math final!!
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 1:13 PM on 5/8/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
1
New cards
ratio
the quotient of two quantities
written as:
x to y
x/y
x:y
the order matters! always put the first term as the numerator
written as:
x to y
x/y
x:y
the order matters! always put the first term as the numerator
2
New cards
extended ratio
compares 3 or more numbers
3
New cards
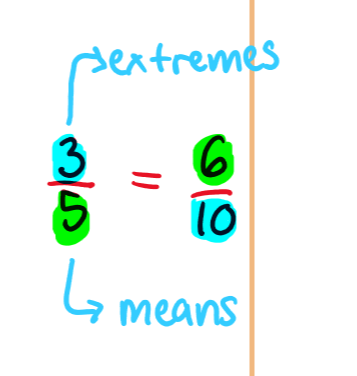
proportion
an equation stating that two ratios are equal
extremes are the first and last numbers in a proportion
means are the middle two
cross products are the product of the means and also the product of the extremes
extremes are the first and last numbers in a proportion
means are the middle two
cross products are the product of the means and also the product of the extremes
4
New cards
cross products property
in a proportion, the products of the extremes and means equal each other

5
New cards
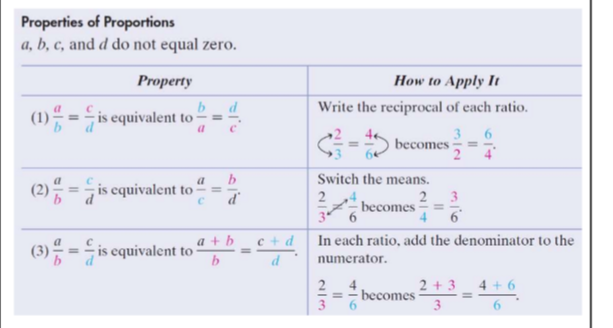
properties of proportions
you can write the reciprocal of each ratio
you can switch the means
you can add the denominator to the numerator and divide by the denominator
you can switch the means
you can add the denominator to the numerator and divide by the denominator
6
New cards
similar figures
figures that have the same shape but not necessarily the same size
corresponding angles are congruent, and corresponding segments are proportional
order matters in congruency statements!
