1. Clinical Manifestations of GI Disorders
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
A ________ ________ is of utmost importance to get you on the correct diagnostic path.
good history
difficulty in eating/swallowing
dysphagia
What does dysphagia commonly occur secondary to?
O
M
F
T
N
oral pain
masses
foreign objects
trauma
neuromuscular dysfunction
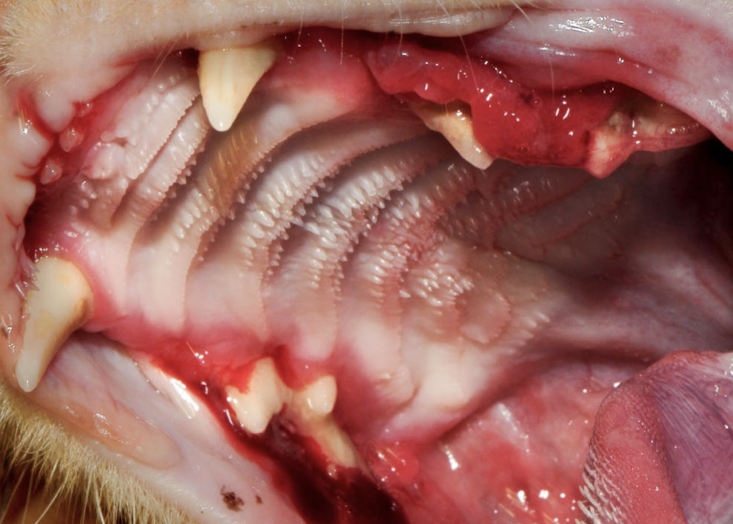
What is this showing?
stomatitis
What are the types of neurogenic dysphagia?
P
P
C
prehensile
pharyngeal
cricopharyngeal
inability to pick up food or food dropping from the mouth
prehensile dysphagia
What should be a concern if an animal is displaying prehensile dysphagia?
rabies
In prehensile dysphagia, with what cranial nerves are their deficits in?
CN V, VII, IX, and XII
What do pharyngeal and cricopharyngeal dysfunction usually result in? Why?
regurgitation; there are swallowing defecits
abnormal bacterial growth, especially pathogenic oral bacteria (anaerobes and gram negatives)
halitosis
How can halitosis present clinically?
T
C
O
tissue necrosis
calculus/periodontal disease
oral/esophageal retention of food
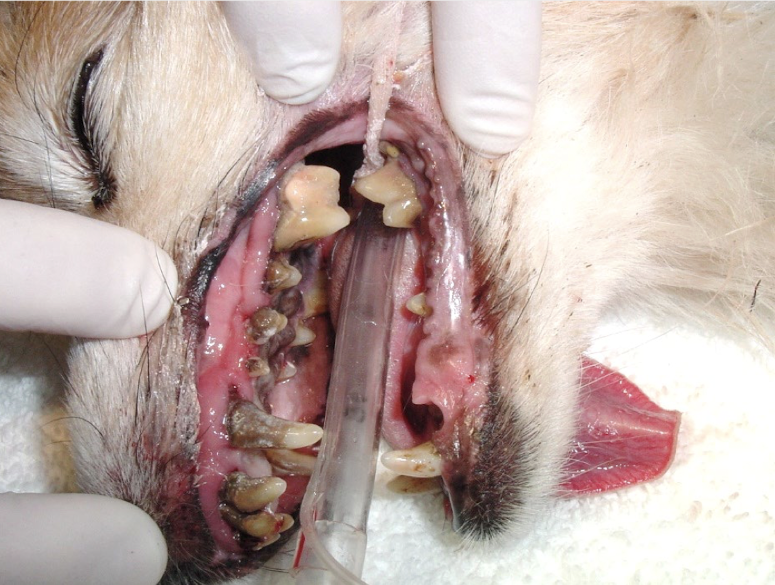
What is this showing?
halitosis
excessive salivation
ptyalism
What is ptyalism usually associated with? What else can it be associated with?
nausea; toxins and sour/bitter tastes
saliva “leaks” from the mouth, as the patient is too painful or unable to swallow
pseudopytalism
expulsion of material from the stomach or intestines
vomiting
Vomiting is an ________ process with _________ ________ and ________ ________.
active; abdominal motion; prodromal nausea
expulsion of food, water, and or saliva from the mouth, pharynx, or esophagus
regurgitation
What type of process is regurgitation?
passive
What does regurgitation have to be differentiated from?
vomiting or expectoration
Is prodromal nausea associated with regurgitation?
no
Is prodromal nausea associated with vomiting?
usually
Is retching associated with regurgitation?
no
Is retching associated with regurgitation?
no
Is food material produced with regurgitation?
±
Is food material produced with vomiting?
±
Is bile produced with regurgitation?
no
Is bile produced with vomiting?
±
Is blood produced with regurgitation? If yes, what type of blood?
±; undigested
Is blood produced with vomiting? If yes, what type of blood?
±; digested or undigested
What amount of material is associated with regurgitation?
any amount
What amount of material is associated with vomiting?
any amount
What is the time relative to eating when it comes to regurgitation?
anytime
What is the time relative to eating when it comes to vomiting?
anytime
Is there distention of the cervical esophagus with regurgitation?
rare
Is there distention of the cervical esophagus with vomiting?
no
What is the pH of the regurgitated material?
>/= 7
What is the pH of the vomited material?
</= 5 or >/= 8
What is vomiting most commonly associated with?
M
I
G
G
T
motion sickness
ingestion of emetogenic substances (drugs, toxins)
GI obstruction
GI inflammation (colitis)
triggering of chemoreceptor trigger zone (CRTZ)
If the patient is regurgitating and is also dysphagic, what should be considered?
oral, pharyngeal, or cricopharyngeal disease
If the patient is regurgitating, but is not dysphagic, what are some of the most likely causes?
E
E
G
M
esophageal strictures (cicatrix)
esophagitis
gastroesophageal reflux (GERD)
megaesophagus
expulsion of material from the respiratory tract that can be confused with regurgitation or vomiting
expectoration
What is expectoration generally associated with? Why?
coughing; coughing in dogs often stimulates a gag reflex and possible vomiting
expulsion of digested blood or fresh blood
hematemesis
True or false: In hematemesis, few flecks of fresh blood can be present due to vigorous vomiting.
true
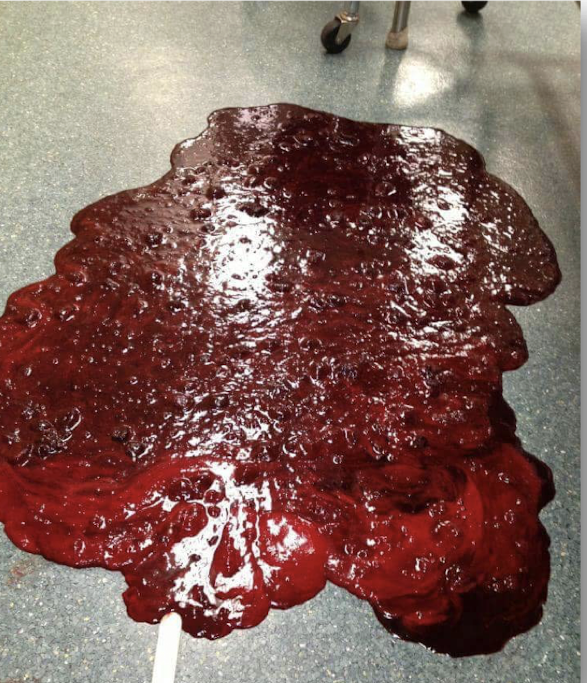

