Geography IGCSE - Population
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Describe and give reasons for the rapid increase in the world’s population
Increasing life expectancy → sanitation, accessibility to healthcare + improved tech
Decreasing death rate → accessibility + cost to healthcare, +improved tech.
Decreasing birth rate → education on reproduction, integration of women in the workforce
Rate of natural change
natural increase/decrease = birth rate - death rate
Carrying capacity
The largest population that the resources of a given environment can support
Optimum population
The best balance between a population and resources available to it → viewed as the population giving highest average living standards in a country.
Underpopulation
too few people in an area to use the resources available effectively
Overpopulation
too many people in an area relative to the resources and the level of technology available
Causes and consequences of under-population
low birth and fertility rate → underused resources → shortage of workers → lower levels of production + exports → lowers country’s wealth → fewer customer for goods and services
Causes and consequences of over-population
high birth and fertility rate → increase levels of pollution → crime rates → unemployment → food and water shortages → pressures on services (e.g. housing + healthcare)
Main causes of a change in the population size
birth rate
death rate
migration → emigration (entering) or immigration (leaving)
Impacts of social factors on birth and death rate
Sanitation
Quality nutrition
Education on healthy lifestyle
Accessibility to healthcare (doctors per 1000)
Cultural expectations
Infant mortality rates
Religion
Resistance to antibiotics
New infectious agents (eg. MERS, SARS, Ebola)
Physical environment
Better education
Improved nutrition
Impacts of economic factors on birth and death rate
Extreme poverty level
Cost of healthy foods
Cost of health care
Wealth
Children in workforce
Poverty
Access to sanitation and clean water
Quality of housing
Type of occupation
Impacts of political factors on birth and death rate
Regulation of safety
Promotion of healthy practices
Regulation of unhealthy products (eg. cigarettes)
Welfare payments
War