corresponding angles are congruent, and corresponding segments are proportional
order matters in congruency statements!
7
New cards
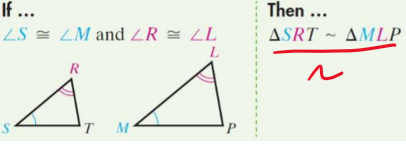
Angle-Angle Similarity Postulate
if two angles of one triangle are congruent to two angles of another triangle, the triangles are similar
8
New cards
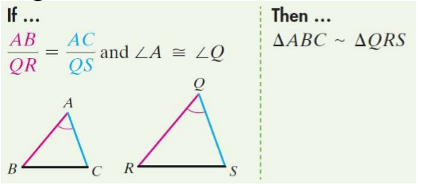
Side-Angle-Side Similarity Theorem
if the angle of one triangle is congruent with the angle of another triangle and the included sides are proportional, the triangles are similar
9
New cards
Side-Side-Side Similarity Theorem
if corresponding sides of triangles are proportional, the triangles are similar
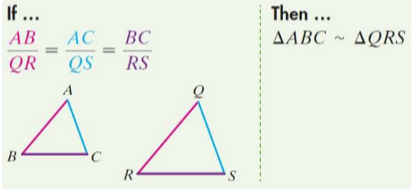
10
New cards
arithmetic sequence
pattern of numbers where any term in the sequence is found by adding or subtracting the previous term by the *common difference*
11
New cards
geometric sequence
pattern of numbers where any term is found by multiplying the previous term by a *common factor*

12
New cards
geometric mean
a term between two terms of a geometric sequence
consecutive terms of a geometric sequence are proportional
formula: a/x = x/b or x=√ab
consecutive terms of a geometric sequence are proportional
formula: a/x = x/b or x=√ab

13
New cards
altitude
segment drawn from a vertex that is perpendicular to the opp. of a triangle
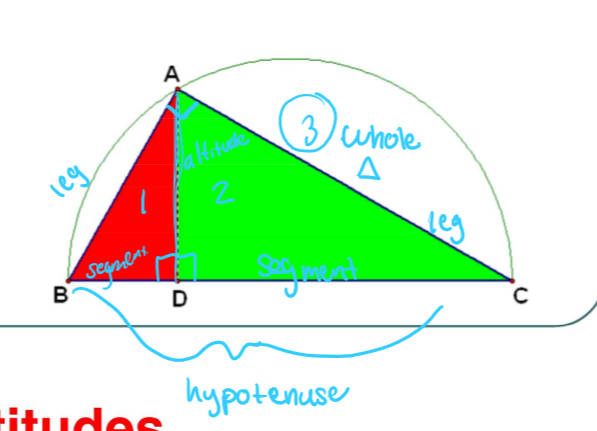
14
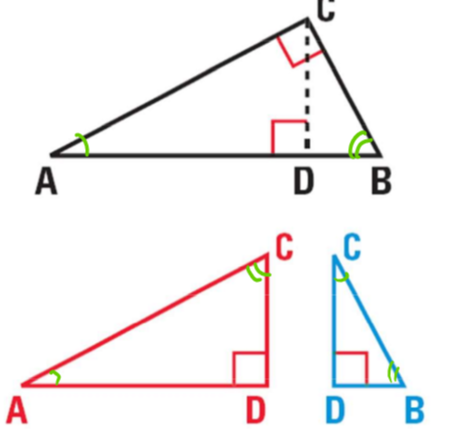
New cards
right triangle similarity theorem
