Reproductive System- Externa Genitalia
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
Chromosomal sex
XX or YY (among other combinations)
Phenotypic sex
appearance of sex
Gender
how a person identifies- may not align with sex
sex and gender occur on spectrum
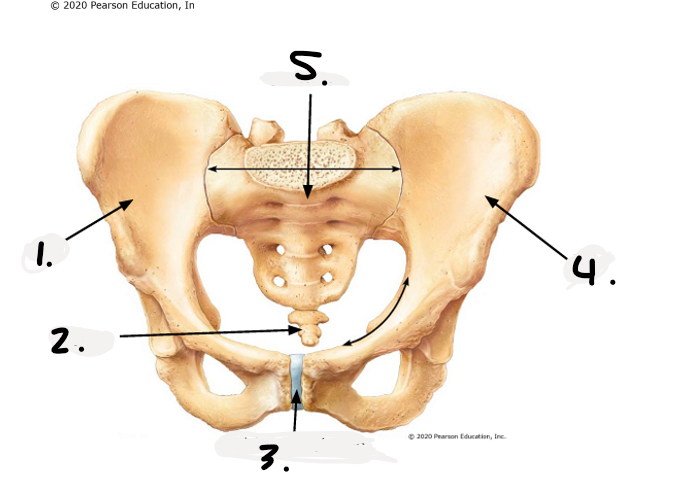
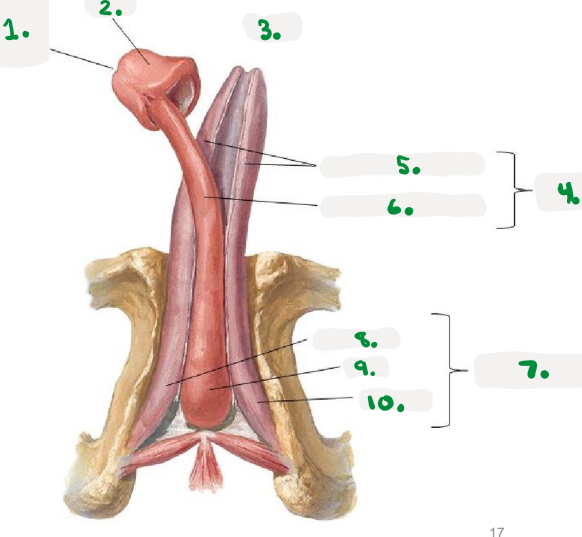
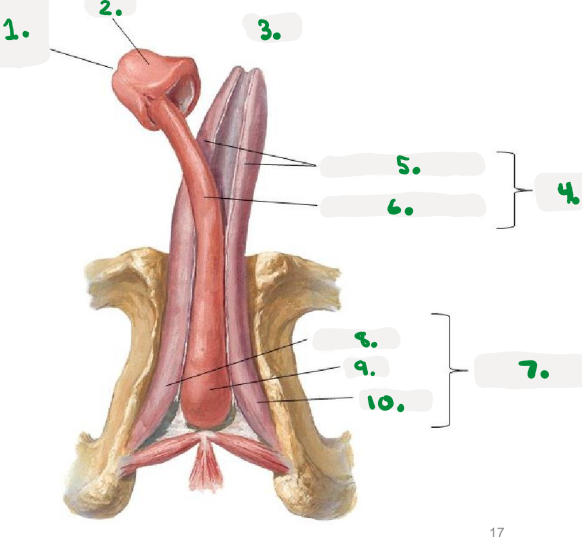
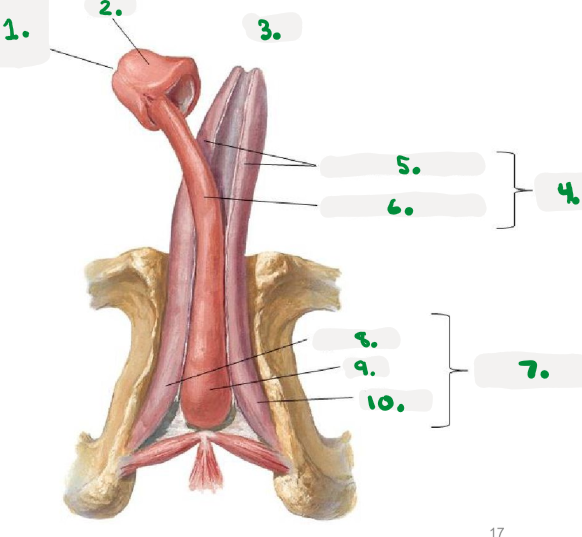
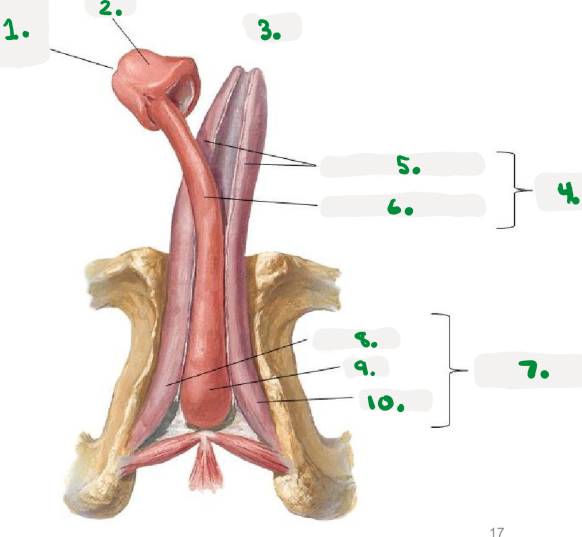
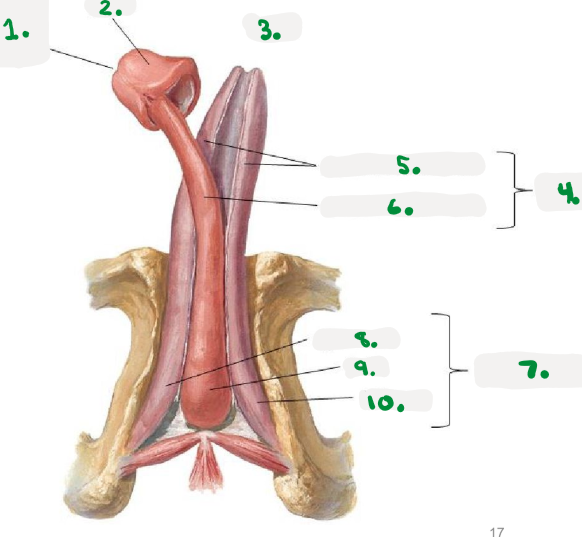
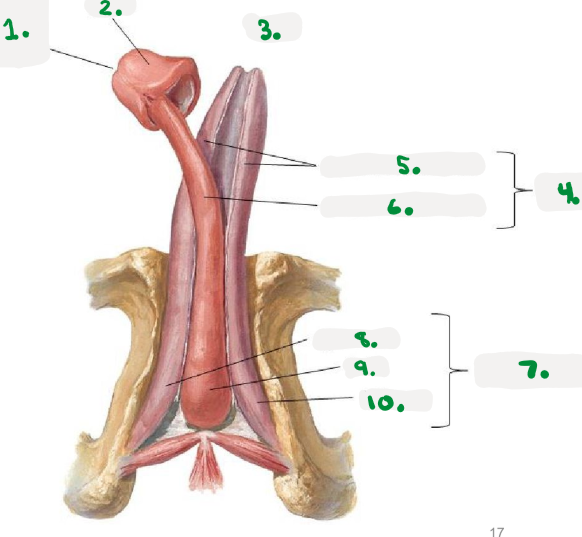
1.
right os coxae
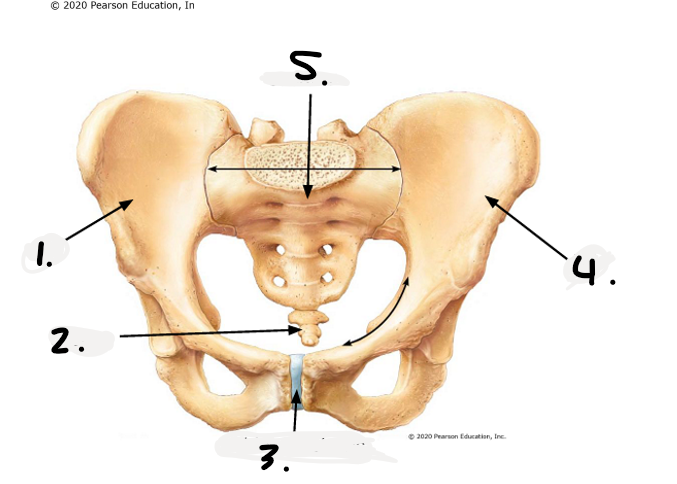
2.
coccyx
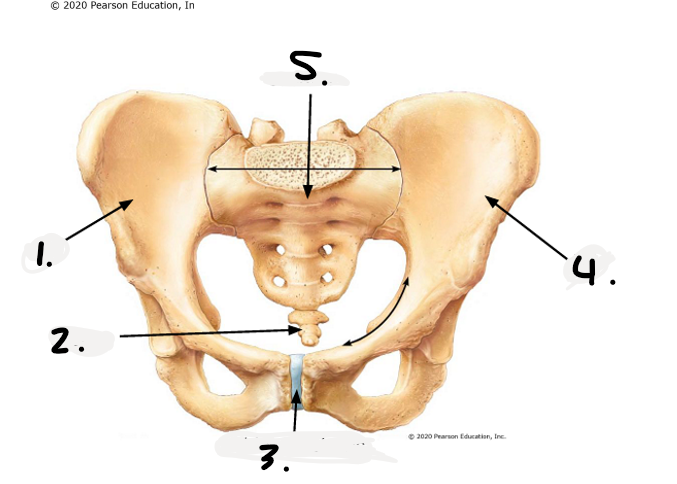
3.
public symphysis
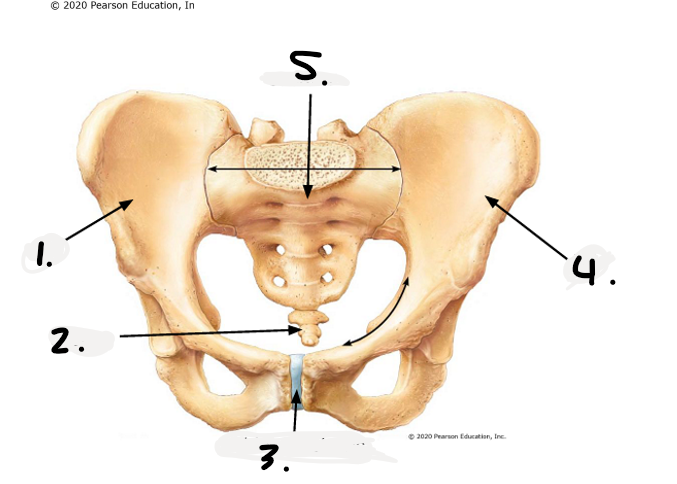
4.
left os coxae
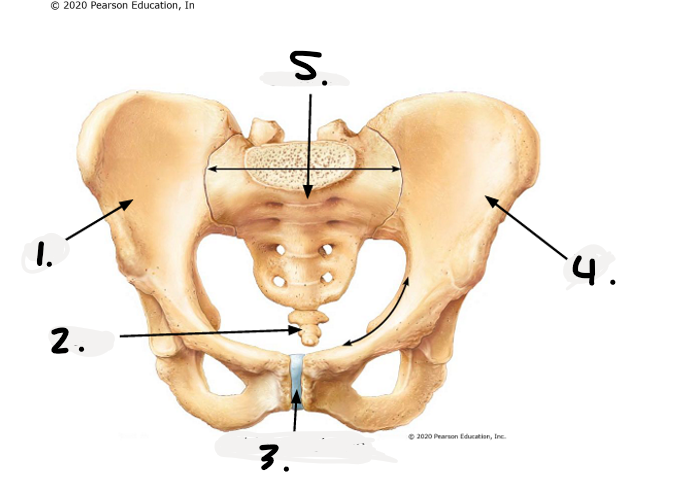
sacrum
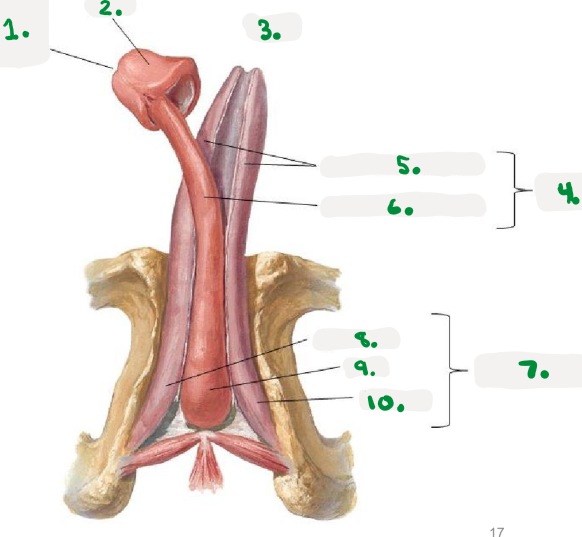
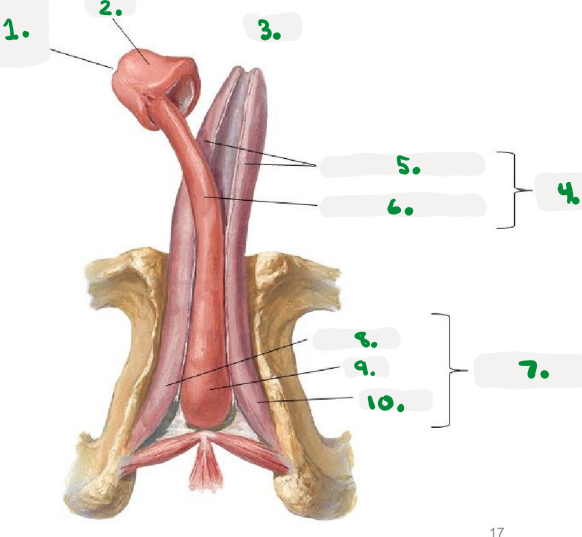
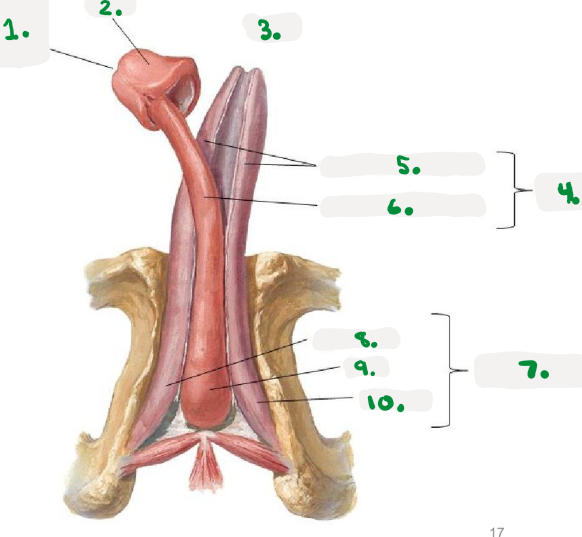
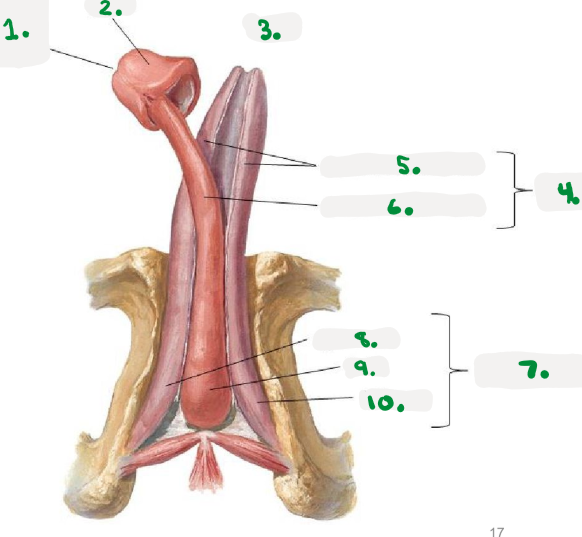
Pelvic diaphragm
>Pelvic floor
>sheets of muscle from pubis to coccyx
>supports pelvic organs
Pelvic organs?
