HOU final
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/145
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 6:42 PM on 5/9/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
146 Terms
1
New cards
The age of the universe is
a)5by
b)13by
c)120my
d)900my
a)5by
b)13by
c)120my
d)900my
13by
2
New cards
The age of our solar system is
a)12by
b)4.6by
c)1my
d) 1by
a)12by
b)4.6by
c)1my
d) 1by
4\.6by
3
New cards
The age of Earth is
a) 2my
b)4.5my
c)2by
d)4.5by
a) 2my
b)4.5my
c)2by
d)4.5by
4\.5 by
4
New cards
The solar system contains about 100 billion stars.
a) True b) False
a) True b) False
false
5
New cards
Which of these groups of particles has the greatest mass?
a) a helium nucleus with two protons and two neutrons
b) four individual protons
c) four electrons
d) four neutrons
a) a helium nucleus with two protons and two neutrons
b) four individual protons
c) four electrons
d) four neutrons
four individual protons
6
New cards
What do we mean when we say a star is in hydrostatic equilibrium?
a) The hydrogen gas in the star is balanced so that it never rises upward or falls downward.
b) The star is able to maintain a steady temperature.
c) This is another way of stating that the star generates energy by nuclear fusion.
d) There is a balance within the star between the outward push of pressure and the inward pull of gravity.
a) The hydrogen gas in the star is balanced so that it never rises upward or falls downward.
b) The star is able to maintain a steady temperature.
c) This is another way of stating that the star generates energy by nuclear fusion.
d) There is a balance within the star between the outward push of pressure and the inward pull of gravity.
There is a balance within the star between the outward push of pressure and the inward pull of gravity.
7
New cards
At the center of the Sun, fusion converts hydrogen into
a) hydrogen compounds.
b) plasma.
c) helium, energy, and neutrinos.
d) radiation and elements like carbon and hydrogen.
a) hydrogen compounds.
b) plasma.
c) helium, energy, and neutrinos.
d) radiation and elements like carbon and hydrogen.
helium, energy, and neutrinos.
8
New cards
What is the name given to 2H?
a) hydrogen
b) helium
c) deuterium
d) tritium
a) hydrogen
b) helium
c) deuterium
d) tritium
deuterium
9
New cards
When an atom loses an electron, it becomes
a) sublimated.
b) dissociated.
c) ionized.
d) an isotope
a) sublimated.
b) dissociated.
c) ionized.
d) an isotope
ionized
10
New cards
From the center outward, which of the following lists the “layers” of the Sun in the correct order?
a) core, radiation zone, convection zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona
b) core, convection zone, radiation zone, corona, chromosphere, photosphere
c) core, radiation zone, convection zone, corona, chromosphere, photosphere
a) core, radiation zone, convection zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona
b) core, convection zone, radiation zone, corona, chromosphere, photosphere
c) core, radiation zone, convection zone, corona, chromosphere, photosphere
core, radiation zone, convection zone, photosphere, chromosphere, corona
11
New cards
Which has the greatest gravitational potential energy? A spread-out stellar cloud or a condensed solar system?
spread out stellar cloud
12
New cards
Explain how the sun shines?
proton-proton chain
13
New cards
How would you define a light-year?
The distance light travels in a year (9.46 trillion km)
14
New cards
What is the definition of luminosity?
a) The total amount of light energy emitted from a star.
b) The total amount of light energy emitted from a star per second.
c) The total amount of light energy emitted from a star per unit area.
d) The intensity of the star per unit area.
a) The total amount of light energy emitted from a star.
b) The total amount of light energy emitted from a star per second.
c) The total amount of light energy emitted from a star per unit area.
d) The intensity of the star per unit area.
The total amount of light energy emitted from a star per second.
15
New cards
The Ecliptic is a plane that contains:
a) the orbit of the Earth
b) the orbit of all the planets
c) the orbit of the moon
c) the equator of the sun
a) the orbit of the Earth
b) the orbit of all the planets
c) the orbit of the moon
c) the equator of the sun
the orbit of all the planets
16
New cards
A blackbody is defined as:
a) a perfectly black object
b) an object that absorbs all the radiation upon it
c) an object that reflects all of the radiation incident upon it
a) a perfectly black object
b) an object that absorbs all the radiation upon it
c) an object that reflects all of the radiation incident upon it
an object that absorbs all the radiation upon it
17
New cards
What is the Universe?
The sum total of all matter and energy.
18
New cards
This scientist proposed the geo-centric model of the Universe:
a) Galileo
b) Miller
c) Ptolemy
d) Copernicus
a) Galileo
b) Miller
c) Ptolemy
d) Copernicus
Ptolemy
19
New cards
This Danish nobleman’s pre-observations reintroduced observational astronomy to the Western Europe:
a) Ptolemy
b) Sascrobasco
c) Brahe
d) Lowell
a) Ptolemy
b) Sascrobasco
c) Brahe
d) Lowell
Brahe
20
New cards
I was a mathematician who joined Tycho in Prague and developed my own set of laws for planetary motion in the solar system:
a) Newton
b) Kepler
c) Ptolemy
d) Aristotle
a) Newton
b) Kepler
c) Ptolemy
d) Aristotle
Kepler
21
New cards
The first person to use the telescope as astronomical tool and one of the first modern experimental scientists known for the motion of falling objects:
a) Giacconi
b) Galileo
c) Kepler
d) Ptolemy
a) Giacconi
b) Galileo
c) Kepler
d) Ptolemy
Galileo
22
New cards
I was able to determine the relationship between how far a distant galaxy is to the speed it is moving away:
a) Hubble
b) Lowell
c) Hynek
d) Russell
a) Hubble
b) Lowell
c) Hynek
d) Russell
Lowell
23
New cards
I am WOMAN see me SOAR with my discovery of classifying stars by their Spectra:
a) Hertzsprung
b) Cannon
c) Hubble
d) Lamarck
a) Hertzsprung
b) Cannon
c) Hubble
d) Lamarck
Cannon
24
New cards
I was one of the scientists who proposed the heliocentric model of the Universe:
a) Eratosthenes
b) Copernicus
c) Kepler
d) Russell
a) Eratosthenes
b) Copernicus
c) Kepler
d) Russell
Copernicus
25
New cards
I was the mystic who formed the foundation for Greek Astronomy
a) Aristotle
b) Kepler
c) Pythagoras
d) Copernicus
a) Aristotle
b) Kepler
c) Pythagoras
d) Copernicus
Pythagoras
26
New cards
What if Earth’s axis had no tilt, would we still have seasons? Why or why not?