if the altitude is drawn to the hyp. of a right triangle the two triangles made + the orginial are similar to each other
15
New cards
Heartbeat (altitude theorem)
the altitude from the right angle to the hyp. divides the hyp. into two segments. the length of the altitude is the GM of the two segments
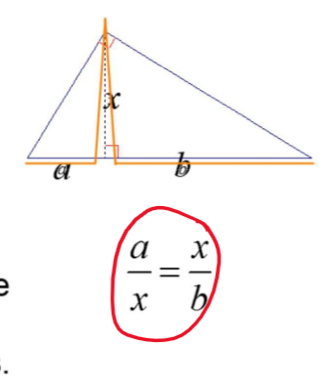
16
New cards
Boomerang (leg theorem)
the length of each leg in a right triangle is the geometric mean of the lengths of the hypotenuse and the segment of the hyp. that is adjacent to the leg
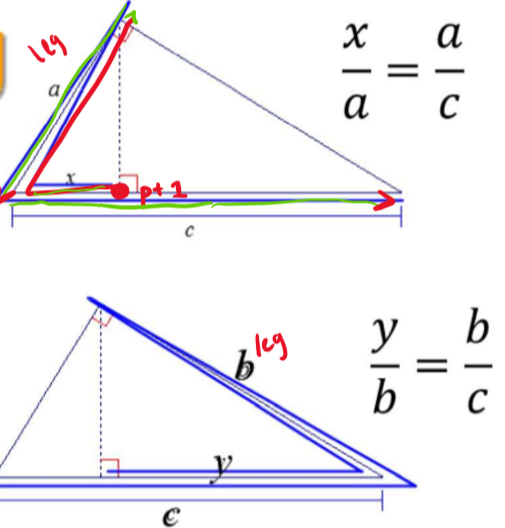
17
New cards
side-splitter theorem
if a line is parallel to one side of a triangle and intersects the other two sides, it divides those sides proportionally
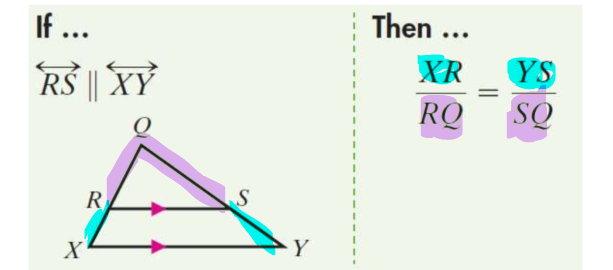
18
New cards
part two of side-splitter
if 3 or more parallel lines intersect two transversals then the segments intercepted on the transversals are proportional
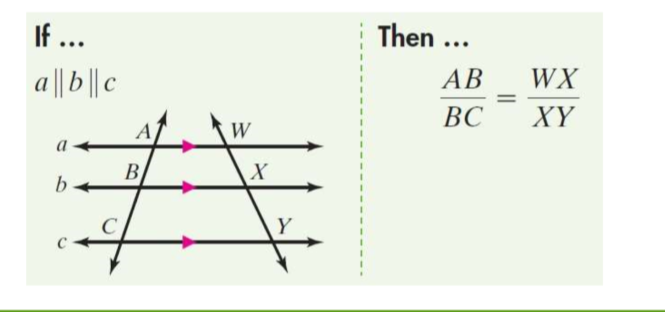
19
New cards
triangle-angle-bisector theorem
if a ray bisects an angle of a triangle it divides the opposite side into 2 segments that are proportional to the other two sides of the triangle
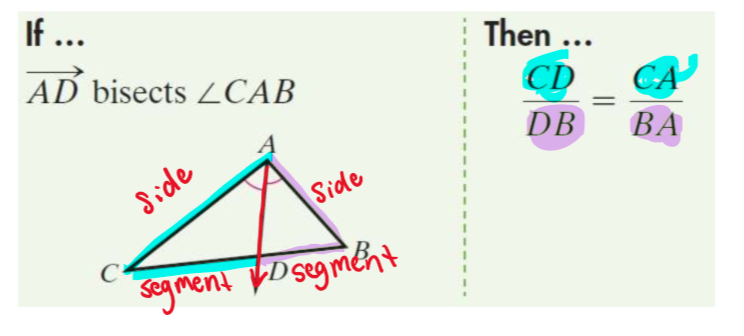
20
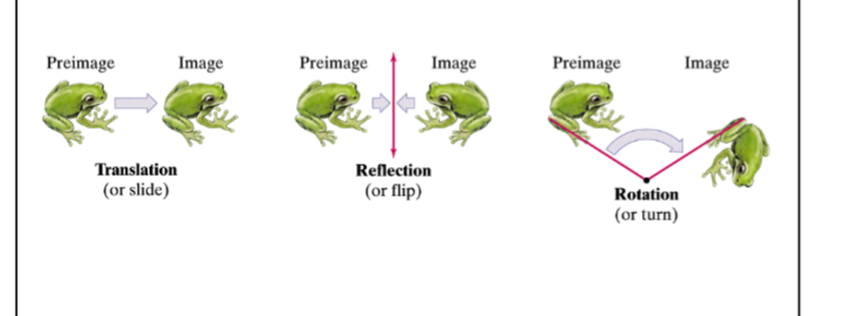
New cards
transformation
when you change the position, shape, or size of a figure
the original figure is the preimage, the result is the image
the original figure is the preimage, the result is the image
21
New cards
isometry
when the preimage and image are congruent, also called a %%rigid transformation%%
