Bone Terms, Skeletal Overview & Skull Bones
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
3 types of cartilages
hyaline cartilage, fibrocartilage, elastic cartilage
hyaline cartilage description
not too tough or not too bendy (happy medium)
hyaline cartilage location
lining the articular ends of bones in movable joints (knee, hip, shoulder), within the respiratory tract (trachea, larynx, bronchi), in the nose, and connecting the ribs to the sternum (costal cartilage)
fibro cartilage description
very tough
fibro cartilage location
intervertebral discs, knee menisci, pubic symphysis, shoulder/hip labrum, wrist (TFCC), and at the insertion points of tendons and ligaments into bone
elastic cartilage description
bendy
elastic cartilage location
external ear (pinna), the epiglottis, and the Eustachian (auditory) tube
bone functions
support, protections, levers for muscle action, minerval storage, blood cell formation, triglyceride energy storage
2 divisions of skeleton
axial skeleton (protection/support), appendicular skeleton(movement)
axial skeleton
skull, vertebral columns, thoracic cage
bones that lie around the body’s center of gravity
appendicular skeleton
limbs, girdles (pectoral and pelvic)
involved in locomotion and manipulation of the environment
classification of bones by shape
long bones, short bones, flat bones, irregular (anything that doesn’t fall in those categories
2 categories of bone marking
projections
depressions/opening
projections bone markings
stuff that pops out of the bone, sites of muscle and ligament attachment, helps form joints
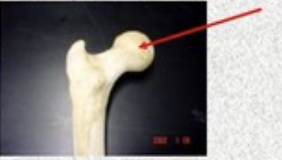
depressions/openings bone markings
indents or holes in bones, passageways for blood vessels and nerves
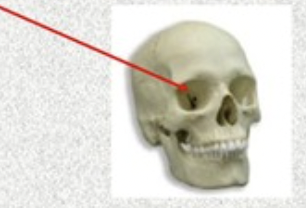
process
any prominence on bone
tuberosity
a large raised roughened projection on bone for the attachment of muscles
crest
projection, narrow ridge on bone, very prominent
trochanter
projection, only found on femur, large blunt irregularly shaped things that stick out
line
projection, a narrow ridge of bone less prominent than crest
tubercle
projection, rounded process that stick out of bone, smaller than tuberosity
spine
projection, sharp slender often pointed
condyle
projection, knuckle like
epicondyle
projection, on or above a condyle
ramus
projection, branch like structure on a bone or arm like bar of bone
cornu
projection, horn shaped
head
projection, rounded process or expansion supported by a constricted/narrowed neck
facet
projection, small smooth/nearly flat surface for articulation
groove
depression/opening, furrow
fissure
depression/opening, narrow slit like opening
foramen
depression/opening, round oval opening (hole) through a bone that allows passage of nerves and or blood vessels
canal
depression/opening, a narrow tube, channel, or passageway through a bone
notch
depression/opening, indentation at the edge of a structure
meatus
depression/opening, canal or tube like passageway through a bone
fossa
depression/opening, shallow basin like depression in a bone often serves as an articular surface
fovea
depression/opening, a deep pit or depression in a bone
sulcus
depression/opening, narrow groove or furrow in a bone
alveolus
depression/opening, deep pit or socket in the mandible or maxillae for a tooth
sinus
depression/opening, a cavity or hollow space in certain skull bones filled with air and lined with mucous membrane
4 in the skull=frontal ethmoidal sphenoidal maxillary sinuses, lighten the skill and help with voice resonance
squama
a flat portion/area on a bone
ala
a wing like portion of bone
visceral skeleton
skeletal elements/bones derived from the embryonic gill arches; not directly part of the main skeleton. Include the ear ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes), the hyoid bone, and portions of the larynx
conchae
a lateral (scroll-like) fold of bone in the nasal cavity that creates a more efficient circulation of inhaled air (increases air flow) by increasing surface area
suture
a line remaining after 2 bones have joined together and fused; seen between skull bones
fontanelle
spaces covered by tough membranes (connective tissue) between the bones of a fetus/infant’s skull; “soft spots” on a baby’s skull where bones haven’t fused. Allow for easier childbirth and brain growth.
2 types of bone texture
compact bone, spongy (cancellous) bone
compact bone
Dense outer layer; looks smooth & solid to naked eye
spongy, cancellous, bone
Inner layer; lots of open space…honeycomb of trabeculae
structure of a long bone, diaphysis
main part of the bone, shaft that forms long axis of the bone; walls composed of thick layer of compact bone; contains the medullary cavity
structure of a long bone, epiphysis
rounded end of the bone, proximal and distal; outer layer of compact bone with internal spongy bone; articular cartilage covers surface (layer of hyaline cartilage where joints form)
structure of a long bone, epiphyseal line
The remnant of the epiphyseal (growth) plate between the diaphysis and epiphysis at each end; marks where bone growth in length occurred
structure of a long bone, medullary cavity
hollow space within the diaphysis; contains yellow bone marrow for fat storage (adipose)
structure of a long bone, periosteum
membrane covering the outer surface of the bone; composed of dense irregular connective tissue; contain bone stem cells
microscopic anatomy of compact bone, osteon/haversian system
circular structural units of compact bone; comprised of multiple concentric layers of calcified matrix (lamellae) surrounding a central canal
microscopic anatomy of compact bone, central/haversian canal
opening in center of each osteon; passageway for blood vessels and nerves
microscopic anatomy of compact bone, lamellae
rings/layers of calcified matrix around the central canal= concentric lamellae; interstitial lamellae= located between osteons; remnants of old osteons
microscopic anatomy of compact bone, osteocytes
mature bone cells; reside in lacunae
microscopic anatomy of compact bone, lacuna
open spaces in matrix that house osteocytes
microscopic anatomy of compact bone, canaliculi
small canals through matrix; appear as “cracks”; contain cytoplasmic extensions of osteocytes; connect lacuna and osteocytes to each other
microscopic anatomy of compact bone, perforating (volkmann’s) canals
passageways that run perpendicular to the central canal; connect blood and nerve supply throughout the bone
Ossification
process of bone formation and development; most bones of the skeleton form by endochondral ossification
endochondral ossification
uses hyaline cartilage as a model or template; this is also how bones grow in length
Epiphyseal (growth) plate
region of a long bone between the diaphysis and epiphyses composed of hyaline cartilage; only present during childhood and adolescence; allows bone to grow in length; has 5 functional zones (from epiphysis to diaphysis)
Resting (quiescent) zone
Small, inactive cartilage cells scattered randomly.
Chondrocytes (inactive)
Anchors the epiphyseal plate to the epiphysis and stores cells for future growth.
Proliferation (growth) zone
Cartilage cells rapidly divide and form columns.
Chondrocytes undergoing mitosis
Lengthens the bone by increasing the number of cartilage cells.
Hypertrophic zone
Older cartilage cells enlarge and mature.
Enlarged chondrocytes
Prepares cartilage for calcification and eventual bone replacement.
Calcification zone
Cartilage matrix hardens; chondrocytes die.
Dead chondrocytes in calcified cartilage
Stops cartilage growth and allows blood vessels to invade.
Ossification (osteogenic) zone
New bone tissue forms on calcified cartilage.
Osteoblasts (forming bone)
Replaces cartilage with bone, contributing to bone lengthening.
