Man & Merchandising Purchasing
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Define “trade exchange”. Why is it useful?
A tool for securing valuable assets
A form of “barter network”
Allows business members to operate outside the cash economy
What is a “barter network”?
A system where people or businesses exchange goods or services directly with one another without using money.
Instead of paying cash, participants trade what they have for what they need.
True or false: “barter network can help creating exchange networks”
True!
How does trade exchange/barter network works?
Members join the network (individuals or businesses).
Each member lists what they can offer (skills, goods, services).
Members trade with others inside the network.
Many networks use trade credits instead of cash:
How does “trade credits” works?
You earn credits when you provide something.
You spend credits to receive something from someone else.
What are some benefits of a trade exchange?
Saves money
Uses unused skills or excess goods
Helps small businesses
Encourages cooperation
Securing assets = more money to invest in growth
Explain what a “market” is?
A composition of systems, institutions, procedures, social relations whereby parties engage in exchange
Rely on sellers offering their goods/services (including labour) to buyers in exchange for money
True or false: “market is the process by which the prices of goods and services are established”
True!
Explain “marketing”
Activities that a company undertakes to promote the buying/selling of a product/service.
What are some examples of marketing?
Advertising
Selling
Delivering products to consumers or other businesses.
What are some purposes of marketing?
Draw in more customers
Maintain relationships with customers
Ensure business profitability by matching the company’s products/services to customers needs.
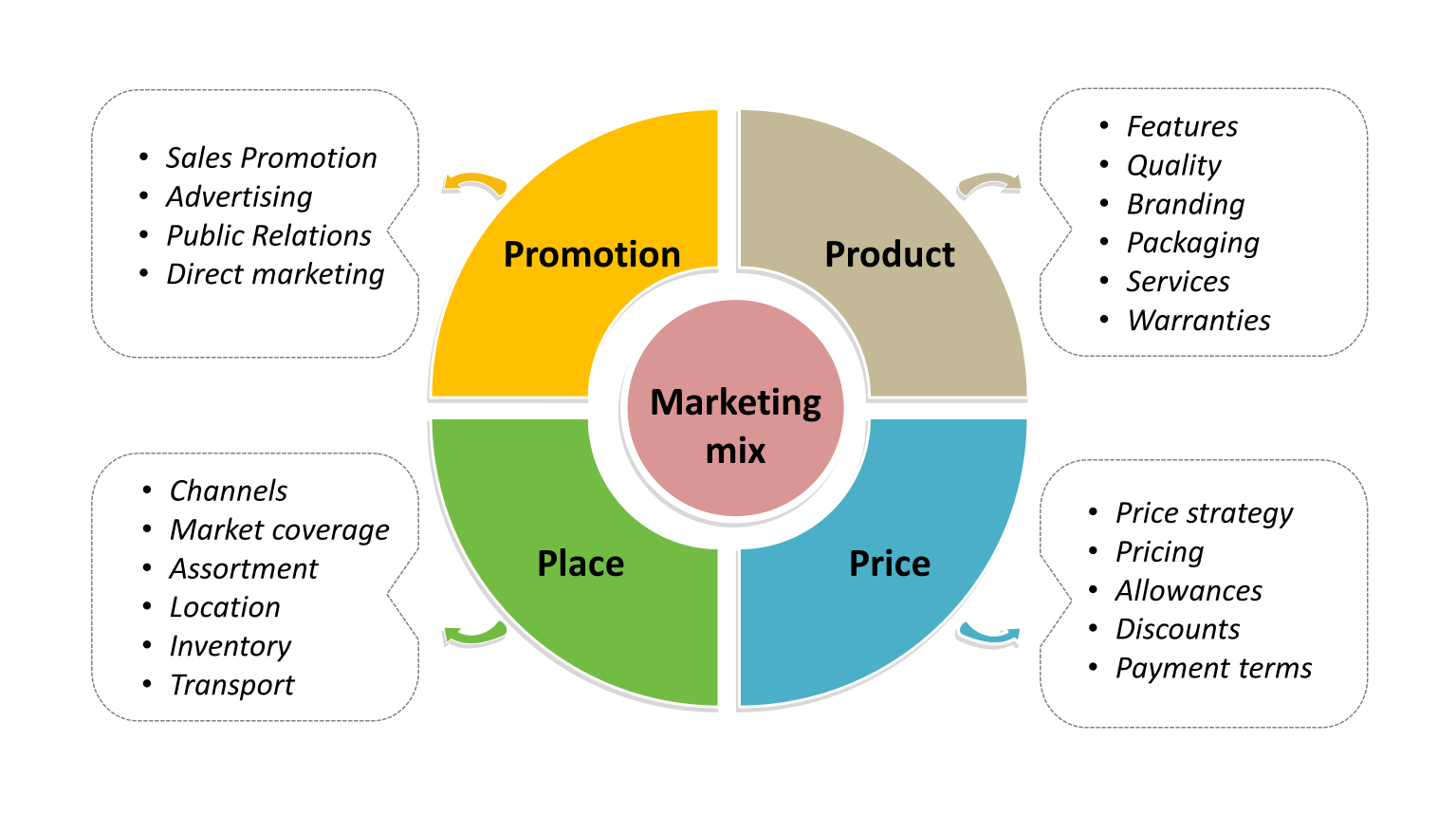
What are the 4Ps (marketing mix)?
