Science Exam Sem 2
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Electromagnetic spectrum
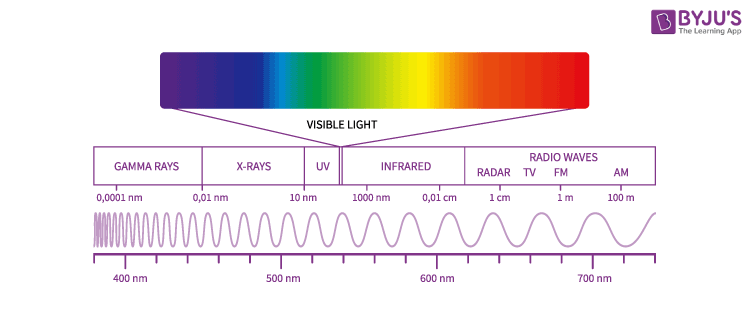
shorter waves = higher frequency, higher energy
longer waves = lower frequency, lower energy
all travel at the same speed
Radio waves
Used to broadcast radio and television
Lowest frequency
Microwaves
Used in cooking, radar, telephone and other signals.
Infrared
Transmits heat from sun, fires, radiators.
Visible light
Makes things able to be seen
Ultraviolet
Absorbed by the skin, used in fluorescent tubes
X - rays
Used to see inside of bodies and objects
Gamma Rays
Used in medicine for killing cancer cells
highest frequency
Colours of the visible spectrum
Red - longest wavelength
Orange
Yellow
Green
Blue
Indigo
Violet - shortest wavelength
Law of Reflection
The angle of incidence = the angle of reflection
Regular reflection
Plane (flat) mirrors reflect light in a regular way (at the same angle).
Diffuse reflection
