Finals Week Physics
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
Sir Isaac Newton is credited with the development of the classical theory of physics
True/False
True
Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle states that the position of an electron can be precisely determined at all times.
True/False
False
The Larmor frequency is determined by the gyromagnetic constant and the strength of the external magnetic field (B0).
True/False
True
Protium is used in MRI due to its scarcity and small magnetic moment.
True/False
False
More RF energy is needed for excitation at higher field strengths because the energy gap between spin populations increases.
True/False
True
Phase refers to the speed of rotation of a magnetic moment, while frequency refers to its position at a given moment in time.
True/False
False
Resonance results in coherent magnetization in the transverse plane.
True/False
True
A voltage is induced in a conductor placed in the transverse plane due to the movement of longitudinal magnetization.
True/False
False
The MR signal used to create an image is based on two characteristics: frequency and amplitude.
True/False
True
The magnetic component (B1) of the RF excitation pulse is responsible for causing resonance.
True/False
True
Classical theory of physics
Developed by Sir Isaac Newton to explain predictable physical laws
Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle
States the exact position and momentum of an electron can't be known simultaneously
Larmor frequency
Frequency at which magnetic moments precess in a magnetic field
Protium in MRI
Chosen for MRI due to its high body abundance and strong magnetic properties
RF energy at high field strength
Requires more energy because of greater difference in spin populations
Phase vs. Frequency
Phase = location in time; Frequency = number of rotations per second
Resonance results
Leads to synchronized (coherent) magnetization in the transverse plane
Voltage induction in MR
Occurs when magnetization moves near a coil and produces a changing voltage
MR signal components
Determined by both frequency and amplitude of the signal
RF excitation pulse component
The B1 magnetic field is the part that flips spins into the transverse plane
The approximate scan time of a rapid spin echo
sequence with a TR of 3500ms, a TE of 90ms, 256 x
256 matrix, 1 excitation, a 220mm FOV and an
echo train length of 5 is ________________ minutes.
2 minutes and 59 seconds
What is one of the most important safety concerns in MRI?
Ferromagnetic attraction
Who first demonstrated a radio signal from the nucleus of the atom?
Isidor Rabi
Which two physicists won a Nobel prize for developing the nuclear induction?
Bloch and Purcell
What year was MRI FDA approved?
1985
In early MRI, what technique was used to study and what did they study?
Spectroscopy, Chemicals
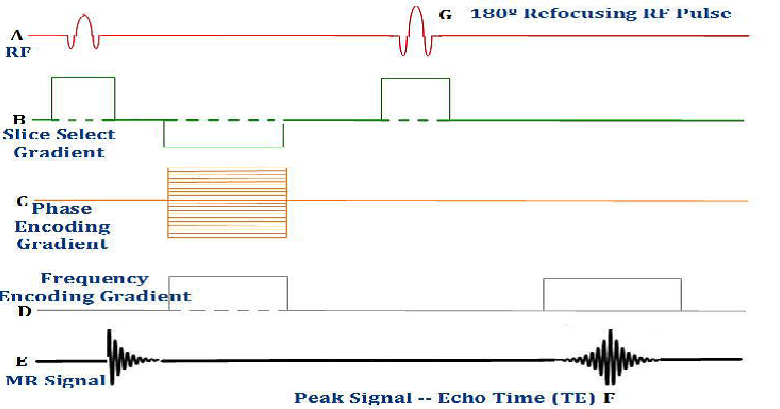
What pulse sequence does this image represent?
CSE
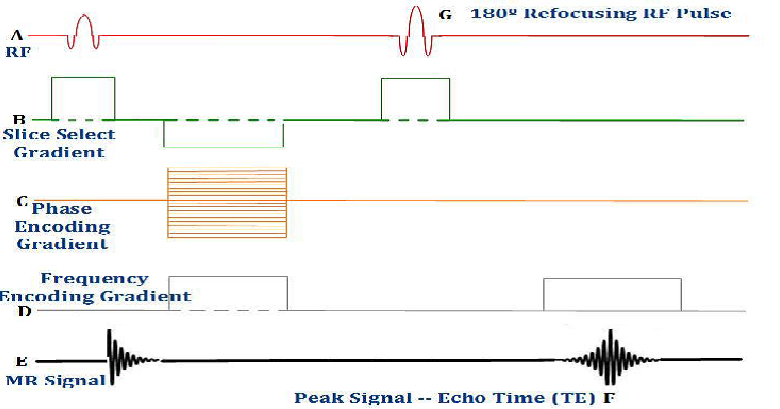
What is one of the advantages of this pulse sequence?
