Ortho E1 -Emphasized and topic list ONLY
1/166
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
167 Terms
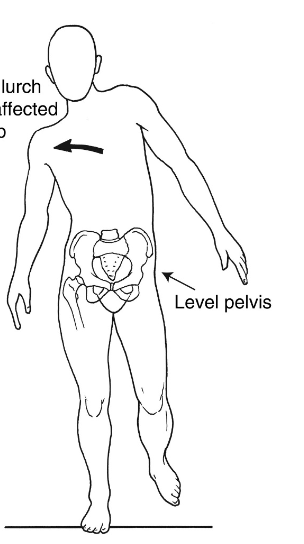
What is Trendelenburg’s Gait?
abductor lurch towards affected painful hip
What causes Osteonecrosis in the hip?
femoral neck fx
What supplies the femoral head w/ blood?
lateral and medial circumflex femoral arteries
What is a Femoral neck fx?
intracapsular hip fx: fx disrupts blood supply of femoral head → nonunion and osteonecrosis/AVN are common
What is an Intertrochanteric hip fx?
extracapsular: need more fixation than fem. neck fx; malalignment → shortening of limb, risk of malunion; lower rate of nonunion or osteonecrosis
How does a fx of the proximal femur present?
s/p fall, hip pain in groin, inability to bear weight, referred pain to the knee, decompression ROM
What is a common complication of a proximal femur fx?
avascular necrosis
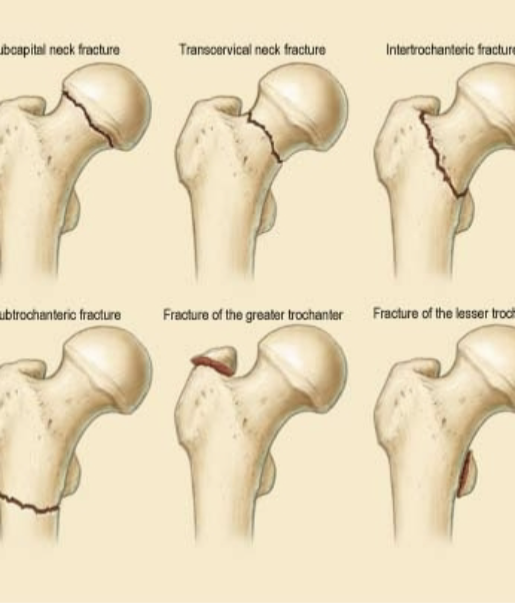
Review femur fx descriptions
:)
If a pt has a fx of the proximal femur, how will their legs sit when lying supine?
injured limb will be in external rotation and ABducted
*if displace will also be shorter
What causes dislocation of the hip?
high energy trauma (MVA or fall)
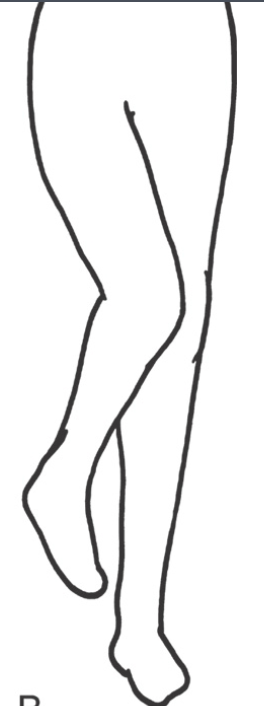
What is the position of the leg in posterior hip dislocations?
*90%
flexion, internal rotation & ADDuction

What position is the leg in w/ anterior hip dislocations?
*rare
external rotation, ABduction, mild flexion
How do posterior hip dislocations present on xrays?
affected femoral head appears smaller & lower than C/L side d/t being further away; normal femoral head
How do anterior hip dislocations look on a xray?
affected femoral head appears larger and higher than C/L side d/t being closer; normal femoral head
How does a Hamstring strain present?
common in athletes; “pop” or pain in posterior thigh; severe bruising follows
What is greater Trochanteric Bursitis?
inflammation of the greater trochanteric bursa
How does greater trochanteric bursitis present?
hip pain, inc w/ walking or climbing stairs, +tenderness w/ pressure over greater trochanter bursa
What testing needs to be done for trochanteric bursitits?
Xray to r/o bony anomaly
What is the tx for Trochanteric Bursitis?
rest, heat, NSAIDs, injection at point of maximal tenderness
What are S&S of AVN?