Most objects reflect irregularly because their surface is NOT perfectly smooth. Light is reflected in all directions.
Wave diagram
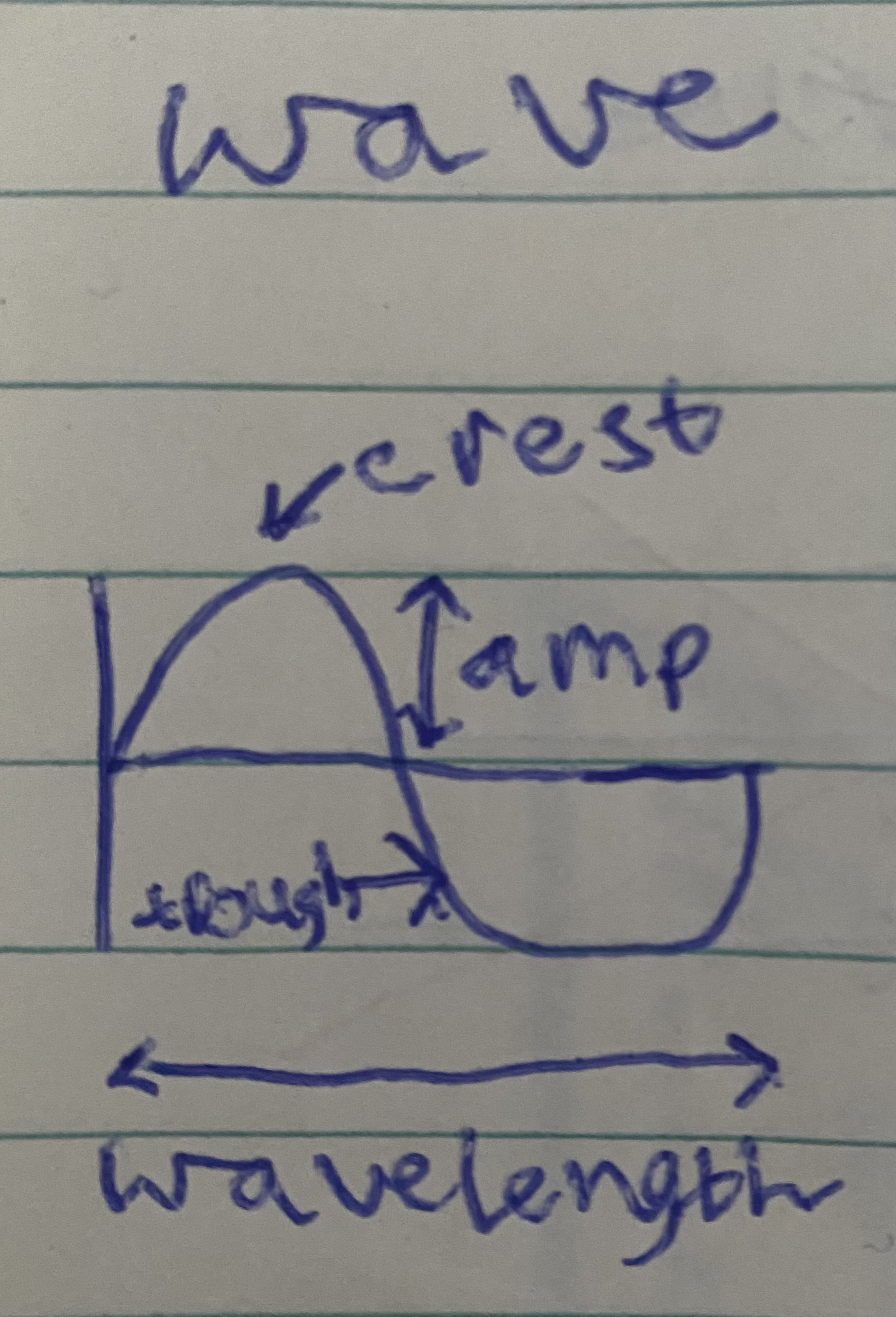
crest, amp, trough
Plane diagram
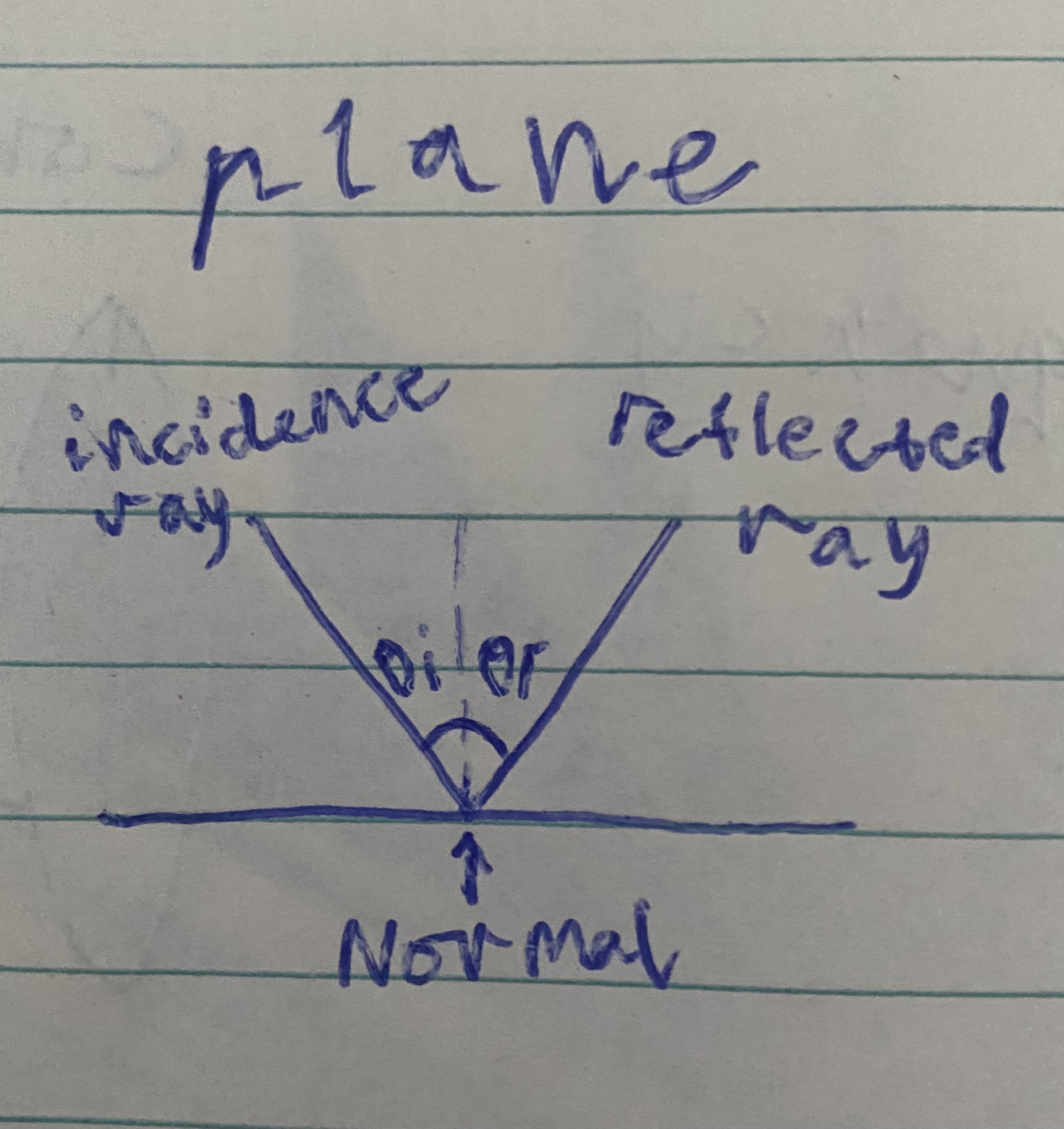
incident ray = reflected ray
Convex mirror diagram
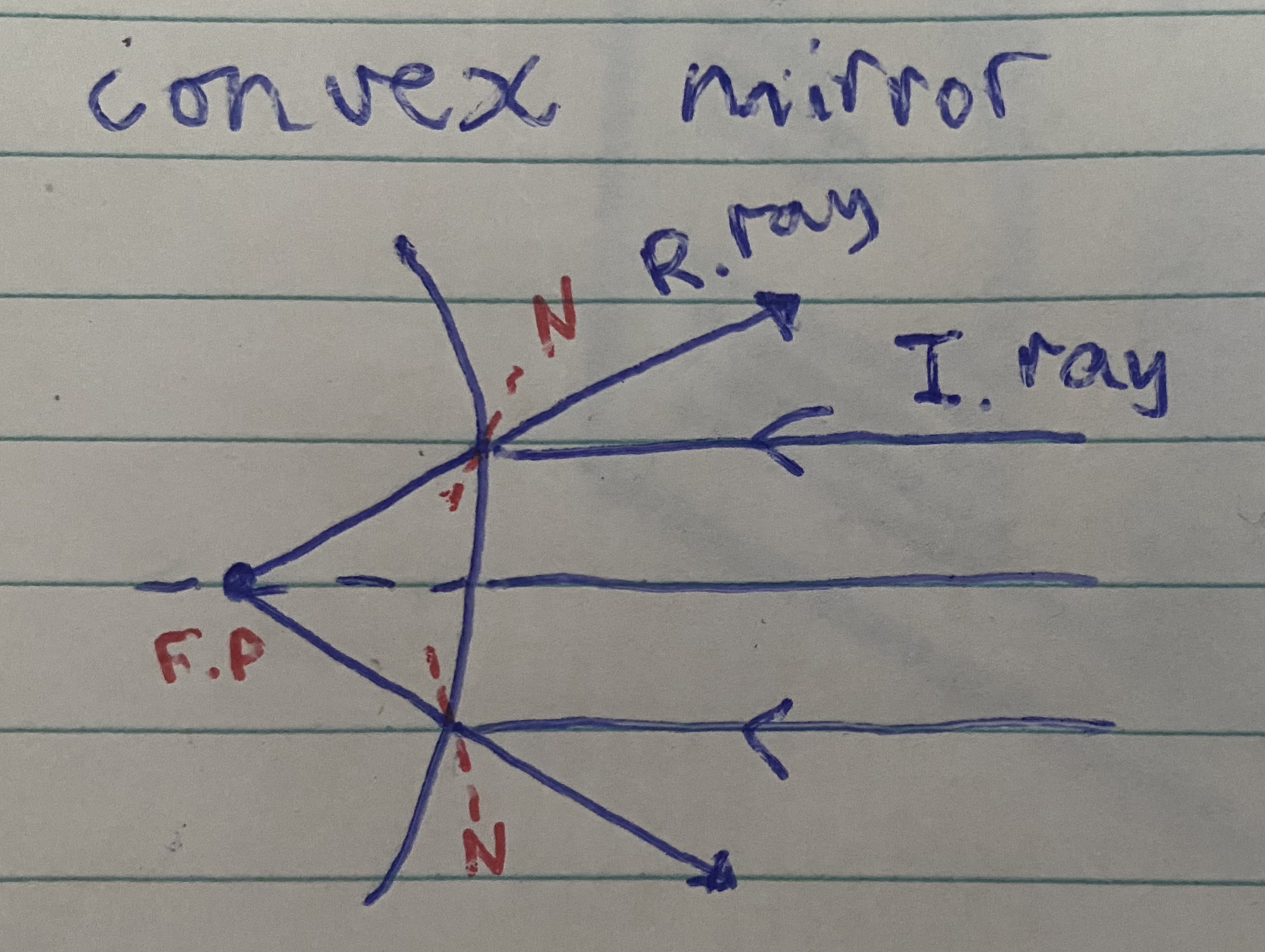
light reflects outwards
Concave mirror diagram
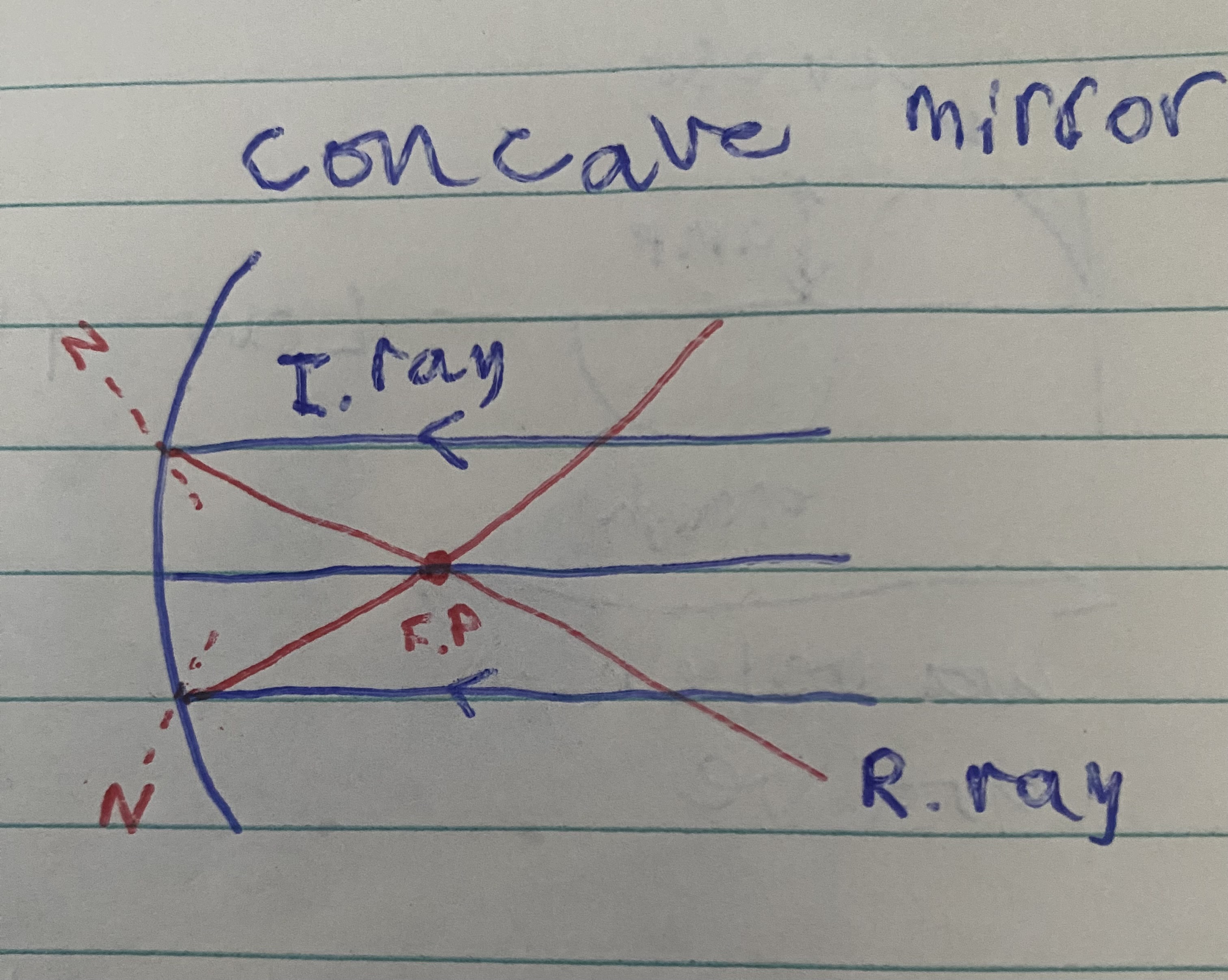
light reflects inwards
How does light pass through different transparent media?