Bladder, vagina, uterus, prostate, rectum.
Damage in pelvic diaphragm =
pelvic floor dysfunction
>difficulty with bathroom (urination+ defecation)
>common after giving birth
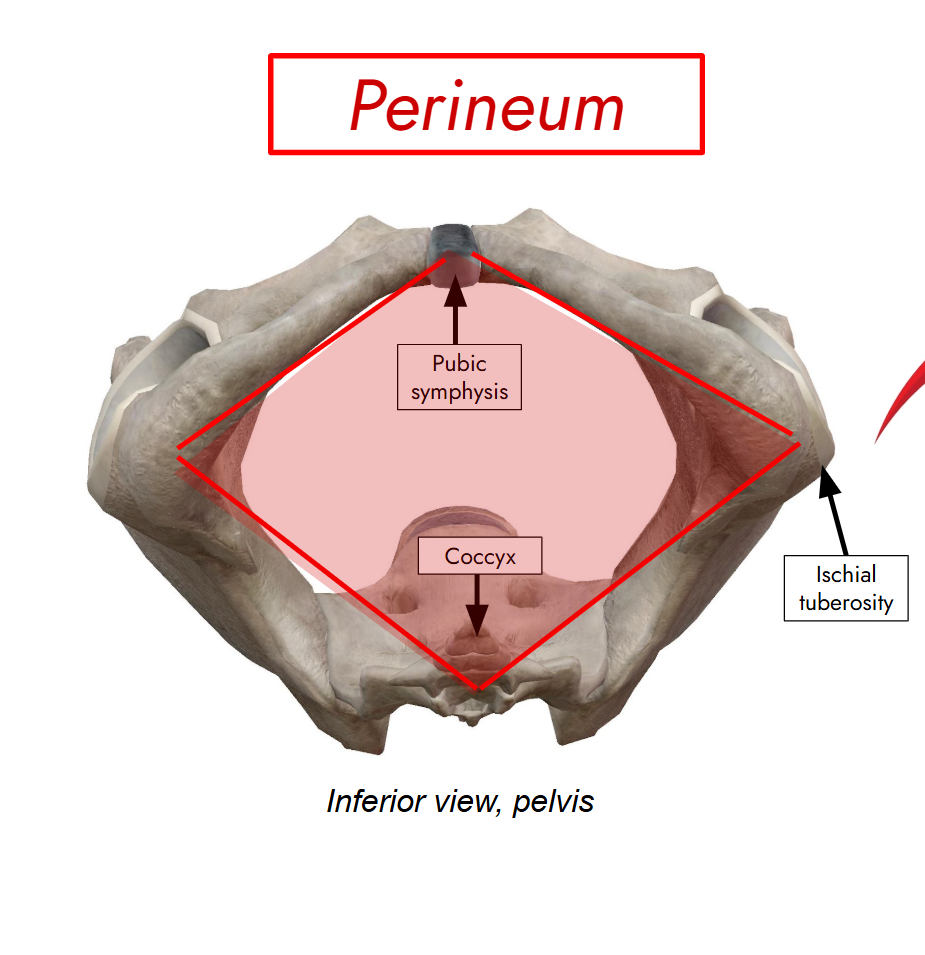
Perineum
area inferior to pelvic floor
divided into:
Urogenital triangle
Anal triangle
Male primary sex organs (gonads)
Testes - sperm
Female primary sex organs (gonads)
Ovaries- egg/ovum
Female secondary structures?
>vulva (external genital)
>vagina, uterus, uterine tubes
>paraurethral glands, greater vestibular glands
Male secondary structures
>epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory ducts, urethra, >penis
> Seminal vesicles, prostate gland, bulbourethral gland
intersex
Individuals born with reproductive or sexual anatomy that does not fit typical male or female definitions.
What are secondary sex organs?
>structures that support/ facilitate reproduction but do not produce gametes
what are the two types of erectile tissue?
Corpora cavernosa
Corpus spongiosum
What features do Corpora Cavernosa and Corpus Spongiosum share?
>Blood supply: Highly vascular
>Innervation: extensive (very sensitive)
>covered in musculature
What features does Corpora Cavernosa have?
>Musculature: ischiocavernosus muscle
>Tunic: THICK tunica albuginea
>FUNC: Erection Potency
What feature does Corpus Spongiosum have?
>Musculature: bulbospongiosus muscle
>Tunic: thin tunica albuginea
>FUNC: Cushioning and patency
Vulva includes
>Mons Pubis
>Labia majora
>Labia Minora
>Vestibule
Vestibule is
space between labia minora
>contain openings for urethra and vagina
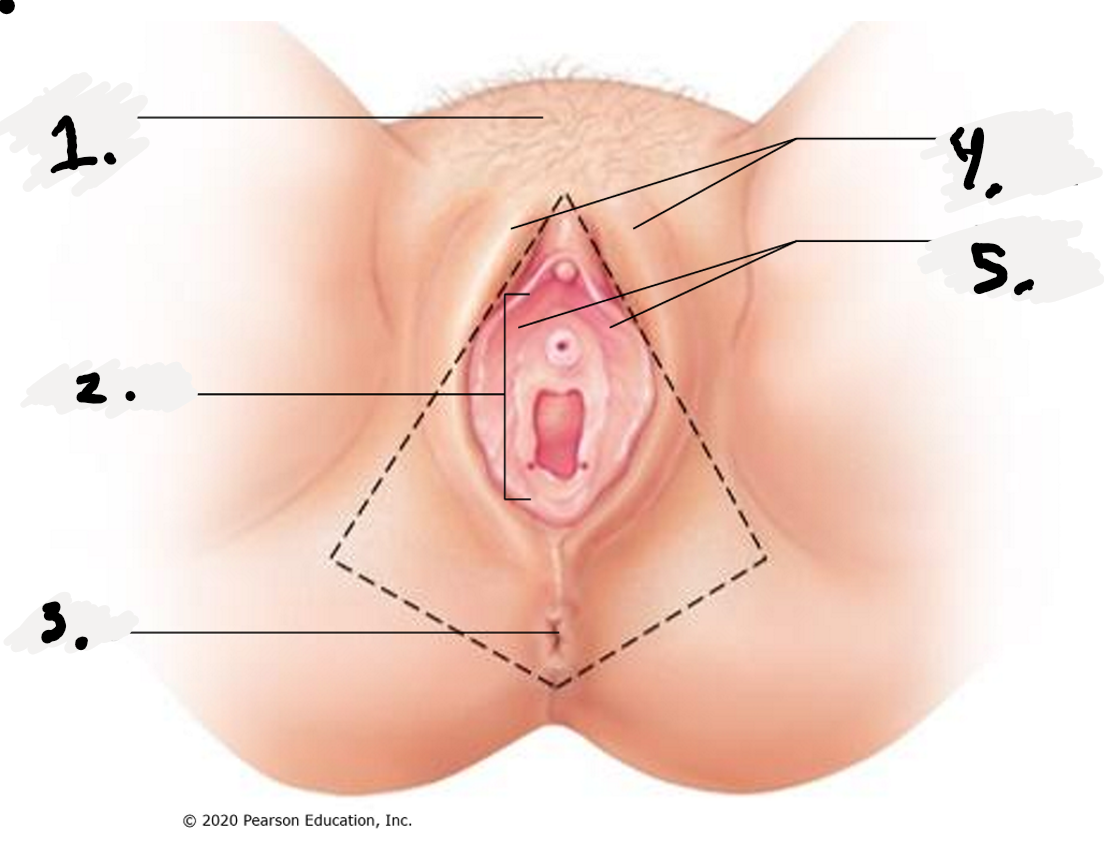
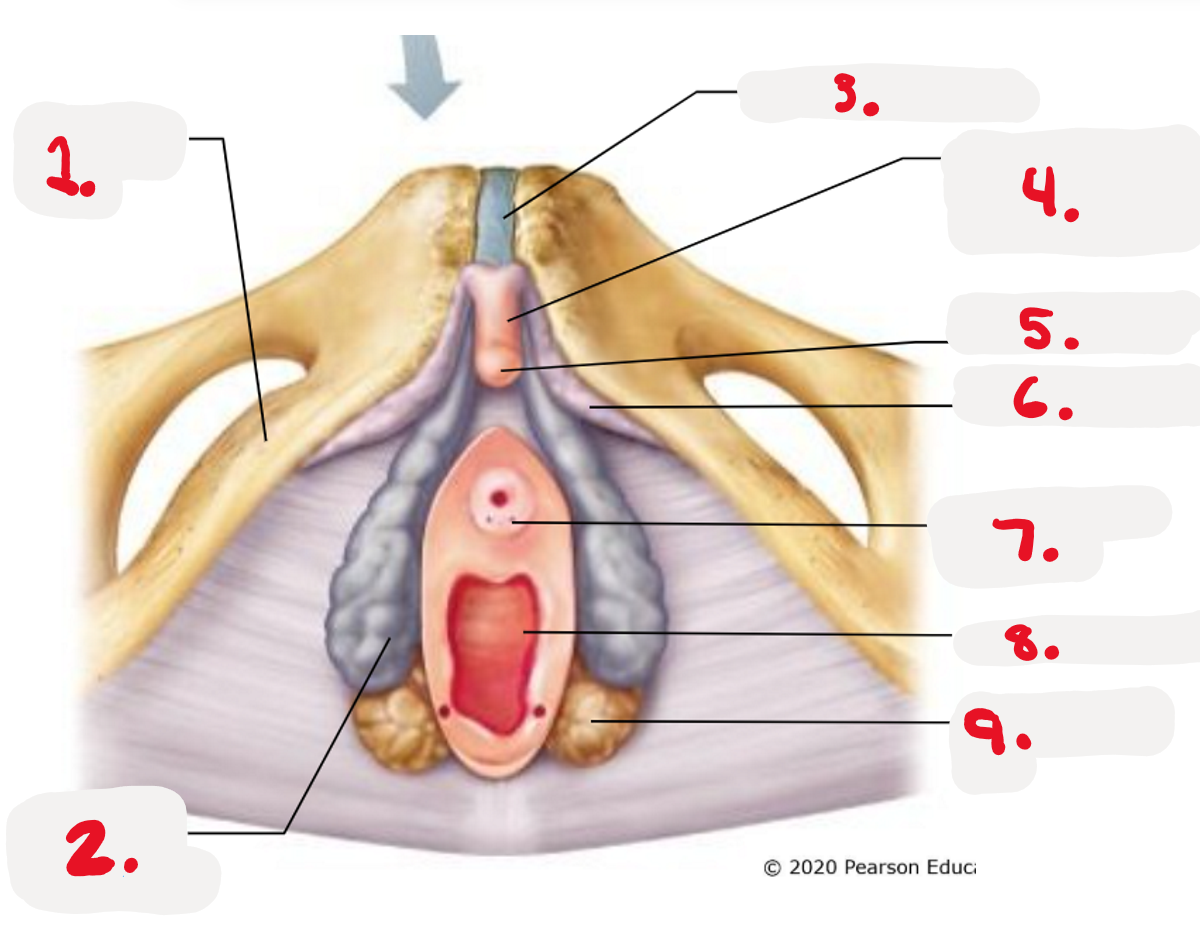
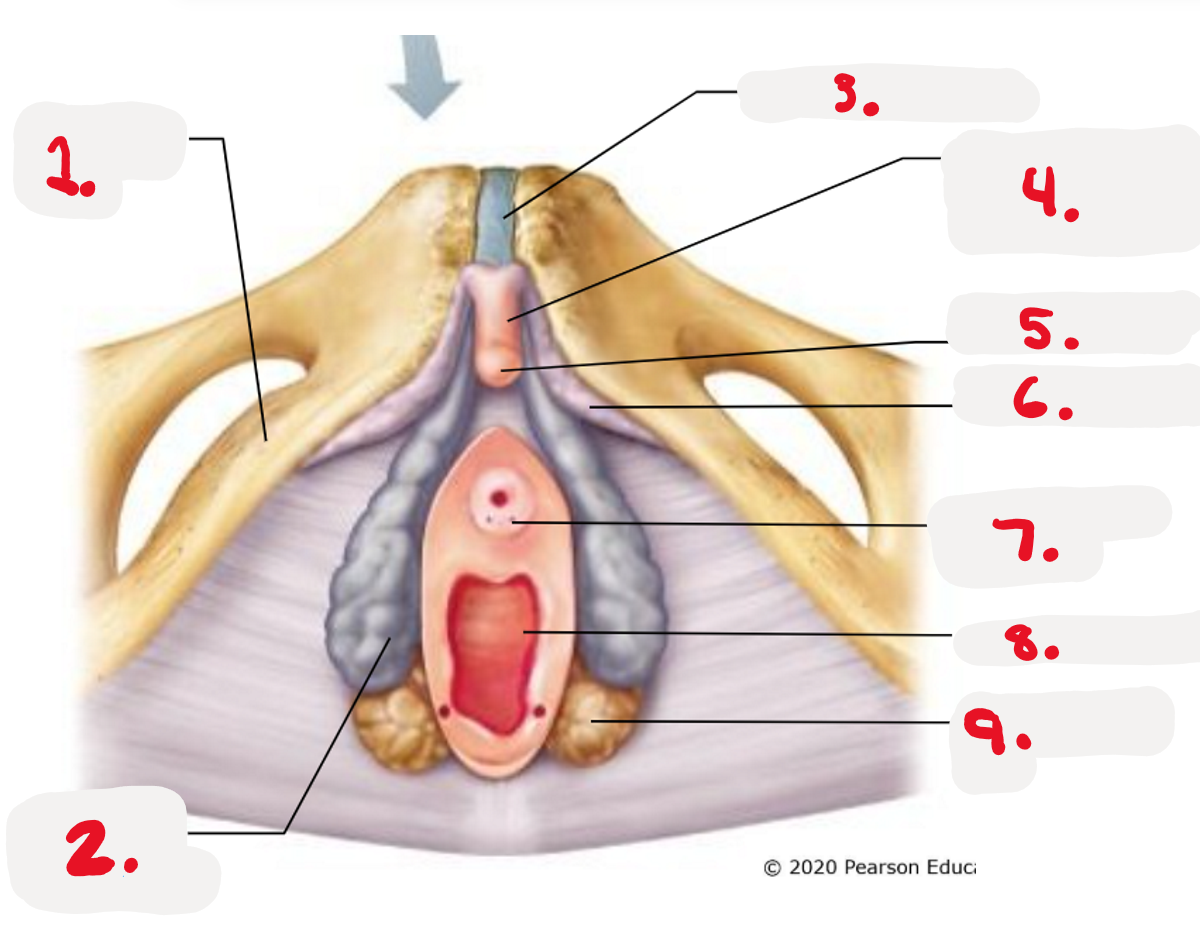
1.