We would not have seasons if Earth had no tilt. There would be equal heating. Distance is not a factor in seasons only the tilt.
27
New cards
Stars located near the North Pole are called what kind of stars?
Circumpolar
28
New cards
The Sun appears to rise and set in our sky because _______________, and you are one year older each time _____________.
a. Earth rotates on its axis; Earth completes one orbit of the Sun
b. the Sun moves across the orbit of Earth; the Sun completes one rotation on its axis
c. Earth’s rotational axis is tilted, Earth completes one rotation on its axis
d. the Sun rotates on its axis; Earth completes one orbit of the Sun
a. Earth rotates on its axis; Earth completes one orbit of the Sun
b. the Sun moves across the orbit of Earth; the Sun completes one rotation on its axis
c. Earth’s rotational axis is tilted, Earth completes one rotation on its axis
d. the Sun rotates on its axis; Earth completes one orbit of the Sun
Earth rotates on its axis; Earth completes one orbit of the Sun
29
New cards
During the new moon phase, how much of the Moon’s total surface is being illuminated by sunlight?
a) none
b) less than half
c) half
d) more than half
a) none
b) less than half
c) half
d) more than half
half
30
New cards
In what phase and location described below will the Moon be when a solar eclipse occurs?
a) New phase and above the plane of Earth’s orbit.
b) Full phase and above the plane of Earth’s orbit.
c) New phase and crossing Earth’s orbital plane.
d) Full phase and crossing Earth’s orbital plane.
e) None of the above
a) New phase and above the plane of Earth’s orbit.
b) Full phase and above the plane of Earth’s orbit.
c) New phase and crossing Earth’s orbital plane.
d) Full phase and crossing Earth’s orbital plane.
e) None of the above
New phase and crossing Earth’s orbital plane.
31
New cards
Viewed north of the Ecliptic, all planets in the Solar System orbit the sun in a
a) clockwise motion
b) counter clockwise motion
a) clockwise motion
b) counter clockwise motion
counter clockwise motion
32
New cards
Which observation first made by Galileo proves that all the planets move directly around the sun?
a) phases of Venus
b) sunspots
c) mountains on the moon
a) phases of Venus
b) sunspots
c) mountains on the moon
phases of Venus
33
New cards
Kepler’s first law states that:
a) the planets orbit the sun with circular orbits,
b) the Sun orbits the planets with elliptical orbits,
c) the sun orbits the planets with circular orbits,
d) the planets orbit the sun with elliptical orbits.
a) the planets orbit the sun with circular orbits,
b) the Sun orbits the planets with elliptical orbits,
c) the sun orbits the planets with circular orbits,
d) the planets orbit the sun with elliptical orbits.
the planets orbit the sun with elliptical orbits.
34
New cards
Kepler’s First Law also states that:
a) The Sun is half-way between the foci of an ellipse,
b) the Earth is at a focus of the ellipse,
c) the center of the solar system is not where the sun is,
d) the sun is at a focus of the ellipse.
a) The Sun is half-way between the foci of an ellipse,
b) the Earth is at a focus of the ellipse,
c) the center of the solar system is not where the sun is,
d) the sun is at a focus of the ellipse.
the sun is at a focus of the ellipse.
35
New cards
Kepler’s second law, which states that as a planet moves around its orbit it sweeps out equal areas in equal times, means that:
a) a planet travels faster when it is nearer to the Sun and slower when it is farther from the Sun.
b) a planet that is farther from the Sun move at slower average speeds than nearer planets.
c) a planet’s period does not depend on the eccentricity of its orbit.
d) planets have circular orbits.
a) a planet travels faster when it is nearer to the Sun and slower when it is farther from the Sun.
b) a planet that is farther from the Sun move at slower average speeds than nearer planets.
c) a planet’s period does not depend on the eccentricity of its orbit.
d) planets have circular orbits.
a planet travels faster when it is nearer to the Sun and slower when it is farther from the Sun.
36
New cards
Kepler’s Third Law states that:
a) the time period of orbits of the planets are directly proportional to the squares of their radii,
b) the time period of the orbits of the planets are inversely proportional to the squares of their radii,
c) the squares of the time periods of orbits of the planets are directly proportional to the squares of their radii,
d) the squares of the time periods of the orbits of the planets are directly proportional to the cubes of their radii
a) the time period of orbits of the planets are directly proportional to the squares of their radii,
b) the time period of the orbits of the planets are inversely proportional to the squares of their radii,
c) the squares of the time periods of orbits of the planets are directly proportional to the squares of their radii,
d) the squares of the time periods of the orbits of the planets are directly proportional to the cubes of their radii
the squares of the time periods of the orbits of the planets are directly proportional to the cubes of their radii
37
New cards
A consequence of Kepler’s Third Law is that:
a) the planets all travel at the same speed around the sun
b) the planets travel faster the further they are away from the sun
c) the planets travel slower the further they are away from the sun
d) the planets travel slower when they are closer to the sun
a) the planets all travel at the same speed around the sun
b) the planets travel faster the further they are away from the sun
c) the planets travel slower the further they are away from the sun
d) the planets travel slower when they are closer to the sun
the planets travel slower the further they are away from the sun
38
New cards
What was the major obstacle in the verification of Kepler’s Third Law:
a) gravity had not been discovered yet
b) the planets did not have an elliptical orbit
c) telescopes had not been invented yet
d) no parallax of nearby stars had been detected
a) gravity had not been discovered yet
b) the planets did not have an elliptical orbit
c) telescopes had not been invented yet
d) no parallax of nearby stars had been detected
gravity had not been discovered yet
39
New cards
From Kepler’s third law, an asteroid with an orbital period of 12 years lies at an average distance from the Sun equal to
a) 1 astronomical unit.