Product
Price
Place
Promotion

What is the main purpose of marketing mix?
Help businesses plan, promote, and sell products effectively.
Help businesses design an effective marketing strategy by offering the right product, at the right price, in the right place, with the right promotion.
Explain how “product” is used in marketing. What are factors that a business have to consider?
Ensure the business offers the right product that satisfies customer needs
Quality
Design
Features
Branding
Packaging
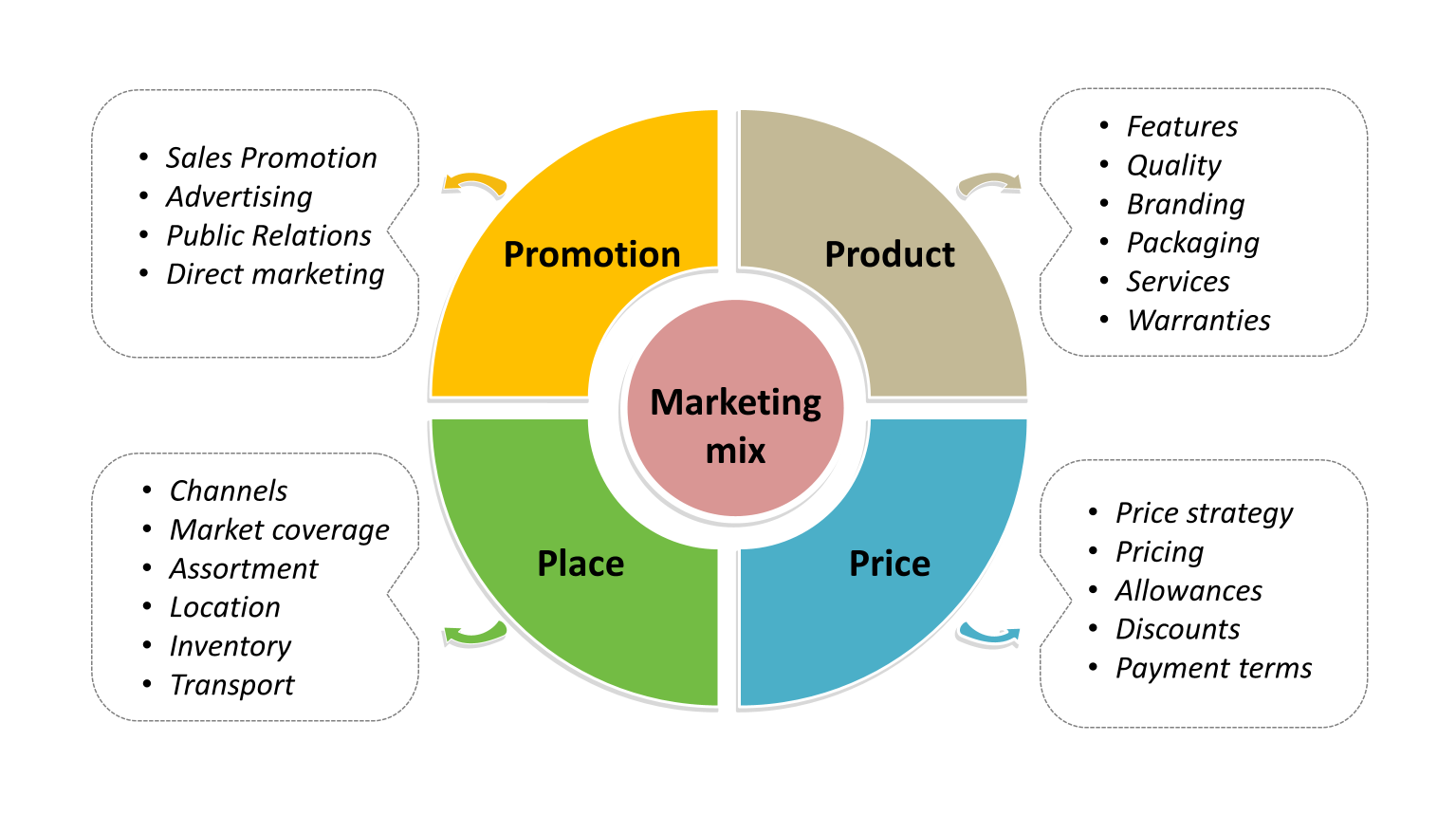
Explain how “price” is used in marketing. What are factors that a business have to consider?
