Anatomy and Physiology Parts of the Skull Identification
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
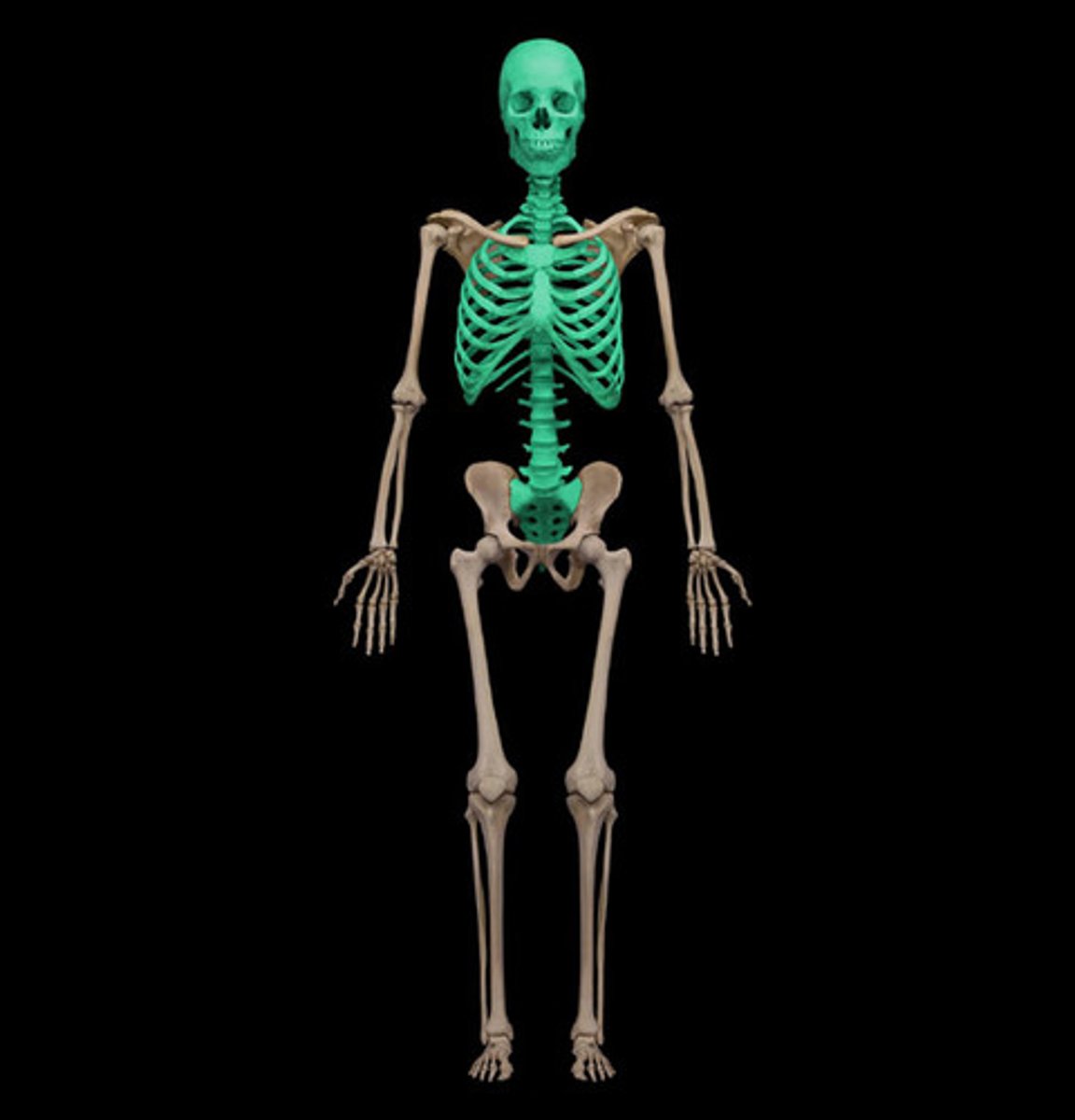
Axial Skeleton
The part of the skeleton that includes the skull, vertebral column, and rib cage, providing support and protection for the brain, spinal cord, and thoracic organs.
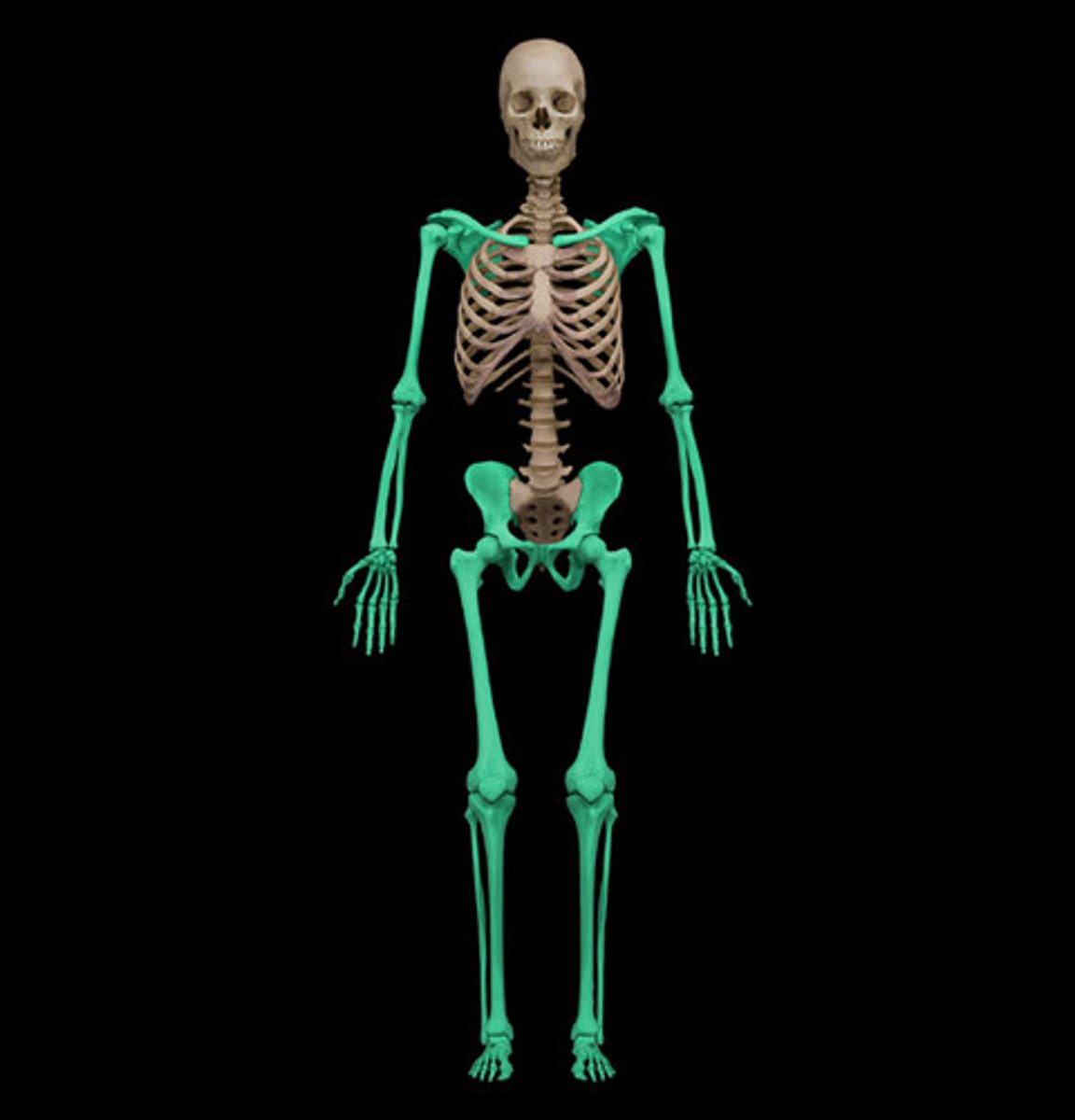
Appendicular Skeleton
The portion of the skeleton that includes the limbs and pelvic and pectoral girdles, facilitating movement and interaction with the environment.
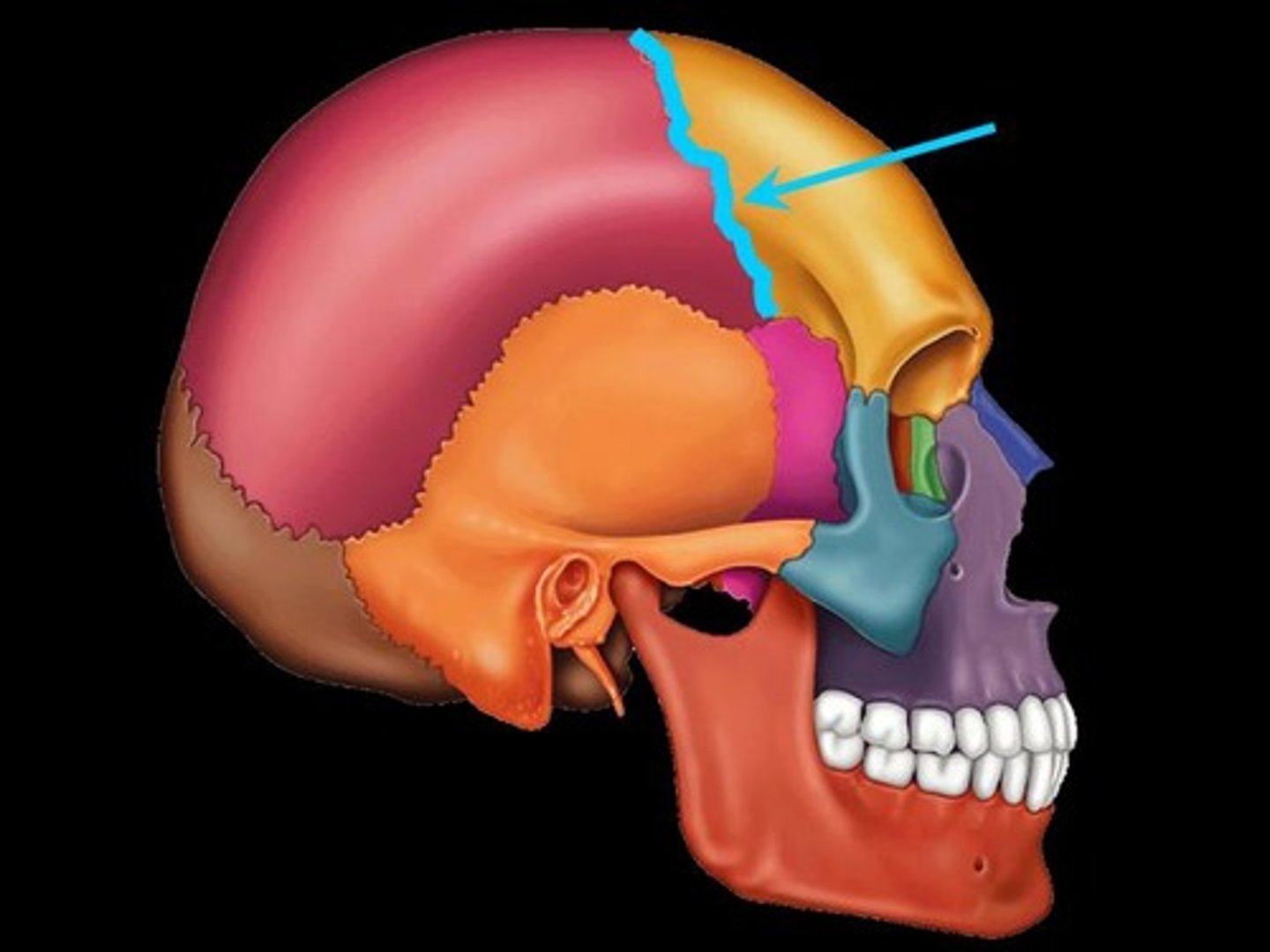
Sutures
Fibrous joints that connect the bones of the skull, allowing for growth and flexibility during infancy and childhood.
Cranial Bones
The eight bones that form the protective cranial cavity, housing and protecting the brain.