b) 5 astronomical units.
c) 7 astronomical units.
d) It depends on the asteroid’s mass.
a) 1 astronomical unit.
b) 5 astronomical units.
c) 7 astronomical units.
d) It depends on the asteroid’s mass.
d3 = a2; d3 = 122 d3 = 144 cube root of d = cube root of 144;
d = 5
d = 5
40
New cards
An object in uniform circular motion (non-zero net force), apply this formula: F = Gm1m2/r2.
Example #1: If two objects are attracted gravitationally and their separation is doubled, the attractive force due to gravity is decreased to 1⁄4 the original force.
Example #2: If two objects are attracted gravitationally and the mass of each is doubled, the attractive force due to gravity will increase four times its original strength.
Example #1: If two objects are attracted gravitationally and their separation is doubled, the attractive force due to gravity is decreased to 1⁄4 the original force.
Example #2: If two objects are attracted gravitationally and the mass of each is doubled, the attractive force due to gravity will increase four times its original strength.
Example #1 F = 1/r2 = 1/22 = ¼
Example #2 F = (m1) x (m2) = 2 x 2 = 4
Example #2 F = (m1) x (m2) = 2 x 2 = 4
41
New cards
What the significance of Galileo discovering moons orbiting Jupiter?
a) there may be life elsewhere in the solar system
b) the heavens are not perfect and unchanging
c) Jupiter is the center of the solar system
a) there may be life elsewhere in the solar system
b) the heavens are not perfect and unchanging
c) Jupiter is the center of the solar system
the heavens are not perfect and unchanging
42
New cards
The Newtonian model predicts that the Universe is:
a) static and infinite,
b) expanding and finite,
c) collapsing and finite,
d) expanding at an increasingly slower rate and finite
a) static and infinite,
b) expanding and finite,
c) collapsing and finite,
d) expanding at an increasingly slower rate and finite
static and infinite
43
New cards
Newton’s 2nd Law: F = ma, mass (m, units; kg), acceleration (a, units m/s2) force (F, Newtons, units; 1N = kg x m/s2).
Example #1: If the mass of the Earth was doubled but the radius stayed the same, objects dropped near the surface of the Earth would accelerate more rapidly.
Example #2: If the Earth shrinked to half its current radius, but the mass stayed the same, an object on or near the surface would accelerate faster due to the fact that it is getting closer to the center of Earth.
Example #1: If the mass of the Earth was doubled but the radius stayed the same, objects dropped near the surface of the Earth would accelerate more rapidly.
Example #2: If the Earth shrinked to half its current radius, but the mass stayed the same, an object on or near the surface would accelerate faster due to the fact that it is getting closer to the center of Earth.
F = ma; 2 x 9.8 m/s2 the object would accelerate more rapidly ½ the radius but mass remain the same (objects are now closer to center (stronger attraction), therefore, would accelerate faster.
44
New cards
The force of gravity is an inverse square law. This means that, if you double the distance between two large masses, the gravitational force between them
a) also doubles.
b) strengthens by a factor of 4.
c) is unaffected.
d) weakens by a factor of 4.
a) also doubles.
b) strengthens by a factor of 4.
c) is unaffected.
d) weakens by a factor of 4.
weakens by a factor of 4.
45
New cards
EM waves in order from longer wavelength to shorter wavelength or lower frequency to higher frequency: radio, microwaves, infrared (heat), visible (ROYGBIV), ultraviolet, x- rays, gamma rays.
EM waves are self-propagating waves made up of both an electric and magnetic field fluctuating together. They are a form of radiant energy created when electric charges accelerate.
EM waves are self-propagating waves made up of both an electric and magnetic field fluctuating together. They are a form of radiant energy created when electric charges accelerate.
c = wavelength x frequency; c = λf E-M waves
V = λf for ordinary waves (beach waves)
V = λf for ordinary waves (beach waves)
46
New cards
If Earth’s atmosphere was able to completely absorb visible light, which of the following would be true?
a) The Earth’s surface temperature would be cooler than it is today.
b) The Earth’s surface temperature would be warmer than it is today.
c) The Earth’s surface temperature would be the same temperature as it is
today.
d) There is not enough information to answer this question.
a) The Earth’s surface temperature would be cooler than it is today.
b) The Earth’s surface temperature would be warmer than it is today.
c) The Earth’s surface temperature would be the same temperature as it is
today.
d) There is not enough information to answer this question.
The Earth’s surface temperature would be cooler than it is today.
