K9 feline final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/339
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:45 PM on 5/1/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
340 Terms
1
New cards
What are inactivated vx, and some ex
Made from virus that’s been killed
EX- rabies, canine influenza, canine lepto
EX- rabies, canine influenza, canine lepto
2
New cards
What are modified live- live and ex
Pathogen that is modified where doesn’t produce disease
Ex- DAPP feline panluekopenia
Ex- DAPP feline panluekopenia
3
New cards
What does DAPP/ DHLPP mean
Distemper, adenovirus, parainfluenza, parvovirus, Lepto
4
New cards
Where are the locations for vx
Rabies- right rear
Lepto DHLPP- left rear
DHPP- right front
Flu- left front
Bordetella- PO IN
Lepto DHLPP- left rear
DHPP- right front
Flu- left front
Bordetella- PO IN
5
New cards
What are feline core vx
Feline calicivirus, panleukopenia, rabies, feline leukemia
6
New cards
What are dog core vx
DA2PP rabies
7
New cards
What does FVRCP stand for
Feline viral rhinotracheitis calicivirus panleukopenia
8
New cards
What are some adverse vx effects
Lethargy mild fever soreness decreased appetite, sneezing, diarrhea, anaphylaxis
9
New cards
What are the Benefits for spay/neuter
Spay- eliminated unwanted pregnancies, mammary cancer, pyometra
Neither- testicular cancer, eliminate roaming, inter male aggression
Neither- testicular cancer, eliminate roaming, inter male aggression
10
New cards
What are the 9 preventable k9 diseases
Rabies zoonotic, canine parvovirus, canine distemper, canine adenovirus, lepto, canine parainfluenza, Lyme disease, Bordetella sis, canine enteric coronavirus
11
New cards
How is rabies passed, CS DX TX
Direct contact with infected tissues
Infectious- tears, saliva, respiratory tract fluids
Non infectious- blood urine feces
CS- progressive- behavioral changes, CNS symptoms
DX- immunofluorecence of greasy brain tissue
TX- no treatment
Infectious- tears, saliva, respiratory tract fluids
Non infectious- blood urine feces
CS- progressive- behavioral changes, CNS symptoms
DX- immunofluorecence of greasy brain tissue
TX- no treatment
12
New cards
How to send rabies specimen
Severe head from body w/o damaging brain/ brain stem
Double bag specimen
Label bags
Fill out rabies submitted form and place in box with specimens
Line box with cold packs/ absorbent paper
Seal container and ship overnight to TDSHS (Texas department of state health services)
Double bag specimen
Label bags
Fill out rabies submitted form and place in box with specimens
Line box with cold packs/ absorbent paper
Seal container and ship overnight to TDSHS (Texas department of state health services)
13
New cards
How is parvovirus passed, CS DX TX and how to prevent
From contact w/diarrhea and saliva (no vx) ,
CS- low WBC, lethargy fever, vomiting, tachycardia
DX- Snap, PCR, CS
TX- fluid therapy, supportive care
Prevention- bleach rescue
CS- low WBC, lethargy fever, vomiting, tachycardia
DX- Snap, PCR, CS
TX- fluid therapy, supportive care
Prevention- bleach rescue
14
New cards
How is adenovirus passed, CS TX
Infectious fluids
CS- high fever, low WBC, clotting abnormalities
TX- blood transfusion, fluid therapy
CS- high fever, low WBC, clotting abnormalities
TX- blood transfusion, fluid therapy
15
New cards
How is distemper passed CS DX TX
Passed- sneezing and coughing
CS-fever, sneezing, vomiting, neurological signs, hyperkeratosis
DX- PCR
TX- supportive care
CS-fever, sneezing, vomiting, neurological signs, hyperkeratosis
DX- PCR
TX- supportive care
16
New cards
How is lepto passes CS DX TX
Zoonotic
Standing water
