Bio Practical
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/165
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:25 PM on 12/5/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
166 Terms
1
New cards
what are genetic mutation?
random changes that occur in genes because of damage from the environment or copy errors that happen during DNA replication
2
New cards
What is sexual reproduction?
which mixes the various alleles of parents into all manner of unique combinations in offspring
3
New cards
What is statistics?
The branch of mathematics devoted to the objective
description and analysis of data
description and analysis of data
4
New cards
what are the two main kind of statistic test?
descriptive: is to use the data measured from a sample to infer the likely characteristics of the population as a whole.
Statistical: use data from samples in order to rigorously answer questions about what might be going on in a system.
Statistical: use data from samples in order to rigorously answer questions about what might be going on in a system.
5
New cards
what is morphology?
Body shape
6
New cards
what is a chi test?
comparison of distribution or frequency
more or less common
more or less common
7
New cards
what is the t test equation?
t= x1-x2/√s1^2/n1+s2^2/n2
Comparison of means
Comparison of means
8
New cards
𝑋1 and 𝑋2 represent?
The mean for the two samples being compared
9
New cards
s2 represents?
the square of the standard deviation for each (a value known as the variance)
10
New cards
what does n stand for?
the sample size of each (number of data points collected = observations made in each case
11
New cards
what is mean?
the average
12
New cards
x̄ (x-bar)
the mean of the sample (actually measured)
13
New cards
µ (mu)
the mean of the whole population from which the sample was taken (inferred/estimated from the sample characteristics)x̄ provides an estimate of µ
14
New cards
what is standard deviation?
the variability about the mean
15
New cards
σ
the standard deviation of the whole population from which the sample was taken (inferred/estimated from the sample characteristics)s provides an estimate of σ
16
New cards
R - values of correlation
r value greater than .7 strong correlation
r value 0-.3 weak correlation
r value .3 - .7 moderate
r value 0-.3 weak correlation
r value .3 - .7 moderate
17
New cards
Proxy
Stand in
18
New cards
Regression analysis
Relationship that exists between 2 variables
19
New cards
Bell shaped curve
Normal Distribution
20
New cards
non random assertive mating
decrease genetic diversity in the population over time
21
New cards
Dominant vs. Recessive Alleles
dominant alleles (indicated by a capital letter) dominate the phenotype
recessive alleles (represented with a lower case letter) only determine the phenotype when no dominant allele is present
recessive alleles (represented with a lower case letter) only determine the phenotype when no dominant allele is present
22
New cards
what do you call a trait that is influenced by multiple genes?
Polygenic
23
New cards
Allele
a particular version of a gene
24
New cards
What are genes?
sequences of DNA that code for particular traits or phenotype
25
New cards
What are genotypes?
the particular combination of alleles an organism carries in its DNA for a given gene or genes
26
New cards
What is the mark-recapture method?
estimating the size of a population involves marking a sample of the relevant organisms (typically animals), allowing the organisms to mix back into the population, and then sampling them again. The proportion of marked organisms in the second sample reveals the proportion of the total population that was originally marked, allowing us to calculate the population size according to the equation
27
New cards
what is the mark recapture equation?
N=MC/R
N= species in the population
M=the first catch you mark
C= amount you caught
R= amount recaptured
N= species in the population
M=the first catch you mark
C= amount you caught
R= amount recaptured
28
New cards
what is modeling?
attempt to in some way artificially replicate a real system
29
New cards
what is discrete population growth?
annual natality occurs in one relatively short burst each year, rather than being spread throughout the year
30
New cards
What is discrete unrestricted growth?
Populations grow according to the equation
31
New cards
what is continuous unrestricted growth?
members of the population become reproductively viable (mature) and give birth throughout the year. We humans are an example of this
32
New cards
what is logistic growth?
population eventually gets large enough that environmental resources become limiting, or environmental factors otherwise start to push back against ongoing rampant growth. per capita rate gets smaller and smaller.