47
New cards
Which of these would be mainly used to analyze elements present in stars?
a) continuous spectrum
b) emission spectrum
c) absorption spectrum
d) visible spectrum
a) continuous spectrum
b) emission spectrum
c) absorption spectrum
d) visible spectrum
absorption spectrum
48
New cards
An electron is promoted from energy level 1 to energy level 3. What would the result be?
a) absorption of energy or b) emission of a photon
a) absorption of energy or b) emission of a photon
absorption of energy
49
New cards
An electron falls from energy level 4 to energy level 2. What would the result be?
a) absorption of energy or b) emission of a photon
a) absorption of energy or b) emission of a photon
emission of a photon
50
New cards
A cool, low density (thin) gas is located in front of a hot solid, an observer looking at the solid through the gas would see:
a) continuous spectrum,
b) absorption spectrum,
c) emission spectrum,
d) no light at all
a) continuous spectrum,
b) absorption spectrum,
c) emission spectrum,
d) no light at all
absorption spectrum
51
New cards
The spectrum of a hot gas seen against a cold background usually shows:
a) emission lines
b) absorption lines
c) continuous blended lines
a) emission lines
b) absorption lines
c) continuous blended lines
emission lines
52
New cards
Be able to use Stefan Boltzmann’s and Wein’s Laws from homework #5 (correction).
53
New cards
Fusion is the:
a) splitting of atoms,
b) combining of atoms,
c) separation of the nucleus from the core
a) splitting of atoms,
b) combining of atoms,
c) separation of the nucleus from the core
combining of atoms
54
New cards
A fusion reaction is a(n):
a) proton-proton reaction,
b) neutron-proton reaction,
c) electron-proton reaction
a) proton-proton reaction,
b) neutron-proton reaction,
c) electron-proton reaction
proton-proton reaction
55
New cards
The most massive element that is produced by the fusion reaction in stars is:
a) Uranium
b) Carbon
c) Helium
d) Iron
a) Uranium
b) Carbon
c) Helium
d) Iron
Iron
56
New cards
Why does Hydrogen fusion occur in a star’s center?
a) enough heat and pressure,
b) speed of light is favorable for the reaction to occur,
c) not enough hydrogen to mix with other elements,
d) heat is transferred downward to the center
a) enough heat and pressure,
b) speed of light is favorable for the reaction to occur,
c) not enough hydrogen to mix with other elements,
d) heat is transferred downward to the center
enough heat and pressure
57
New cards
When the core of a star shrinks after hydrogen fusion stops:
a) the core cools and the star expands
b) the core cools and the star contracts
c) the core heats and the star expands
d) the core heats and the star contracts
a) the core cools and the star expands
b) the core cools and the star contracts
c) the core heats and the star expands
d) the core heats and the star contracts
the core heats and the star expands
58
New cards
Star G has an apparent magnitude of 5.0 and an absolute magnitude of 4.0 Star H has an apparent magnitude of 4.0 and absolute magnitude of 5.0 Which of the following statements is true about viewing these two stars from Earth?
a) Star G will appear brighter than Star H.
b) The two stars will appear to have the same brightness.
c) Star H will appear brighter than Star G.
d) None of the above.
a) Star G will appear brighter than Star H.
b) The two stars will appear to have the same brightness.
c) Star H will appear brighter than Star G.
d) None of the above.
Star H will appear brighter than Star G.
59
New cards
A st*a*r’s luminosity is the or what is luminosity?
a) apparent brightness of the star in our sky.
b) surface temperature of the star.
c) lifetime of the star.
d) total amount of light that the star will radiate over its entire lifetime
e) total amount of light that the star radiates each second.
a) apparent brightness of the star in our sky.
b) surface temperature of the star.
c) lifetime of the star.
d) total amount of light that the star will radiate over its entire lifetime
e) total amount of light that the star radiates each second.
total amount of light that the star radiates each second.
60
New cards
If the distance between us and a star is doubled, with everything else remaining the same, the luminosity
a) is decreased by a factor of four, and apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of four.
b) is decreased by a factor of two, and the apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of two.
c) remains the same, but the apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of two.
d) remains the same, but the apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of four.
a) is decreased by a factor of four, and apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of four.
b) is decreased by a factor of two, and the apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of two.
c) remains the same, but the apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of two.
d) remains the same, but the apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of four.
remains the same, but the apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of four.
61
New cards
What is the difference between absolute and apparent magnitude and how do they describe stellar luminosities? What is the inverse square law? Why do some stars appear brighter than others in the night sky? Explain.
Absolute magnitude is a star’s intrinsic brightness (luminosity). Apparent magnitude is how a star’s brightness appears to our eyes here on Earth. The inverse square law is 1/d^2, so if you double the distance between you and the star it appears 1⁄4 as bright. Distance has a lot to do with how bright stars appear to your eyes.
62
New cards
The apparent brightness of a star depends only on its luminosity.
a) True b) False
a) True b) False
false
63
New cards
If the distance between us and a star is quadrupled, the apparent brightness is decreased by a factor of sixteen.
a) True b) False
a) True b) False
true
64
New cards
Two Stars, Fred and Barney, are of the same size. Fred has spectral F, while Barney has spectral type B. Which one is more luminous? Why?
Barney
65
New cards
A 10 solar mass star is about ten times more luminous than a 1 solar mass star.
a) True b) False
a) True b) False
false
66
New cards
If a star’s absolute magnitude is lower than its apparent magnitude, will it appear brighter than it actually is, or dimmer than it actually is?
It will appear dimmer.
67
New cards
Based on Venus and Sirius absolute magnitudes, which star is brighter?
a) Venus: -4.4
b) Sirius: -1.1
a) Venus: -4.4
b) Sirius: -1.1
venus
68
New cards
What is the difference between apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude? What is the relationship between m and M in regards to our imagination of stars at the same distance and our comparison of their brightness? What is this distance (in pc or ly)?
Apparent magnitude (m) compares how bright different stars appear in the sky and directly related to apparent brightness except that the scales run backwards, i.e. Sirius -1.46 (more negative the number, the brighter the star). Absolute Magnitude (M) is the apparent magnitude it would have if it were at a distance of 10 pc from Earth. Sun’s absolute magnitude is about 4.8, which means it would have an apparent magnitude of 4.8 if it were 10 pc away from us.
