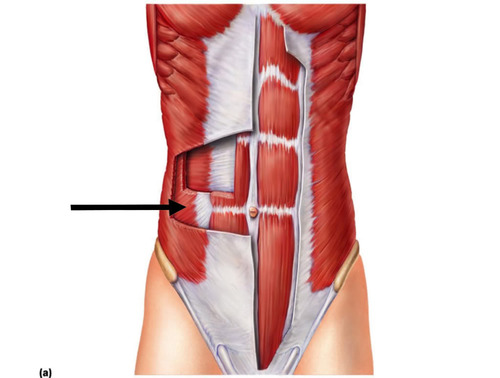
flexion of lumbar spine
rectus abdominis

compression of abdomen
internal obliques
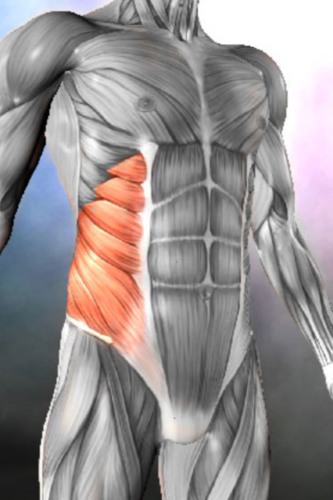
rotation of torso
external obliques
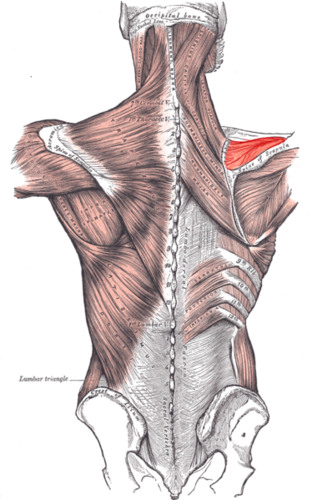
elevates, depresses, retracts, and rotates the scapula
trapezius
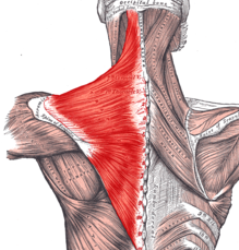
origin - occipital protuberance and spinous process of C7-T12
insertion - lateral clavicle, spine of scapula, acromion process
trapezius origin & insertion

retracts scapula
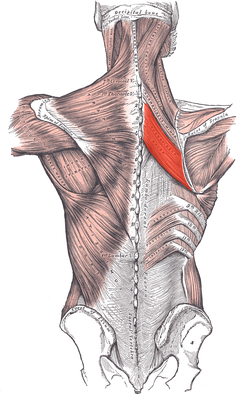
rhomboid major
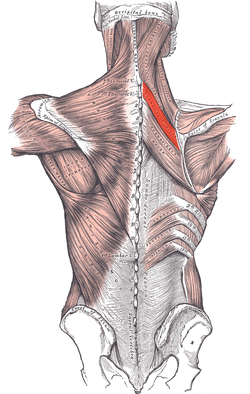
retracts scapula and minor rotation of scapula
rhomboid minor
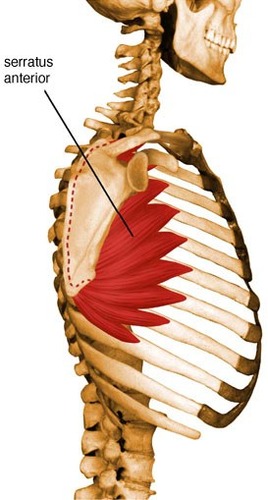
protraction of scapula and assists in upward rotation
serratus anterior
stabilizes scapula
pectoralis minor
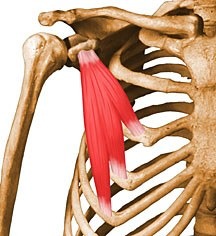
abducts arm
supraspinatus
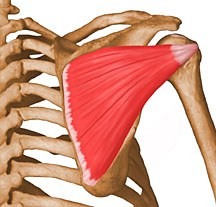
rotates arm laterally
infraspinatus
rotates arm laterally
teres minor
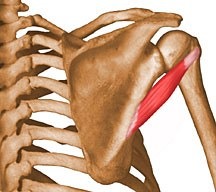
medially rotates arm
subscapular
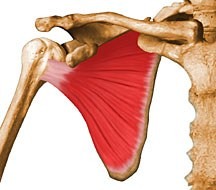
shoulder abduction, flexion and extension
deltoid
origin - anterior portion of the clavicle, acromion, and scapular spine
insertion - deltoid tuberosity
deltiod origin & insertion
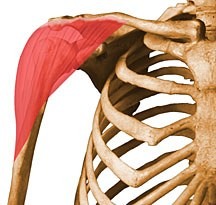
adduction and medial rotation of humerus, draws scapula anteriorly
pectoralis major
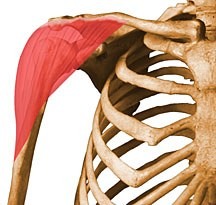
origin - clavicle (anterior/medial) and sternum (anterior)
insertion - intertubracle groove (humerus)
pectoralis major origin & insertion