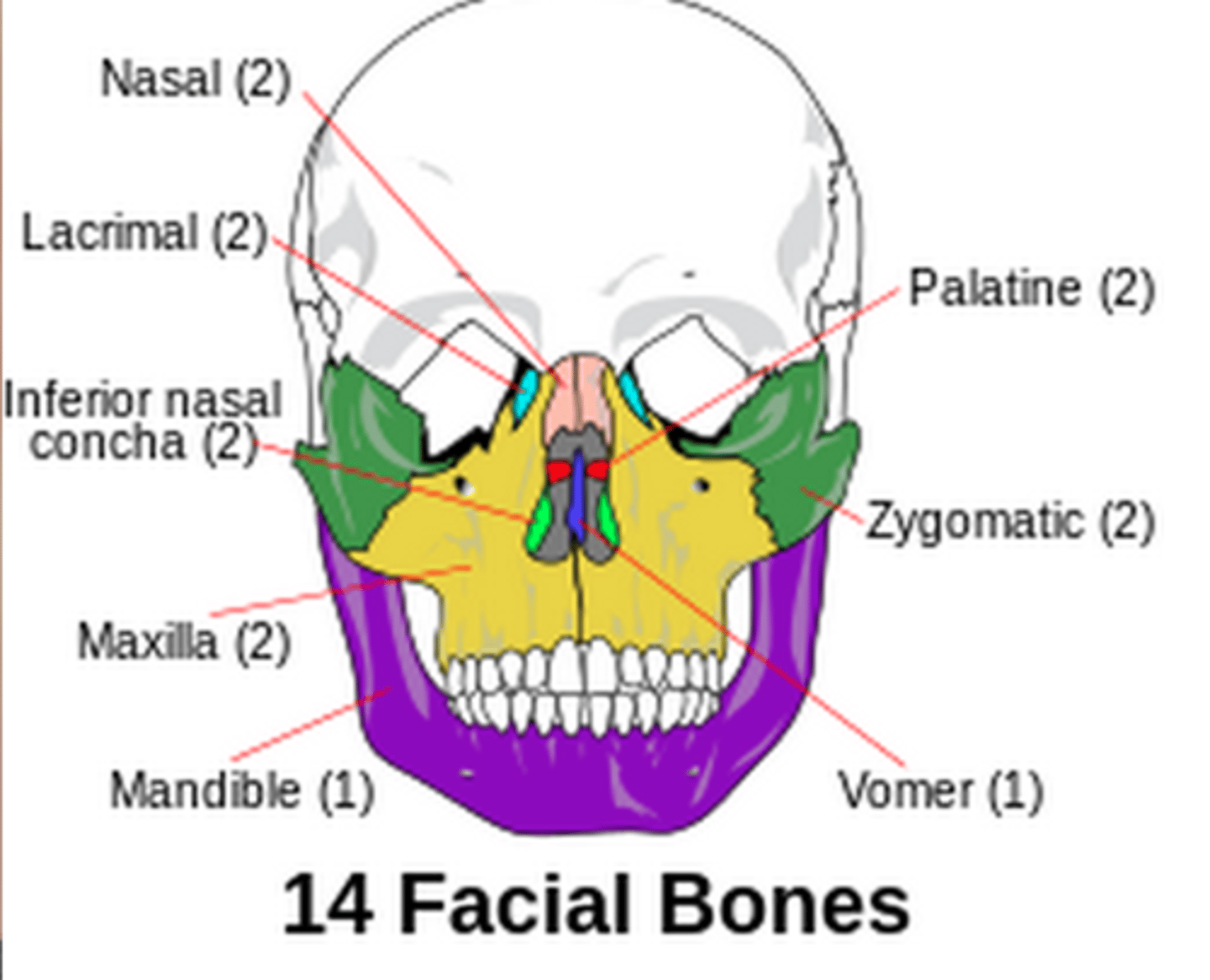
Facial Bones
The bones that form the structure of the face, including the nasal cavity and support for the teeth.
Frontal Bone
The bone that forms the forehead and the upper part of the eye sockets.

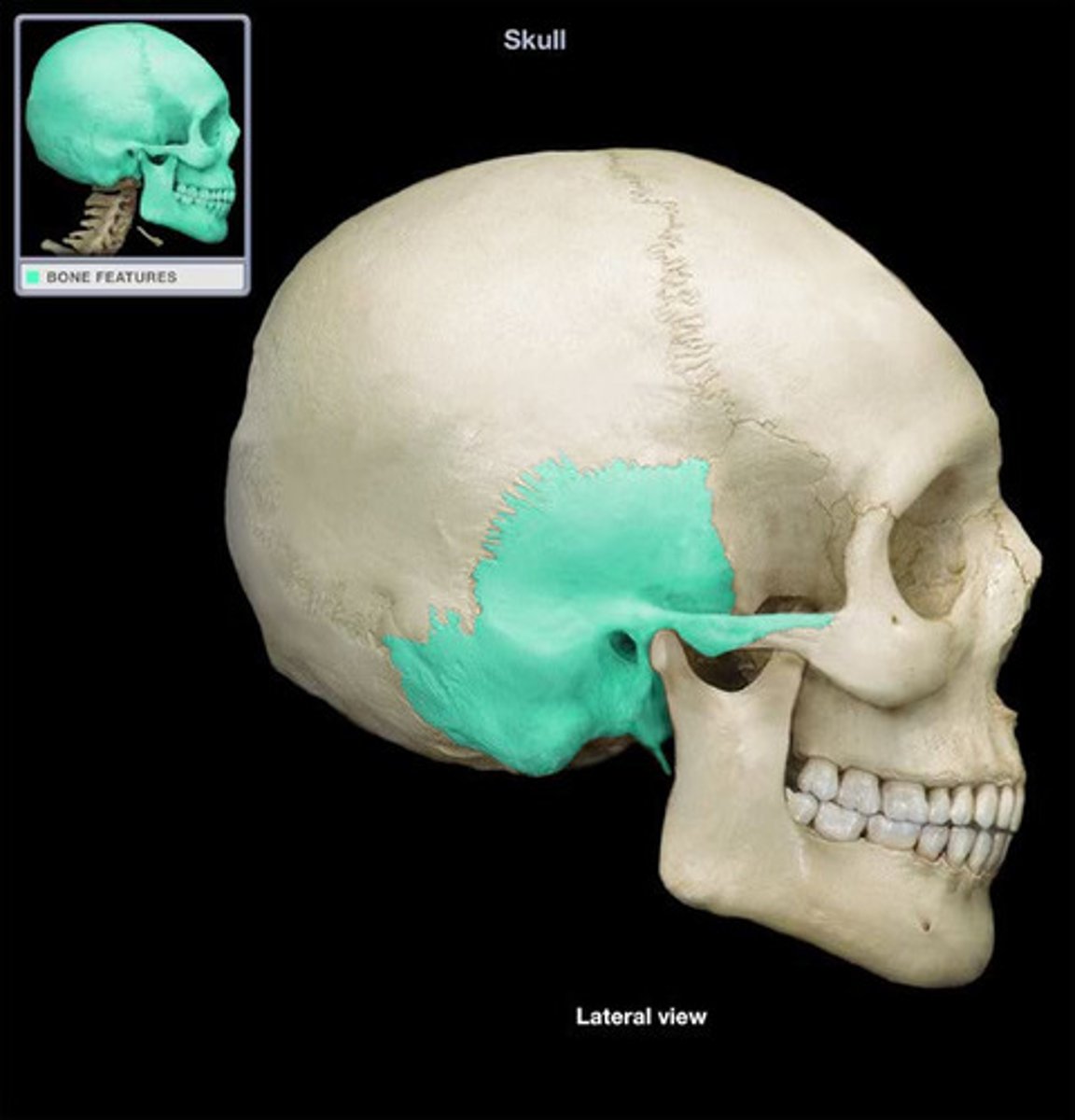
Temporal Bone
The bone located on the sides and base of the skull, housing structures for hearing and balance.
Squamous Suture
The fibrous joint that connects the parietal bone to the temporal bone on each side of the skull.

External Acoustic Meatus
The ear canal that leads from the outer ear to the eardrum.

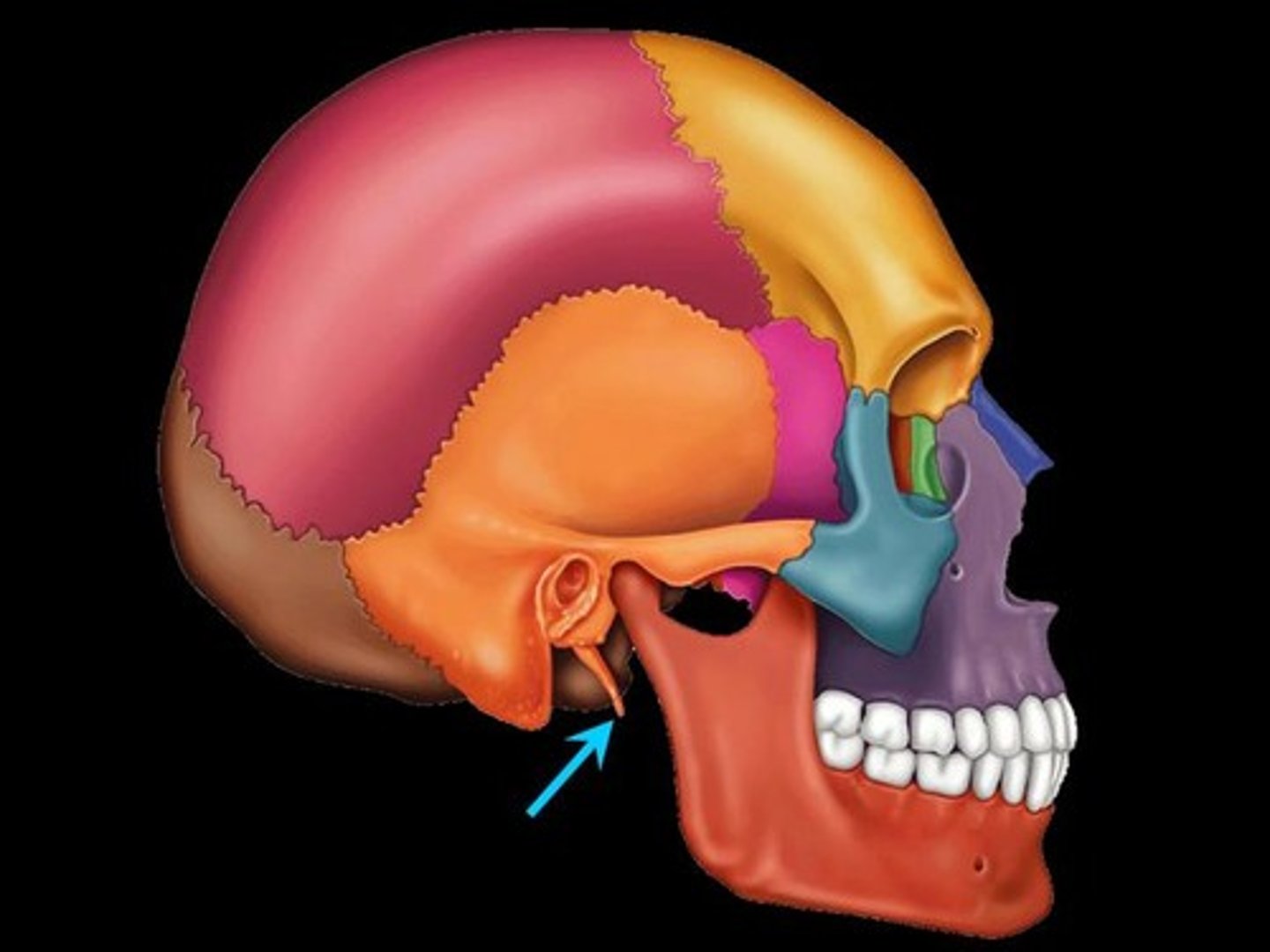
Styloid Process
A slender, pointed piece of bone just below the ear, serving as an attachment point for muscles and ligaments.
Zygomatic Process
A bony projection of the temporal bone that forms part of the zygomatic arch, contributing to the cheekbone structure.

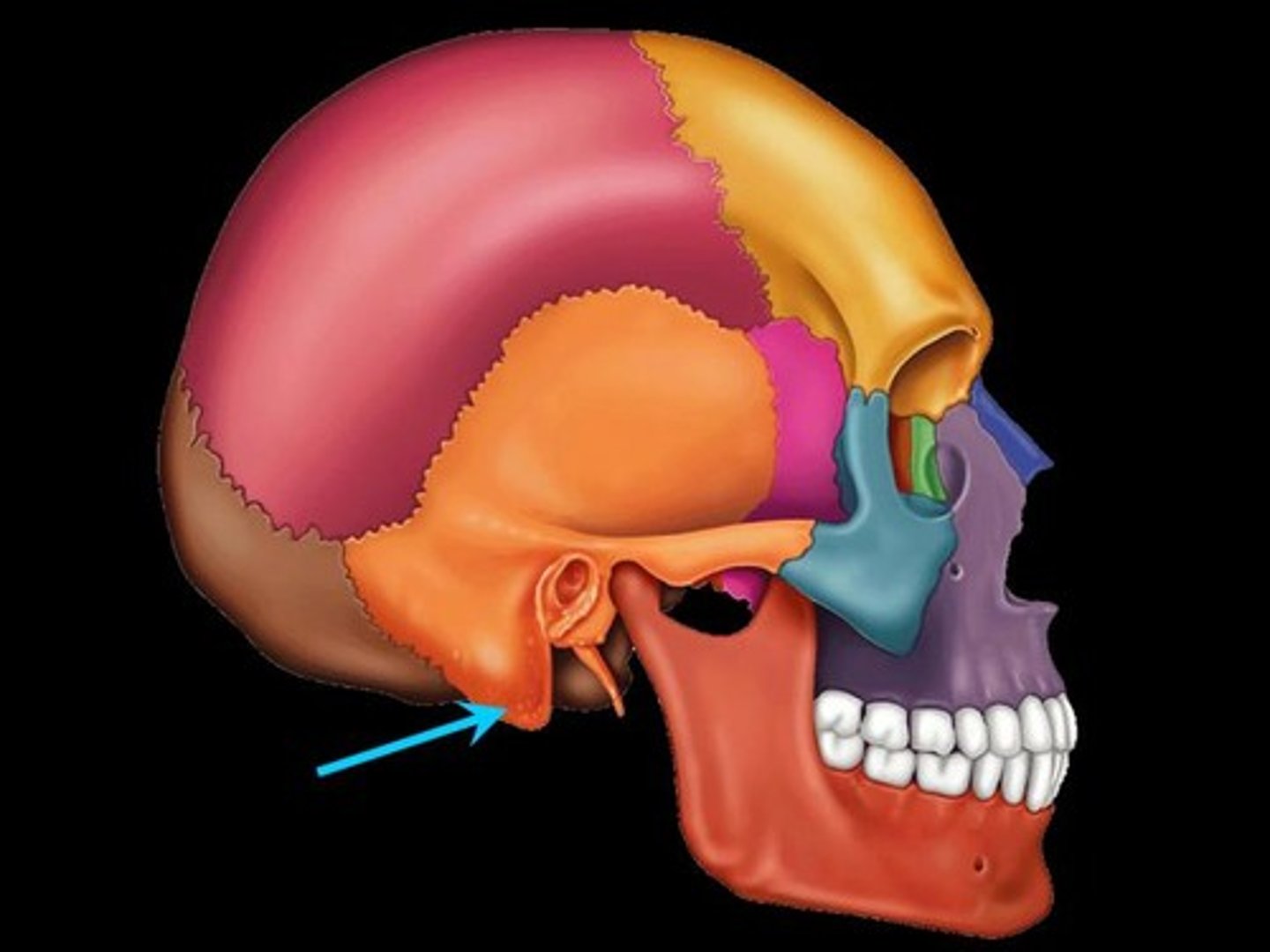
Mastoid Process
A bony prominence located behind the ear, providing attachment for neck muscles.