CS- Glucosuria, lethargic, bleeding disorder
DX- clinical finding, microscopic agglutination test MAT, PCR assay
TX- supportive care doxy
Standing water
CS- Glucosuria, lethargic, bleeding disorder
DX- clinical finding, microscopic agglutination test MAT, PCR assay
TX- supportive care doxy
17
New cards
How is canine parainfluenza passes, CS DX TX
Respiratory tract (tracheobronchitis)
CS- coughing sneezing nasal discharge
DX- oral swab for PCR test
TX- antibiotics/ cough suppressants
CS- coughing sneezing nasal discharge
DX- oral swab for PCR test
TX- antibiotics/ cough suppressants
18
New cards
How is Lyme disease passes, CS TX
By deer tick
CS- acute/ chronic renal failure, fever anorexia, swollen painful joints
DX- history, PCR, western blot test
TX- doxy over amoxicillin, gabapenitn
CS- acute/ chronic renal failure, fever anorexia, swollen painful joints
DX- history, PCR, western blot test
TX- doxy over amoxicillin, gabapenitn
19
New cards
How is Bordetellosis passed CS DX TX
May pass to human from dog/cat
CS- hacking, sneezing, nasal discharge
DX- PCR respiratory signs and CS
TX- antibiotics, cough suppressants
CS- hacking, sneezing, nasal discharge
DX- PCR respiratory signs and CS
TX- antibiotics, cough suppressants
20
New cards
How is canine enteric coronavirus passed CS DX TX
Infected/ secretions/ feces
CS- anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea colored), lethargy
DX- PCR, CS
TX- supportive care antibiotics
CS- anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea colored), lethargy
DX- PCR, CS
TX- supportive care antibiotics
21
New cards
What are some feline preventable diseases
Rabies, panleukopenia, rhinotracheitis, calicivirus, leukemia, feline immunodeficiency viral infection
22
New cards
Another name for feline panleukopenia, how its passed, CS DX TX
Feline distemper
Attacks bone marrow and CNS, infected secretions
CS- enlarged lymph nodes, diarrhea, low RBC, seizures
DX- CS PCR testing outside, CPV test
TX- supportive care, fluid therapy
Attacks bone marrow and CNS, infected secretions
CS- enlarged lymph nodes, diarrhea, low RBC, seizures
DX- CS PCR testing outside, CPV test
TX- supportive care, fluid therapy
23
New cards
What is another name for feline rhinotracheitis, passes CS DX TX
Causes URI
Feline herpesvirus
Through air
CS- high fever, mouth sores, frequent sneezing, corneal ulcers
DX- PCR panel Respiratory panel
TX- nebulization, fluid therapy, eye ointment
Feline herpesvirus
Through air
CS- high fever, mouth sores, frequent sneezing, corneal ulcers
DX- PCR panel Respiratory panel
TX- nebulization, fluid therapy, eye ointment
24
New cards
What is calicivirus CS DX TX
Causes URI
CS- limping syndrome, ulcerations sneezing, ocular/ nasal discharge
DX- PCR thorax radiographs,
TX- supportive care, anti inflammatory ex
CS- limping syndrome, ulcerations sneezing, ocular/ nasal discharge
DX- PCR thorax radiographs,
TX- supportive care, anti inflammatory ex
25
New cards
How is feline leukemia passed, CS DX TX
Bite wounds, mutual grooming
CS- blood disorders, weight loss, poor coat, causes cell death
DX- PCR testing, ELISA, IFA
TX- no cure
CS- blood disorders, weight loss, poor coat, causes cell death
DX- PCR testing, ELISA, IFA
TX- no cure
26
New cards
What is feline immunodeficiency virus CS DX TX
Passed by fighting/ bites
CS- Fever, lethargy, asymptomatic- Stomatitis, chronic infections
DX- ELISA test, PCR,
TX- routine BW, live alone, wellness visits 6 months
CS- Fever, lethargy, asymptomatic- Stomatitis, chronic infections
DX- ELISA test, PCR,
TX- routine BW, live alone, wellness visits 6 months
27
New cards
What is the modified triadan system
