hormones
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
define a hormone
A chemical messenger secreted by the endocrine glands and carried in blood plasma to target cells
describe how hormones have an effect
hormones are made in special cells called the endocrine gland
They secrete hormones into the blood stream . Its carried by blood into the plasma.
This is carried across the body in the blood these eventually reach target cells with receptors on there surface.
Receptors have specific shapes and the hormone has to be complimentary to bind to the hormone. this means it doesn’t bind to receptors on non target cells
the binding of a hormone to the complimentary receptor acts as a signal to trigger changes inside. This exact process depends on the the type of hormone
what is the speed and target / size of impact compared to nervous control
hormonal responses are slower and target a larger area and effect lasts longer.
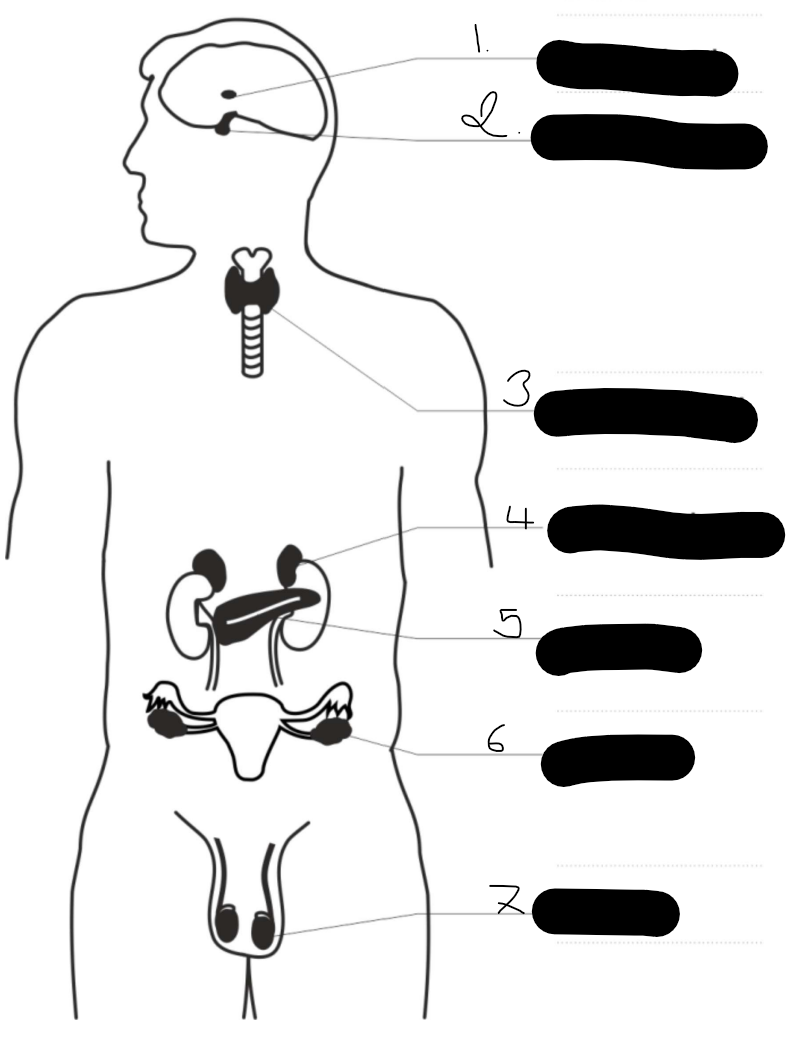
pineal gland
pituitary gland
thyroid gland
adrenal gland
pancreas
ovaries
testes
pineal gland
hormone
function
melatonin
regulates the sleep wake cycle / biological clock
pituitary gland
hormone
function
growth hormone many others eg FSH LH oxytocin
master gland
thyroid gland
hormone
target organ
function
thyroxine
liver
controls metabolic rate
adrenal gland
hormone
function
adrenaline+ cortisol
play a role in fight or flight
pancreas
hormone
target organ
function
glucagon and insulin
liver
control glucose levels in the blood
ovaries
hormone
target organ
function
oestrogen + progesterone
uterus
controls menstrual cycle
testes
hormone
function
testosterone
male characteristics
what are the 2 lobes of the pituitary gland
anterior and posterior
which area of the brain regulates the pituitary gland
hypothalamus
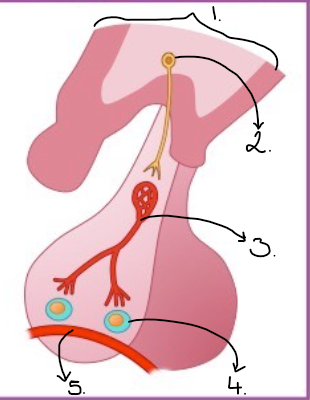
Is this the anterior or posterior lobe+ fill in labels
hypothalamus
neurone secretary cell
portal vessel
endocrine cell ( releases hormone into blood stream)
blood vessel
anterior
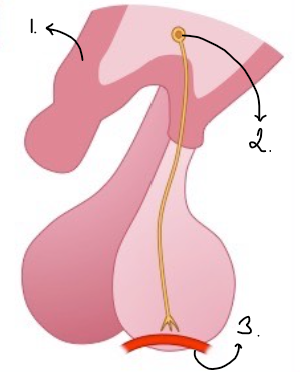
