Radiology6- Periodontal Disease and Radiographic Assessment
1/66
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key terms and concepts related to periodontal disease and its radiographic assessment, aiding in the understanding of diagnosis and classification.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Periodontium
Specialized support structures around the teeth, including periodontal ligament, cementum, gingiva, and alveolar bone.
Hesy-Re
The first recorded dentist from 2600 BC, known as the 'Great one of the ivory cutters'.
Radiographs
Imaging technique used in periodontal diagnosis to assess bone and tissue condition surrounding teeth.
Alveolar crest
The highest point of alveolar bone that supports the teeth, should be between 0.5 - 2 mm from the CEJ.
Staging and Grading of Periodontitis
Staging refers to the extent of disease, while grading refers to the progression of the disease over time.
Vertical bitewings
A type of dental radiograph better suited for evaluating moderate to severe bone loss.
Cortical outline of alveolar bone
The outer layer of the alveolar bone, which appears well-defined and radiopaque on radiographs.
Localized periodontitis
A form of periodontal disease involving less than 30% of teeth affected; may show vertical osseous defects.
Furcation involvement
An indication of periodontal disease where the bone loss occurs in the furcation area of multirooted teeth.
CAL
Clinical attachment level, used to measure the extent of periodontal disease.
Sclerotic bone
Bone that appears denser or radiopaque in chronic periodontitis, usually indicative of a chronic inflammatory response.
'Floating Tooth' appearance
A clinical presentation of a tooth that has lost significant support structure due to bone loss, giving the appearance of being suspended.
Primary criteria for grading
Includes direct evidence such as longitudinal data of radiographic bone loss or CAL.
Direct evidence of progression
Observable changes in clinical attachment level (CAL) over time or changes in radiographic bone loss.
Calculus
Tartar build-up on teeth, a local initiating factor that can contribute to periodontal disease.
Pathologic considerations in radiographs
Refers to potential issues like caries, periapical lesions, and root resorption, which can affect periodontal health.
Moderate chronic periodontitis
A clinical diagnosis may result in a variety of bone defects and shows horizontal bone loss.
Bone loss patterns
Classified as localized, generalized, or molar/incisor pattern based on the extent of the affected sites.
perio dontium
around teeth
radiographs purpose
permanent records of periodontium
Bitewings used for
interproximal caries and bone loss
used to view anterior crestal bone
normal PA, can take BW but not common
vertical bitewings
used to view bone levels, 3 can be taken
vertical angulation
separates tooth cusps and gives improper view of bone
Bitewings used to test bone
because of proper vertical angulation to view bone and interproximal spaces
Bitewings are more accurate than PAs
due to lack of distortion by incorrect vertical angle
localized patterns of bone loss/change