Order of epiphyseal (growth) plate
Resting (quiescent) zone Proliferation (growth) zone Hypertrophic zone Calcification zone Ossification (osteogenic) zone
Chemical Composition of Bone
organic and inorganic
organic chemical composition of bone
bone cells & organic part of the matrix (ground substance & collagen fibers); provides bone with flexibility
inorganic chemical composition of bone
mineral salts in the matrix (e.g., calcium); provides bone with characteristic hardness
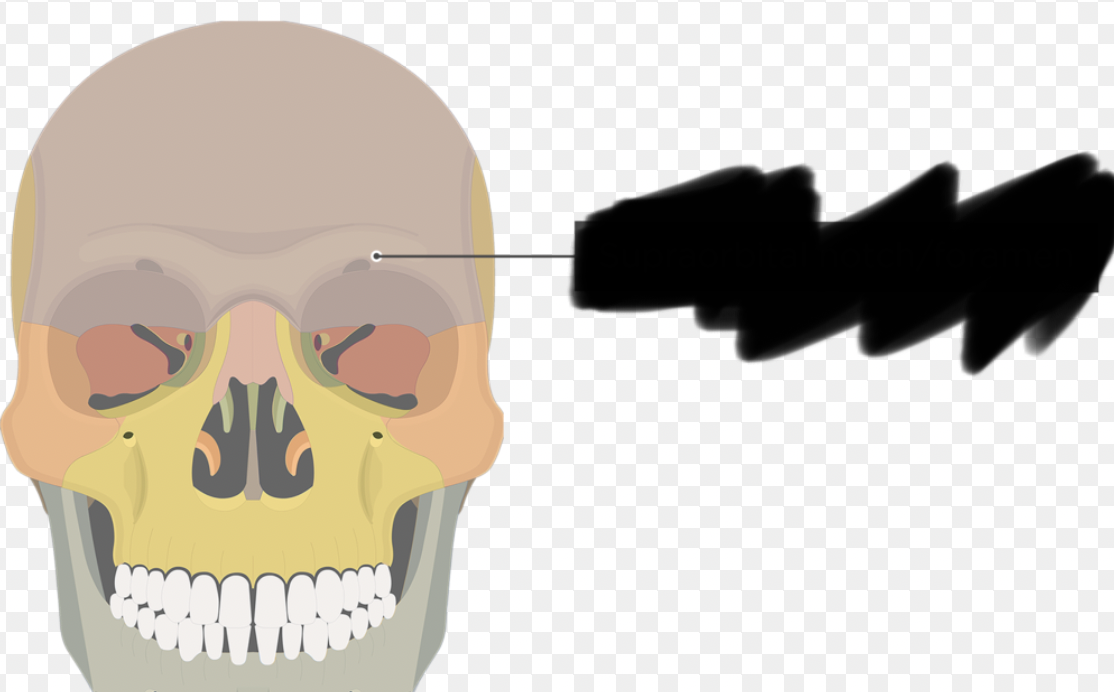
frontal bone
anterior cranium; articulates posteriorly with parietal bones @ coronal suture; contains sinuses
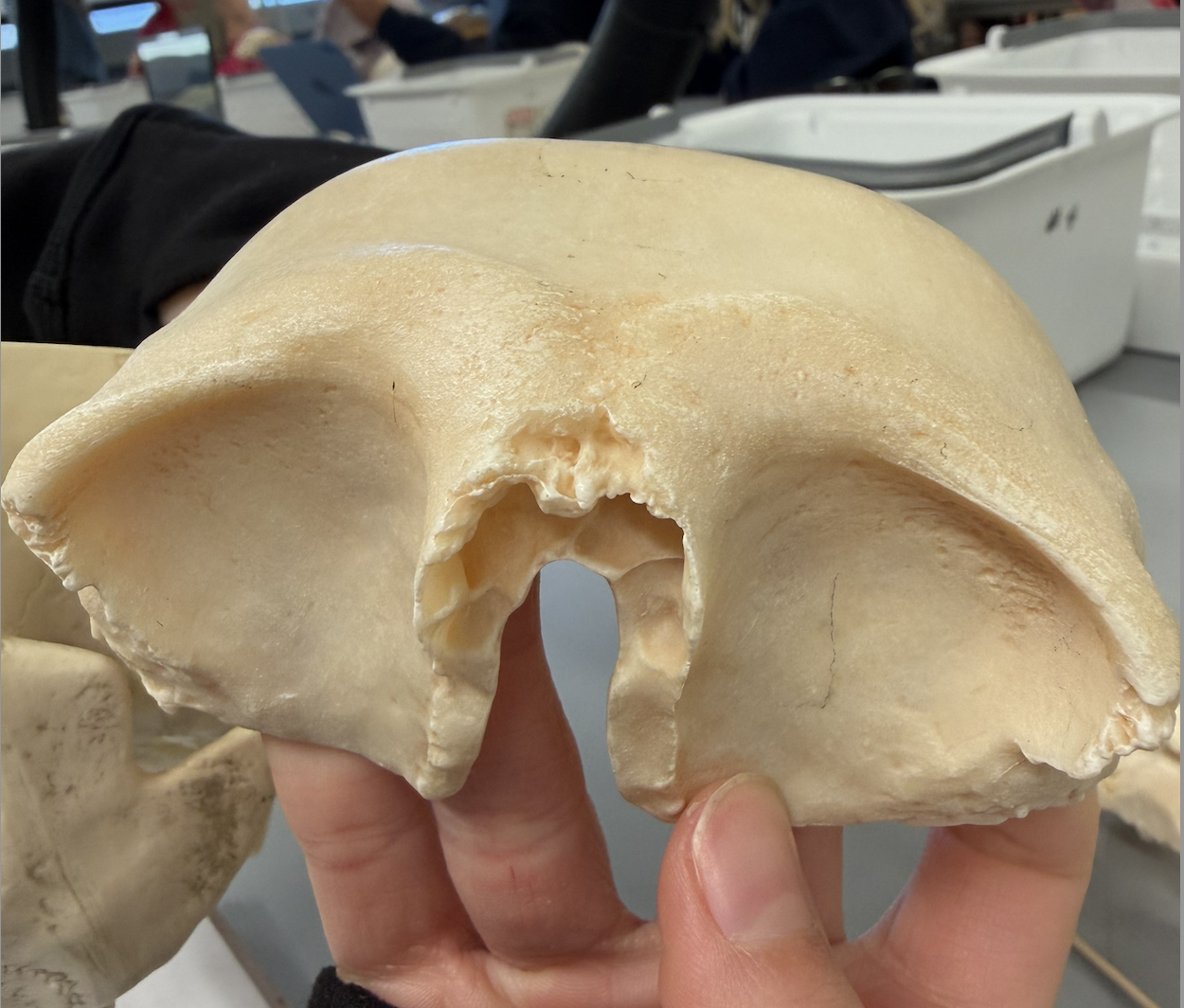
frontal bone (squama/squamous part)