69
New cards
The star Krok has an apparent magnitude of +0.03 and an absolute magnitude of +3.0. If it were moved 10 times farther from Earth as it is now, which one of the following would occur?
a. absolute magnitude number would decrease (gets smaller)
b. apparent magnitude number would decrease (gets smaller)
c. apparent magnitude number would stay the same
d. absolute magnitude number would increase (gets bigger)
e. apparent magnitude number would increase (gets bigger)
a. absolute magnitude number would decrease (gets smaller)
b. apparent magnitude number would decrease (gets smaller)
c. apparent magnitude number would stay the same
d. absolute magnitude number would increase (gets bigger)
e. apparent magnitude number would increase (gets bigger)
apparent magnitude number would increase (gets bigger)
70
New cards
The star Aprilia is 3 parsecs away. Its apparent magnitude is +3.0. What is most likely its absolute magnitude?
a. +6.0
b. +3.0
c. +0.30
d. -3.0
e. -6.0
a. +6.0
b. +3.0
c. +0.30
d. -3.0
e. -6.0
\+6.0
71
New cards
Which of the following persons reorganized the spectral classification scheme into the one we use today and personally classified over 400,000 stars?
a) Annie Jump Cannon
b) Williamina Fleming
c) Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin
d) Henry Draper
a) Annie Jump Cannon
b) Williamina Fleming
c) Cecilia Payne-Gaposchkin
d) Henry Draper
Annie Jump Cannon
72
New cards
The spectral sequence in order of decreasing temperature is
A) OFBAGKM
B) OBAGFKM
C) OBAFGKM
D) ABFGKMO
A) OFBAGKM
B) OBAGFKM
C) OBAFGKM
D) ABFGKMO
OBAFGKM
73
New cards
Spectral type, surface temperature, and color all describe the same basic characteristic of a Star?
a) True b) False
a) True b) False
true
74
New cards
Two stars have the same luminosity. Star X is spectral type F, while Star Y is spectral type K. Therefore, Star X is larger in radius than Star Y.
a) True b) False
a) True b) False
false
75
New cards
Which of the following sequences correctly describes the stages of life for a low-mass star?
a) red giant, protostar, main-sequence, white dwarf
b) white dwarf, main-sequence, red giant, protostar
c) interstellar cloud, red giant, main-sequence, white dwarf
d) interstellar cloud, main-sequence, red giant, white dwarf
a) red giant, protostar, main-sequence, white dwarf
b) white dwarf, main-sequence, red giant, protostar
c) interstellar cloud, red giant, main-sequence, white dwarf
d) interstellar cloud, main-sequence, red giant, white dwarf
interstellar cloud, main-sequence, red giant, white dwarf
76
New cards
Where would a brown dwarf be located on an H-R diagram?
a) upper right
b) on the lower part of the main sequence
c) below and to the right of the lowest part of the main sequence
d) lower left
a) upper right
b) on the lower part of the main sequence
c) below and to the right of the lowest part of the main sequence
d) lower left
below and to the right of the lowest part of the main
77
New cards
What can we learn about a star from a life track on an H-R diagram? \n a) how long ago it was born,
b) when it will die,
c) where it is located,
d) what surface
temperature and luminosity it will have at each stage of its life, e) all of the above
b) when it will die,
c) where it is located,
d) what surface
temperature and luminosity it will have at each stage of its life, e) all of the above
all of the above
78
New cards
Which one property of a star will determine the rest of the characteristics of that star’s life?
a. Luminosity
b. Temperature
c. Color
d. Mass
e. Spectral type
a. Luminosity
b. Temperature
c. Color
d. Mass
e. Spectral type
mass
79
New cards
A star on the lower right-hand part of the main sequence will be less massive than a star on the upper left-hand part of the main sequence.
a) True b) False
a) True b) False
true
80
New cards
The thermal pressure of a gas depends on:
a) density only.
b) temperature only.
c) density and temperature.
d) composition.
a) density only.
b) temperature only.
c) density and temperature.
d) composition.
density and temperature.
81
New cards
Enzo star gives off the same amount of energy as Ferdinand star.But Enzo star is much hotter than Ferdinand star. Which star has the greater surface area?