Jugular Foramen
An opening in the skull that allows for the passage of the jugular vein and cranial nerves.
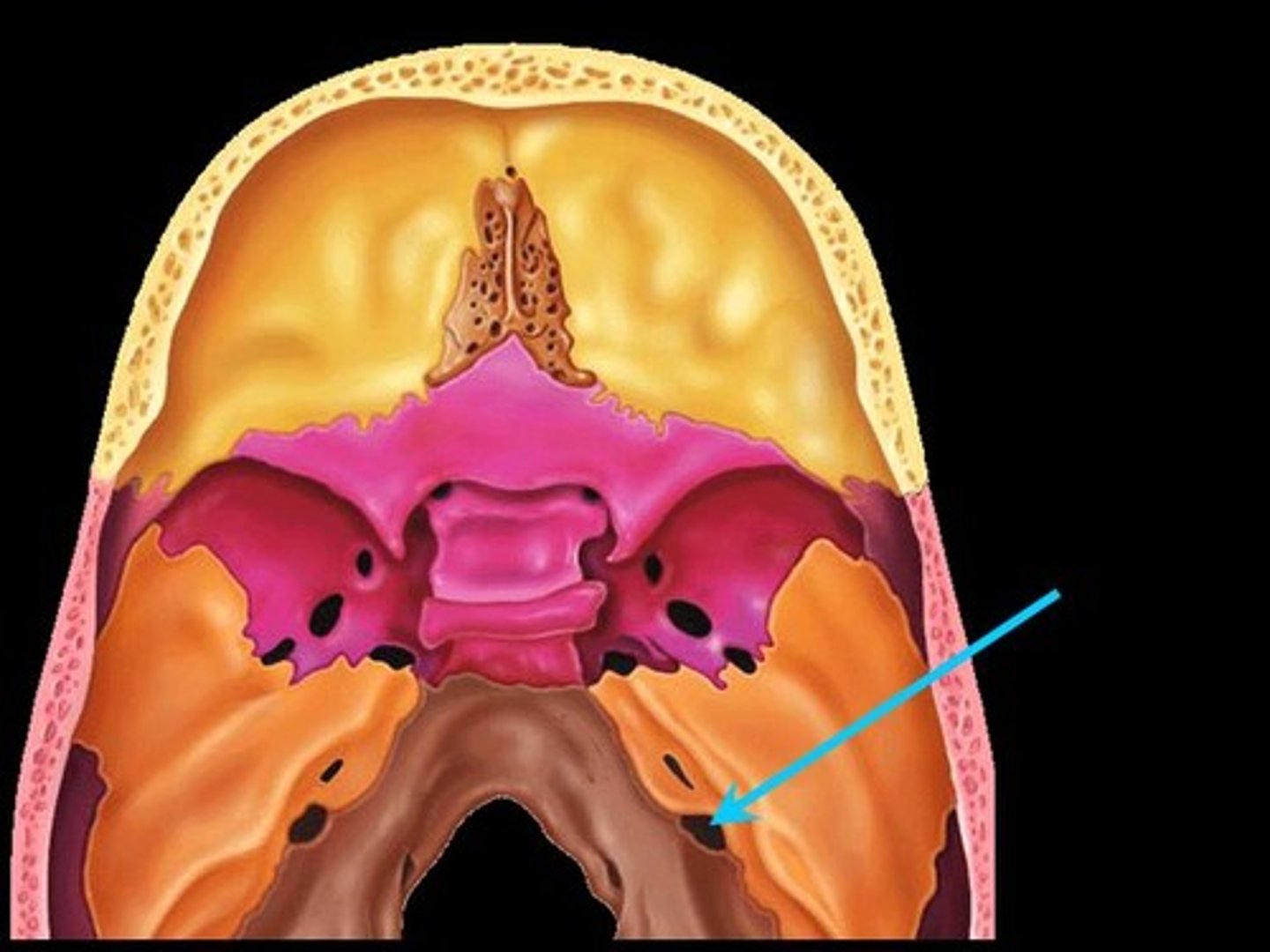
Internal Acoustic Meatus
A canal in the temporal bone that carries nerves and blood vessels to the inner ear.
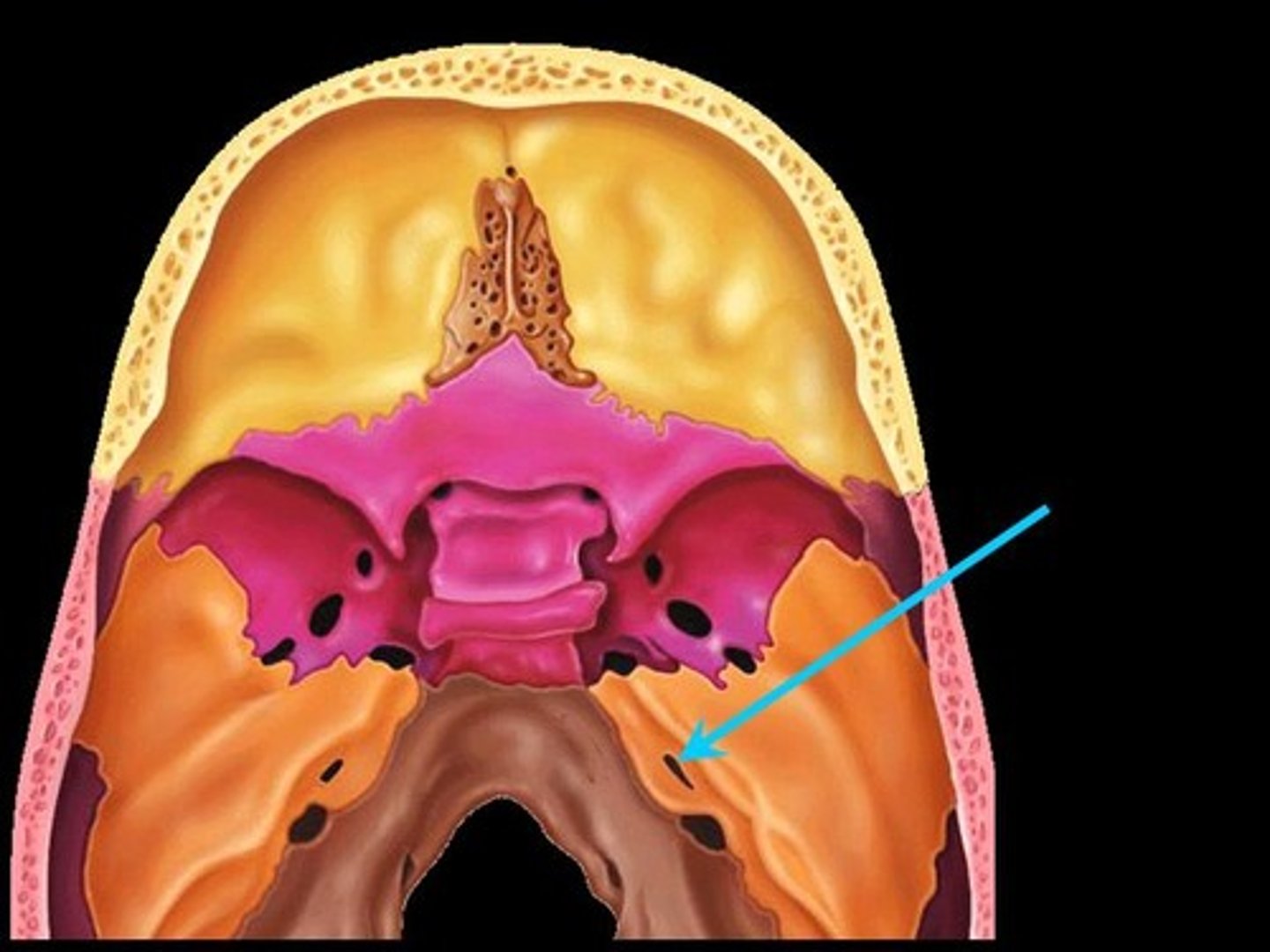
Temporomandibular Joint
The joint that connects the jawbone (mandible) to the skull, allowing for movement of the jaw.
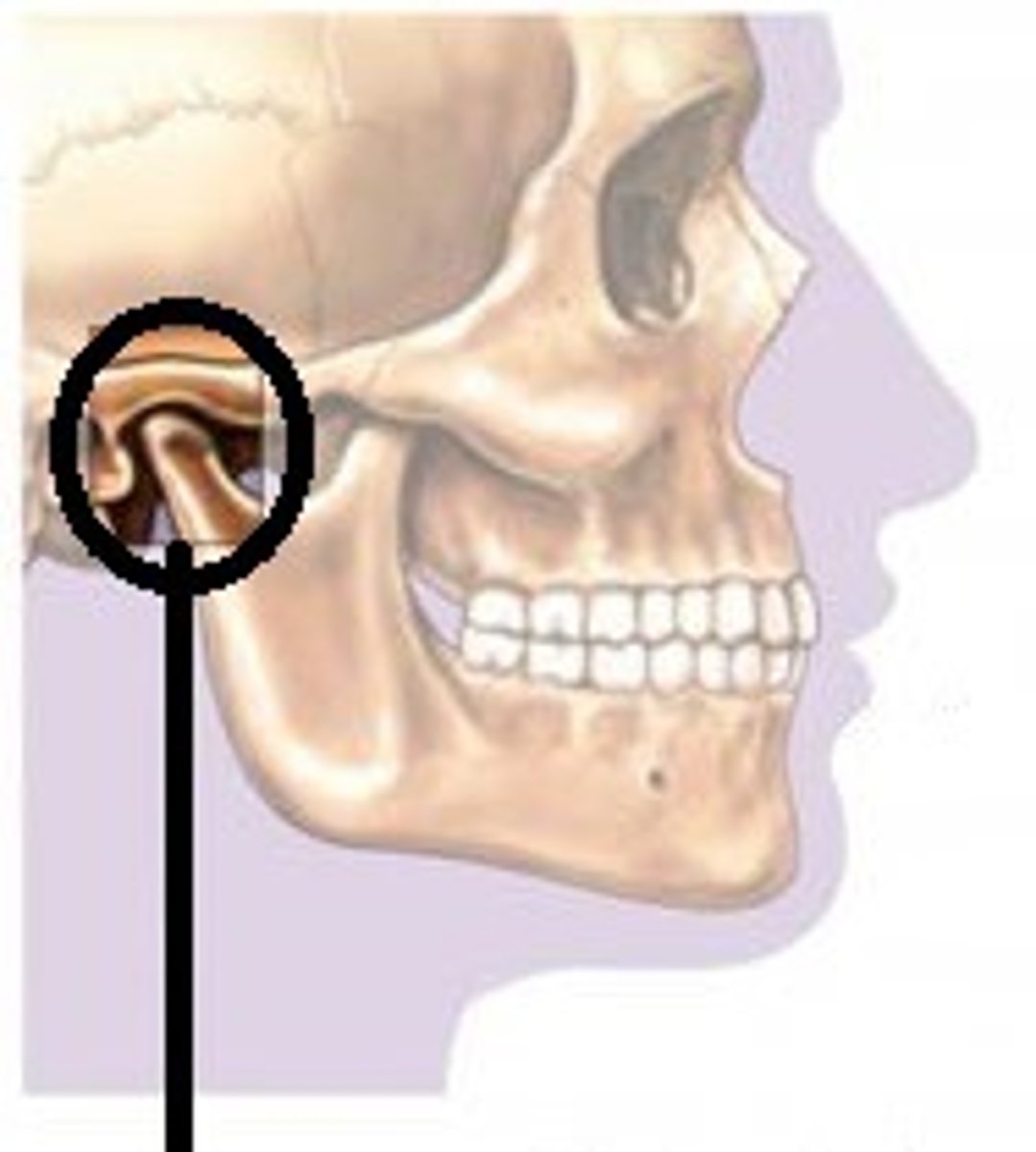
Parietal Bones
The two bones that form the sides and roof of the cranial cavity.
