USMLE quiz
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
what bones are formed in endochondral ossification
long bones (femur, humerus, tibia, fibula, radius, ulna)
carpals, tarsals
vertebrae
pelvic girdle
base of the skull
what disease affects endochondral ossification and what are its symptoms?
achondroplasia.
autosomal dominant mutation of the FGFR3 gene. short stature, large head, midface hypoplasia.
what is the pierre robin sequence
first pharyngeal arch fails to form the mandible, causing mucrognathia.
this doesn’t allow the tongue to to descend normally causing glossoptosis
cleft palate.
what are the molecular makeup of the 3 types of hemoglobin in humans?
Embryonic Hb - zeta2 epsilon2
Fetal Hb - alpha2 gamma2
Adult Hb - alpha2 beta2
When is HbE present?
present in the yolk sac and liver of the embryo, and is present until 8-10w gestation.
When is HbF present? What are the differences in affinity compared to HbA?
Present until 6-12m after birth.
It has a higher affinity to oxygen, and a lower affinity of 2,3BPG
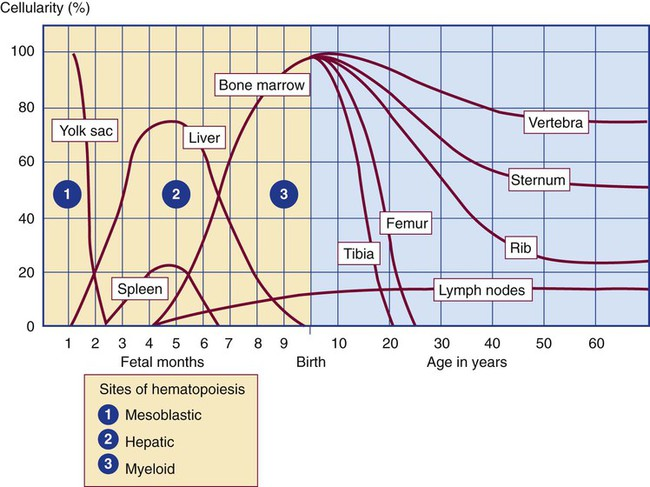
Where is the main site of hematopoiesis at 5 weeks gestation?
yolk sac.
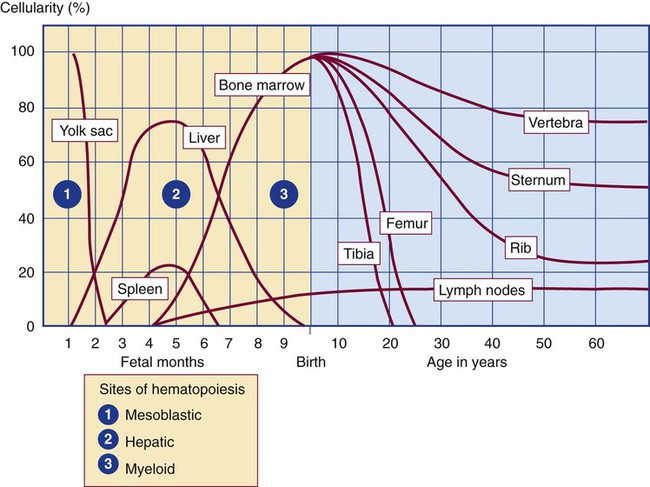
Where is the main site of hematopoiesis at 8 weeks gestation?
liver
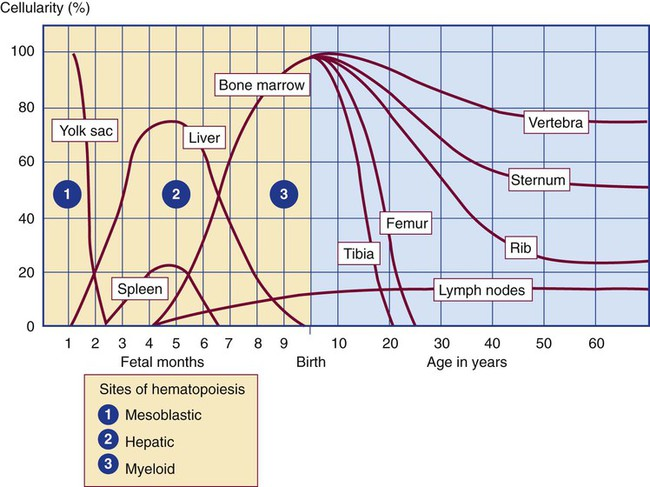
Where is the main site of hematopoiesis at 15 weeks gestation?