S shaped curve
r=rmax (1-n/k)
S shaped curve
r=rmax (1-n/k)
33
New cards
what is unrestricted exponential growth?
a population's per capita (per individual) growth rate stays the same regardless of population size, making the population grow faster and faster as it gets larger.
34
New cards
What is a dichotomous key?
a tool used to identify organisms by successively narrowing them into separate groups based on the characteristics they have.
35
New cards
Transpiration demonstration
Vascular plants transport water into and through their bodies. During transpiration water evaporates from leaves through pores called stomata.
36
New cards
what are leaves 3 main tissues?
upper epidermis: receives the most intense sunlight
mesophyll: consisting of the columnar palisade
mesophyll above and the irregular and airy spongy
mesophyll below rich in chloroplast
chlorenchyma
mesophyll: consisting of the columnar palisade
mesophyll above and the irregular and airy spongy
mesophyll below rich in chloroplast
chlorenchyma
37
New cards
dicot leaf model
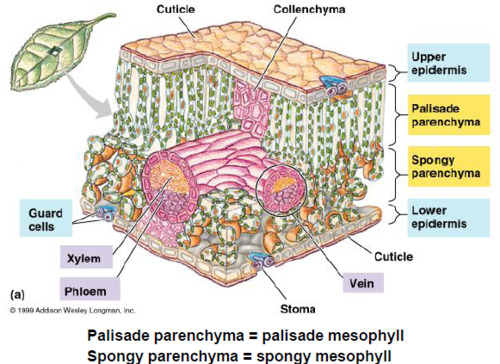
38
New cards
xylem and phloem
The xylem distributes water and dissolved minerals upward through the plant, from the roots to the leaves. The phloem carries food downward from the leaves to the roots.
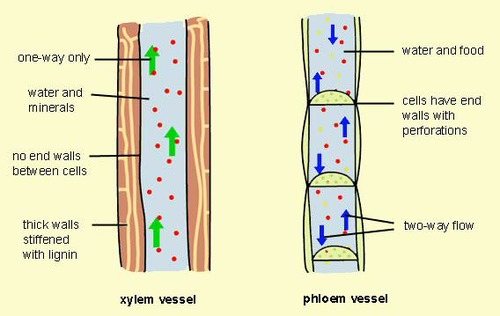
39
New cards
What is a meristem?
where most roots and plant grows... lots of cell division happening
40
New cards
what is the very tip of the root called?
root cap
41
New cards
Apical meristem
composed of rapidly dividing, undifferentiated cells from which the root grows
42
New cards
zone of elongation
cells lengthen to effectively extend the root forward
43
New cards
monocot vs dicot
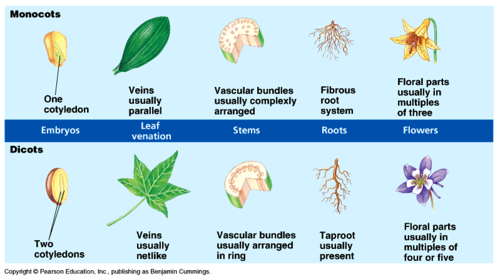
44
New cards
What is the stomata?
to take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen
45
New cards
flower model
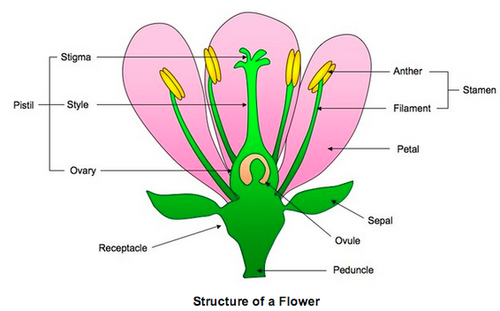
46
New cards
what are phylum cnidara?
alternate between sessile polyps and free swimming medusae over the course of their life cycle. may reproduce asexually by budding of polyps, or sexually via specialized gonozoid polyps which release medusae (which in turn go on to produce eggs or sperm by meiosis for sexual reproduction).
