CLINICAL EXAM - brain stem SDL
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
what are components of the brain stem?
midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata

What are the functions of the brain stem?
Cardiovascular system- controlled by the medulla oblongata.
Respiration- medulla oblongata.
Pain sensitivity- midbrain.
Alertness, awareness, consciousness- pons.
what are causes of brain stem disease?
Haemorrhage - escape of blood from a ruptured vessel
Tumours
Ischaemia - restriction in blood supply to tissues, causing a shortage of oxygen needed for cellular metabolism.
Stroke
what are the 4 types of brain haemorrhage?
Subdural
- collection of blood gathers between inner layer of dura mater and arachnoid mater
Extradural
- bleeding occurs between the dura mater and the skull
Subarachnoid
- bleeding into the subarachnoid space
Intracerebral
- intracranial bleed that occurs within the brain tissue or ventricles, caused by hypertension, or head trauma.
how is a stroke caused?
caused by poor blood flow to the brain, resulting in cell death
2 main types;
- ischemic - due to lack of blood flow, e.g a blockage
- haemorrhagic - due to bleeding
what is vestibular disease?
sudden non-progressive disturbance of balance
2 types - peripheral and central
what is peripheral vestibular disease?
outside the CNS
lesions in the vestibular portion of cranial nerve VIII
what is central vestibular disease?
Inside the CNS, the brainstem
lesions in the vestibular nuclei in the medulla oblongata
what is the structure of the brainstem?
white matter with bits of gray matter scattered through it
connection between the cerebral hemispheres with the medulla and the cerebellum.
what is the structure and function of the midbrain? (mesencephalon)
involved in vision, hearing, motor control, sleep/wake, arousal and temperature regulation.
Caudally joins the pons and rostrally it adjoins the diencephalon (thalamus,hypothalamus, etc.).
what is superior colliculus?
a structure in the midbrain that control of eye movements
what is the red nucleus?
midbrain structure involved in coordination of muscle contractions
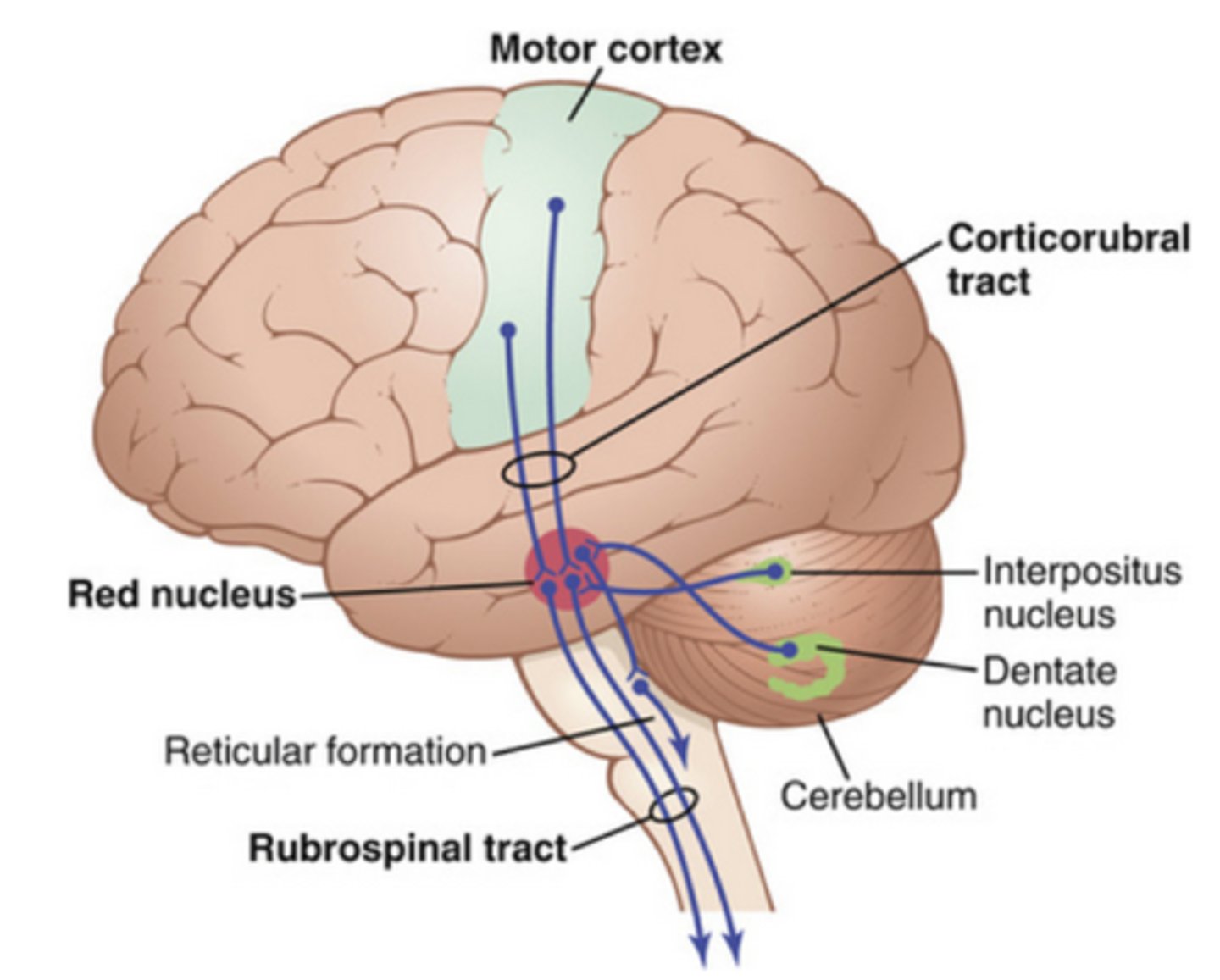
what is the structure and function of the pons?
Arousal, controlling autonomic functions, relaying sensory information between the cerebrum and cerebellum, a sleep centre- dreams
Which portion of the brainstem is continuous with the spinal cord?
medulla oblongata
Which is NOT a part of the brainstem?
A) medulla oblongata
B) midbrain
C) pons
D) thalamus
thalamus
