Lecture 15 Positive Interactions
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
12 Terms
What are positive interactions?
Interactions that involve two or more organisms in which neither participant is negatively affected and at least one participant benefits
List the three main types of positive interactions.
Facilitation
Mutualism
Symbioses
Facilitation
One participant gains from the relationship (0, +)
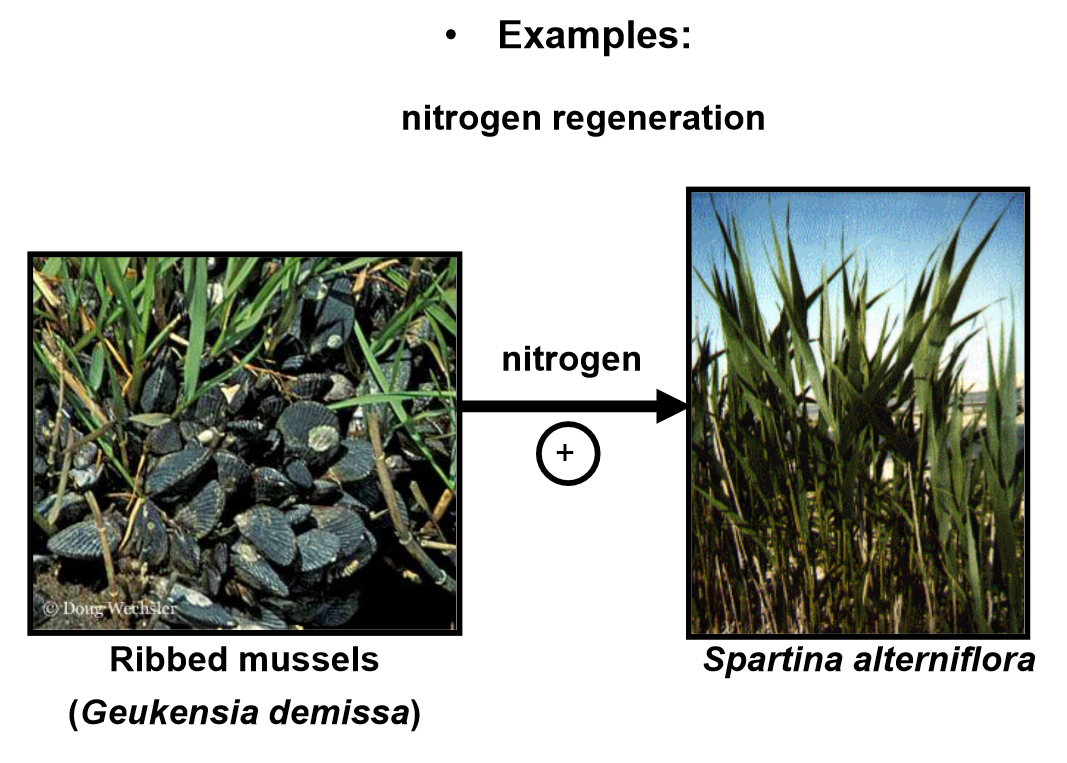
Examples:
ribbed mussels filter feed and expel detritus (unwanted matter) that acts as a source of nitrogen for saltwater plants
palatable seaweeds are protected from consumption when associated with unpalatable seaweeds
Mutualism
Both participants gain from the relationship (+, +)