47
New cards
what are examples of phylum cnidara
hydra, coral skeltons, jellies
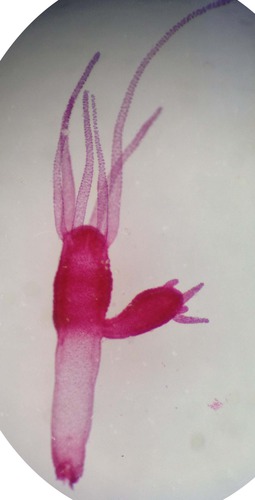
48
New cards
Dorsal vs Ventral(Squid)
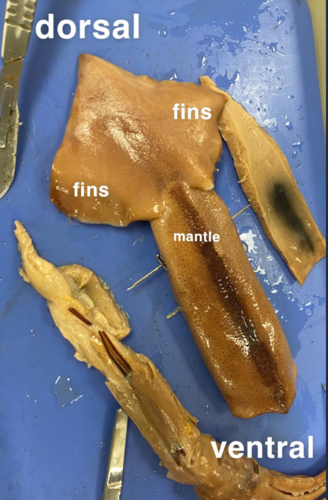
49
New cards
posterior side of squid
with the siphon pointed up
50
New cards
fins squid
used for locomotion
51
New cards
Chromatophore (squid)
dark dots of pigment on the surface of the squid
52
New cards
siphon
when the mantle tissue contracts, water trapped between the mantle and underlying visceral mass is forced out the siphon
53
New cards
squid eyes
do not posses a blind spot
54
New cards
squid internal anatomy (anterior)
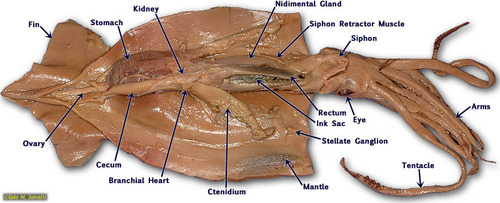
55
New cards
Gills (squid)
red injected vein (brachial vein) and red arteries associated with it
56
New cards
branchial vein (squid)
red vein carrying oxygen blood from the gill
57
New cards
branchial heart (squid)
circular blue structures located at the top of the gills. they pump non oxygenated blood into the gills
58
New cards
What is a microtome used for?
holds specimen in place to get thin slice
59
New cards
what is grafting?
the process of fusing parts from two plants together
60
New cards
what is the above ground part of the cell?
the scion
61
New cards
what is a plant that retains its own root system?
stock or rootstock
62
New cards
What is osmosis?
The movement of water by diffusion
63
New cards
What is plasmolysis?
the separation (pulling away) of a plant's cell membrane from its cell wall, which occurs when the cell loses its water.
64
New cards
What is plant tissue culture?
the growing and manipulation of plant tissues
65
New cards
how do you accomplish plant tissue culture?
transferring a small tissue sample (explant) or even isolated cells to growth media under conditions that encourage formation of a (callus,) which is a mass of undifferentiated cells that forms as a normal part of the plant wound response
66
New cards
What is micropropagatiotn?
the practice of producing a multitude of new plants from a single callus via plant tissue culture.
67
New cards
What is histology?
the study of tissues in thin section.
68
New cards
what are the 5 main steps of histology?
fix, process, section, stain, mount
69
New cards
what is the fix step?
put the specimen in a permanent unchanging state, usually by chemical treatment with a fixative such as formalin (formaldehyde).
70
New cards
what is the process step?
dehydrate clear embedded
dehydrating the tissue using hygroscopic chemicals (frequently ethanol), treating the tissue with clearing agents that displace the dehydrate, and finally embedding the tissue in a medium such as paraffin or plastic resin
dehydrating the tissue using hygroscopic chemicals (frequently ethanol), treating the tissue with clearing agents that displace the dehydrate, and finally embedding the tissue in a medium such as paraffin or plastic resin
71
New cards
what is embedding?
first infiltrating and then encasing the tissue with the embedding medium to produce a rigid and fully structurally supported sample (i.e., holding everything physically in place so it doesn't squash and deform).