Mon Pubis
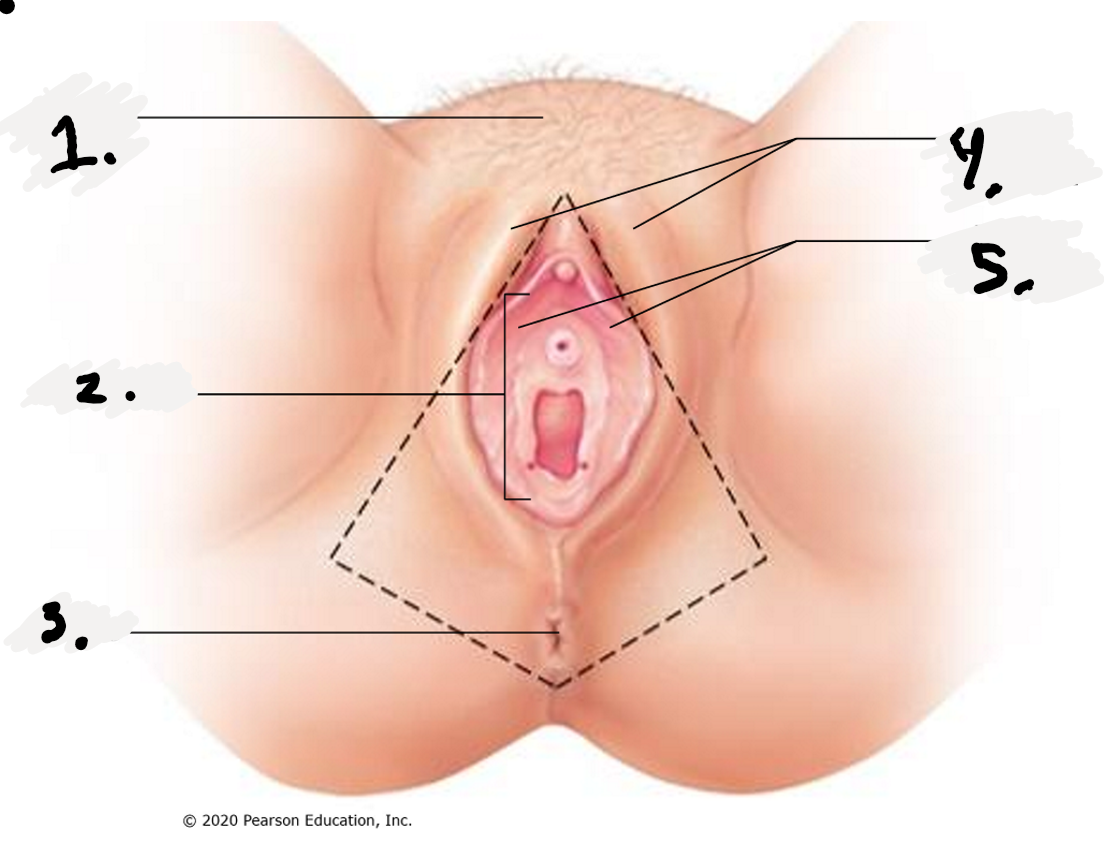
2.
Vestibule
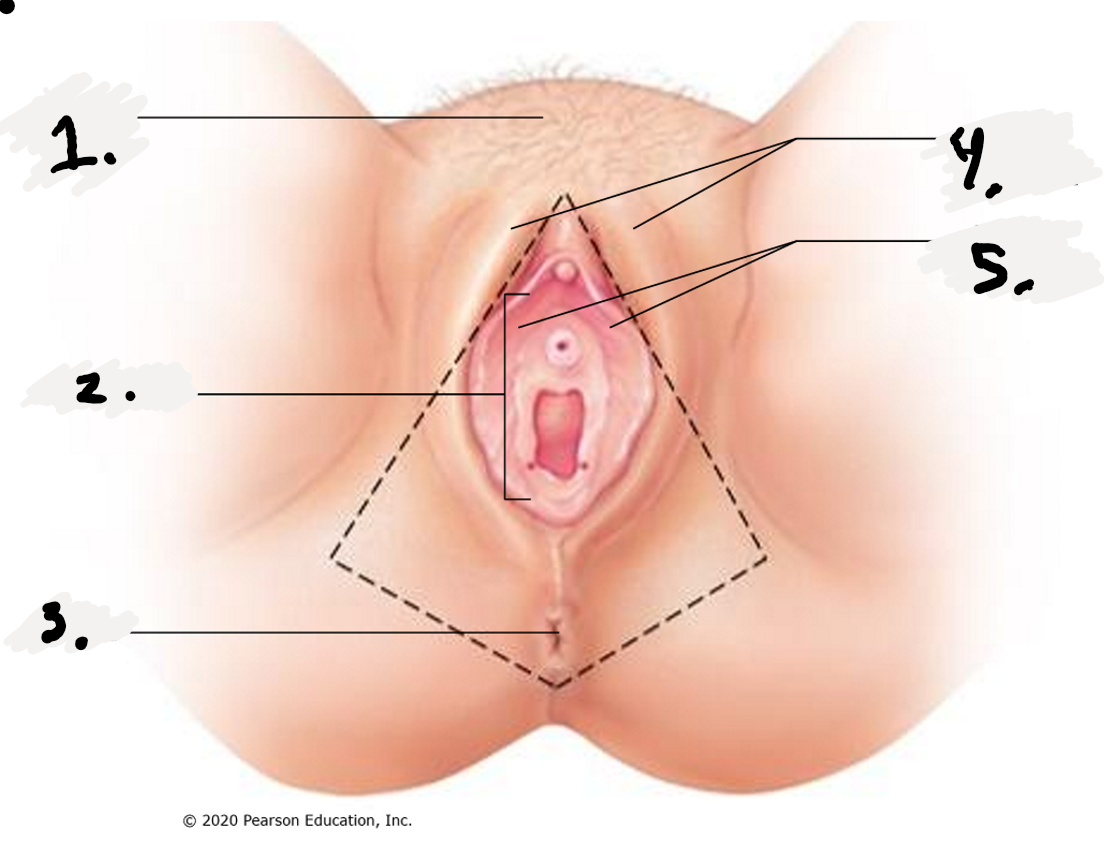
3.
Anus
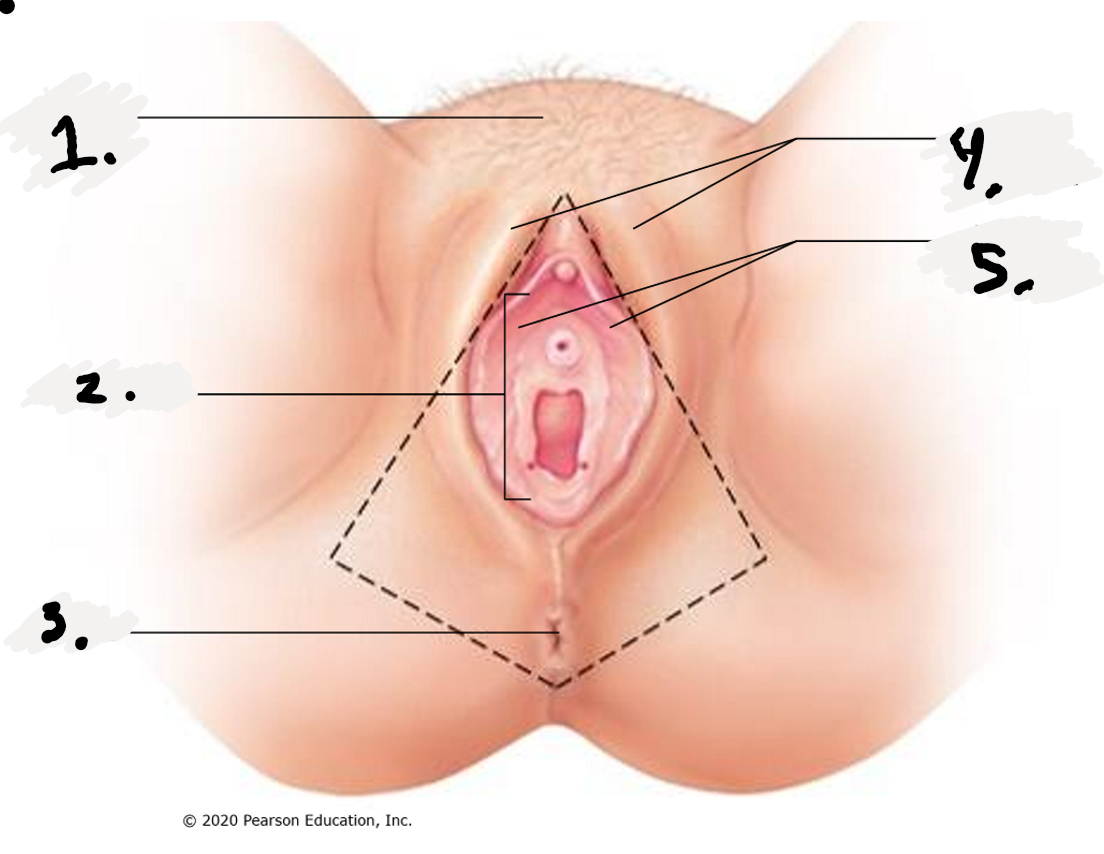
4.
Labial Majora-The outer folds
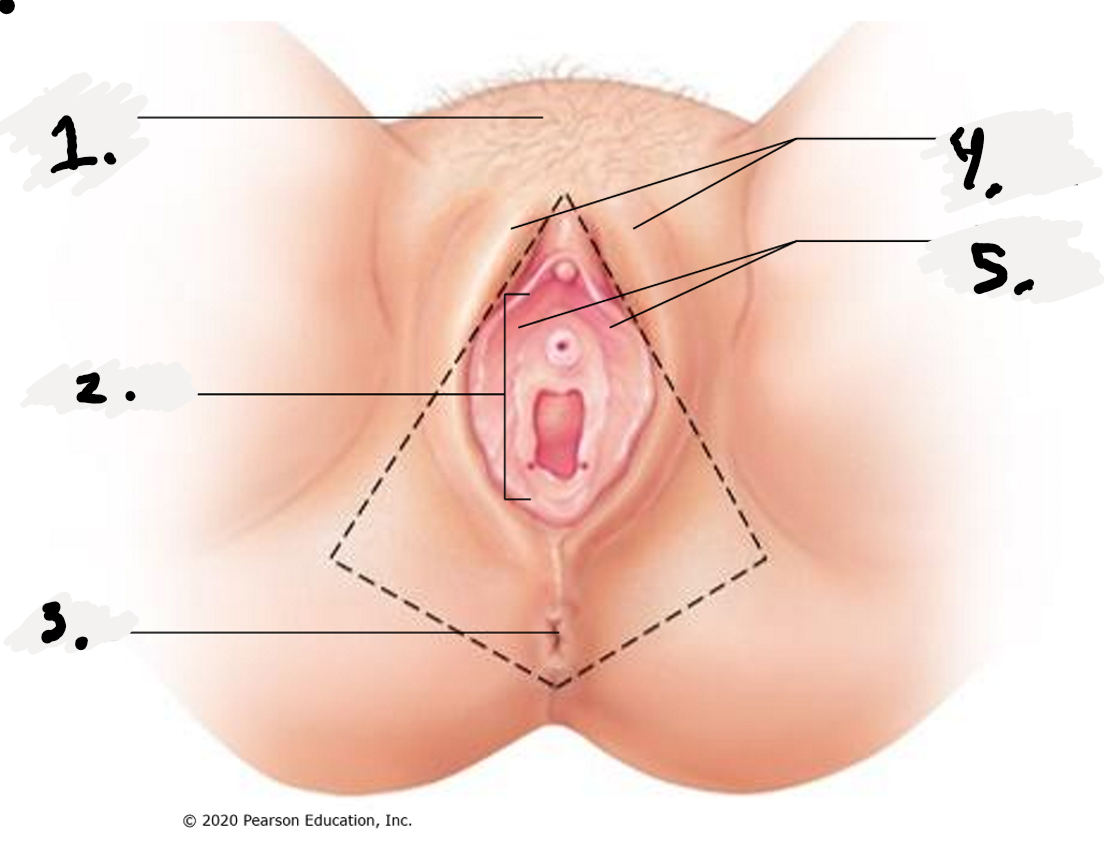
5.
