Unit E. Space Exploration First Half Quiz
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
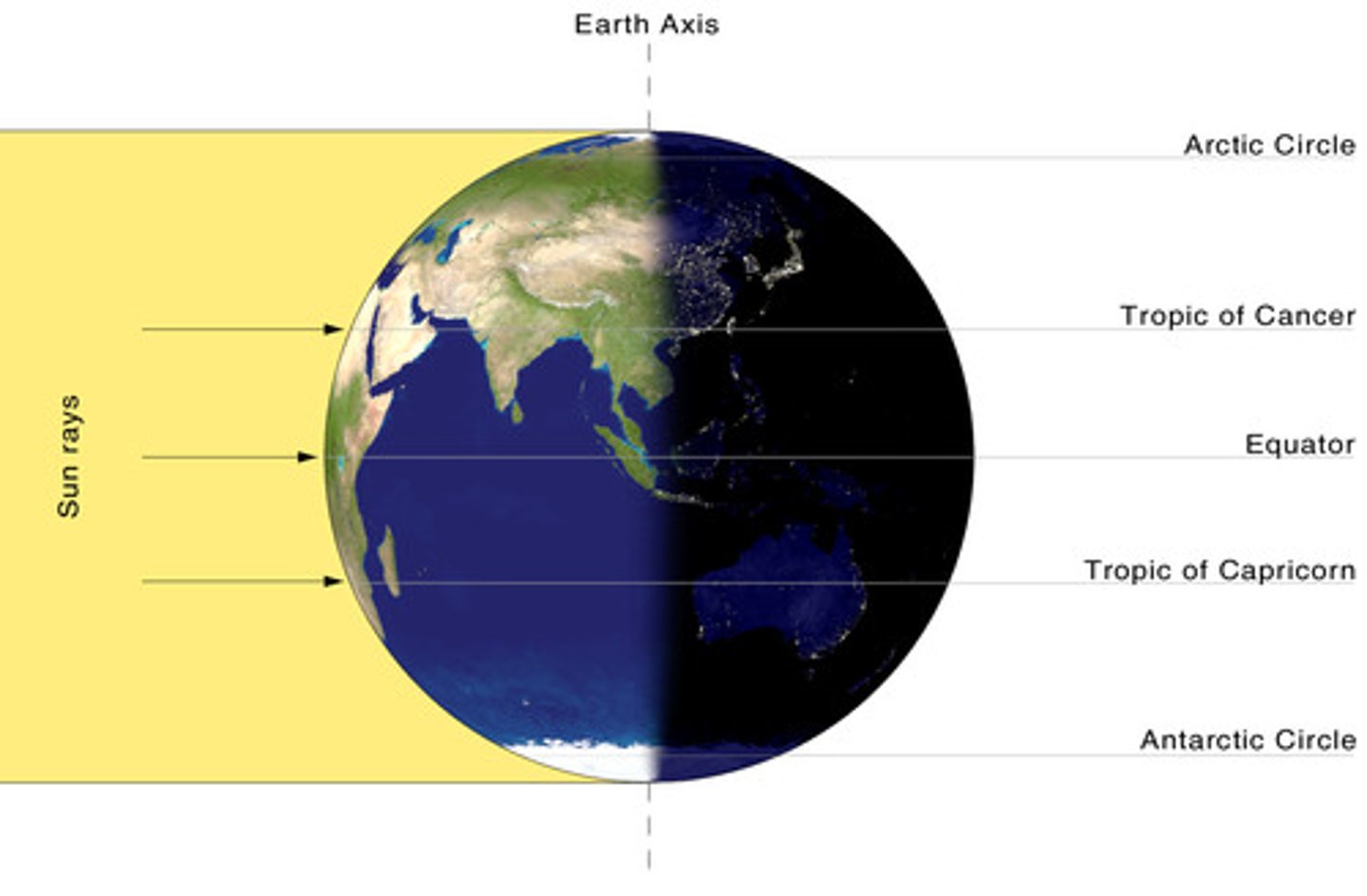
Solstice
Longest or shortest day of the year
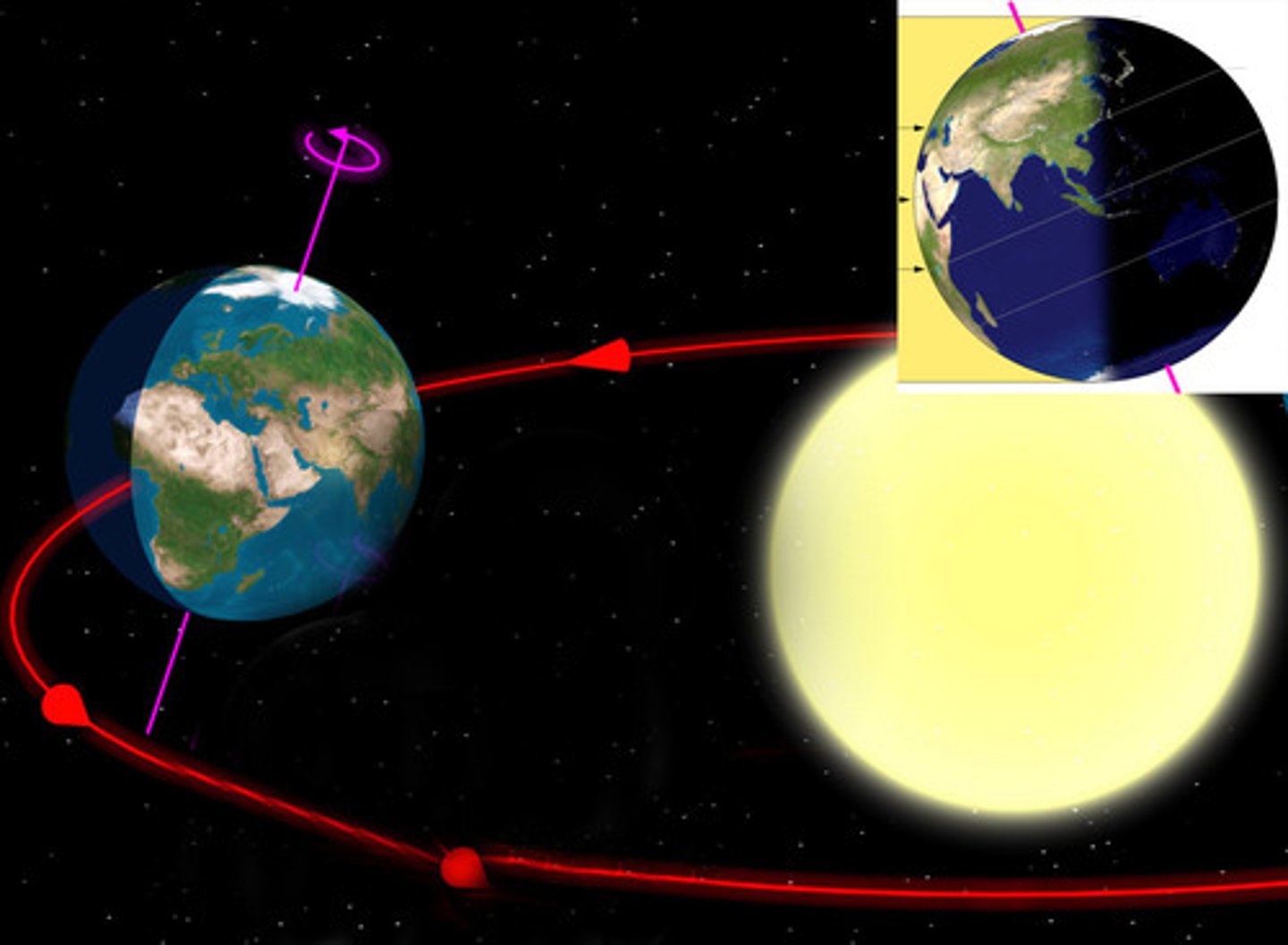
Equinox
Each of the two times of the year when days and nights are of equal length