72
New cards
what is section step?
slice ultrathin
73
New cards
what is the stain step?
selectively color
74
New cards
what is the mount step?
secure to slide
75
New cards
how sponges eat
onges pass water through their bodies in a process known as filter-feeding. Water is drawn into the sponge through tiny holes called incurrent pores.
76
New cards
Fungi
mushroom, lichens, yeast, moles
77
New cards
typical monocot leaf
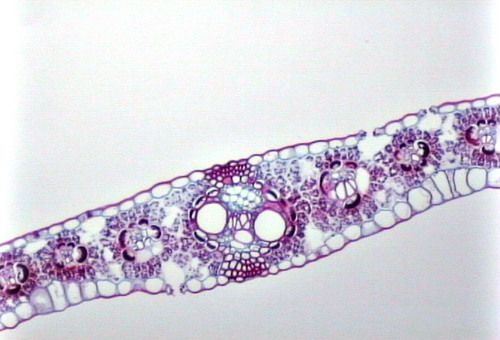
78
New cards
typical dicot leaf
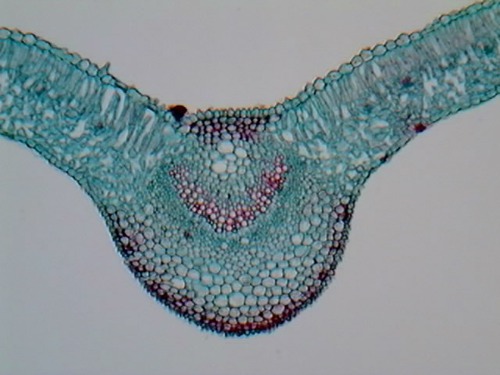
79
New cards
tilia stem
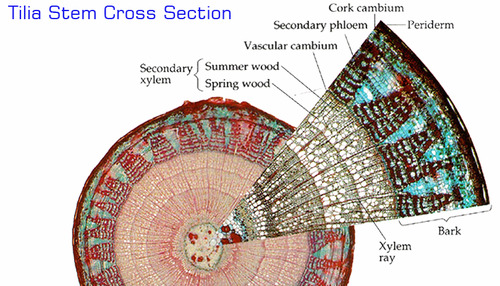
80
New cards
typical herbaceous dicot stem
epidermis: the outer layer of cells in the stem
Cortex: supportive collenchyma cells
vascular bundle: rings in dicot stems and contain transport tissue include the phloem, cambium, xylem and supportive sclerenchyma fiber cells.
phloem: transports synthesized food from the leaves to the rest of the plants.
xylem: conducts water and dissolved minerals through the stems to the leaves.
the cambium: located in the little white circles right below the phloem.
it is a non conclusive layer of cells between the xylem and phloem that contributes to secondary growth in the woody dicots
pith: the soft inner portion of the stem is composed of a thin walled parenchyma cells called the pith
Cortex: supportive collenchyma cells
vascular bundle: rings in dicot stems and contain transport tissue include the phloem, cambium, xylem and supportive sclerenchyma fiber cells.
phloem: transports synthesized food from the leaves to the rest of the plants.
xylem: conducts water and dissolved minerals through the stems to the leaves.
the cambium: located in the little white circles right below the phloem.
it is a non conclusive layer of cells between the xylem and phloem that contributes to secondary growth in the woody dicots
pith: the soft inner portion of the stem is composed of a thin walled parenchyma cells called the pith
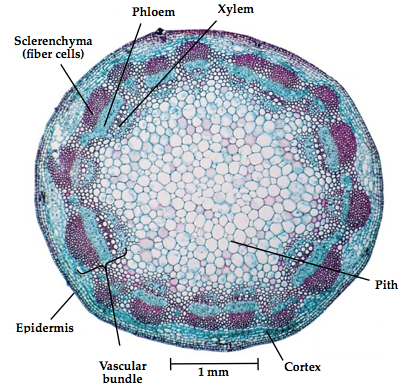
81
New cards
typical monocot stem
Epidermis: the outer layer of the stem
sclerenchyma cells: beneath the epidermis are thick walled cells that provide support for the stem.