Labial Minora
What structures are found within vestibule?
>external urethra orifice
>Vaginal orifice
>Paraurethral glands
>Greater Vestibular glands
>clitoris and prepuce
Paraurethral glands
>Lateral to urethra
>Secrete mucus lubricate/protect vaginal orifice
>Source of ejaculation during sexual arousal
Greater Vestibular gland
>lateral to vaginal orifice
>secrete lubricating mucus in2 vagina during arousal
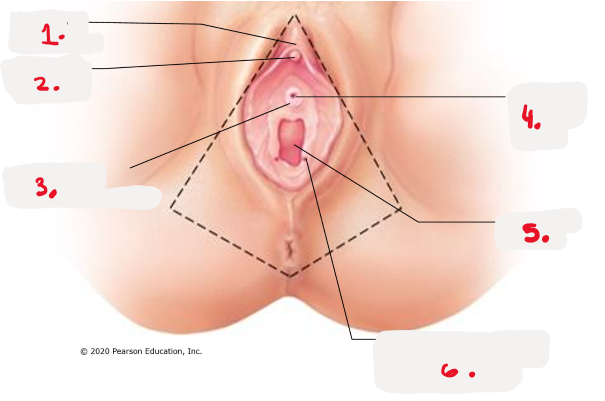
1.
prepuce to clitoris
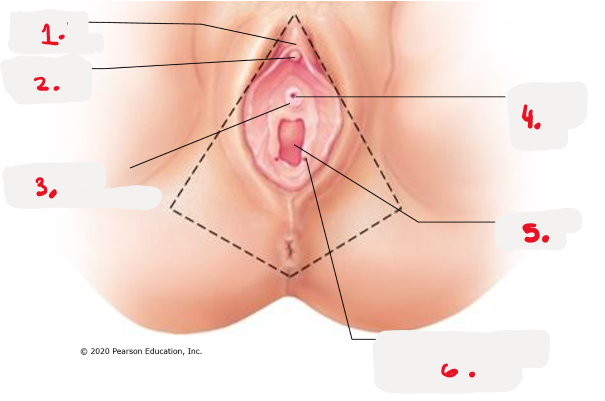
clitoris (glans) pic
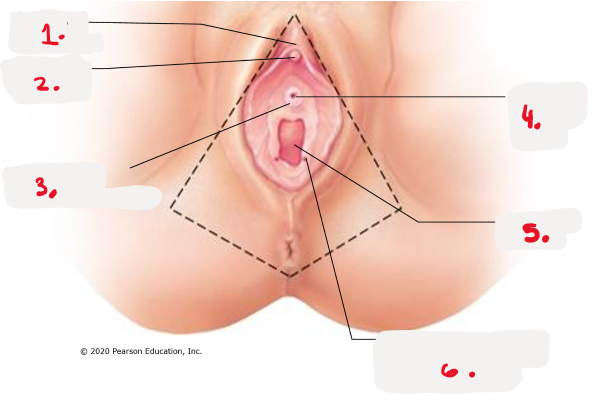
3.
opening for paraurethral gland pic
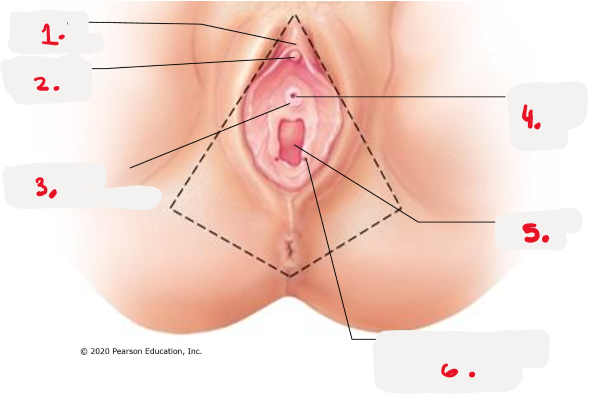
4.
external urethral orifice pic
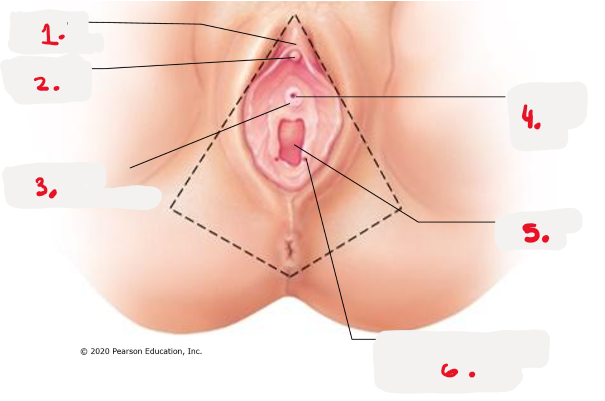
5.
vaginal orifice pic
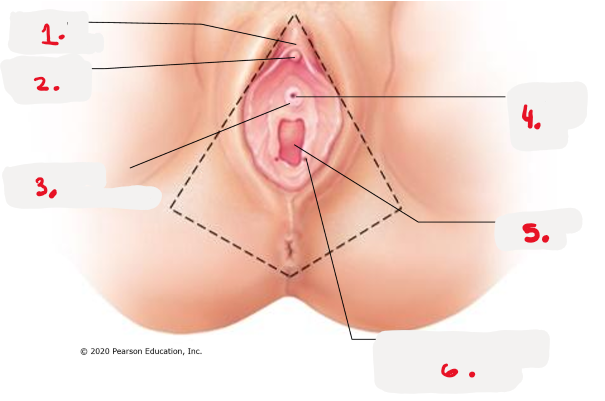
6.
opening of duct for greater vestibular gland pic
prepuce
= foreskin
>fold of skin surrounding clitoris
Erectile tissues?
>clitoris
>bulbs of vestibule
clitoris
body- corpora cavernosa
glands- corpus spongiosum
body extend posteriorly as crura along ischiopubic ramus
Bulb of vestibule
composed of corpus spongiosum
>erectile tissue on either side of vaginal orifice
>anchors on2 perineum
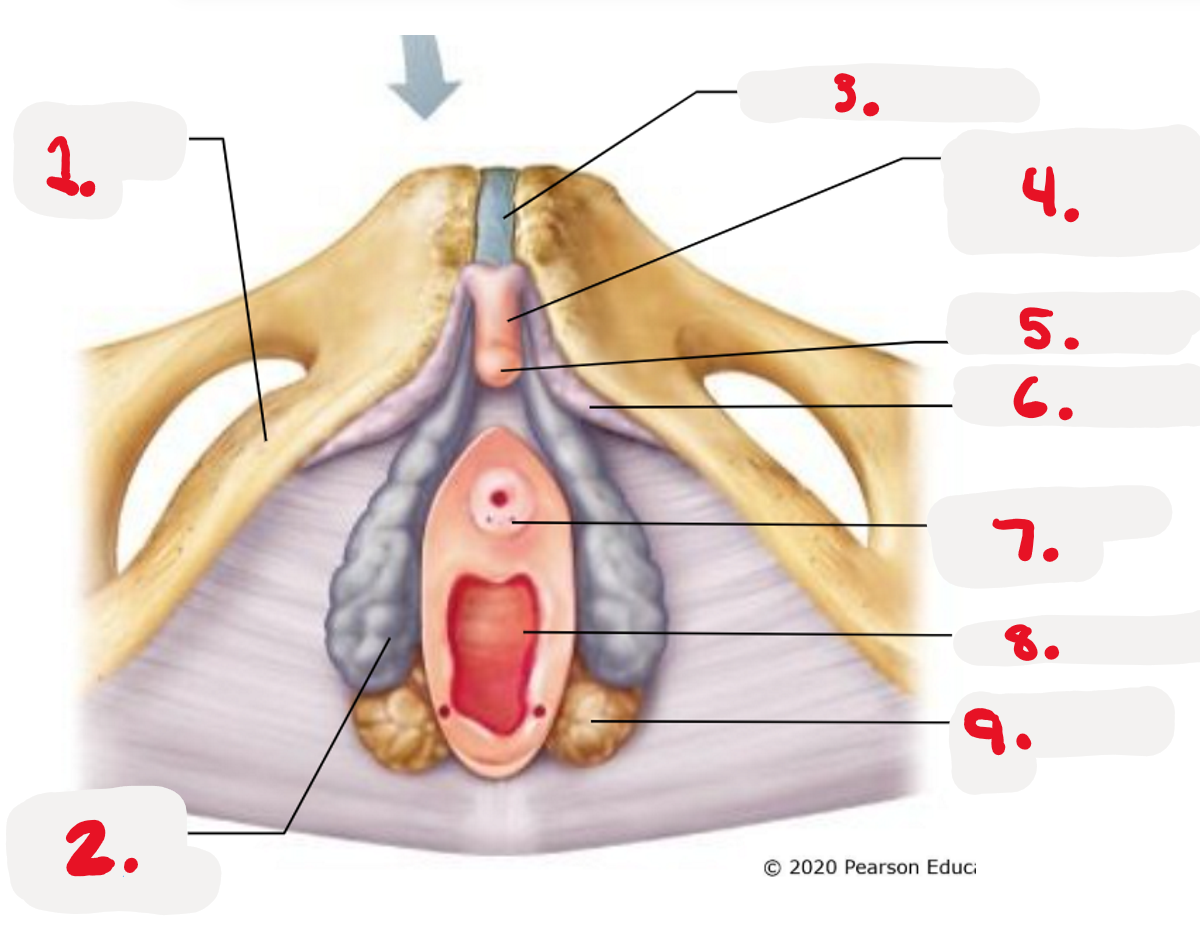
1.
ischiopubic ramus
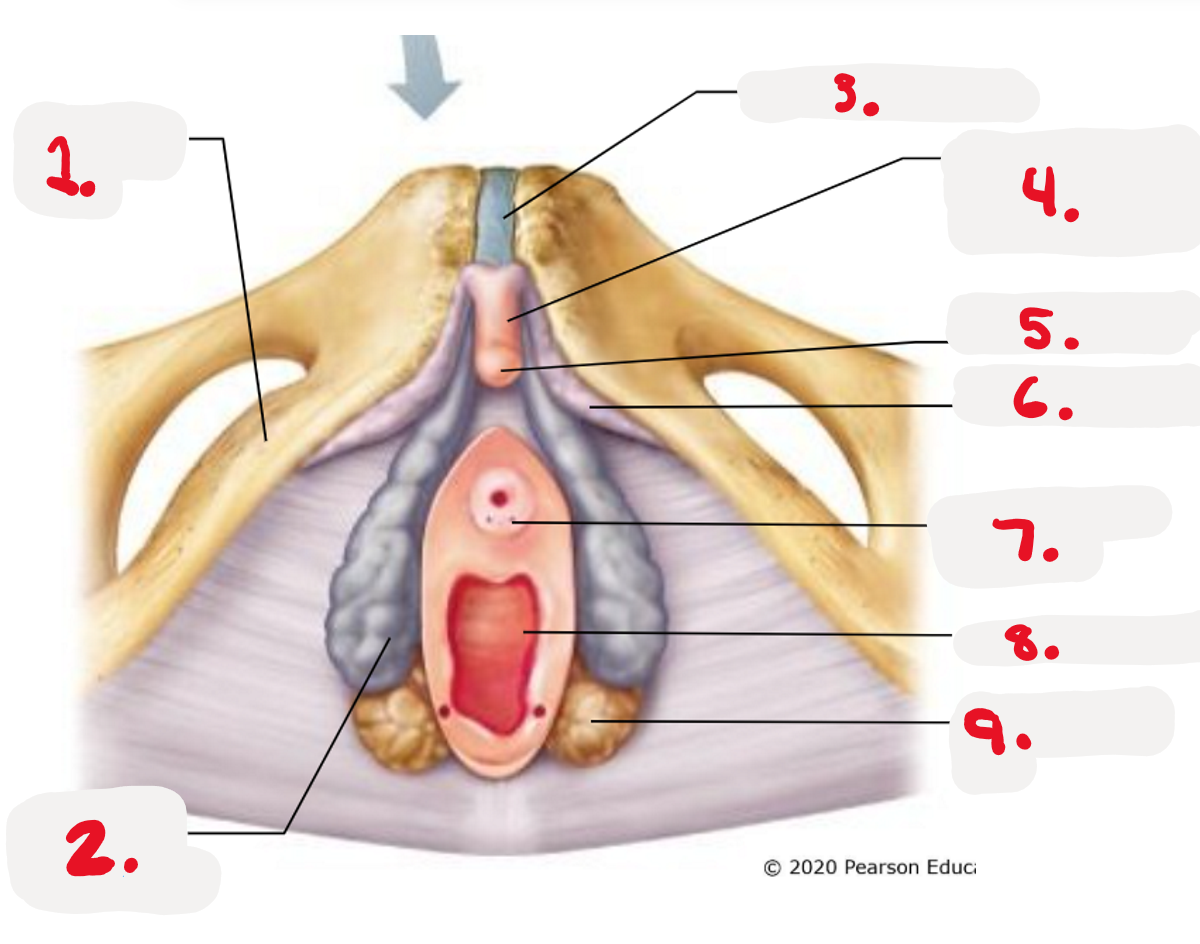
2.
