Chapter 5 (Externalities, Environmental Policy, and Public Goods)
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Externality (5.1)
- Benefit/Cost that affects someone who is NOT DIRECTLY INVOLVED in the production/consumption of a good or service
- Similar to a side-effect
-
- +/- results in DEADWEIGHT LOSS
----- ^ ex of market failure
- eg: pollution
Private Costs
- Costs to firms that is the sum of the costs of production for a good/service
Social Cost
- Higher than Private Costs
- Includes both the private cost and the external cost of things like pollution
Positive Externality
- Social Benefits EXCEED Private Benefits
----- ex: college
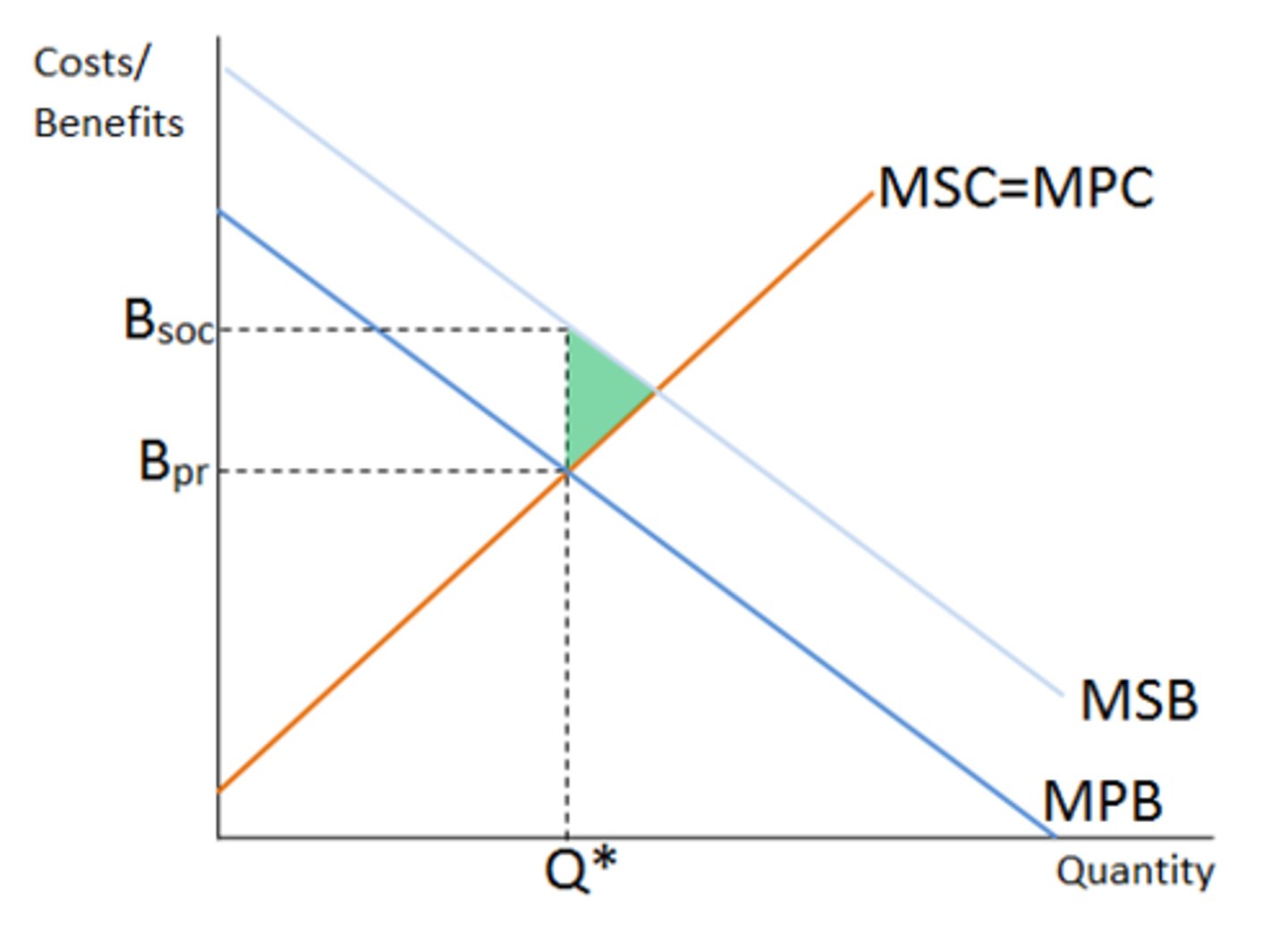
Negative Externality
-
----- ex: second hand smoke
Private Benefit
- Benefit received by CONSUMER of a good/service
Social Benefit
- Total Benefit from consuming a good/service that includes BOTH the Private Benefit and ANY external benefit
Market Failure
- Situation in which the market fails to produce the efficient level of output
- Caused by deadweight loss
- Larger the externality, the greater likelihood the size of the deadweight loss (extent of market failure)
Cause of Externalities
- Includes: Incomplete Property Rights, difficulty of enforcing Property Rights in certain situations
Property Rights
- The rights individuals/businesses have to the exclusive use of the property
- Includes the right to buy/sell it
- Having good ______ avoids market failure
Externalities (ex)
- A Farmer and Paper Mill share a stream
- (1) No-one owns the stream:
----- Paper mill discharges waste into a stream making it unusable for the farmer
- (2) The Farmer owns the stream:
----- Has option to......
