Introduction to Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
Organic Chemistry
Study of carbon-based compounds and their reactions.
Pharmaceutical Organic Chemistry
Focus on organic compounds in pharmaceuticals.
Functional Groups
Atoms/groups in molecules with predictable properties.
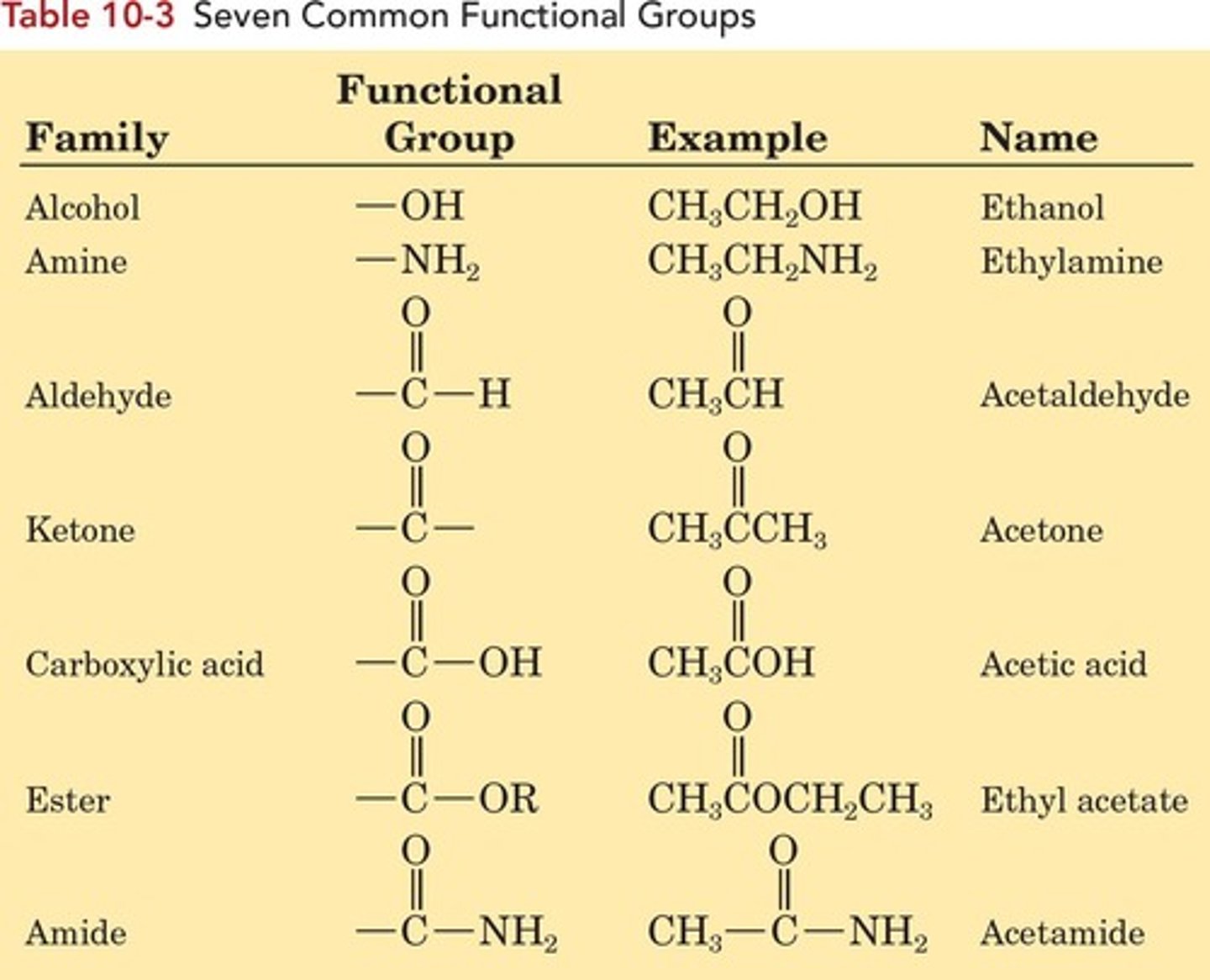