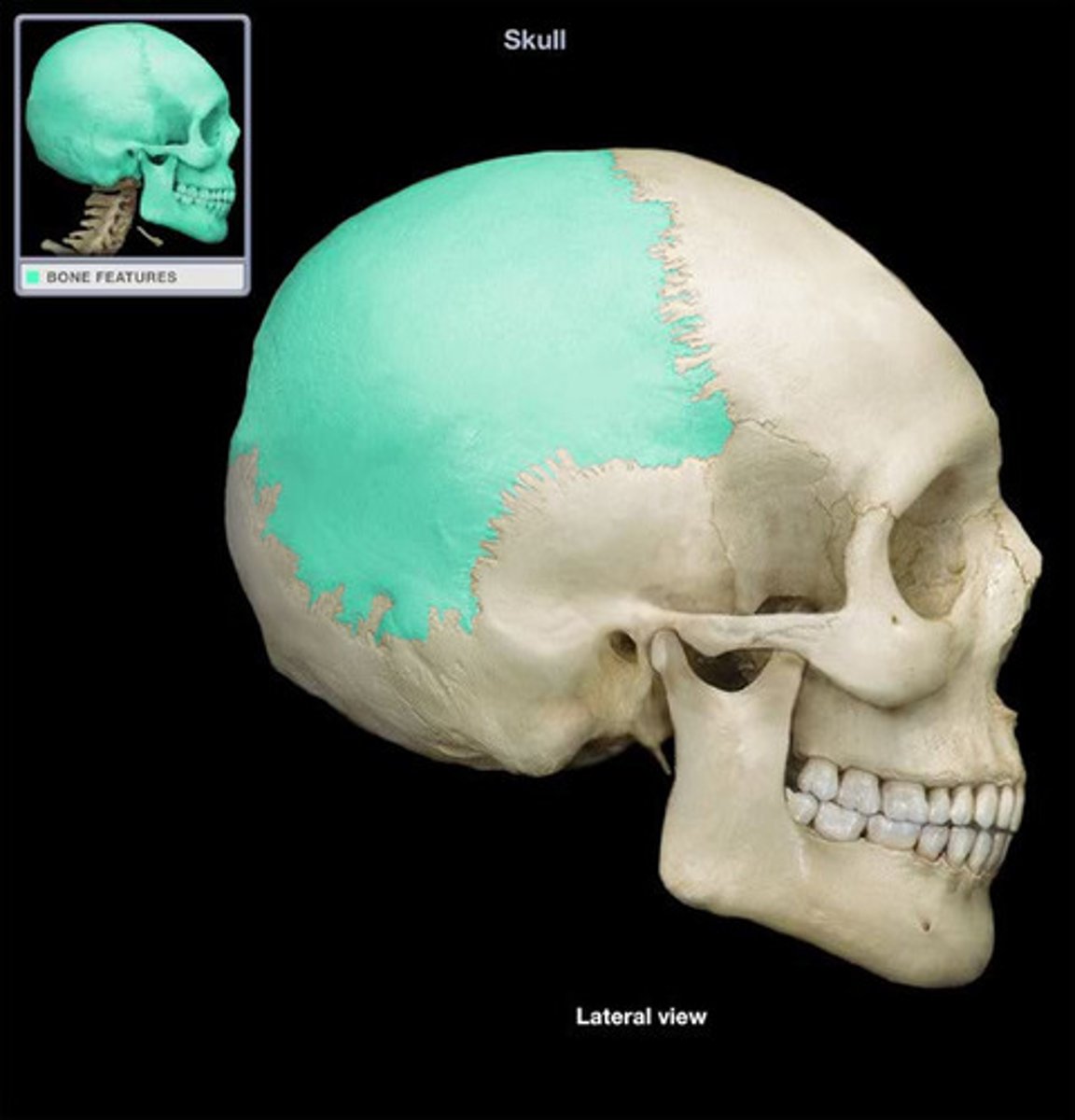
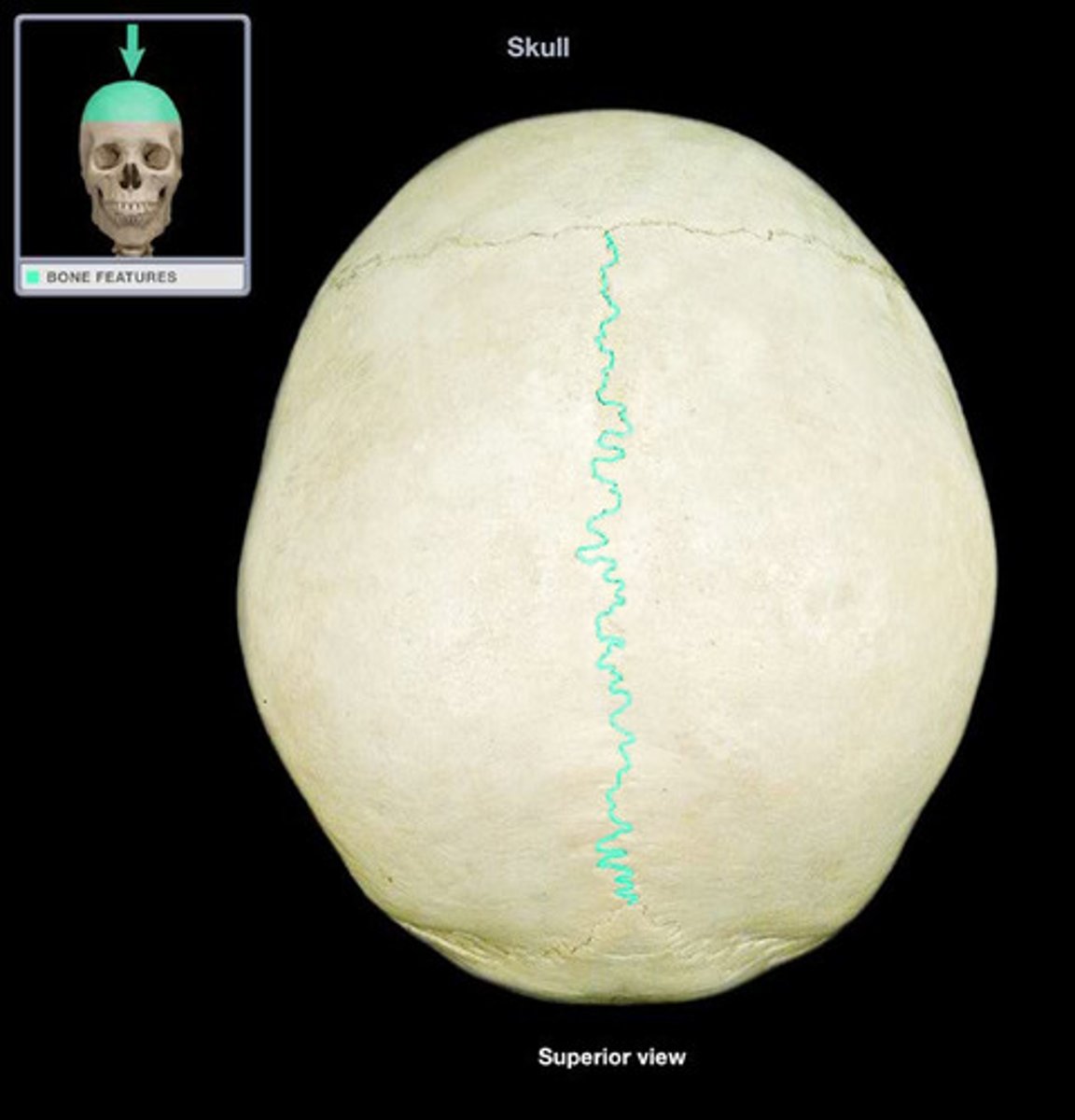
Sagittal Suture
The fibrous joint that connects the two parietal bones along the midline of the skull.
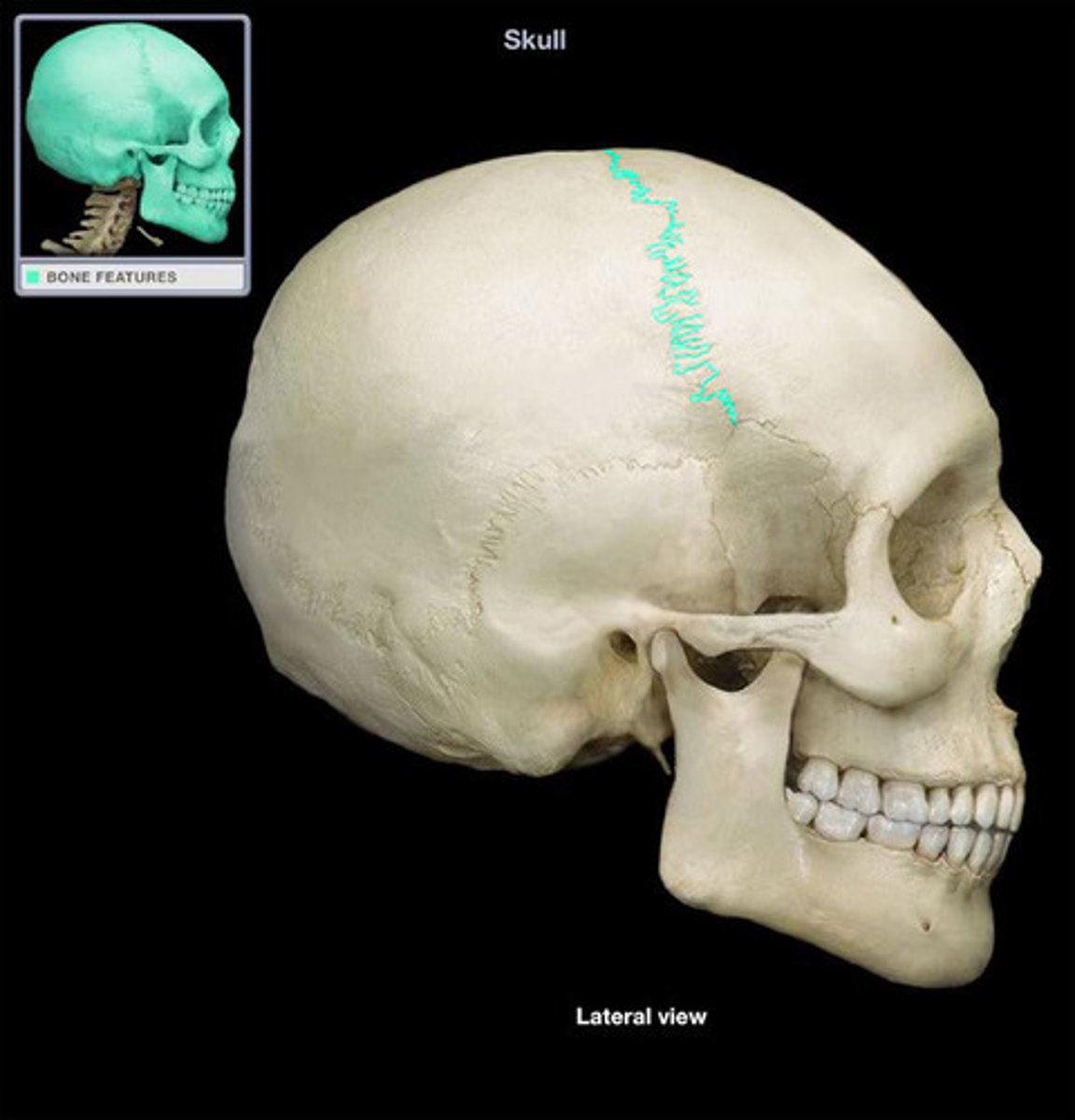
Coronal Suture
The fibrous joint that connects the frontal bone to the parietal bones.
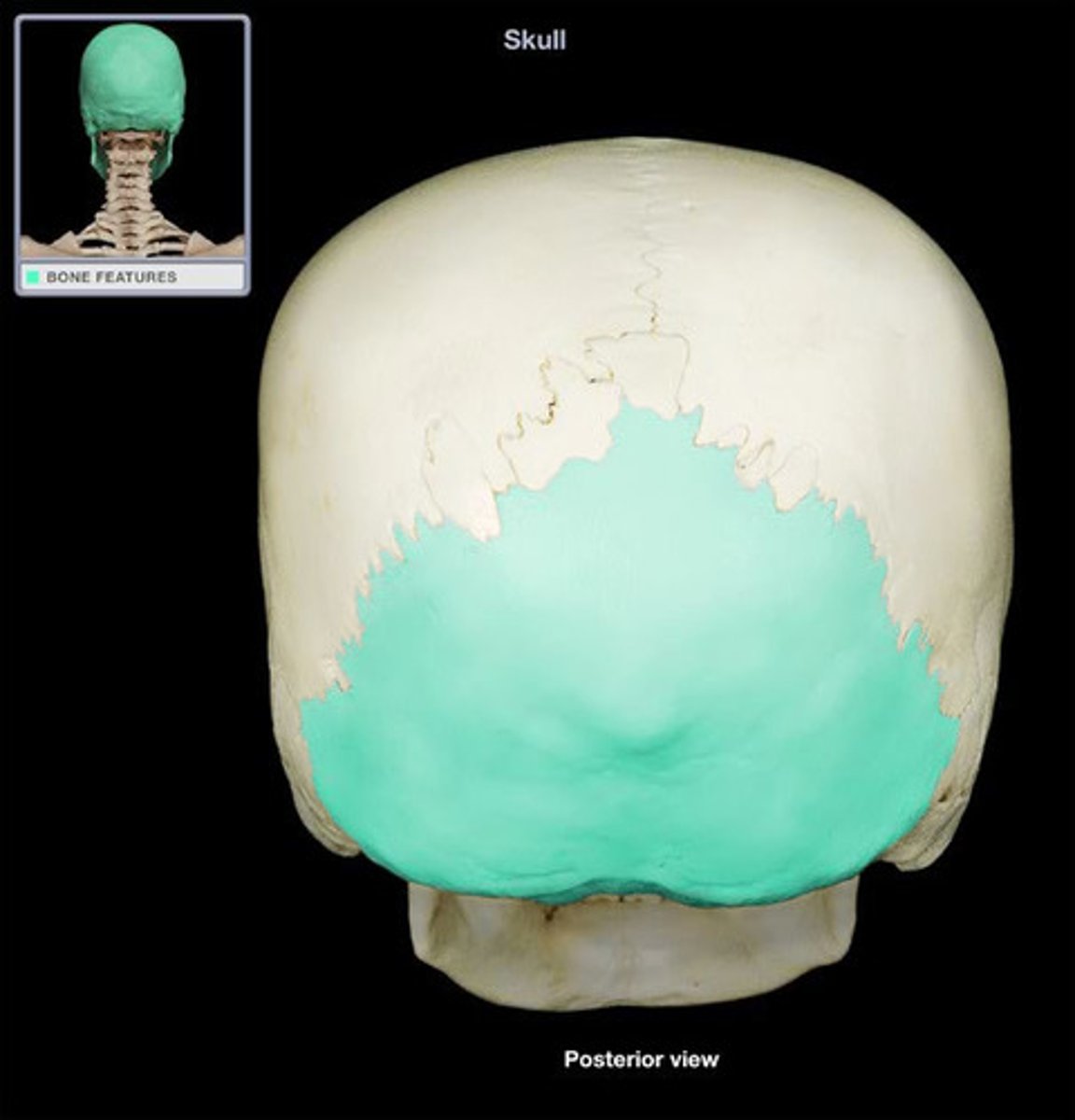
Occipital Bone
The bone at the back and base of the skull, containing the foramen magnum through which the spinal cord passes.
