10: buffer overflow attacks
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
you have to tell the compiler how to manage memory in
languages like c
memory mismanagement can allow
attackers to make your application execute arbitrary code
if more characters are written to a buffer than there is space allowed for in memory
things get overwritten
stack can be corrupted
EIP can be changed
attacker can input code and then set the old EIP to the start of the inputted code in the stack, instead of returning
the x86 architecture
the stack is mostly LIFO
can write and read to the top of the stack
can write to stack with push
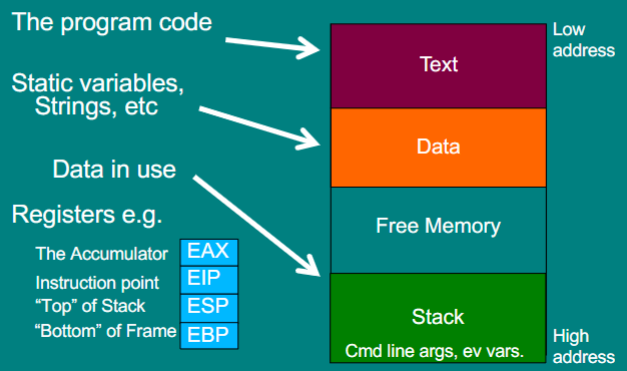
what happens when a function is called
address of the function put into EIP
old EIP stored on the stack for returning
ESP
points to the top of the stack
when you push or pop data onto the stack, it goes here and the ESP is then adjusted to reflect the new stack head
EBP
points to the base of the stack frame
when you call a function, this is saved on the stack and the EBP now points to the base of the new stack frame
all local variables can be found relative to this pointer
stack frame
section of the stack dedicated to a particular function call
defense - the NX bit
code should be in the text area of memory, not on the satck
this provides a hardware distinction between the text and the stack
when enabled, the program will crash if the EIP ever points to the stack
resuse code
attack against NX bit
reusing code from the executable part of memory
jump to another function in the program
jump to a function from the standard C library (return to libc)
string together little pieces of existing code (return oriented programming)
return to libc
libc is the standard c library
often packaged with executables to provide a runtime environment
includes lots of useful calls like “system”, which runs any command
links to executable memory, so bypasses nx bit protections
address space layout randomisation (ASLR)
adds a random offset to the stack and code base each time the program runs
jumps in the program are altered to point to the right line
the idea is that its now hard for an attacker to guess the address of where they inject code or the address of particular functions
on by default in all OS
NOP slide
in x86, the op code assembly instruction 0×90 does nothing
if the stack is 2MB, I could inject 999000 bytes of 0x90 followed by my shell
code
I then guess a return address and hope it is somewhere in the 2MB of NOPs
if it is, the program slides down the NOPs to my shell code
often used with other methods of guessing the randomness
metasploit
framework for testing and executing known buffer overflow attacks
if a vulnerability in an application is well known, there will be a metasploit module for it
if an application is unpatched, it can probably be taken over with metasploit
also includes a library of shell code which can be injected