'23 - '24 Anat. & Phys. Final 2402
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
What is the job of Sertoli cells?
Throughout the development of spermatogenic cells, Sertoli cells:
- Support
- Nourish
- Regulate
Trace the pathway sperm would follow from the testes to the urethra:
1.) Seminiferous tubules
2.) Rete testis
3.) Epididymis
4.) Ductus (vas) Deferens
5.) Ejaculatory duct
6.) Urethra
What three structures release hormones that are important in the male reproductive system?
- Hypothalamus
- Anterior pituitary gland
- Testes
Look at the steps of Oogenesis and understand the steps (Look at Figure 22.27):
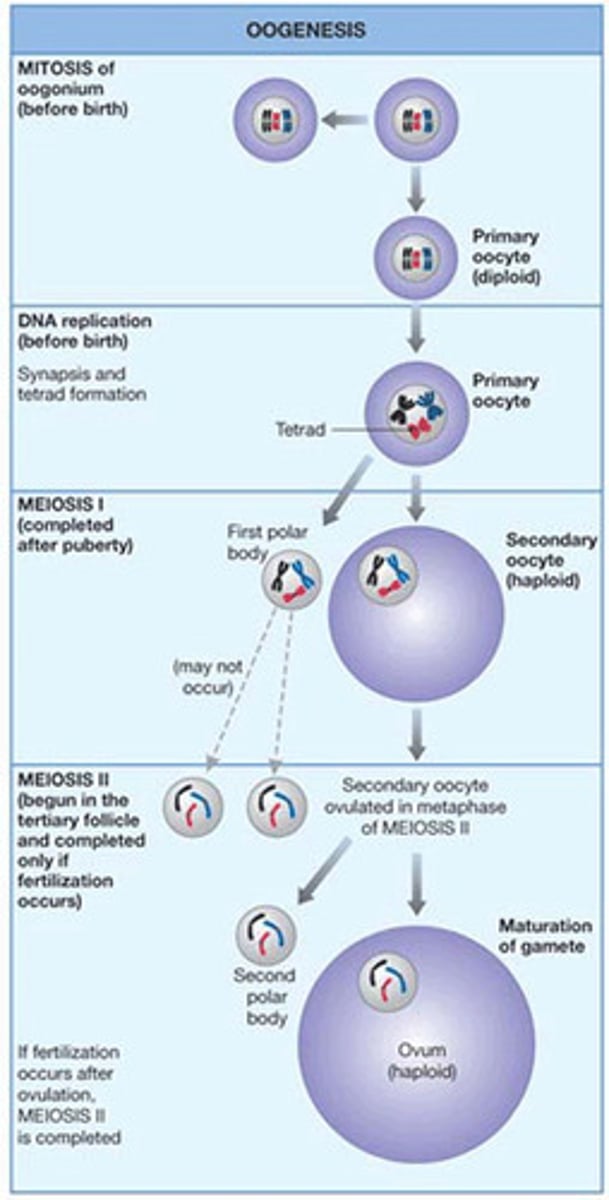
What happens to primary oocyte? (see step 6 in figure 22.27)
- Primary oocyte completes meiosis I
- Primary oocyte separates into second oocyte and first polar body
- Secondary oocyte is to be fertilised
What happens to the secondary oocyte if it becomes fertilized?
- Becomes a zygote
Which hormone triggers ovulation?
- Estrogen
What gland secretes estrogen?
- Anterior pituitary gland
What role do androgens play in a female?
- Facial/body hair growth
- Receding hairline
- Irregular menstrual cycle
- Deepening of voice
- Tumors
What structures produce milk in a lactating female?
- Alveolar glands
Which layer of the uterine wall is the mucosa, serosa, and muscle layer?
- Endometrium: mucosa (inner)
- Myometrium: muscularis (middle)
- Perimetrium: serosa (outer)
Define hormone
- Hormones exert effects by altering metabolic processes
- Chemical messenger**
Define target cell:
- Receptors for hormone
What are the functions of hormones?