System from numbering each tooth in mouth
28
New cards
What are the quadrants and numbers along with it
100- right upper maxillary
200- left upper maxillary
300- left lower mandibular
400- right lower mandibular
200- left upper maxillary
300- left lower mandibular
400- right lower mandibular
29
New cards
What are deciduous
Baby teeth
30
New cards
What does I C P M stand for in dental formulas
I- incisors
C- canines
P- premolars
M- molars
C- canines
P- premolars
M- molars
31
New cards
What are a dogs dental formula for deciduous and permanent
D- 2( I 3/3 C 1/1 P 3/3) = 28
P- 2( 1 3/3, C 1/1, P 4/4 M 2/3)= 42
P- 2( 1 3/3, C 1/1, P 4/4 M 2/3)= 42
32
New cards
What are the dental formulas for felines deciduous and permanent
D- 2( I 3/3 C 1/1 P 3/2)= 26
P- 2( I 3/3 C 1/1 P 3/2 M 1/1)= 30
P- 2( I 3/3 C 1/1 P 3/2 M 1/1)= 30
33
New cards
What is the difference between immediate and direct supervision
Immediate- DVM is in audible and visual range
Direct- physically onsite
Direct- physically onsite
34
New cards
What is positional and directional
Positional is left side
Directional is right side
Directional is right side
35
New cards
Define enamel
Hard substance around only crown
36
New cards
Define dentin
Hard substance around pulp cavity
37
New cards
Define pulp
Nerve tissue forming inner tooth
38
New cards
Define periodontal ligament
Connective tissue where root attaches socket
39
New cards
Define cementum
Hard tissue forming surface of root
40
New cards
Define apical delta
Branches at tip of root
41
New cards
Define furcation
Space between root of same tooth
42
New cards
Define apical
Direction of tip of root
43
New cards
Define crown
Part protruding above gingiva
44
New cards
Define coronal
Direction of tip of crown
45
New cards
What are some common dental condition of canine
Periodontitis, oral trauma, benign oral tumors, gingivitis, deciduous teeth complications
46
New cards
What are the four periodontal tissues
Gingiva, cementum, alveolar bone and periodontal ligament
47
New cards
What is the normal gingival sulcus for cats/ dogs
Cats- 0.5-1 mm
Dogs 0.5-3 mm
Dogs 0.5-3 mm
48
New cards
What are the stages of periodontitis
1- plaque formation (reverse with home care)
2- deepening of sulcus (some attachment loss)
3- moderate attachment loss ( destruct ligament)
4- severe attachment loss (bone and gum loss)
2- deepening of sulcus (some attachment loss)
3- moderate attachment loss ( destruct ligament)
4- severe attachment loss (bone and gum loss)
49
New cards
What are some periodontitis preventions
Barrier sealants to reduce plaque and bacteria
Antiseptic reduce bacteria in cavity
Dental diets cleanse tooth surfaces T/D
Antiseptic reduce bacteria in cavity
Dental diets cleanse tooth surfaces T/D
50
New cards
What are the types of dental fractures
Uncomplicated- crack or chip in enamel not exposing pulp
Complicated- broken, exposing pulp cavity
Complicated- broken, exposing pulp cavity
51
New cards
How can you repair uncomplicated fractures
Sealing site, adding bonding agent
52
New cards
How to treat complicated fractures
Root canal- removing pulp from canal
53
New cards
What are some types of oral tumors that can occur CS DX
Benign- slow growing and don’t spread
Malignant- aggressive and spread
CS- ulcerations, infections, pigmented or non pigmented
DX- FNA, histological exam
Malignant- aggressive and spread
CS- ulcerations, infections, pigmented or non pigmented
DX- FNA, histological exam
54
New cards
What is gingival hyperplasia and TX
Excessive growth/ thickening or gum tissue
TX- gingivectomy
TX- gingivectomy
55
New cards
What are peripheral odontogenic fibromas, TX
