circulatory system
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
what are the two methods of blood circulation?
cardiovascular and lymphatic system
How does gas (O2) get to tissues?
blood
What is blood?
a transport medium!
transports
nutrients (diffuse across capillary walls)
signaling molecules (hormones from endocrine glands)
respiratory gases (O2 and CO2)
wastes (lactate and CO2
what are some other functions of blood?
stabilizes pH and electrolytes, prevents fluid loss (clotting), provides defense system (t-cells), thermoregulation (evaporation of sweat = cooling)
what is blood circulation powered by?
pumping action of the heart
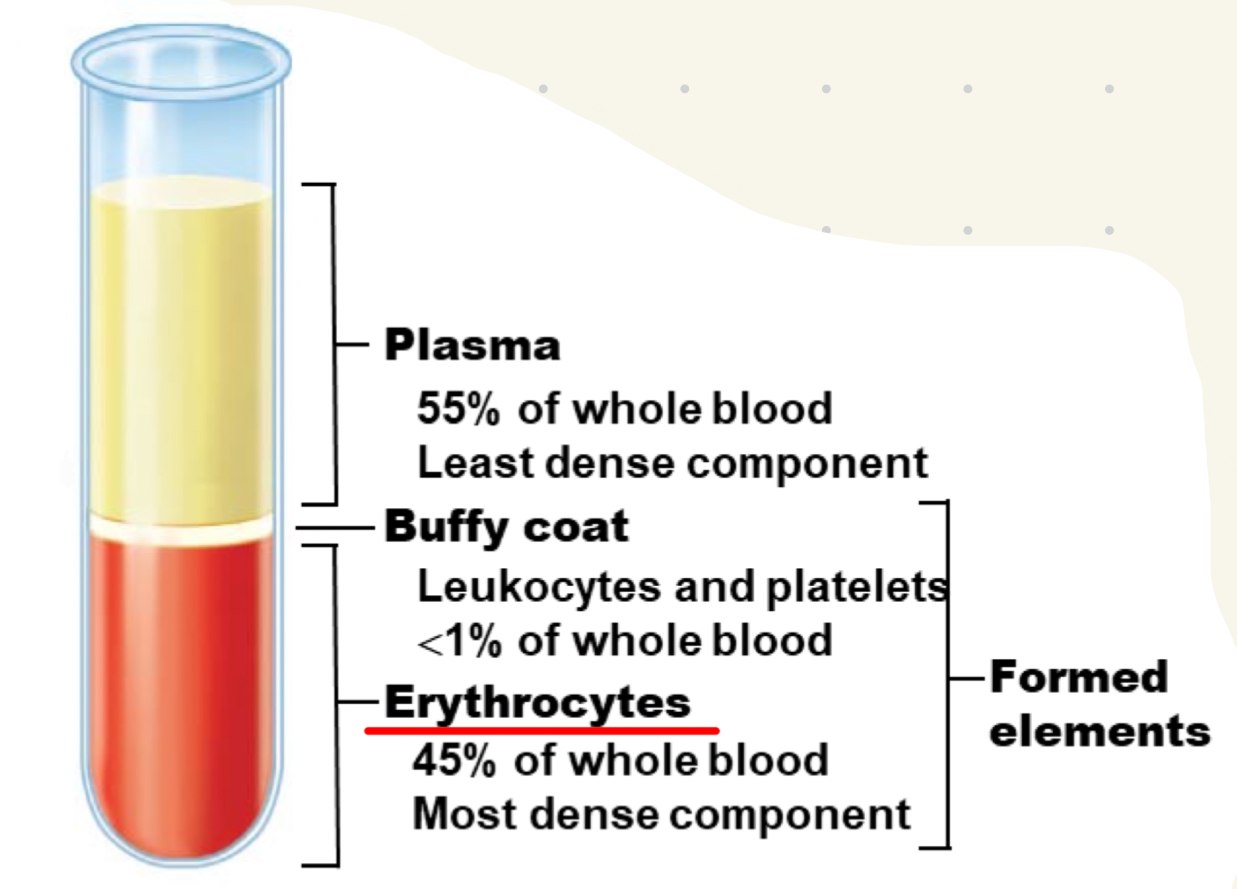
what makes up blood composition?
