econ theme 1
1/330
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
331 Terms
what is economics
social science
production/consumption/distribution of goods + services
allocation of scarce resources to provide for unlimited human wants
what does aggregate mean
total
what are economic agents
groups of people involved in a transaction
what are the three economic agents
consumer
producer
government
what does ceteris paribus mean
all other things remaining equal
all variables held constant
why is economics considered a social science
unable to carry out scientific experiments
uses scientific methods of data collection and observing human behaviours
makes models using assumptions to explain economic interactions
how are economic models built
identify variables to study
make assumptions
simplify complex human behaviours
what is the purpose of economic models
explain tendencies
simplify observations
why is ceteris paribus needed for economic models
helps simplify observations
people are complex and always changing
impossible to consider all variables
what is positive economics
objective statements on how a market/economy works
can be proven/tested with real data
what is normative economics
value judgement on hypothetical economic solutions/policies
cannot be proven
shoulds/worlds
what is value judgement
evaluative statement on how good/bad you think idea is
how does value judgement influence economic decisions
individuals/businesses/governments use value judgement
what is the basic economic problem
limited resources but unlimited human wants
why does the economic problem exist
there is scarcity
economic agents are forced to make choice because of this
what is scarcity in economics
limited resources
how does scarcity affect prices in a free market
scarcer resources have higher prices due to higher demand
how does scarcity affect economic decision-making
choices have to be made about best use of limited resources
what is opportunity cost
value of next best alternative alternative that is foregone when making decision
what are renewable resources in economics
can be replenished
no opportunity cost
what are non-renewable resources in economics
available in limited quantities and cannot be replenished in a human lifespan
have opportunity cost
what are factors of production
resources used in production of goods/services
measured in quantity/quality
what are the four factors or production
capital
land
labour
enterprise
what is capital
manmade/physical assets used to produce goods/services
what is land
natural resources used to produce goods/services
what is labour
workers needed to produce goods/services
what is enterprise
risk takers who combine other FOP to produce goods/services
what is production possibility frontier
economic model showing maximum production of two goods/services
shows idea of opportunity cost
what does PPF curve represent
full/efficient use of FOP
how is opportunity cost shown on PPF
downwards sloping curve
amount of one good that is foregone to produce more of other good
what causes outward shift of PPF
economic growth and increase in quantity/quality of FOP
what does point inside PPF curve represent
insufficient production and use of resources/FOP
what does point outside PPF curve represent
unattainable production given level of FOP
what are consumer goods