- Maintain homeostasis
- Stimulate growth (growth hormone)
- Regulate development
- Stimulate reproduction
Hormones secreted by the posterior pituitary gland are synthesized where?
- Hypothalamus
What controls the secretion of the parathyroid hormone?
- Imbalanced secretion of calcium
What effect does glucagon have on the body?
- Stimulate liver to break down glycogen to glucose
- Increase glucose levels in blood
What is upregulation?
- Increase number of receptors on target cell
- Decrease in hormone level
What is downregulation?
- Decrease in number receptor on target cell
- Increase in hormone level
What type of relationship of does upregulation and downregulation have?
- Indirect
- Increase of receptor = decrease in hormones
- Decrease of receptor = increase in hormones
Define tropic hormones:
- Hormones that act on other glands
- Stimulate other glands to release hormones
What percentage of human blood is composed of red blood cells?
- Women: 35% - 46%
- Men: 40% - 54%
Define hematocrit
- Percentage of RBC's in blood sample
- Determined by RBC count
List the granulocytes:
- Neutrophil
- Eosinophil
- Basinophil
** THE PHILS **
List the agranulocytes:
- Lymphocyte
- Monocyte
- Leukocyte (WBC)
** THE CYTES **
How is an individual's blood type determined? Think of the structure of blood cells.
- Proteins (antigens) are on surface of red blood cells
Describe blood type A:
- Antigen: A
- Antibodies: B
Describe blood type B:
- Antigen: B
- Antibodies: A
Describe blood type AB:
- Antigen: A & B
- Antibodies: none
Describe blood type O:
- Antigen: none
- Antibodies: A & B
Understand the blood types when it comes to receiving and donating.
- Negatives receive only -
- Positives can receive both + & -
What is the function of lymhphocytes?
- Provide immunity against foreign substances
What is the function of neutrophils?
- First to arrive at bacterial infection
- Raised levels of neutrophils when there is a bacterial infection
- Phagocytise small particles
What is the function of eosinophils?
- Kills parasites
- Moderates allergic reactions
What is the function of basophils?
- Releases histamine and heparin
What does histamine do?
- Stimulates inflammation
What does heparin
- Medication to thin blood
- Decrease blood clotting
What is pernicious anemia?
- Inadequate amount of vitamin B12
What is aplastic anemia?
- Destruction of bone marrow
What is sickle cell anemia?
- Caused by genetics
- Abnormal hemoglobin
- African Americans are the population who are most affected
What is the function of the systemic circuit?
- Transports oxygen-rich blood & nutrients to body cells
- Removes wastes from cells
- Transport oxygen-poor blood back to heart
List out the blood flow of the heart.
1.) Superior/Inferior Vena Cava
2.) Right Atrium
3.) Tricuspid Valve
4.) Right Ventricle
5.) Pulmonary Valve
6.) Pulmonary Trunk
7.) Pulmonary Arteries
8.) Lungs
9.) Pulmonary Veins
10.) Left Atrium
11.) Bicuspid (Mitral) Valve
12.) Left Atrium
13.) Aortic Valve
14.) Aorta
15.) Body
The blood from the coronary sinus dumps into what structure of the heart?
- Right atrium
List the sequence of the components of the cardiac conductions system.
1.) SA Node **
2.) Internodal Atrial Muscle **
3.) AV Node **
4.) AV Bundle (Bundle of His) **
5.) Bundle Branches
6) Purkinje Fibres **
What happens if the aortic baroreceptors sense stretching of the aorta?
Stretched aorta causes aortic baroreceptors to:
- Detect increased blood pressure (baroreceptors)
- Stimulates PNS to decrease blood pressure (bring it back to normal)
Where would you find the popliteal artery?
- Posterior (back) side of knee
What happens to the valves during ventricular contraction?