Is this the anterior or posterior lobe+ fill in labels
hypothalamus
neurone secretary cell
blood vessel
posterior
describe how a hormone is released from the anterior lobe
The hypothalamus has a neurosensory cells these are never cells which produce and secretions from the end of there axon. One group of these neurosensory cells produces releasing factor which are released into the portal blood vessel. This causes the endocrine with in the cells to release specific hormones into the blood stream
describe how a hormone is released from the posterior lobe
The posterior lobe releases the hormones that have been produced by the hypothalamus itself. Neurosensory cells extend from the hypothalamus into the posterior lobe. There stores here before being released into the blood stream.
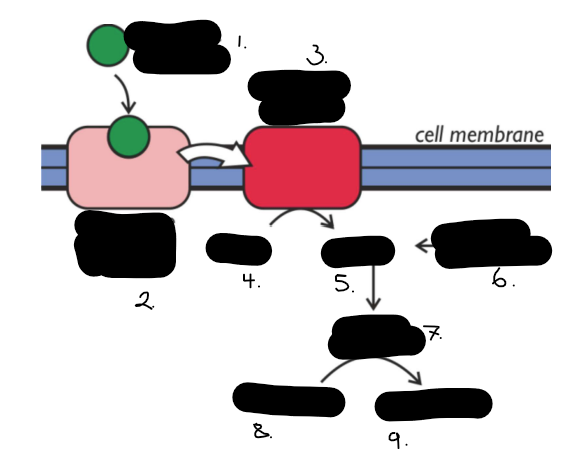
is this insoluble and soluble
hormone
hormone receptor complex
adenylate cyclase
ATP
cAMP
secondary messenger
active enzyme
glycogen
glucose
describe how insoluble hormones impact a cell
most hormone do not enter the cell but bind to a receptor protein on the cell membrane to form a hormone receptor complex. This complex then activates the enzyme adenylate cyclase which catalyses the production of chemicals cyclic AMP cAMP from ATP in the cytoplasm . The cAMP in turn activates a cascade of enzymes resulting in the breakdown of glycogen to glucose. The cAMP is called a second messenger.
hormone
hormone receptor complex
nuclear membrane
DNA
RNA polymerase
transcription
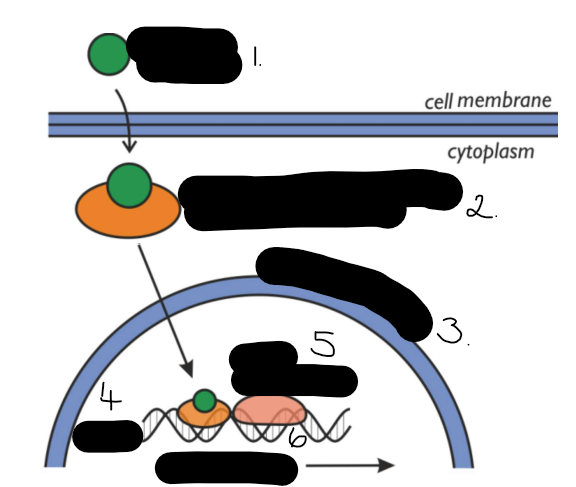
describe how soluble hormones impact a cell
The hormone is lipid soluble so can easily pass through the cell membrane by lipid diffusion. They bind to receptor proteins to form a hormone receptor complex in the cytoplasm which enters the nucleus and stimulates protein synthesis by binding to DNA and acting as a transcription factor. For example the steroid hormone oestrogen stimulates the growth of the uterus lining by being a transcription factor.
what is another name for a soluble hormone
steroid