tangible products sold to consumer to satisfy current needs/wants
what does an inward/left shift of ppf show
decrease in quantity or quality of FOP
economic decline
possible reasons for left shift
war
natural disaster
aging population/retirement rate increases
emigration (Human Capital flight)
resource depletion
deforestation
what is the impact of war on FOP
decrease in:
land
labour (death rate/draft)
enterprise
what is the impact of natural disasters on FOP
decrease in:
land
labour (death rate)
capital (destroyed
enterprise
what does an outward/right shift of ppf show
increase in quantity or quality of FOP
economic growth
possible reasons for outward/right shift of ppf
increase in education
increase in training/development
increase in trade
immigration
tax breaks
increased birth rate
grants/subsidies
increase in minimum wage
what is the impact of increase in education on FOP
higher quality of labour
what is the impact of increase in training on FOP
higher quality of labour
what is the impact of increase in trade on FOP
more land
what is the impact of increase in education on FOP
higher quantity and quality of labour
what is the impact of tax breaks on FOP
more enterprise
what is the impact of grants/subsidiaries on FOP
more enterprise
what is the impact of increase in minimum wage
more incentive to work
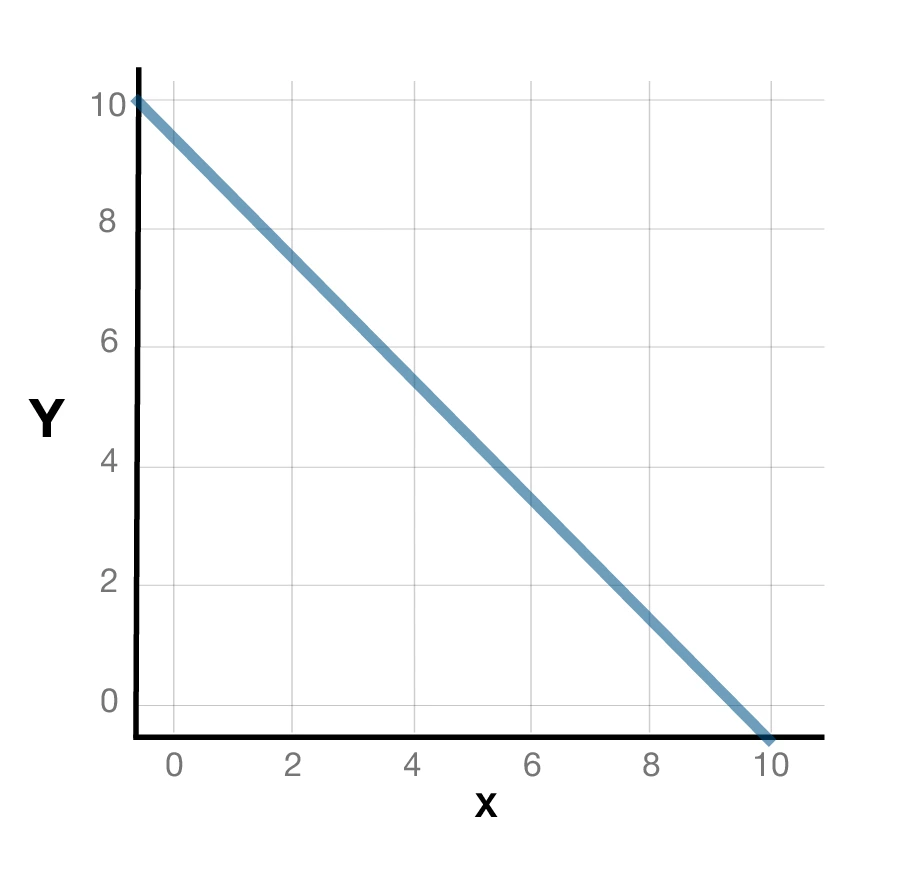
what does a linear PPF graph show
constant opportunity cost
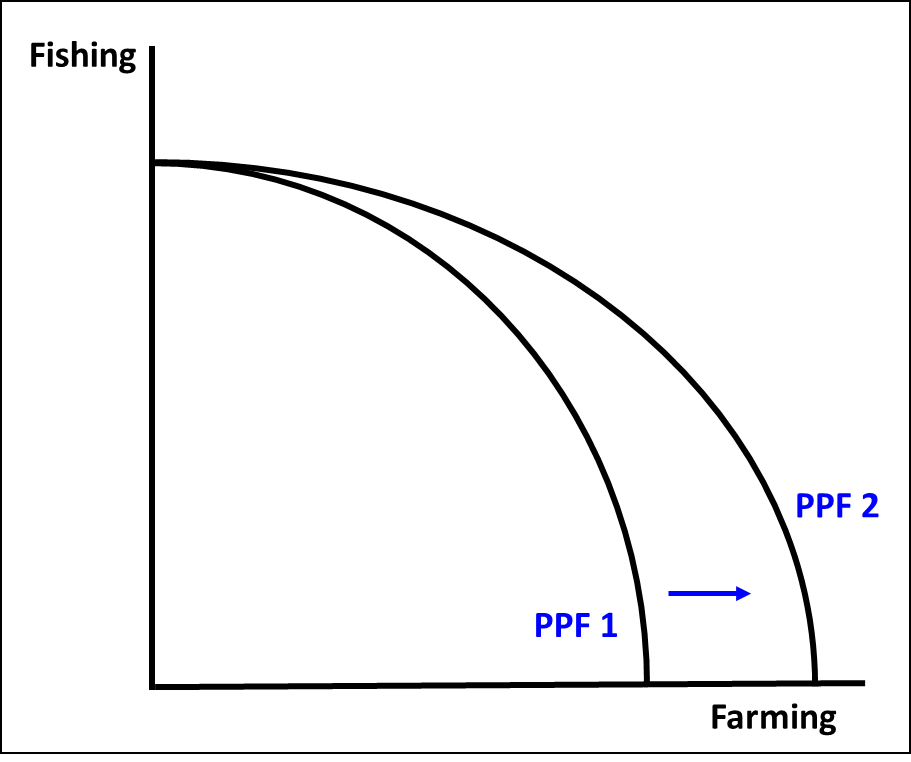
what does a ppf shift in one good show
investment in FOP favouring one good over the other
what is specialisation
when a individual/firm/country focuses on producing goods/services in which they are advantageous in
what is division of labour
dividing up tasks into smaller units of work so specialisation can take place
what are the benefits of the specialisation and division of labour
increased productivity
increased quality of produce + labour
less time spent on moving between tasks
repetition of limited range of tasks leading to expertise
higher output
low labour costs per unit
reduction in average costs - firm is price competitive
increased profits
what are the drawback of the specialisation and division of labour
boredom from repetitive tasks leading to low productivity
loss of skills once specialised
if one stage of production breaks, production may stop
lack of variety in goods
what are the macro benefits of the specialisation and division of labour
high economic growth
more choice as country can trade
low price due to economies of scale
what are the macro drawbacks of the specialisation and division of labour
economic growth is not sustainable as it’s dependent on external factors
domestic producers may not be able to compete against imported goods/services
price fluctuations
what is economies of scale
the more you produce the cost per unit is cheaper so is sold at lower cost
what is the impact of specialisation on FOP
increase in quality of labour
increase in quantity and quality of labour
output increases
define production
number of outputs
define productivity
number of outputs per given time
what is the objective of producers
profit maximise
what is the objective of consumers
maximise utilities (satisfaction)
what is the objective of govt
maximise social welfare
what are the three main economic questions
what to produce?
