WGU Data Management - Foundations - D426
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
Which requirement within large, complex databases ensures users have limited access to the database?
Recovery
Performance
Authorization
Confidentiality
Authorization
Which design type specifies database requirements without regard to a specific database system?
Physical design
Conceptual design
Logical design
Abstract design
Conceptual design
3. What characterizes the rules of relational databases?
-They are logical constraints that ensure the data is valid.
-They are based on business policy and specific databases.
-They represent data volumes and rapidly changing data structures.
-They embody the theoretical foundation of the SQL language.
They are logical constraints that ensure the data is valid.
4. Which event will result in an error code and error description when using MySQL Server?
When the server or updates are incorrectly installed
When an SQL statement is entered to locate errors in the database
When an SQL statement is syntactically incorrect
When a Mac OS shortcut code is used on a Windows OS
When an SQL statement is syntactically incorrect
5. Which data type should be used to store whole integer values, such as age?
NUM
VARCHAR
DATE
INT
INT
6. Which text-based interface is included in the MySQL Server Download?
MySQL Command-Line Client
MySQL Workbench
MySQL Enterprise
MySQL Community
MySQL Command-Line Client
7. Which database system includes the World database during its installation?
MySQL
MongoDB
Oracle
PostgreSQL
MySQL
8. What is the standardized language of relational database systems?
Contextual Query Language
Structured Query Language
Select Query Language
Object Query Language
Structured Query Language
9. Which SQL sublanguage is used to manage database access?
Data Definition Language (DDL)
Data Query Language (DQL)
Data Manipulation Language (DML)
Data Control Language (DCL)
Data Control Language (DCL)
10. Which SQL sublanguage is used to roll back database changes?
Data Transaction Language (DTL)
Data Manipulation Language (DML)
Data Query Language (DQL)
Data Control Language (DCL)
Data Transaction Language (DTL)
11. Which format is used by the TIME data type in MySQL?
YYYY-MM-DD
YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss
hh:mm:ss
hh:mm:ss YYYY-MM-DD
hh:mm:ss
12. Which MySQL operator is the last in the order of operator precedence?
-
OR
NOT
=
OR
13. Which operator is used to compare columns from the left and right tables in MySQL?
<=
+
=
*
=
14. Which type of join combines two tables without comparing columns?
SELF
EQUIJOIN
OUTER
CROSS
CROSS
15. Which type of join compares columns using only the = operator?
Equijoin
Non-equijoin
Outer join
Inner join
Equijoin
16. Which type of join is demonstrated by the following query?
SELECT Dog.Nickname, Kennel.Address
FROM Dog, Kennel
WHERE Dog.KennelID = Kennel.ID
NON-EQUIJOIN
SELF JOIN
CROSS JOIN
EQUIJOIN
EQUIJOIN
17. What is another name for a subquery?
Outer query
Nested query
Correlated query
Search query
Nested query
18. Which operator is used to compare against a list of values when determining a match in a WHERE clause?
IN
BETWEEN
LIKE
OR
IN
19. Which wildcard character is used to represent zero or more characters when searching for a specified pattern using a LIKE operator?
%
_
<
>
%
20. Which function is considered an aggregating function in SQL?
TRIM
REPLACE
MIN
SUBSTRING
MIN
21. Which clause or function is used with aggregate functions to produce summary rows?
TRIM
REPLACE
ORDER BY
GROUP BY
GROUP BY
22. Which type of join returns only the matching values when selecting rows from two or more tables?
Full Join
Outer Join
Equijoin
Inner Join
Inner Join
23. Which join type selects only matching left and right table rows?
Full Join
Left Join
Right Join
Inner Join
Inner Join
24. Which phrase refers to the view in which data is persisted and is automatically changed as the underlying data is changed?
Virtual View
Snapshot View
Denormalized View
Materialized View
Materialized View
25. Which SQL command uses the correct syntax to update the salary of an employee in the Employee table?
CHANGE Employee Salary = 50000 WHERE ID = 1;
UPDATE Employee SET Salary = 50000 WHERE ID = 1;
ALTER Employee SET Salary = 50000 WHERE ID = 1;
UPDATE Employee (Salary) = (50000) WHERE ID = 1;
UPDATE Employee SET Salary = 50000 WHERE ID = 1;
26. What describes elements such as column name and data type?
Alter
Table
Metadata
CRUD
Metadata
27. Which term identifies an ordered collection of elements enclosed in parenthesis in a tablespace?
Cell
Field
Column
Tuple
Tuple
28. Which SQL command uses the correct syntax to select the name and salary columns from the Employee table where the salary is greater than 50000, and sort the results by salary in descending order?