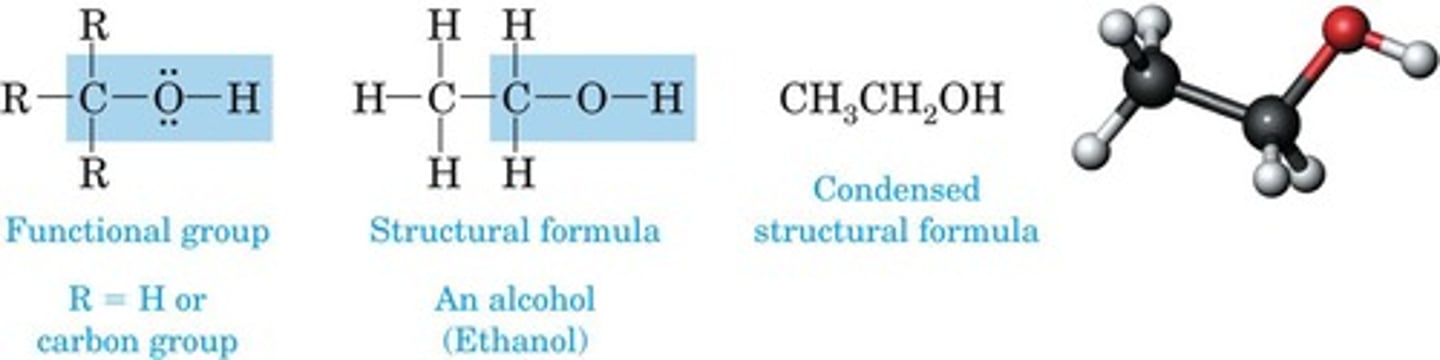
Alcohol
Contains hydroxyl (-OH) group on carbon.
Primary Alcohol
Hydroxyl group on a primary carbon.
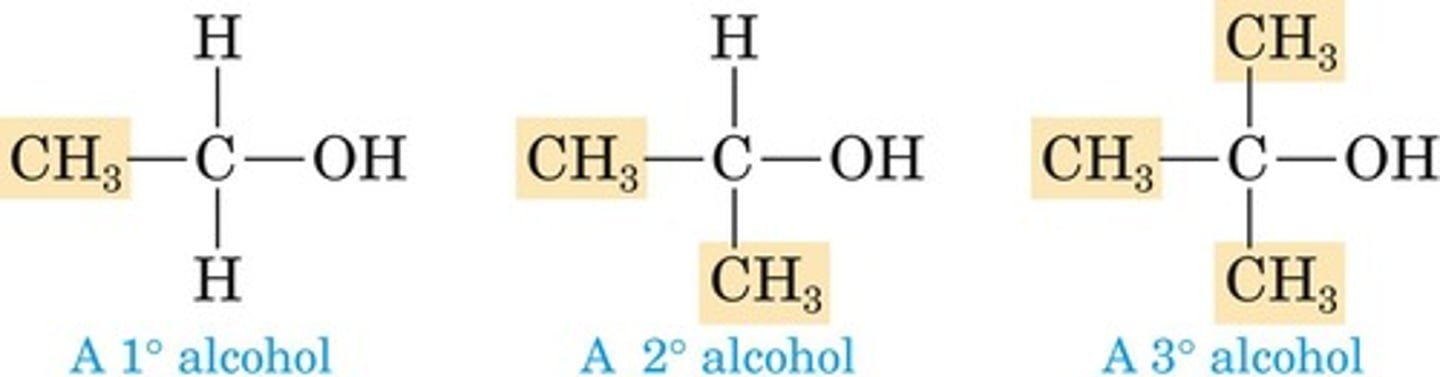
Secondary Alcohol
Hydroxyl group on a secondary carbon.
Tertiary Alcohol
Hydroxyl group on a tertiary carbon.
Amine
Contains nitrogen atom(s) bonded to carbon.