Set a price that is acceptable to customers and profitable for the business
Pricing strategy
Profit
Discount
Payment method
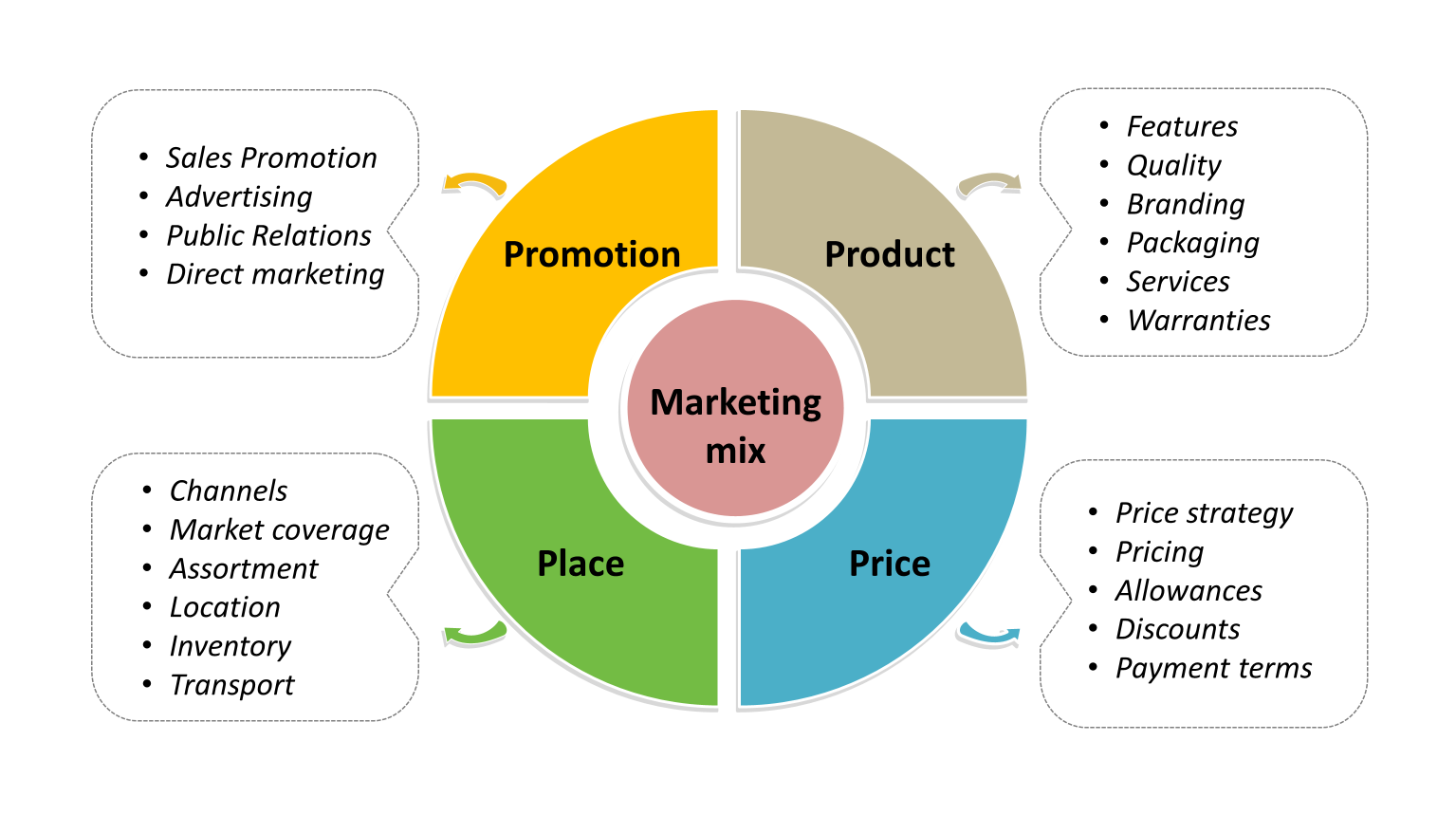
Explain how “place” is used in marketing. What are factors that a business have to consider?
Make a product available at the right location and time
Distribution channel
Logistics
Accessibility
Inventory
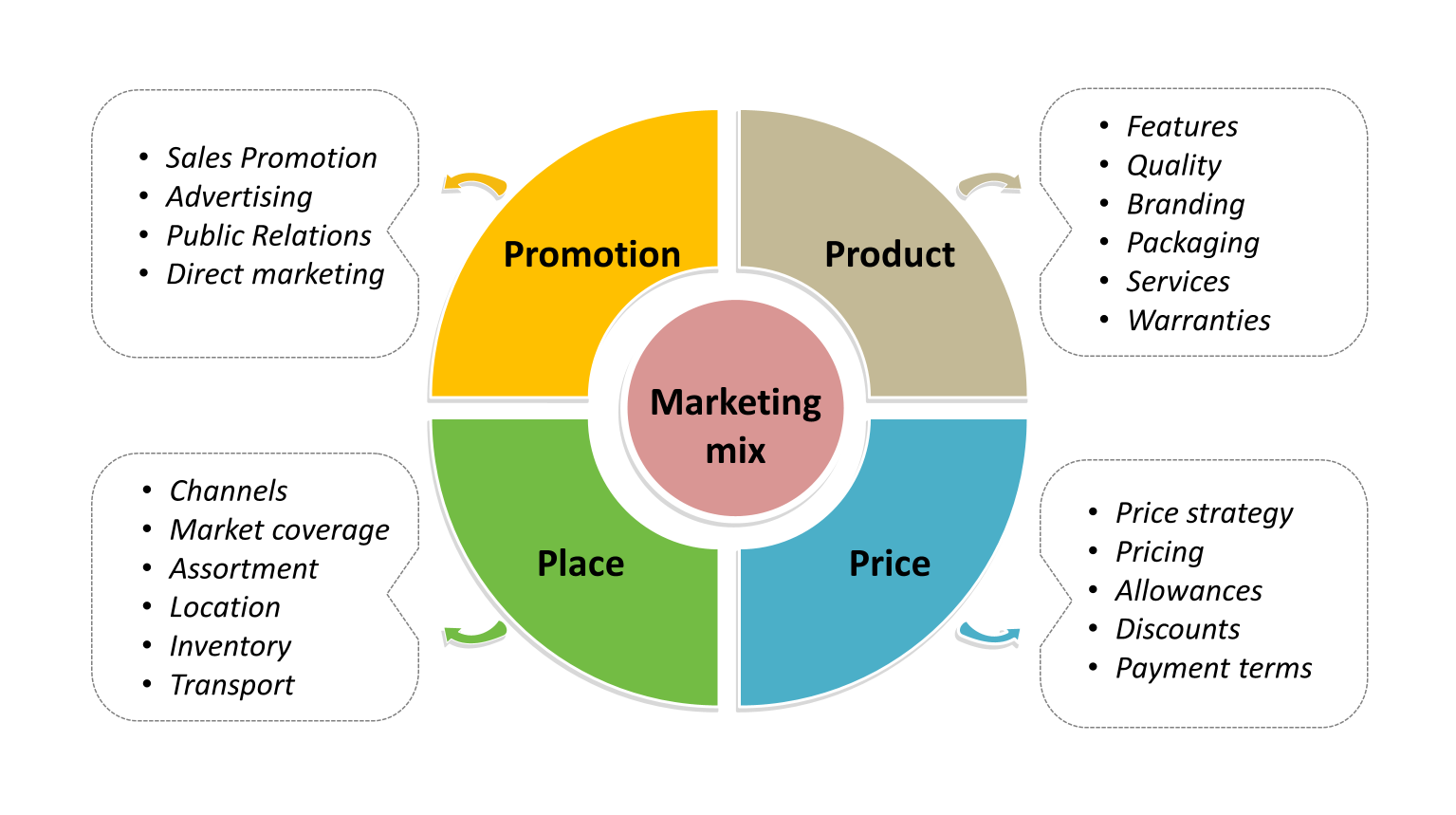