(scale-like)- large, rounded superior part of bone above orbits
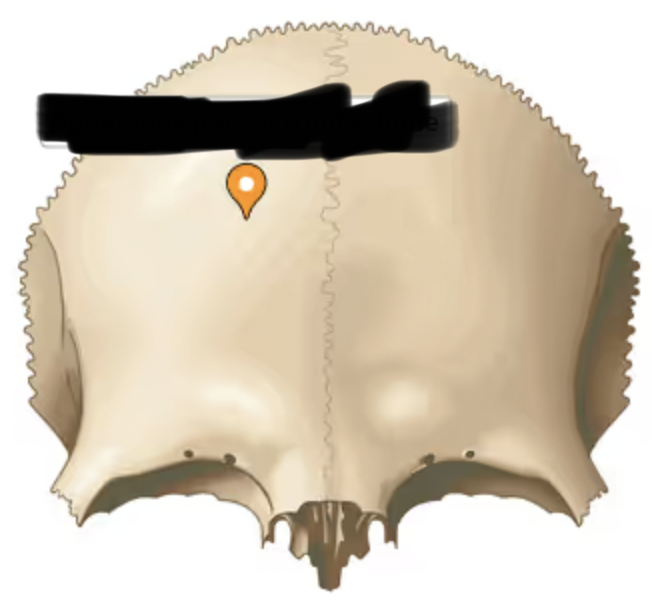
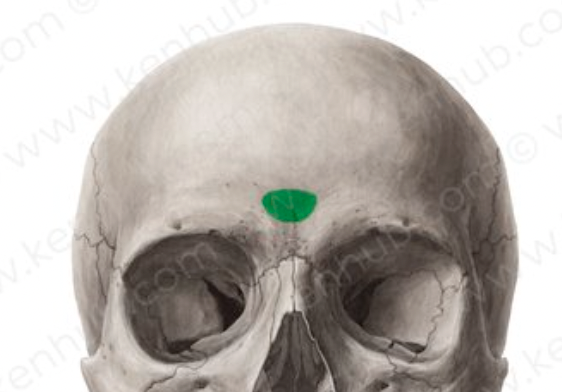
frontal bone (glabella part)
(hairless, smooth)- smooth area between the orbits
frontal bone (supraorbital margin part)
thick, superior border of the eye socket
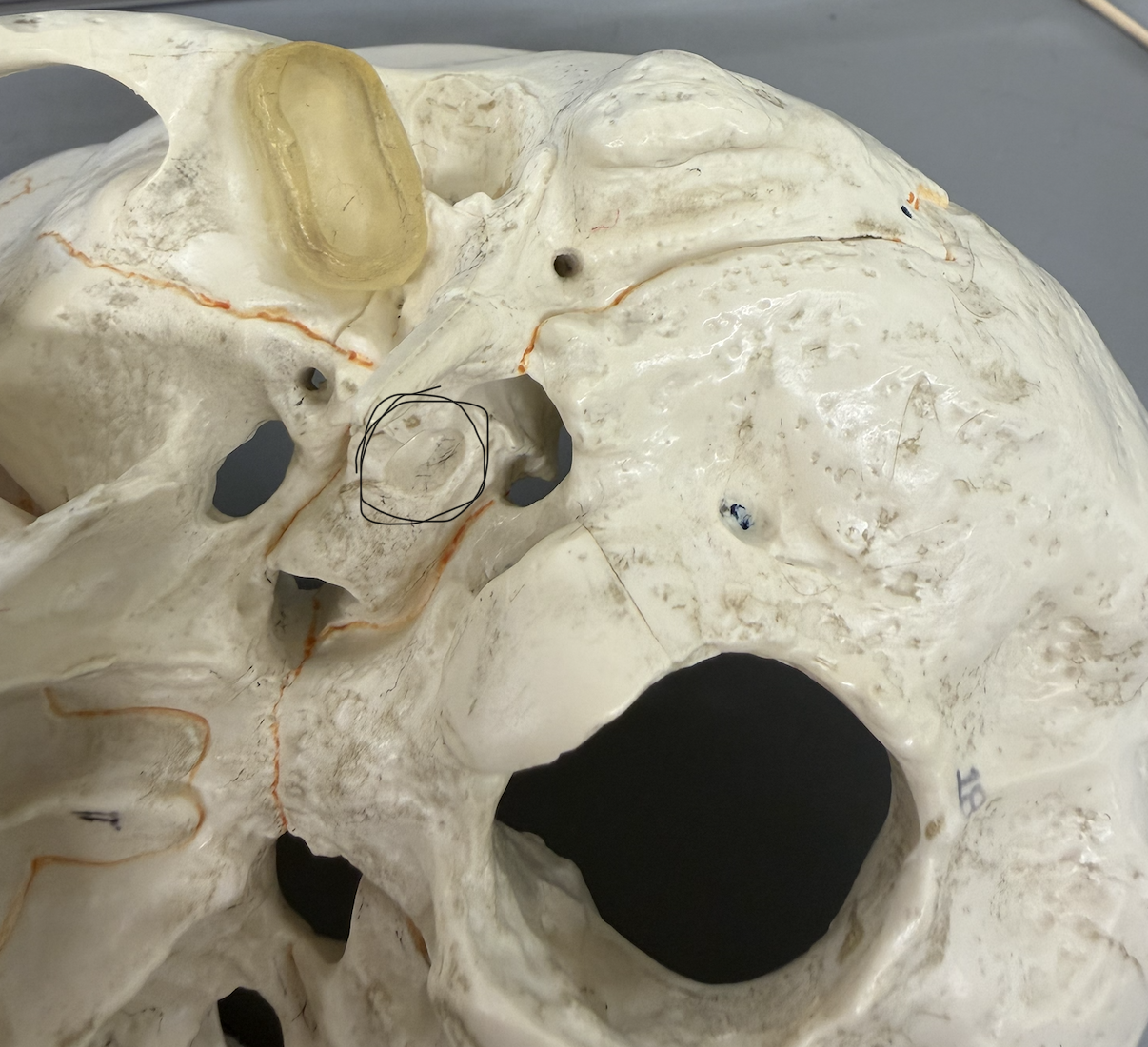
frontal bone (supraorbital foreamen/notch part)
small hole/indentation in supraorbital margin
parietal bone
(wall)- curved, rectangular bones behind frontal bone; form most of superior and lateral portion of skull; join at midline @ sagittal suture
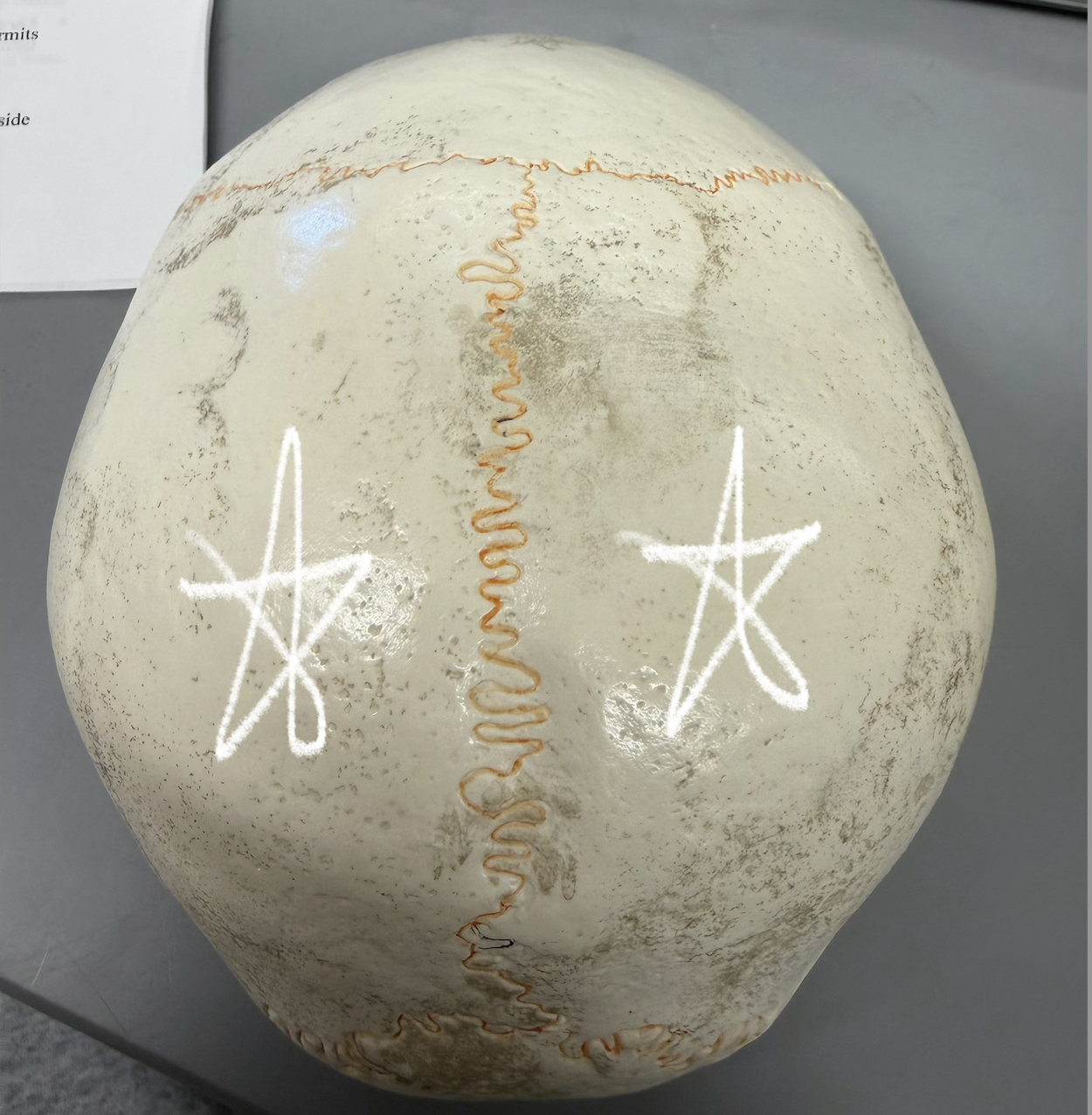

occipital bone
forms most of skull’s posterior wall and base; has large hole in its base; articulates anteriorly with parietal bones and temporal bones; also joins with sphenoid bone in cranial floor