Slow growing tumors arising from periodontal structures,
TX-surgical removal
TX-surgical removal
56
New cards
What are some malignant tumors
Malignant melanomas, fibrosarcoma, squamous cell carcinomas
57
New cards
What are some types of malocclusions
Occlusion, dental malocclusion and skeletal malocclusion
58
New cards
What are neutroclusion
Jaw length normal, teeth abnormal position
59
New cards
What is mandibular distoclusion and another name for this condition
Lower jaw is shorter then upper
Mandibular brachgnathism
Class 2
Overbite
Mandibular brachgnathism
Class 2
Overbite
60
New cards
What is mandibular mesioclusion and other names for this issue
Lower teeth protrude upper teeth
Underbite
Class 3
Prognathsim
Underbite
Class 3
Prognathsim
61
New cards
What is maxillary mandibular asymmetry
Wry mouth
Once side of jaw grows diff then other
Once side of jaw grows diff then other
62
New cards
What are the types of immunities
Non specific (innate) and specific (adaptive)
63
New cards
What are some innate immunity components
Physical chemical Barrie’s or cellular defenses
64
New cards
What are some adaptive immunity components
Passive (maternal/ artificial) active (natural, vx)
65
New cards
What are the lines of defense
1- skin
2- enzymes ( inflammatory)
3- specific immunity ( lymphocytes)
2- enzymes ( inflammatory)
3- specific immunity ( lymphocytes)
66
New cards
What is species resistance and what is it based on
Provide defense against certain pathogens
Based on physiological anatomical and biochemical differences
Based on physiological anatomical and biochemical differences
67
New cards
What is your equipment for dental machines
Mobile dental machine
Ultrasonic scaler- uses sound waves into vibrations. Only 10-15 sec creates heat
Dental polishing hand piece- Smoothes enamel surface. Only 2-3 sec 5000rpm. NEVER SUBMERGE IN WATER
Oral irrigator
Aspiration (suction)
Ultrasonic scaler- uses sound waves into vibrations. Only 10-15 sec creates heat
Dental polishing hand piece- Smoothes enamel surface. Only 2-3 sec 5000rpm. NEVER SUBMERGE IN WATER
Oral irrigator
Aspiration (suction)
68
New cards
What is the purpose of probing and charting
Measure depth of gingival sulcus, 1mm bands- 3mm bands
69
New cards
What to keep in mind when talking to clients for dental procedures, and discharge
Authorization prior to treatment, photos before/ after
Discharge- NSAID, oral reinsert, recheck schedule, dental chew samples
Discharge- NSAID, oral reinsert, recheck schedule, dental chew samples
70
New cards
What is dirofilaria immitus and how is it transmitted
Canine heart worms.
1- mosquito bites infected host
2- mosquito passes microfilaria through bite wound
3- microfilaria flow to heart and begin to grow for about 6 months before adults
1- mosquito bites infected host
2- mosquito passes microfilaria through bite wound
3- microfilaria flow to heart and begin to grow for about 6 months before adults
71
New cards
What are some clinical signs for canine heart worms TX
Cs- coughing cyanosis, exercise intolerance
Secondary- congestive failure, ascites- fluids build up in ab
Doxy, ivermectin, melarsomine
Secondary- congestive failure, ascites- fluids build up in ab
Doxy, ivermectin, melarsomine
72
New cards
What are some complications of heart worm migration and what will you see in X-rays with HW
Pulmonary thromboembolism- worm fragments lodge in pulmonary artery blocking blood flow
Caval syndrome- heart failure
Backwards D
Caval syndrome- heart failure
Backwards D
73
New cards
What are some clinical signs for feline heart worms DX
CS- asthma, respiratory distress, sudden death.