plasma
Buffy coat
erythrocytes
blood facts
blood volume higher in males
is cellular and liquid, specialized CT
blood cells- formed elements
plasma - liquid
what is hematocrit?
percent of blood volume with RBCs; higher in males (47% vs. 42%)
what is the Buffy coat?
portion with leukocytes (WBCs) and platelets, between the plasma and the RBCs
what is plasma?
the sticky, fluid portion of blood
around 90% water
what does plasma contain?
ions: Na+ and Cl
wastes: CO2, urea, ammonia
nutrients: sugars, lipids, amino acids
porteins
albumin- prevent H2O diffusion from blood vessel
globulins- antibodies and blood proteins that transport lipids, Fe, Cu
fibrinogen- in runs for blood clotting
erythrocytes (RBCs) facts
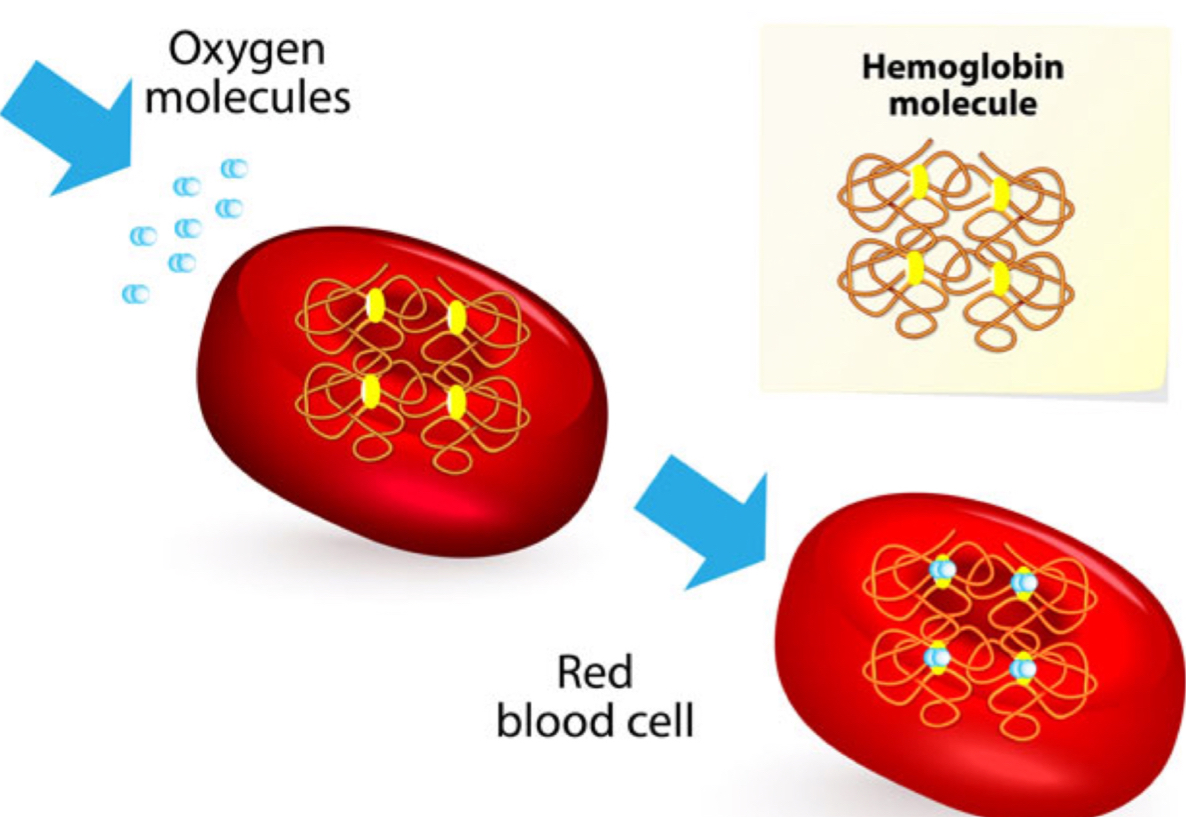