bulb of vestibule
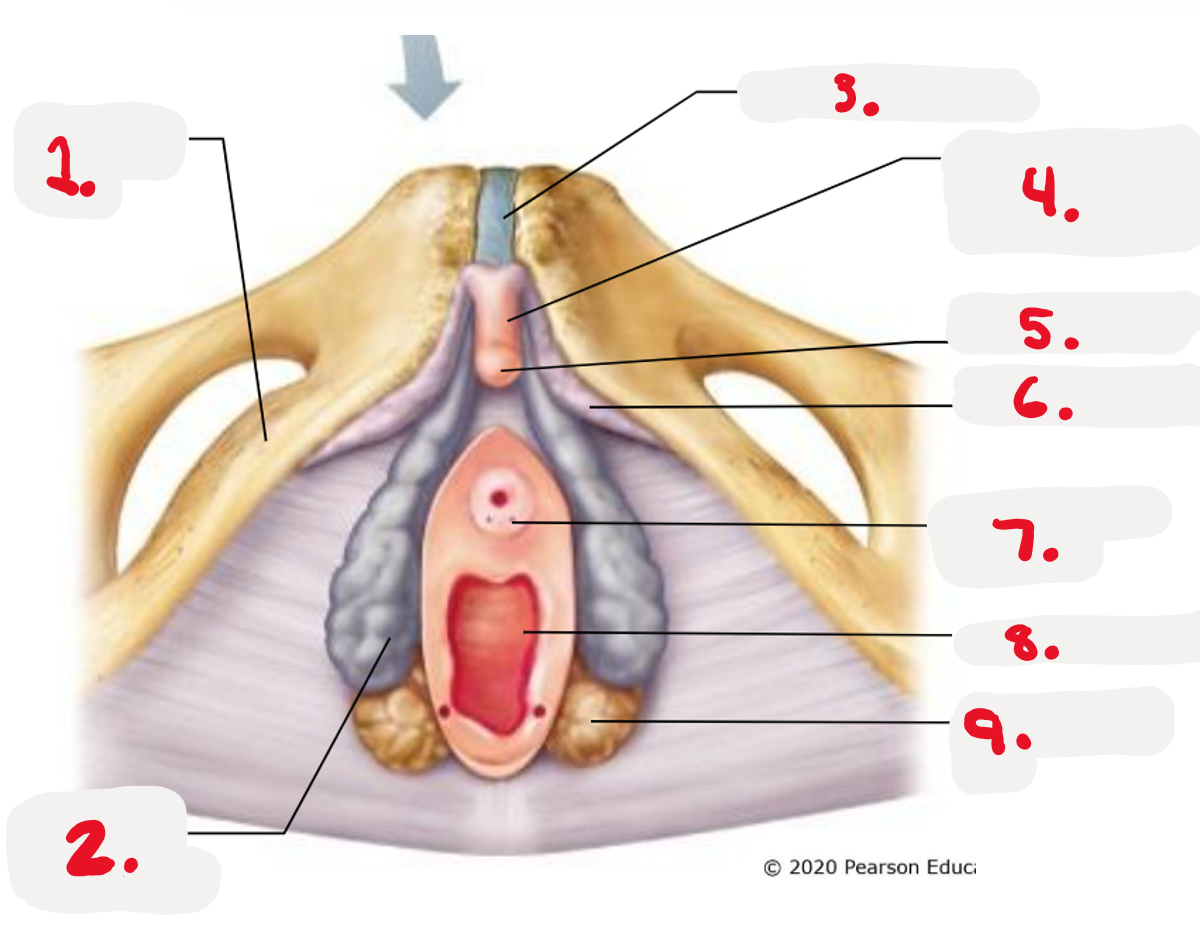
3.
pubic symphysis
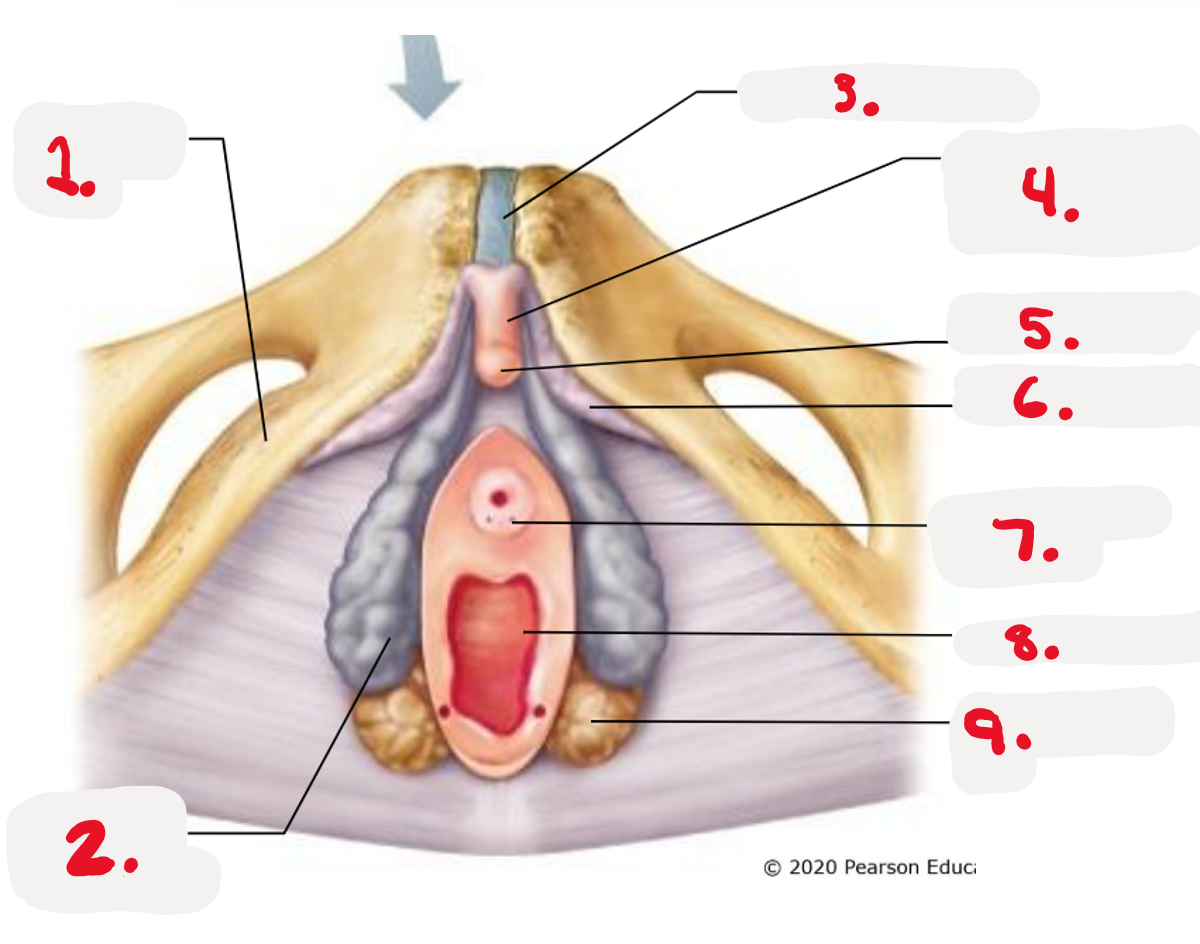
4.
Body of clitoris ~ Corpora cavernosa
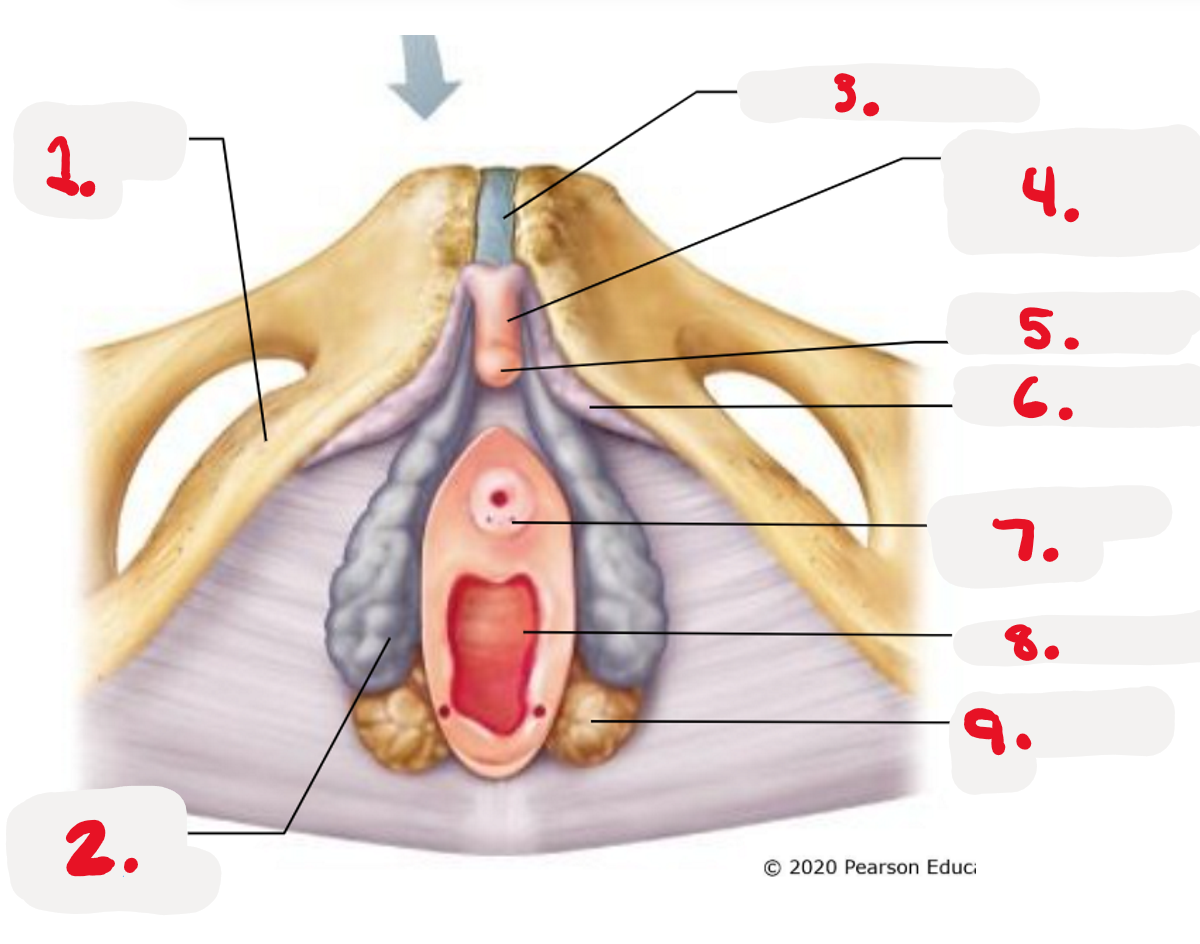
5.
Glands of clitoris ~ Corpus Spongiosum
(the head)
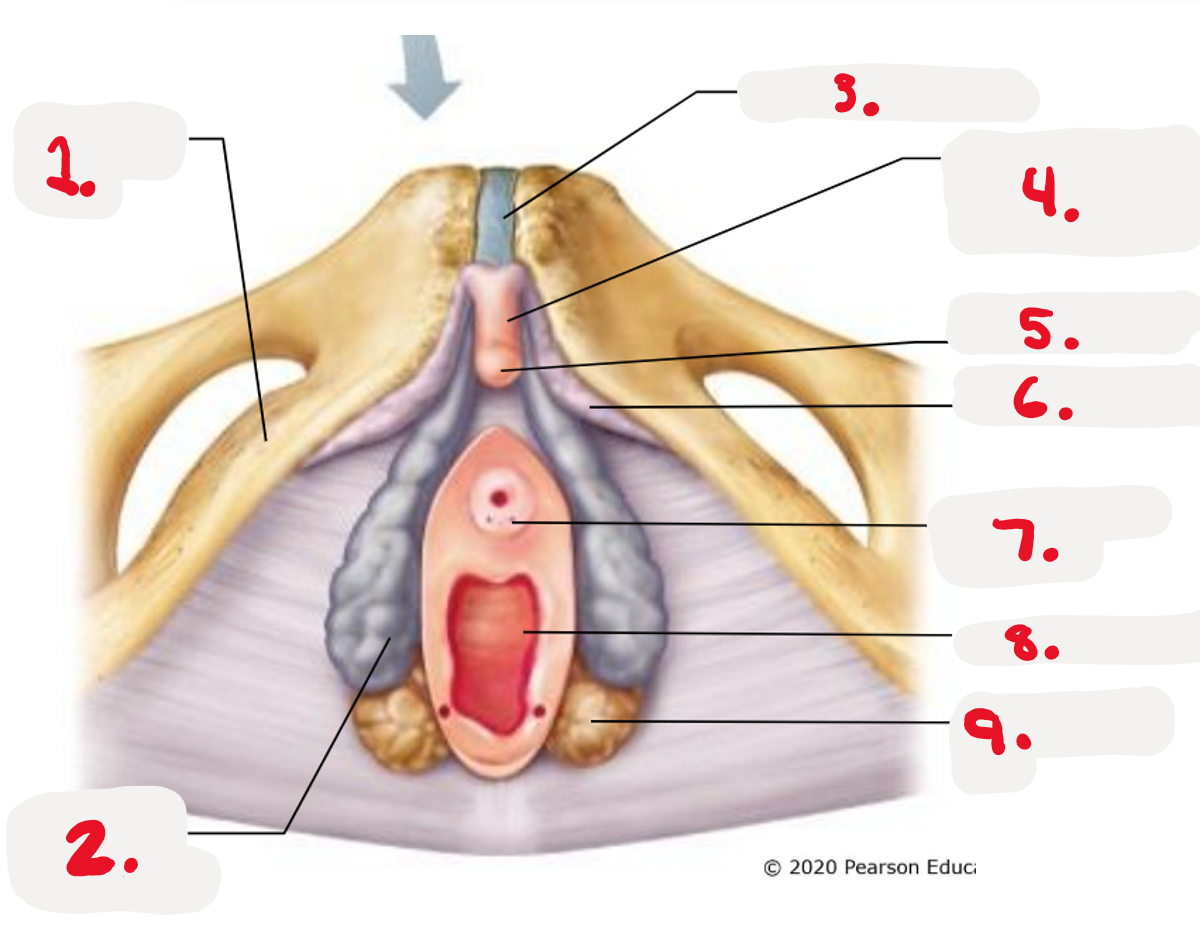
6.