DX- heart guard, prednisone
DX- heart guard, prednisone
74
New cards
What are some considerations for adulticide treatment
Risk of thromboembolism, owner compliance and cost concerns
75
New cards
Arteries carry what blood where the heart
Oxygenated, away from SYSTOLIC first sound
76
New cards
Veins carry what blood where the heart
Non-oxygenated towards second sound
77
New cards
Are are the names of the atrioventricular valves
Mitral/ tricuspid
78
New cards
How does the blood flow
1- deoxygenated blood returns heart via vena cava
2- from vena cava blood enters right atrium
3- tricuspid valve opens allowing flow to right atrium from right ventricle
4- right ventricle contract, pushing blood through pulmonary valve to pulmonary arteries
5- blood is oxygenated in pulmonary capillaries and returns to heart by pulmonary vein
6- from pulmonary veins O2 blood enters left atrium
7- blood flow through mitral valve into left ventricle
8- left ventricle contacts flowing blood into aortic valve in aorta
9- from aorta, o2 blood circulates in system to reach body tissues
2- from vena cava blood enters right atrium
3- tricuspid valve opens allowing flow to right atrium from right ventricle
4- right ventricle contract, pushing blood through pulmonary valve to pulmonary arteries
5- blood is oxygenated in pulmonary capillaries and returns to heart by pulmonary vein
6- from pulmonary veins O2 blood enters left atrium
7- blood flow through mitral valve into left ventricle
8- left ventricle contacts flowing blood into aortic valve in aorta
9- from aorta, o2 blood circulates in system to reach body tissues
79
New cards
Where are ECG leads placed and what are ECG
Records electrical impulses of heart
White- front right leg
Black- front left leg
Red- left hind leg
Green- right hind leg
White on right
Snow on trees smoke over fire
White- front right leg
Black- front left leg
Red- left hind leg
Green- right hind leg
White on right
Snow on trees smoke over fire
80
New cards