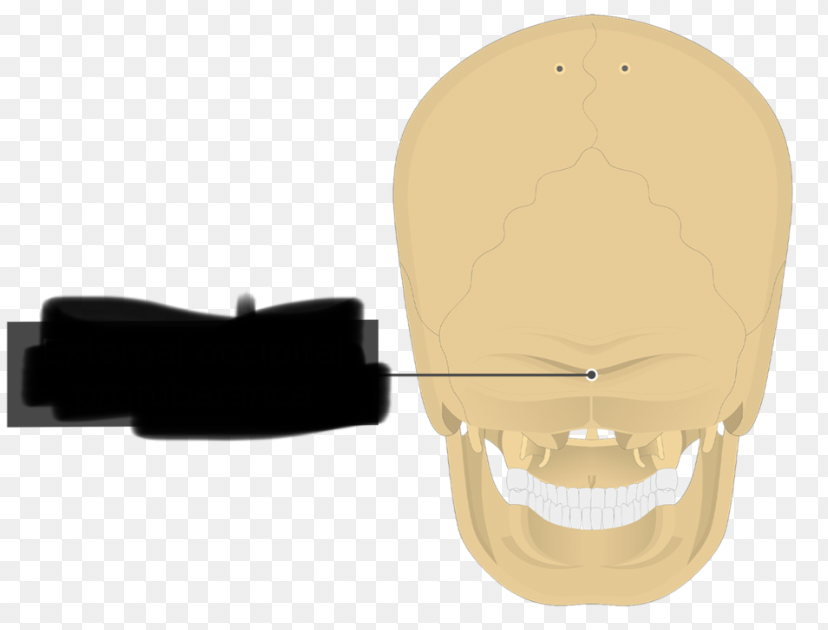
occipital bone (External Occipital Protuberance)
external median protrusion; knoblike; can feel it just below most bulging part of skull
occipital bone (Superior Nuchal Line)
inconspicuous ridge spanning laterally from the externaloccipital protuberance
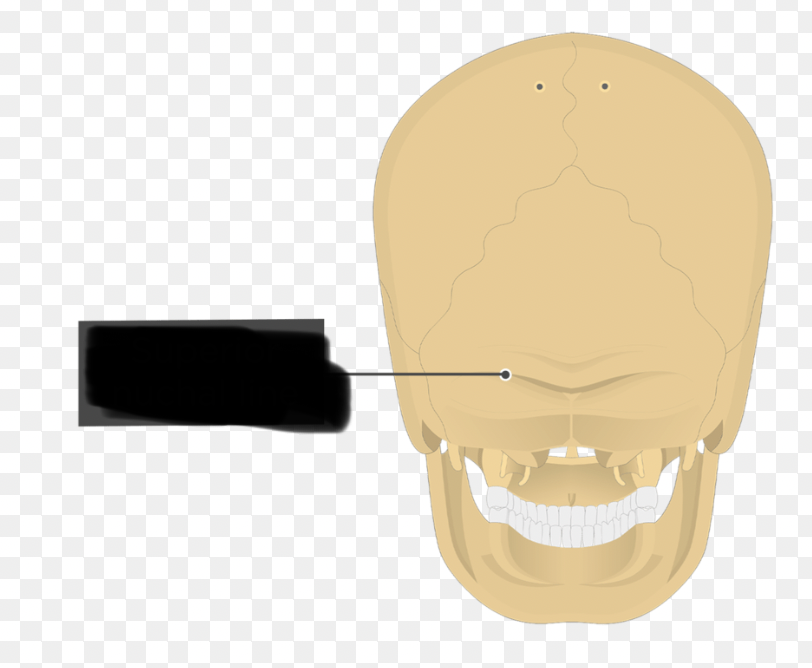
occipital bone (Infeorior Nuchal Line)
inconspicuous ridge spanning laterally; located below superior nuchal line
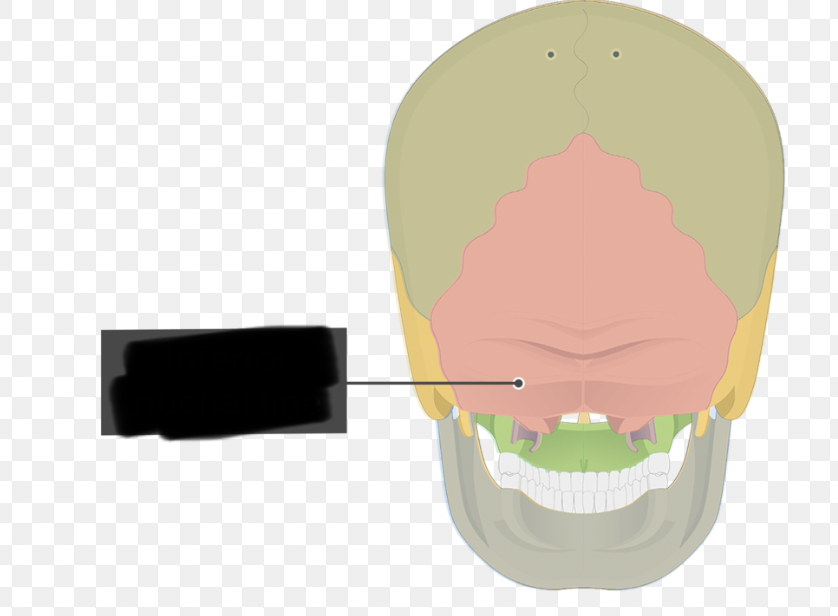
occipital bone (foramen magnum)
large hole in base of bone; flanked laterally by condyles; passageway for spinal cord to exit skull
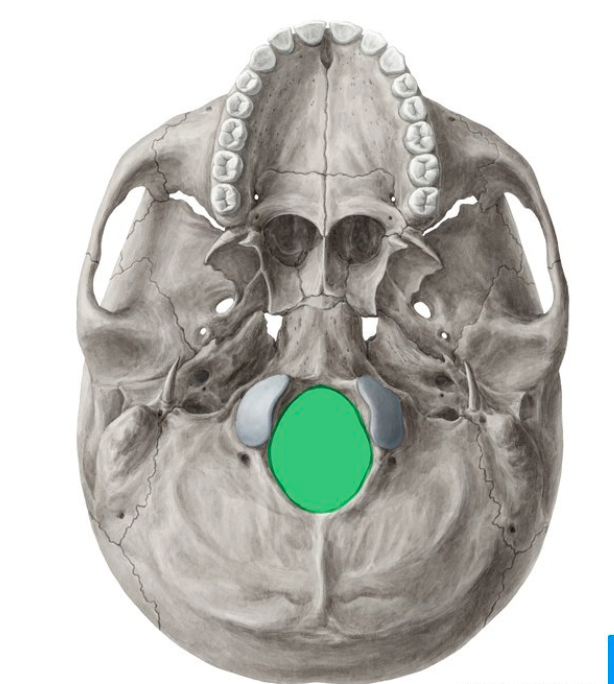
