Economic Growth
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Define Economic Growth
The increase in the total output of an economy over time, measured by GDP.
What is Real GDP?
Value of GDP adjusted for inflation
e.g. if the economy grew by 4% but inflation was 1%, real economic growth was 3%
What is Nominal GDP?
GDP that isn’t adjusted for inflation
Often misleading as growth appears higher
What is the Economic Cycle?
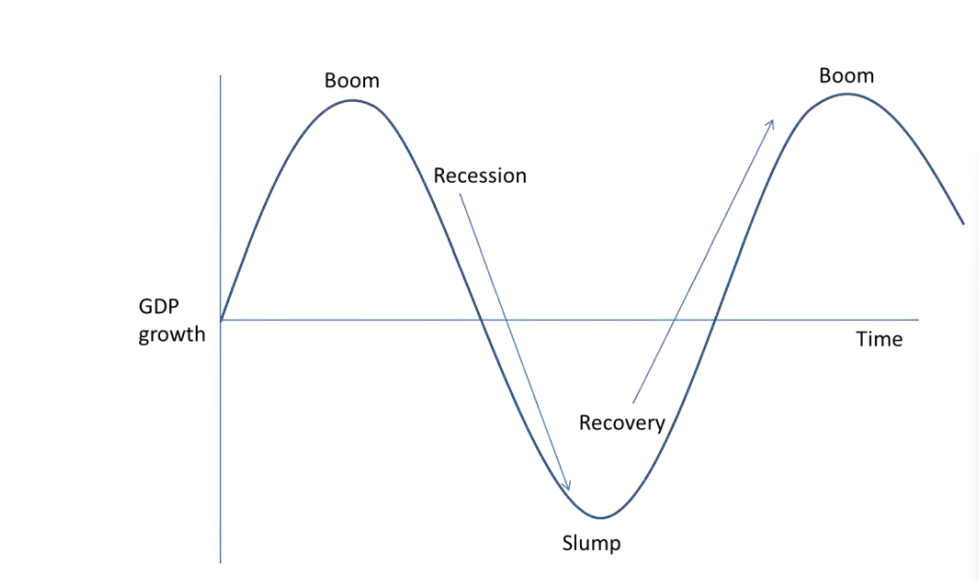
What are characteristics of an economic boom?
High economic growth
Near full productive capacity, or positive output gaps
Demand-Pull inflation
Improved government budget due to higher tax revenues and less spending on welfare payments
What is a recession?
2 consecutive quarters of negative economic growth
What are characteristics of a recession?
Negative economic growth
Far from full productive capacity and negative output gaps
Low Inflation rates
Government budget worsens due to less tax revenue and more welfare payments
What is Short-Run Economic Growth?
An increase in the actual output of a country’s economy over time
What factors increases Short-Run Economic Growth?
Increased AD
Expansionary Fiscal Policy (Tax Cuts and increased gov spending)
Expansionary Monetary Policy (Lower interest rates)
Lower Unemployment (Shifts economy closer to PPC)