a) Enzo
b) Ferdinand
c) They have the same surface area
d) There is insufficient information to answer this question
a) Enzo
b) Ferdinand
c) They have the same surface area
d) There is insufficient information to answer this question
Ferdinand
82
New cards
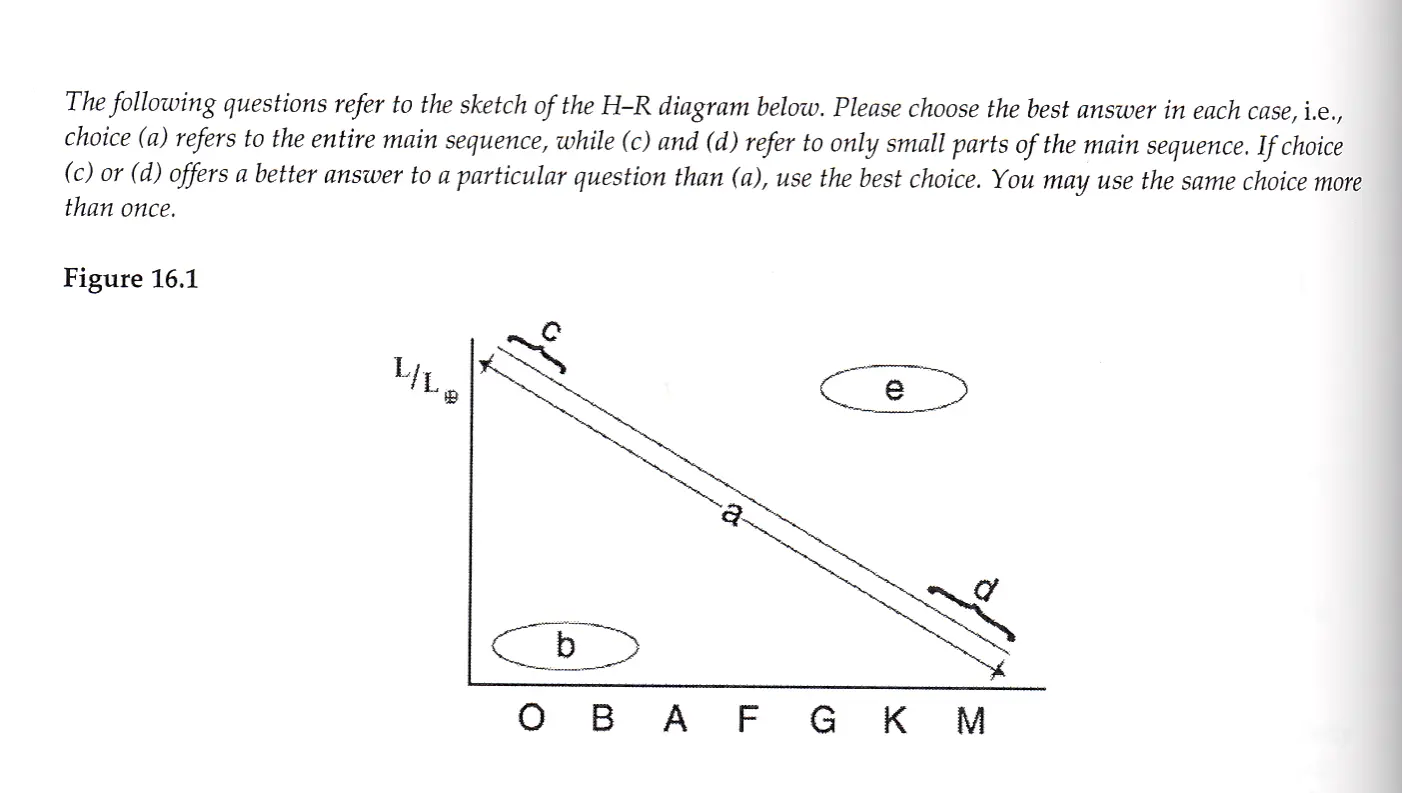
Which group represents stars that are cool and dim?
a) a
b) b
c) c
d) d
e) e
a) a
b) b
c) c
d) d
e) e
d
83
New cards
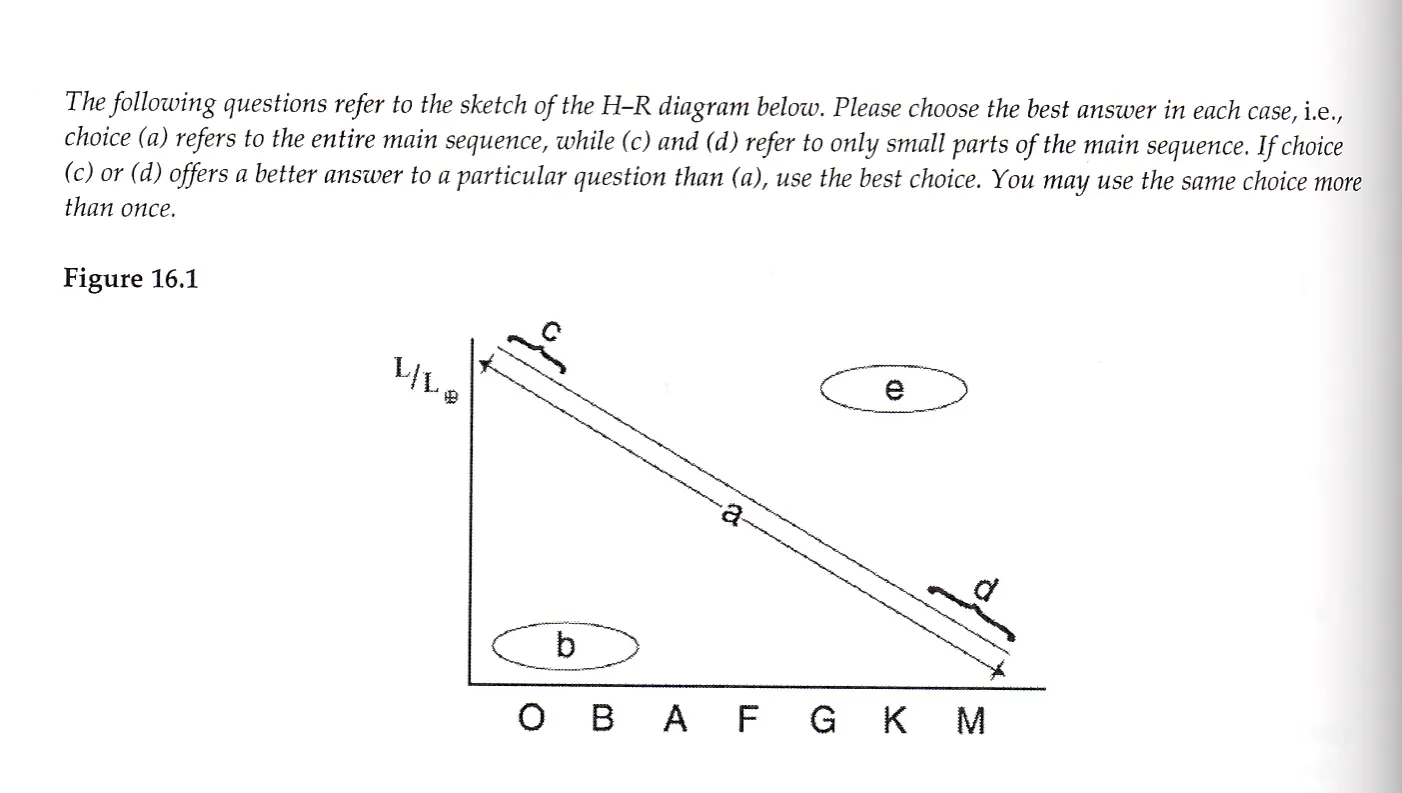
Which group of stars has the largest radii?