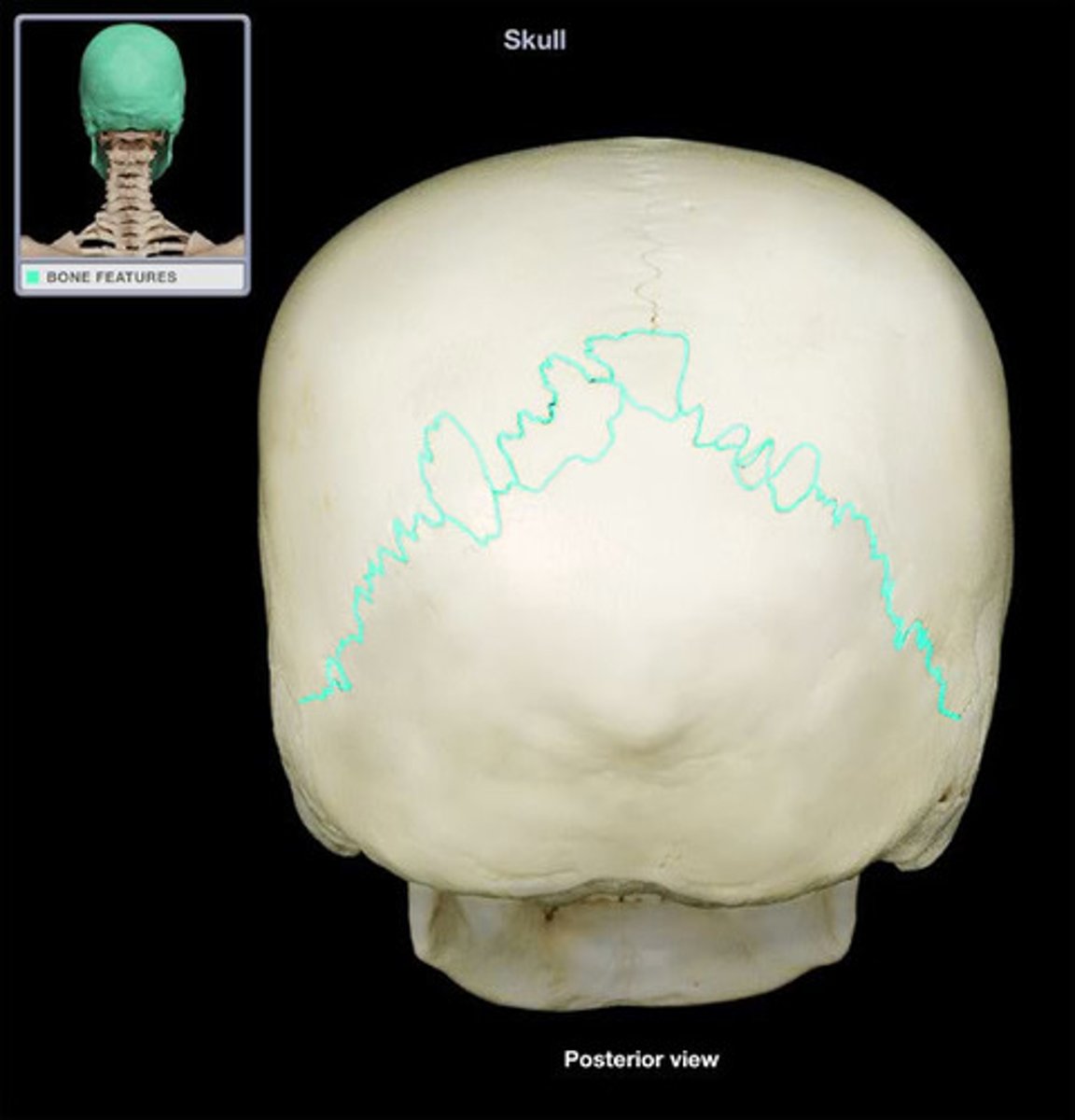
Lambdoid Suture
The fibrous joint that connects the occipital bone with the parietal bones.
Foramen Magnum
The large opening at the base of the skull that allows the spinal cord to connect with the brain.

Occipital Condyles
The rounded projections on the occipital bone that articulate with the first cervical vertebra (atlas).
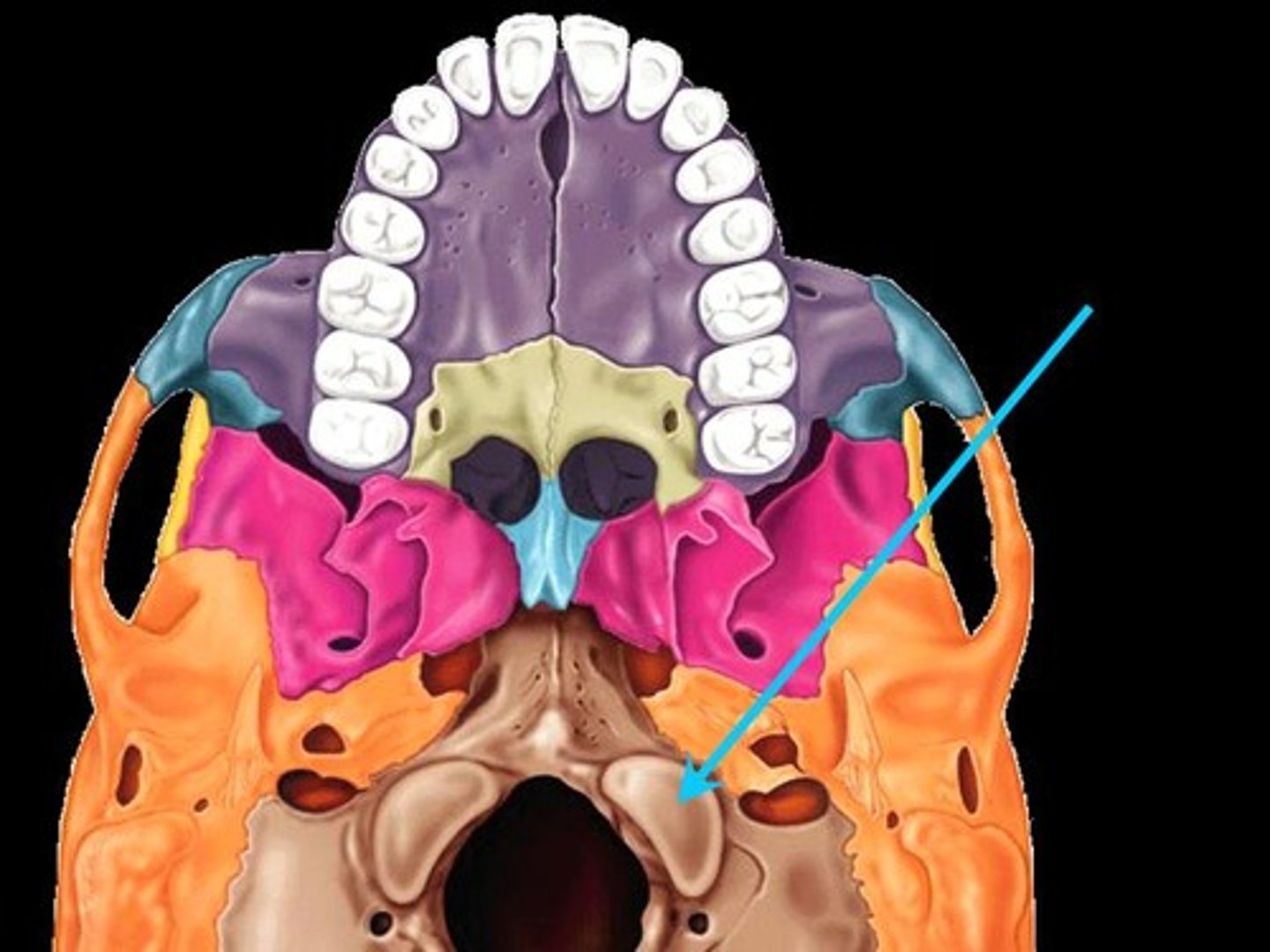
Ethmoid Bone
A complex bone located between the nasal cavity and the orbits, contributing to the structure of the nasal cavity and the orbits.
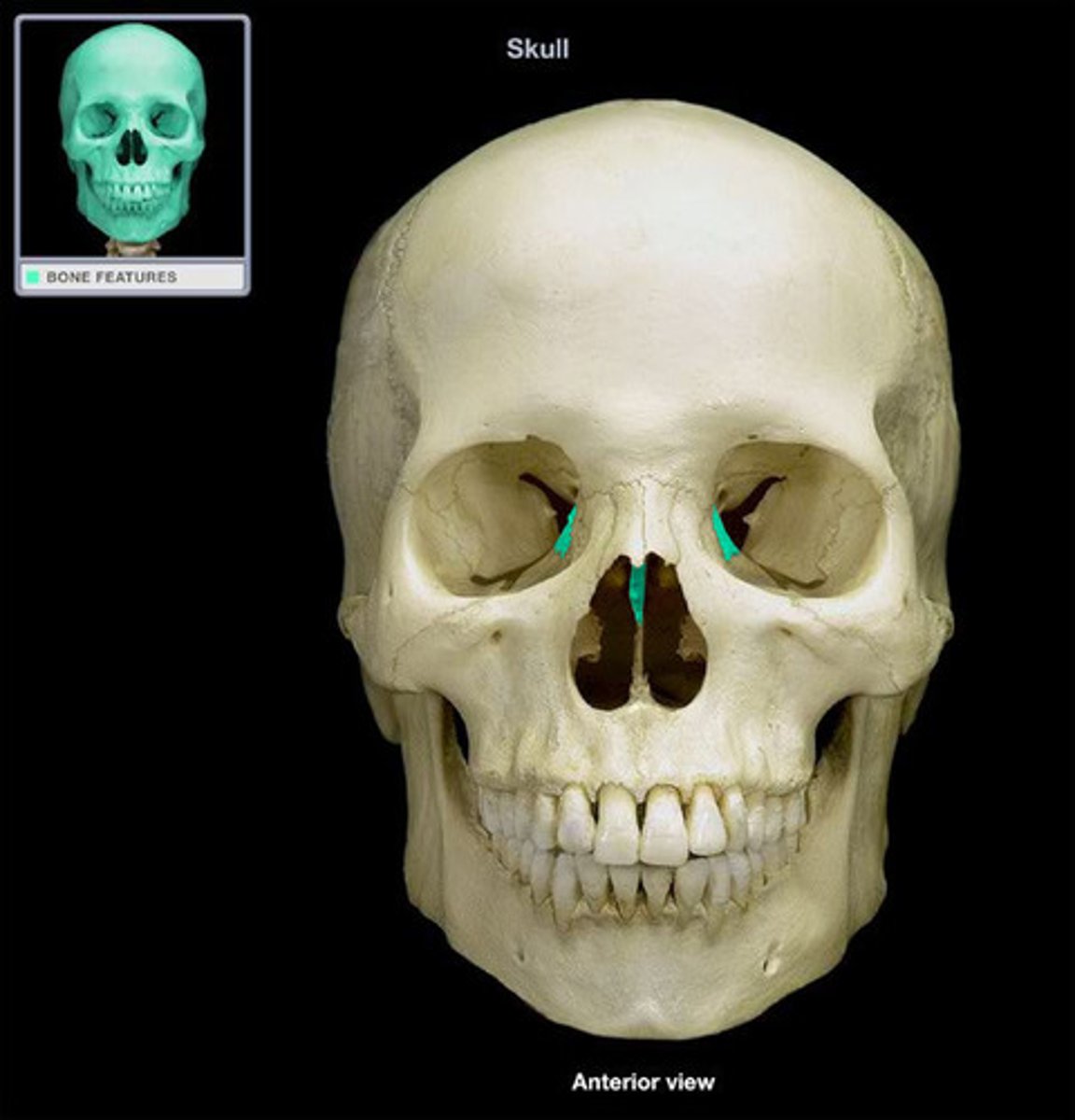
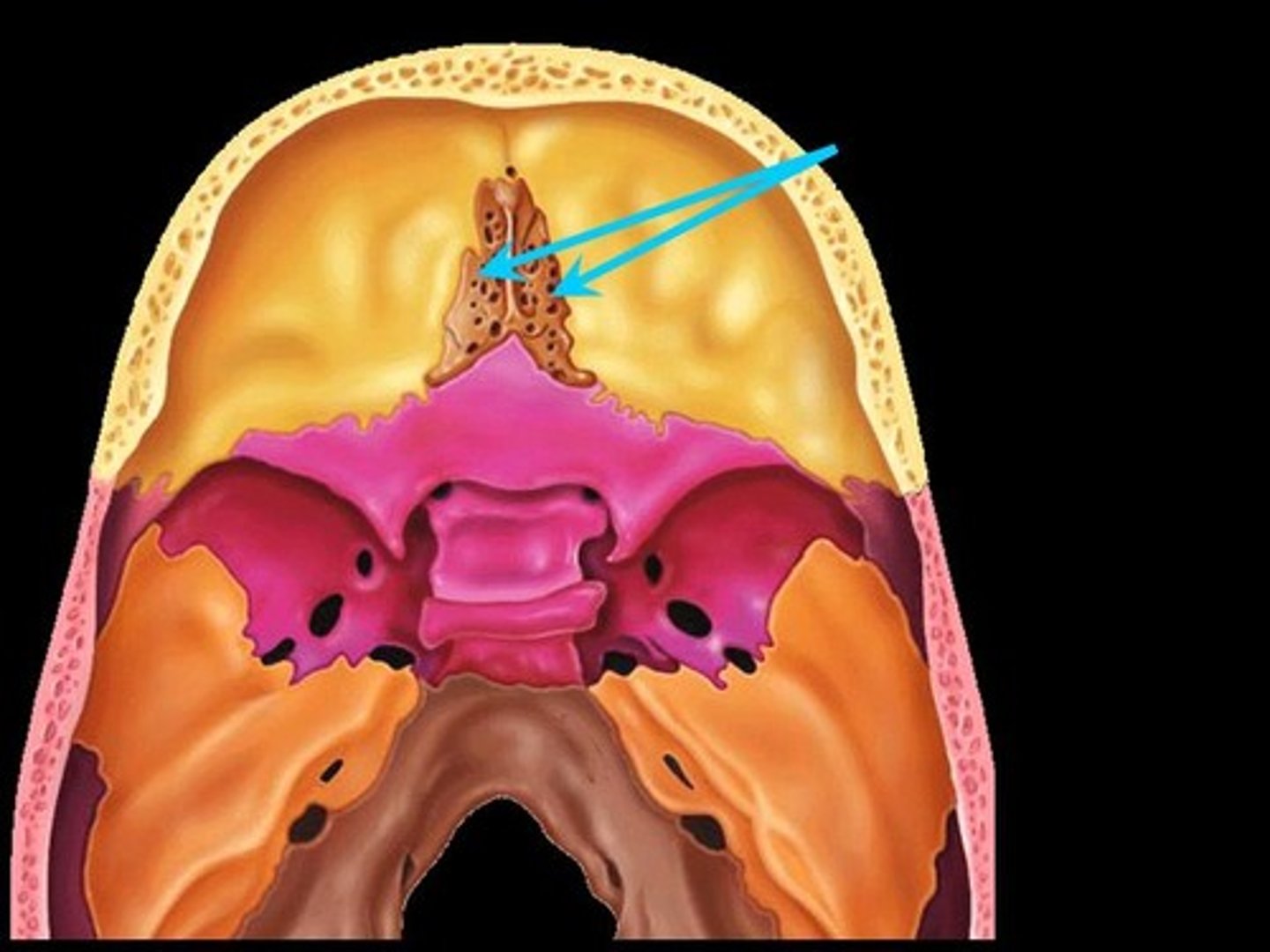
Crista Galli
A vertical projection of the ethmoid bone that serves as an attachment point for the dura mater, the membrane covering the brain.