Vascular bundles: are scattered throughout the monocot stem and contain xylem and phloem within the bundle.
xylem : translocation of food, water, and minerals through the stem to the upper parts of the plants.
supportive sclerenchyma cells:outline the vascular bundles and no vascular cambium is present.
phloem: provides a passageway for the transport of nutrients produced during photosynthesis to the rest of the plant.
parenchyma cells: the soft inner portion of the stem is composed of thin wall
sclerenchyma cells: beneath the epidermis are thick walled cells that provide support for the stem.
Vascular bundles: are scattered throughout the monocot stem and contain xylem and phloem within the bundle.
xylem : translocation of food, water, and minerals through the stem to the upper parts of the plants.
supportive sclerenchyma cells:outline the vascular bundles and no vascular cambium is present.
phloem: provides a passageway for the transport of nutrients produced during photosynthesis to the rest of the plant.
parenchyma cells: the soft inner portion of the stem is composed of thin wall
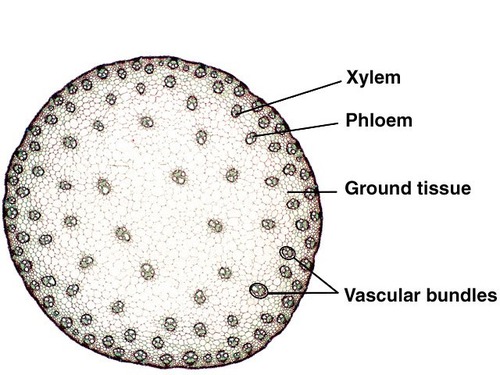
82
New cards
typical dicot root
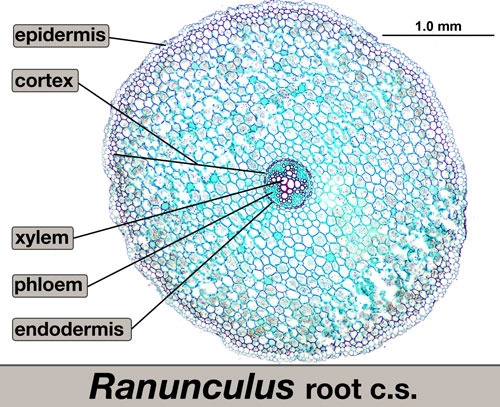
83
New cards
Typical Monocot Roots
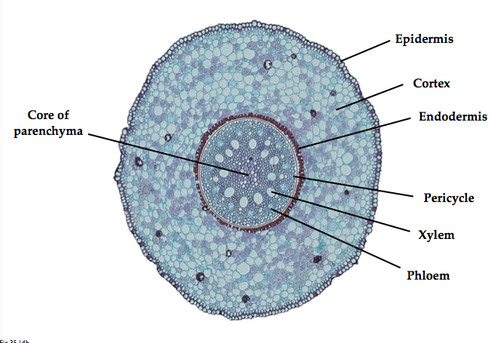
84
New cards
porifera
sponges, no symmetry, germ layers, coelom, digestion is cell dependent

85
New cards
porifera pt 2
fresh water and marine, simplest of all animals, asymmetrical, no systems for repro, digestion, respiration, sensory, extortion

86
New cards
gastropoda
shells, snails, and slugs.
typically have a large foot with a flat sole for crawling, a single coiled shell that covers the soft body, and a head that bears a pair of eyes and tentacles. However, they are so diverse that some forms lack shells, while animals in one genus have shells with two halves, like bivalves.
typically have a large foot with a flat sole for crawling, a single coiled shell that covers the soft body, and a head that bears a pair of eyes and tentacles. However, they are so diverse that some forms lack shells, while animals in one genus have shells with two halves, like bivalves.
