Metals, Metallurgy, and Metallurgical Engineering
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Metals
can be an element or an alloy
Metals
good conductors of heat and electricity
Metals
malleable and ductile
Stone Age (7000 BC)
wood and stone
tools are made of Gold (Au), Silver (Ag), and Copper (Cu) for hunting, plowing, farming and decorative artifacts
Bronze Age (4500 BC)
copper and bronze (first alloy) for tools, ornaments, jewelry, and weapons
brass
copper + zinc =
bronze
copper + tin =
Iron Age (1400 BC)
iron (wrought) cast
iron and steel
steel
carbon + iron =
Gold
Copper
Silver
Lead
Iron
Mercury
Tin
Seven Metals of Antiquity
De Re Metallica (“On the nature of metals”)
contains a comprehensive description of the mining industry during the early Renaissance
De la Pirotechnia
one the the earliest printed books on Metallurgy
Metallurgy
the art and science of extracting and refining metals from primary and secondary sources to characterize, process, and fabricate for application and use at profit with utmost consideration of the environment
Minerals
naturally occurring
inorganic
homogeneous solid
definite composition
ordered structures (crystalline properties)
Ore
a mineral deposit with sufficient utility and value to be mine at a profit or economically exploited to become a source or supply of a particular material
Run-of-Mine (ROM)
as mined ore which consists of valuable minerals and gangue
Concentrate
valuable minerals obtained from the recovery processes and product of mineral processing
Gangue
minerals of no value and disposed
Tailings
predominantly the gangue materials
may contain very small amount of valuable mineral
Ore Dressing / Benefication
preparation required for ores before the extraction process
Extraction
recovery of valuable metal from concentrates or ore
Recovery / Winning
process involving the production or recovery of pure metals
Grade / Assay
metal content or measure of the concentration of metal
Grade / Assay
used to ascertain the content of valuable metal in ore
Cut-off Grade
lowest grade of mineralized material considered economic
Native Ore
Sulfide Ore
Oxidized Ore
Types of Ores
Native Ore
metal is present in elementary form
Gold
Silver
Copper
give example(s) of native ore
Sulfide Ore
contain metals as sulfides
Chalcopyrite (CuFeS2)
Chalcocite (Cu2S)
Pyrite (FeS2)
give example(s) of sulfide ore
Oxidized Ore
valuable mineral may be present as oxide, sulfides, sulfates, silicates, carbonates
Unit Operations
individual sequential steps in producing metal from the ore involving purely physical changes
Unit Operations
can use chemicals as long as it will not alter the ore chemically
Unit Processes
individual sequential steps in producing metal from the ore involving chemical changes and/or changes in the state of aggregation
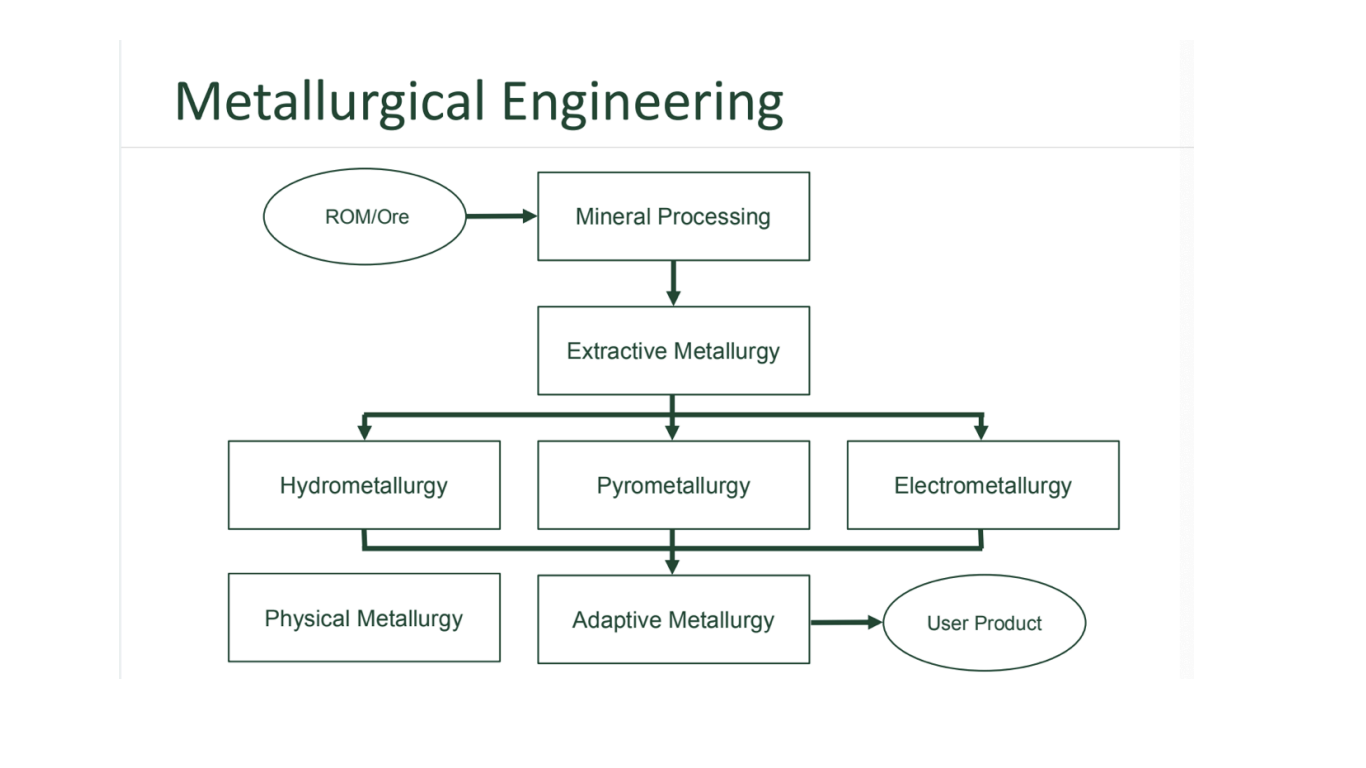
Metallurgical Engineering Process
Miller Process
Wohlwill Process
CIP / CIL / CIC
Direct Smelting
Merrill-Crowe Process
MacArthur-Forrest Process
Gold Production Processes
HPAL
Moa Bay Process
Sherritt-Gordon Process
Direct Smelting
Nickel Production Processes
High Pressure Acid Leach
HPAL meaning
Blast Furnace Smelting
Midrex Process
Corex Process
Basic Oxygen Furnace Smelting
Iron Production Processes
Heap Leaching
Mitsubishi Process
Flash Smelting
Electrorefining
Copper Production Processes