packed w/ hemoglobin, oxygen carrying protein → LOVE OXYGEN
most numerous cells
pick up O2 @ lung capillaries (external respiration)
release O2 across tissue capillaries (internal)
hemoglobin structure
4 chains of amino acids
each amino acids bears Fe and 4 heme molecules which BIND to O2 molecule
oxidation of Fe gives blood red color
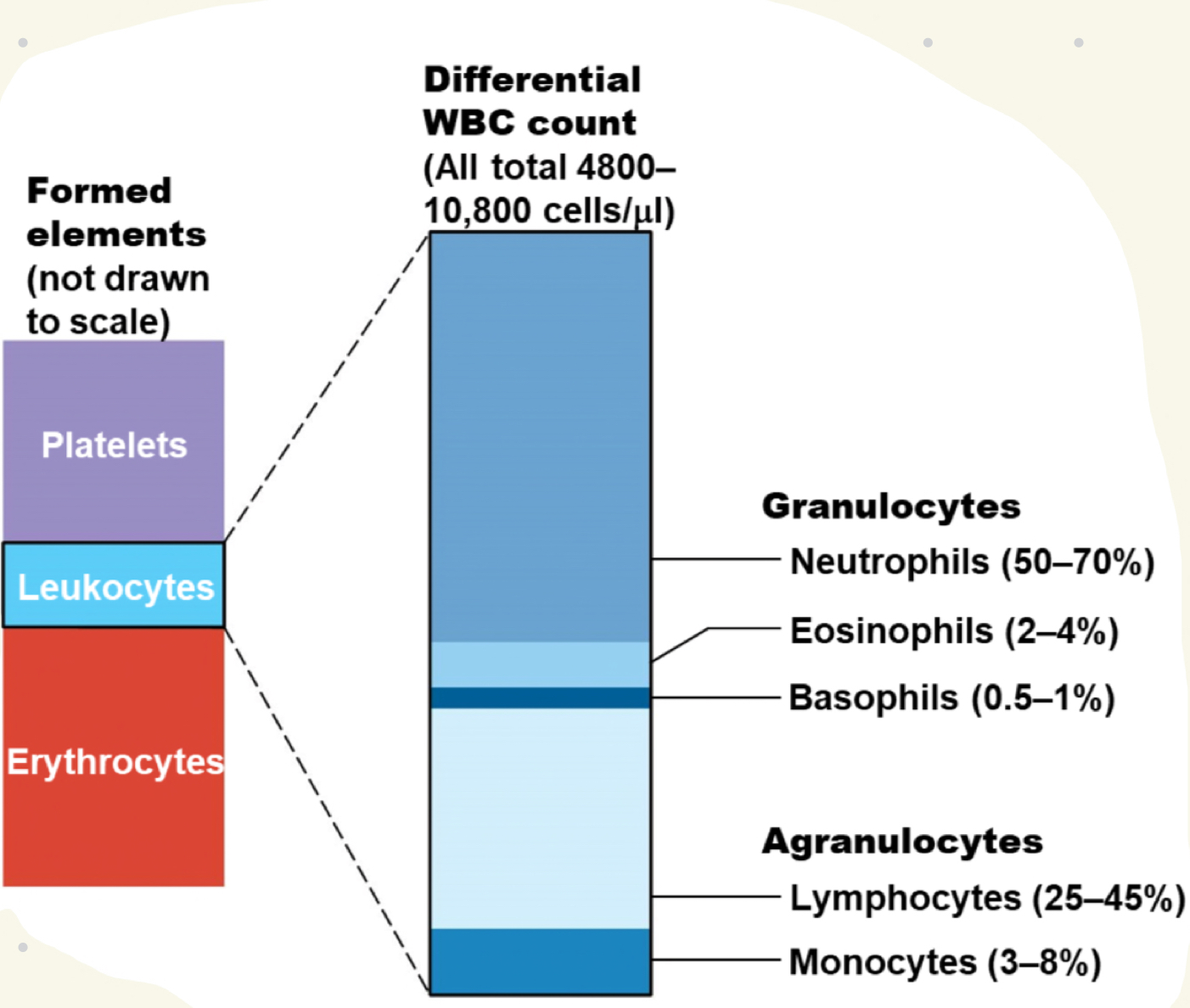
leukocytes (WBCs) facts
PROTECT body from infectious microorganisms
function OUTSIDE bloodstream in loose CT
2 types
granulocytes: neutro/eosino/basophils
agranulocytes: lymph/monocytes
what is the mnemonic for relative abundance of lymphocytes (most → least)
Never Let Monkeys Eat Bananas
what is a open system? What is an closed system?