Explain how “promotion” is used in marketing. What are factors that a business have to consider?
Inform, persuade, and remind customers about the product
Advertising
Sales promotion
Public relations
Social media
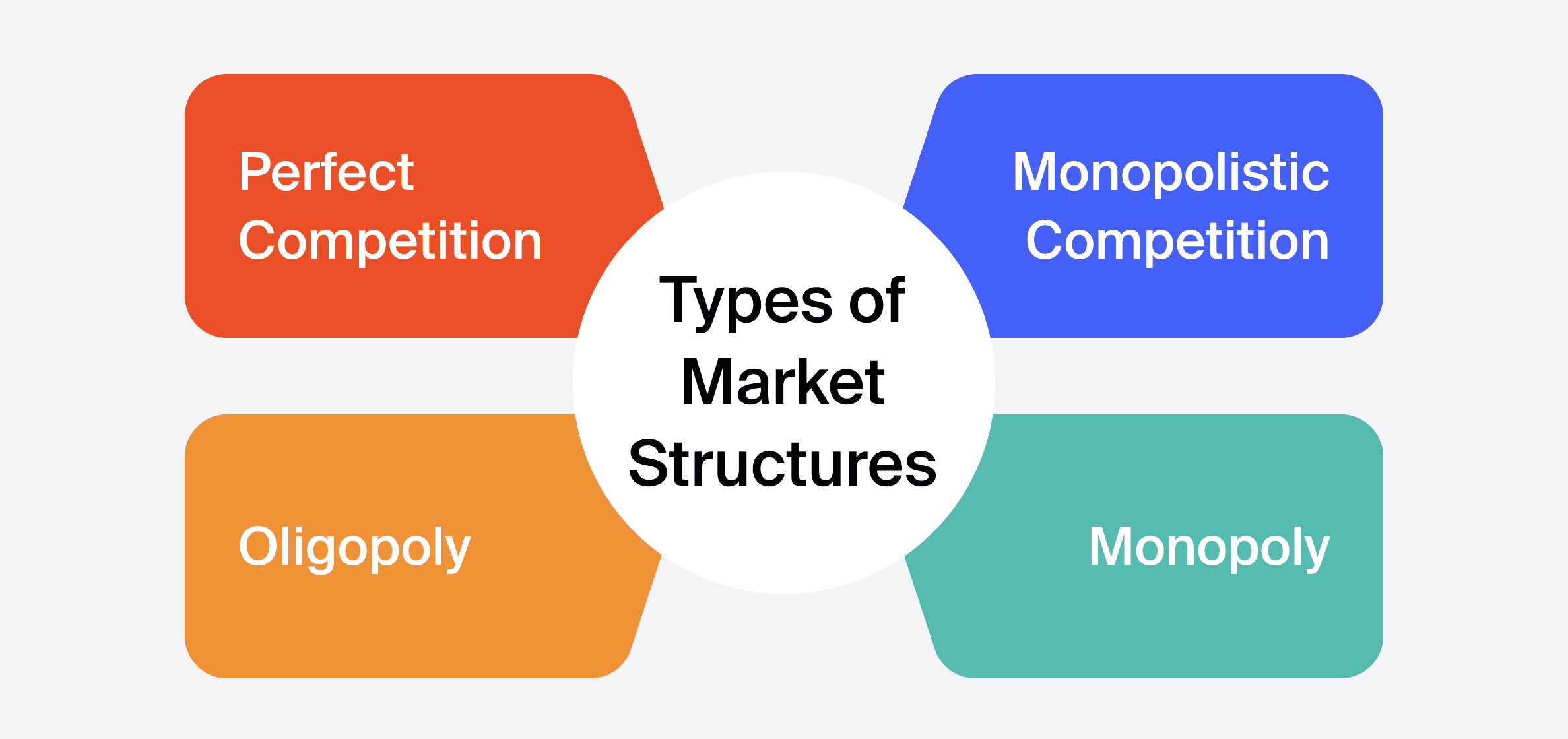
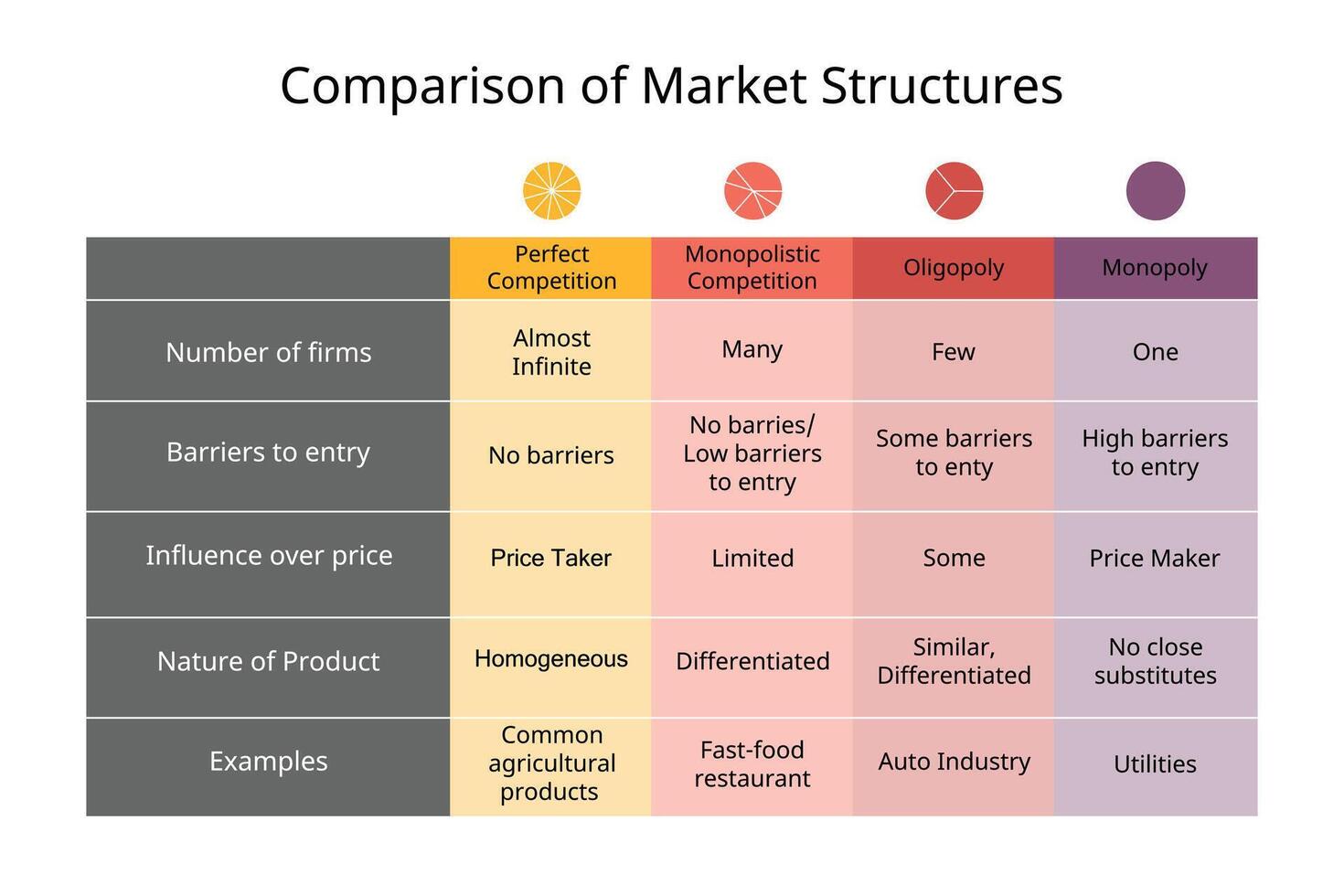
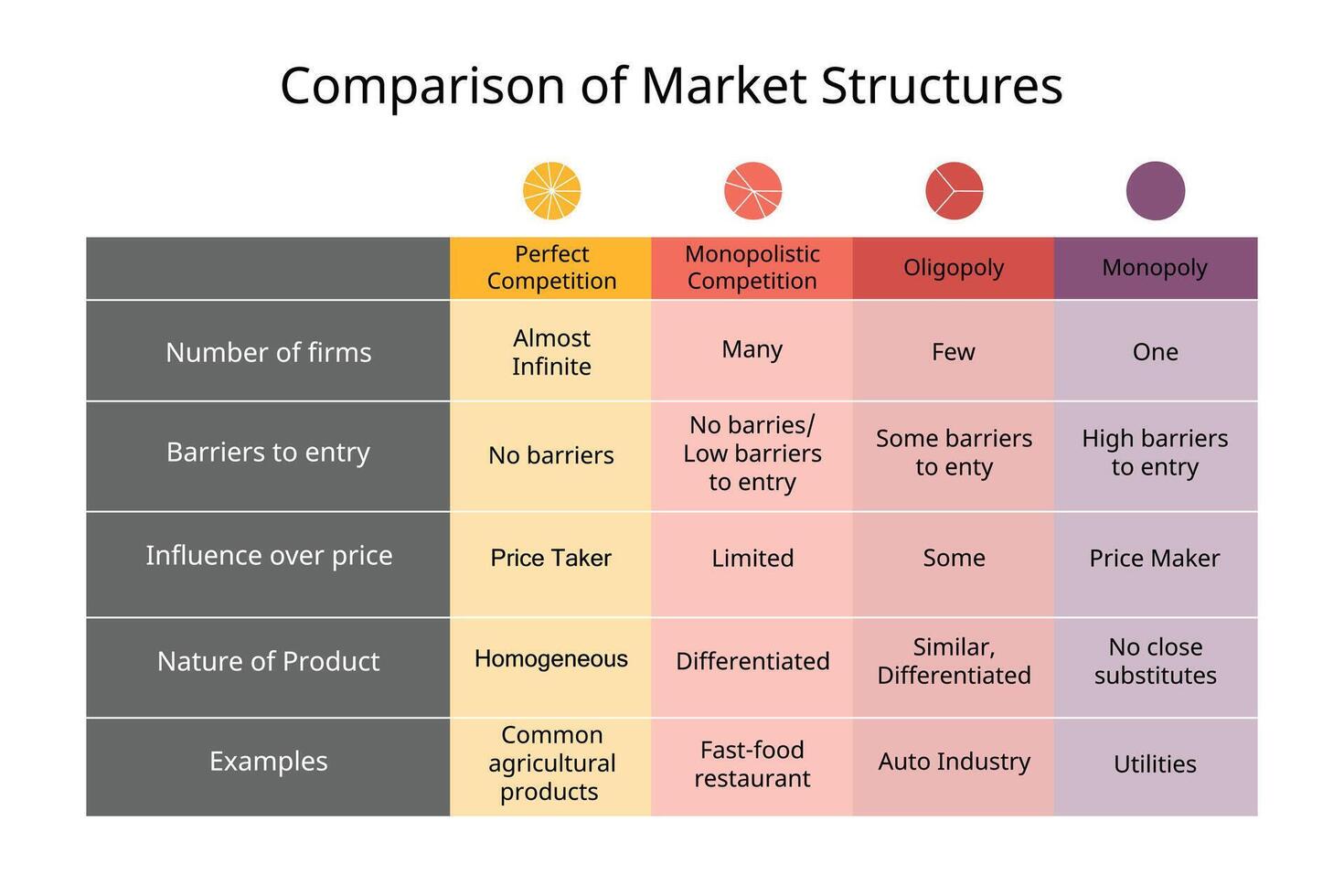
What are the 4 market structures?
Perfect competition (most competitive)
Monopolistic competition
Oligopoly
Monopoly (least competitive)