What is the sinoatrial node
Electrical stimulus is generated
81
New cards
What is NSR, depolarization repolarization and what does P QRS T mean
Normal sinus rhythm- healthy heart
De- contraction
Re- filling
P- atrial de-polarization
QRS- ventricular de-polarization
T- ventricular re-polarization
De- contraction
Re- filling
P- atrial de-polarization
QRS- ventricular de-polarization
T- ventricular re-polarization
82
New cards
What is sinus brachycardia what does it look like and CS TX
NSR that’s slower
CS- syncope collapse episodic weakness
TX- atropine- increase HR
CS- syncope collapse episodic weakness
TX- atropine- increase HR
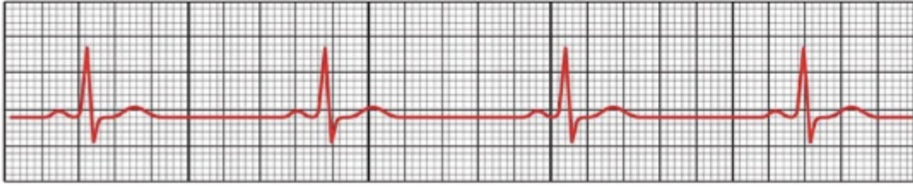
83
New cards
What is sinus tachycardia what does it look like CS TX
NRS but faster
CS- fear, anemia, pain, heart failure
TX- none if from pain, NSAID, analgesia, blood transfusion
CS- fear, anemia, pain, heart failure
TX- none if from pain, NSAID, analgesia, blood transfusion
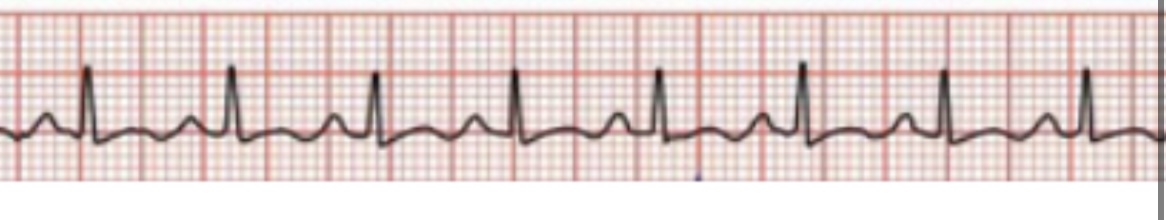
84
New cards
What is sinus arrhythmia, what does it look like
Normal sinus irregular rhythm
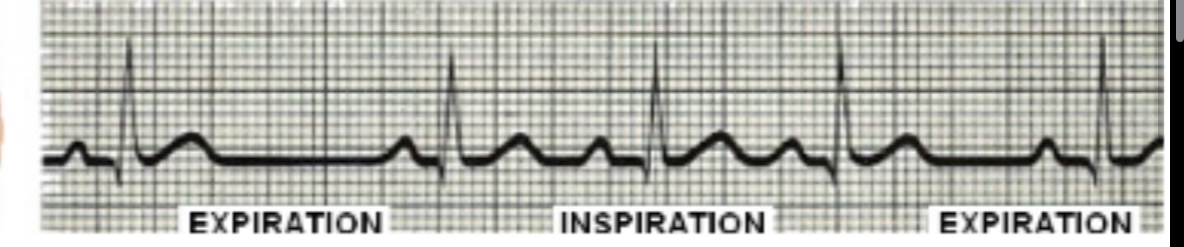
85
New cards
What is atrial fibrillation what does it look like CS TX
No P waves seen
CS- weakness, rapid irregular heart beat
TX- digoxin- slow HR, No cure CHF will develop
CS- weakness, rapid irregular heart beat
TX- digoxin- slow HR, No cure CHF will develop
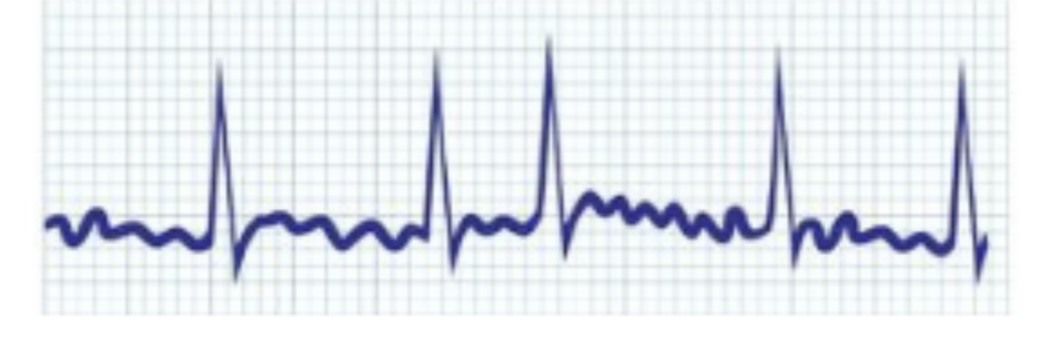
86
New cards
What is ventricular fibrillation, what does it look like CS TX
Lack QRS, lack heart sounds
CS- absence of O2, shock, electrolyte imbalances
TX- epinephrine, precordial thump- sharp blow to chest with hand
CS- absence of O2, shock, electrolyte imbalances
TX- epinephrine, precordial thump- sharp blow to chest with hand

87
New cards
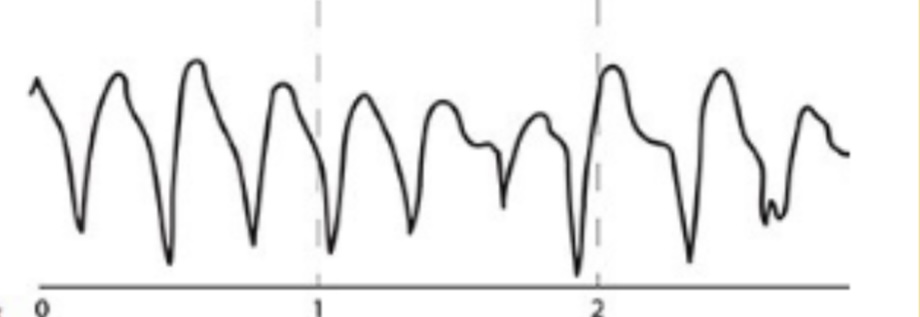
what is ventricular tachycardia, what does it look like CS TX
Rapid repetitive contractions of ventricles
CS- abnormal calcium/ potassium levels, GI diseases
TX- lidocaine IV