respiratory; circulatory
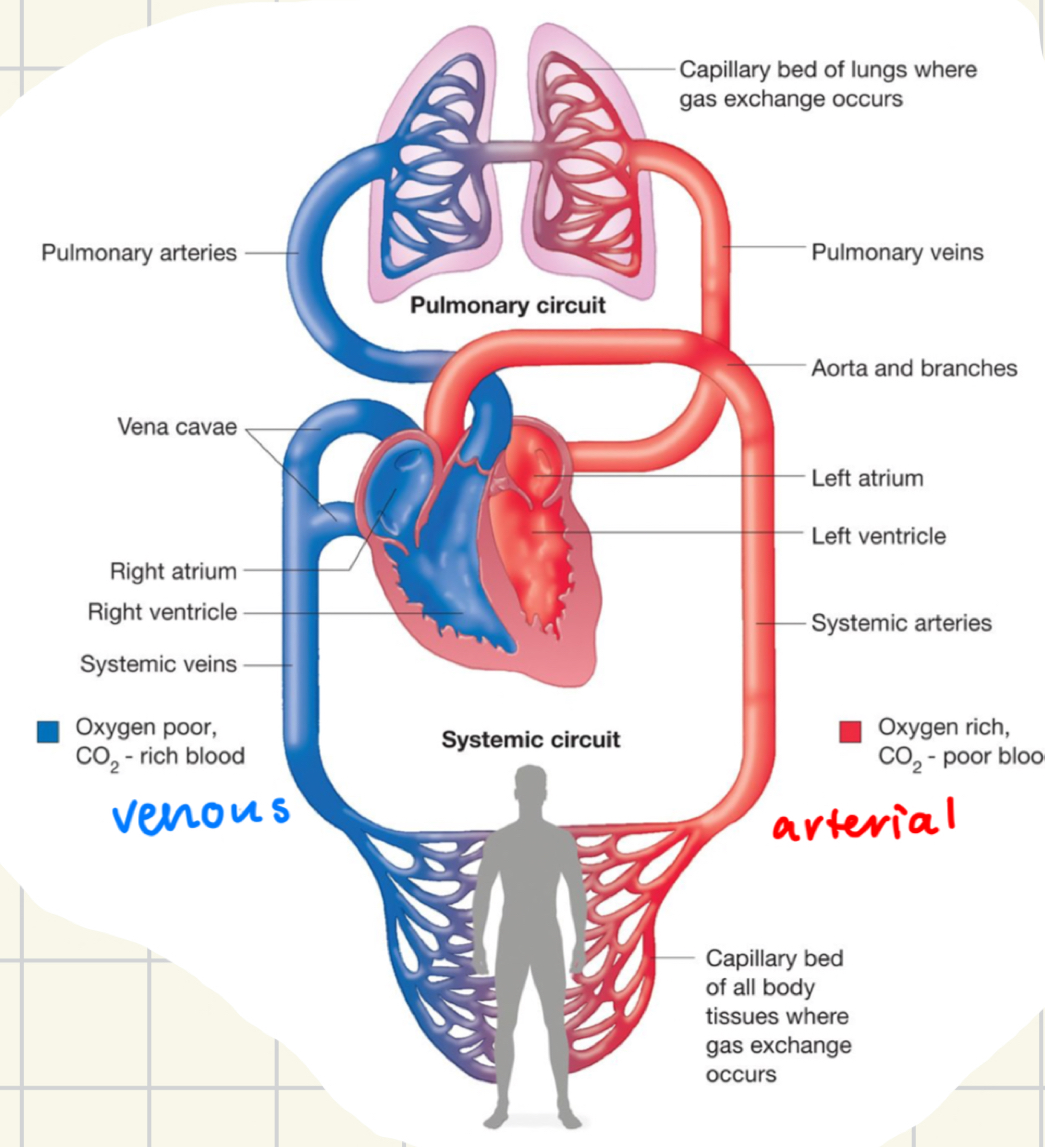
arterial circulation facts
circulation carries blood away
HIGH pressure
venous circulation facts
circulation that carries blood towards heart
LOW pressure
“lazy river”
blood vessels in order from thick → thin
arteries - highest pressure
arterioles - small artery
capillaries - smallest
venues - receive from capillaries, tiny veins
veins - receive from venues
what are the two types of arteries?