the three types are: @@translations@@, reflections, and ==rotations==
the three types are: @@translations@@, reflections, and ==rotations==
22
New cards
naming images
arrow notation (→)
prime notation (‘) is used to identity image points
example: K→K’
prime notation (‘) is used to identity image points
example: K→K’
23
New cards
translation rule
ex: (x,y) → (x-3,y+2)
or:
or:
24
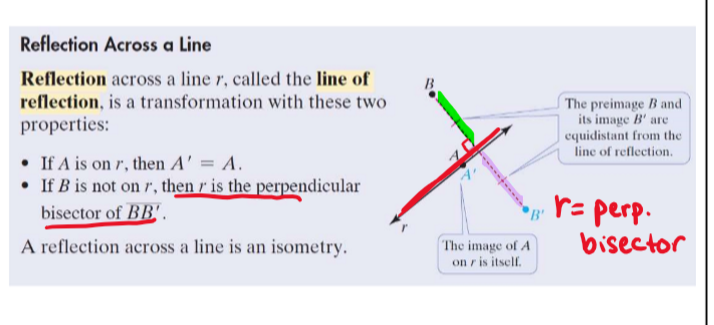
New cards
reflections
when a figure flips across a line, the preimage and image are congruent with opposite orientations
25
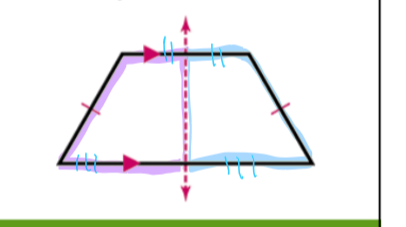
New cards
line symmetry/reflectional symmetry
figures are reflections on either sides of the line, and are congruent
the line of symmetry divides these parts
the line of symmetry divides these parts
26
New cards
rotations
the center of rotation is what an object rotates from
always counter clockwise
always counter clockwise
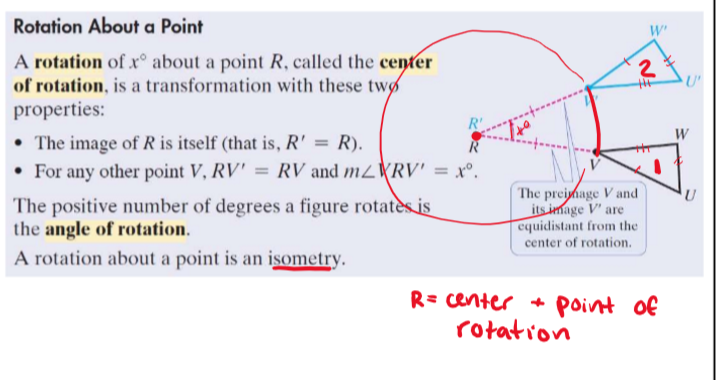
27
New cards
center of a regular polygon
point that is equidistant from its vertices
the amount of vertices determine the number of congruent triangles
the amount of vertices determine the number of congruent triangles
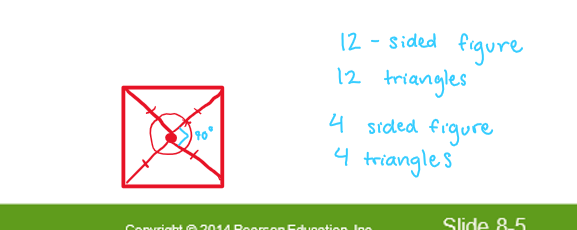
28
New cards
rotational symetry
if a figure rotates ≤180° and becomes its own image
angle of rotation is the smallest angle needed for this to happen
angle of rotation is the smallest angle needed for this to happen
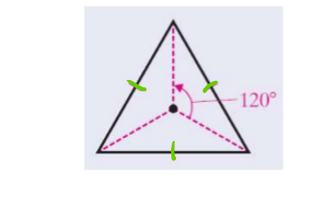
29