Define “perfect competition markets”
A type of market structure where many sellers and many buyers trade identical products, and no single firm can influence the market price.
The most competitive type
What are some characteristics of the “perfect competition markets”?
Large number of firms
Selling identical products
Freedom of entry and exit
Consumers and producers have perfect knowledge about the market
What is the best example of “perfect competition market”?
Agricultural markets (e.g. rice, corn, vegetables)
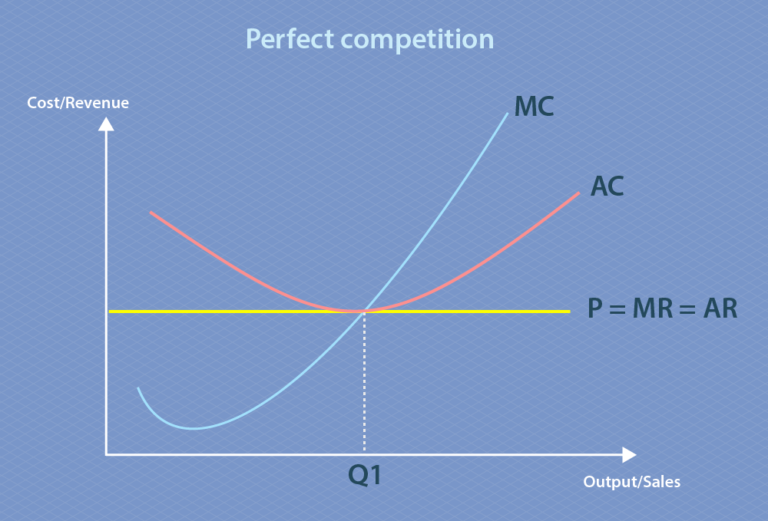
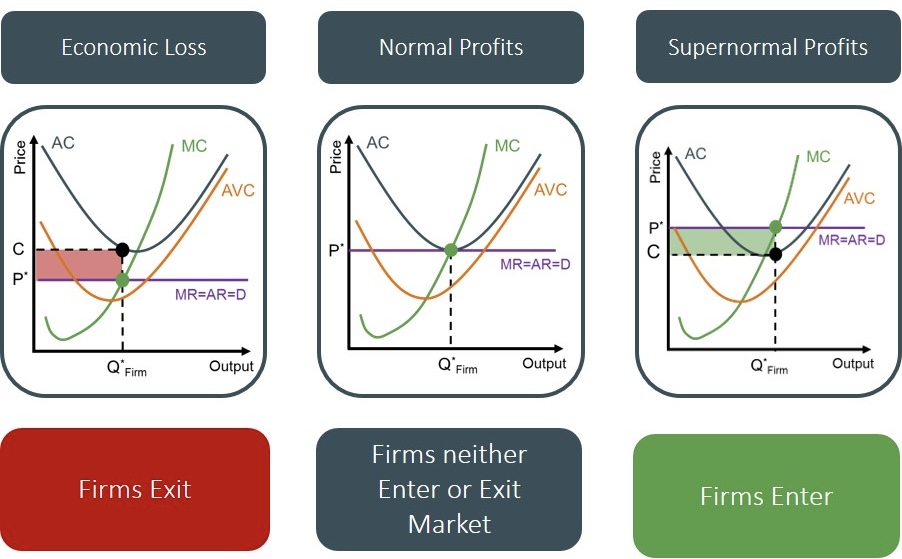
Explain the following graph of perfect competition
Horizontal line = the selling price/MR/AR/demand set by the market (businesses can’t change them)
U-shaped = cost curve (MC = cost of making 1 more unit, AC = cost per unit)
Where MC meets the price line = the quantity needed to be produced to make the most money.