elastic and muscular
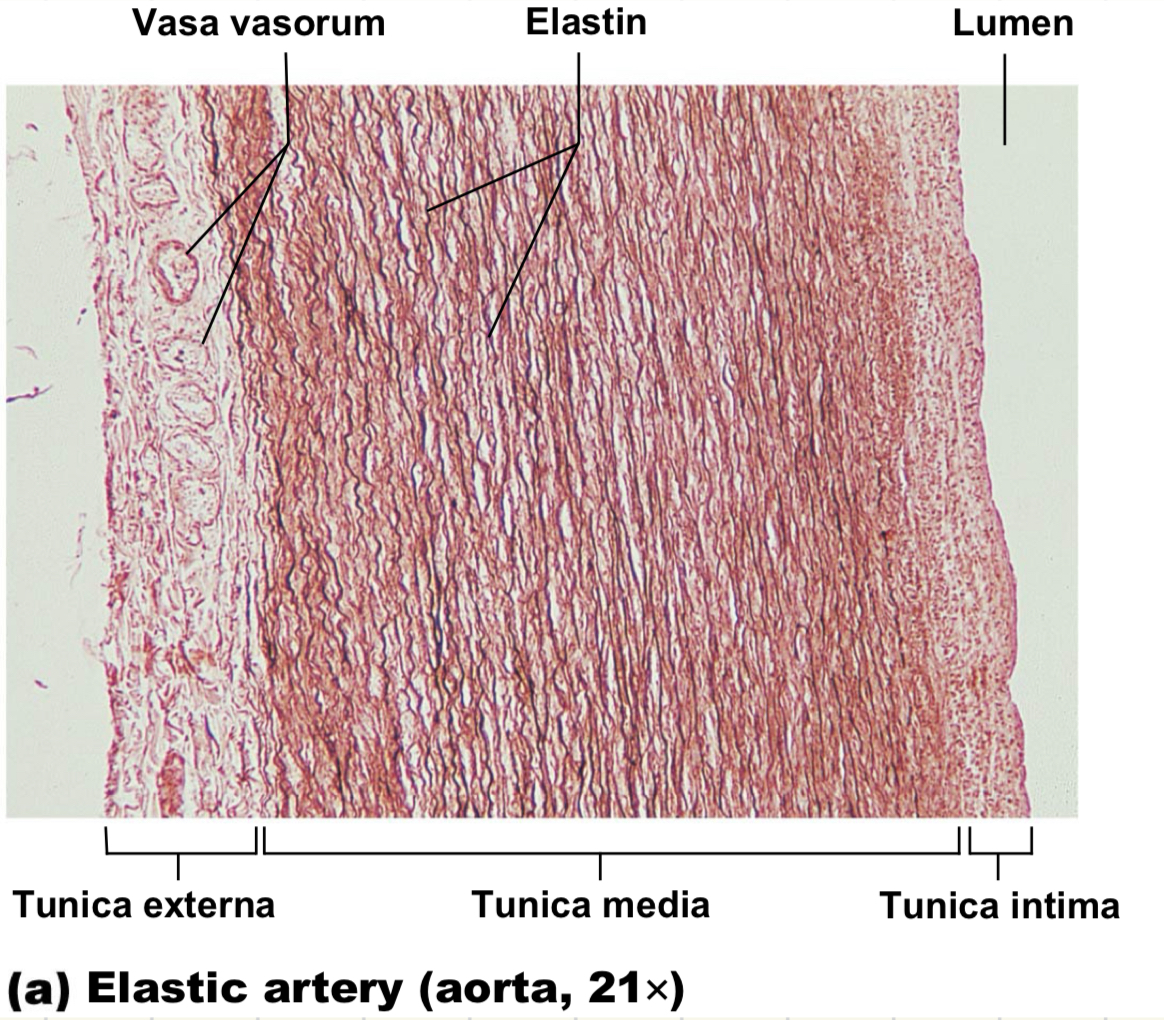
elastic arteries facts
aka conducting
largest arteries
aorta and major branches
brachiocephalic trunk
left subclavian
left common carotid
high elastin dampens pressure; rubber band
muscular arteries facts
aka distributing because take from elastic arteries → body