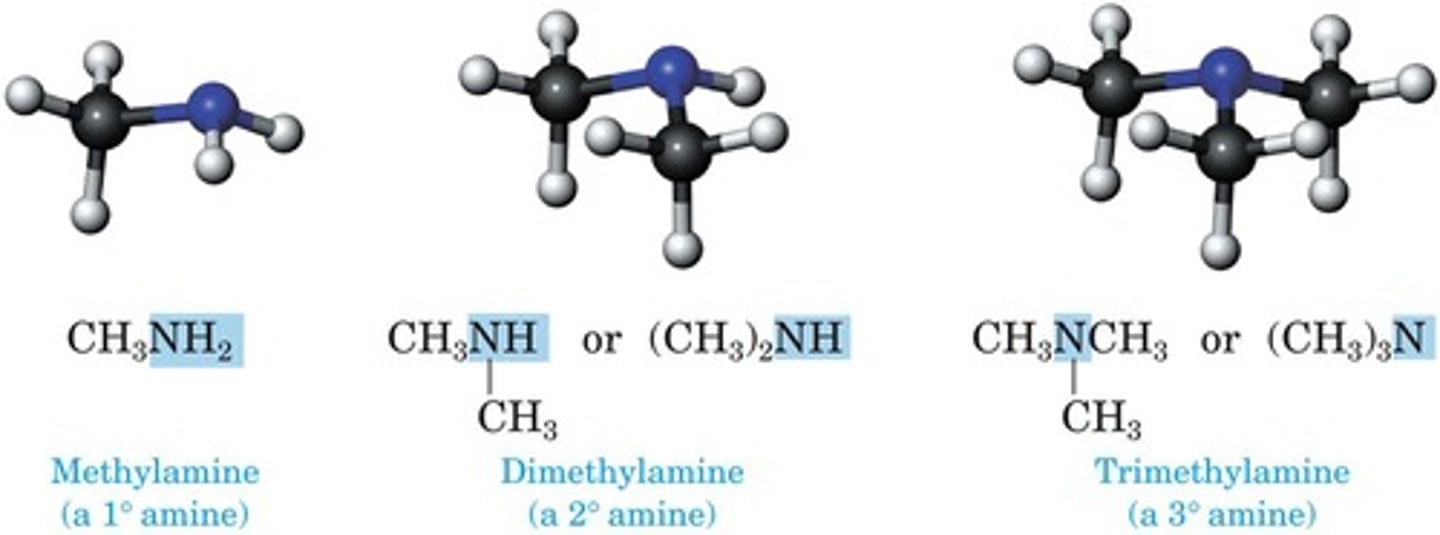
Primary Amine
One carbon attached to nitrogen (RNH2).
Secondary Amine
Two carbons attached to nitrogen (R2NH).
Tertiary Amine
Three carbons attached to nitrogen (R3N).
Aldehyde
Contains carbonyl group bonded to hydrogen.