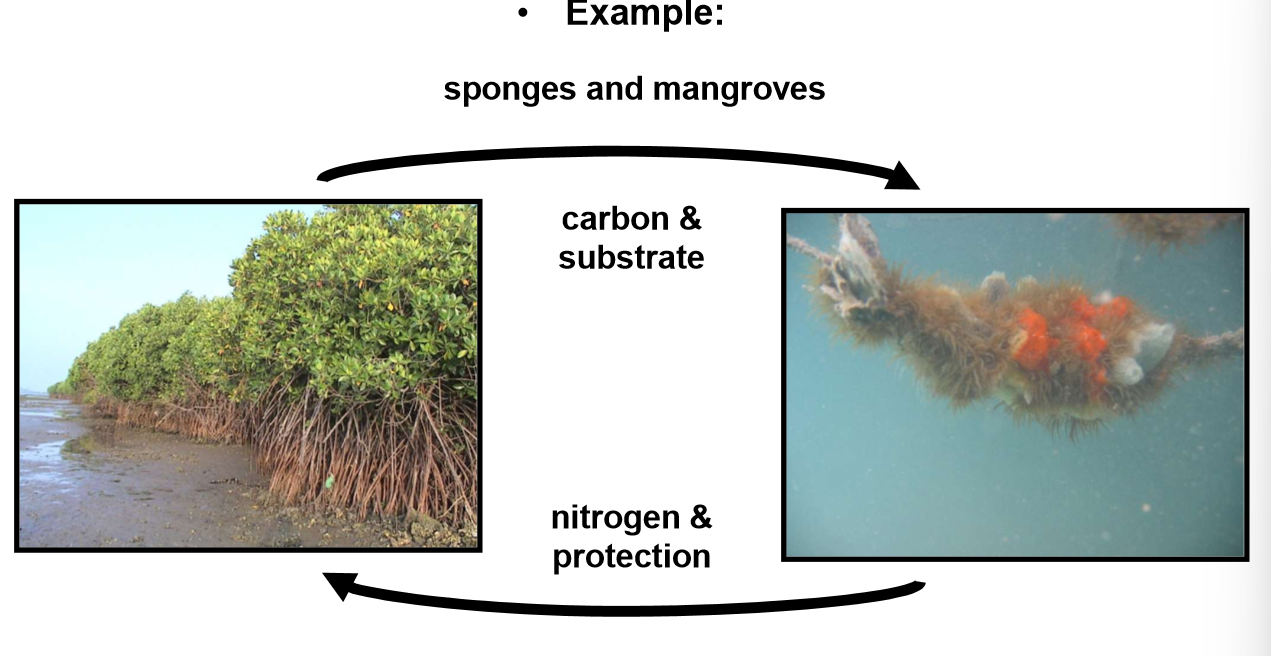
Example:
Mangroves capture atmospheric CO2 and store carbon in their biomass and surrounding sediments. Sponges and other organisms grow on the mangrove roots and excrete nitrogen which helps the mangrove grow.
Symbiosis
An interaction by which one or more participants gains access to novel metabolic capacities
“Living together” of different species (can also include parasitism)
ex. coral-dinoflagellates interaction, coral “gain” the ability to fix carbon
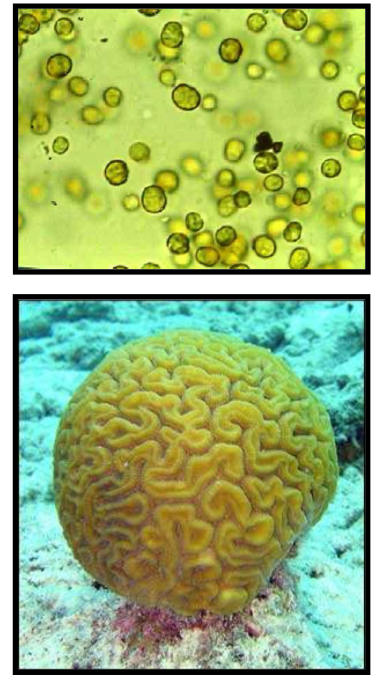
How do corals benefit from their symbiotic relationship with zooxanthellae?
Zooxanthellae are dinoflagellates that live in coral tissue and provide coral with carbohydrates which increase calcification.