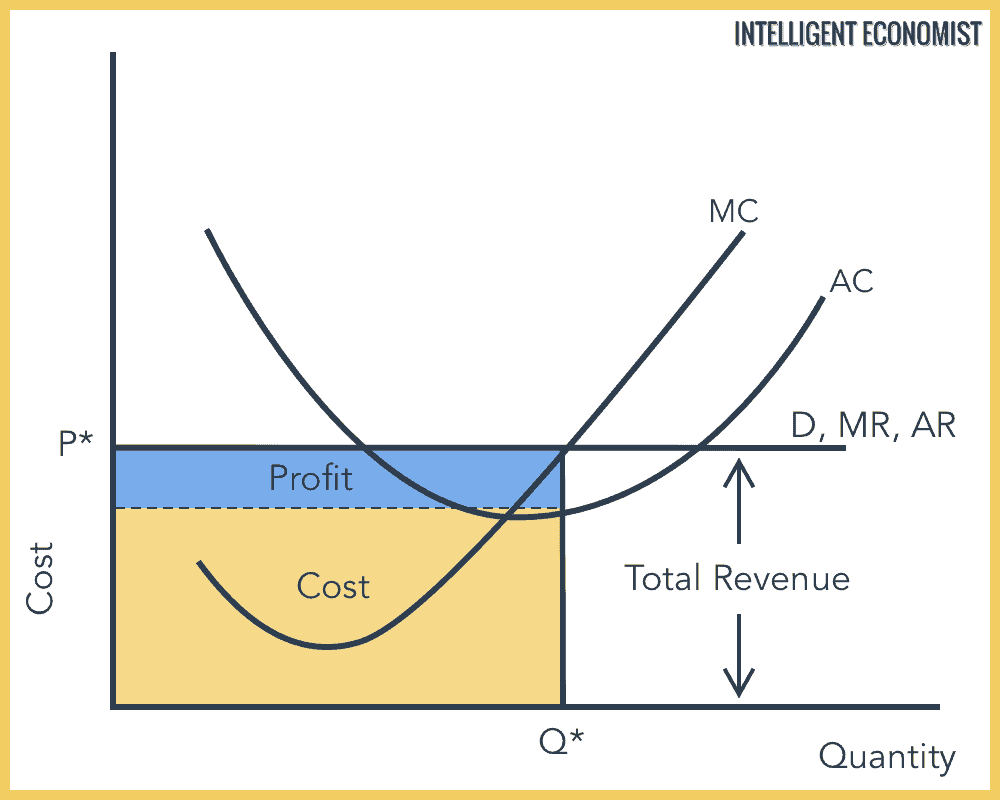
How do you know whether the firm experience profit or loss?