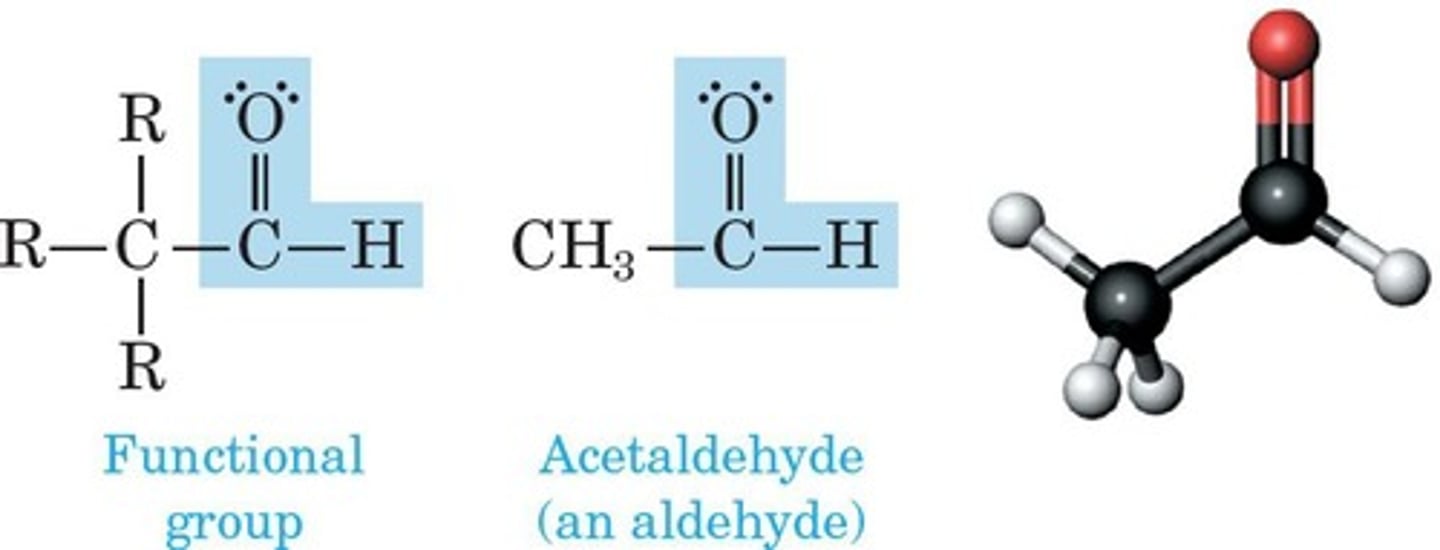
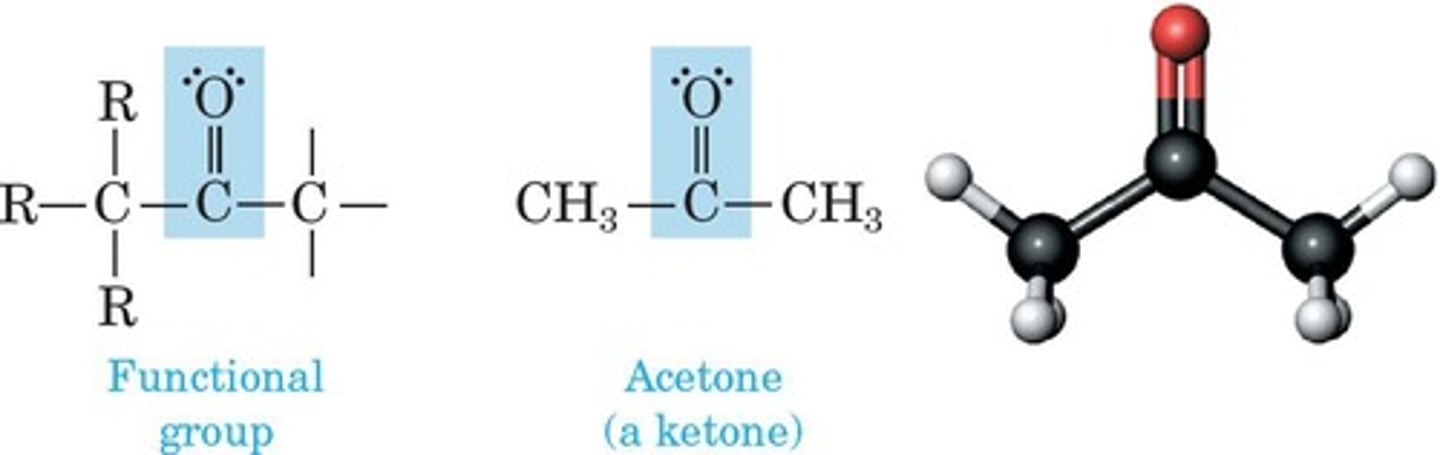
Ketone
Contains carbonyl group bonded to two carbons.
Carboxylic Acid
Contains carboxyl group (-COOH) in structure.
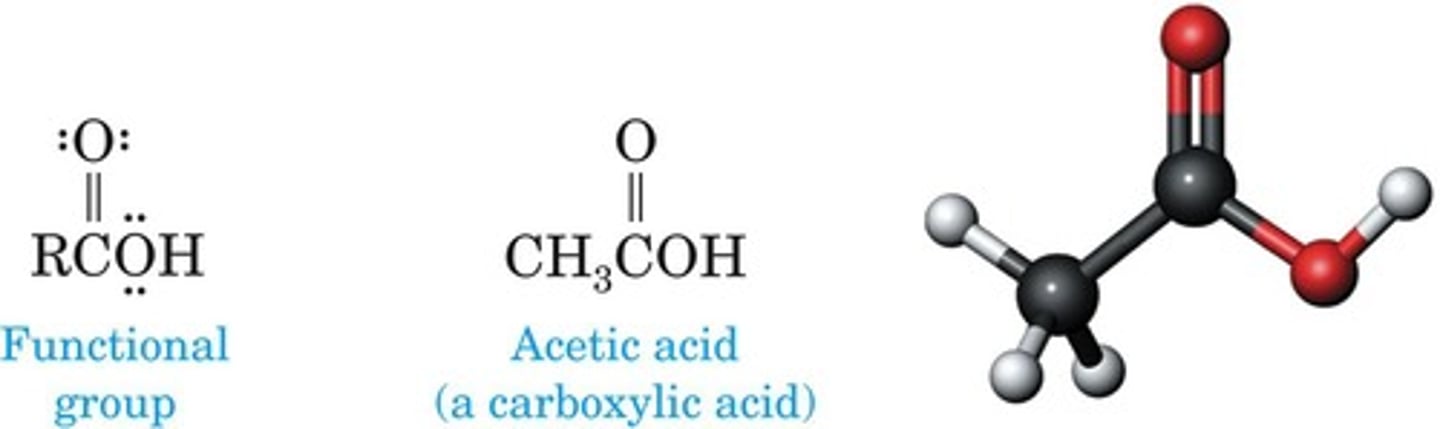
Carboxyl Group
Combination of carbonyl and hydroxyl groups.