-SELECT name, salary FROM Employee WHERE salary > 50000 ORDER + BY salary DESC;
-SELECT Employee.name, Employee.salary WHERE Employee.salary > 50000 SORT BY Employee.salary DESC;
-SELECT name, salary FROM Employee SORT BY salary DESC WHERE salary > 50000;
-SELECT name, salary FROM Employee WHERE salary > 50000 SORT BY salary ASC;
SELECT name, salary FROM Employee WHERE salary > 50000 ORDER + BY salary DESC;
29. Which INSERT statement demonstrates valid syntax in SQL?
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2) SET value1, value2;
INSERT INTO table_name VALUES (value1, value2);
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2) VALUES (value1, value2);
INSERT INTO table_name SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2;
INSERT INTO table_name (column1, column2) VALUES (value1, value2);
30. Which UPDATE statement uses valid syntax in SQL?
UPDATE table_name column_name= value1 WHERE condition
UPDATE table_name SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2 WHERE condition;
UPDATE SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2 WHERE condition IN table_name;
UPDATE table_name SET column_name = value1
UPDATE table_name SET column1 = value1, column2 = value2 WHERE condition;
31. Which statement used to remove data from temporary tables?
DROP
DELETE
DEFAULT
TRUNCATE
TRUNCATE
32. Which keyword is a DDL (data definition language) keyword in SQL?
INSERT
UPDATE
DELETE
CREATE
CREATE
33. Which property is enforced by a primary key field?
Not Null
Null
Duplicate
Numeric
Not Null
34. Which property or function allows SQL to insert a field value?
Composite
Simple
Auto-increment
Numeric
Auto-increment
35. Which property specifies an expression on one or more columns of a table?
CHECK
RESTRICT
CASCADE
UNIQUE
CHECK
36. Which type of key is a single column in a table used to identify a row?
Super key
Simple primary key
Foreign key
Composite primary key
Simple primary key
37. Which type of key is often represented by parentheses to show multiple columns?
Composite
Simple
Unique
Foreign
Composite
38. Which primary key characteristic means it includes information that is easy to type and store?
Non-null
Meaningless
Stable
Simple
Simple
39. Which part of a junction table in a relational database establishes a many-to-many relationship between two tables?
Primary key
Foreign key
Composite key
Candidate key
Foreign key
40. Which type of relationship is established by a foreign key in a relational database?
Aggregation
Composition
One-to-many
Many-to-many
One-to-many
41. Which statements may be rejected when a foreign key constraint is specified?
INSERT
CHECK
SELECT
ORDER BY
INSERT
42. Which key describes the unique columns in a table that do not contain a primary key?
Foreign key
Simple key
Candidate key
Composite key
Candidate key
43. Which index stores column values and row pointers in a hierarchy?
Dense index
Sparse index
Multi-level index
Secondary index
Multi-level index
44. Which type of index refers to entries that are assigned to buckets?
Bitmap index
Logical index
Hash index
Secondary index
Hash index
45. Which type of index is a grid of bits where each index row corresponds to a unique row in a table?
Multi-level index
Logical index
Hash index
Bitmap index
Bitmap index
46. Which type of development activity is used to convert an entity-relationship model (ERM) into tables, columns, and keys?
Execution
Physical design
Analysis
Logical design
Logical design
47. Which term addresses columns of A being a subset of the columns of B, with A always depending on B?
Third normal form
Candidate key
Trivial dependency
Non-trivial dependency
Trivial dependency
48. Which term describes the process of denormalization?
Merging tables
Candidate key
Trivial dependency
Third normal form
Merging tables
49. A database designer is working with a table that has a primary key and no duplicate rows. What can be concluded about the table?
It is a Boyce-Codd table.
It contains trivial dependency.
The table contains a non-key column.
It is a first normal form table.
It is a first normal form table.
