2 - molecular basis of pain sensation: TRP channels
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
hyperalgesia
increased pain from stimulus that normally provokes pain
inflammatory
pain that occurs when tissue is damaged
coordinated response to help tissue heal
nociceptive pain
arises from actual or threatened damage to non-neural tissue
due to activation of nociceptive
allodynia
due to stimulus that does not normally provoke pain
ex.) light feather touch causing pain
neuropathic pain
caused by lesion or disease of the somatosensory NS
nociception
neural process of encoding noxious stimuli
nociceptive neuron
central or peripheral neuron of somatosensory NS that is capable of encoding noxious stimuli
nociceptive stimulus
actually or potentially tissue-damaging event transduced and encoded by nociceptors
nociceptor
high-threshold sensory receptor (i.e. an ion channel) of the peripheral somatosensory nervous system that can transduce and encode noxious stimuli
noxious stimuli
stimulus that is damaging or threatens damage to normal tissues
pain pathway steps review
noxious stimuli convert into electrical signals by nociceptors
activation of ion channels alter resting membrane potention
depolarization evokes AP
large drg neuron
diameter = large
myelination = heavy
fiber = Aβ
conduction speed = very fast
soma size = large
medium drg neuron
diameter = medium
myelination = moderate
fiber = Aδ (delta)
conduction speed = fast
soma size = medium
small drg neuron
diameter = small
myelination = none
fiber = C
conduction speed = slow
soma size = small
current clamp
records changes in ion channel conductance
Ohm’s law
V = I R
depolarization makes membrane porentials more ______
positive
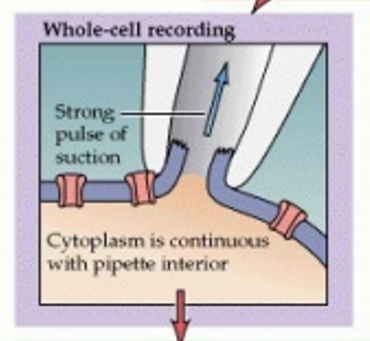
whole-cell voltage clamp
measures total ion currents across an entire cell membrane by using a glass micropipette to "clamp" the membrane potential at a set voltage
selectivity filter
narrowest point permeating ions pass through
gated ion channels
open + close depending on type
voltage, ligand and mechanical
TRP channels
mediate sensation of pain, temperature and chemical irritants
in drg
TRPA1
detector for allyl isothiocynate (wasabi) and is pain detector
TRPM8
mint
TRPV3
camphor
TRPV1
detector for capsaicin (chili) and noxious heat sensory
polymodal peptidergic receptors
express multiple pain-responsive ion channels
TRP channel step 1
agonists for TRP channels that cause pain activate TRPA1 channels
TRP channel step 2
compounds including bradykinin are released
binds to BDKRB2 receptor (GPCR)
activates TRP channels
TRP channel step 3
activation of TRP channels allow influx of Ca2+ to depolarize the cell
AP to spinal cord step 4
when terminal reaches above threshold, nociceptive neurons initiate APs
propogate along C and Aδ fibers
AP to spinal cord step 5
pain fibers found in laminae 1 and 2 of dorsal horn
AP to spinal cord step 6
nerve terminals release neurotransmitters
glutamate, substance P and calcitonin gene related peptide
activates postsynaptic receptors spinothalamic tract neurons
isothiocyanates
natural compounds found in horseradish and wasabi that activate the TRPA1 channel
also found in broccoli, kale and cababge
how do isothiocyanates bind to TRPA1
covalently binds to sulfur atom of the cytesine residue in TRPA1 to form a disulfide bond
modified cytesines open TRPA1
depolarization initiates AP
non-selective cation channels
callow cations such as Na+, K+ and Ca2+
ex.) TRP channels
fluorescent calcium indicators
used to look at TRP channel activity
measure intracellular Ca2+ concentrations
fura-2
chemical calcium indicator
Ca2+ free and Ca2+ bound have 2 different absorption properties that can be used to quantify Ca2+ change
GCaMP
genetically encodable Ca2+ indicator
“split” GFP molecule that is brought together by Ca2+ binding domains
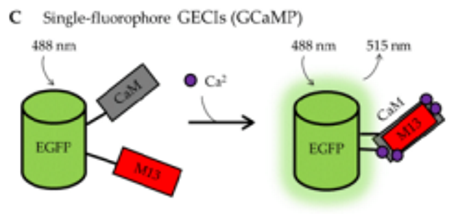
CaM
calcium binding domain of calmodulin
M13
calmodulin binding domain of skeletal muscle myosin light chain
cameleon
also GECI and Ca2+ brinsg together 2 different fluorescent proteins to allow fluorescent energy transfer (FRET)
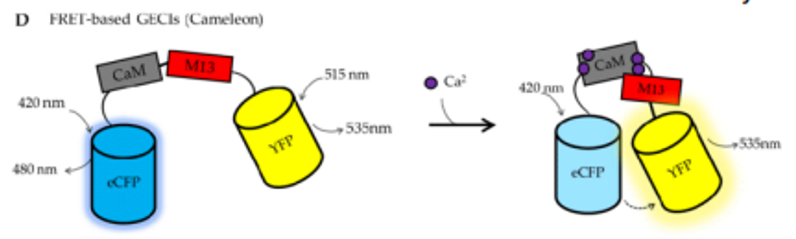
ratiometric Ca2+ indicators
measure Ca2+ by emitting light at 2 different wavelengths
negatively charged compounds are ______
cell impermeant and require invasive loading techniques
acetoxymethyl (AM) ester modification
masks negatively charged caroxylic groups and produces uncharged hydrophobic molecules that can be passively loaded into live cells
Fure2-AM
cell permeable and distributes evenly when it enters the cell
cellular esterases remove the acetoxymethyl group once in the cell and allow Fura2 to chelate calcium
Ca2+ free Fura2 AM imaging
excitation max at ~380nm and emits 510nm
Ca2+ bound Fura2 AM imaging
excitation max at ~340nm and emits 510nm