What is this showing?
hematemesis
excessive fecal water
diarrhea
It is important to distinguish between ________ and ________ diarrhea, as well as if it is ________ or ________ intestinal in origin.
acute; chronic; large; small
What is acute diarrhea most commonly due to?
D
P
I
diet
parasites
infectious disease
What is chronic diarrhea most commonly due to?
P
I
N
I
parasites
infiltrative disease
neoplasia
immune mediated disease
Is weight loss expected with small intestinal diarrhea?
yes
Is weight loss expected with large intestinal diarrhea?
it is uncommon
Is polyphagia expected with small intestinal diarrhea?
sometimes
Is polyphagia expected with large intestinal diarrhea?
rare to absent
What is the frequency of bowel movements with small intestinal diarrhea?
often near normal
What is the frequency of bowel movements with large intestinal diarrhea?
sometimes very increased but often normal
What is the volume of feces when it comes to small intestinal diarrhea?
often increased, but can be normal
What is the volume of feces when it comes to large intestinal diarrhea?
sometimes decreased (because of the increased frequency) but can be normal
What blood is associated with small intestinal diarrhea?
melena (rare)
What blood is associated with large intestinal diarrhea?
hematochezia (sometimes)
Is there usually mucus in the feces with small intestinal diarrhea?
uncommon
Is there usually mucus in the feces with large intestinal diarrhea?
sometimes
Is there tenesmus associated with small intestinal diarrhea?
uncommon (but may occur later in chronic cases)
Is there usually mucus in the feces with large intestinal diarrhea?
sometimes
Is vomiting associated with small intestinal diarrhea?
may be seen
Is vomiting associated with large intestinal diarrhea?
may be seen
What are the different categories of chronic small intestinal diarrhea?
M
M
maldigestion
malabsorption
When it comes to chronic small intestinal diarrhea, what are the different types of malabsorption?
N
P
non-protein losing
protein losing
What are important things to do when it comes to chronic large intestinal diarrhea?
E
T
F
evaluate rectal and colonic mucosa first (neoplasia, fungal disease)
therapeutic trials
further diagnostics
What is the fecal score scale?
1-7
What fecal score is ideal?
2
Describe a 1 fecal score.
H
I
R
N
hard and dry
individual pellets
requires much effort to expel from the body
no residue left on the ground when picked up
Describe a 2 fecal score.
F
S
L
firm but not hard
segmented in appearance
little or no residue on ground when picked up
Describe a 3 fecal score.
L
L
M
L
log shaped
little or no visible segmentation
moist surface
leaves residue on ground, but holds form when picked up
Describe a 4 fecal score.
V
L
L
very moist and soggy
log shaped
leaves residue and loses form when picked up
Describe a 5 fecal score.
V
P
L
very moist but has a distinct shape
piles rather than distinct logs
leaves residue and loses form when picked up
Describe a 6 fecal score.
H
P
L
has texture but no defined shape
present as piles or spots
leaves residue when picked up
Describe a 7 fecal score.
W
N
F
watery
no texture
flat puddles