liver and spleen
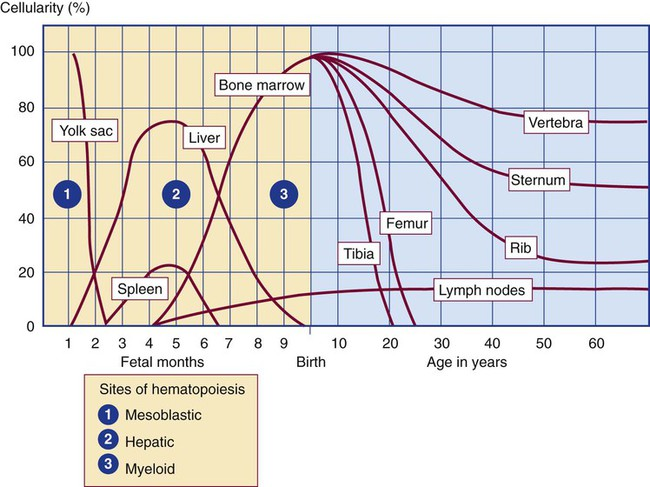
Where is the main site of hematopoiesis at 30 weeks gestation?
bone marrow
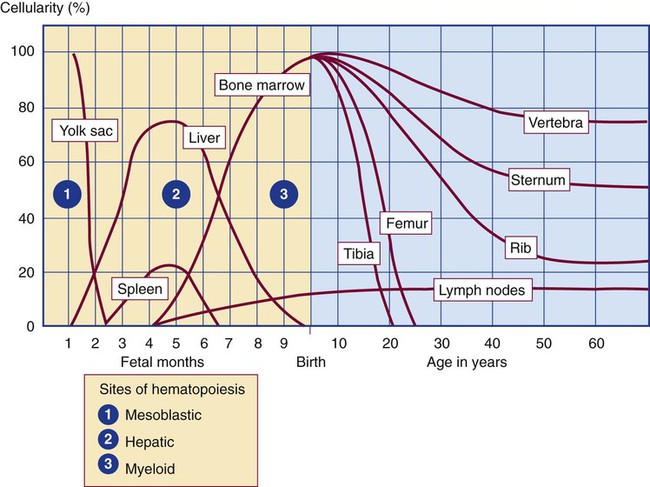
Where is the main site of hematopoiesis 1 month after birth?
bone marrow
When does the embryoblast turn into the bilaminar disc?
second week of gestation (by day 14.)
What are the 2 layers of the bilaminar disc?
epiblast and hypoblast
What does the hypoblast give rise to?
the yolk sac
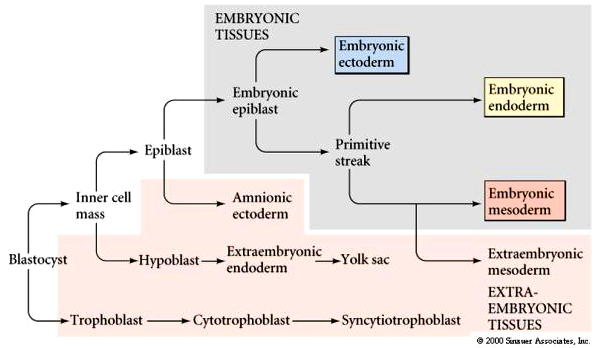
What does the epiblast give rise to?
the embryonic epiblast and primitive streak, which later develops into the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
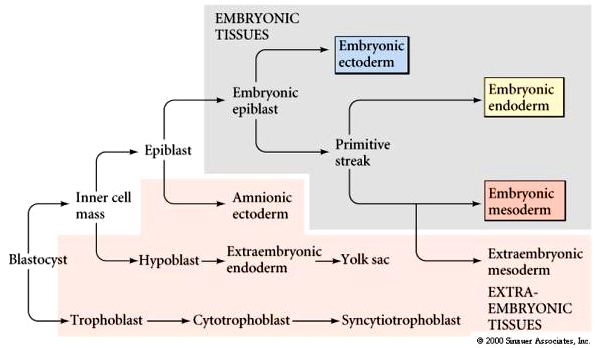
When does the allantois develop?