----- a) Prevent mill from discharging
----- b) Allow discharge but for a fee
Coase Theorem
- Private Solution to Externalities
- Works as long as PROPERTY RIGHTS ASSIGNED (doesn't matter to whom)
- Both parties have full information about costs/benefits
- Claims that Private Parties can SOLVE Externality Problem through PRIVATE BARGAINING
----- Property Rights are assigned/enforceable
----- Transaction costs are low
Net Benefit
Look at flashcard
Transaction Costs
- Costs in time/other resources that parties incur in the process of agreeing to/carrying out an exchange of goods/services
Government Policies and Externalities (5.3)
A tax of the right size can cancel out both...
--- 1. Inefficiency (deadweight loss)
--- 2. Reducing Production Efficiency
Corrective Taxes (negative externalities)
- Solves Negative Externalities:
----- p: too much being produced
----- s: taxes reduce amount of output
- Shifts SUPPLY curve UP
- Comes from the sum of both the marginal SOCIAL and PRIVATE cost (after tax)
- Equilibrium market QUANTITY FALLS to economically efficient level
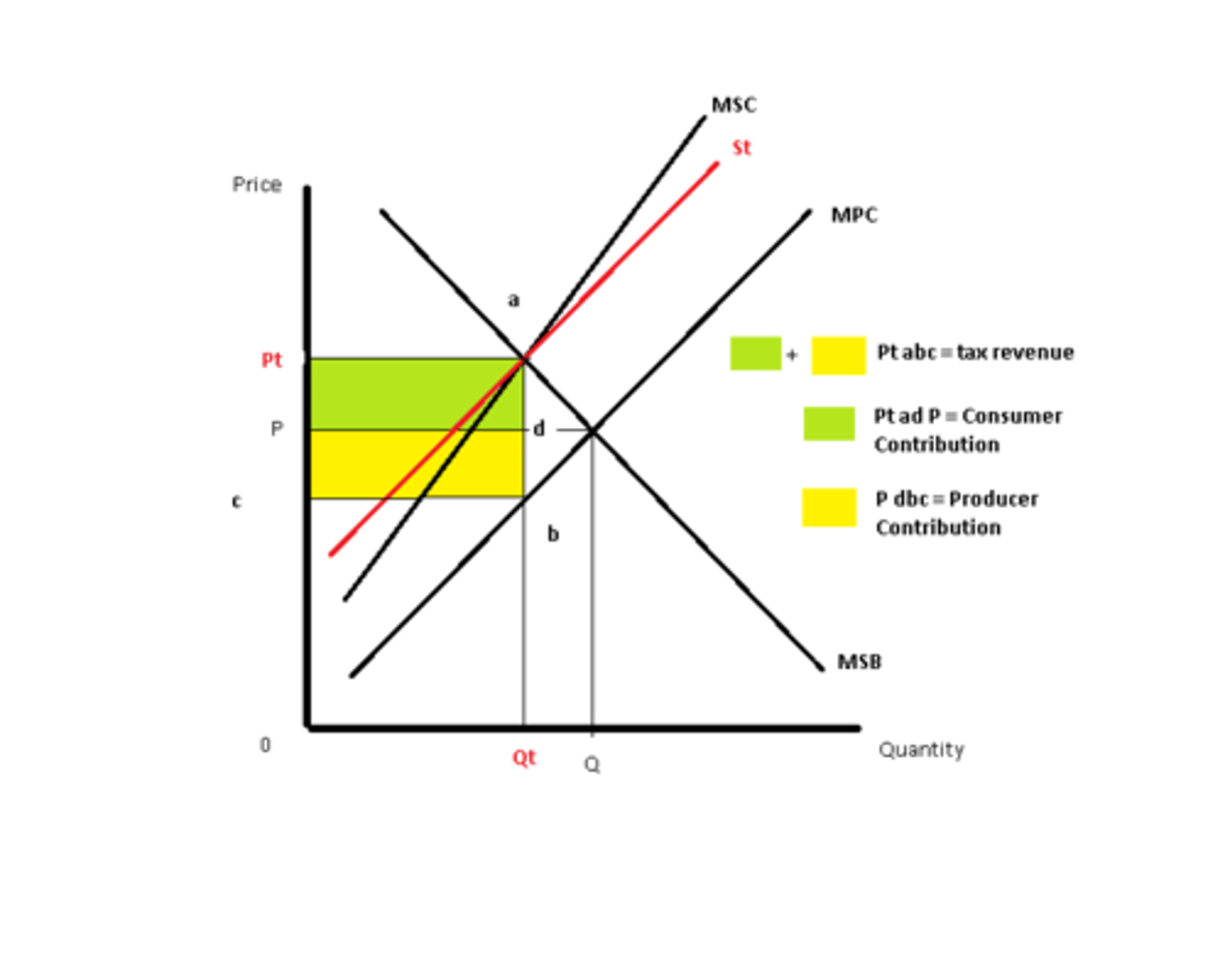
Negative Externalities
- Situation in which TOO MUCH will be produced
----- OR -----
- Consumption is too high
- Shifts supply curve UP: Simply means supply will need to decrease to achieve efficient output. NOT that supply has decreased
Subsidies (positive externalities)
- An amount paid to producers/consumers to encourage either the production or consumption of a good
- Shifts DEMAND Curve UP
Positive Externalities
- Situation in which TOO LITTLE is produced
Pigovian Taxes and Subsidies
- Another name of "Corrective Taxes and Subsidies"
- Named after English Economis Arthur Cecil Pigou
- Use of taxes/subsidies used to bring an efficient level of output in the presence of externalities
Pigovian Tax
- Shifts DEMAND Curve DOWN
- Negative Externality = soda tax
- Look at flashcard
Command and Control
- Traditional solution to externality
- Involves government imposing QUANTITATIVE LIMITS or ALTERNATIVE SOLUTIONS
- Emission ex:
--- (1) limit pollution allowed to be emitted
--- or
--- (2) require firms to install Alternatives
Solving Externalities (ex)
Background:
--- Negative Externality; too much pollution
--- Ford is able to reduce pollution cheaply
--- GM has high pollution reduction costs
Proposed Solutions:
--- (1) Command and Control. Ask Ford to reduce pollution more than GM [Though efficient, not fair to Ford]
--- (2) Capitalize and Control. Most efficient and fair solution is to have Ford do more pollution reduction but have GM compensate Ford [Both companies are better off. Pollution reduction remains the same, even cheaper for Ford and GM
Cap and Trade
- Ability for firms to trade "responsibilities" as a solution to dealing with externalities
Cap and Trade (ex)
Background:
--- Government establishes an "allowable" amount of emissions
--- Emission permits are distributed
--- Some firms reduce emissions for less than others