What fecal score is this?
1

What fecal score is this?
2

What fecal score is this?
3

What fecal score is this?
4

What fecal score is this?
5

What fecal score is this?
6

What fecal score is this?
7
fresh blood in/on the feces
hematochezia
With what disease is hematochezia associated with?
large bowel disease
digested blood that is coal black (not dark brown or green)
melena
With what disease is melena associated with?
small bowel or upper GI disease
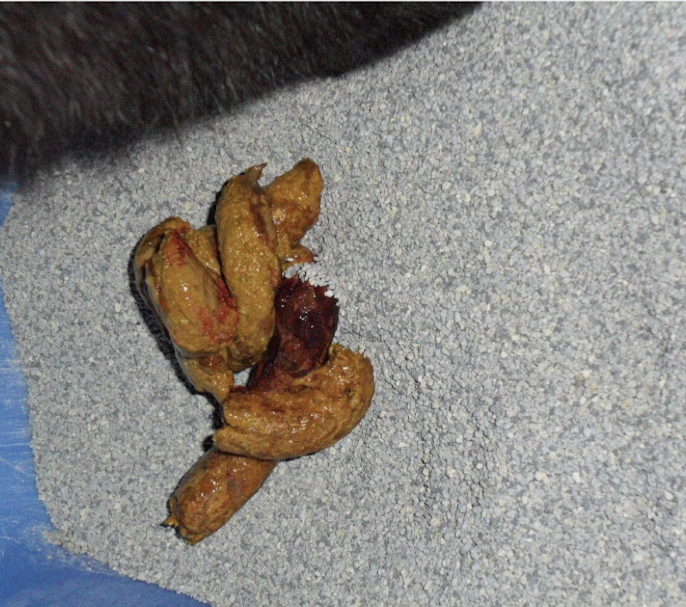
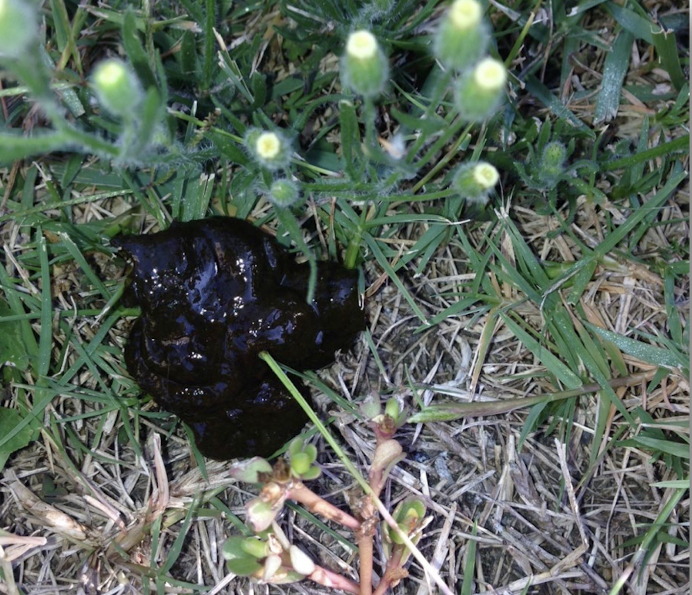
What is this showing?
hematochezia