New cards
dilation
scale factor makes a smaller or larger copy of a figure that is similar
enlargements are if the scale factor is greater than 1
reductions are if the scale factor is b/t 0 and 1
enlargements are if the scale factor is greater than 1
reductions are if the scale factor is b/t 0 and 1
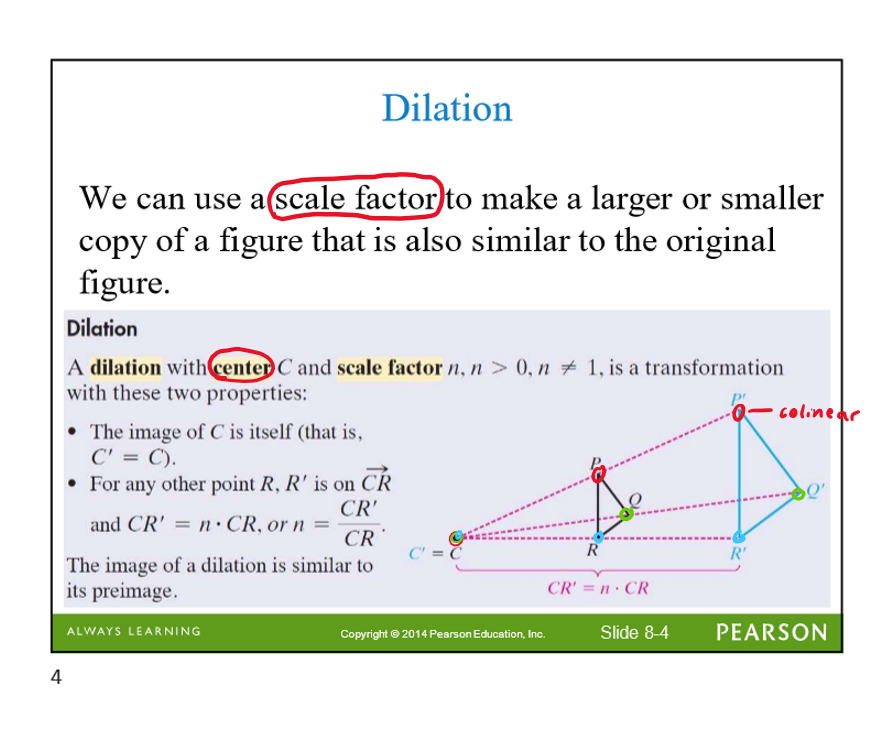
30
New cards
pythagorean theorem
a²+b²=c²
%%c= hypotenuse%%
pythagorean triples are integers that work
if c² > a²+b² the triangle is obtuse
if c²< a²+b² the triangle is acute
%%c= hypotenuse%%
pythagorean triples are integers that work
if c² > a²+b² the triangle is obtuse
if c²< a²+b² the triangle is acute
31
New cards
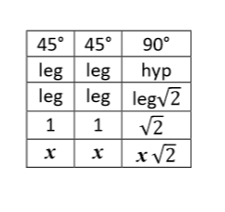
45-45-90 Triangles
isosceles right triangles
hyp = leg x √2
hyp = leg x √2
32
New cards
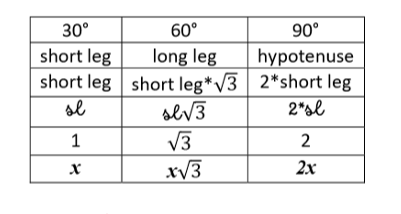
30-60-90 Triangles
\-can seperate equilateral triangles into 2 of these
long leg = short leg x √3
hyp. = short leg x 2
long leg = short leg x √3
hyp. = short leg x 2
33
New cards
trigonometry!!
\-calc in degrees mode
\-round to the nearest thousandth
\-round to the nearest thousandth
34
New cards
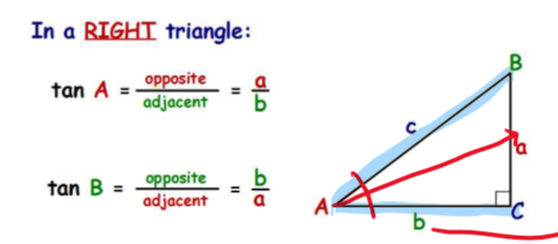
tangent ratio
tan = opposite leg/adjacent leg
tangent ratios cannot be 0 or negative
tangent ratios cannot be 0 or negative
35
New cards
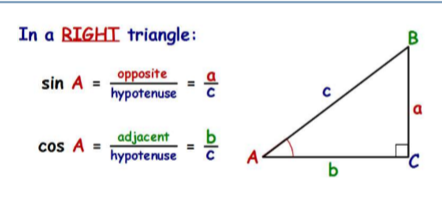
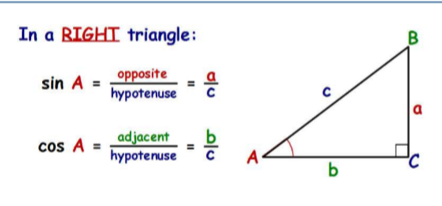
sine
sin = opposite leg/hypotenuse
always b/t 0 and 1
always b/t 0 and 1
36
New cards
cosine
cos = adjacent/hyp.