Draw the PPC to show short-run economic growth
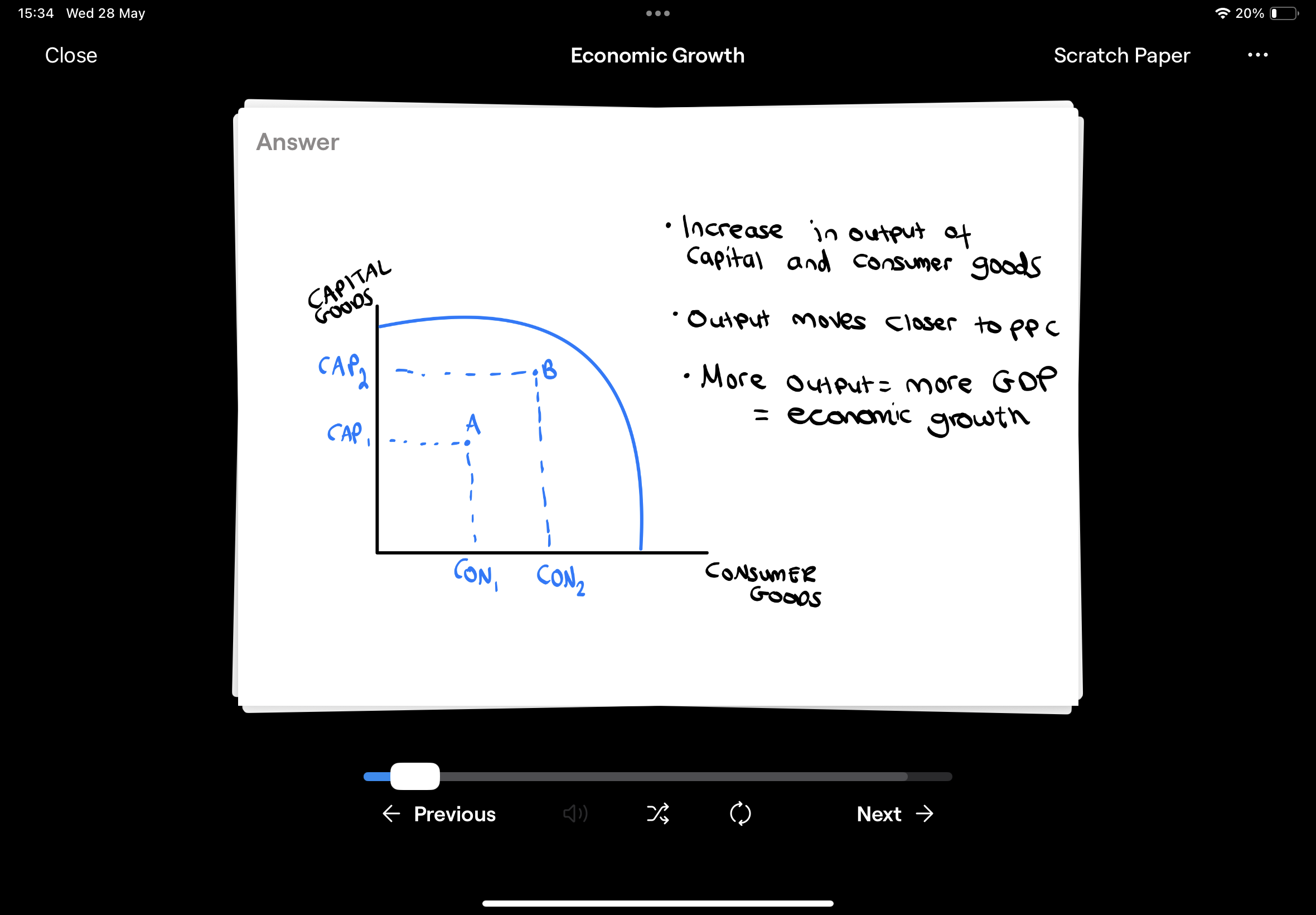
Draw the Keynesian AD/AS Diagram for short-run economic growth
Benefits to consumers of economic growth
Average incomes increase as more people in employment and wages rise
Consumers feel more confident encouraging consumption
Costs to consumers of economic growth
Demand-pull inflation
Shoe leather costs as prices rise, people look for cheapest goods, so more money spent on petrol etc
Those on low incomes are badly affected due to inflation
Benefits to firms of economic growth
Firms make more profits so investment increases
Greater investment means greater ability to develop technology to improve productivity and lower long run average costs
Costs to firms of economic growth
Menu costs as prices on websites, menus etc have to be changed due to inflation
Benefits to government of economic growth
More tax revenue and less welfare payments so could decrease the cyclical budget deficit
Costs to government of economic growth
May have to increase healthcare spending if consumption of demerit goods increases, e.g. cigarettes
Define Long-Run Economic Growth
Expansion of an economy’s productive capacity.
i.e. how much they ‘could produce’ if they maximise the utility of all factors of production
What Increases Long-Run Economic Growth?