Light refracts in a different direction. This occurs because light travels at different speeds for different media.
Refraction diagram
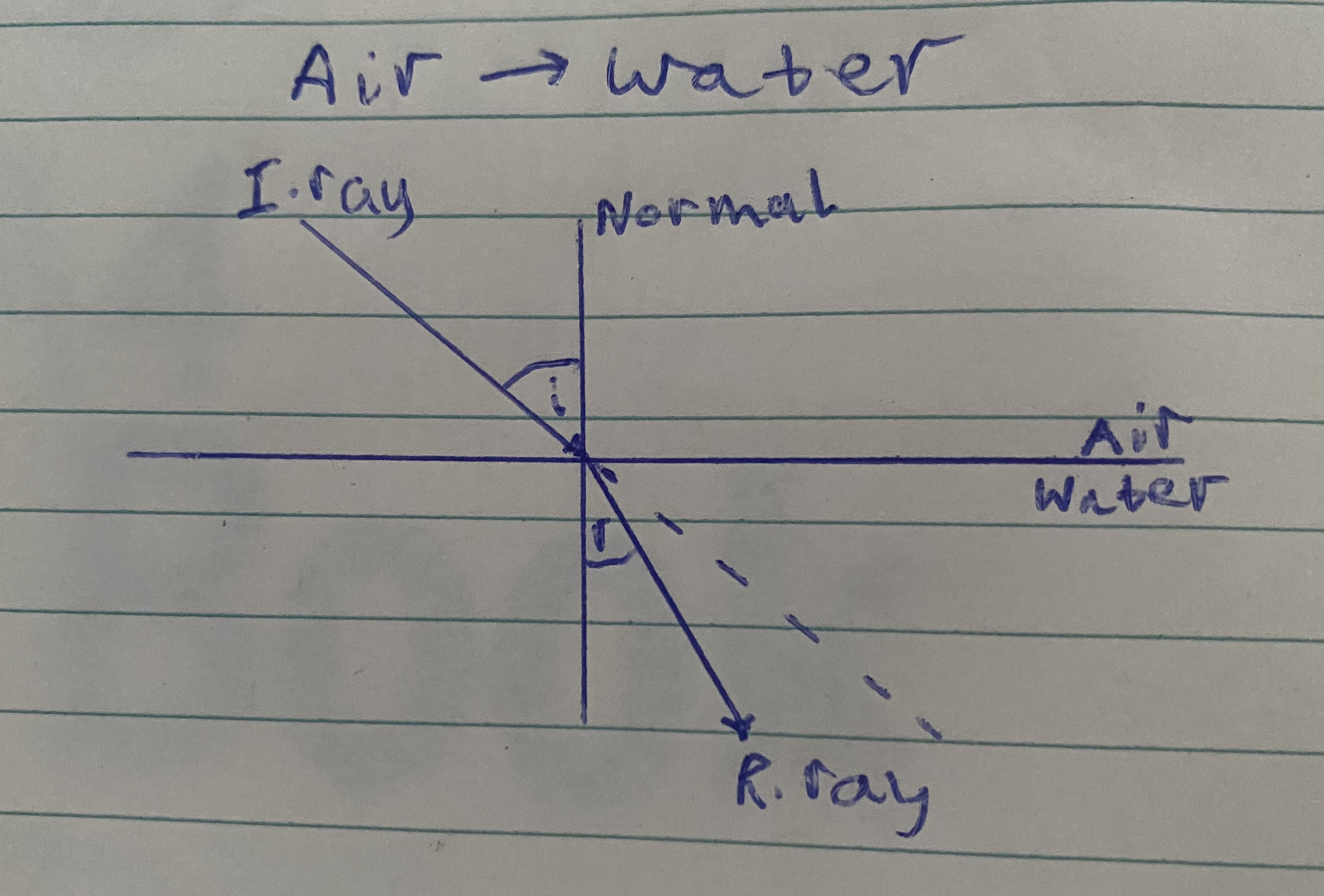
light refracts towards the normal
Refraction
As light passes through different transparent medium, light bends.
This is because as light travels from one medium to another it speeds up or slows down
Rules of refraction
When light enters a more dense medium at an angle it is bent towards the normal (because the light slows down).
When light enters a less dense medium at an angle it is bent away from the normal (because the light speeds up).