Carboxylic Ester
Derived from carboxylic acid, H replaced by alkyl.
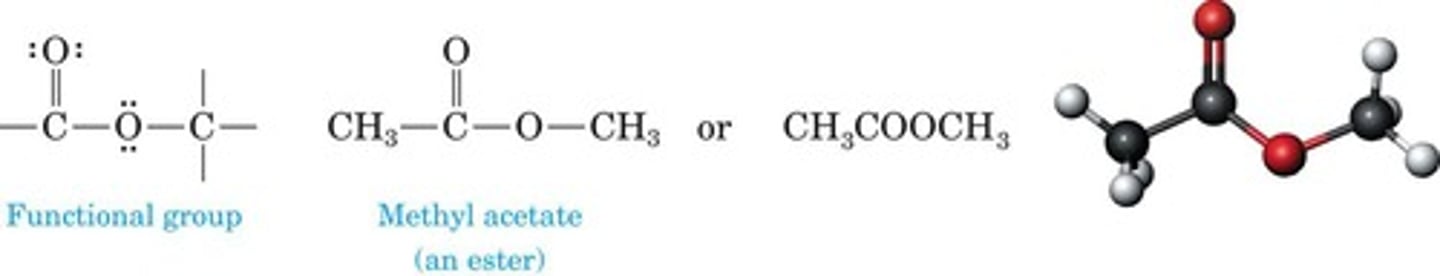
Branches of Chemistry
Includes organic, inorganic, analytical, physical, biochemistry.
Wöhler's Experiment
First synthesis of organic compound from inorganic source.
Organic Compounds
Over 10 million known, primarily carbon-based.
Inorganic Compounds
Estimated 1.7 million known, non-carbon based.
Vital Force Theory
Historical belief that living organisms produce organic compounds.
Carbon Structures
Framework for organic compounds, essential for life.
Biological Molecules
Includes proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, lipids.
Chemical Reactions
Processes involving the transformation of substances.
Amide
Derivative of carboxylic acid with —OH replaced.
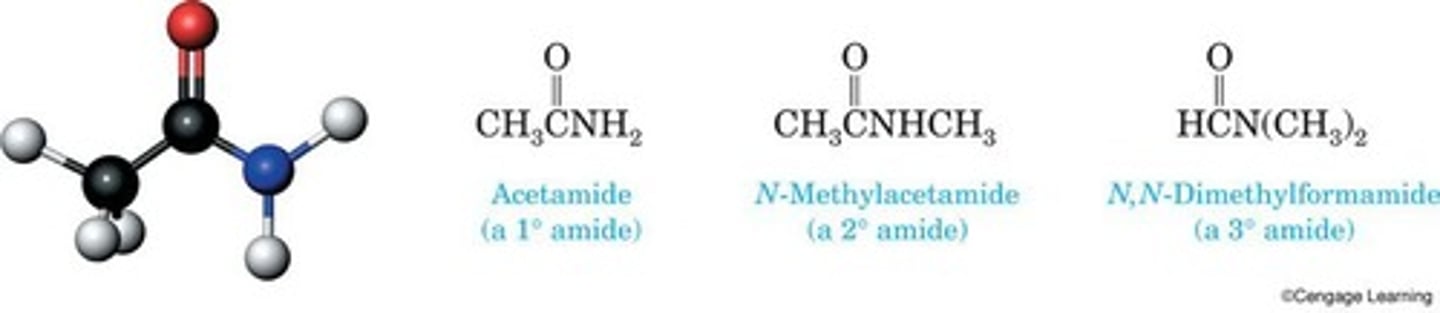
Structural formula
Depicts atoms and bonds in a molecule.