CS- abnormal calcium/ potassium levels, GI diseases
TX- lidocaine IV
88
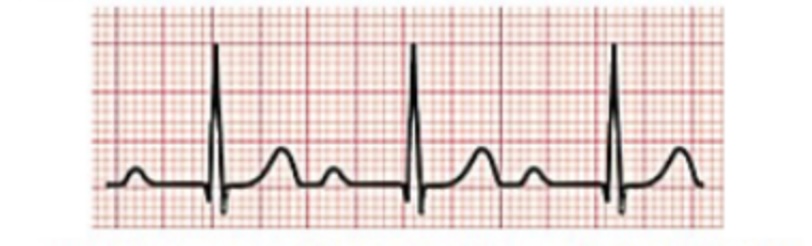
New cards
What is first degree AV block, what does it look like CS TX
Fixed but prolonged PR
CS- calcium deficiency, tumors atropine
TX- underlying cause
CS- calcium deficiency, tumors atropine
TX- underlying cause
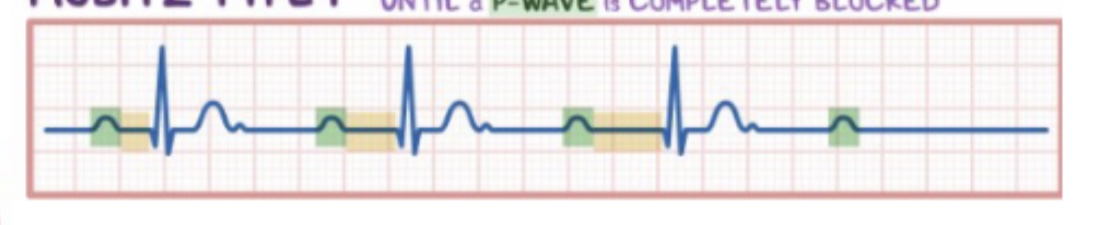
89
New cards
What is second degree AV block type 1 what does it look like
Progressive lengthening of PR till beat drops
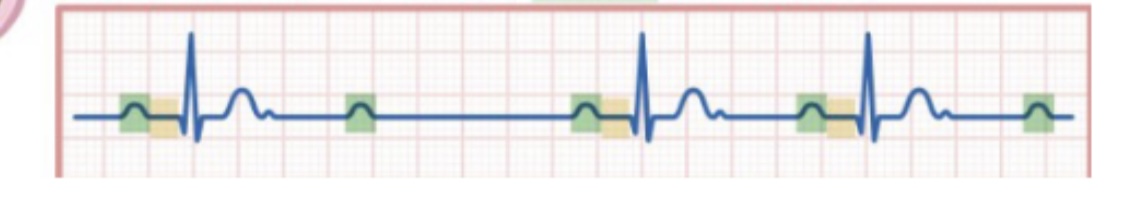
90
New cards
What is second degree AV block type 2 and what does it look like and what is required for this to be”fixed”
Sudden drop of QRS without warning, pacemaker
91
New cards
What is third degree AV block and what is required to fix it what does it look like
Complete heart block, causing abnormal slow HR
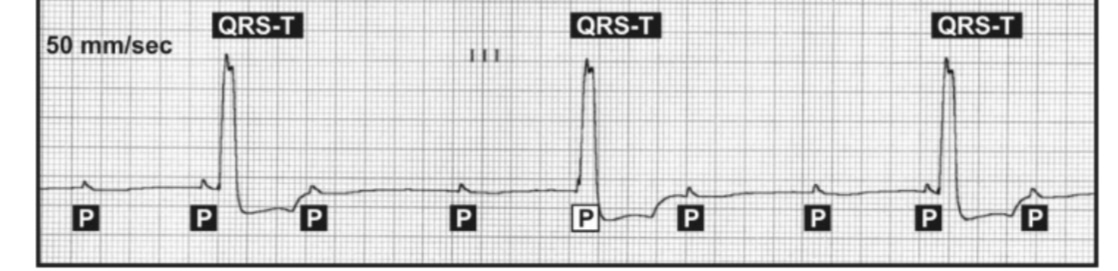
92
New cards
What are some causes for heart diseases and a small explanation of them
Valvular disease- valves fail to open/close
Myocardial disease- heart muscle pump weak
Arrhythmia- heart beats too slow
Vascular disease- blood vessels cause interference of blood flow
Cardiac shunts- opening on L or R side of heart
Extracardiac shunts- abnormal blood flow between body/lungs
Parasitism- heart worms
Myocardial disease- heart muscle pump weak
Arrhythmia- heart beats too slow
Vascular disease- blood vessels cause interference of blood flow
Cardiac shunts- opening on L or R side of heart
Extracardiac shunts- abnormal blood flow between body/lungs
Parasitism- heart worms
93
New cards
What is chronic mitral valve insufficiency, another name for it CS DX
Myxomatous mitral valve disease
Progressive deterioration of mitral valve in heart causing back flow and enlargement of L atrium/ ventricle
CS- deep cough, dyspnea, tachypnea, mitral valve regurgitation (whooshing sound)
DX- echocardiogram, thoracic radiograph
Progressive deterioration of mitral valve in heart causing back flow and enlargement of L atrium/ ventricle
