biomechanics
1/110
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
what causes linear motion
direct force applied to the body through the COM
what causes angular motion
eccentric force applied to a body outside of the COM
5 ways to increase acceleartion
increase force/velocity/speed
increase friction
reduce mass/weight
improve technique
decrease air resistance
1. body position
2. athlete body shape
3. gender
1. increase mass of body
2. increase size of base support
3. lower COM
4. increase number of contact points
5. bring line of gravity inside the base support
direction of friction
acts in the opposite direction to motion
1. roughness of footwear/object
2. roughness of ground
3. size of down force
4. temperature of surface
1. shape of object
2. velocity
3. frontal cross sectional area
4. smoothness of surface
1. technique
2. footwork
3. conditions
4. body shape
1. force
2. air resitsance
3. body shape
what is a load arm
the perpendicular distance from the fulcrum to the load
what is the effort arm
the perpendicular distance from the fulcrum to the effort
what is a 1st class lever
fulcrum in the middle
what is a 2nd class lever
load in the middle
what is a 3rd class lever
effort in the middle
example of 1st class lever
header (fulcrum= joint between atlas and skull, load= weight of head, effort= trapezius )
example of 2nd class lever
pirouette in ballet (fulcrum= joint between phalanges and metatarsals, load= weight of body, effort= plantarflexion)
example of a 3rd class lever
bicep curl (fulcrum= elbow, load= weight, effort= biceps brachii)
which lever has mechanical advantage
2nd class
what is mechanical advantage
ability to move large load with small effort, larger effort arm than load arm
what lever has mechanical disadvantage
3rd class lever
what is mechanical disadvanatge
lever struggles with heavy load, load arm is longer than the effort arm
what is limb kinematics
the study of motion, limbs and movement through video, 3D analysis.
what is a strength of limb kinematics
improve technique, improve posture, helps with injury rehabilitation
what is a weakness of limb kinematics
accessibility, cost, requires specialist data to interpret
what are force plates
rectangular metal plates in the ground that measure force
what is a strength of force plates
to design prothesistics, to improve technique, rehabilitation
what is a weakness of force plates
expensive, requires specialist training, must be calibrated
what are wind tunnels
they are used to stimulate air resistance
what are postives of wind tunnels
improve technique (aerodynamic), to test equipment design
what are weaknesses of wind tunnels
accessibility, cost, training to interpret data
what are the key factors of linear motion
distance, displacement, speed, velocity, acceleration
what is distance
total length from start to finish (m)
what is displacement
the shortest straight line route from start to finish (m)
what is speed
the rate of change in distance (m/s)
what is velocity
the rate of change in displacement (m/s)
what is acceleration
the rate of change in velocity (m/s/s)
what are the graphs of linear motion
distance/time graphs, speed/time graphs, velocity/time graph
what is torque
a turning force- the greater the eccentric force, the greater the angular motion
what are the 3 axis of rotation
longitudinal (from head to toe)
transverse (from side to side)
frontal (from front to back)
what is angular motion measured in
radians (rad/s)
what is angular velocity
the rate of change in angular displacement
what is the equation for angular velocity
AV (rad/s)= angular displacement (rad)/time (s)
what is moment of inertia
the resistance if a body to change its state of angular motion
what is the equation for moment of inertia
MI (kgm2)= mass(kg) x distribution of mass from axis of rotation (m2)
what 2 factors affect MI
mass
distribution of mass from the axis of rotation
mass (moment of inertia)
the greater the mass, the greater the moment of inertia, decreases angular velocity
distribution of mass (moment of inertia)
close mass distribution from axis, decrease moment of inertia, increase angular velocity
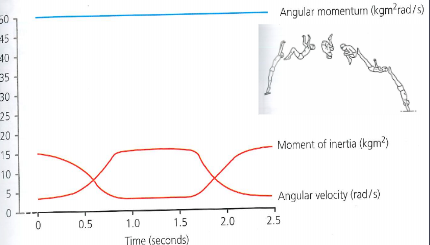
what is angular momentum
the quantity of angular motion possessed by a body
what is the equation foo angular momentum
AM= MI x AV
conservation of angular momentum
AM is constant. As MI increases, AV decreases
what can affect drag and air resistance
velocity (greater velocity= greater drag and AR)
frontal cross-sectional area (larger= greater drag and AR)
shape (more streamlined= less drag and AR)
surface characteristics (smooth surface= less drag and AR)
what is projectile motion
movement of a body through air flowing a curved flight path under the force of gravity
what 4 things can imapct projectile motion
speed of release
angle of release
height of release
aerodynamics
how does the speed of release impact projectile motion
the greater force applied to projectile, greater acceleration, so travels further
how does the angle of release impact projectile motion
45- optimal angles= greatest distance
less than 45- not enough height
what is a parabolic flight path
a uniform curve, symmetrical about its highest point, unaffected by air resistance caused by a dominant weight force
what is a non parabolic flight path
asymmetric about its highest point caused by the dominant force of air resistance on the projectile
what is Bernoulli’s principle
the higher the velocity of air flows the lower the surrounding pressure
what is Bernoulli principle (explanation)
aerofoil shape causes air to travel a greater distance with a greater velocity so low pressure above, air travels a shorter distance so lower velocity so high pressure below, air moves from high to low pressure down the pressure gradient so creates a lift force