occipital bone (Occipital Condyles)
rocker-like projections; articulate with first vertebrae; permits nodding of head
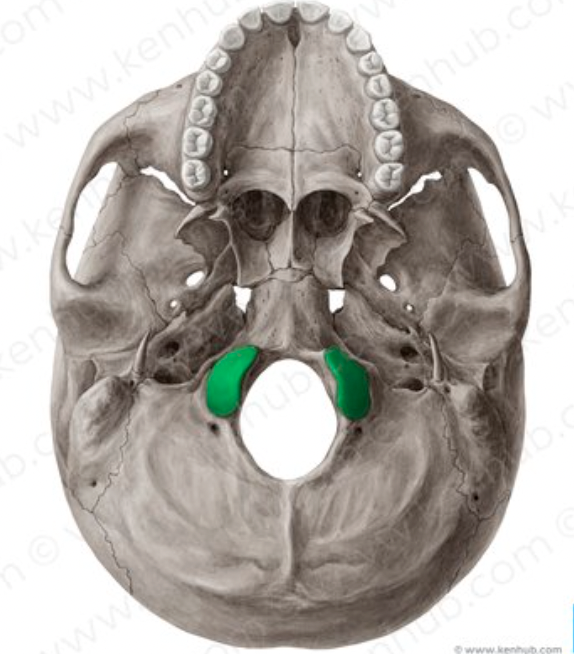
occipital bone (Condylar Canal)
opening posterior to condyle; seen on inferior view of bone
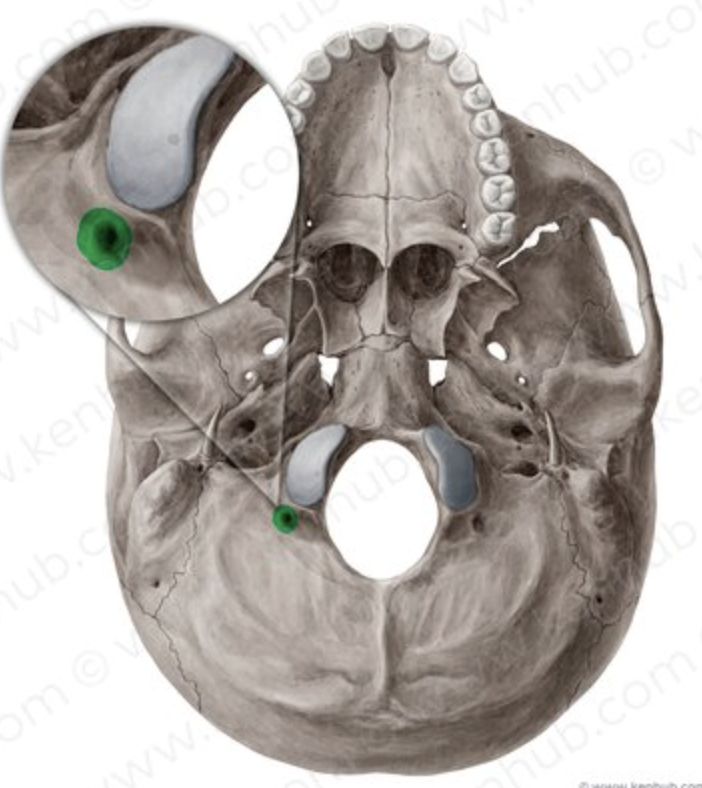
occipital bone (Hypoglossal Canal)
passageway running through condyle; can be seen from inside foramen magnum
Wormian/Sutural Bones
tiny, irregular shaped bones/bone clusters that appear within sutures; most often seen at lambdoidal suture; unimportant, # varies, not all skulls have them
temporal bone
forms lateral wall of skull and part of cranial floor; complicated shape; has several processes & foramina