Crus of clitoris
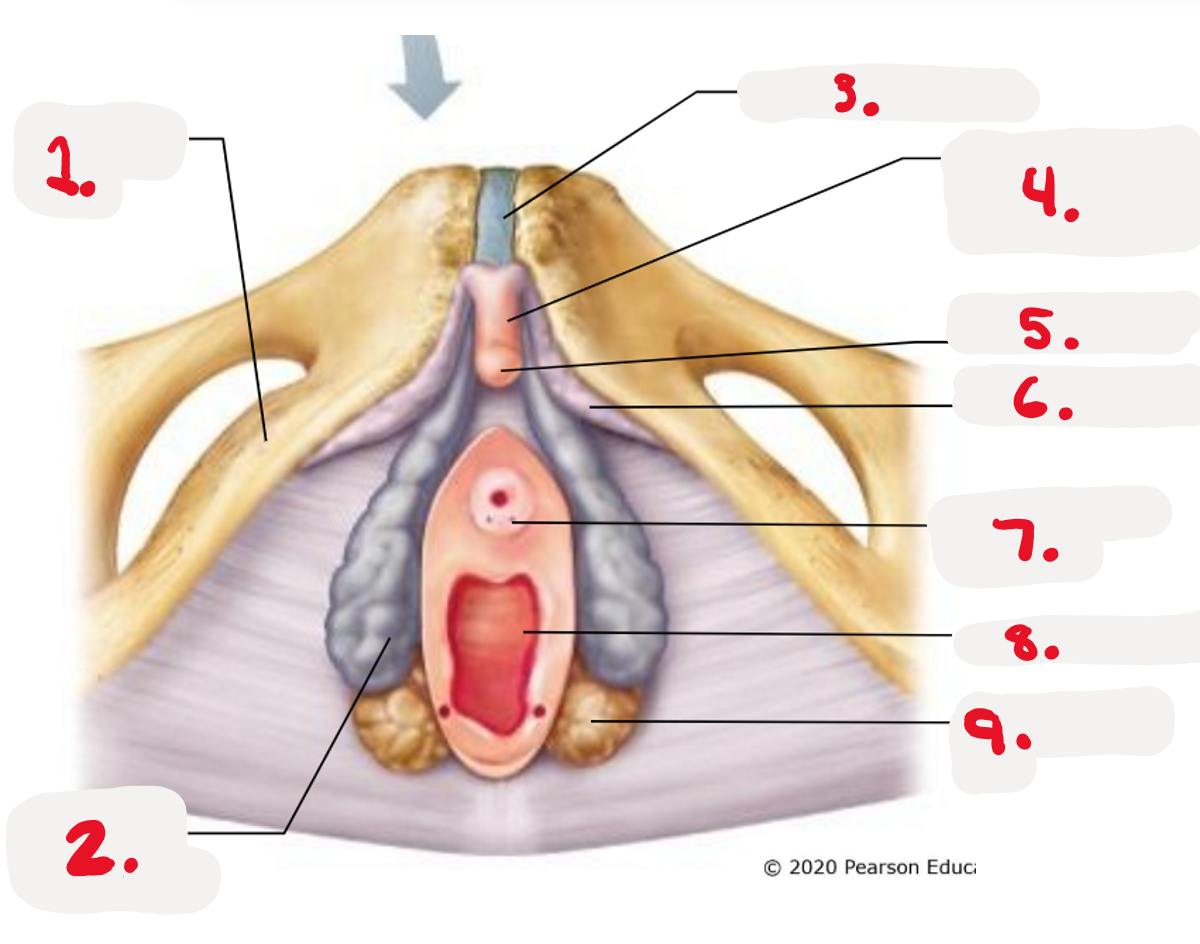
7.
Opening for paraurethral gland (pic)
8.
vaginal orifice (pic)
9.
greater vestibule gland (pic)
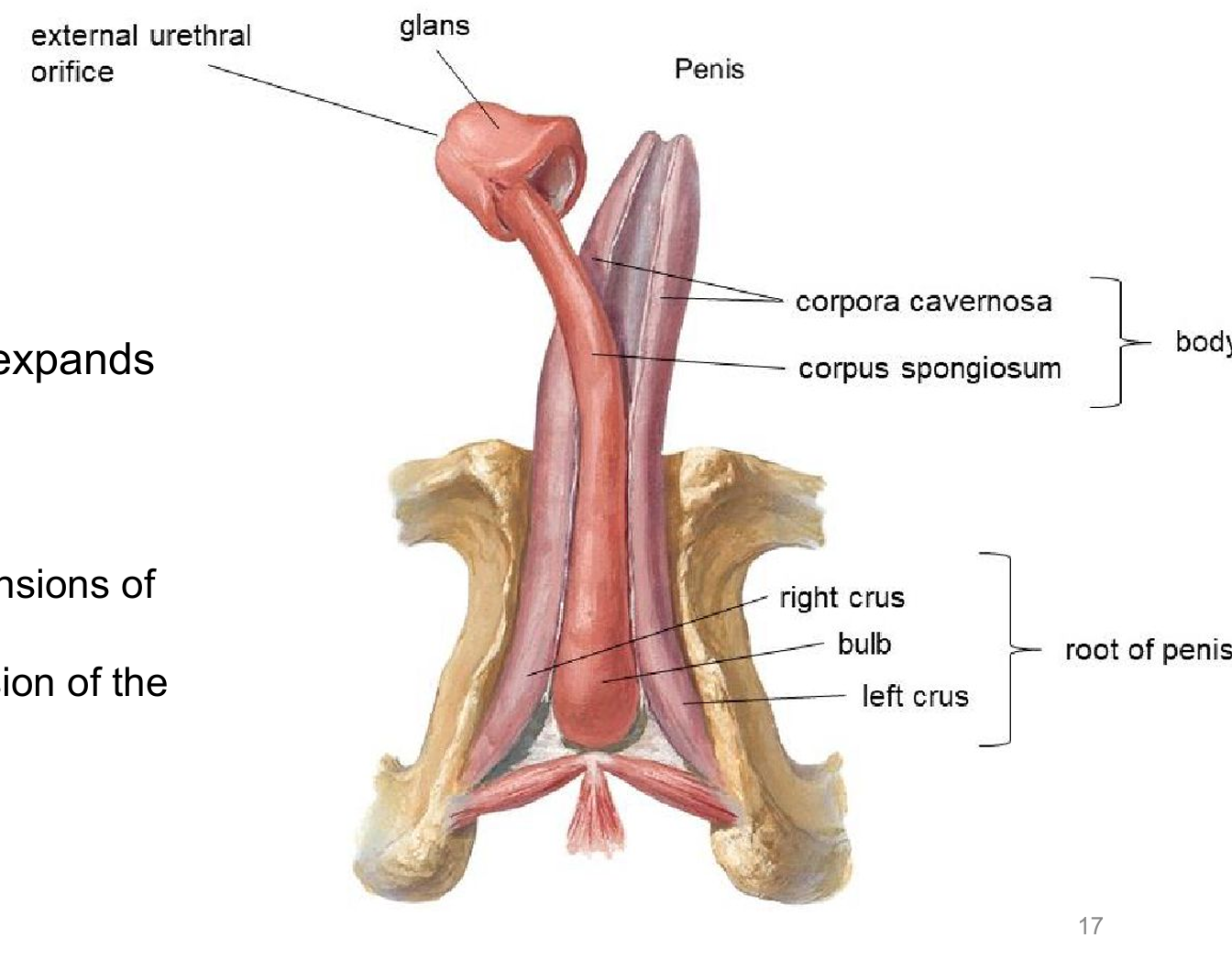
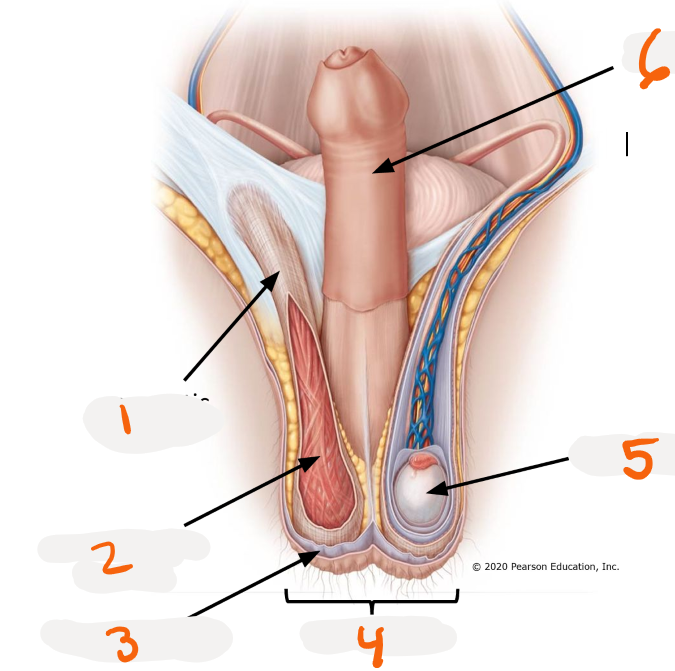
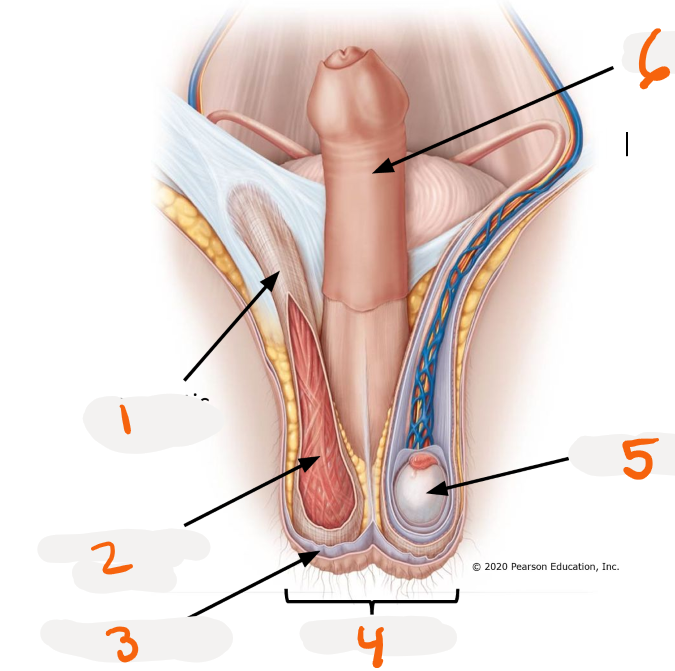
Penis
-body of penis
-glands
>prepuce
>external urethral orifice
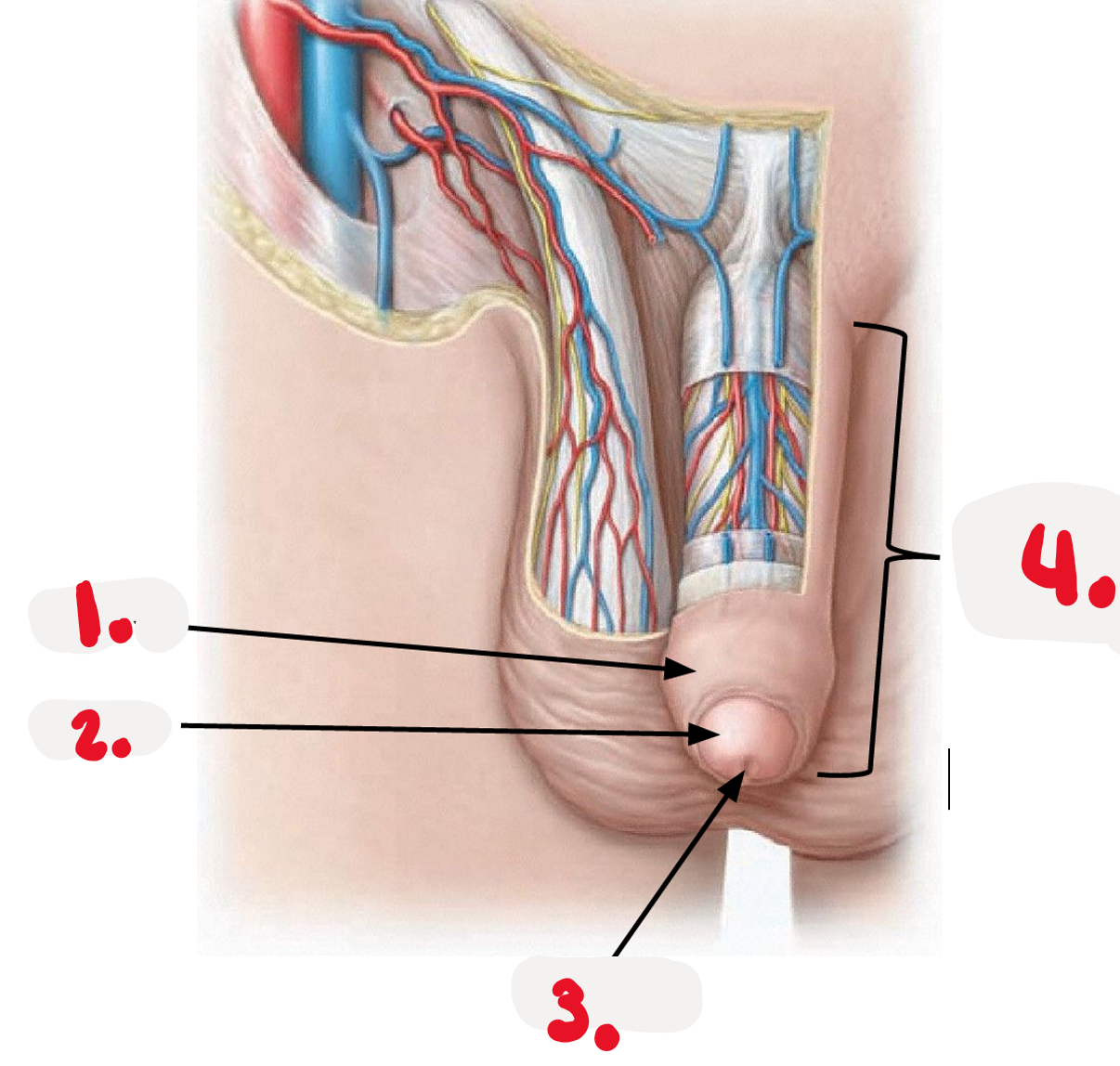
1.
