Chemical Reactivity
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
define: surface area
a measure of the proportion of particles on a surface of a substance that are exposed and so able to react
(will purely affect the frequency of collisions)
describe: increasing surface area effect on reaction
increasing surface area (using powder form)
-means proportion of particles that are exposed and able to react is increased
-this leads to an increase in the frequency of collisions
-as a result, this means that there is an increase in the frequency of successful collisions
-however the proportion of successful collisions remains the same
-leads to an increase in the rate of reaction
define: catalyst
provides an alternate reaction pathway with lower activation energy, without being used up
describe: catalyst effect on reaction
since it provides an alternate reaction pathway, without being used up
-means activation energy is lower
-means that the proportion of particles that have sufficient kinetic energy to overcome activation energy barrier will increase
-thus, there is an increase in the frequency of successful collisions
-leads to an increase in the rate of reaction
define: temperature
the measure of the average kinetic energy of the particles inside a substance
describe: increase in temperature effect on reaction
increase in temperature
-means that the average kinetic energy of particles will increase
-particles are moving faster
-there is an increase in the frequency of collisions occurring
-also means that a higher proportion of particles will have sufficient kinetic energy to overcome the activation energy barrier
-means there is an increase in the frequency of successful collisions
-the rate of reaction is increased
define: concentration
a measure of the amount of particles per unit of volume
describe: increase in concentration effect on reaction
increasing the concentration:
-means there will be in an increase in the number of particles in a set space
-lead to an increase in the frequency of collisions
-leads to an increase in the frequency of successful collisions
-however, proportion of collisions that are successful remain the same
-rate of reaction is increased
describe: collision theory
states that in order for a reaction between two particles to occur:
-particles must collide with the correct orientation
-particles must have sufficient kinetic energy to overcome the activation energy barrier
describe: dynamic equilibrium
when the forward and reverse reactions have the same rate, and so there is no ret reaction, or change in the system
describe: conditions needed for dynamic equilibrium to be established
-can only exist in a closed system (so no reactants/products can escape)
-can only occur with reversible reactions
-must be held at a constant temperature and pressure
-the concentrations of substances do not change (but may not necessarily be the same)
describe: what Kc value means
if Kc is greater than 1: at equilibrium, the reaction will favour the products, so there will be more products than reactants
if Kc is less than 1: at equilibrium, the reaction will favour the reactants, only a small amount of product is formed, more reactants than products
describe: what Qc value indicates
Qc= represents the calculated value for an equilibrium reaction that has not reached equilibrium yet
-if Qc is larger than Kc, the reaction will proceed in reverse (increase in reactants) until equilibrium is established (rate of forward + reverse is equal)
-if Qc is smaller than Kc, the reaction will proceed forward (increase products) until equilibrium is established (rate of forward + reverse is equal)
what is the only thing that can change Kc?
temperature is the only thing that can change this value
describe: effects of pressure
increase in pressure, means a decrease in volume= system will act to oppose change, favouring side with fewer number of gaseous moles to decrease the number of gas particles to re-establish equilibrium
decrease in pressure, means an increase in volume= system will act to oppose the change, favouring the side with largest number of gaseous moles, to increase the number of gas particles to re-establish equilibrium
-does not affect the value of Kc
describe: effects of temperature
increase in temperature, means heat is being added= system will favour the endothermic reaction, absorbing the increased heat energy supplied to the system to re-establish equilibrium
decrease in temperature, means heat is being removed= system will favour the exothermic reaction, releasing heat energy to re-establish equilibrium
describe: effects of pressure where number of gaseous moles is the same
a change in pressure will have no effect on the equilibrium position
describe: what side reaction favours with increasing/decreasing Kc
increasing Kc- will favour the products
decreasing Kc- will favour the reactants
describe: le chatalier's principle
states that when an equilibrium is stressed, it will respond by moving in the opposite direction to minimise the change
describe: effects of concentration
increase in concentration, extra product/reactant being added to mixture= reaction will favour the other side of the reaction, to use up some of added substance to re-establish equilbrium
decrease in concentration, reactant/products being removed from mixture= reaction will favour side of that material, to produce more of the removed substance to re-establish equilibrium
describe: effects of catalyst
provides alternate reaction pathway with lower activation energy
-higher proportion of particles have sufficient kinetic energy to overcome activation energy barrier
-reaction is faster
-both the forward and reverse reactions are affected the same way
-allows equilibrium to be established more quickly, but no change in the position of equilibrium
define: acid and base + reaction
acid= donates protons
base= accepts protons
acid-base reaction= one in which a proton is transferred from an acid to a base
what is Kw?