Type of government (e.g. democracy)
Pro natalist policies
policies with the purpose of increasing the birth rate/fertility rate of an area
Anti natalist policy
encourage people to plan smaller families, lower fertility rates and reduce the number of births
Reasons for rural - urban migration
more work opportunities
higher wages
better living conditions
Better health care in cities
Greater educational opportunities
Bright light perception
International voluntary migration
people chose to emigrate to another country
Forced migration
people having to leave their homes due to factors such as violent conflict, infrastructure projects, natural disasters, or the effects of climate change
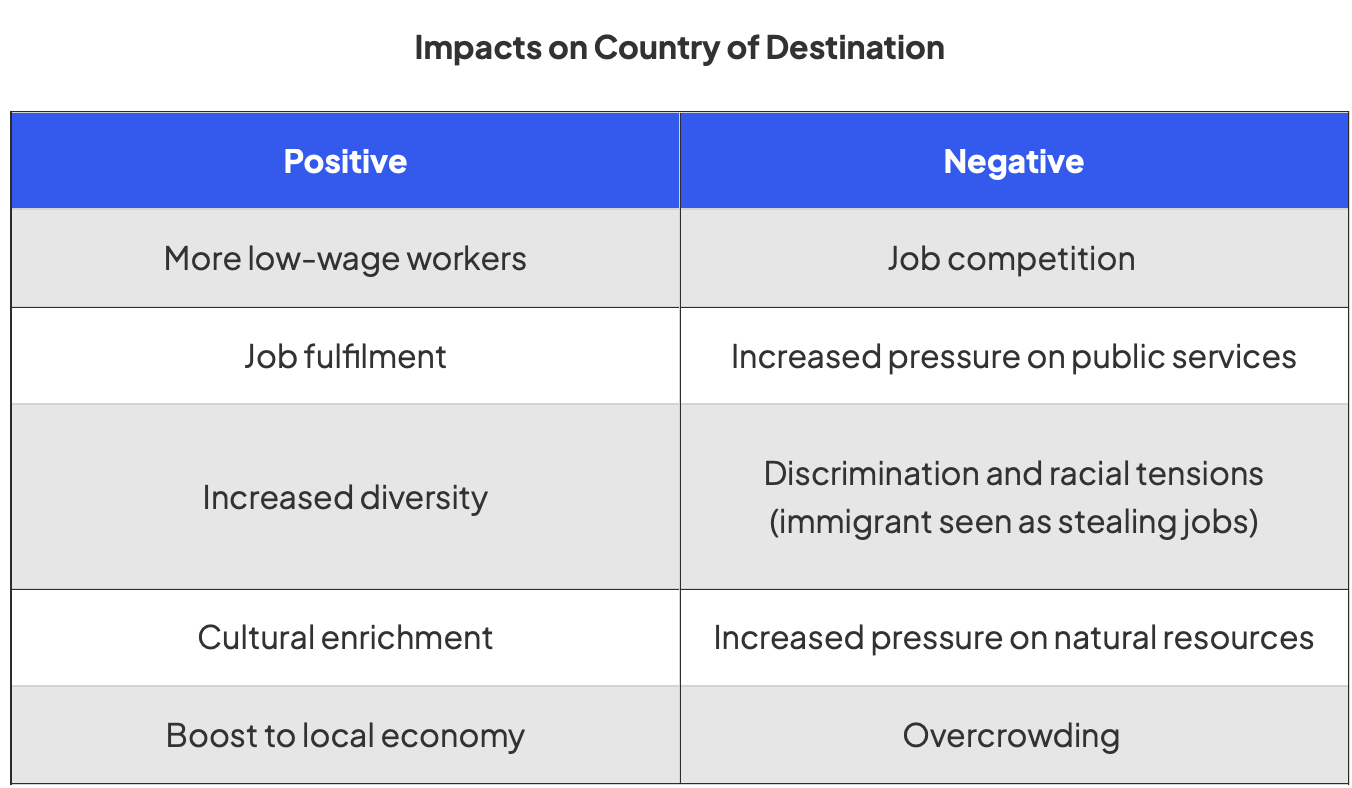
impacts on the destination
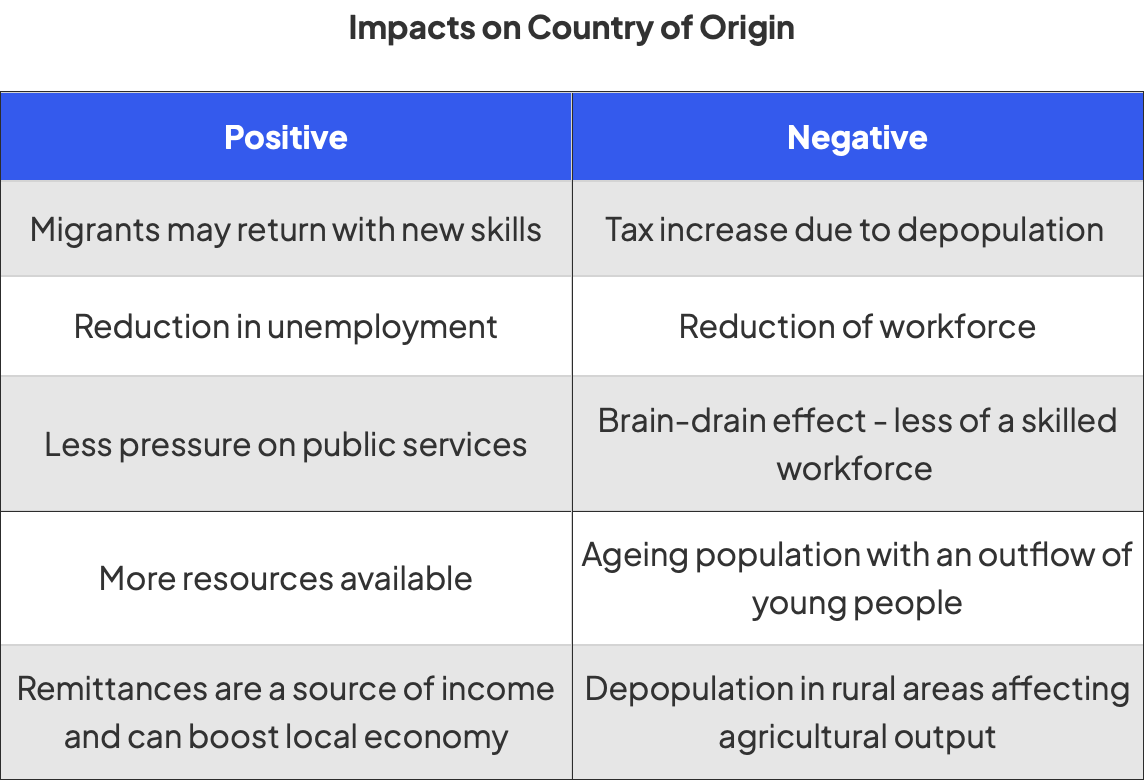
impacts on the country of origin
impacts on migrants themselves

Describe the social factors influencing the density and distribution of population
Security → high levels of crime discourage people from settling in an area → low population density Low crime rates can encourage people to move to an area → high population density.
Describe the physical factors influencing the density and distribution of population
Relief and landforms → Lowland plains, flat river valleys and deltas and volcanic areas with fertile soil tend to have high population densities
Weather and climate → Temperate areas which experience few extremes of weather and climate → more attracted than areas which experience extremes.
Soil type and quality → Areas that have rich, fertile soils allowing successful agriculture tend to have higher population densities
Water supply → Water supply is essential for human survival and development → areas which have sufficient water tend to have denser populations.
Raw materials/natural resources → wealth of natural resources such as oil, coal or minerals
Natural threats → affect population density as people may try to avoid areas where pests, threatening animals and diseases
Describe the economic factors influencing the density and distribution of population
Job opportunities
Infrastructure
Accessibility
Describe the political factors influencing the density and distribution of population
Public services
War + conflict
Political decisions