Viruses 🦠
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Viruses vs. Cells
Viruses lack organelles, cytoplasm, and membranes.
They consist of genetic material (DNA or RNA) enclosed in a protein coat (capsid), sometimes with a lipid envelope.
Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have membranes, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and metabolic machinery.
Properties of Life in Viruses
Viruses can evolve and reproduce, but only inside a host. They do not independently metabolize, grow, or maintain homeostasis.
DNA Viruses
Contain DNA as genetic material; replicate using host DNA polymerase (e.g., herpesvirus).
Low mutation rate; only require one vaccination
RNA Viruses
Contain RNA as genetic material; often replicate using RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (e.g., influenza virus).
High mutation rate (RNA polymeres cannot proofread DNA); may require yearly vaccinations
Lytic Cycle
Virus immediately replicates inside host, causing cell lysis and death (e.g., bacteriophage T4).
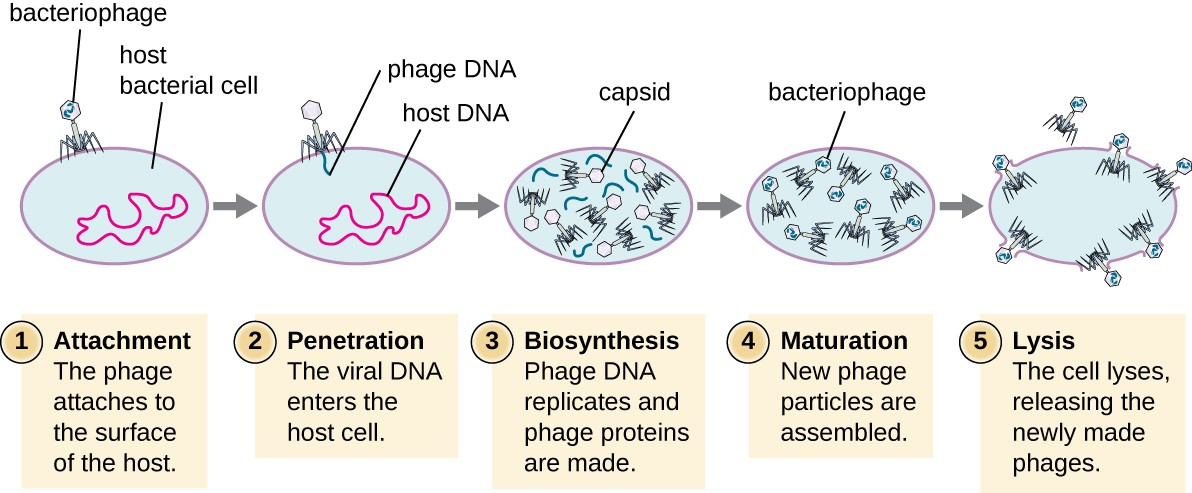
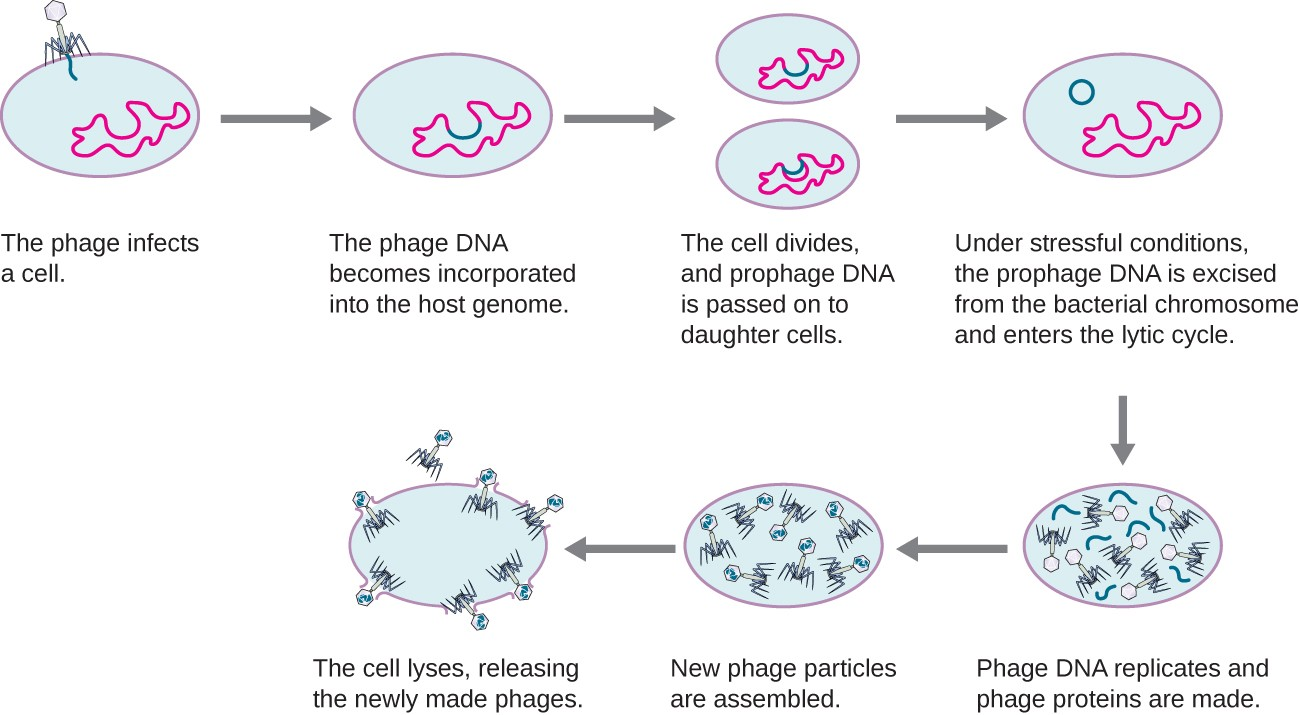
Lysogenic Cycle
Viral DNA integrates into host genome, replicates silently until triggered to enter lytic cycle (e.g., bacteriophage λ).
Vaccination: One-Time
Stable DNA viruses (e.g., measles) require one vaccination because their antigens rarely change.
Vaccination: Annual
Rapidly mutating RNA viruses (e.g., influenza) require annual vaccines due to frequent antigenic shifts/drifts.