- Semilunar valves open (pulmonary/aortic)
- Atrial Ventricular (AV) valves close (tricuspid/bicuspid)
What is the pacemaker of the heart?
- Sinoatrial Node (SA node)
Define pathogens:
- Disease causing agent
You would not find lymph nodes in this part of the body. (Think organs or structures)
- Brain
- Spinal cord
How would you describe the spleen's structure?
- Looks like a large lymph node
- Divided into lobules
- Surrounded by connective tissue
What is the function of incisors?
- Incisors: biting
What is the function of molars/premolars?
- Molars/premolars: grinding
What is the function of canines?
- Canines: ripping & tearing
Where do you find the lingual frenulum?
- Floor of mouth
- Fold of tissue that anchors the tongue
What structures are affected or involved when you have a hiatal hernia?
- Lower esophagus
- Stomach
- Diaphragm
Define the body of the stomach:
- Body: main portion of stomach
Define the fundus of the stomach:
- Fundus: superior part of the stomach
List the functions of the liver.
- Detoxification
- Carbohydrate metabolism: *converts non-carbohydrates to glucose*
- Lipid metabolism: *synthesized lipoproteins*
- Storage
- Blood filtering
- Secretes bile
What organs are part of the GI tract?
1.) Oral cavity
2.) Pharynx
3.) Esophagus
4.) Stomach
5.) Small intestine
6.) Large intestine
7.) Anal canal
How is hepatitis B transmitted?
- Bodily fluids (Blood & semen)
- Dirty/shared needles
- Hepatitis-B infected mother to child during birth.
List the blood flow through the liver. Start with hepatic portal vein and end with inferior vena cava.
- Hepatic portal vein
- Central vein
- Hepatic vein
- Inferior vena cava
Which disorders are categorized as COPD's?
- Chronic bronchitis
- Emphysema
The nasal cavity is lined with what type of epithelium?
- Pseudostratified ciliated epithelium
Define vital capacity:
- Maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after taking the deepest breath possible
Define tidal volume:
- Volume of air moved in and out of the lungs of respiratory cycle (500 mL)
** REGULAR BREATHING **
Define expiratory reserve volume:
- The extra amount of air above normal volume exhaled during a forceful breath
Define Boyle's Law:
- Pressure and volume of gases are inversely proportional (HIGH TO LOW)
What forms the respiratory membrane?
- Alveolar wall
- Blood capillary wall
- Fused Basement Membrane
- Two layers of simple epithelium and their membranes
List the order of the sections of the pharynx from superior to inferior.
SUPERIOR TO INFERIOR
1.) Nasopharynx
2.) Oropharynx
3.) Laryngopharynx
Define pneumothorax.
- Air fills within the pleural space in between the membranes
- Should just be fluid not air
- If air separates the visceral and parietal layers then it results in pneumothorax
- Can cause collapsed lung
What is minute ventilation?
- Volume of air moved into the respiratory passages each minute
How is minute ventilation calculated?
- TV (Tidal Volume) x breathing rate
What organs are part of the urinary system?
- Kidneys
- Ureters
- Urinary bladder
- Urethra
What would you find in the renal medulla?
- Renal pyramids
What would you find in the renal cortex?
- Renal corpuscles
Define renal corpuscle.
- Capillary cluster: Filters
- Glomerular (Bowman's) capsule: Collects
Define renal tubule.
- Extends from glomerular capsule to collecting duct
What happens in the first capillary bed associated with nephrons?
- Glomerular filtrate (filtration of blood)
Sequence the blood flow through the kidneys:
1.) Segmental artery →
2.) Interlobar artery →
3.) Arcuate artery →
4.) Cortical radiate artery →
5.) Afferent arteriole →
6.) Glomerulus →
7.) Pfferent arteriole →
8.) Peritubular capillaries or vasa recta →
9.) Cortical radiate vein →
10.) Arcuate vein →
11.) Interlobar vein →
12.) Renal vein →
13.) Inferior vena cava