16-19 days gestation (3rd week)
What structure does the allantois turn into?
urinary bladder and umbilical cord
What is the function of the urachus?
connects the bladder to the umbilical cord.
When does the urachus normally close? What structure does it turn into?
the urachus closes at 12 weeks gestation and turn into the median umbilical ligament.
What are the symptoms of a patent urachus?
umbilical discharge
abnormal belly button
What does the ductus arteriosus turn into after birth?
ligamentum arteriosum
What does the foramen ovale turn into after birth?
fossa ovalis
What does the ductus venosus turn into after birth?
ligamentum venosum
What do the umbilical arteries turn into after birth?
medial umbilical ligaments and superior vesical arteries
What does the umbilical vein turn into after birth?
round ligament of liver
What is the function of the omphalomesenteric (vitelline) duct? What happens when the duct fails to close?
it connects the yolk sac to the midgut.
if it fails to close, it will cause the child to have meckel’s diverticulum.
What is the cause of VACTERL (VATER) syndrome? What are its clinical signs?
vertebral defects
anal atresia
cardiac defects
tracheo-esophageal fistula
renal abnormalities
limb defects
What is the cortical reaction? What ion is involved?
the release of enzymes from the egg's cortical granules into the space surrounding the egg, modifying the zona pellucida (a protective layer) and preventing further sperm entry.
fusion of egg and sperm triggers the release of calcium.
What is the function of the hyaline layer of the oocyte?
This layer forms in the extracellular matrix and functions as an adhesive substance for the blastomeres
What is the function of the cortical granules of an oocyte?
preventing polyspermy
When does gastrulation occur?
3rd week of gestation
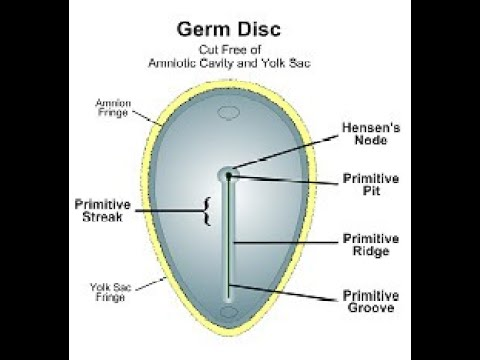
What structure in an embryo defines the cranial caudal axis and symmetry of the embryo?
primitive streak
What structures are included in the primitive streak?
primitive groove, primitive ridge, primitive pit.
what is the function of the Sonic the hedgehog gene?
signals for limb, CNS and facial development.
what is the function of Wnt-7?
signals for synapse formation, CNS, limb, and female reproductive system development.
what is the function of Fibroblast growth factor gene?
development of nervous system and skeletal system in embryo
what is the function of Homeobox gene?
act as transcription factors, regulating gene expression during development, cell differentiation, and morphogenesis
what is the function of the PAX gene?
organ development and pattern development in the fetus.
What are the 3 stages of gonadal development in a male fetus?
gonadal: the early period where the gonadal ridges are undifferentiated and have the potential to develop into either male testes or female ovaries. This stage begins around the fourth or fifth week of development and lasts until the seventh or eighth week, at which point a specific gene on the Y chromosome (SRY gene) triggers differentiation into male testes, or without it, they develop into ovaries.
ductal: presence of testosterone causes the Wolffian ducts to develop into the internal male reproductive organs like the epididymis, vas deferens, and seminal vesicles, while the Müllerian ducts (paramesonephric ducts) regress.
genital: masculinization of structures into recognizable male organs by about the 9th week.
What is the difference of epispadias and hypospadias?