VSEPR model
Predicts molecular geometry based on electron pairs.
Covalent bond
Chemical bond formed by shared electron pairs.
Atomic number (Z)
Number of protons in an atom's nucleus.
Mass number (A)
Total of protons and neutrons in nucleus.
Isotopes
Atoms with same element, different neutron counts.
Atomic mass
Weighted average mass of isotopes in amu.
Electron cloud
Region around nucleus containing negatively charged electrons.
Wave function
Mathematical description of electron's probable location.
Orbital
Region in space where electrons are likely found.
s orbital
Spherical orbital centered around nucleus.
p orbital
Dumbbell-shaped orbital with two lobes.
Electron shell
Energy level containing one or more orbitals.
Aufbau principle
Lowest-energy orbitals fill before higher ones.
Pauli exclusion principle
No two electrons can have identical quantum states.
Hund's rule
Electrons fill degenerate orbitals singly first.
First shell
Contains one s orbital, holds two electrons.
Second shell
Contains one s and three p orbitals, holds eight electrons.
Third shell
Contains one s, three p, and five d orbitals, holds eighteen electrons.
Node
Region in p orbital with zero electron density.
Quantum mechanics
Describes electron energies and behavior.
August Kekulé
Independently observed carbon always has four bonds.
Archibald Couper
Co-discovered carbon's four bond structure.
Tetrahedron
Shape formed by atoms surrounding carbon.
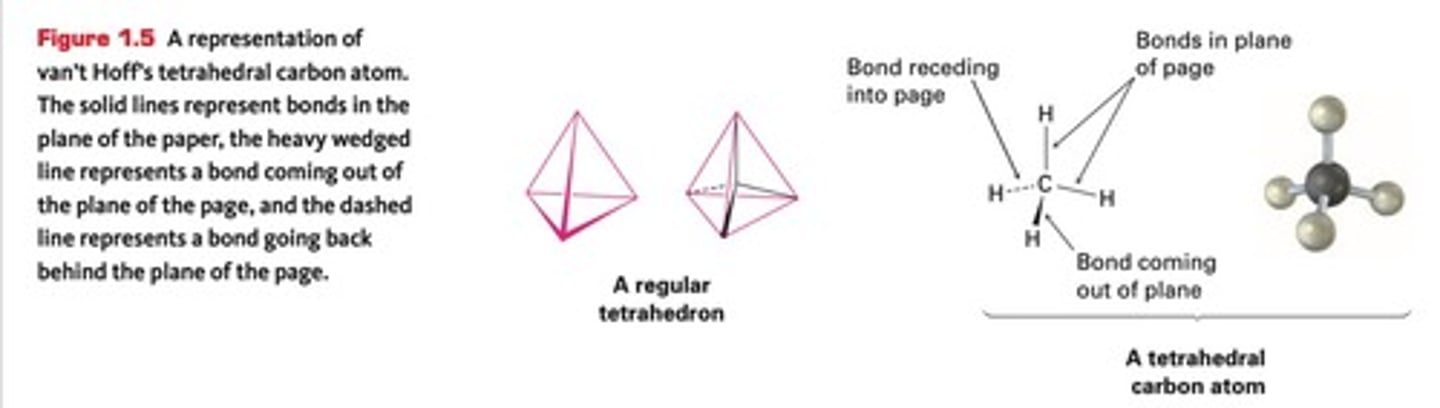
Jacobus van't Hoff
Proposed specific spatial directions for carbon bonds.
Le Bel
Contributed to understanding carbon bond orientation.
Chemical Bond
Attractive force holding atoms together in compounds.
Ionic Bond
Forms through electron transfer between atoms.
Lewis Structures
Diagrams showing valence electrons as dots.
Valence Electrons
Electrons in the outermost shell of an atom.
Stable Molecule
Achieved when atoms complete their electron shells.
Octet Rule
Atoms are stable with eight valence electrons.