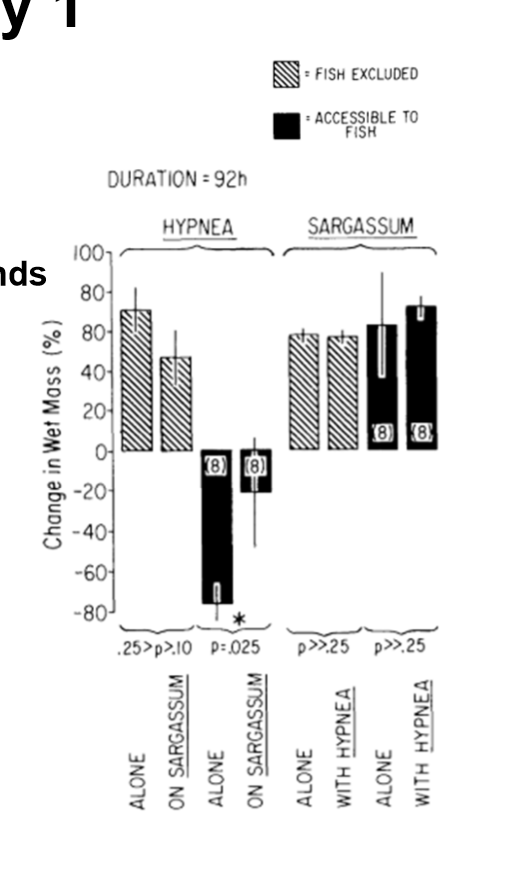
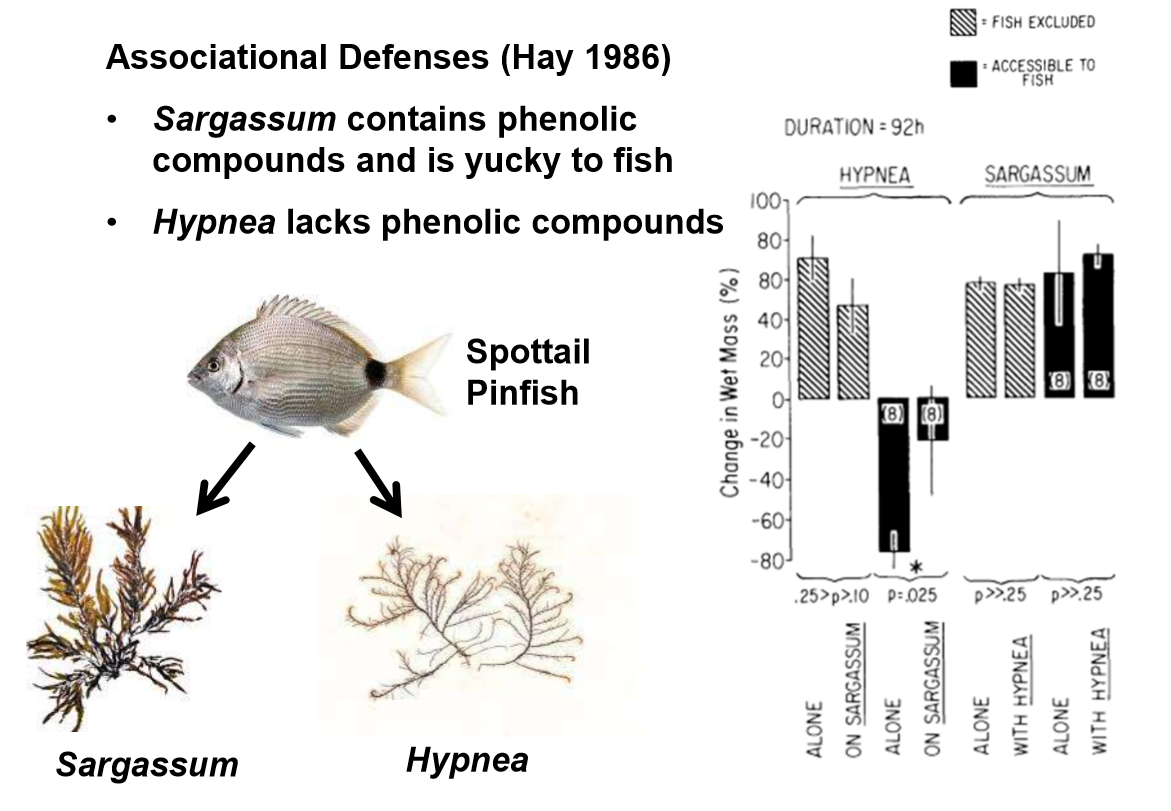
Case study 1: Associational Defenses
Does Hypnea do better alone or when Sargassum is present? Why?
When the seaweeds are accessible to fish, Hypnea do better when Sargassum is present. Sargassum has phenolic compounds that make it unpalatable to fish. When Hypnea (palatable) grows together with Sargassum, it gains an associational defense. This is an example of facilitation.