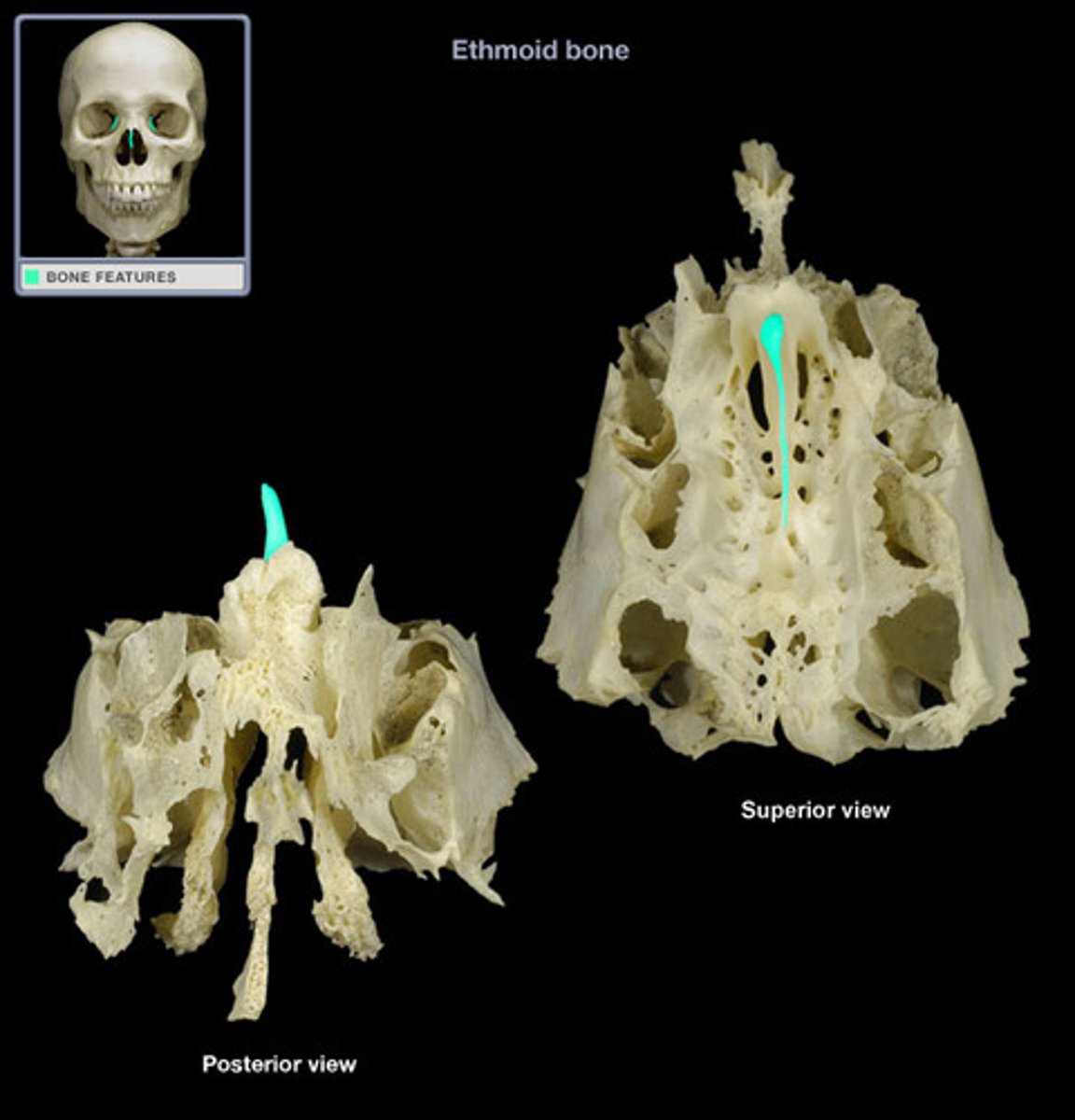
Cribiform Plates
The thin, bony structures of the ethmoid bone that contain foramina for the passage of olfactory nerves.
Sphenoid Bone
A butterfly-shaped bone that forms part of the base of the skull and the floor of the eye sockets.
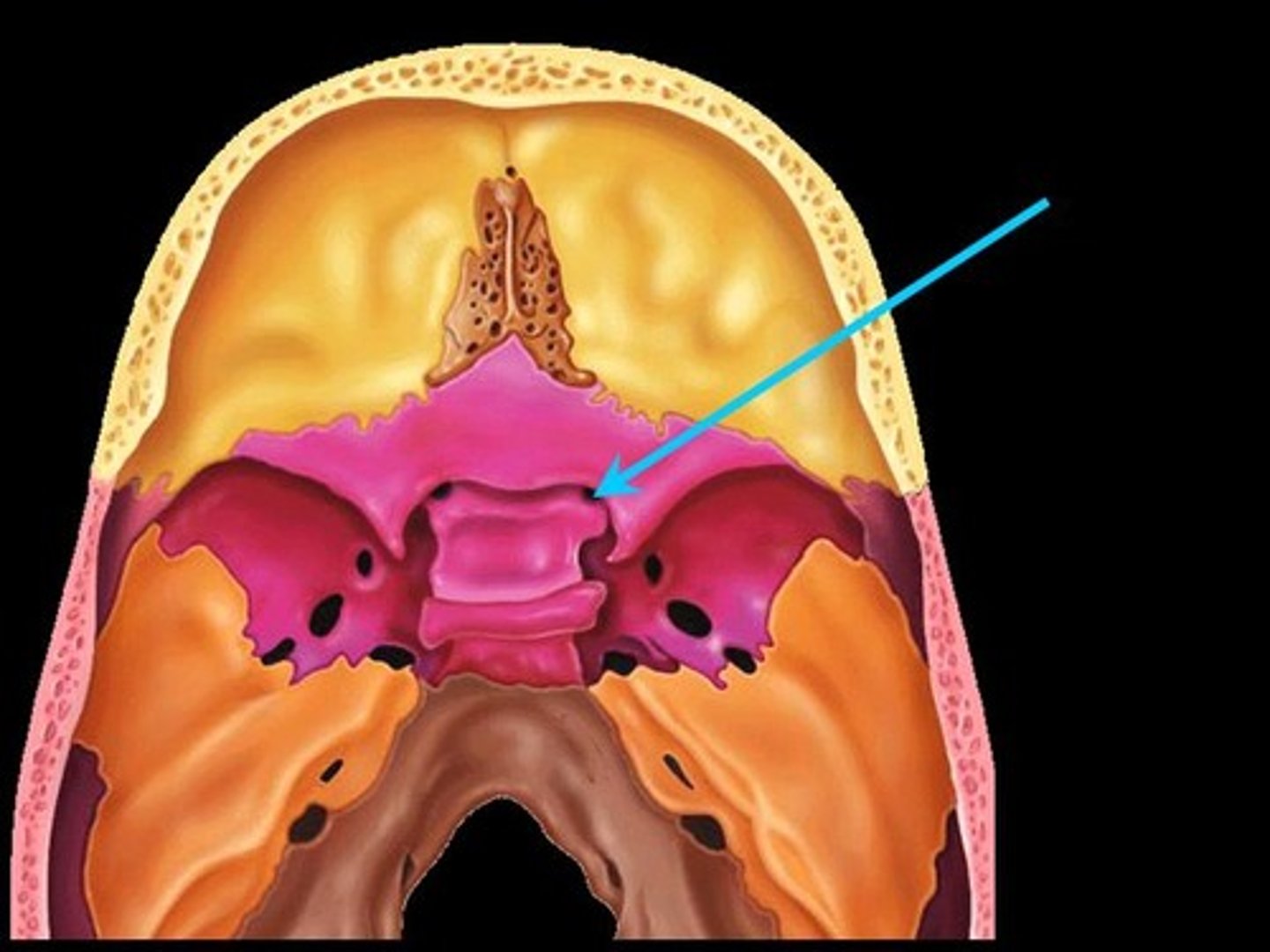
Sella Turcica
A depression in the sphenoid bone that houses the pituitary gland.

Foramen Ovale
An oval-shaped opening in the sphenoid bone that allows for the passage of nerves and blood vessels.
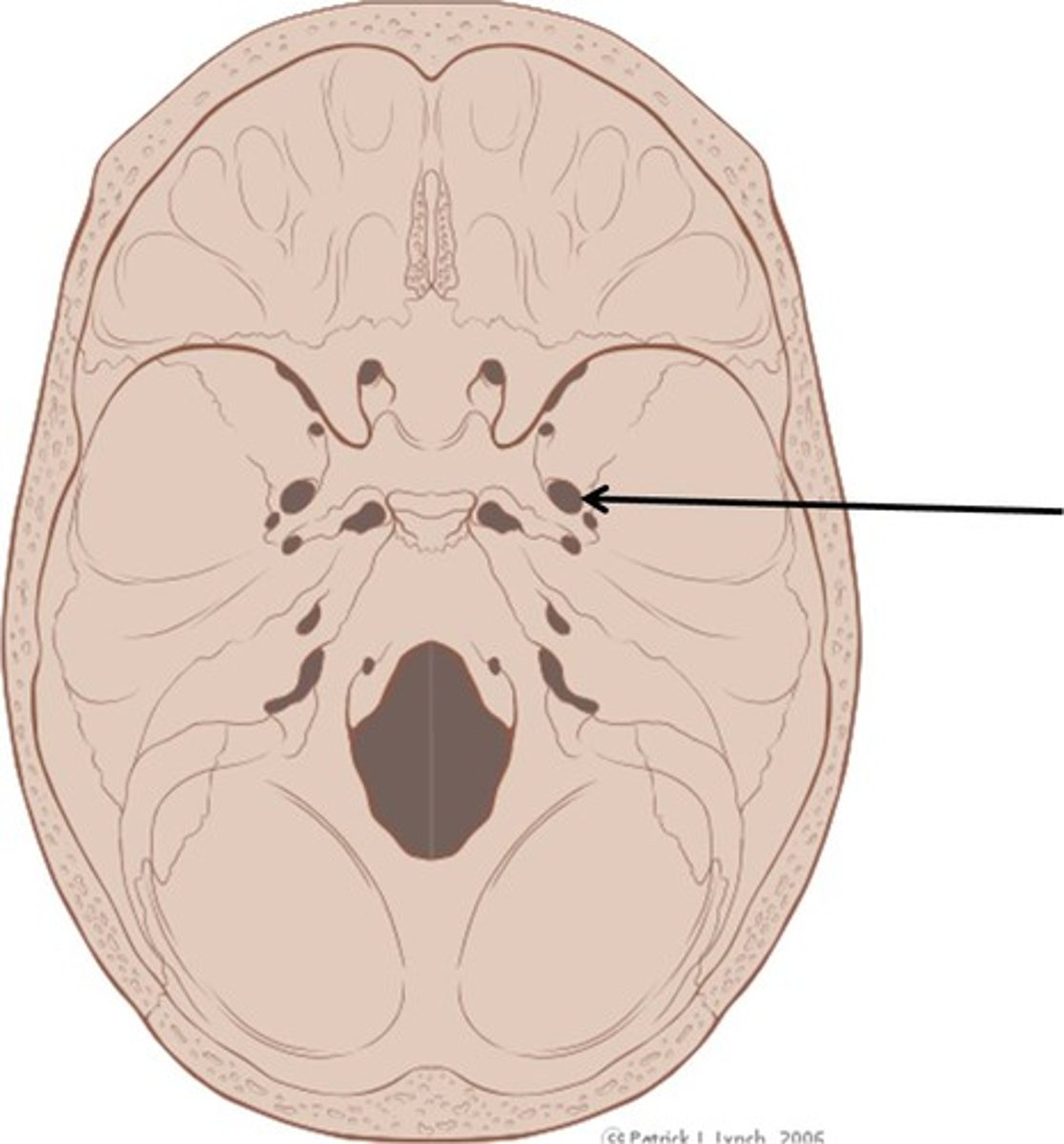
Optic Canal
A passage in the sphenoid bone that transmits the optic nerve from the eye to the brain.
