Year 10 MIM - Disease and Bacteria
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Scientific Method
Obvious
Discussion with results and procedure
Conclusion
Koch's Postulates
Disease must be found in the diseased but not in the healthy
Disease must be isolated and grown
Cultured microorganism should cause disease in healthy host
Disease must be isolated and identified as the same to the original agent
Infectious Disease
A condition that impairs body functioning caused by pathogens transmitted from one organism to another
Zoonotic
Refers to diseases that can be transmitted from animals to humans
Religion
Historically used to explain diseases
Agricultural Revolution
Zoonotic diseases could spread more easily
Deadly diseases could survive
Pathogenic Organisms vs. Agents
Organisms:
Bacteria
Fungi
Protozoa
Multicellular parasites
Agents:
Viruses
Prions
Germ Theory
Microorganism, known as pathogens or "germs", can cause disease
Incubation Period
The time between infection and symptoms
The duration during which a host can transmit a disease to others
Case Fatality
The proportion of individuals who die after contracting a specific disease
Bare Reproductive Rate (R)
Amount of people exposed who get infected
Emerging Infectious Disease
A new disease, has a major mutation, or major increase in fatalities/cases
Vector Borne Diseases
A disease that can be transferred from human to animal easily
Pathogen
An infectious agent that causes disease
Virulence
The relative ability of a pathogen to cause rapid and severe disease in a host
Transmission Types
Air
Food/Water
Direct contact
Animals
Body fluids
Acute vs. Chronic vs. Latent Duration
Acute comes and goes fast
Chronic is slower, usually less severe, but stays for much longer
Latent has no symptoms
Local vs. System Infection
Local is one part of the body
System is most of the body
How Agents Kill:
Destroy cells and tissue
Invasion and destruction of host cells
Triggering host's immune system
Coccus vs. Bacilli vs. Spirals
Coccus are round
Bacilli are rectangular
Spirals are shaped as spirals
Spiral types
Vibrio
Sprili
Spirochaete
Deviations of the above:
Diplo... is two connected bacteria
Strepto... is a change of bacteria
Staphylo... is a cluster of bacteria
Diagram of a Bacteria
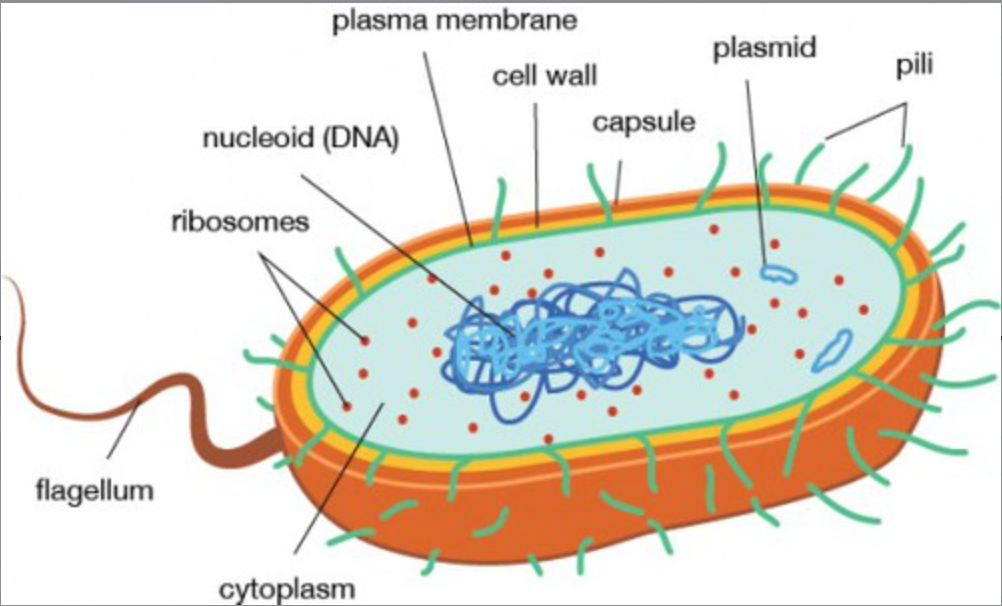
Peptidoglycan
A mesh-like structure made of sugars and amino acids that forms the cell wall of bacteria
Gram Positive vs. Negative
Positive have a thick cell wall
Negative has a thinner wall with an outer membrane
Binary Fusion
The process of a single-celled organism dividing into two identical cells