20-40 yo; gradual onset of hip pain 4-6 mon, slight limp w/ walk, inc groin pain w/ IR, s/p fall or trauma, can also be caused by alcoholism and long term steroid use
What is the tx for AVN?
ortho consult
What testing is done for AVN?
plain films: AVN evident or fx; later, necrosis of femoral head
MRI: assists in dx
What is Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis?
progressive displacement of the upper portion of the femur occurs in relation to the capital femoral epiphysis
When does Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis occur?
slip thru the physis during adolescent growth spurt
Where do blood vessels to the epiphysis travel?
run along the side of the femoral neck; disruption can result in loss of blood supply to the epiphysis
How does Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis present?
adolescent (10-15) M > F; obese, AA > causians/hispanic; inc pain in groin/medial thigh/knee, Trendelenburg’s gait
What would an xray of SCFE show?
apparent varus angulation of epiphysis: “ice cream falling off cone”
“Kline’s lines” - loss of intersection of ephiphysis by femoral neck
“pistol grip deformity” - chronic stage
What population does Legg-Calve-Perthes Diseases affect?
4-8 yo males
Which affects a younger demographic?
Legg-Calve-Perthes
What is Legg-Calve-Perthes?
hip disorder caused by AVN of the whole femoral head
What are S&S of Legg-Calve-Perthes?
limp -MC, ± pain, limited abduction & IR, Trendelenburg’s gait, atrophy of thigh, calf, & buttocks, unequal leg length, groin pain
How does OA of the hip present?
achey pain over hip, pain in ant. groin that radiates to medial knee, dec ROM
What will plain films of hip DJD show?
(+) arthritis
What would an Xray of Legg-Calve-Perthes show?
AVN of femoral head
What is the MC site of acute osteomyelitis?
Metaphyseal end of long bone near joints (knee common)
What is the tx for acute osteomyelitis?
IV abx 4-6 weeks
(Cefazolin, Clindamycin, Vanc, FQ -if Pseudomonas)
What are sx of acute osteomyelitis?
+ hx trauma, RA, immunocompromised, DM, sickle cell, IV drug use; limp, fever, swelling/heat/erythema to soft tissue
What is the gold standard for diagnosis of acute osteomyelitis?
Open biopsy & bone aspiration
When treating acute osteomyelitis, what should be done before giving abx?
Joint aspiration
What is the MC pathogen for acute osteomyelitis?
Staph aureus
What is the MC cause of chronic osteomyelitis?
Open fx or wound of extremities
What are sx of chronic osteomyelitis?
s/p open fx, fever, pain, soft tissue swelling/inflammation, cellulitis
What would you see on an Xray showing Chronic osteomyelitis?
irregular sclerotic bone destruction w/ areas of radiolucency & involcrum (dead bone)
What is the tx for chronic osteomyelitis?
Ortho & ID consults, I&D, IV abx
What medication can you give to slow benign bone tumors?
Biphosphonates
What is an Osteochondroma?
cartilage-capped bony spur arising on the external surface of a bone; usually long bone near knee or proximal humerus
What is an Osteochondroma look like on an XR?
bone arising from stalk or "bump" on bone
Where are enchondromas commonly found?
Hands/fingers, Metaphysis of long bones
What does an Enchondroma show on an XR?
lucency of hands/fingers or matrix calcification of long bones on XR, usually an incidental finding
What are the MC locations of Ewing's sarcoma?
Femur, Pelvis, Upper arm, Ribs in diaphysis
What population most commonly presents with Ewing's sarcoma?
5-20 yo; MC- males
What type of bone tumor may mimic symptoms of osteomyelitis? (fever, pain, weight loss)
Ewing's sarcoma
What does Ewing's sarcoma show on an XR?
lytic lesions w/ "onion peel" appearance
What is the tx for Ewing's sarcoma?
Chemo, surgery, radiation
Which joints does Osteoarthritis MC affect?
weight bearing joints (LEs & spine)
How does Osteoarthritis present?
stiffness, dec ROM, pain worsening w/ movement and relieved w/ rest, tender to palpation, deformity
What is the MC location of Osteoarthritis?
knee joints
What is the MC type of arthritis?
Osteoarthritis
Which type of arthritis is symmetric?
RA
Which joints are spared in RA?
DIP
What extraarticular manifestations can RA cause?
nodules, vasculitis, pericarditis, tenosynovitis, scleritis
How does Rheumatoid Arthritis present?
morning stiffness, symmetric swelling, nodules, +RF, radiologic changes, claw deformity of foot, ulnar drifting
Who is MC affected by Reactive Arthritis?
young men
What causes reactive arthritis?
inflammation triggered by GI or GU infxn (STDs and dysenteric)
*Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, Shigella, Salmonella, Campylobacter
What is the triad of sx associated with reactive arthritis?
Conjunctivitis, Urethritis, Oligoarticular arthritis
(can't see, can't pee, can't climb a tree)
What antigen might be present in some pts (63%) w/ Reactive Arthritis?
HLA-B27
What does Psoriatic arthritis show on an XR?