a) a
b) b
c) c
d) d
e) e
a) a
b) b
c) c
d) d
e) e
e
84
New cards
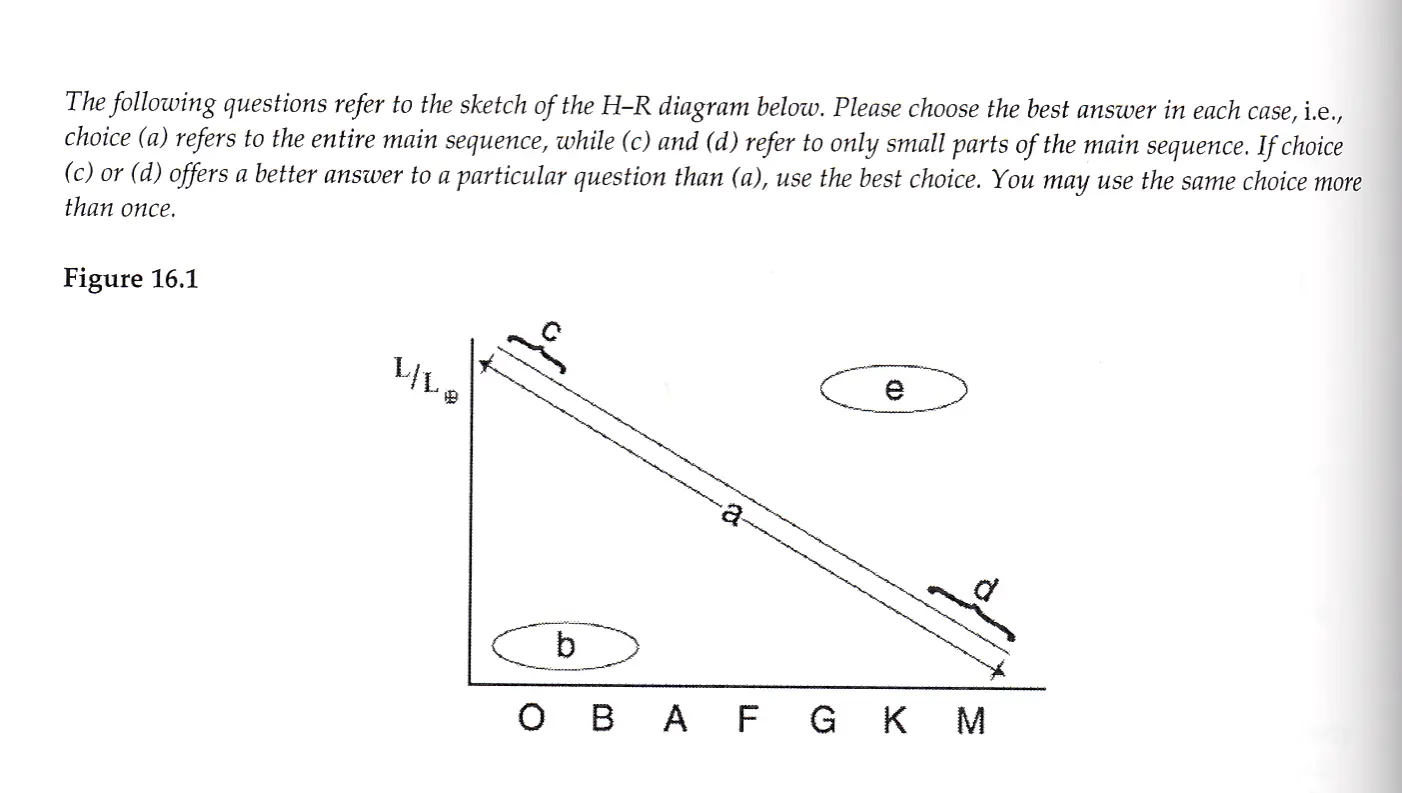
Where on the H-R diagram would you find white dwarfs?
a) a
b) b
c) c
d) d
e) e
a) a
b) b
c) c
d) d
e) e
b
85
New cards
Chili Pepper is a main sequence star that appears red when viewed from Earth, as a result which of the following is (always) true:
a) It is hotter than an O spectral type main sequence star.
b) It will appear dimmer than a white dwarf.
c) It will live longer than a B spectral type main sequence star.
d) It is the same size as a red giant star of the same temperature.
e) None of the above are correct.
a) It is hotter than an O spectral type main sequence star.
b) It will appear dimmer than a white dwarf.
c) It will live longer than a B spectral type main sequence star.
d) It is the same size as a red giant star of the same temperature.
e) None of the above are correct.
It will live longer than a B spectral type main sequence star.