Profit = price above ATC
Normal = price touches ATC
Loss = price below ATC
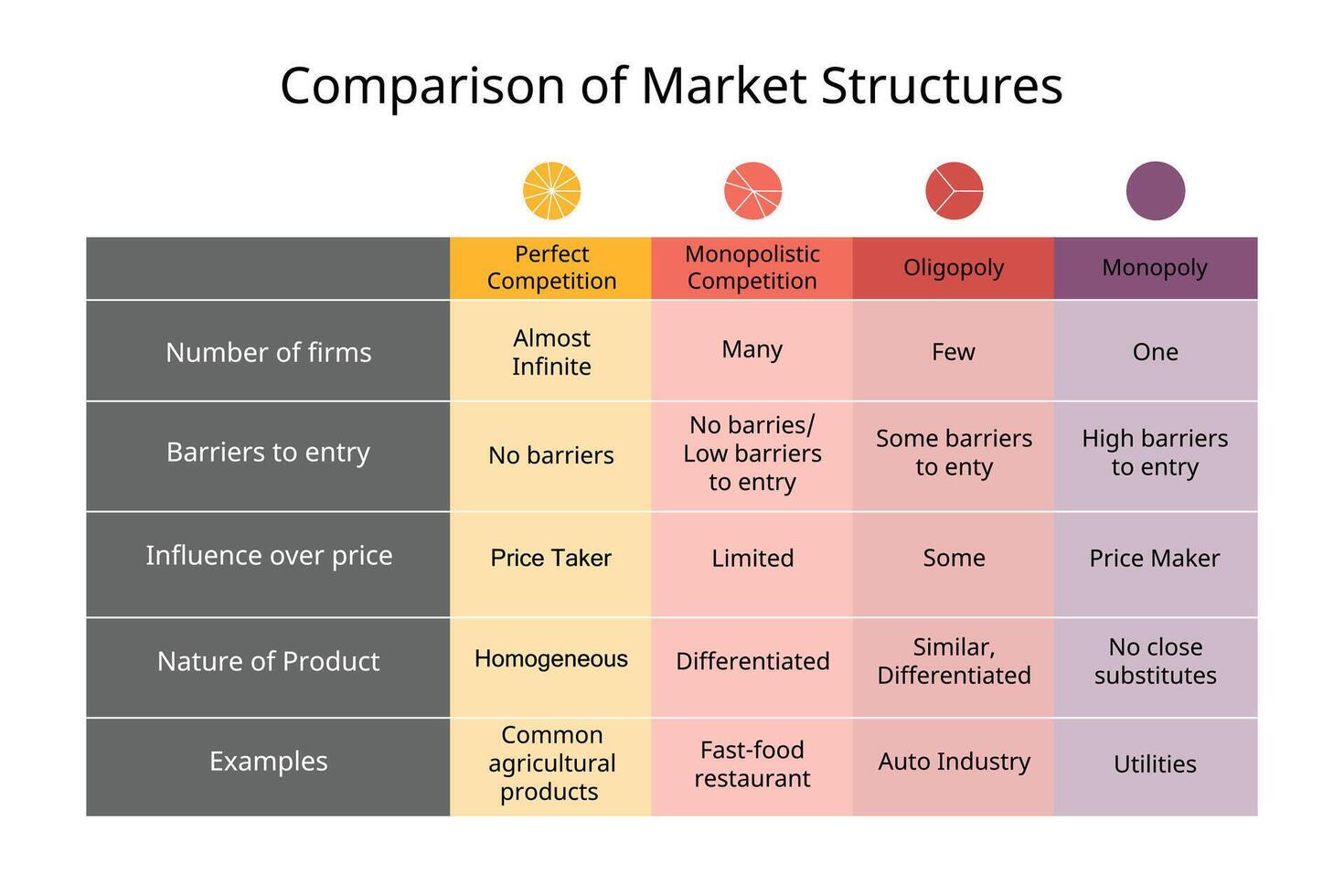
What are the 3 non-perfectly competitive markets?
Monopolistic competition market (กึ่งแข่งขันกึ่งผูกขาด)
Pure monopoly market (ผูกขาดอย่างแท้จริง)
Oligopoly market (ผู้ขายน้อยราย)
Define “monopolistic competition market”
A market structure which combines elements of monopoly and competitive markets.
Many sellers, but products are slightly different.
What are some characteristics of the “monopolistic competitive market”?
Many firms
Freedom of entry and exit
Firms can differentiate their products
Inelastic demand curve (they can set prices)
Make normal profit in the long run
Make supernormal profit in the short term
What is the best example of “monopolistic competitive market”?
Restaurant
Clothing brands
Define “oligopoly market”
A market dominated by a few large firms, none of which can keep the others from having significant influence.
What are some characteristics of the “oligopoly market”?
Few sellers
High barriers to entry
Firms are interdependent
Price wars may occur
What is the best example of “oligopoly market”?
Airlines
Mobile networks
Car manufacturer
Define “pure monopoly market”
A market with only one seller and no close substitutes.
Only one company is the single source for a product.
Rarest type of market structure
There must be barriers preventing competitors from entering the market
What are the 3 types of barriers in monopoly market? (Hint: LEC)
Legal barrier
Control of resources
Economies of scale
What are some characteristics of the “monopoly market”?
Single seller
Unique product
High barriers to entry
Firm is a price maker
What is the best example of “pure monopoly market”?
Electricity authority
Water supply
True or false: “Government CANNOT intervene in market pricing”
False!
(Government can control the prices of certain items)
Define “international trade”
The exchange of capital, goods, and services across international borders/territories.
Consists of 2 key processes: importation & exportation
What is a “free trade agreement (FTAs)”?
An agreement between two or more countries to reduce or remove trade barriers so they can trade more easily with each other.
Give 3 examples of “trade barriers”
Tariffs (import taxes)
Quotas (limits on imports)
Trade restrictions
Give 2 real-world examples of “free trade agreements”.
ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA)
EU Free Trade Agreements
USMCA (USA–Mexico–Canada)
Thailand–Australia FTA
What is the opposite concept of FTA?
“Trade protectionism” or “Economic isolationism”
What are the advantages of FTA?
Cheaper imported goods
More product variety
Increased exports
More jobs
Stronger economic cooperation
What does “import” and “export” means?
Import = Buying goods or services from another country.
Export = Selling domestic goods or services to another country.
What does “GDP” stand for? Explain the term
“Gross Domestic Product”
National income
The total value of all final goods and services produced within a country during one year.
Measures the size of a country’s economy.
How to calculate GDP?
Look at the photo!

What are the 4 factors that help “decrease imports” but “increase exports”
Taxes and quotas
Subsidies (เงินอุดหนุน)
Trade agreements
Currency devaluation