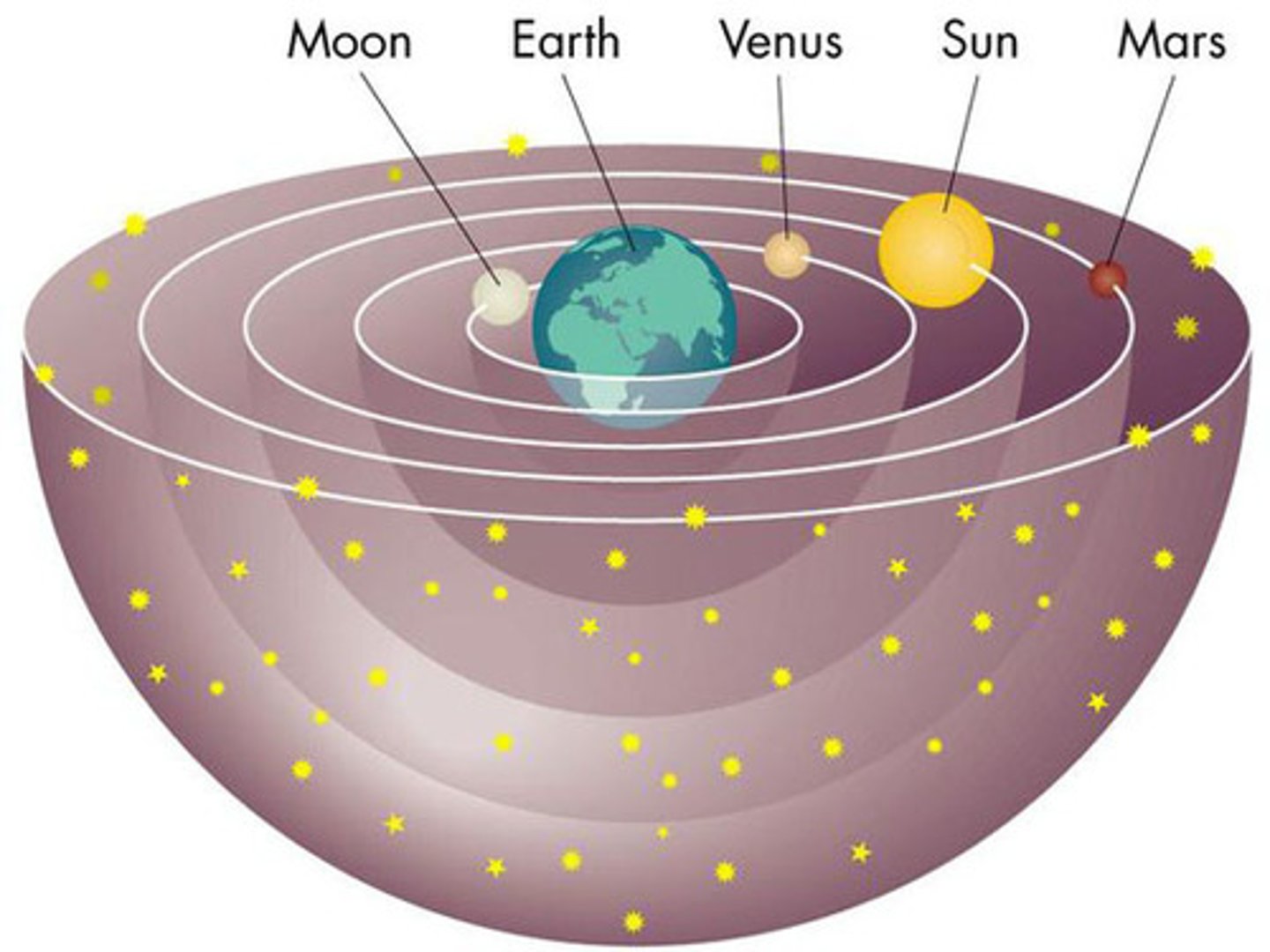
Geocentric Model
Earth is the center of the Universe
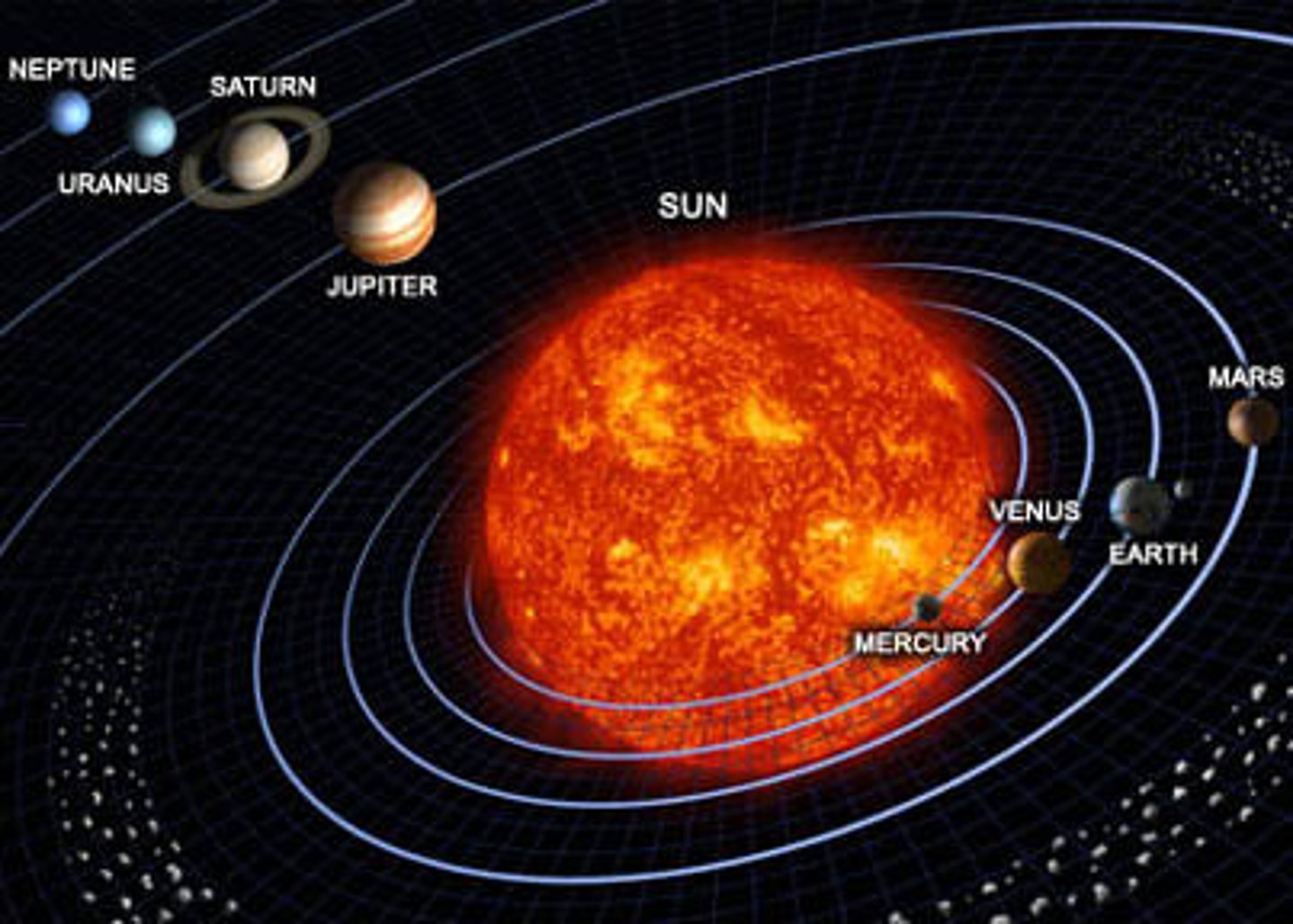
Heliocentric Model
Sun is the center of the universe
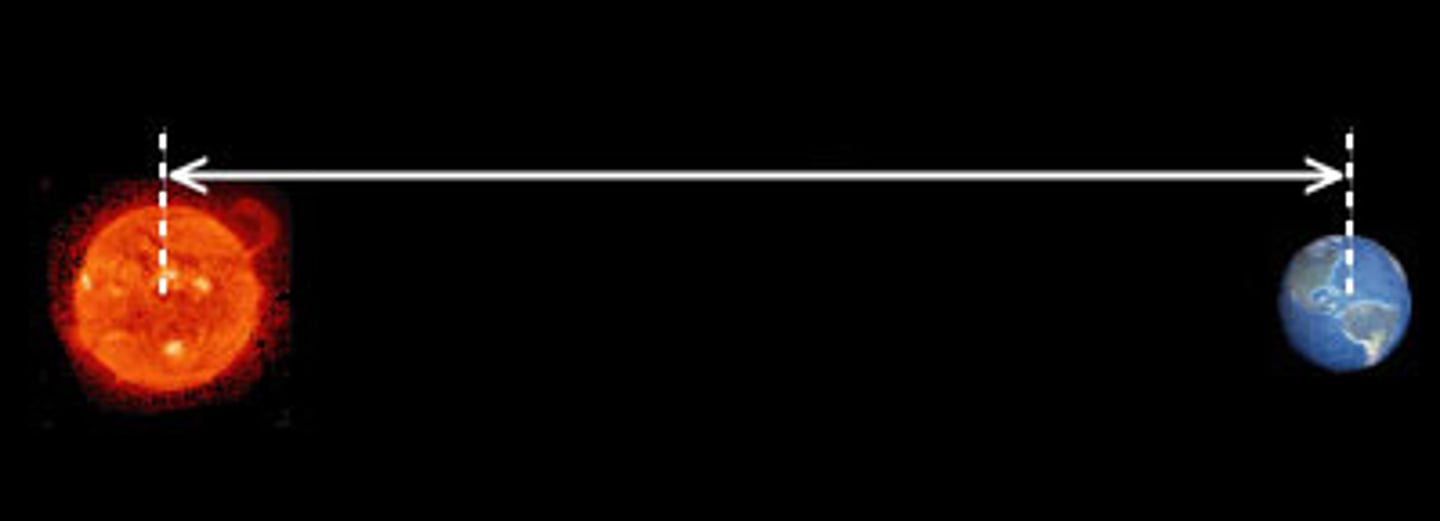
Astronomical Unit (AU)
the average distance between Earth and the sun, about 150 million km

light year
the distance light travels in one year
sun-like stars
one of the two main types of stars that can form. (smaller in mass than the massive stars)
constellations
official patterns of stars in the sky

Asterism
An unofficial small grouping of stars
galaxy
A collection of stars, dust, and gas bound together by gravity

Massive Star
brightest stars, white or blue, large mass, short lifespan

Asteroids
a small rocky body orbiting the sun

comet
A ball of frozen dust and rock that orbits the sun and has a tail that glows

Meteoroid
A chunk of rock or dust in space

meteor
a rock burning in the atmosphere
meteorite
A meteoroid that passes through the atmosphere and hits Earth's surface.

Azimuth
A horizontal angle measured clockwise from north or south.