Bond Formation
Atoms bond to achieve greater stability.
Non-bonding Electrons
Valence electrons not involved in bonding.
Valence Bond Theory
Describes how covalent bonds form through orbital overlap.
Bond Energy
Energy released when bonds form, measured in kJ/mol.
Bond Length
Distance between nuclei in a bonded molecule.
sp3 Hybrid Orbitals
Combination of s and p orbitals for bonding.
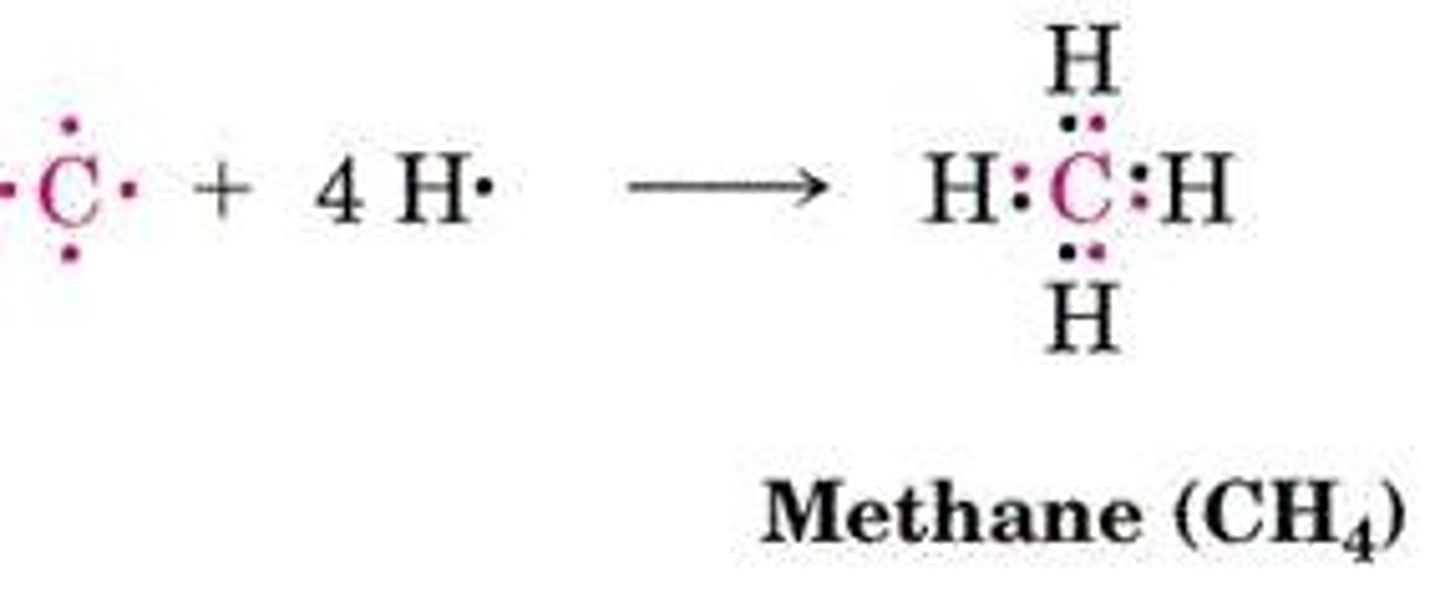
C-H Bonds in CH4
Identical bonds oriented tetrahedrally around carbon.
Bond Strength
Energy required to break a bond.
Covalent Bond Overlap
Occurs when orbitals from two atoms overlap.