always b/t 0 and 1
always b/t 0 and 1
37
New cards
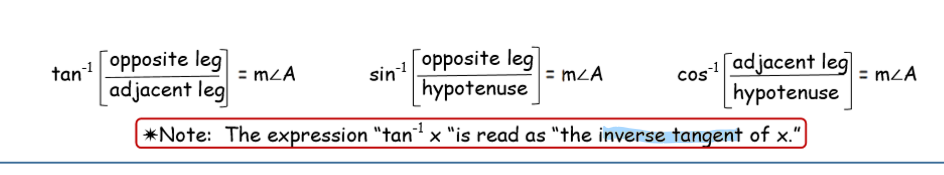
inverse ratios
use to find missing angles
(tan, sin, cos) to the negative first power on ur calc
(tan, sin, cos) to the negative first power on ur calc
38
New cards
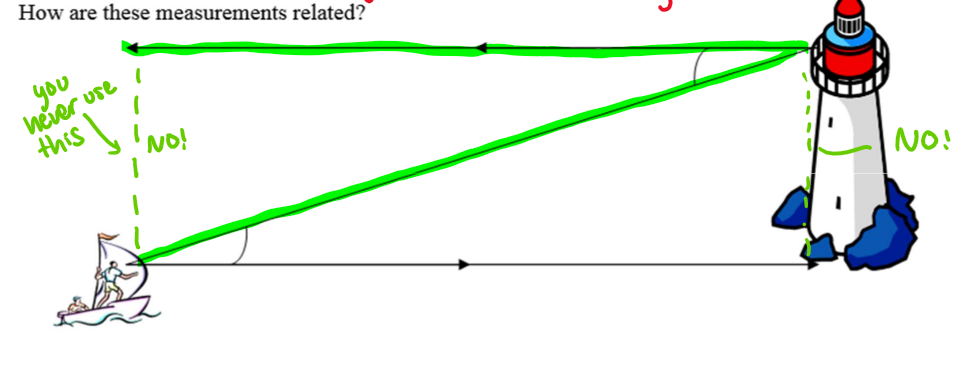
elevation and depression angles
A of E - the angle formed between the horizontal and diagonal when looking up
A of D - the angle formed between the horizontal and diagonal when looking %%down%%
the line of sight is what you see
DONT USE THE VERTICAL SIDE!!!
A of D - the angle formed between the horizontal and diagonal when looking %%down%%
the line of sight is what you see
DONT USE THE VERTICAL SIDE!!!
39
New cards
skipping unit 10!
refer back to those other flashcards for that :)
40
New cards
3 dimensional nets
A 3D net is a 2D pattern that can be folded to create a 3D shape. It shows all the faces of the shape and how they connect.
41
New cards
Surface area
the area of the surface the solid
LA + area of the bases
SA = 2B + Ph
B = area of the base
LA + area of the bases
SA = 2B + Ph
B = area of the base
42
New cards
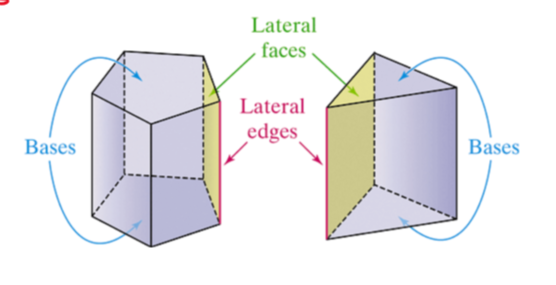
prism
polyhedron with two congruent parallel faces (bases),
the other face are lateral faces
name a prism using the base shapes
the other face are lateral faces
name a prism using the base shapes
43
New cards
Lateral area
the sum of the areas of the lateral faces