What is this showing?
melena
ineffectual or painful straining at urination or defecation
tenesmus
True or false: You must differentiate tenesmus between urination and defecation, especially in cats.
true
painful or difficult elimination of feces from the rectum
dyschezia
infrequent and difficult evacuation of feces
constipation
What can be some causes of constipation?
D
B
D
O
W
drugs
behavioral
dietary
obstruction
weakness
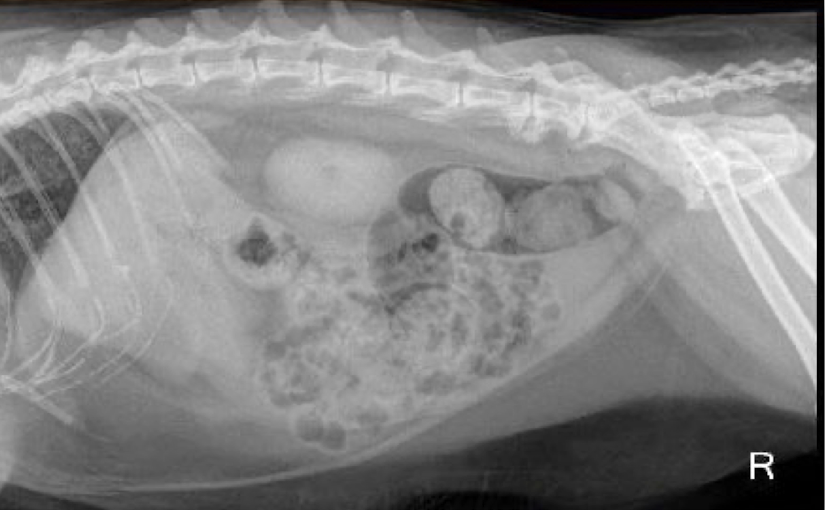
What is this animal most likely suffering from?
constipation
intractable constipation
obstipation
What is an example of obstipation?
megacolon in cats
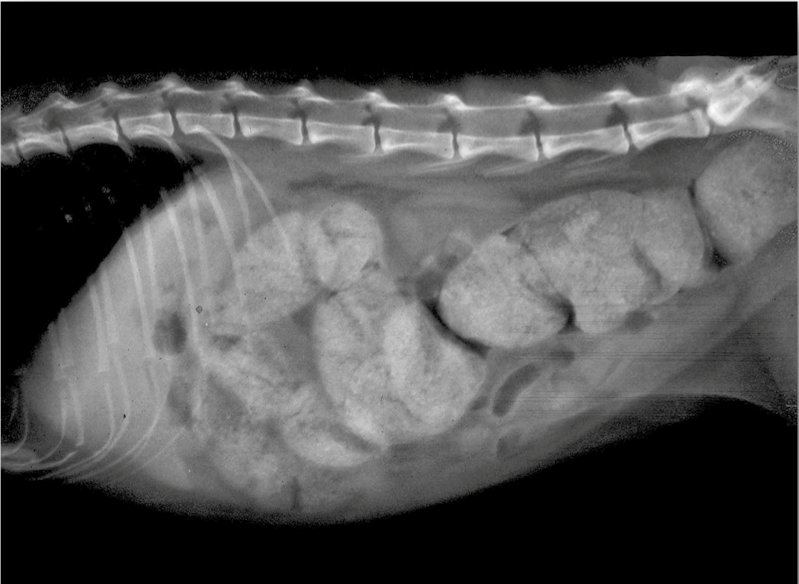
What is this showing?
obstipation