Pencil-in-cup deformity = joint destruction; resorption of terminal phalanges
*aggressive and destructive
What demographic is most affected by Psoriatic arthritis?
M=F 1:1; onset in 30s
What is the tx for psoriatic arthritis?
DMARD- methotrexate
What differentiates Psoriatic arthritis from RA?
DIP joint involvement and absence of nodules
Gout or Pseudogout:
Bony erosions & spurs on XR
Gout
Gout or Pseudogout:
Punctate or linear calcifications of cartilage (chondrocalcinosis)
Pseudogout
Gout or Pseudogout:
Negatively birefringent urate crystals
Gout
Gout or Pseudogout:
Weakly positive birefringent rhomboid-shaped crystals
Pseudogout
Gout or Pseudogout:
Serum uric acid (+)
Gout
What is the tx for gout?
Indomethacin -1st line, Colchicine -2nd line, NSAIDs, steroids
Long term: Allopurinol or Probenecid (inc urine excretion)
What is the tx for pseudogout?
Joint aspiration, Intra-articular steroids, NSAIDs
Acute: Colchicine
What is a precursor to Osteoporosis?
Osteopenia
What is the GOLD standard for diagnosing osteoporosis?
DEXA
Normal bone density T score
+1.0 to -1.0
T scores less than ____ indicate osteoporosis
-2.5
T scores between ____ and ____ indicate osteopenia
-1.0 to -2.5
T score of -1.0 has ___x risk of fractures
2x
T score of -2.0 has ___x risk of fractures
4x
T score of -3.0 has ___x risk of fractures
8x
What are the sx of CRPS?
pain is out of proportion to what would be expected after the original injury (distal to site of injury); affects extremities
What is the hallmark pain quality for CRPS?
Burning or throbbing
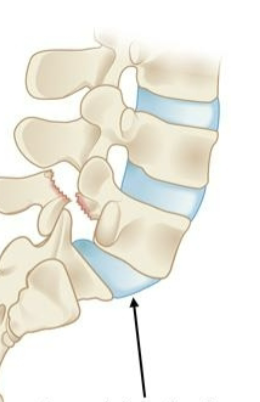
What is Spondylolisthesis?
slipping of the vertebrae + fx
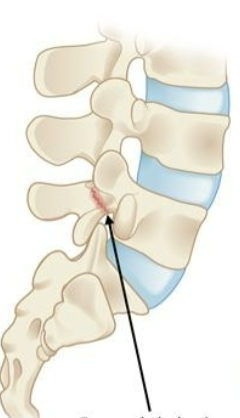
What is Spondylolysis?
dissolution or loosening of a vertebra + stress fx
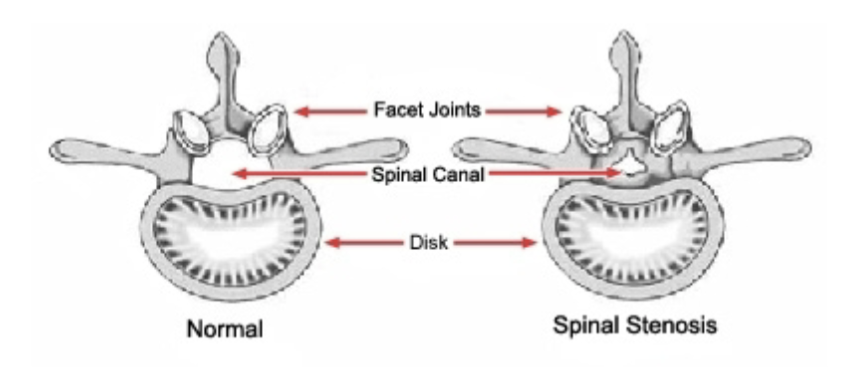
What is Spondylosis (stenosis)?
degenerative disease of a vertebrae and disc; narrowing of spinal canal
Which type of Kyphosis is seen in adolescents?
*starts ~11 yo
Scheuermann’s
What would imaging of Scheuermann’s Kyphosis show?
Schmorl’s nodes, discs are flattened & irregular, thickened ant longitudinal ligament, vertebral bodies are wedged; > 40 degree curve
What is the MC curve in idiopathic scoliosis?
R thoracic
What are S&S of Scoliosis?
“rib hump”, lateral curvature > 10 degree, F>M 11-13 yo
What is the tx for Scoliosis at a 10-25 degree angle?
PT & monitor
What is the tx for Scoliosis at a 25-45 degree angle?
brace & PT
What is the tx for Scoliosis at a >45 degree angle?
surgery & PT
What causes Spondylolysis?
repetitive injury on pars causes a stress fracture
Where do the majority of Spondylolysis cases occur?
L5
What is bilateral spondylolysis?
spondylolisthesis