Population Growth
Better education and training
Healthcare improvements (less days off sick)
Technology improvements (AI)
Investment in machinery / equipment
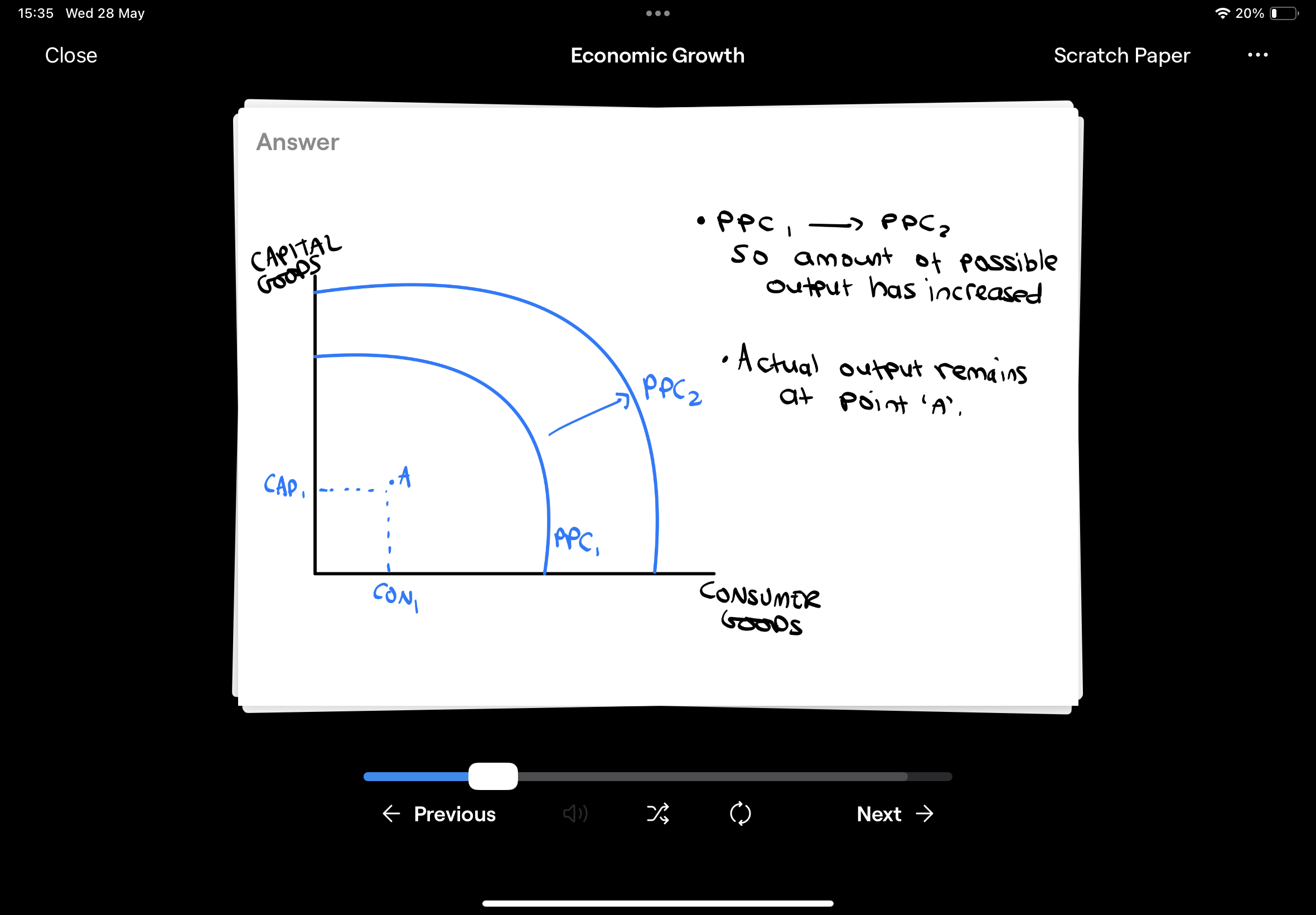
Show Long-Run economic growth on a PPC
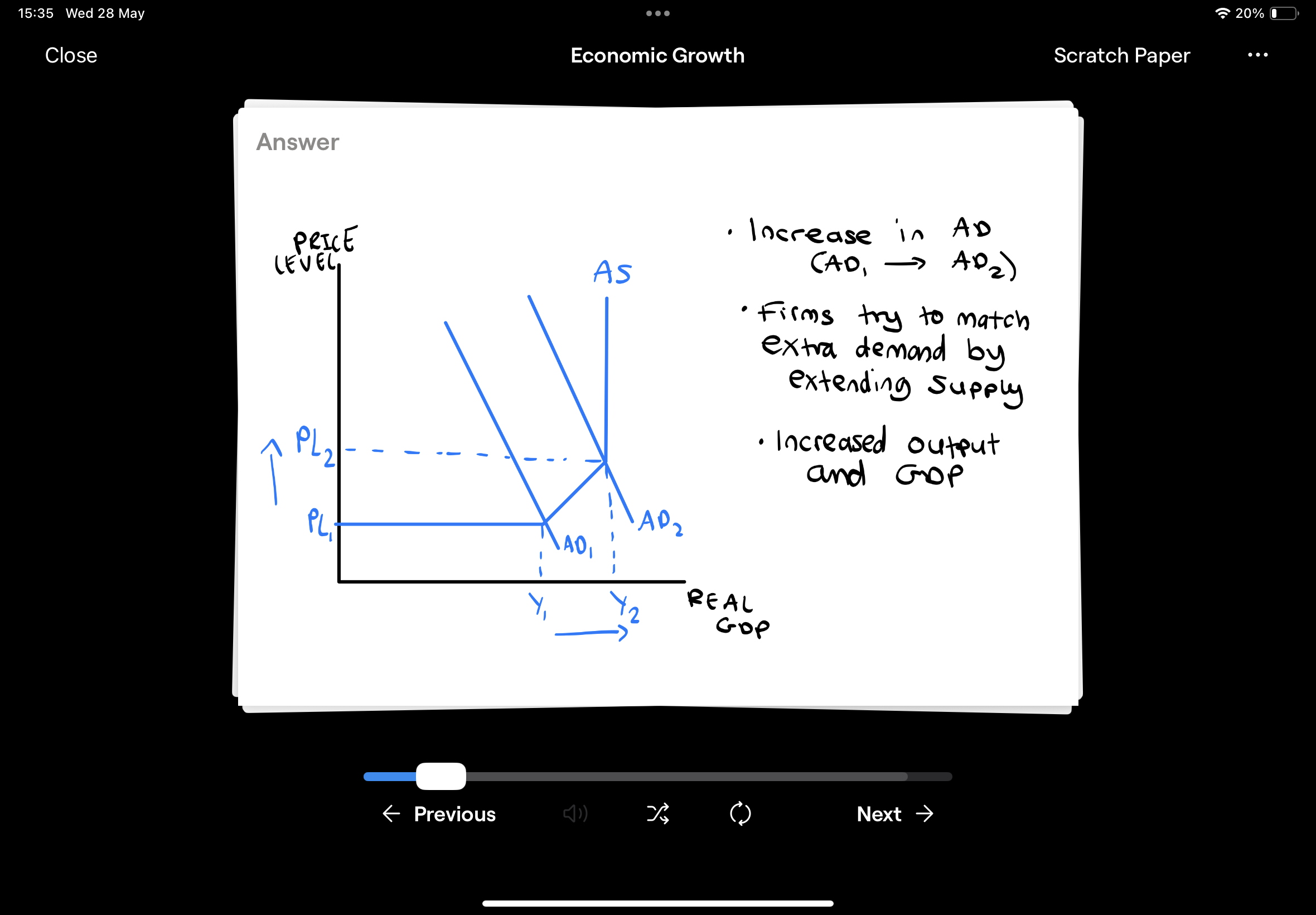
Show Long-Run Economic Growth on a Keynesian AD/AS Diagram
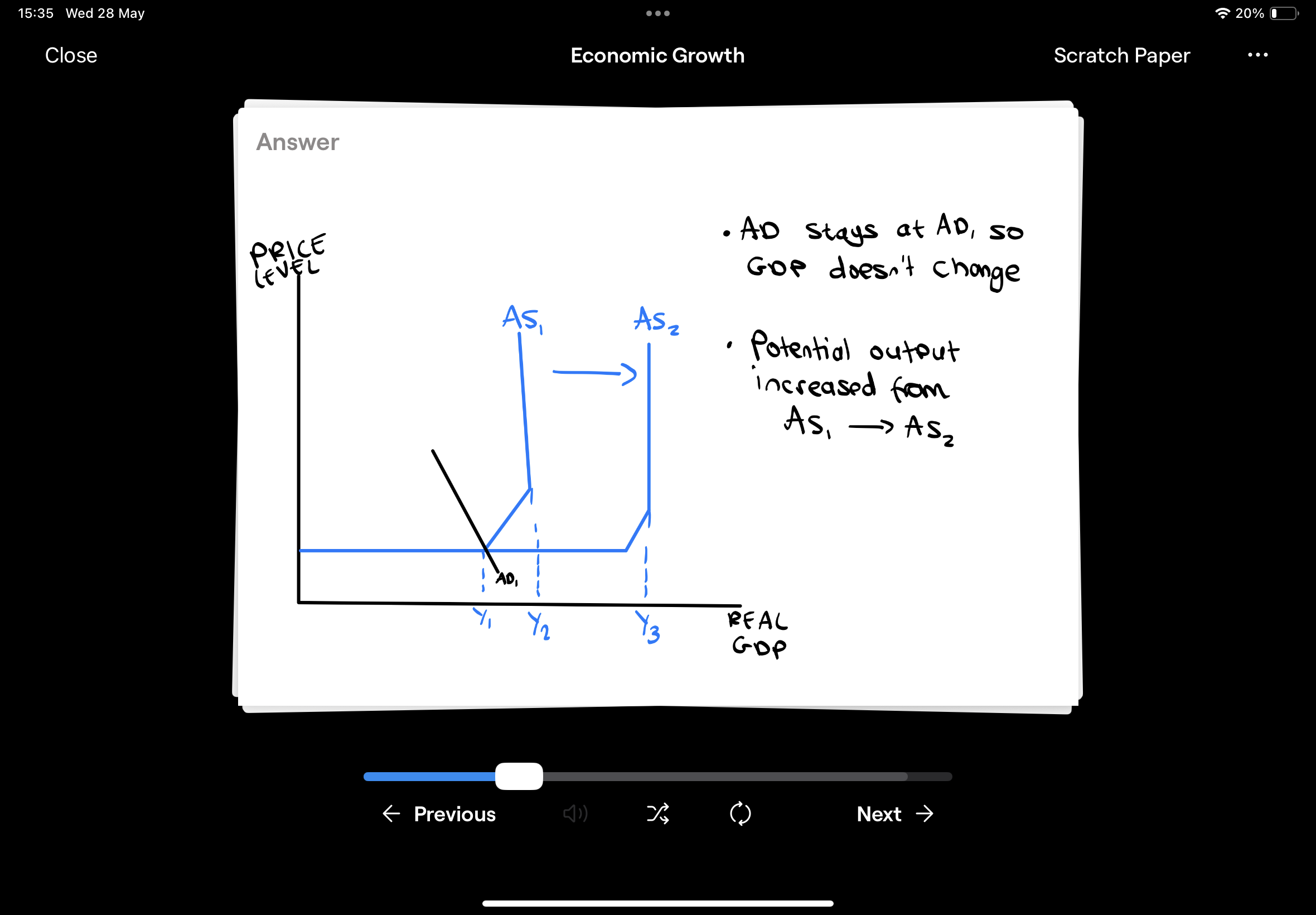
What is the policy objective of economic growth?
Ensuring that it is sustainable for the economy, environment and society
What is economic sustainability?
The ability to meet the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
What is environmental sustainability?
The ability of the environment to fulfil its role as a waste disposer, resource provider and producer of amenities.
e.g. growth with pollution isn’t sustainable as it may harm crops
What is social sustainability?
The ability for an economy to grow without compromising the social needs of the future.
e.g. building factories on football pitches isn’t socially sustainable as football pitches are a social amenity
What does the 'classical school of thought’ believe about AS?