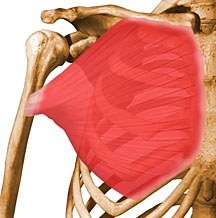
extends, adducts, and rotates arm internally
latissimus dorsi
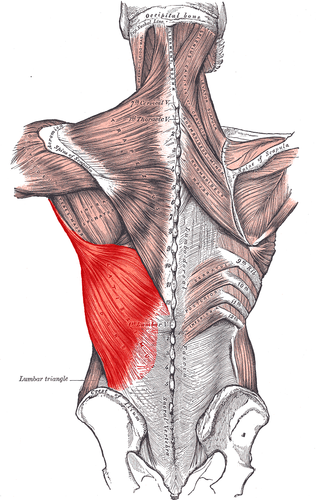
origin: spinous process T7-L5, illiac crest, inferior angle (scapula), ribs 9-12
insertion: intratubracular groove (humerus
latissimus dorsi origin & insertion
internal rotation of the humerus
teres major

felxion at the elbow, supination of the forearm
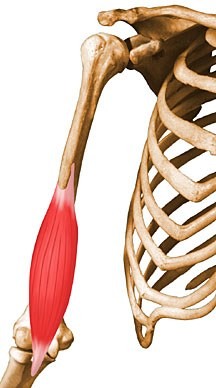
biceps brachii
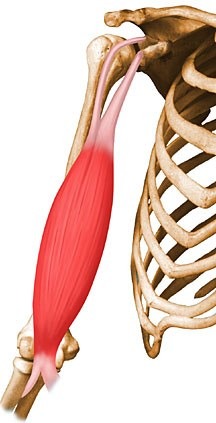
origin: coracoid process and supraglenoid tubracle
insertion: radial tuberosity
biceps brachii origin & insertion
extension at the elbow, extension of the shoulder
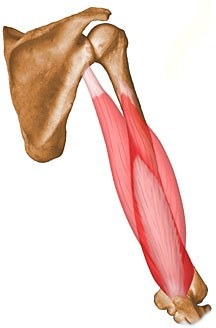
triceps brachii
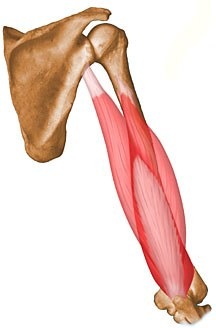
origin: infraglenoid tuberacle of scapula (long head), shaft of humerus (medial and lateral head)
triceps brachii origin & insertion
flexion of elbow
brachialis
pronation of forearm, flexion of elbow
pronator teres
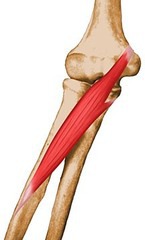
assists with extension of the elbow (blends with triceps)
Anconeus
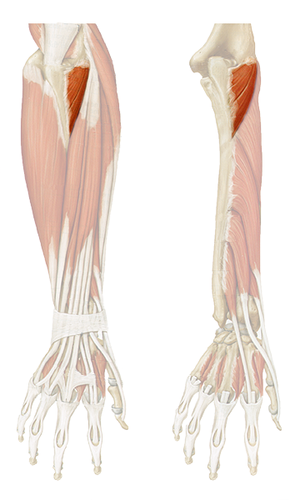
flexion of wrist
flexor carpi radialis
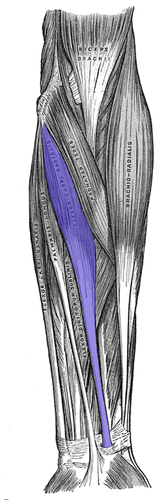
flexion of wrist
flexor carpi ulnaris