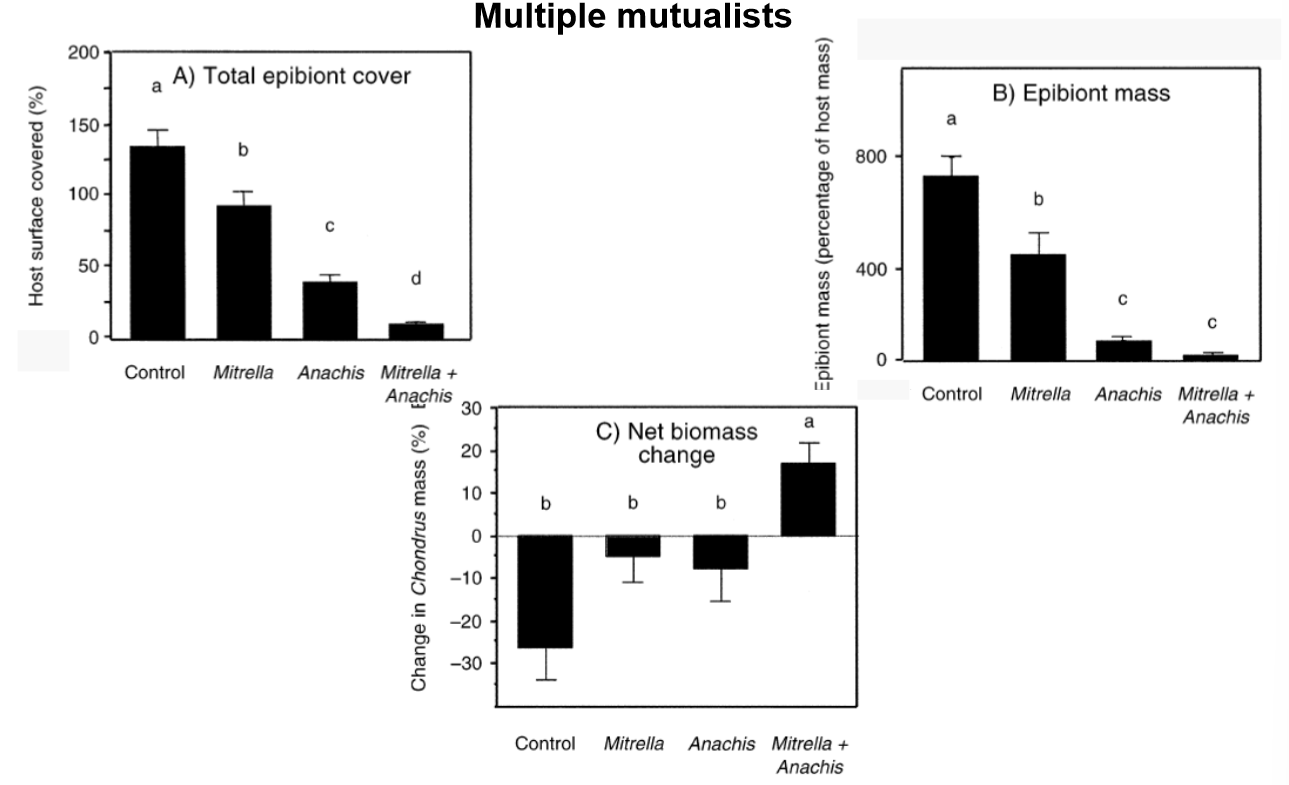
Case study 2: Multiple mutualists
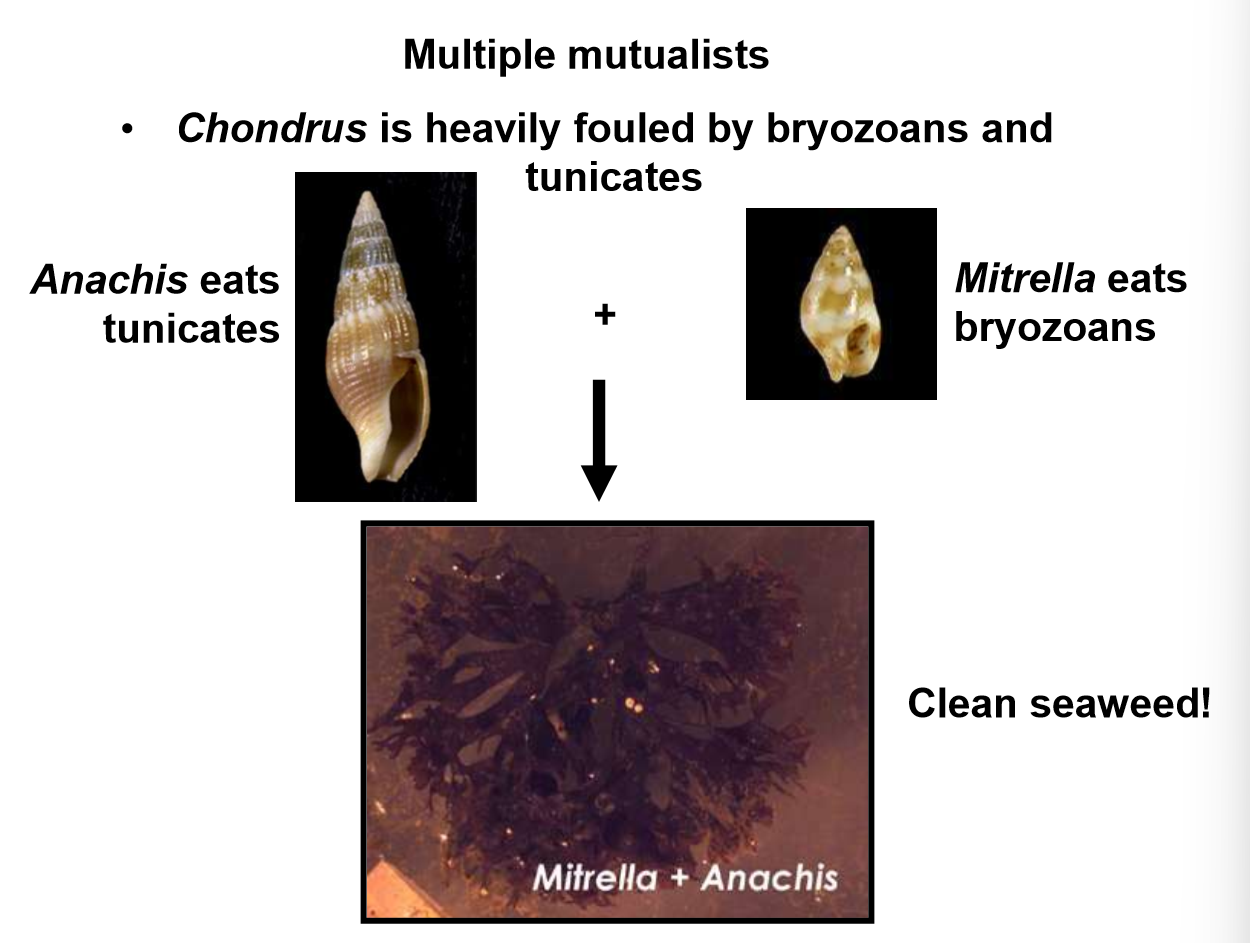
How did both gastropod species Anachis and Mitrella provide complementary benefits to their seaweed host Chondrus?
Chondrus is a seaweed that is vulnerable to fouling by bryozoans and tunicates. When both Mitrella