foreskin - prepuce
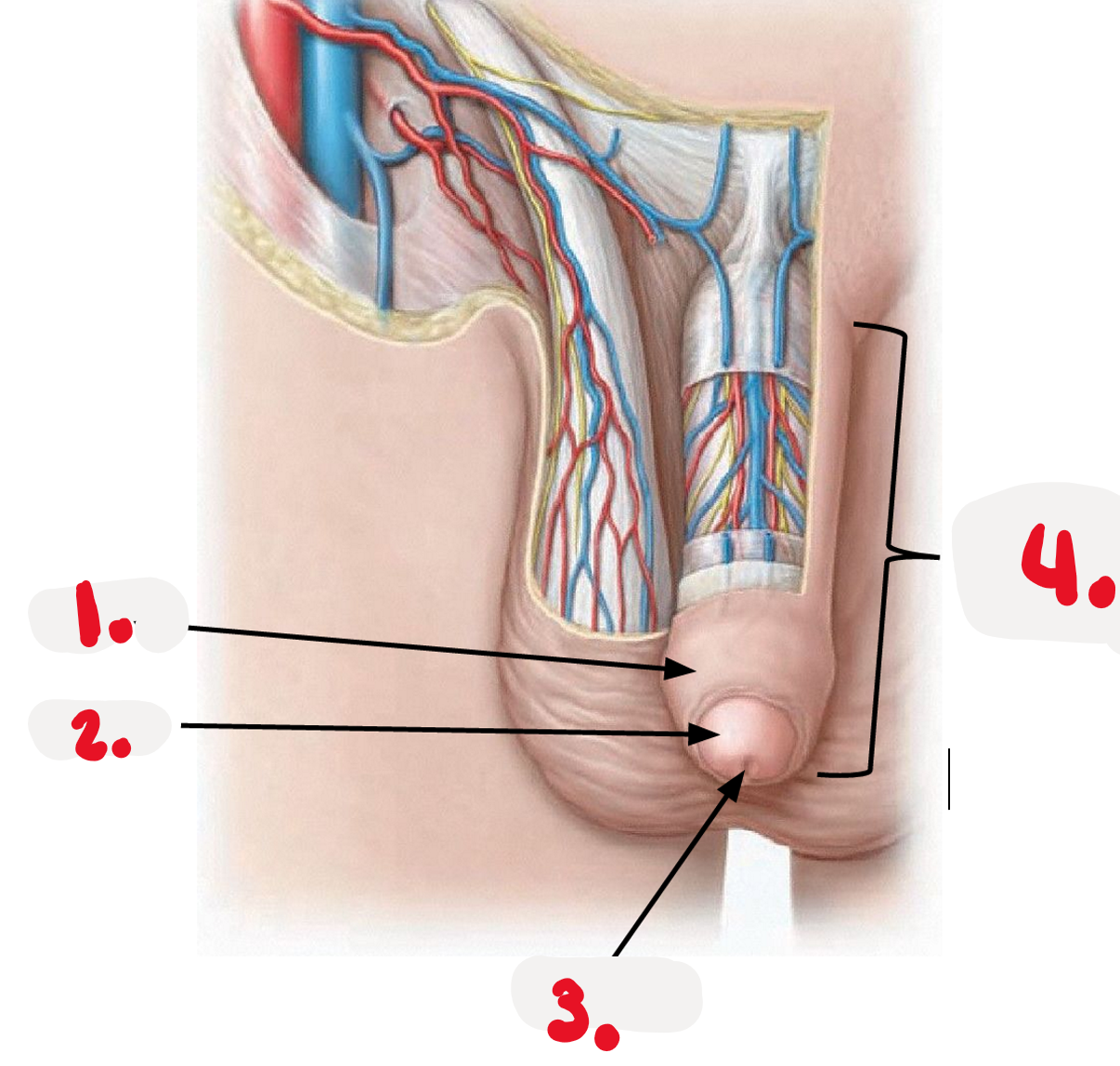
2.
>glans
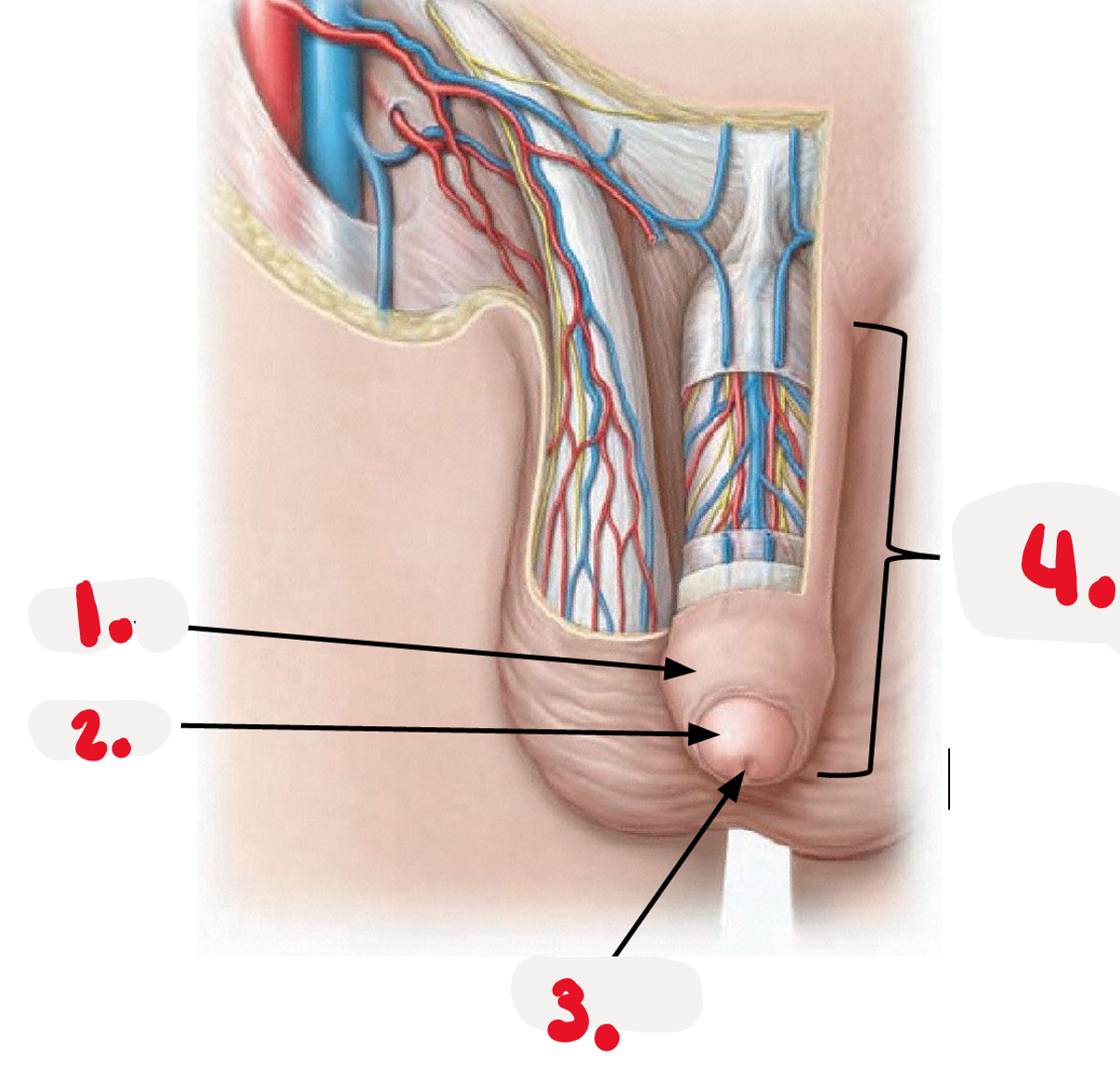
3.
>external urethra orifice
4.
penis body - free external portion
Root of penis location?
below pubic symphysis
Body of penis location?
hangs from pubic symphysis
Body of penis erectile tissues?
Corpora cavernosa - outer ~ paired
Corpus spongiosum - inner, expands distally as glands, surrounds urethra
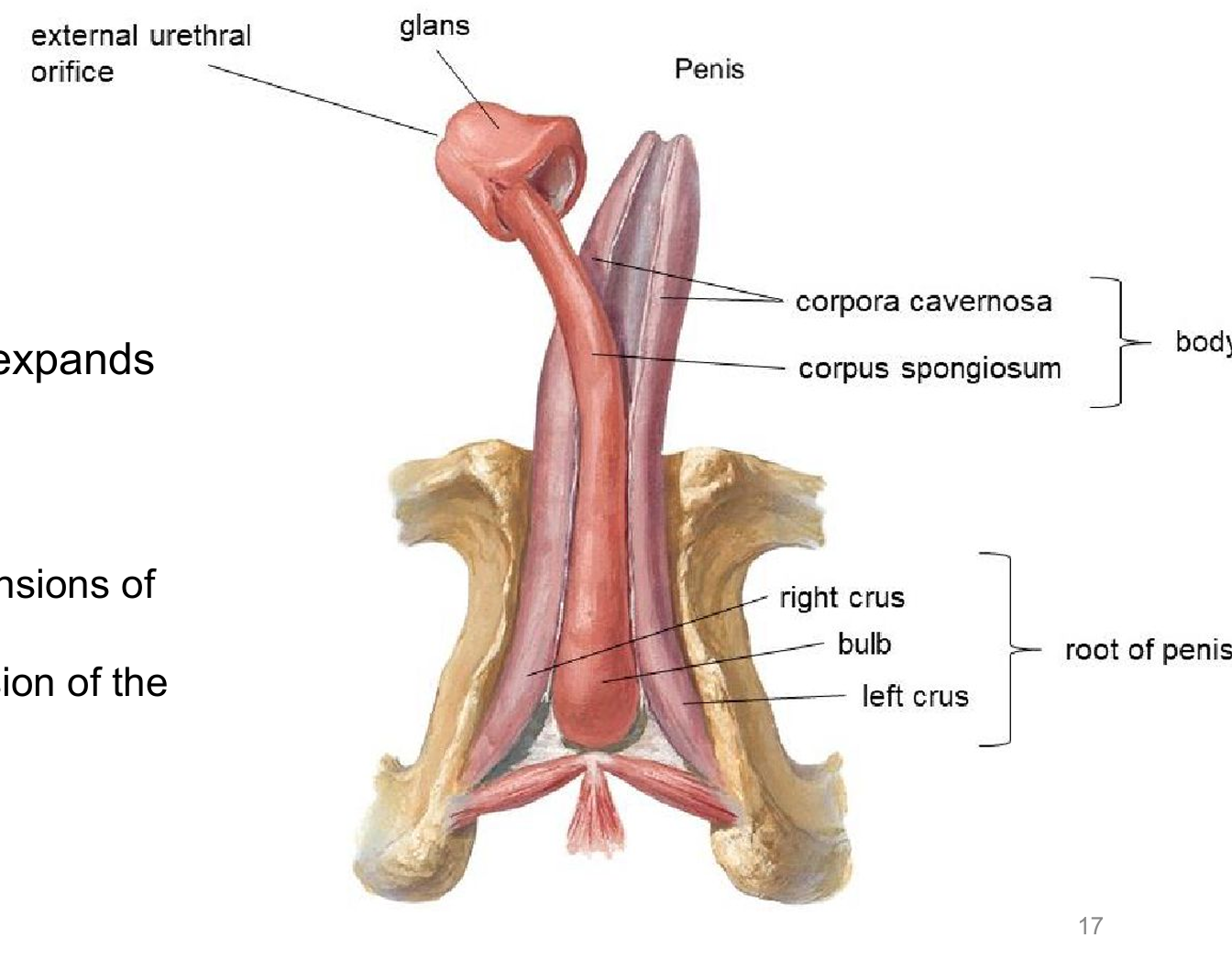
Roots of penis erectile tissues?