Refraction in water
Water is denser
Converging lens
Light refracts inwards - biconvex lens
Diverging lens
Light refracts outwards - biconcave lens
Biconvex lens diagram
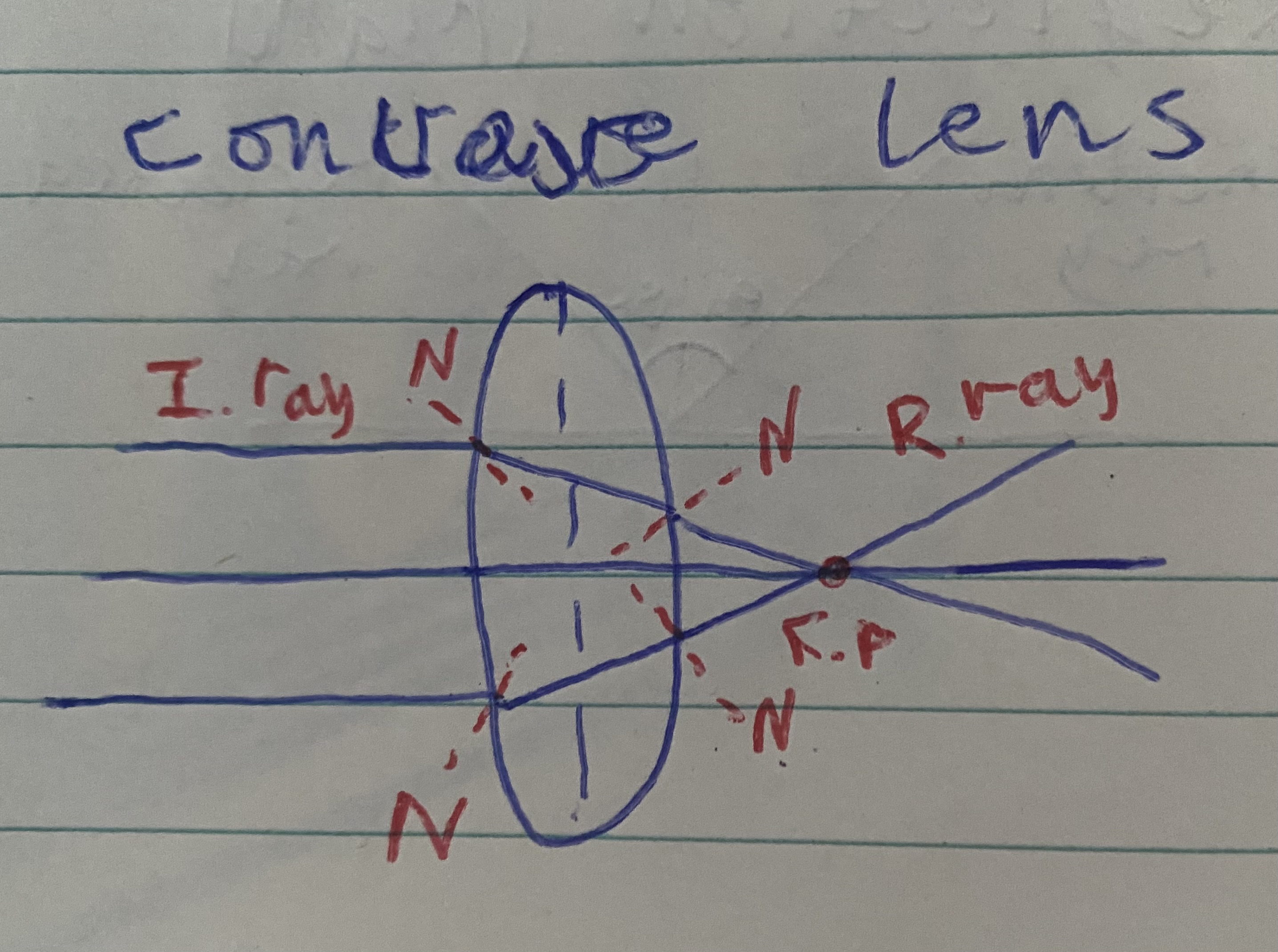
light refracts inwards
Biconcave lens diagram
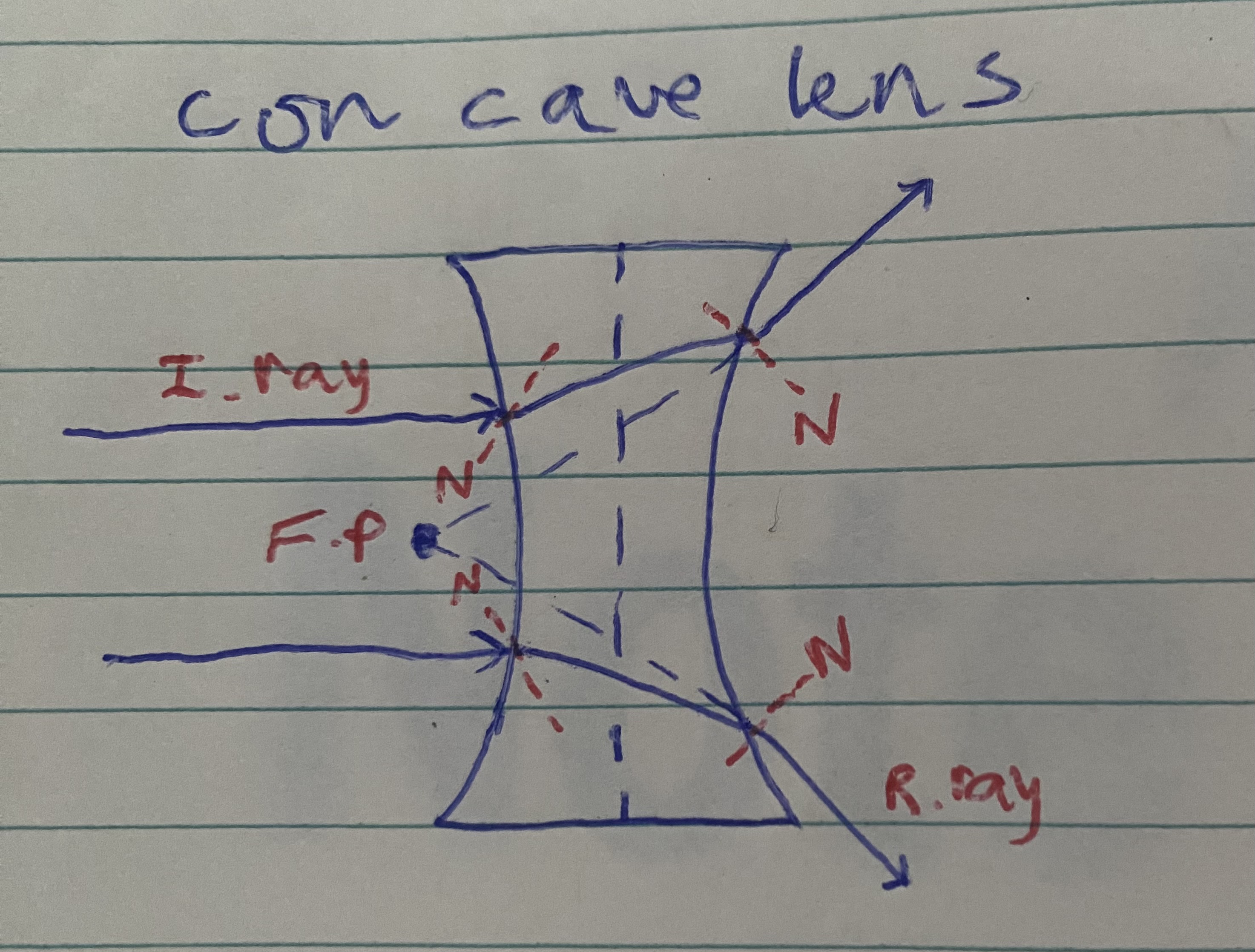
light refracts outwards
Real images
Will be flipped and smaller. This is because the image is beyond the focal point. When light crosses - concave mirror, biconcave lens
Virtual images
An image between the lens and the focal point will be upright and enlarged. When light doesn’t cross - convex mirror, convex lens
Why do objects appear white
when they reflect all of the colours of the spectrum
Why do objects appear black
Objects appear black when all of the colours of the spectrum in light are absorbed
Why does an object appear green
An object appears green because it reflects green and absorbs all other colours