and Anachis are present, both tunicate and bryozoan coverage were reduced. A positive net biomass change is only seen when both gastropods are present because the seaweed is clean and can efficiently photosynthesize.

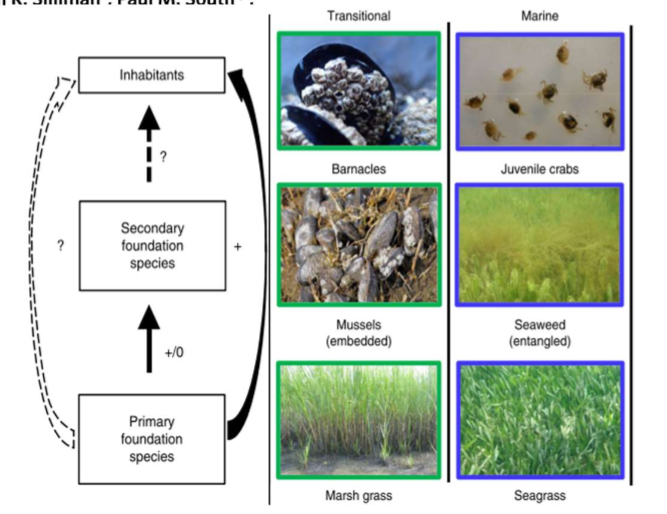
Case study 3: Facilitation Cascades
What is a “facilitation cascade”?