extention of wrist
extensor capri radialis longus
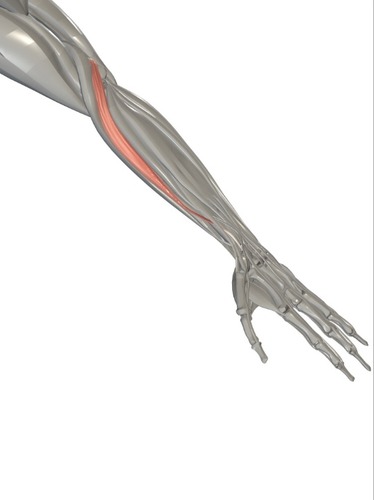
extension of wrist
extensor carpi ulnaris
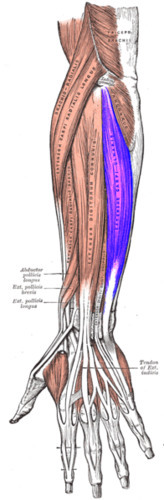
extension and external rotation of hip
gluteus maximus

origin: gluteal surface of ilium and sacrum
insertion: gluteal tuberosity (femur), IT tract
gluteus maximus origin & insertion
abduction of hip
gluteus medius
abduction of hip
gluteus minimus

felxion of hip/trunk
ilipsoas major

felxion of hip/trunk
ilipsoas minor
external rotation of the thigh
piriformis
flexion, abduction, and medial rotation of thigh
tensor fasciae latae
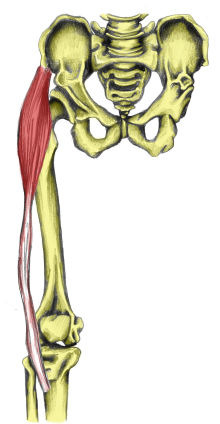
extension of hip, flexion of knee
semimenbranosus (hamstring)
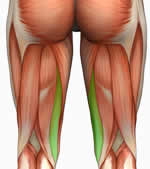
extension of hip, flexion of knee
semitendinosus (hamstring)
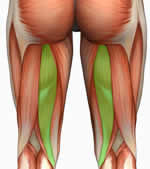
extension of hip, flexion of knee
biceps femoris (hamstring)

adduction of hip
pectinues
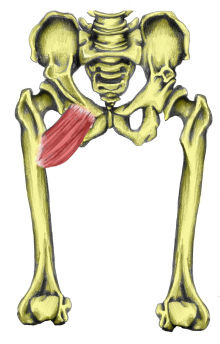
adduction of hip
adductor brevis
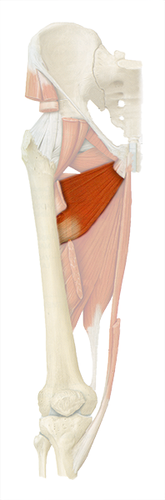
adduction of hip
adductor longus
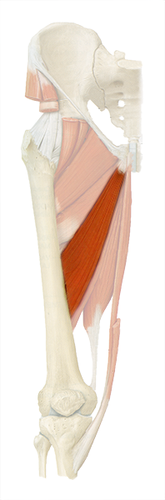
adduction, flexion, extension of hip
adductor magnus
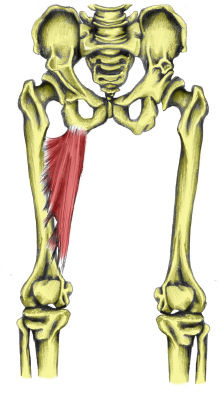
abduction, flexion, lateral rotation of hip
sartorius
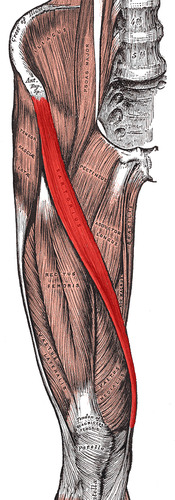
extension of knee, flexion of hip
rectus femoris
origin: anterior inferior portion of iliac spine
insertion: quadriceps tendon via patella
rectus femoris origin & insertion
extension of knee
vastus lateralis
extension of knee
vastus intermedius
extension of knee
vastus medialis
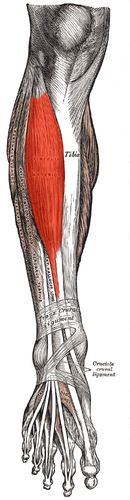
dorsiflexion and inversion
tibialis anterior
extension of toes (lateral 4), dorsiflexion
extensor digitorum longus