<30% of teeth involved
generalized bone loss pattern
molar/incisor bone loss pattern
staging
extent of disease
grading
progression of disease over time
radiographs asses
bone in mm/%
alveolar crest health
bone loss at furcation
width of PDL
initiating factors (restorative overhang/calculus)
root length and morph
crown to root ratio
anatomical perio eval considerations
root proximity
proximity to maxillary sinus
missing, supernumerary and impacted teeth
pathologic considerations of perio eval
caries, lesions, root resorption
stages
1,2,3,4
grade
a,b,c
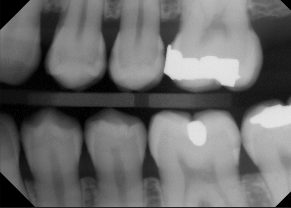
normal alveolar bone
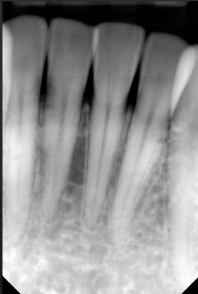
normal alveolar bone
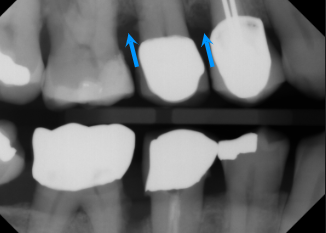
first sign of bone loss is loss of cortication of interproximal bone
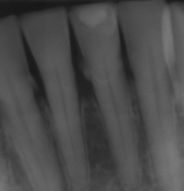
local/initiating factor
calculus
limitations to radiographs
two dimensions
underestimation of bone loss and caries
lacks soft tissue visibility
periodontal disease is diagnosed
clinically not radiographically
horizontal bone loss
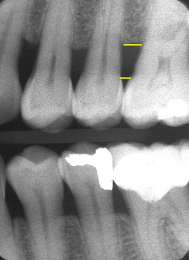
horizontal bone loss
parallel movement of alveolar crests towards the apex of the tooth
mild horizontal bone loss
blunting of alveolar crests and slight loss of height
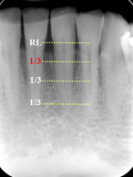
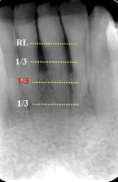
loss of height around multiple teeth may involve furcation
moderate horizontal bone loss
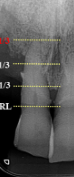
severe horizontal bone loss
vertical bone loss
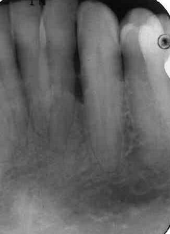
vertical bone loss
vertical bone loss
seen on radiographs as a non parallel line of bone loss
bone loss with furcation involvment
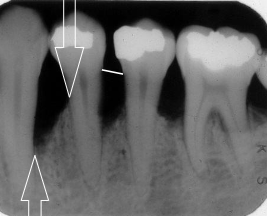
first sign of vertical bone loss
PDL space widens towards the crest
first radiographic sign of furcation involvement
pdl widening at furcation
circumferential bone loss
known as cratering in a localized area around the tooth, indicating periodontal disease.
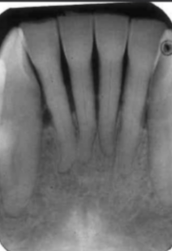
moderate to severe horizontal bone loss
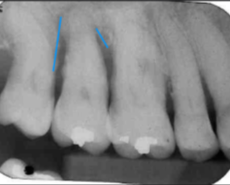
moderate to severe horizontal bone loss
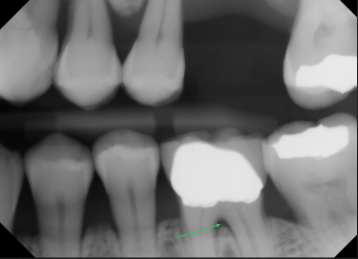
vertical bone loss M/D of #2
effects of bone loss on adjacent bone
inflammatory response to perio lesions and
more sclerotic/ radiolucent peripheral bone
sclerotic reaction of adjacent bone in perio
usually to chronic cases
radiolucent or lytic response of adjacent bone
more common in acute cases
condensing osteitis
sclerotic bone in areas of chronic periodontitis
advanced stages of perio
extensive horizontal bone loss or extensive vertical defects
osseous defects in furcation of multirooted teeth
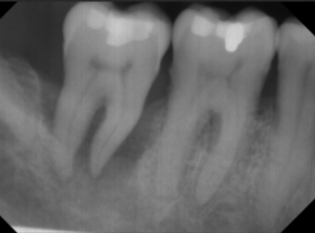
floating tooth
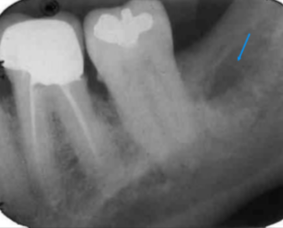
bone scar after extraction
periodontal abscess
rapidly destructive lesion originating in deep soft tissue pocket
if acute=no radiographic signs
localized bone loss
less than 30% of sites effected
vertical osseous defects
severe and rapid loss
worse on incisors and first molars
generalized bone loss
more than 30% of sites affected
stage IV perio