LA = Ph
P = perimeter of one base
h = height of the prism
LA = Ph
P = perimeter of one base
h = height of the prism
44
New cards
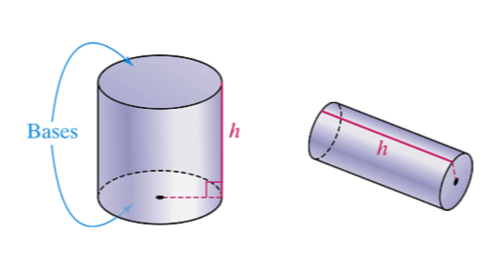
cylinder
Surface area of a cylinder
2B + 2πrh or 2πr²+2πrh
2B + 2πrh or 2πr²+2πrh
45
New cards
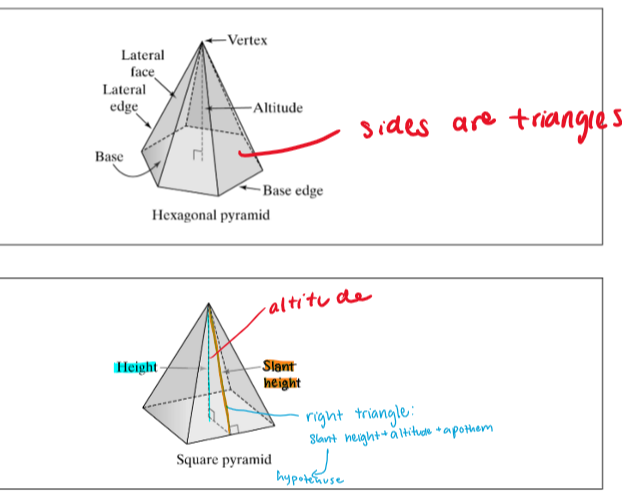
pyramid
a polyhedron where the base it a polygon and the lateral faces are triangles that meet
Sa=B+½Pl
l = fancy squiggly l, aka the slant height
Sa=B+½Pl
l = fancy squiggly l, aka the slant height
46
New cards
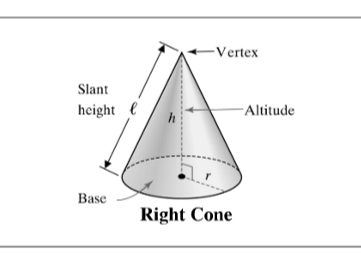
cone
the base of a cone is always a circle
SA = B + πrl
or SA = πr²+πrl
l= fancy l aka slant height
SA = B + πrl
or SA = πr²+πrl
l= fancy l aka slant height
47
New cards
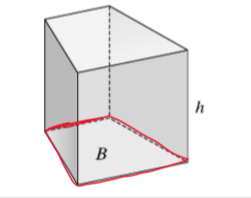
volume of a prism
volume is the amount of space a figure occupies
V = Bh
B= area of the base
V = Bh
B= area of the base
48
New cards
Cavalieri’s Principle
if two solids have the same height and same area at every cross section they have the same volume
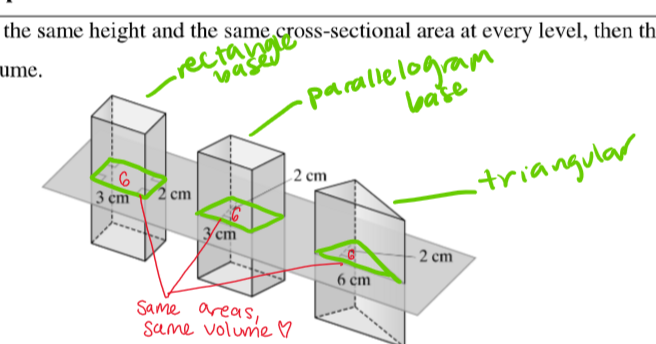
49
New cards
volume of a cylinder
V=Bh
V=πr²h
V=πr²h
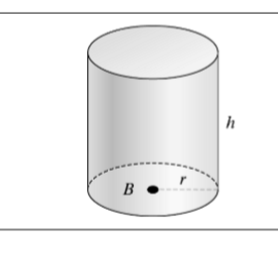
50
New cards
composite solid
combination of two simple solids
51
New cards
volume of a pyramid
V=1/3Bh
it is one third the volume of a prism
it is one third the volume of a prism
52
New cards
volume of a cone
V=1/3Bh
V=1/3πr²h
V=1/3πr²h