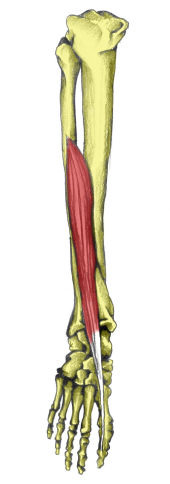
extension of big toe, dorsiflexion
extensor hallucis longus
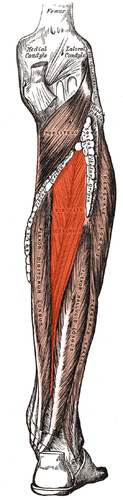
planatar flexion, inversion
tibialis posterior
flexion of toes (lateral 4), plantar flexion
flexor digitorum longus
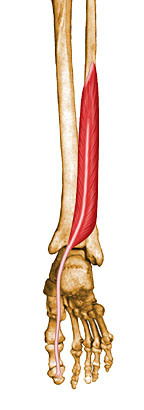
flexion of big toe, plantar flextion
flexor hallucis longus
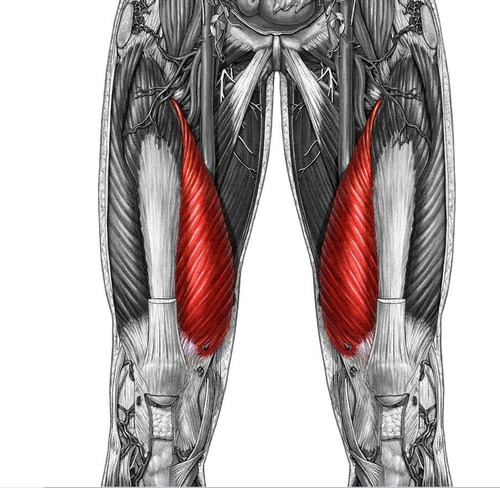
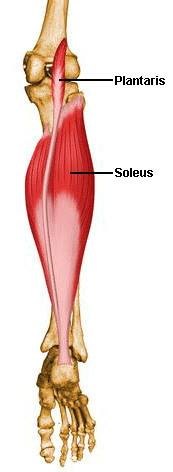
plantar flexion
soleus
plantar flexion, flexion of knee
gastrocnemius
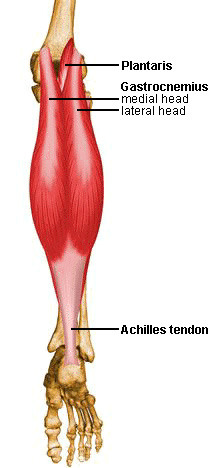
origin: lateral and medial condyles of femur
insertion: achillies tendon via calcaneus
gastrocnemius origin & insertion
muscle tissue found only in the heart, involuntary
cardiac muscle
muscle tissue found only in internal organs, involuntary
smooth muscle
a muscle that is connected to the skeleton that allows movement, voluntary
skeletal muscle