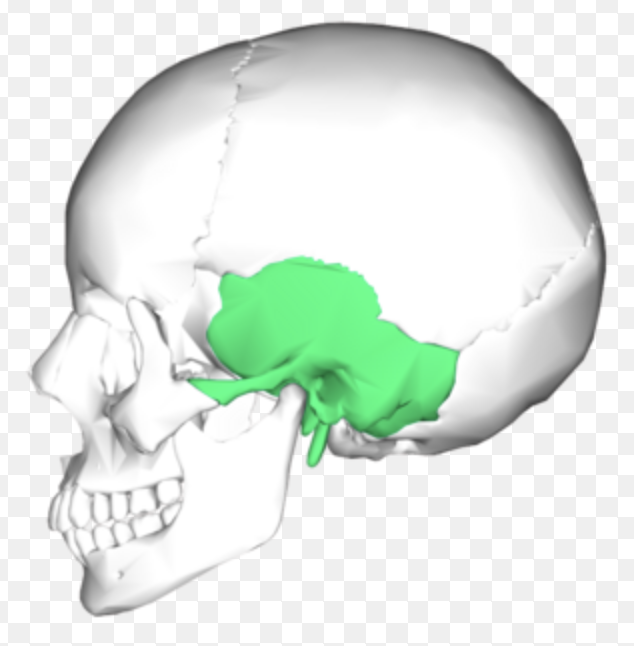
temporal bone (Zygomatic Process)
long projection that articulates with zygomatic bone anteriorly (forms part of zygomatic arch!)
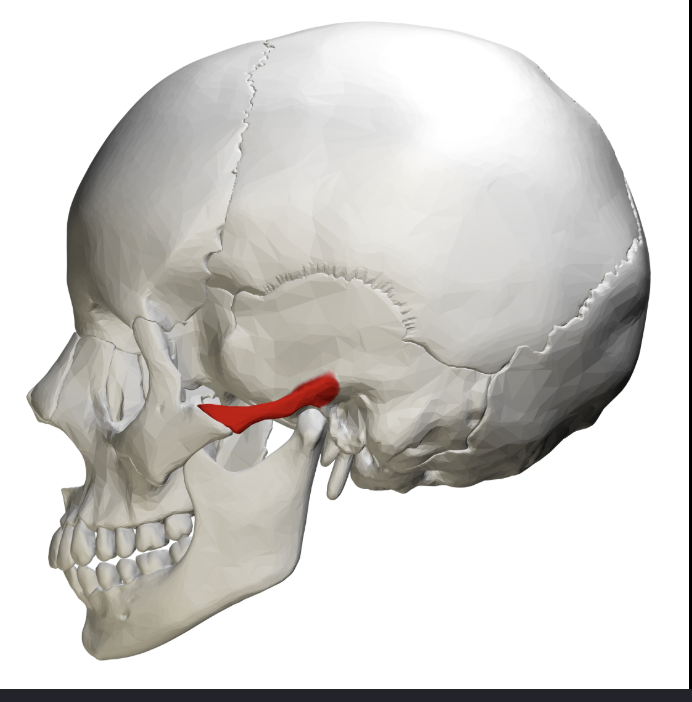
temporal bone (styloid Process)
(projection like a writing stylus/pen)- sharp, needle-like projection pointing inferiorly; located below external acoustic meatus
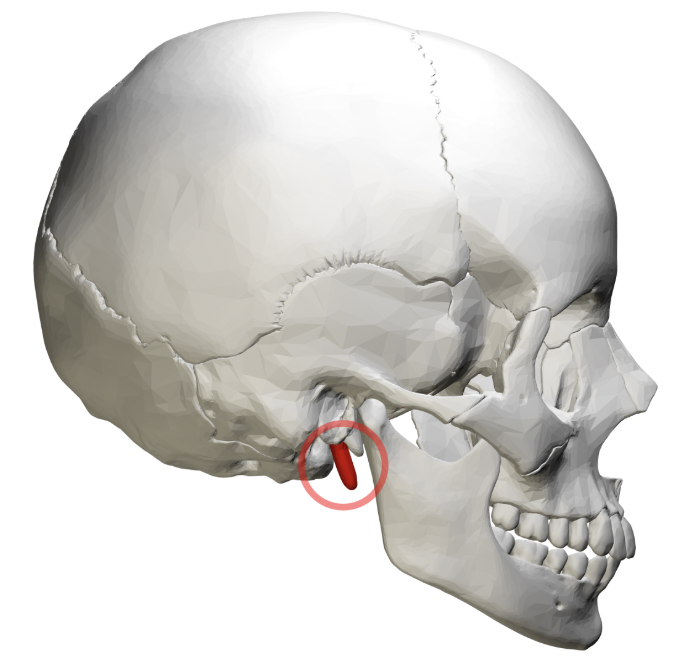
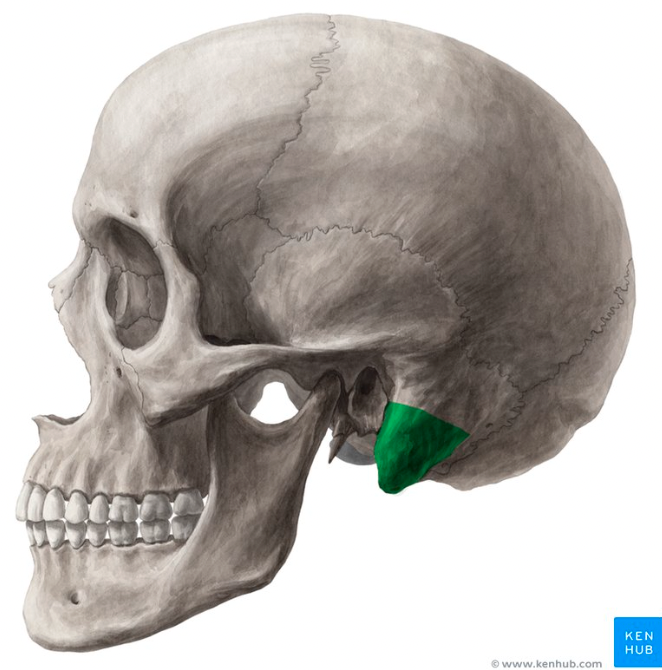
temporal bone (mastoid Process)
(breast-shaped)- thick, rounded projection on inferior, posterior part of bone; can feel it- lump posterior to your ear
temporal bone (Squamous Portion/Part)
(thin & flat like a fish’s scale): flaring, flat part of bone; joins parietal bone @ squamous suture