87
New cards
Bilalvia
possessing two shells secreted by a mantle that extends in a sheet on either side of the body. The oldest part of the shell, the umbo, can be recognized as a large hump on the anterior end of the dorsal side of each shell.
88
New cards
Agaricus bisporus
mushroom
89
New cards
monocot plant
Flower parts in multiples of three, marked by seeds with a single cotyledon, parallel-veined leaves, Stem vascular bundles scattered, Roots are adventitious
90
New cards
dicot plant
their vascular structures form net-like veins, instead of parallel ones, Flower parts in multiples of four or five, Stem vascular bundles in a ring, Roots develop from radicle
91
New cards
fern
non flowering, hat possess true roots, stems, and complex leaves and that reproduce by spores. gynosperms
92
New cards
dicot leaf epidermis
Dicot leaf has a thin layer of cuticle on both the upper and lower epidermis, whereas monocot leaf has thick cuticle on the upper epidermis and thin on the lower epidermis
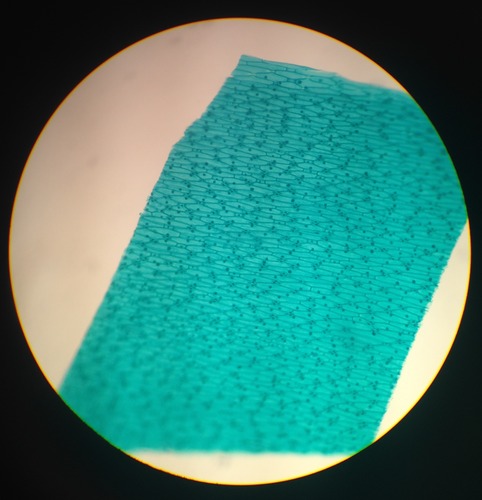
93
New cards
monocot vs dicot
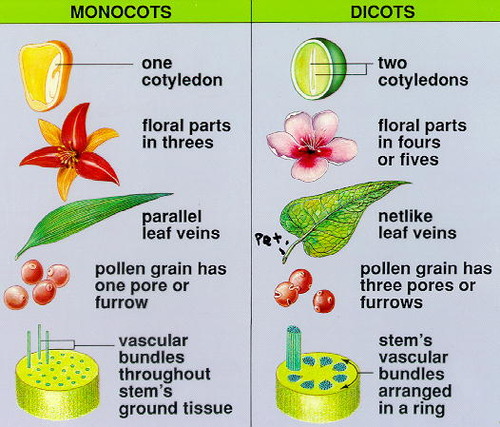
94
New cards
phylum porifera
Sponges are sessile filter feeders that use flagellated cells called choanocytes
95
New cards
what are examples of phylum porifera?
Sponges

96
New cards
what are phylum rotifera?
aquatic animals that capture food via a (trochal disk), which is a ring of cilia surrounding their mouth.
97
New cards
what is an example of phylum rotifera
rotifers
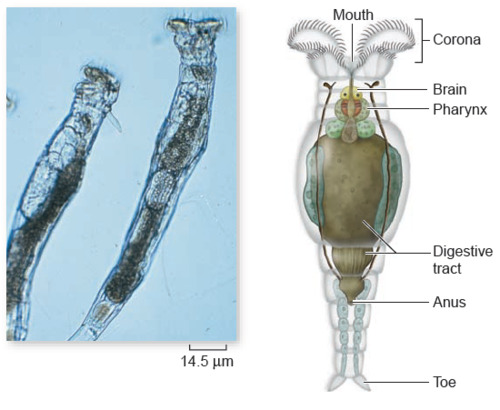
98
New cards
What are Phylum Platyhelminthes?
known as flatworms. can be segmented or unsegmented.
no circularly system
no circularly system
99
New cards
what are examples of Phylum Platyhelminthes
tapeworm and flatworms, planaria

100
New cards
what are Phylum Annelida
segmented worms that are not flat.