50. Which process eliminates redundancy by decomposing a table into two or more tables in a higher normal form?
Merging
Creation of a candidate key
Evaluation of trivial dependency
Normalization
Normalization
51. Which term describes the optimal normal form for frequent inserts, updates, and deletes of data?
Boyce-Codd normal form
Candidate key
Trivial dependency
Third normal form
Boyce-Codd normal form
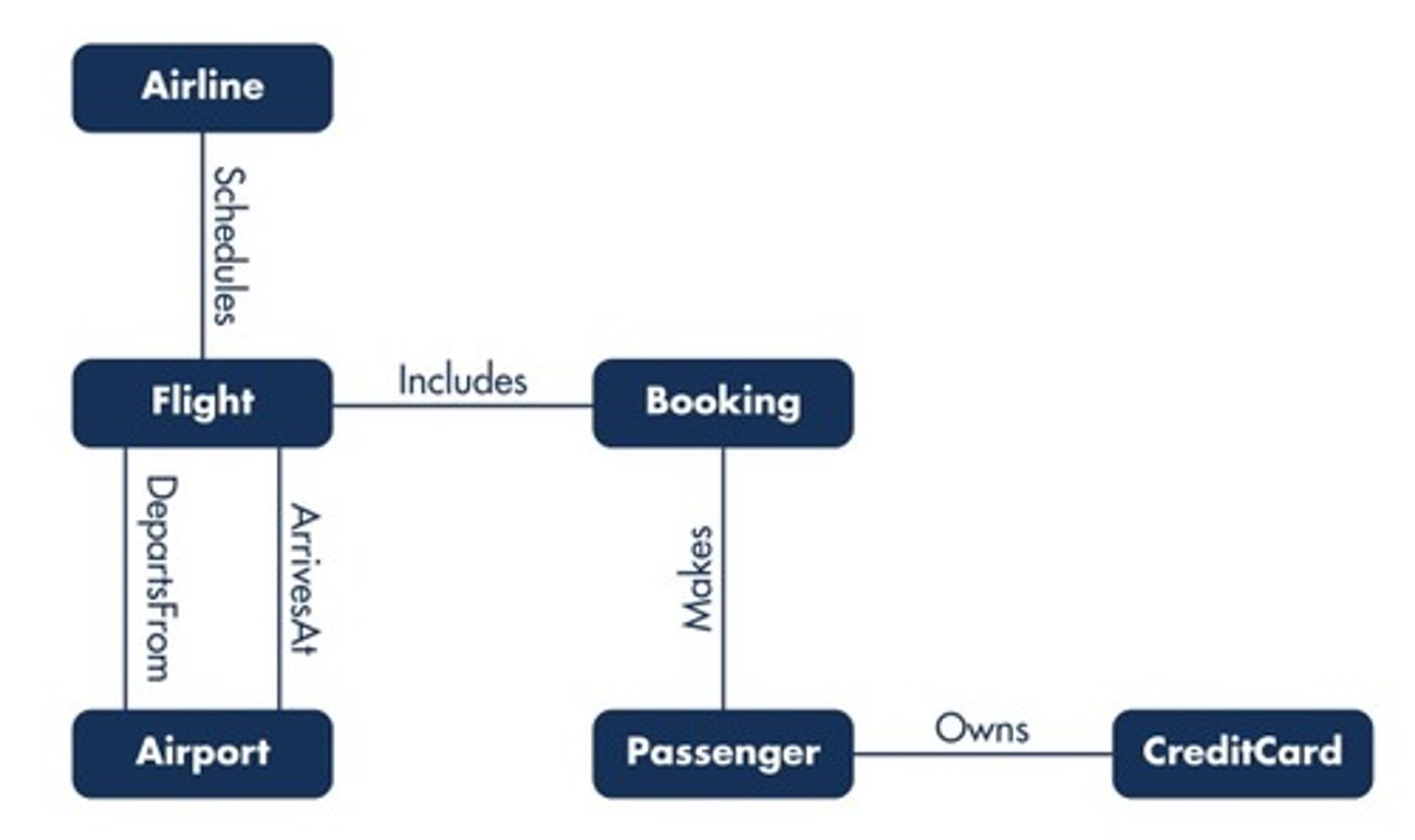
52. Which relationship is depicted in the following entity-relationship (ER) diagram?
Ternary
Many-to-many
One-to-one
One-to-many
One-to-many
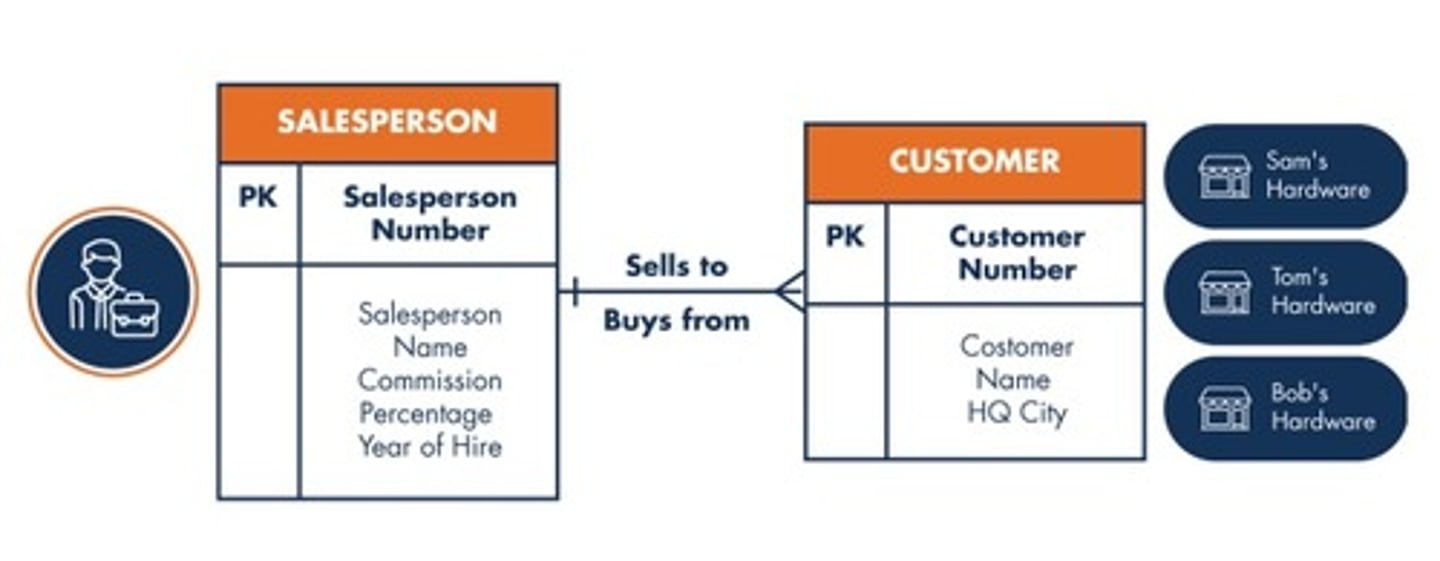
53. Which relationship or association exists between a supertype entity and its subtype entities?
IsA relationship
Weak entity
Associative entity
Unary relationship
IsA relationship
54. Which symbol is used in an entity-relationship (ER) diagram for an entity?
Diamond
Square
Circle
Line
Square
55. Which symbol is used in an entity-relationship (ER) diagram to indicate an attribute?
Diamond
Square
Circle
Line
Circle
56. What must be done before creating supertype and subtype entities?
Identify entities.
Document entities.
Determine attribute maxima.
Document cardinality
Identify entities.
57. Which real-world object can be distinctly identified and grouped, such as all employees in a company?
Entity-relationship (ER) diagram
Glossary
Entity
Attribute type
Entity
Which item in an entity-relationship (ER) diagram follows the attribute name and is placed outside of parentheses?
Weak entity
Attribute maximum
Attribute minimum
Physical design
Attribute maximum
59. Which strategy can be used to identify primary keys when investigating data relationships?
Trend analysis
Unique identifier analysis
Hypothesis testing
Visualization
Unique identifier analysis
60. How should an entity relationship phrase be read to correctly understand how one entity relates to another entity in an entity-relationship diagram (ER diagram)?
From top to bottom
In the direction the entity box is facing
In the direction the relationship verb is facing
From left to right
In the direction the relationship verb is facing