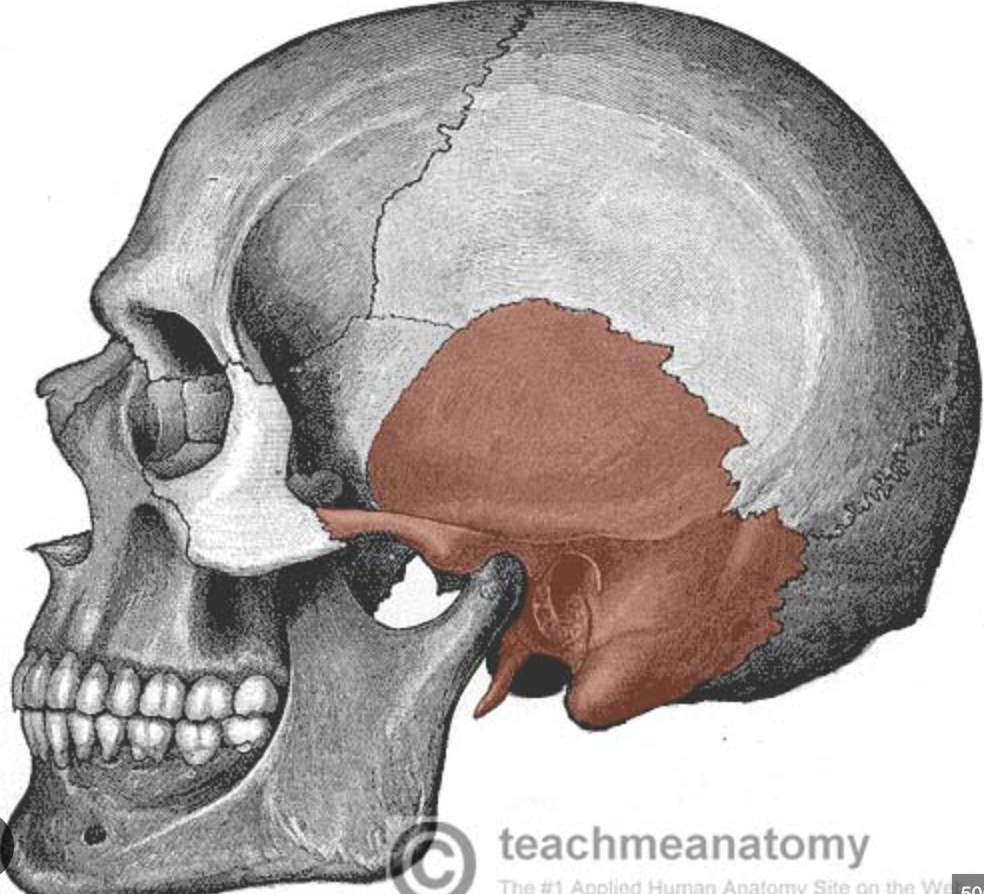
temporal bone (Petrous Portion)
(stone, rock)- “rocky” part of bone that contributes to cranial base; mini mountain ridge between occipital bone and sphenoid bone seen inside articulated skull
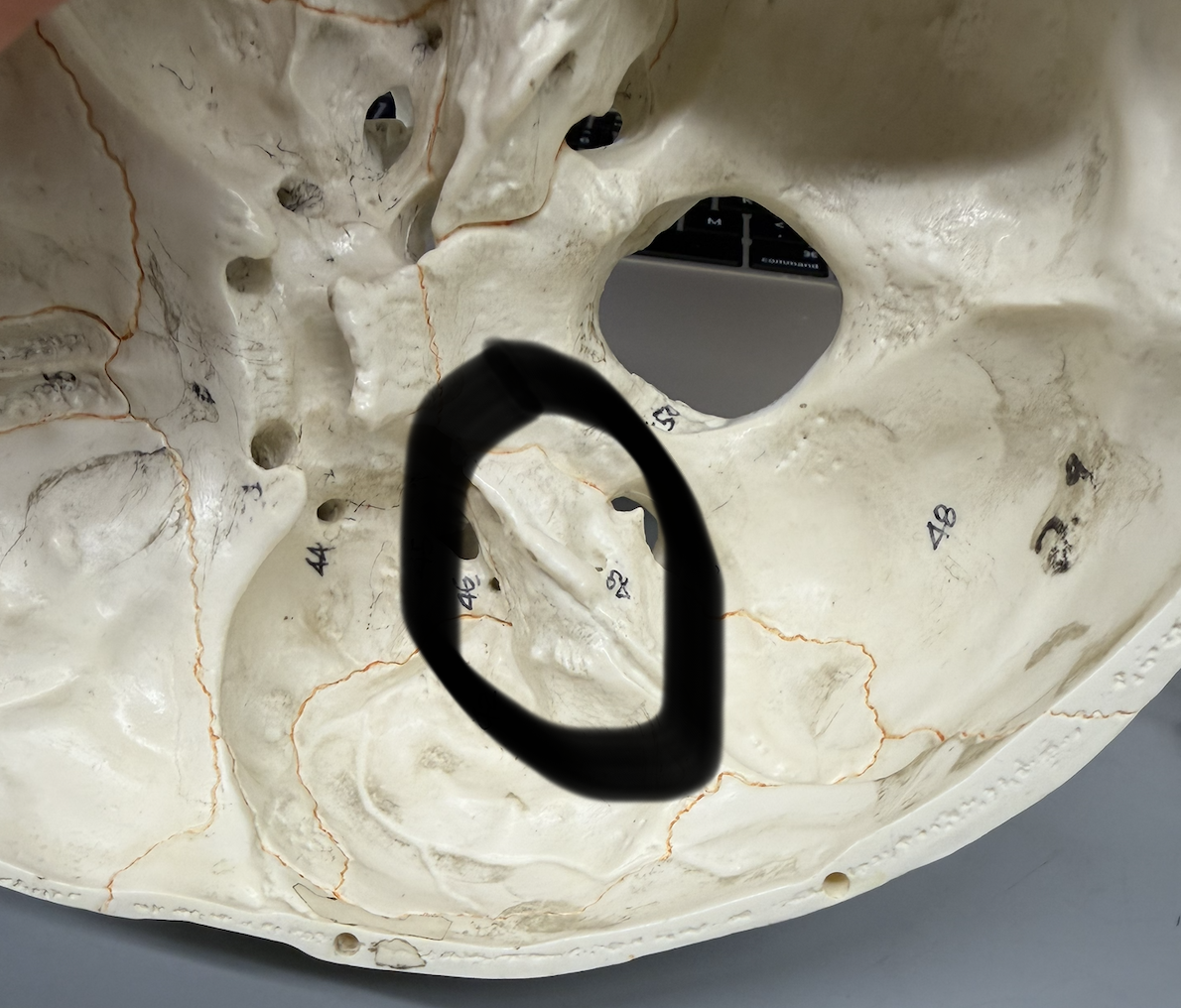
temporal bone (Mandibular Fossa)
oval basin/depression on inferior of bone; located anterior to external acoustic meatus; articulates with mandibular condyle to form TMJ
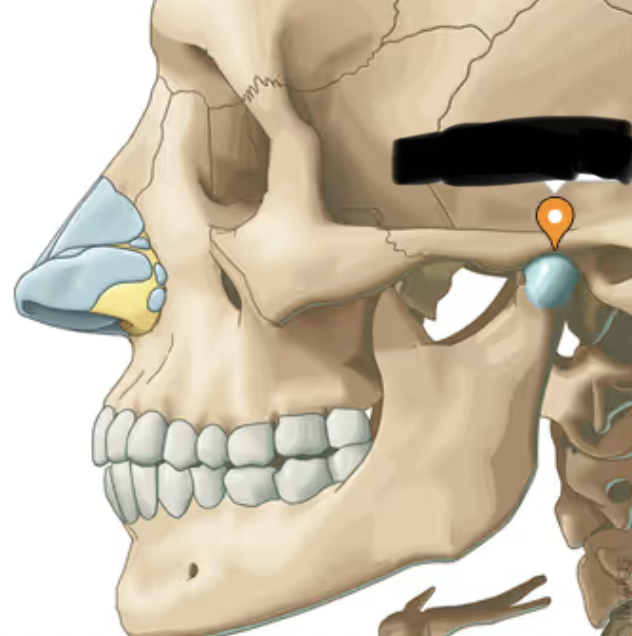
temporal bone (External Acoustic Meatus)
large hole on lateral side of bone; canal through which sound enters leading to middle ear and eardrum
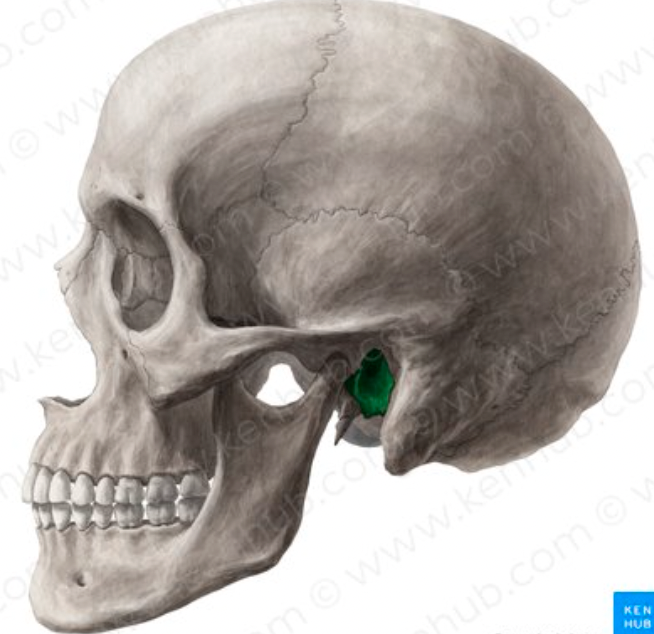
temporal bone (Internal Acoustic Meatus)
