Mendelian disease
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Pattern of autosomal dominant on a pedigree chart
Female and male both affected
through generations
high rate of mutations through out
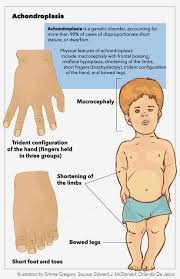
Achondroplasia as autosomal dominant
1/10,000 live birth
Short limbs
Normal sized head, body and intelligence
Due to mutation in FGFR3 gene (inhibition of bone growth) - mutation in the transmembrane domain
Mutation causes the receptor to signal in the absence of ligand
What are complications to autosomal dominant pedigrees?
Variable expressivity
Penetrance
Variation in the age of onset
New mutations with advanced paternal age
What is variable expressivity?
Variation in the severity of the problems arising from a particular genetic defect
Always exhibit some symptoms
Manifestation of phenotype - development of symptoms differs in people with the same genotype
Within family, different members show different features of the syndrome
Variable expressivity - in Marfan syndrome
1/5000
Tall thin stature with long arms
Long double-jointed fingers
Short torso and very long legs
However, not all individuals exhibit these features
What is incomplete penetrance
The penetrance rate is the probability of a heterozygote presenting with the disease
Penetrance = the proportion of individuals with a given genotype who actually express the associated phenotype
Reduced penetrance = skipping of generation
Complete penetrance example - cystic fibrosis
Neurofibromatosis type 1
1/4000 individals
6 or more cafe au lait spots
Neurofibromas occur anywhere along the nerve
Most lead to normal life, but learning disability is frequent
Mutation in NF1 gene, and also exhibits variable expressivity
Incomplete penetrance example- breast cancer due to BRCA gene
Breast cancer penetrance to age 70 estimated at 68% and increase as gets older
Similar with ovarian cancer
Variation in the age of onset - penetrance referred to in terms of a time scale
Example : Huntington disease
Paternal age effect - new mutations with advanced paternal age
The mother transmit about 15 mutation to offspring regardless of age, but mutation transferred from dad increases with age
Could be associated with “selfish spermatogonia selection” : random mutation in a sperm cell gives it a growth advantage, leading to clonal expansion in the testis
As the individual age the proportion of sperm carrying this mutation gets higher
Majority are missense mutation that changes a single amino acid on fibroblast growth receptor
Random X activation in female
A mechanism of dosage compensation by epigenetic silencing
Females are therefore mosaics
Occurs within the first week of embryogenesis
The regressed chromosome forms a heterochomatic mass (Barr bodies)
However approx 15% of X-linked genes show biallelic expresson and are expressed from active and inactive X chromosome
X-linked disease: Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Affects 1/3500 males
Most severe and common MD
Progressive wasting of muscles, death by age 30
The DMD gene Dystrophin is on Xp21 hat is prone to internal deletion → No dystrophin at all
Mutations which affect the DMD gene are mostly frameshift but can be new mutations
DMD gene and dystrophin function
the DMD gene codes fo dystrophin, which provides strength to muscle cells by linking the internal cytoskeleton to the surface membrane
Without the dystrophin, the cell membrane becomes permeable and the internal pressure inside the cell makes it burst and the damage is so extreme to the point where stem cells cannot repair
Becker muscular dystrophy
Milder than DMD, age of onset is after 10y and may require wheelchair from 40-50 though normal life span
Cardiomypathy - rare feature
Due to deletions and other mutations, the proteins are truncated leading to a partially functional protein
Characteristics of X-linked mutations
Affects both sex, mor females affected
Females more mildly affected
No male-to-male transmission
Example : incontinentia pigmenti