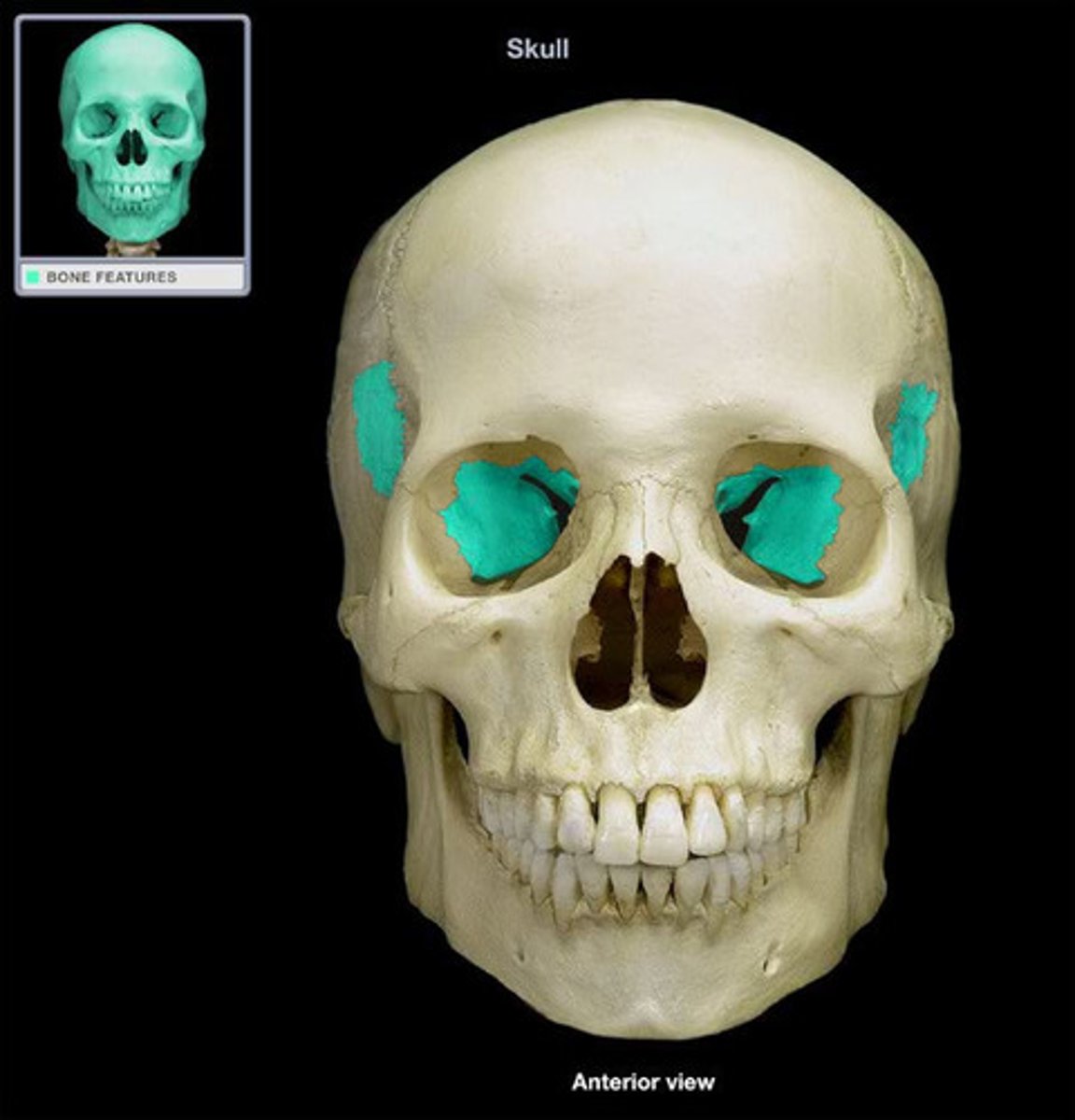
Superior Orbital Fissure
A slit-like opening in the sphenoid bone that allows for the passage of cranial nerves and blood vessels to the orbit.

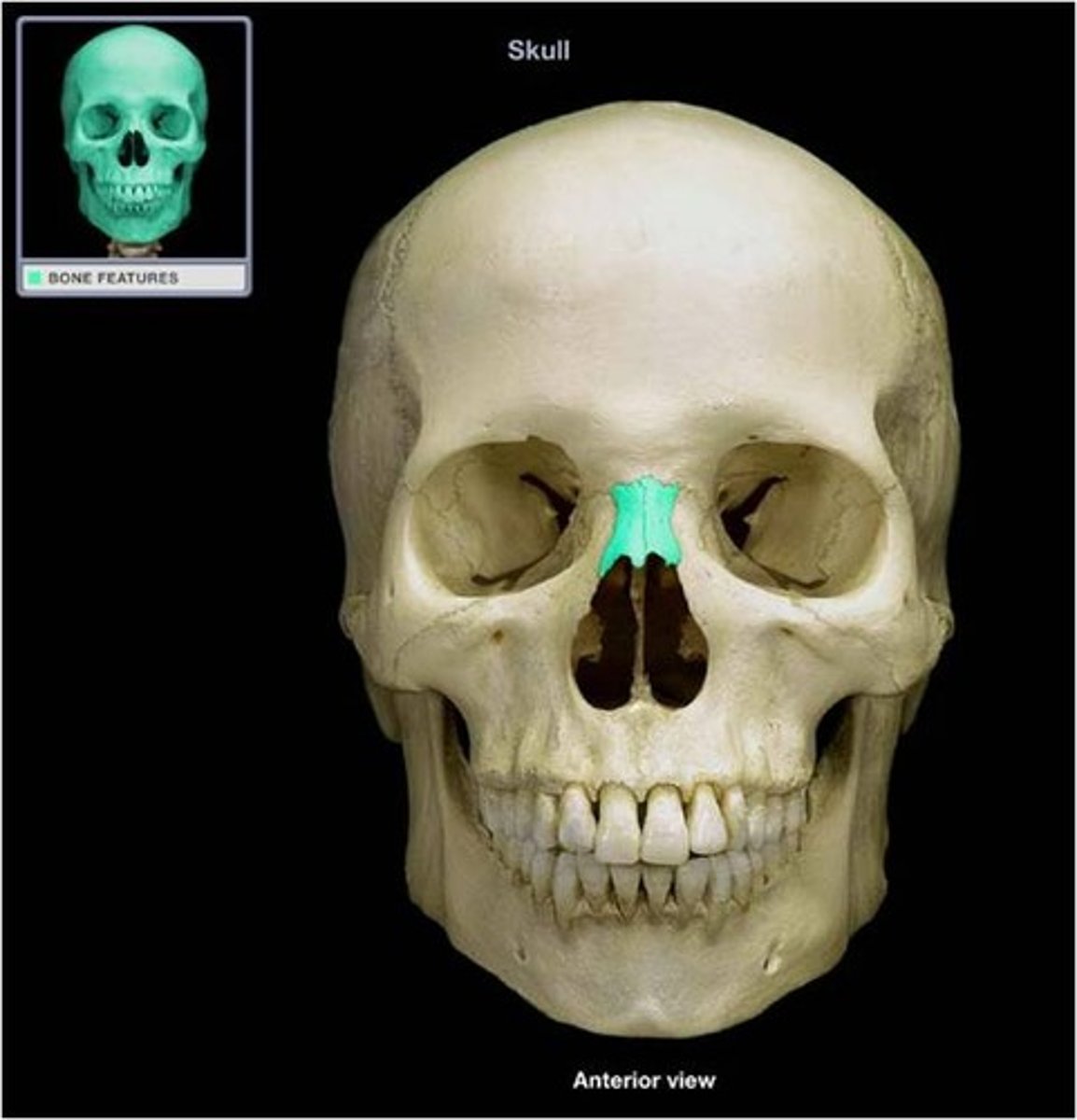
Nasal Bone
The two small bones that form the bridge of the nose.
Lacrimal Bones
Small, thin bones located in the medial wall of each orbit, containing the tear ducts.
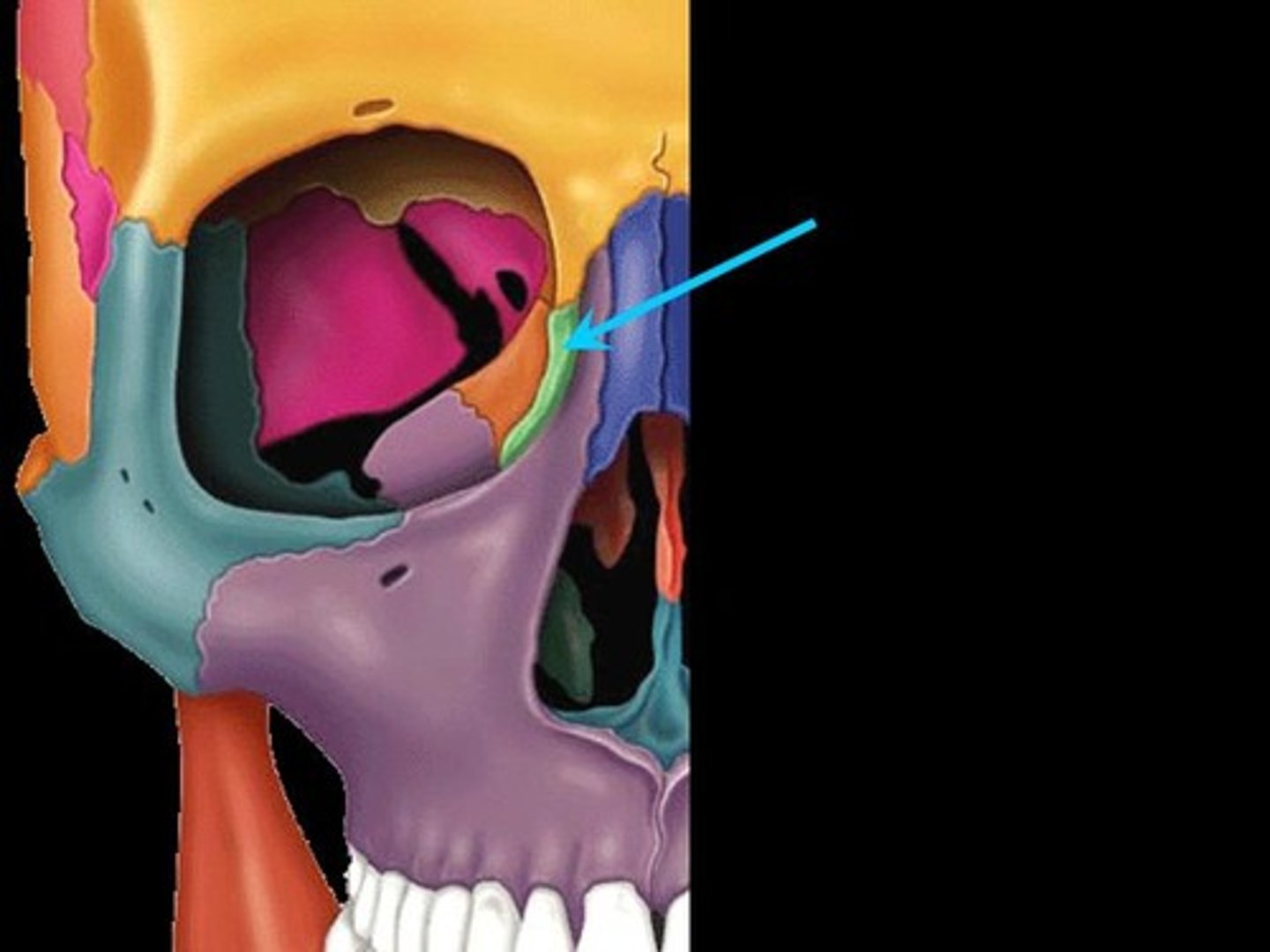
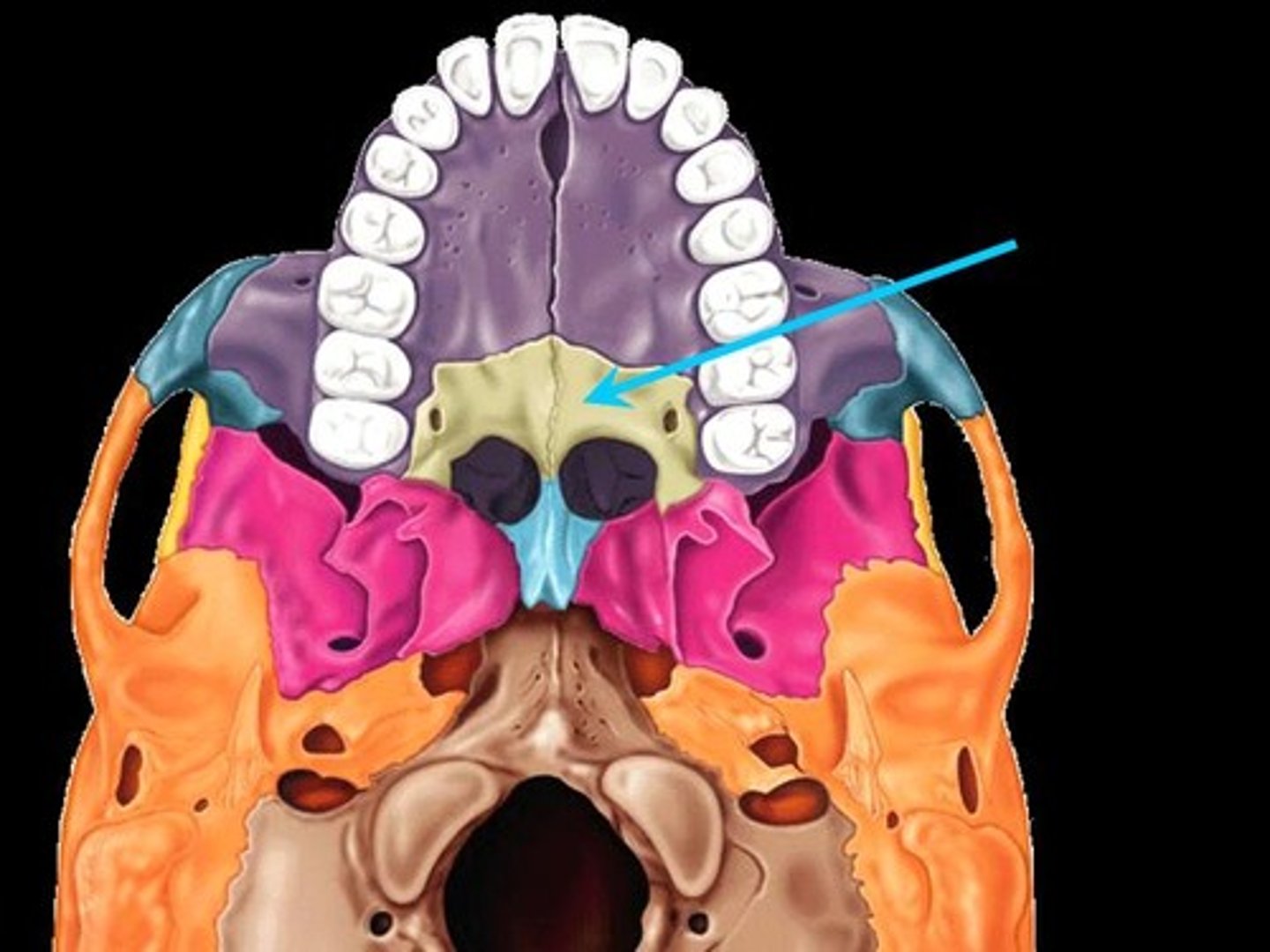
Maxillae
The two fused bones that form the upper jaw and part of the orbits and nasal cavity.