86
New cards
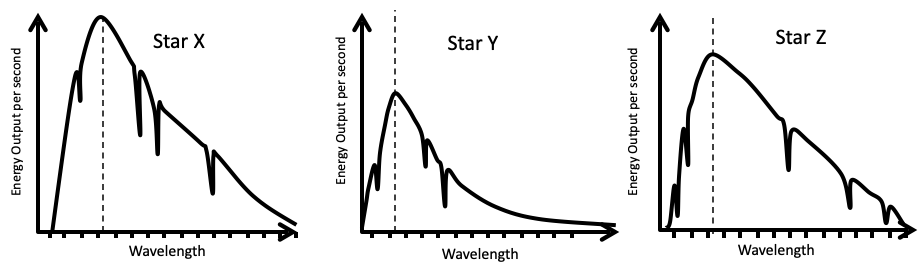
The three spectral curves shown in the graphs below illustrate the energy output versus wavelength for three unknown stars X, Y, and Z? Which of the following is the correct ranking for the temperature of the stars, from hottest to coldest.
Y>Z>X
87
New cards
When does a star become a main-sequence star?
a) When the protostar assembles from a molecular cloud
b) The instant when hydrogen fusion first begins in the star’s core
c) When the rate of hydrogen fusion within the star’s core is high enough to maintain gravitational equilibrium
d) When a star becomes luminous enough to emit thermal radiation
a) When the protostar assembles from a molecular cloud
b) The instant when hydrogen fusion first begins in the star’s core
c) When the rate of hydrogen fusion within the star’s core is high enough to maintain gravitational equilibrium
d) When a star becomes luminous enough to emit thermal radiation
When the rate of hydrogen fusion within the star’s core is high enough to maintain gravitational equilibrium
88
New cards
Our Sun will not become a nova because this only happens to stars
a) much more massive than the Sun.
b) much less massive than the Sun.
c) with a binary companion.
d) that have no planetary systems.
a) much more massive than the Sun.
b) much less massive than the Sun.
c) with a binary companion.
d) that have no planetary systems.
with a binary companion.
89
New cards
Black holes are formed by
a) a lack of any light in a region of space.
b) supernovae from the most massive stars.
c) supernovae from binary stars.
d) collapsed dark nebulae.
a) a lack of any light in a region of space.
b) supernovae from the most massive stars.
c) supernovae from binary stars.
d) collapsed dark nebulae.
supernovae from the most massive stars.
90
New cards
Which of the following lists, in the correct order, a possible evolutionary path for a star?
a) Red Giant, Neutron Star, White Dwarf, Nothing
b) Red Giant, Type II Supernova, Black Hole, Nothing
c) Red Giant, Type II Supernova, Planetary Nebula, Neutron Star
d) Red Giant, Planetary Nebula, White Dwarf
e) Red Giant, Planetary Nebula, Black Hole
a) Red Giant, Neutron Star, White Dwarf, Nothing
b) Red Giant, Type II Supernova, Black Hole, Nothing
c) Red Giant, Type II Supernova, Planetary Nebula, Neutron Star
d) Red Giant, Planetary Nebula, White Dwarf
e) Red Giant, Planetary Nebula, Black Hole
Red Giant, Planetary Nebula, White Dwarf
91
New cards
For a white dwarf to become a nova it is necessary for it to
a) have a binary companion.
b) become a black hole.
c) have begun life as a high-mass star
d) rejoin the main sequence.
a) have a binary companion.
b) become a black hole.
c) have begun life as a high-mass star
d) rejoin the main sequence.
have a binary companion.
92
New cards
What happens when a star exhausts its core hydrogen supply?
a) Its core contracts, but its outer layers expand and the star becomes bigger and brighter.
b) It contracts, becoming smaller and dimmer.
c) It contracts, becoming hotter and brighter.
d) It expands, becoming bigger but dimmer.
a) Its core contracts, but its outer layers expand and the star becomes bigger and brighter.
b) It contracts, becoming smaller and dimmer.
c) It contracts, becoming hotter and brighter.
d) It expands, becoming bigger but dimmer.
Its core contracts, but its outer layers expand and the star becomes bigger and brighter.
93
New cards
What is a planetary nebula?
a) A disk of gas surrounding a protostar that may form into planets.
b) What is left of the planets around a star after a low-mass star has ended its life.
c) The expanding shell of gas that is no longer gravitationally held to the remnant of a low-mass star.
d) The molecular cloud from which protostar form.
a) A disk of gas surrounding a protostar that may form into planets.
b) What is left of the planets around a star after a low-mass star has ended its life.
c) The expanding shell of gas that is no longer gravitationally held to the remnant of a low-mass star.
d) The molecular cloud from which protostar form.
The expanding shell of gas that is no longer gravitationally held to the remnant of a low-mass star.
94
New cards
What happens to the core of a star after a planetary nebula occurs?
a) It contracts from a protostar to a main-sequence star.
b) It breaks apart in a violent explosion.
c) It becomes a white dwarf.
d) It becomes a neutron star.
a) It contracts from a protostar to a main-sequence star.
b) It breaks apart in a violent explosion.
c) It becomes a white dwarf.
d) It becomes a neutron star.
It becomes a white dwarf.
95
New cards
What are the five stages in the life of a low mass star that does have a companion?
(interstellar cloud, main sequence, red giant, Nova, white dwarf)
96
New cards
why does an interstellar gas cloud flatten as it collapses?
particles with the cloud collide; Look at Lecture 10A,Twinkle Twinkle Little Star
97
New cards
When stars first begin to form, which is the most important element in the gas cloud?
Hydrogen
98
New cards
Will a high mass or low mass star have a greater core temperature and density?
high mass
99
New cards
Stars spend 90% of their lives as:
a) binary stars
b) high mass stars
c) main sequence stars
d) all of the above
a) binary stars
b) high mass stars
c) main sequence stars
d) all of the above
main sequence stars
100
New cards
Stars condense from clouds of gas and dust. The gas is hydrogen, while the dust is made up of mainly_____ and ________.
carbon & silicon