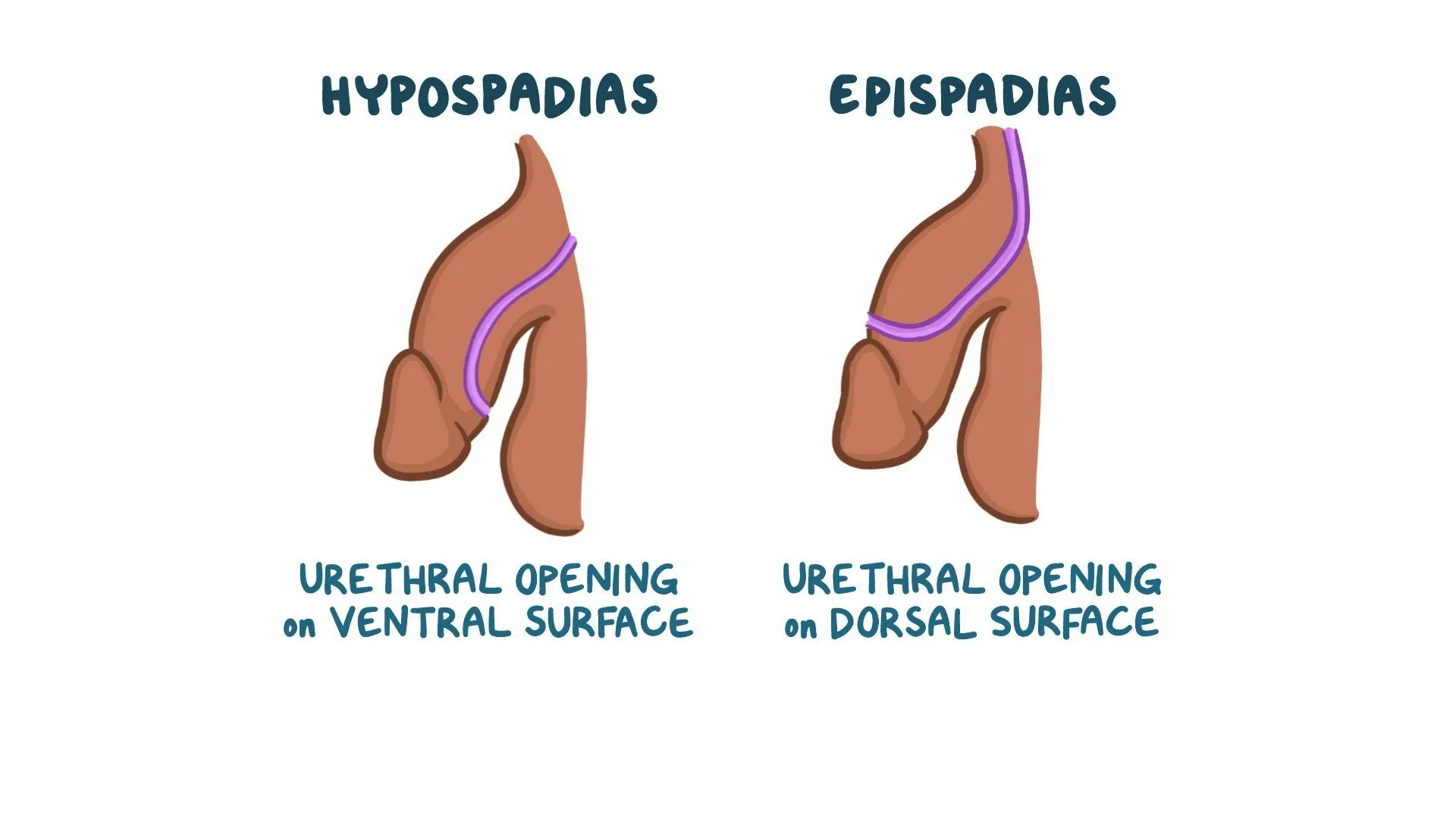
When does the respiratory system start developing?
the lung bud appears during the 4th week of pregnancy
what disease is caused by the abnormal partitioning of the esophagus and trachea?
tracheosophageal fistula
when does surfactant synthesis begin?
20-26w gestation
When do surfactant levels reach mature levels in the fetus?
34-36w gestation
in palate development in the fetus, when does the primary palate originate from?
during week 6 of development, paired medial nasal processes (or prominences) that form the intermaxillary segment.
where does the secondary palate originate from?
the left and right palatal shelves
what causes a cleft lip?
failure of fusion of the medial nasal processes
what causes a cleft palate?
failure of fusion of the palatine shelves.
what is released from lysed bacterial cells or from blebs of gram - bacteria?
endotoxins?
what type of bacteria holds