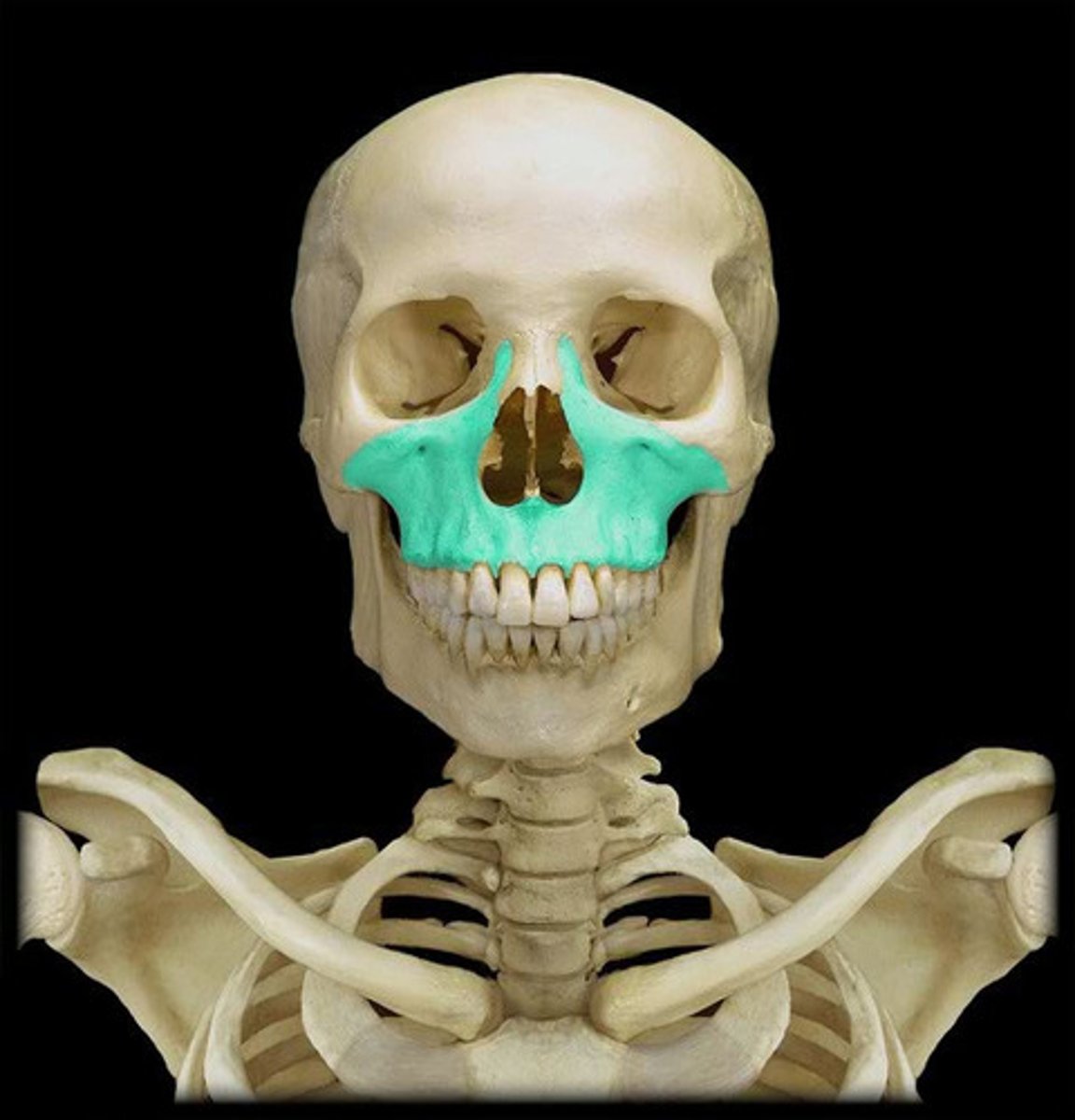
Zygomatic Bones
The bones that form the cheekbones and part of the orbits.
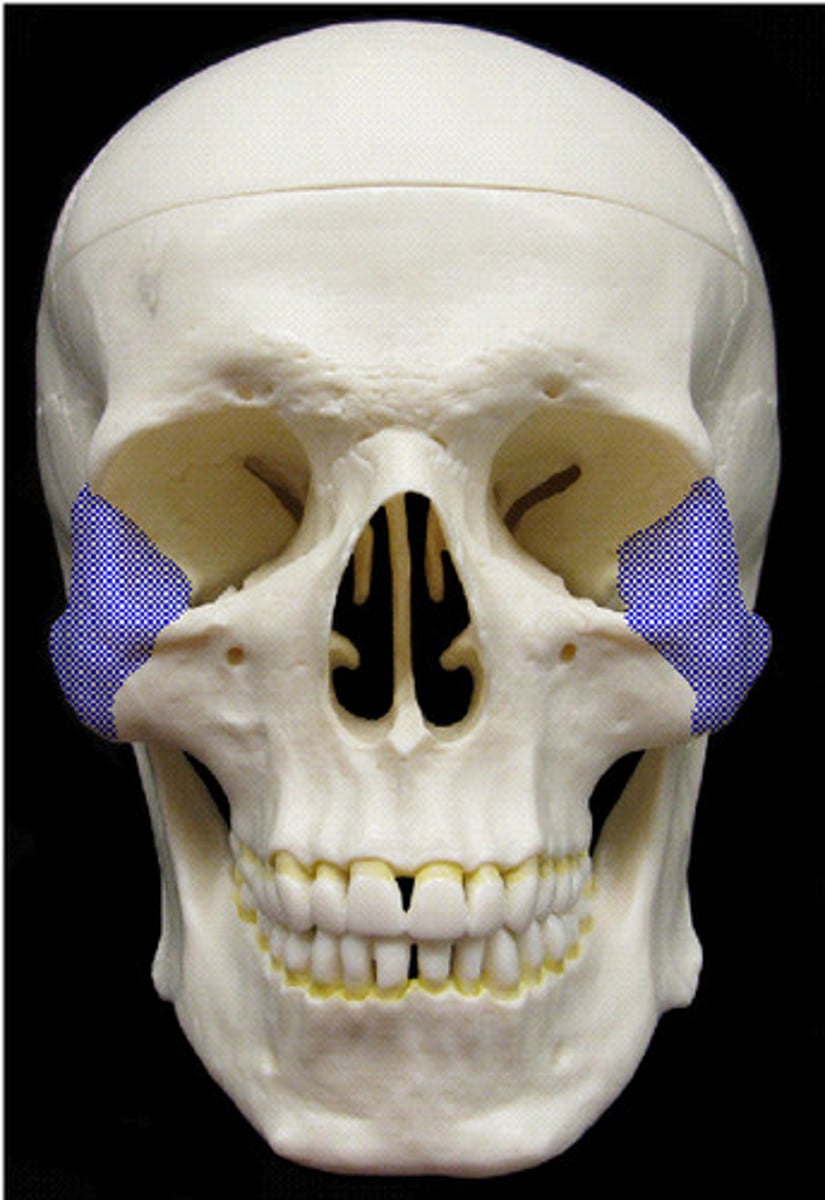
Mandible
The lower jawbone, the largest and strongest bone of the face, which holds the lower teeth.

Vomer
A thin, flat bone that forms part of the nasal septum.

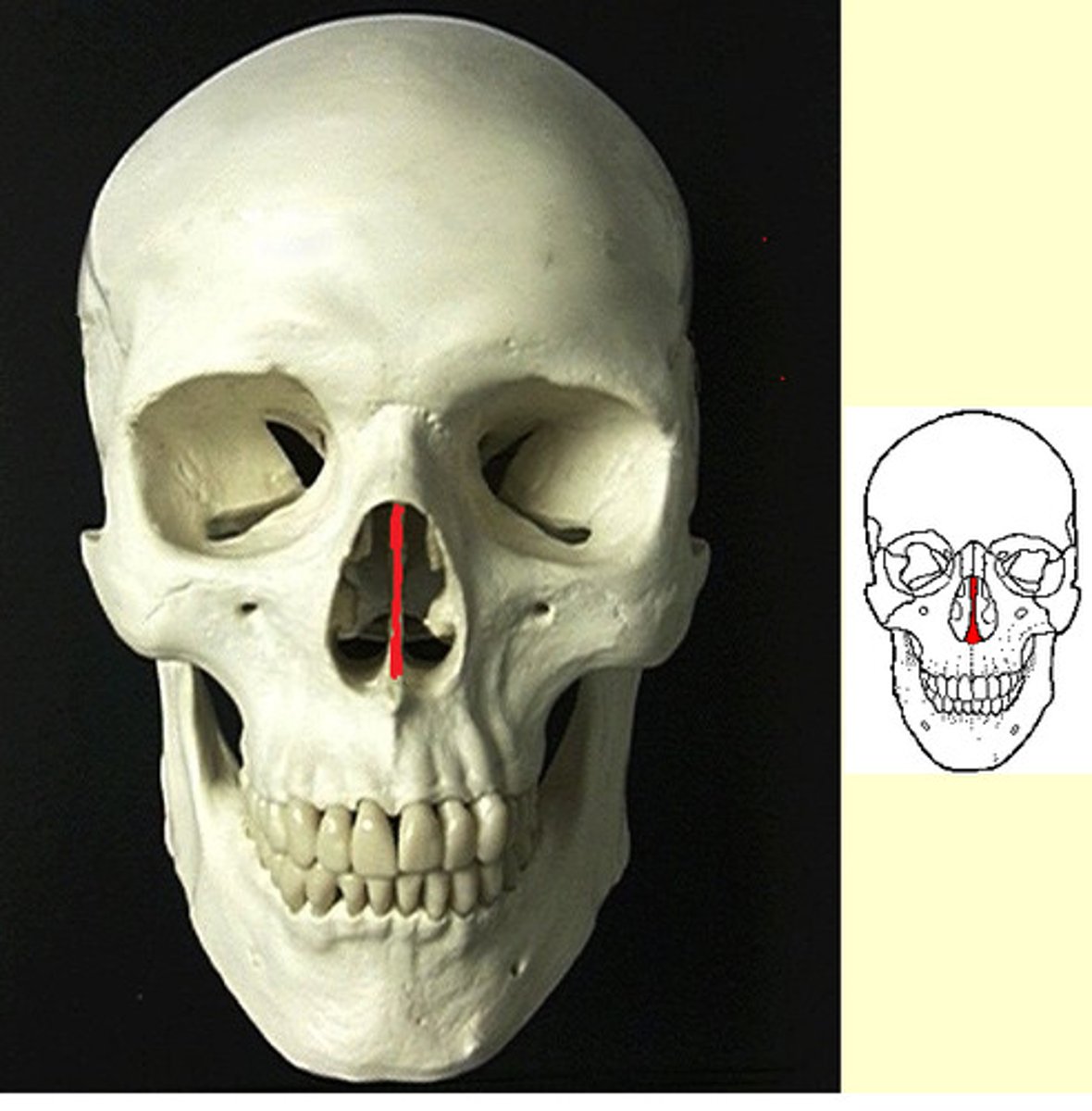
Septum
The partition that divides the nasal cavity into right and left sides.
Palate
The structure that forms the roof of the mouth, separating the oral cavity from the nasal cavity.

Palatine Bones
The bones that form the back part of the hard palate of the mouth and part of the nasal cavity.