altitude
height above eye level or the horizon
satellite
An object that revolves around another object in space

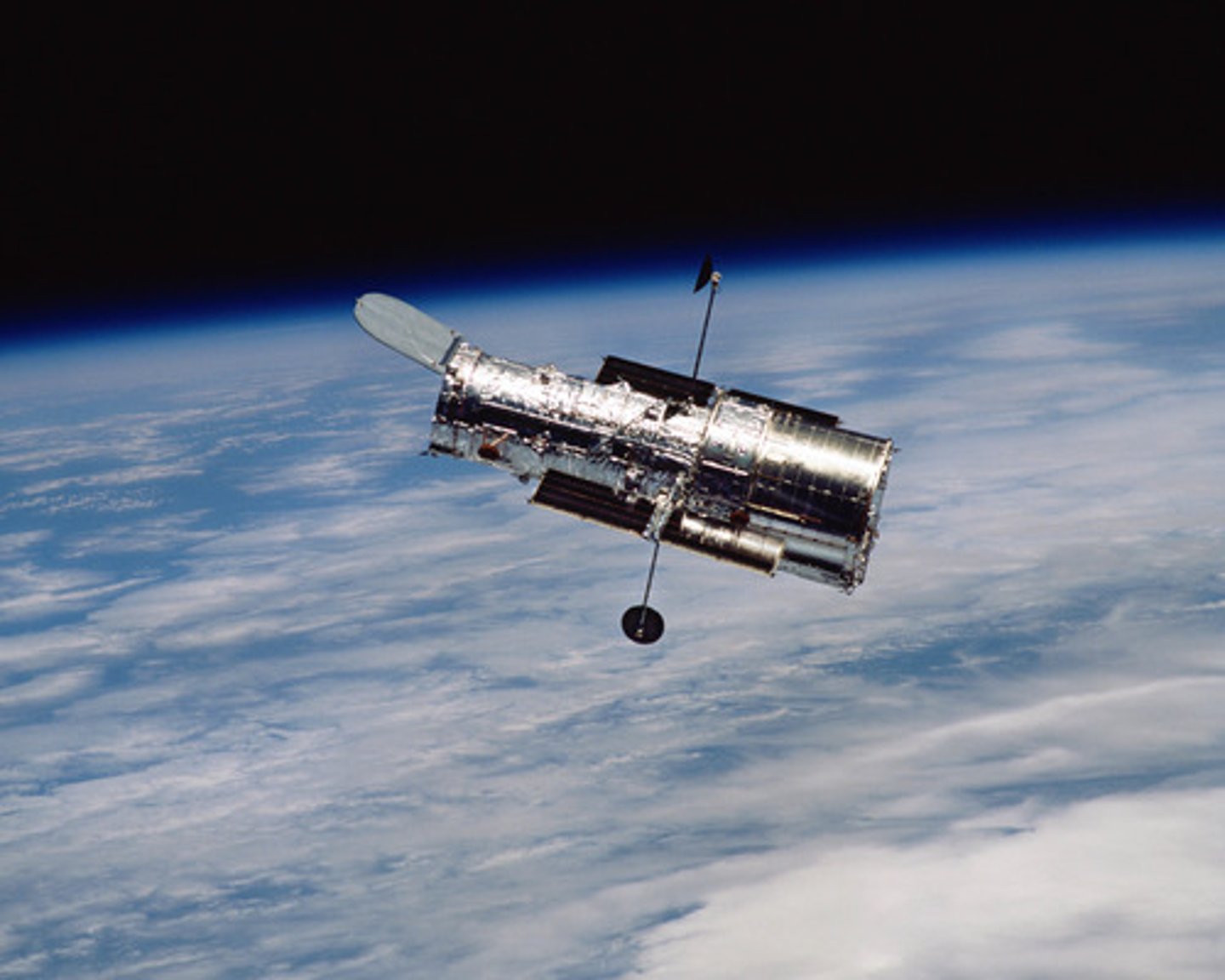
. Hubble Space Telescope
this telescope has improved our knowledge of the Universe

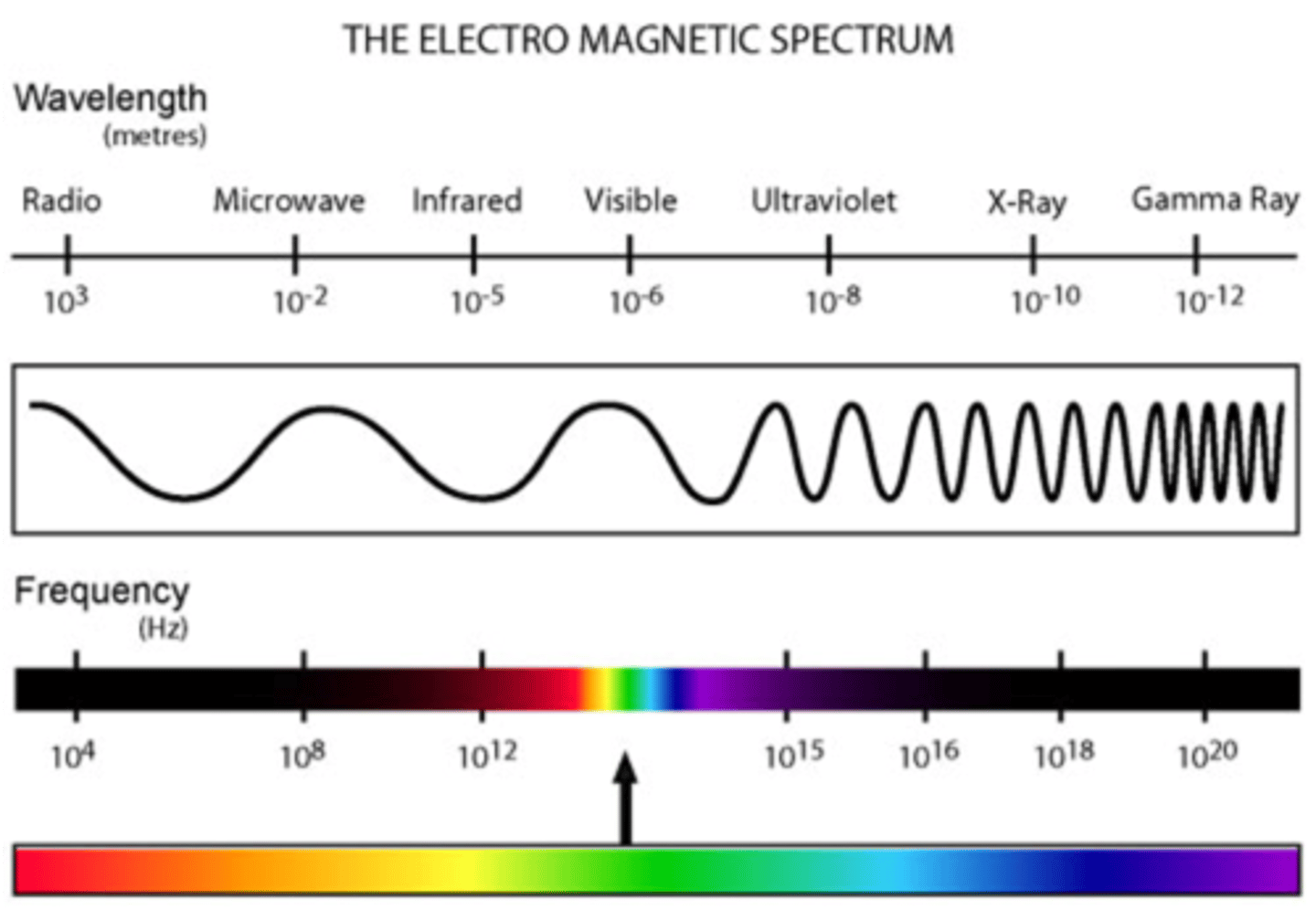
electromagnetic spectrum
the complete range of electromagnetic waves placed in order of increasing frequency
space probes
A vehicle that carries scientific instruments to planets or other bodies in space

interstellar matter
Debris from artificial objects orbiting earth
inner planets
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars
Jovian Planets
Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
dwarf planet
Pluto
Milky Way
The name of our galaxy
east
90 degrees
south
180 degrees
west
270 degrees
horizon
zero degrees altitude
north east
45 degrees
south east
135 degrees
south west
225 degrees
north west
315 degrees
white dwarf
A small, hot, dim star that is the leftover center of an old star
black dwarf
A white dwarf that has burnt out completely.
neutron star
the small, dense remains of a high-mass star after a supernova
black hole
An object in space whose gravity is so strong not even light can escape.
orbit
The path of an object as it revolves around another object in space