Chapter 2 - What chemical processes support life?
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Define the term Metabolic
It is the term that means “related to metabolism.” E.G- A disease can have metabolic causes, or metabolic effects.
Define the term Metabolism
It is the sum of all biological transformations of energy and matter in an organism
flow that air takes
nasal/oral cavity → pharynx → larynx → trachea → bronchi → bronchioles → alveoli
Anabolic reactions
Anabolic Reactions: Energy + Smaller molecules → larger molecule
Building muscles (making proteins)
Photosynthesis
Catabolic reactions
catabolic Reactions: Larger molecule → energy + smaller molecules
Digestion
Cellular respiration
What affects the rates of reaction?
concentration
surface area
temperature
presence of a catalyst
pressure
State the word equation for anaerobic respiration
Glucose → ethanol + carbon dioxide + energy (ATP)
State the word and balanced chemical equation for aerobic respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O
Glucose + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
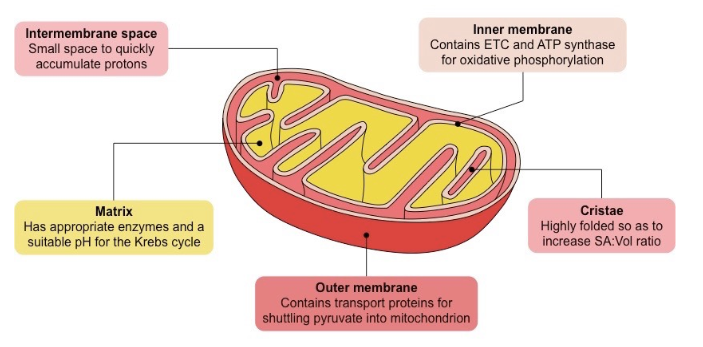
Label the structure of a mitochondrion and describe the functions of the parts
Inner membrane folds → ATP synthesizing proteins
cristae → folds → more places for reaction → more usable energy
matrix → suitable pH for Kreb’s cycle
Outline the process of ventilation
Inspiration: taking in air rich in oxygen. During inspiration, the ribs are lifted up and the diaphragm flattens. This increases the volume of the thoracic cavity, decrease in air pressure pulls air into the lungs
Expiration: giving out carbon dioxide. During expiration, the ribs move downward and back to their original position and the diaphragm moves upward back to its dome shape. This decreases the volume of the thoracic cavity and increases air pressure and pushes air out of lungs
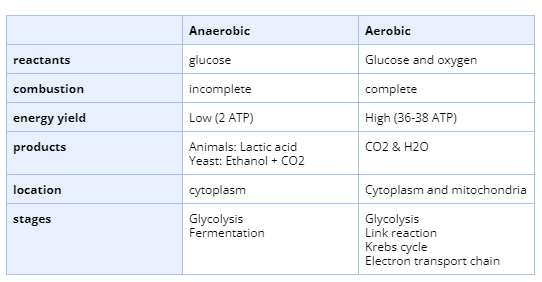
Compare aerobic and anaerobic respiration
aerobic: 36-38 ATP per glucose molecule, complete oxidation of glucose to water n h20
anaerobic: opp + oxygen debt due to incomplete oxidation
Define photosynthesis
Photosynthesis: the process is which light energy is converted to chemical energy in the forms of sugars.
State the word and balanced chemical equation for photosynthesis
6CO2+6H2O→C6H12O6+6O2
Carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
Discuss the limiting factors that affect the rate of photosynthesis
Light intensity: rapidly increases to a certain point. It stays relatively the same throughout the rest of the graph. Start at the origin.
Carbon dioxide concentration: Rapidly increases then stays relatively the same afterwards. Also starts at the origin.
Temperature: Rapidly increases, reaching its peak, then rapidly decreases. Start at the origin.
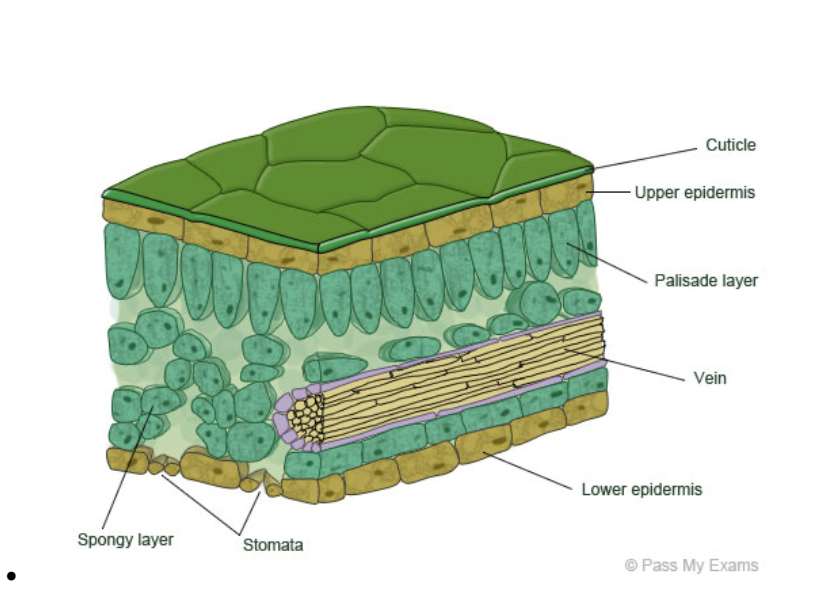
Draw and label the structure of a leaf
Describe the structure and function of enzymes
Structure: They’re basically large proteins/a chain of amino acids
Function: They are biological catalysts that speed up the rate of reaction.
Define catalyst
A substance that increases the speed of a reaction without being changed or used in the process.
Define Active site
Region of the enzyme with a specific shape to the substrate molecules.
Explain what is meant by the lock and key theory
In the lock and key hypothesis, the shape of the active site matches the shape of its substrate molecules. This makes enzymes highly specific and that each type of enzyme can usually catalyse only one type of reaction. (some may do more though)
Distinguish between substrate, enzyme, product and enzyme-substrate complex
Substrate: A reactant used in an enzyme
Enzyme: Biological catalysts to increase speed in reactions
Product: substances after a biological process has occurred.
outline respiration
Respiration: This is the chemical process of breaking down food particles in the cells in presence of oxygen and releasing energy.
talk abt aerobic and anaerobic
uses for anaerobic respiration in industry
bread (yeast goes thru anaerobic respiration to release CO2 and ethanol), alcohol (yeast fermentation for the glugs)