Facilitation cascades occur where one habitat-forming species facilitates another habitat-forming species, with synergistic effects on biodiversity.
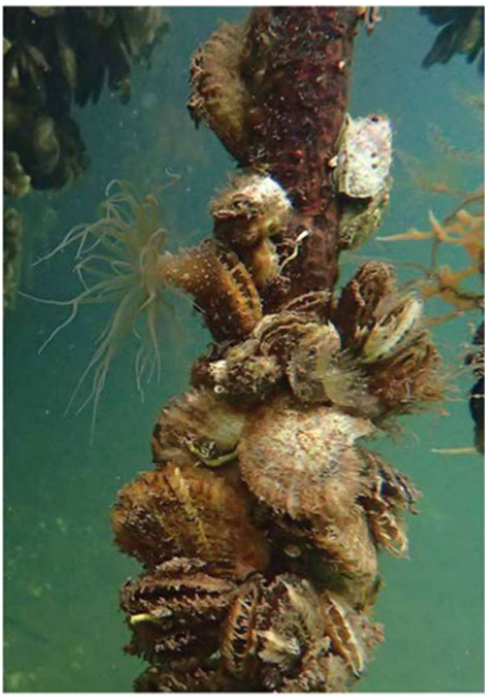

Case study 3: Facilitation Cascades
What are the similarities and differences between trophic cascades and facilitation cascades?
Facilitation cascades are related to habitat whereas trophic cascades are related to consumption. For trophic cascades, the keystone species are the top consumers. For facilitation cascades, the primary habitat former is the basal species.
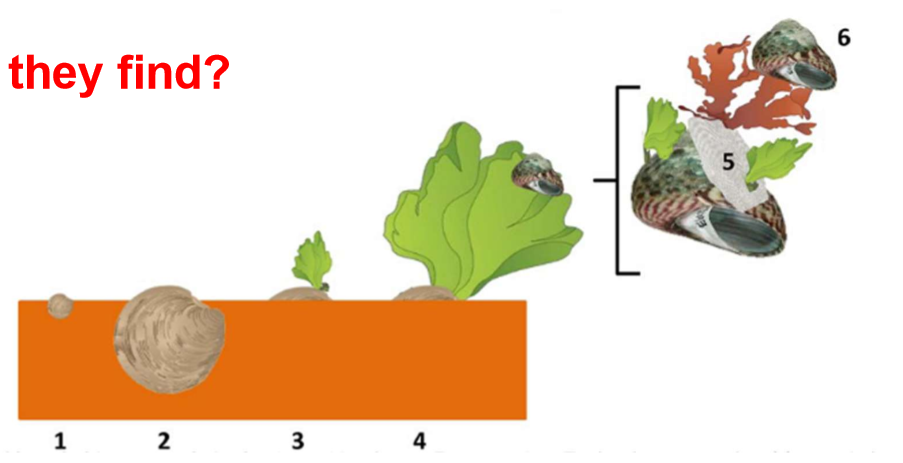
Case study 3: Facilitation Cascades
What experimental manipulations did the authors conduct to evaluate this cascade? What did they find?