CS- deep cough, dyspnea, tachypnea, mitral valve regurgitation (whooshing sound)
DX- echocardiogram, thoracic radiograph
94
New cards
What is canine dilated cardiomyopathy, CS DX TX
Heart muscles become weak causing abnormal heart beat
CS-
Right side heart failure- ascites, weight loss
Left side heart failure- coughing pulmonary edema, mitral valve regurgitation murmur
DX- Brain natriretic peptide bio maker, cardiac troponin biomaker
TX- no cure, enalapril, vetmedin, diuretics
CS-
Right side heart failure- ascites, weight loss
Left side heart failure- coughing pulmonary edema, mitral valve regurgitation murmur
DX- Brain natriretic peptide bio maker, cardiac troponin biomaker
TX- no cure, enalapril, vetmedin, diuretics
95
New cards
What is hypertrophic cardiomyopathy CS
Muscular walls of heart thicken more on L side
CS- systolic murmurs, gallop rhythms, sudden thromboembolism
CS- systolic murmurs, gallop rhythms, sudden thromboembolism
96
New cards
What is patent ductus arteriosus CS TX
Ducts fail to close after birth,
CS- washing machine murmur
TX- surgical duct ligation before 2 years
CS- washing machine murmur
TX- surgical duct ligation before 2 years
97
New cards
What are the heart murmur intensity levels
1- barley audible
2- audible but quiet
3- moderate loud
4- Loud
5- very loud heard with stethoscope partially off chest
6- extremely Loud heard with stethoscope off chest
2- audible but quiet
3- moderate loud
4- Loud
5- very loud heard with stethoscope partially off chest
6- extremely Loud heard with stethoscope off chest
98
New cards
What are the goals to help cardiovascular diseases
CC or H/D diets, Lower sodium intake, electrolyte balance, omega 3 fatty adics, amino acids (taurine, carnitine, arginine)
\
\
99
New cards
What is consisted in the upper respiratory system
Nasal cavity, sinuses, nasopharynx, larynx
100
New cards
What is consisted in the lower respiratory system
Trachea, bronchi, lungs, pleural cavity