maller hole on medial side of bone; located on petrous portion
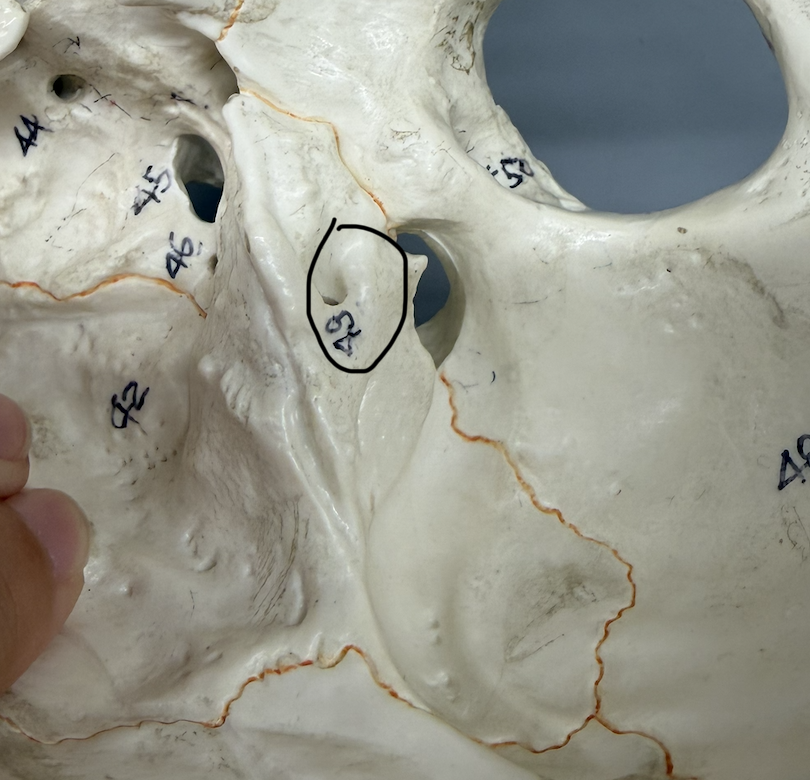
temporal bone (Mastoid Foramen)
small hole on superior, posterior part of mastoid process
temporal bone (Stylomastoid Foramen)
hole between styloid process & mastoid processes
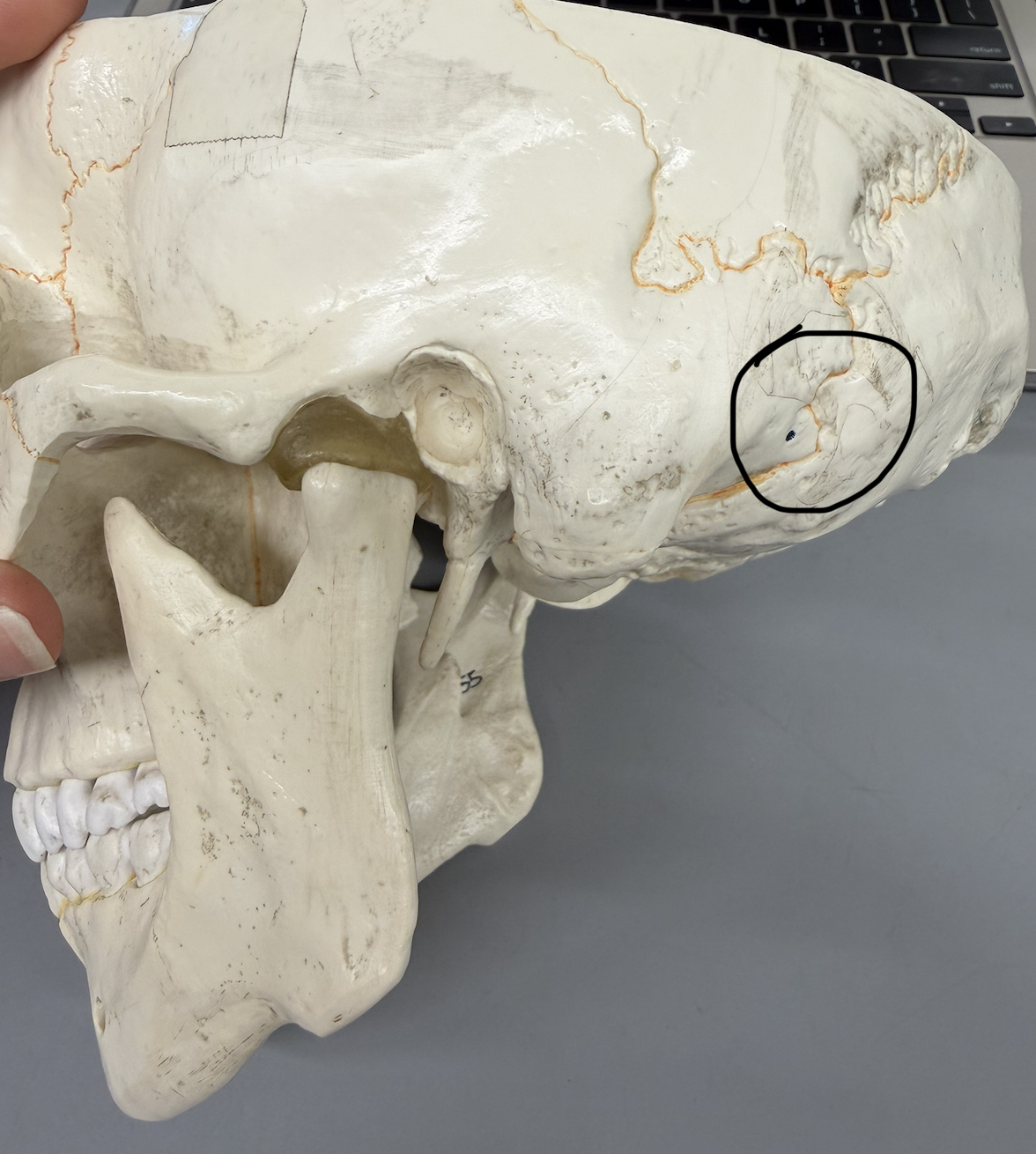
temporal bone (Jugular Foramen)
large hole on petrous portion of bone where joins occipital bone; near internal acoustic meatus; passageway for jugular vein; only seen in articulated skull
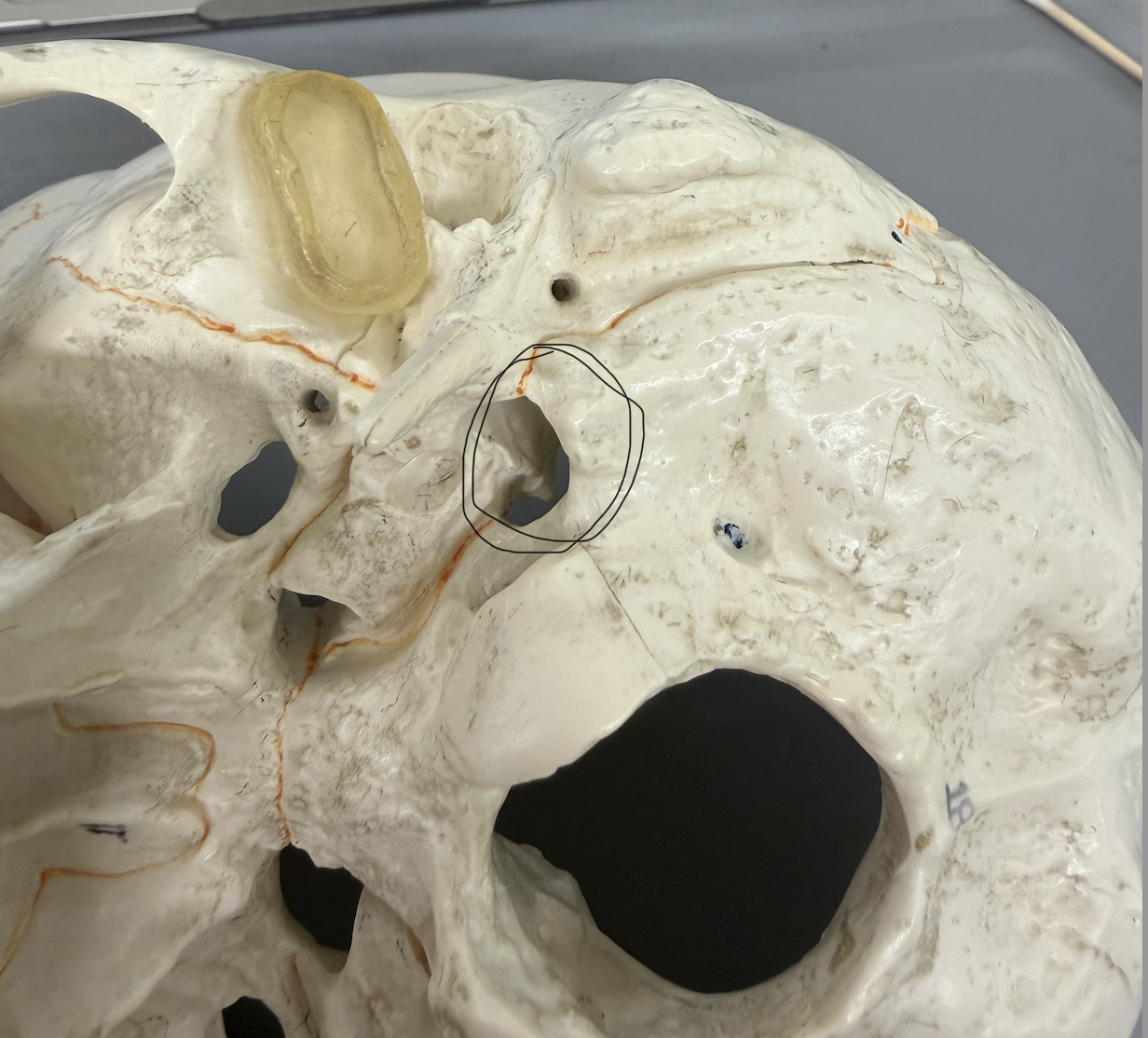
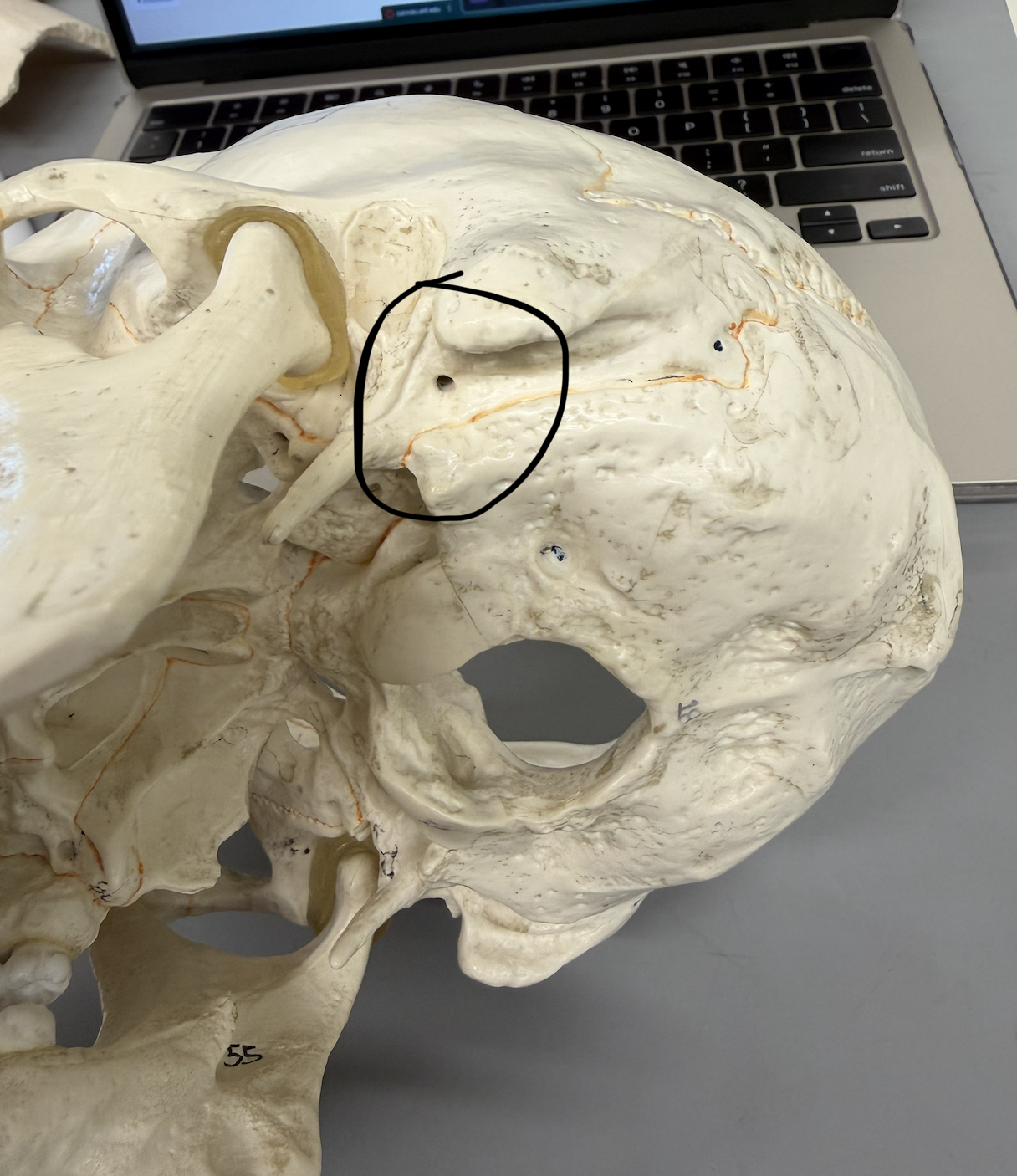
temporal bone (Carotid Canal)
large, deep opening on inferior side of petrous portion of bone; passes through petrous portion; passageway for carotid artery