Which of the following brain regions does NOT belong with the others?
A) medulla oblongata
B) midbrain
C) pons
D) thalamus
thalamus
What are the enlargements on the medulla oblongata that are involved in conscious skeletal muscle control?
pyramids
Which of the following serves as a motor center that is involved in maintaining muscle tone and coordinating movements?
A) inferior olivary nucleus
B) red nucleus
C) substantia nigra
D) suprachaismatic nucleus
c. substantia nigra
Because of injuries received in an automobile accident, a young man remains hospitalized in a coma. It is likely the injuries affected his
A) amygdala.
B) hippocampus.
C) limbic system.
D) reticular formation
D. reticular formation
Another term for "midbrain" is
A) pons.
B) mesencephalon.
C) cerebrum.
D) cerebellum.
mesencephalon
The _________ is the most-specific part of the midbrain that is an integral part of the auditory pathway.
A) corpora quadrigemina
B) superior colliculi
C) inferior colliculi
D) tectum
c. inferior colliculi
Which of the following is NOT one of the three large nerve tracts connecting the cerebellum to the rest of the central nervous system?
A) superior cerebellar peduncles
B) middle cerebellar peduncles
C) inferior cerebellar peduncles
D) anterior cerebellar peduncles
anterior cerebellar peduncles
Cerebral cortex ridges are called
folia
The simplest part of the cerebellum is (are) the
flocculonodular lobe
Which of the following is (are) NOT a major part of the cerebellum?
A) tegmentum
B) flocculonodular lobe
C) vermis
D) lateral hemispheres
tegmentum
Which of the following is the largest feature of the diencephalon?
A) thalamus
B) subthalamus
C) epithalamus
D) hypothalamus
thalamus
The small stalk connecting the two lateral portions of the thalamus is known as the
A) interthalamic adhesion
B) intermediate mass
C) Both A and B.
D) Neither A nor B.
C. Both A and B.
Axons carrying auditory information synapse in the
A) medial geniculate nucleus
B) lateral geniculate nucleus
C) ventral geniculate nucleus
D) None of the above.
medial geniculate nucleus
Axons carrying visual information synapse in the
A) medial geniculate nucleus
B) lateral geniculate nucleus
C) ventral geniculate nucleus
D) None of the above.
B) lateral geniculate nucleus
Axons carrying information other than visual or auditory information synapse in the
A) medial geniculate nucleus
B) lateral geniculate nucleus
C) ventral geniculate nucleus
D) None of the above.
C) ventral geniculate nucleus
Which of the following is NOT a part of the diencephalons?
A) hypothalamus
B) pineal gland
C) pons
D) thalamus
pons