-is the dissociation constant/ionic product of water
1 x 10⁻¹⁴
describe: exothermic reaction in relation to activation energy
total energy released is greater than the activation energy for the reaction
-energy released by initial exothermic reaction is used to provide activation energy for other particles to react
-once exothermic reaction begins, it will continue until one of the reactants is used up or some other change occurs
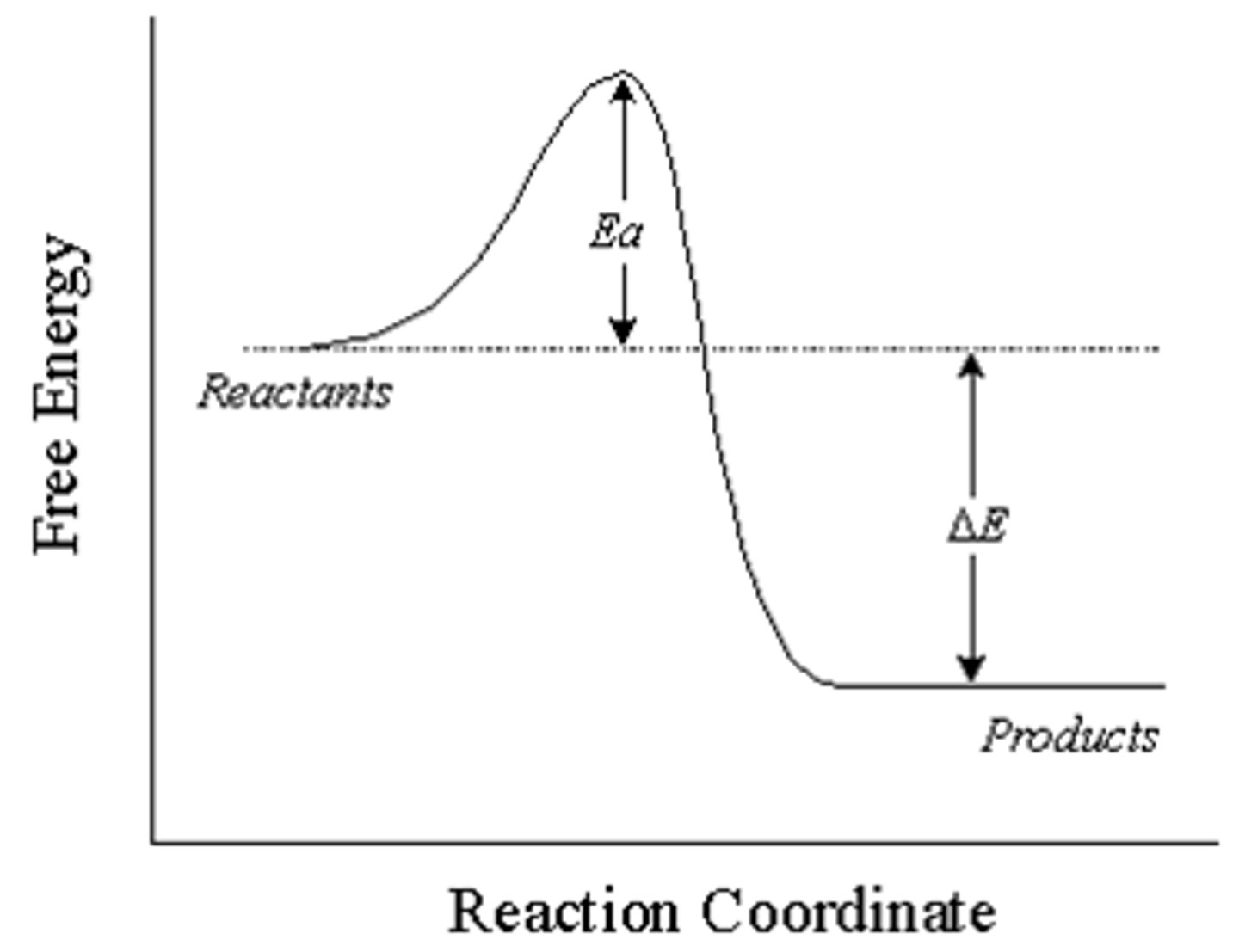
describe: endothermic reaction in relation to activation energy
energy released is less than the activation energy for the reaction
-these reactions have a different driving force which allows colliding particles to gain sufficient activation energy
describe: the two main ways rate of reaction can be increased
-increasing the frequency of collisions occurring (surface area, concentration and temperature)
-increasing the energy of the collisions, so more collisions are effective (temperature, catalyst)
describe: ionisation/dissociation
-the transfer of hydrogen ions (since ions are formed)
state: ways to define acids
-damp blue litmus paper turning red
-hydrogen gas is released when a metal is added (with pop sound when ignited in air)
-carbon dioxide gas is released when calcium carbonate is added (becomes milky when passed through limewater)
state: ways to define bases
-damp red litmus paper turning blue
-ammonia gas is released when added to a warmed ammonium compound (smell/turns litmus blue)
define: amphiprotic
-it can act as a proton donor in neutral/basic conditions
-it can act as a proton acceptor in acidic conditions
define: strong acid + properties
dissociate completely in water
-have a low pH
-react rapidly with magnesium ribbon
-are good conductors of electricity
define: weak acid + properties
partially dissociate in water
-have a pH less than 7 but seldom below 3
-react slowly with magnesium ribbon
-are poor conductors of electricity
define: strong bases +properties
completely dissociate in water
-have a high pH
-react rapidly with ammonium compounds to release ammonia gas
-are good conductors of electricity
define: weak bases + properties
only react to a small extent with water
-have a pH above 7 but seldom above 11
-react slowly with ammonium compounds to release ammonia gas
-are poor conductors of electricity
state: common strong acids
HNO₃
HCl
H₂SO₄
HBR
state: common weak acids
NH₄⁺
CH₃COOH
CHOOH
HF
CH₃NH₃⁺
HCN
state: common weak bases
NH₃
CH₃COO⁻
CHOO⁻
F⁻
CH₃NH₂
CN⁻
state: common strong bases
NaOH
KOH
S²⁻
state common salts
NH₄Cl
CH₃COONa
CH₃NH₃Cl