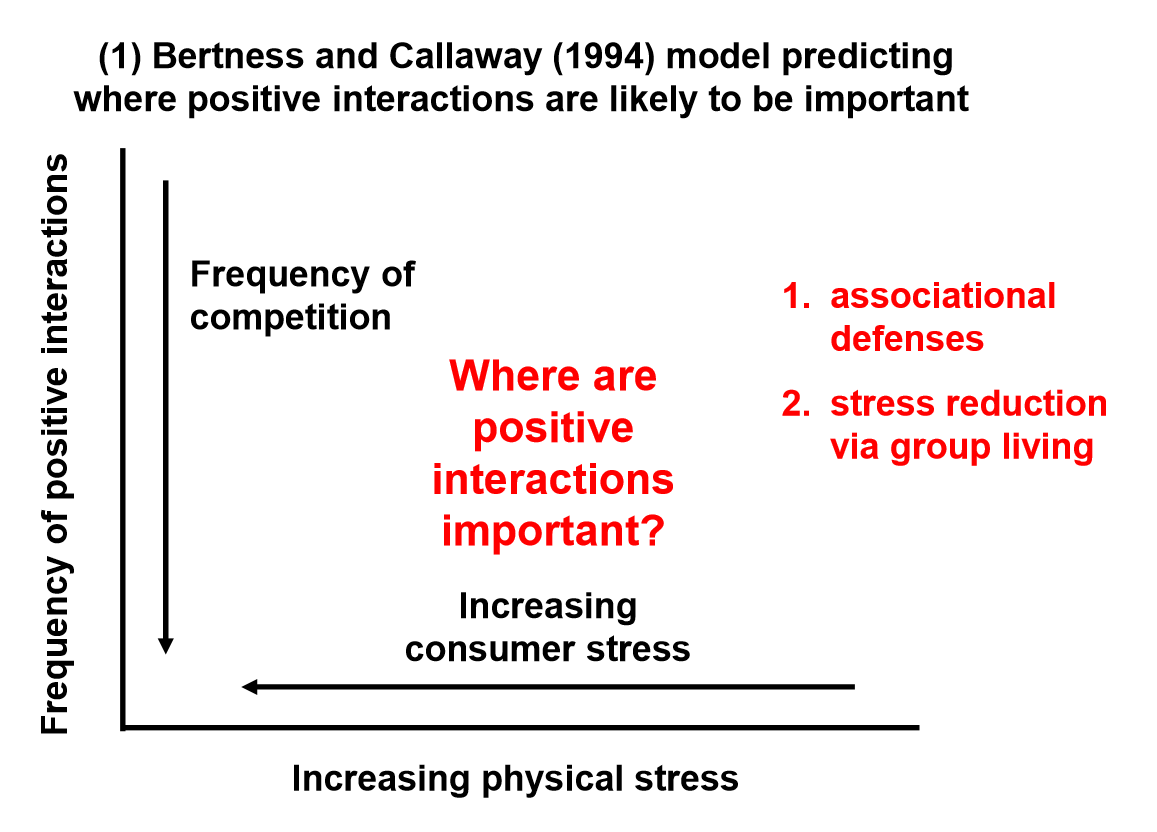
Conceptual Models
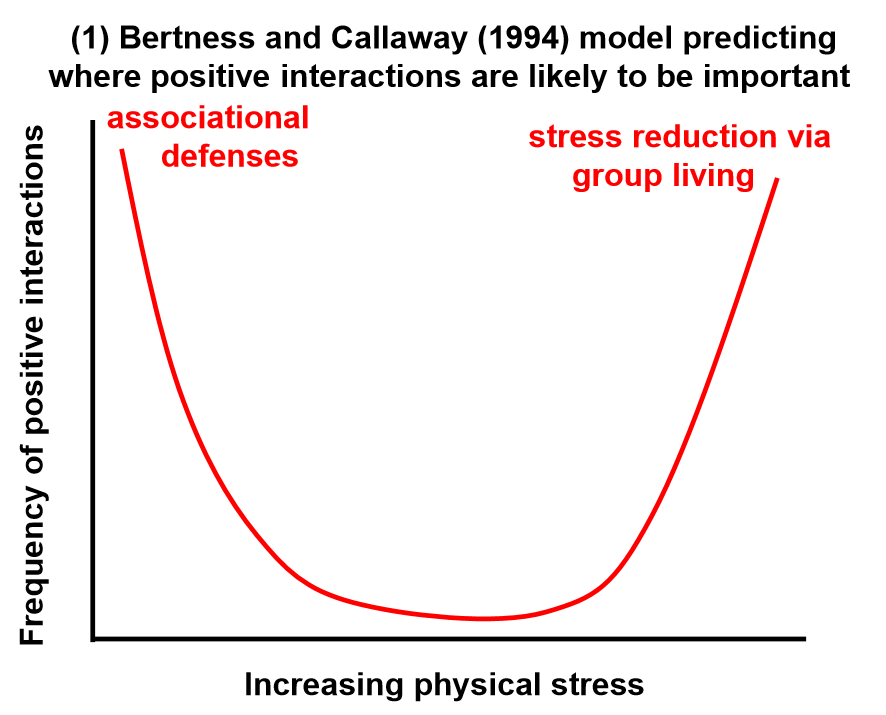
Where are each type of positive interaction (1. associational defenses & 2. stress reduction via group living) most important?
Associational defenses are most important when consumer stress is highest (low physical stress).
Stress reduction via group living is most important when physical stress is high (low consumer stress).