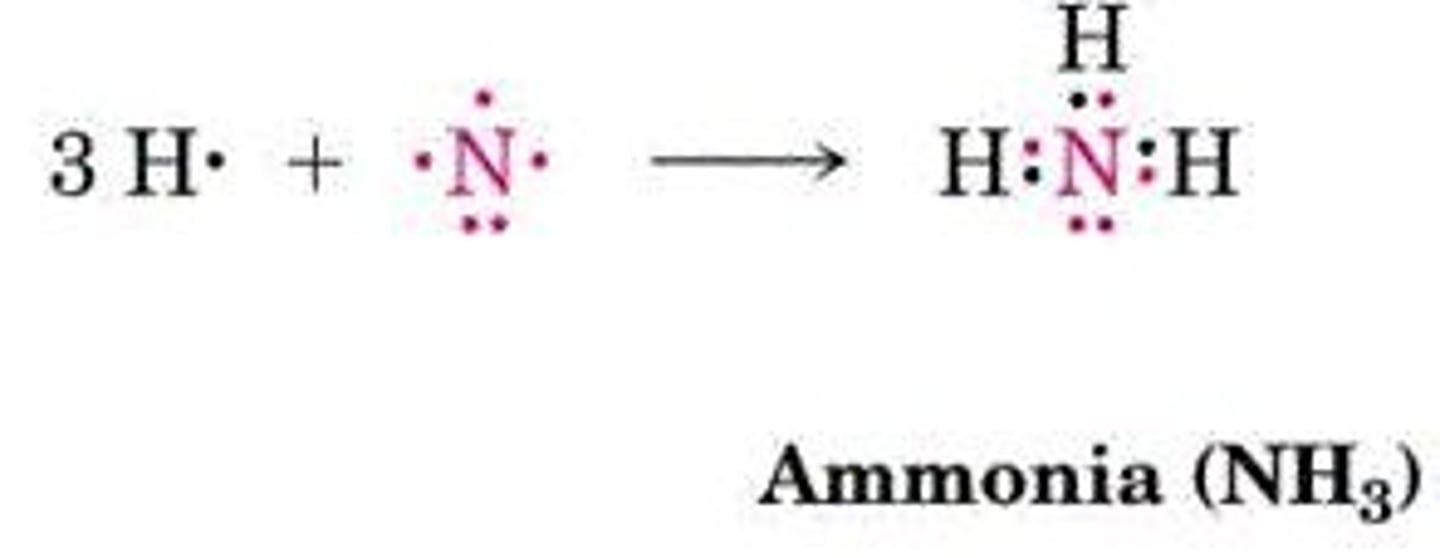
Ammonia (NH3) Bonds
Nitrogen forms three bonds with one lone pair.
Hydrogen Bond Strength
H-H bond strength is 436 kJ/mol.
Hybridization
Mixing atomic orbitals to form new orbitals.
sp3 Hybridization
One s and three p orbitals combine.
Tetrahedral Structure
Shape with bond angles of 109.5°.
C-H Bond Strength (Methane)
Strength of 438 kJ/mol for C-H bond.
C-H Bond Length (Methane)
Length of 110 pm for C-H bond.
Ethane Structure
Contains six C-H bonds from sp3 overlap.
C-C Bond Strength (Ethane)
Strength of 376 kJ/mol for C-C bond.
C-C Bond Length (Ethane)
Length of 154 pm for C-C bond.
sp2 Hybridization
One s and two p orbitals combine.
Ethylene Bond Angles
Bond angles of 120° in ethylene.
C-C Double Bond
Formed by one sigma and one pi bond.
Sigma Bond
Head-on orbital overlap forming a single bond.
Pi Bond
Sideways orbital overlap forming a double bond.
Molecular Orbital (MO)
Region where electrons are likely found.
Bonding MO
Lower energy orbital from additive combination.
Antibonding MO
Higher energy orbital from subtractive combination.
Hybridization of Nitrogen
Nitrogen forms four sp3 orbitals in ammonia.
H-N-H Bond Angle
Bond angle of 107.3° in ammonia.
Hybridization of Oxygen
Oxygen is sp3 hybridized in water.
H-O-H Bond Angle
Bond angle of 104.5° in water.
Covalent Bonds
Electron pairs shared between atoms.
sp hybridization
Two sp orbitals for linear triple bonds.
Polar covalent bond
Unequal sharing of electrons between atoms.
Electronegativity (EN)
Atom's ability to attract shared electrons.
Electronegativity scale
Fluorine (EN=4.0) is most electronegative.
Electronegativity trend
Increases left to right, decreases top to bottom.
Partial positive charge
Indicated by !+; electron-poor atom.
Partial negative charge
Indicated by !-; electron-rich atom.
Electrostatic potential maps
Visual representation of charge distribution in molecules.
Bond polarity
Determined by differences in electronegativity.
Methanol (CH3OH)
C-O bond is polar covalent.
Methyllithium (CH3Li)
C-Li bond is polarized with carbon negative.