True image weighting is obtained
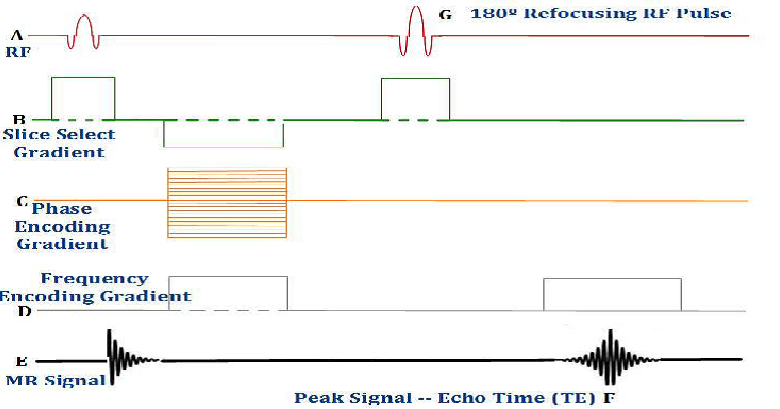
During read out time of the echo, which gradient switches on?
Frequency
What is the Larmor precessional frequency of hydrogen in a 1.5T magnet?
63.86 MHz
What law states that “a moving magnetic field induces a voltage in a conductor coil”?
Faraday
How are T1-weighted images characterized?
Bright fat and dark water
What does “spin” refer to in spinning?
Nuclei
Which of the following is NOT an extrinsic parameter?
PD
TRUE OR FALSE?
Fat has a shorter decay time than water.
TRUE
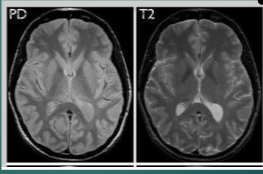
Which pulse sequence creates the following images in one TR period?
Dual Echo
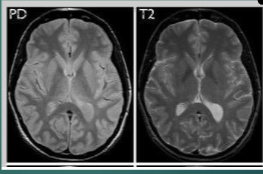
What is an extrinsic factor of the following images?
All of the above
A technique that uses the differences in magnetic susceptibility
between oxyhemoglobin and deoxyhemoglobin to images areas of activated cerebral cortex is:
BOLD
The point in a tissue’s longitudinal recovery where there is no
component of magnetization and therefore no signal created on an IR pulse sequence is called:
Null point
Which of the following combinations of TR & TE create a T2-weighted image?
TE 90ms, TR 4000ms
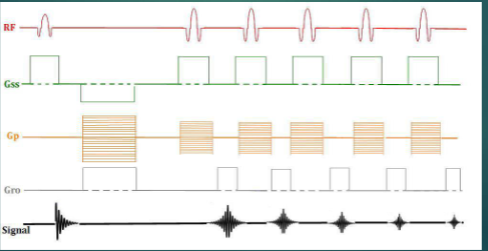
The following image represents what type of pulse sequence?
FSE/TSE
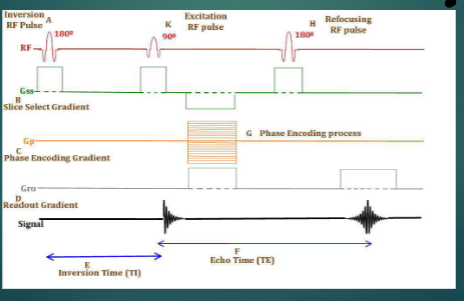
For the following image, what type of pulse sequence does it
represent?
Inversion Recovery (IR)
Who can sign the MRI screening form?
the patient,a legal representative,a legal guardian
What is the first thing that should be done for a patient who is having a medical emergency during an MRI?
Remove patient from the scanner and put them in zone 3, secure the MRI scan room door, and then call for help!
When would a tattoo be considered MR unsafe?
If it has iron oxide inks
What is the most important consideration for a patient who has had a cardiac pacemaker removed?
That the pacer wires are also removed; or need to be evaluated
for safety.
Where is a common place for a vascular filter?
IVC
What is a cochlear implant?
an implant in the inner ear
Why should a patient have their kidney function tested before an MRI is performed with IV gadolinium contrast injection?
To evaluate kidney function and make sure the contrast will be
filtered out from the body in a reasonable amount of time
What can cause NSF?
Due to poor kidney function. Certain types of gadolinium
contrast remaining in the human body too long
What does NSF stand for ?
Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis
What is an "active" implant?
An implanted device that has a power source other than the
human body itself
What is the FDA recommended amount of SAR for the head averaged over 10 minutes?
3 W/kg
What level of sedation requires physiological monitoring?
parenteral,enteral,general anesthesia,any patient who is unconscious
What is required if the MRI table is not detachable?
There must be an MRI safe gurney readily available
TR 9000, TE 125, TI 2200 ,FM 256, PM 224, 10 ETL, slice thickness 5mm, 2mm gap would yield images with what weighting ?
T2 FLAIR
The Larmor precessional frequency of hydrogen in a 3T magnet is:
127.74 MHz