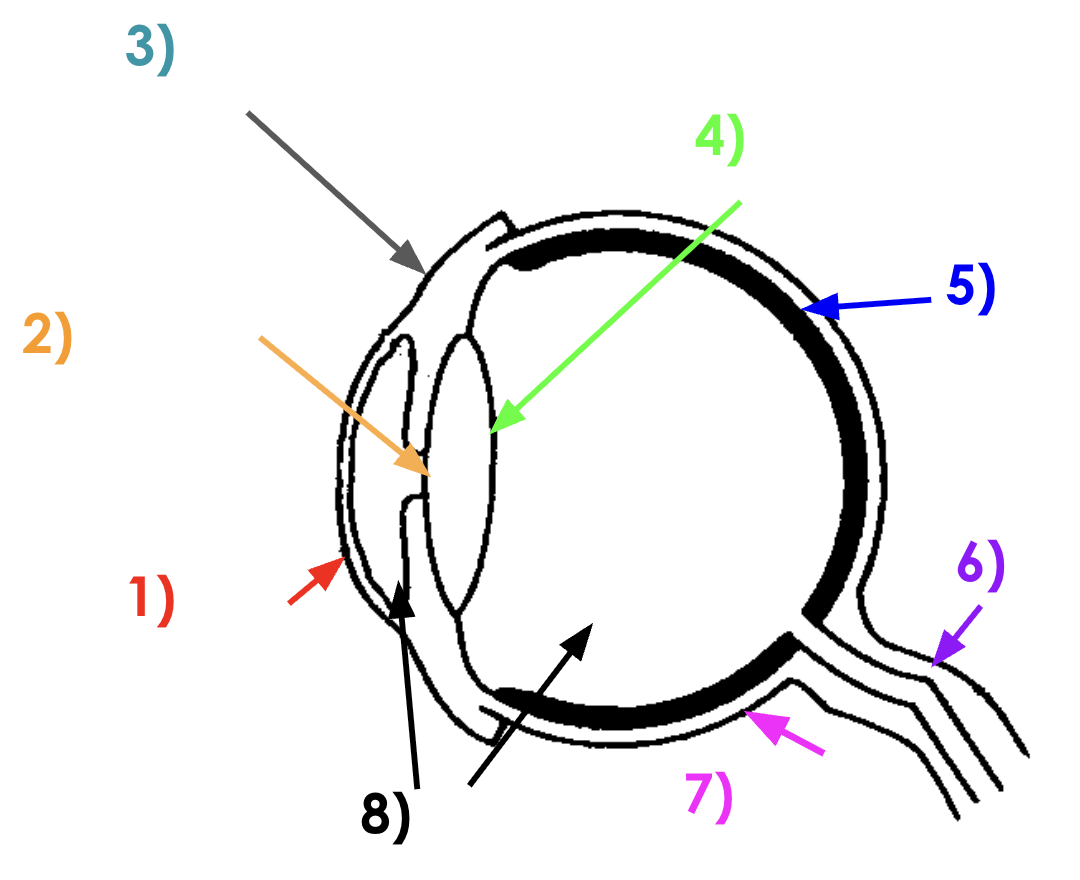
Eye diagram
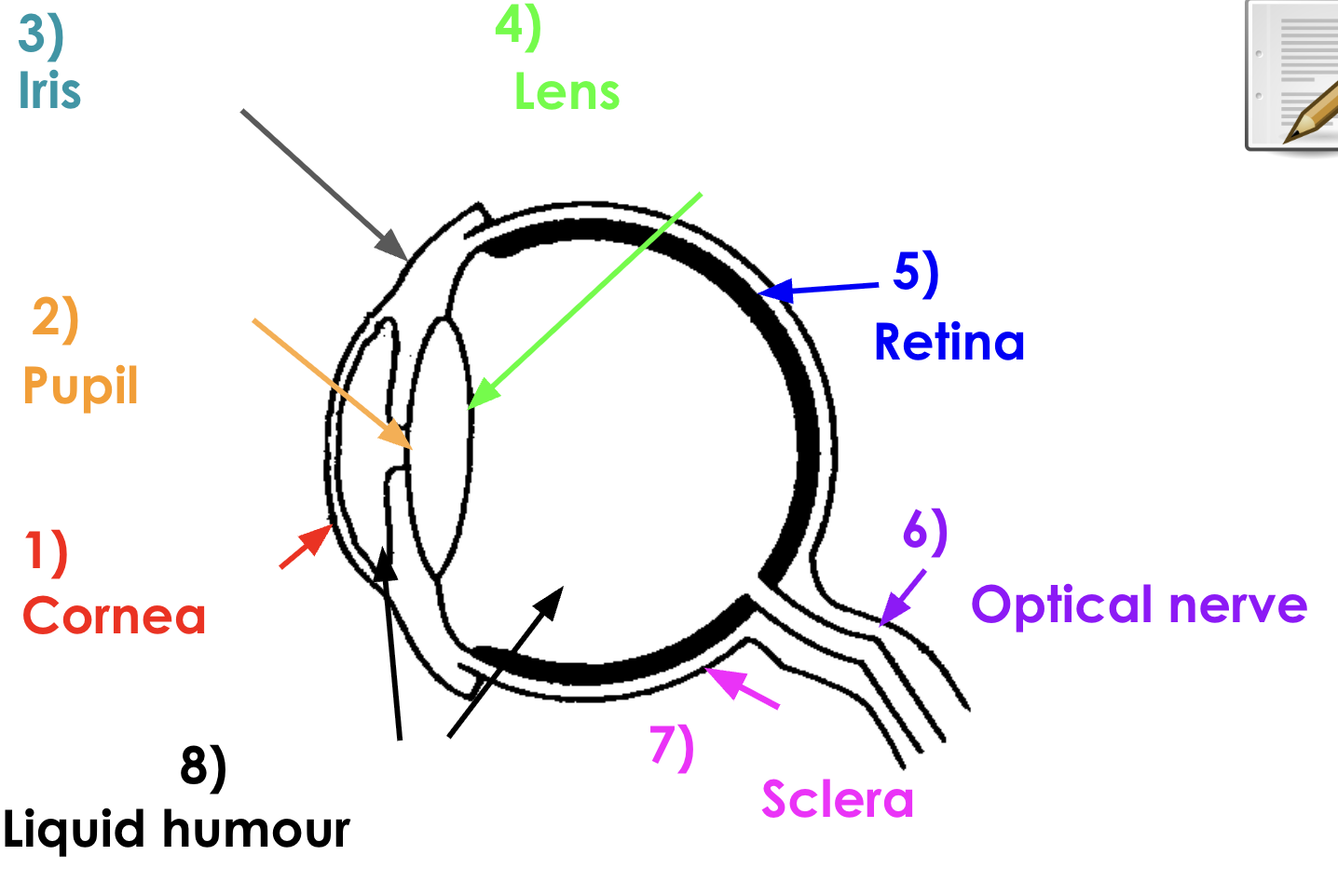
answers
Cornea function
Clear window, refracts light, helps to focus the light
Pupil function
Hole in the iris, which allows light to enter the eye
Iris function
Coloured, changes size to control the amount of light entering the eye
Lens function
Refracts light to focus image on the retina. Focal length adjusted by ciliary muscles
Retina function
Light sensitive cells (rods & cones) which change light energy to nerve impulses.
Optical nerve function
Takes messages from the retina to the brain
Sclera function
The white, tough outer layer that protects the eye.
Liquid humour function
Watery at the front, jelly at the back, helps to keep eye’s shape and provide medium for light to travel through.
What parts of the eye will a light ray pass through to strike the retina?
To reach the retina, light rays first enter through the cornea, then pass through the pupil (its size regulated by the iris), and finally through the lens which focuses the light onto the retina
How does brightness change the eye in light or darkness?
In bright light, the eye's pupil constricts (becomes smaller) to limit the amount of light entering, while in darkness, the pupil dilates (becomes larger) to allow more light in. This is a reflex action controlled by the iris, which contains muscles that adjust the pupil's size.
Rods
Rods are sensitive to light and dark, shape and movement. They only have one type of light-sensitive pigment.
We use mainly rods when trying to see in a dark room – hence why we don’t really see colour in the dark!
Cones
Cones aren’t as sensitive to light, but they are each sensitive to one of the three primary colours.