> right and left crura ~ extensions of the corpora cavernosa
>bulb of penis ~ extensions of corpus spongiosum
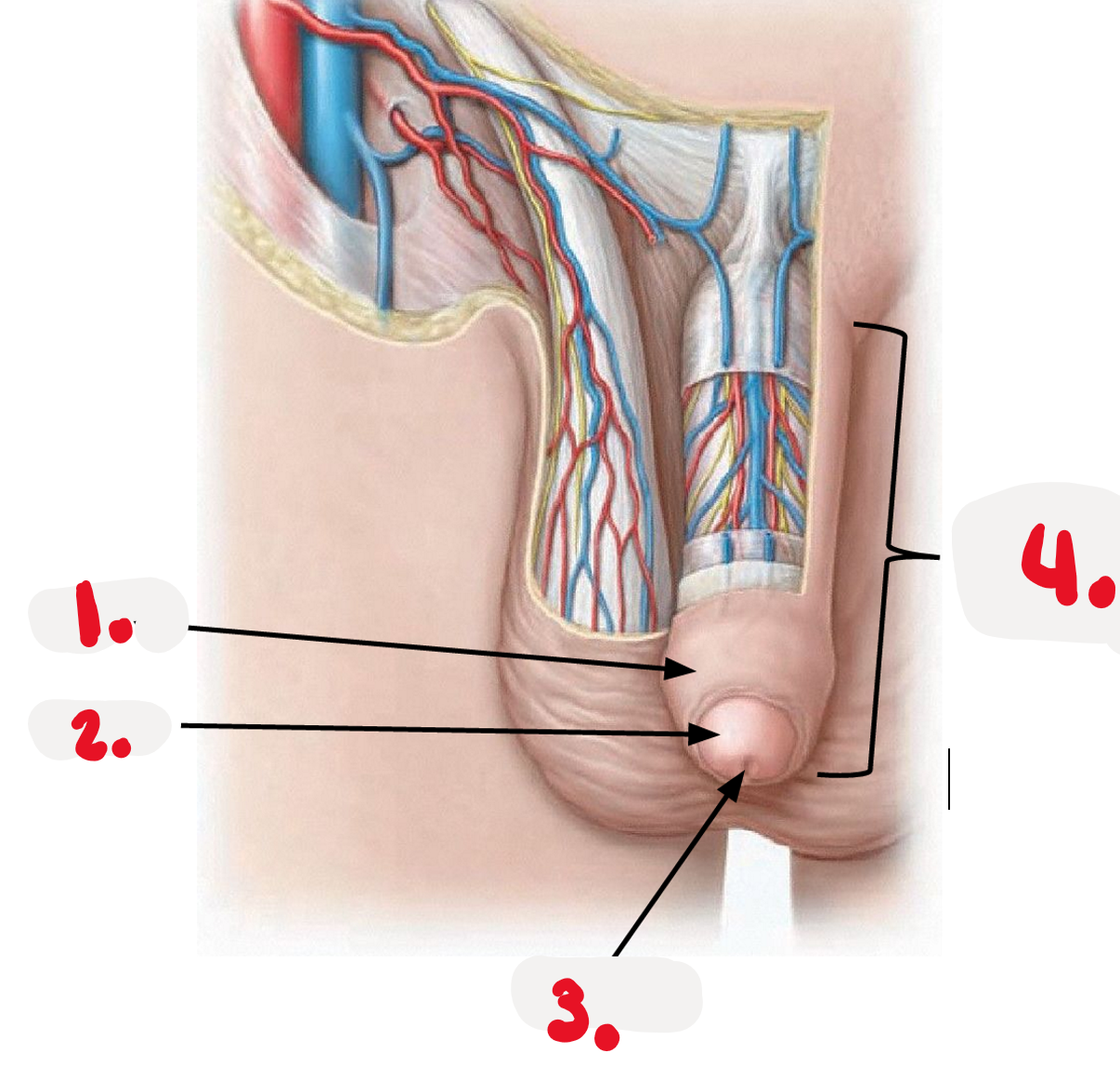
1.
external urethra orifice
2.
glans
3.
penis
4.
body of penis
5.
corpora cavernosa - body
6
Corpus spongiosum - body
7
root of penis
8
right crus
9
corpus spongiosum- root
10
left crus
Where tissue does penis urethra run through
runs through corpus spongiosum
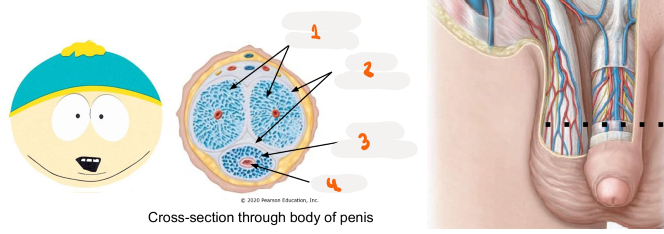
1
corpora cavernosa
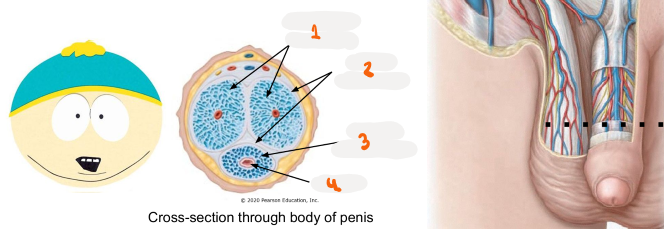
2
tunica aluginea
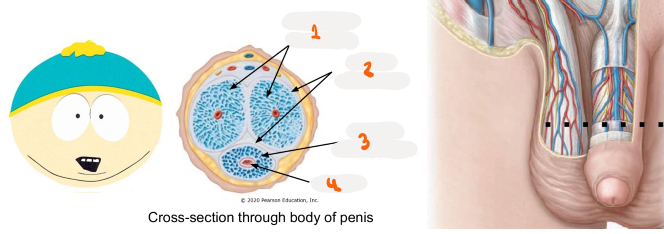
3
corpus spongiosum
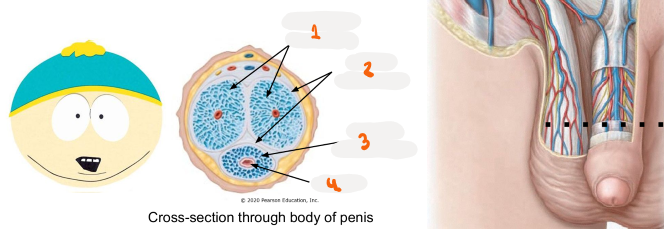
4
urethra
Penile circumcision
>remove foreskin of penis
>Possible health benefits ~ reduced risk of UTI in infant
>Drawbacks ~ loss of sensation, lack on consent for surgery, possibility of infection
bulbospongiosus muscle
cover bulb of vestibule and penis
>assist with expulsion of fluid from urethra(male) and emptying of greater vestibular glands(female)
Ischiocavernous muscle
cover crura of clitoris and penis
>assist with maintaining erection of penis and clitoris
Scrotum
pouch for testes
>respond to external temperature
>Dartos muscles and Cremaster muscle
Dartos muscle ~ Scrotum
smooth muscle in scrotum
>create wrinkles on skin regulate surface area and heat loss
Cremaster muscle ~ Scrotum
skeletal muscle in scrotum
>elevate and lower testes to regulate testes temperature
1.
spermatic cord
2.
cremaster muscle
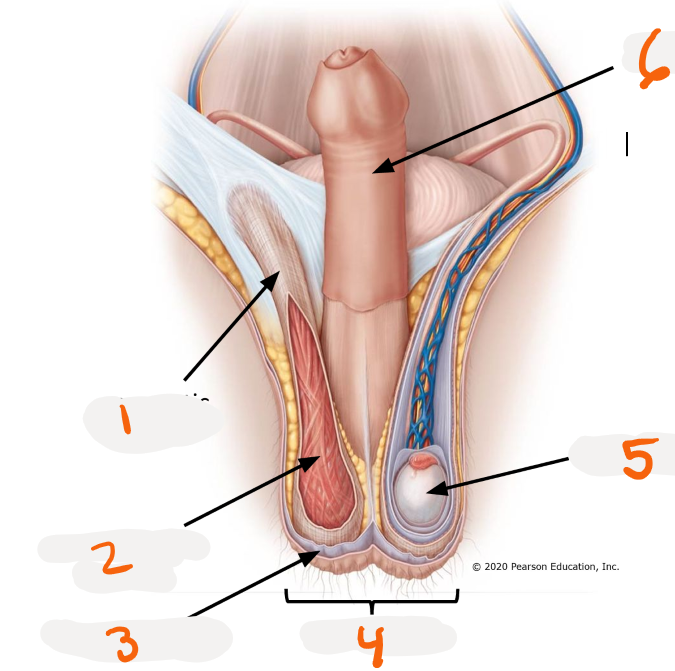
3.
dartos muscle
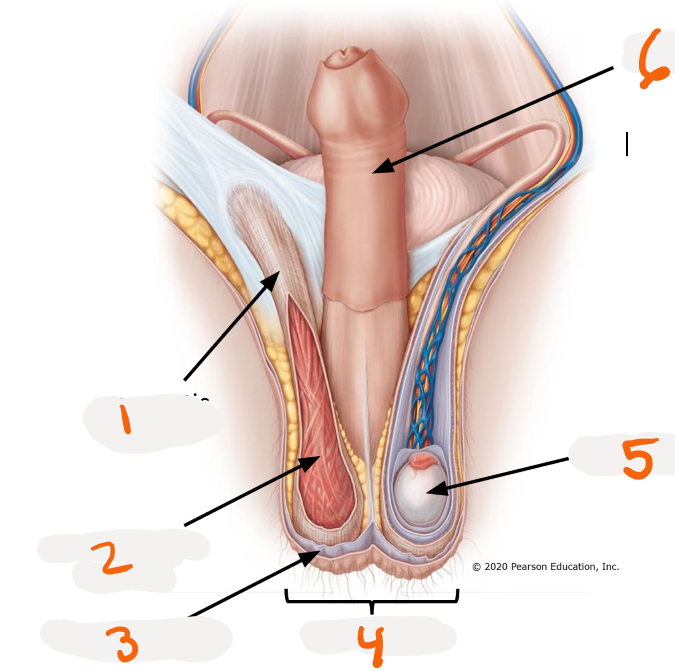
4.
scrotum
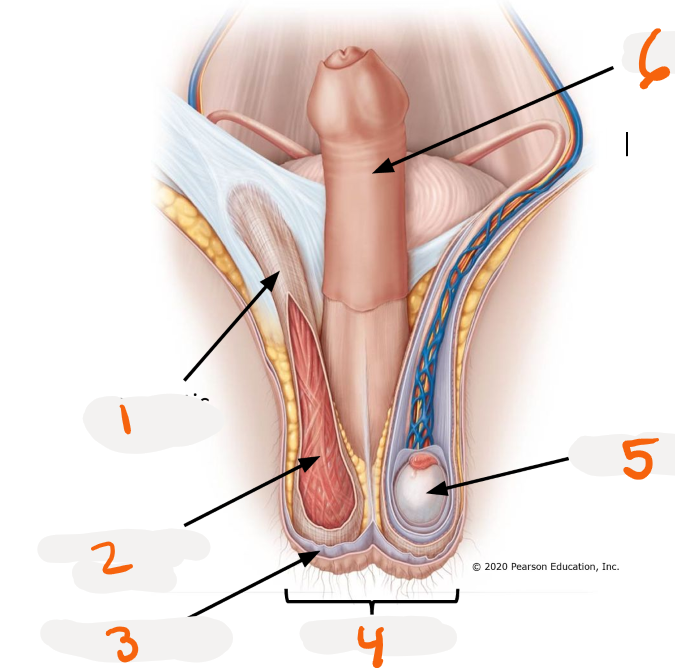
5.
testis
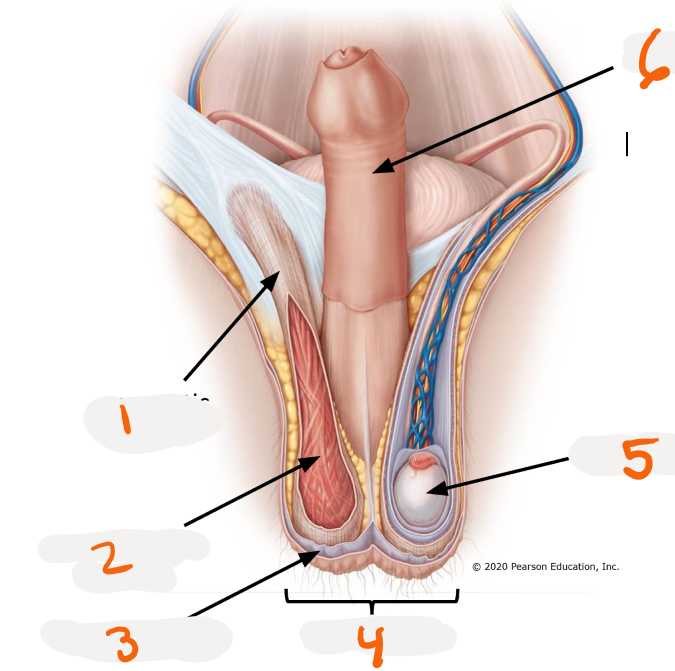
6.
penis
Tunica vaginalis
>serous sac covering testis
from peritoneum
tunica albuginea
>fibrous capsule of testis
>separates lobules (which contains seminiferous tubules)
seminiferous tubules
>site of sperm production
>sperm is carried from seminiferous tubules to epididymis
Epididymis
contains highly coiled duct
>sperm becomes fully mature, becomes motile
>take 20 days
>sperm can be stored for several months and then phagocytized if not released
>enter ductus deferens
Pathway of SPERM
Seminiferous tubules
Sperm is produced
Epididymis
Sperm matures & becomes motile (~20 days)
Ductus (vas) deferens
Transports sperm during ejaculation
Ejaculatory duct
Vas deferens + seminal vesicle duct
Urethra
Prostatic → membranous → spongy
External urethral orifice
Sperm exits the body
Spermatic cord
>tube of fascia
>structure travel from (abdomen→ inguinal canal → scrotum→ scrotum)
Spermatic cord features?
>Testicular (gonadal) artery
>Pampiniform plexus
>ductus vas deferens
>Testicular (gonadal) artery
blood supply to testes
>Pampiniform plexus
testicular veins branch out into plexus in spermatic cord
•Surround testicular artery to cool blood supply to testes