Solution: (cap and trade)
--- Firms with high costs of reducing pollution will buy permits from firms with low costs. Ensures pollution is reduced at the lowest possible cost
--- Market used to achieve EFFICIENT pollution reduction
Categories of Goods (5.4)
(1) Private Goods:
----- Rival and Excludable
----- ex: Running shoes, Cups, etc.
(2) Common Resources:
----- Rival and NON-Excludable
----- ex: Fish in the sea, public pasture land
(3) Quasi-Public Goods:
----- NON-Rival and Excludable
----- ex: Cable TV, Toll Roads
(4) Public Goods:
----- NON-Rival and NON-Excludable
----- ex: National Defense, Court System
Rival
- Type of relationship between goods
- Situation that occurs when one person's consumption of a good means no one else can consume it
Excludability
- Type of relationship between goods
- Situation in which anyone who does not pay for a good cannot consume it
Markets and Goods
(1) Private Goods:
- Good. Works efficiently because the person making decisions about how much to purchase tends to be the only one benefiting from the good so only their preferences matter
(2) Common Resources:
- Not so good. Little Incentive to conserve. Leads to OVER-CONSUMPTION.
(3) Quasi-Public Goods:
- Profit-Maximization tends to lead too many people to be EXCLUDED
(4) Public Goods :
- Not so Good. FREE-RIDE. People can enjoy the benefits w/o playing for them
Market Demand Curves (Private Goods)
- Add HORIZONTALLY the QUANTITY of good demanded at each price by the consumer
Market Demand Curves (Public Goods)
- Add VERTICALLY the PRICE at which the consumer is willing to purchase at a quantity of the good
Efficient Production of a Public Good (4)
(1) Background:
---Where Supply and Demand Curves intersect
(2) Problem:
--- Finding Market DEMAND Curve can be difficult; no incentive to reveal willingness to pay for public goods
(3) Solution:
--- Use COST-BENEFIT Analysis to determine the correct level of Public Goods
Cost-Benefit Analysis
- Useful for understanding willingness to pay for public goods
- Study that compares the costs and benefits to society of providing a public good
Efficient Consumption of a Common Resource (2)
(1) Background:
--- These tend to be OVER-CONSUMED.
(2) Problem:
--- Consumption is RIVAL and NONexclusive
--- Negative Externality
(3) Solution:
--- PIGOVIAN Taxes; ideally make people pay for consumption
(4) Worst-Case Scenario:
--- Tragedy of the Commons
Tragedy of the Commons
(1) What;
---Situation where the Common Resource is OVERUSED
(2) When:
--- Pigovian Taxes cannot be enforced
--- Enforcing Property Rights isn't feasible
(3) Solution:
--- a. If geographic area is LIMITED and SMALL number of people involved, then...Access can be restricted through LAWS and NORMS
--- b. If geographic area/people involved is large, then... LEGAL RESTRICTIONS
Legal Restrictions
- A solution to "Tragedy of Commons"
- Legal Restriction of access to common goods
- eg: Taxes, Quotas, Tradable Permits on Access