Cones are used for finer details and seeing colour
People who are colour-blind will either be missing one type of cone or it is weaker.
ecosystem
Involves the interaction of biotic and abiotic things in a given area, contains habitats where organisms live e.g. forests, deserts, coral reefs
community
Is made of different populations interacting with eachother e.g. forest (trees, bears, funghi)
population
a group of the same species of organisms
e.g. a herd of zebras, a school of fish
biotic factors
living factors
abiotic factors
non living factors
Leaf diagram
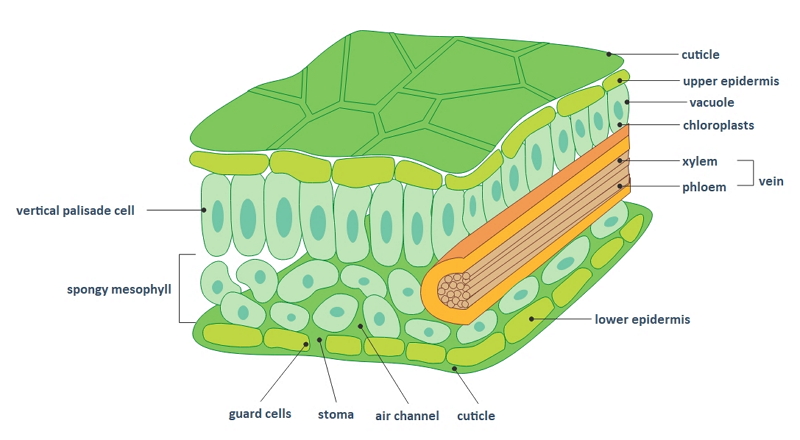
Leaf structure and functions
Palisade mesophyll - contain chloroplast
Stomata - allow carbon dioxide to enter and oxygen to be released
Spongy mesophyll - gaseous exchange
Phloem - transports food from the leaves to the rest of the plant
Xylem - transports water from the roots to the leaves
Guard cells - open and close the stomata
Process of photosynthesis
photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of the mesophyll. Chloroplast absorbs light energy from the sun, when combined with carbon dioxide and water, it traps this energy in the chemical bonds of glucose.
Chemical equation
CO2+H2O = C6H12O6O2
Carbon dioxide + water with the sunlight make glucose + oxygen
Cellular respiration
The process of converting stored energy into usable energy. It occurs in the mitochondria.
Process of cellular respiration
The energy stored in plants (as glucose) is released as a molecule called ATP
Chemical equation
Oxygen + glucose = carbon dioxide + water + ATP
aerobic respiration
Produces more ATP
Occurs in mitochondria
Produces carbon dioxide and water as a waste product
Requires oxygen
Used when heart rate and breathing rate rise
anaerobic respiration
Doesn’t require oxygen
Occurs in cytoplasm
Used in the first 1 - 2 minutes of exercise
Produces less ATP
Produces lactic acid as a waste product (animals)
aerobic equation
Glucose + oxygen = Carbon dioxide + water + ATP
anaerobic equation
Glucose = lactic acid + ATP
(lactic acid broken down by liver)
Anaerobic respiration (funghi, yeast and bacteria)
Glucose = ethanol + carbon dioxide + ATP
food chain
feeding relationship
food web
Shows all the connections between the food chains, it has multiple paths
Energy loss and transferal
Only ten percent is passed from each level
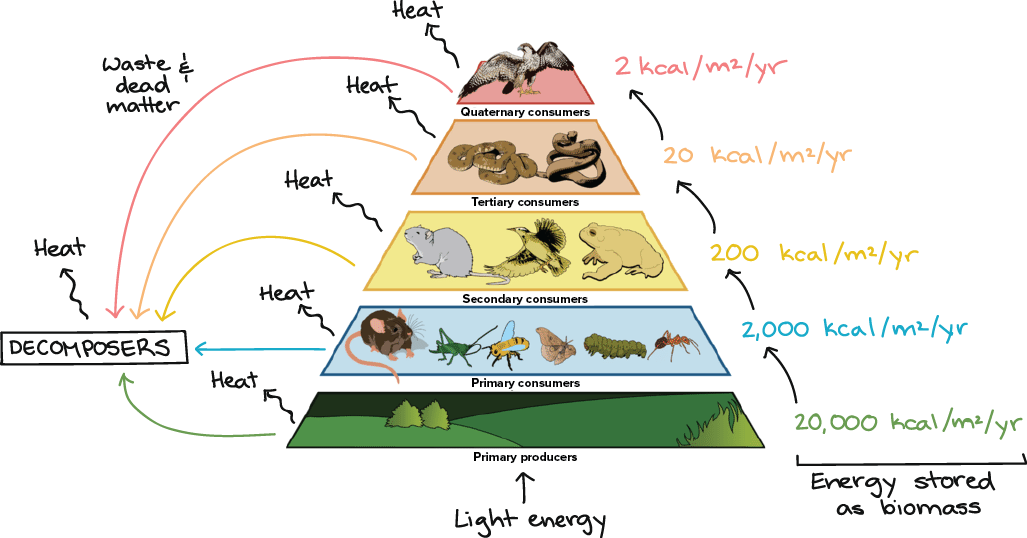
producers vs consumers
Producer - organisms that can photosynthesise
Consumer - Primary consumers eat producers
Secondary consumers eat primary consumers
role of decomposers
Break down dead organic matter into simpler inorganic substances.
Factors that disrupt ecosystems
Natural disasters and human activities
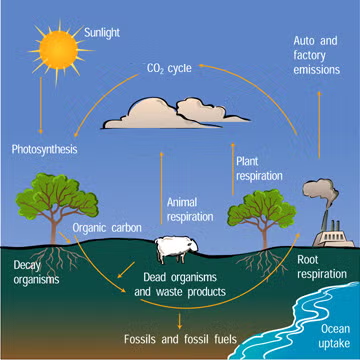
The Carbon Cycle
Carbon cycle examples
CO2+H2O = C6H12O2
C6H12O6+O2 = H2O+CO2+ATP