They believe that the economy will always self-adjust to be at its full capacity again
Illustrate a recession using the classical theory
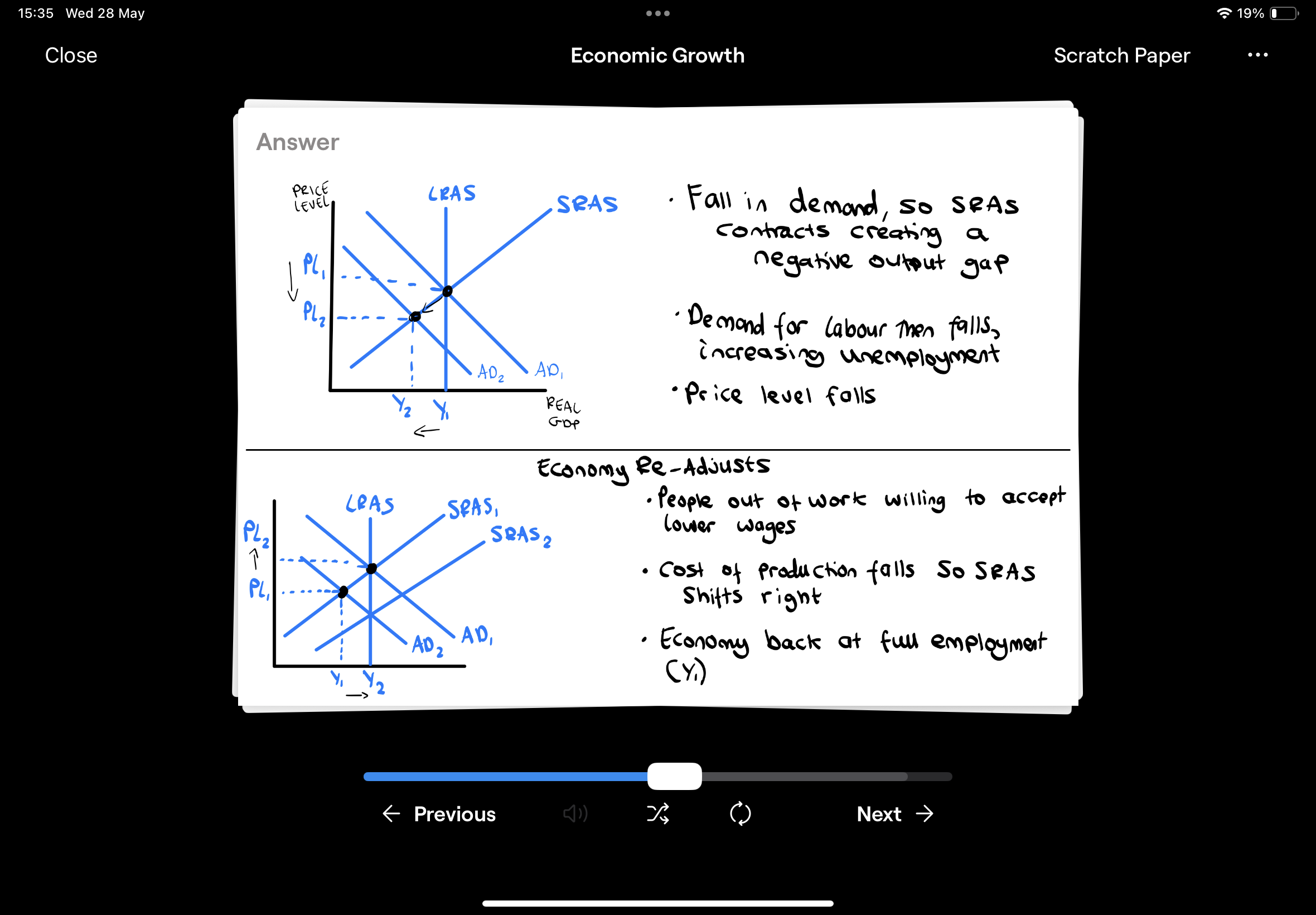
What is a negative output gap?
Occurs when actual output is less than the potential full capacity
What is fiscal policy?
The policy that makes changes to the level of government spending or taxation
How does Fiscal Policy increase economic growth?
If income tax falls, disposable income increases, consumer spending increases, increasing AD, firms increase their supply, increased total output = economic growth
What does the effectiveness of fiscal policy depend on? (EVALUATE Q)
Size of the tax cut
Interest Rates
Consumer Confidence (people save if confidence is low)
What is Monetary Policy?
Changes to interest rates, supply of money and exchange rates
How can monetary policy be used to achieve economic growth?
If the central bank reduces the base rate:
Cheaper for commercial banks to borrow
Commercial banks then decrease interest rates to attract borrowers
Increased borrowing
Increased consumer spending
Increased AD
Increased supply by firms due to profit motive
Increased total output = economic growth
What policy should be used if the productive capacity of the economy isn’t increasing?
i.e. to increase LRAS
Supply-side policy
What is Supply-Side Policy?
Policy attempting to increase productive capacity of the economy
e.g. coorporation tax cuts, deregulation, education, training
How is Supply Side Policy used in Education?
Increased investment in education
Improved quality of education
People leave education with greater skills
Increased productivity in the workplace as they require less training and are more skilled
Productive capacity increases (LRAS shifts right)