who to produce for?
how to produce?
what is a free market system
market forces determine allocation of scarce resources
controlled by invisible hand
run on price mechanism (resources allocated based on price - supply/demand)
what are the features of free market
motive for production is profit
freedom of choice for producers and consumers
no government intervention
right to private ownership
how does competition affect free market
better quality of goods/services, lower prices, and encourages innovation
more choice
what are the advantages of free market
consumer sovereignty
efficiency - profit motive encourages producers to reduce cost and increase profit
no bureaucracy nor planners needed to allocate resources
greater economic growth from increased outputs
what is consumer sovereignty
consumers in market economies determine what is to be produced via their purchasing decisions
what are the disadvantages of free market
unequal distribution of income/wealth
booms and slumps (trade cycle) - macroeconomic instability
external costs (market failure)
lower provision of public and merit goods (good for society)
producer sovereignty - monopolies
consumer exploitation
what is a command economy system
govt determines how all resources are allocated according to common good
no price mechanism
no markets
what are features of command economy system
FOP belong to govt
central plan on how to allocate resources established by govt
no enterprise unless permitted by govt
complete govt intervention
what are advantages of a command economy system
equality
macroeconomic stability
fewer externalities (effect of third parties)
full employment
what are disadvantages of a command economy system
inefficiency as no profit motive and equal wages
lack of incentives and creativity
less choice
shortages and surpluses
what is mixed economy
combines features of planned and free market economies
govt supply public and merit goods
what are features of mixed economy
more even distribution of income
ownership/production and resource allocation by state and individuals
business compete with each other for FOP
freedom of choice
prices regulated by state in public sector
prices regulated by market forces in private sector
motive of production - public sector maximises social welfare while private maximises profit
how does govt intervene in mixed economy
taxes
govt spending
regulation to redistribute income
discourage production of less desirable goods/services
what are advantages of mixed economy
freedom of choice
more competition
more creativity
more economic growth
less social + external costs
provision of public and merit goods
what are the disadvantages of mixed economy
some inequality
govt failure
difficult to control power of govt
same drawbacks as the other two
what are the functions of money
medium of exchange
unit of account
store of value
standard of deferred payment
what is medium of exchange
facilitates business transactions
allows economic agents to exchange for goods/services
addresses double coincidence of wants in barter system
what is barter system
exchange of goods/services for other goods/services without using money
what is unit of account
money allows economic agents to compare prices and keep account
what is store of value
allows economic agents to save for future use
what is standard of deferred payment
allows economic agents to buy now and pay later
eg. credit cards
what is one precaution with function of money
inflation erodes value of money
what is the classic economic theory
economic agents make rational decision
what is the assumption of rational decision making
economic agents select the choice with the highest benefit
how do consumers act rationally
maximise utility
what does utility mean
amount of satisfaction gained from consuming good/service
what is total utility
total satisfaction consumer gets from consumption of units of good within period of time
what is marginal utility
additional utility gained from each additional unit of consumption
what is diminishing marginal utility
as more units are consumed the additional units will provide less additional satisfaction
how do producers act rationally
maximise profit
how are producers able to profit maximise
produce goods/services desired by consumers
produce at lowest cost while gaining as much revenue as possible
what is the formula for profit
total revenue - total costs
what is revenue
money received from sales (income)
price x quantity
how do workers act rationally
maximise welfare at work
how do workers maximise welfare
consider pay, working conditions, benefits, commute, cost of finding alternative employment
what is the issue with pay for workers
conflict of objectives
what is the issue with benefits for workers
raises cost of business