connect bone to bone
ligaments

connects muscle to bone
tendons
avascular connective tissue, provides structure support and cushioning
cartilage
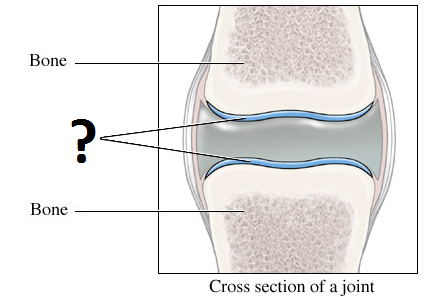
found at ends of bone and free moving joints
hyaline cartilage
liquid filled membrane that protects soft tissues, reduces friction where 2 bony parts of the body rub together
bursa
vascular, elastic ablility
muscles properties
Myosin filaments attach to actin filaments when calcium is relased and the tropomysoin and troponin that prevents the myosin and actin from attaching is "distracted" by the calcium. ADP + Pi is released when the myosin and actin attach, the myosin pulls the actin forward then relases. An ATP molecule then attaches to the myosin which allows it to "reload" and attach to another actin and repeat the process until the calcium are removed and the tropomysoin and troponin return to their normal state.
Sliding fliament theory
attachement to an immovable bone, proximal
origin
attachment to movable bone, distal
insertion
the action/motion when the muscle is activated
function
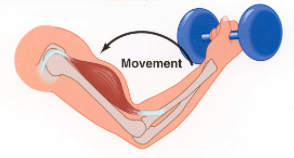
muscle fibres shorten
concentric contraction
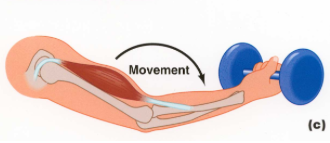
muscle fibres lengthen
eccentric contraction
muscle fibres do not change in length
issometric contraction
controlled shortening and lengthening of the muscle
isotonic exercise
muscle fibres maintain a constant length throughout contraction
isometric exercise
use of machines to control speed of contractions, combines best parts of isometric and isotonic exercise
isokinetic exercise
epimysum extends past the muscle as a tendon which attaches to the periosteum of a bone
inderect muscle attachment
epimysium adheres to and fuses to the periosteum
direct muscle attachment
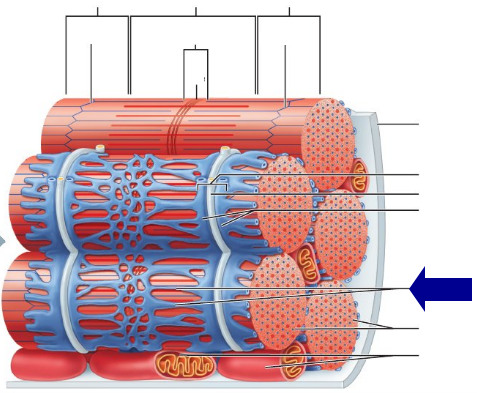
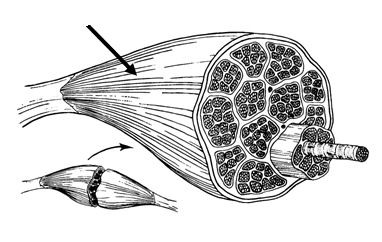
binds muscle fibres together
perimysium
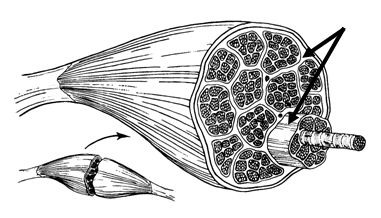
surrounds entire muscle
epimysium
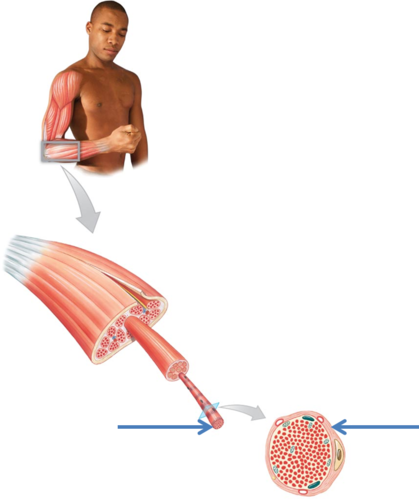
connective tissue surrounding a muscle fiber
endomysium
cytoplasm (sarcoplasm) of a muscle cell, lies beneath the endomyuism
sarcolemma
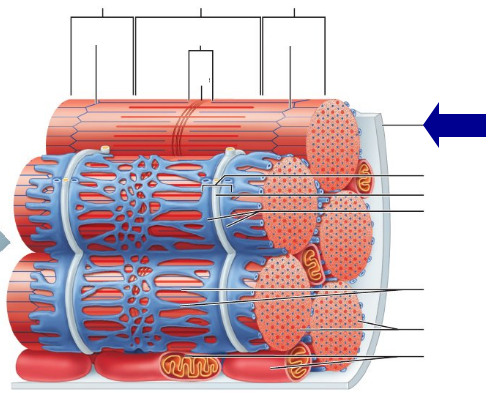
threadlike structures that contain actin and myosin
myofibrils
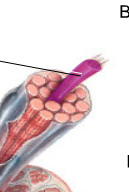
compartments of myosin and actin
sarcomeres
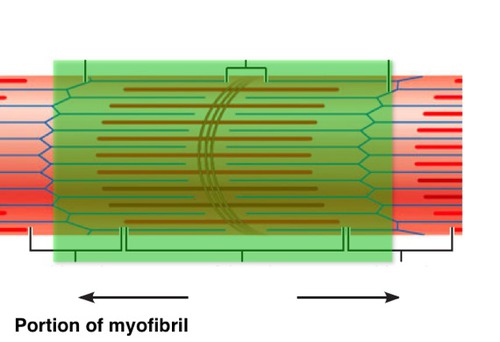
cytoplasm of a muscle cell, contained by the sarcolemma
sarcoplasm
network of channels in each muscle fibre that transports electrochemical substances involved in muscle activation
sarcoplasmic reticulum