THICK tunica media
in/external elastic membrane
“muscle” so contract = increase pressure and dilate = decrease pressure
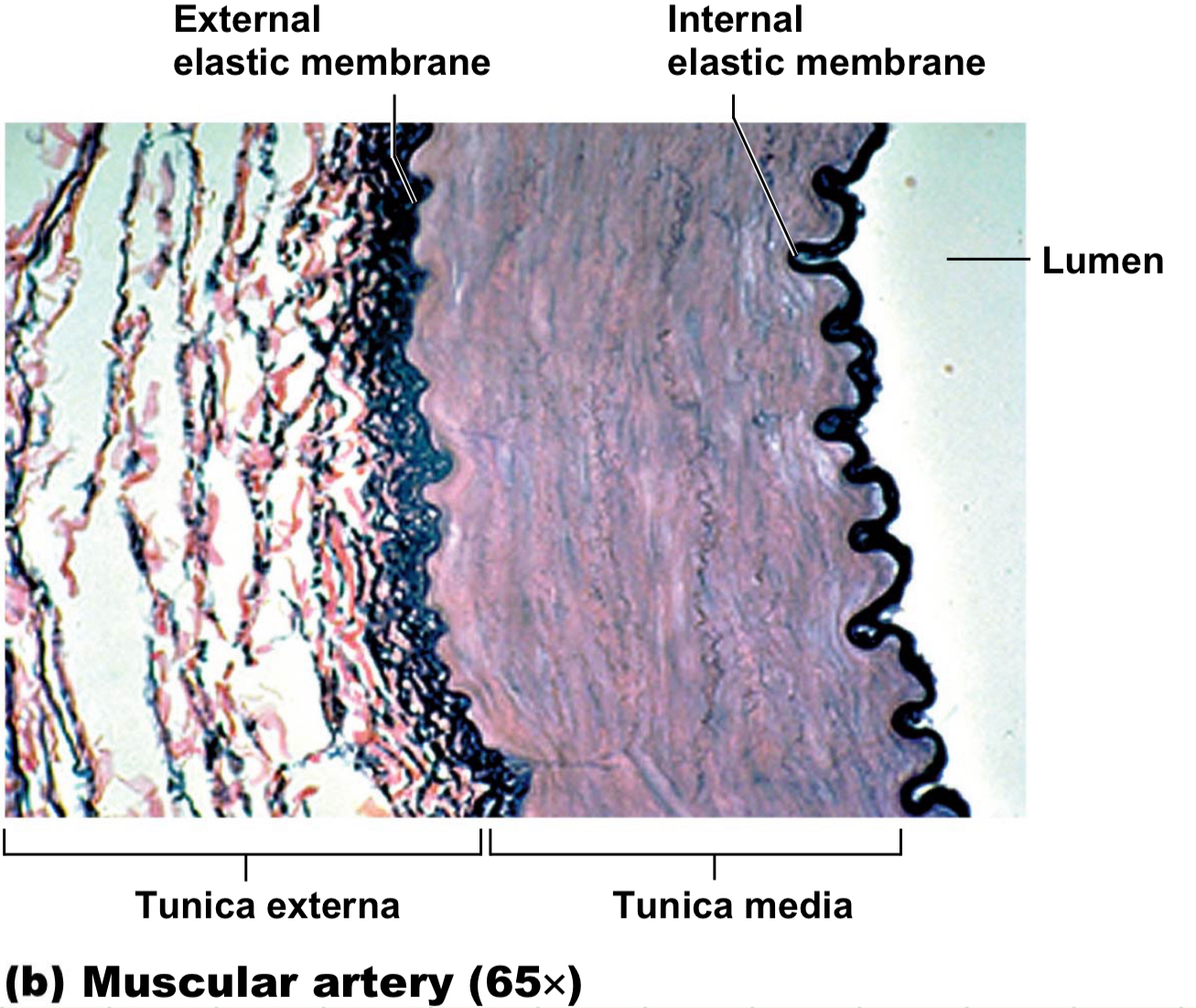
what are the three layers of blood vessels?
tunica intema, media and externa; lumen is the hole in the middle where blood goes
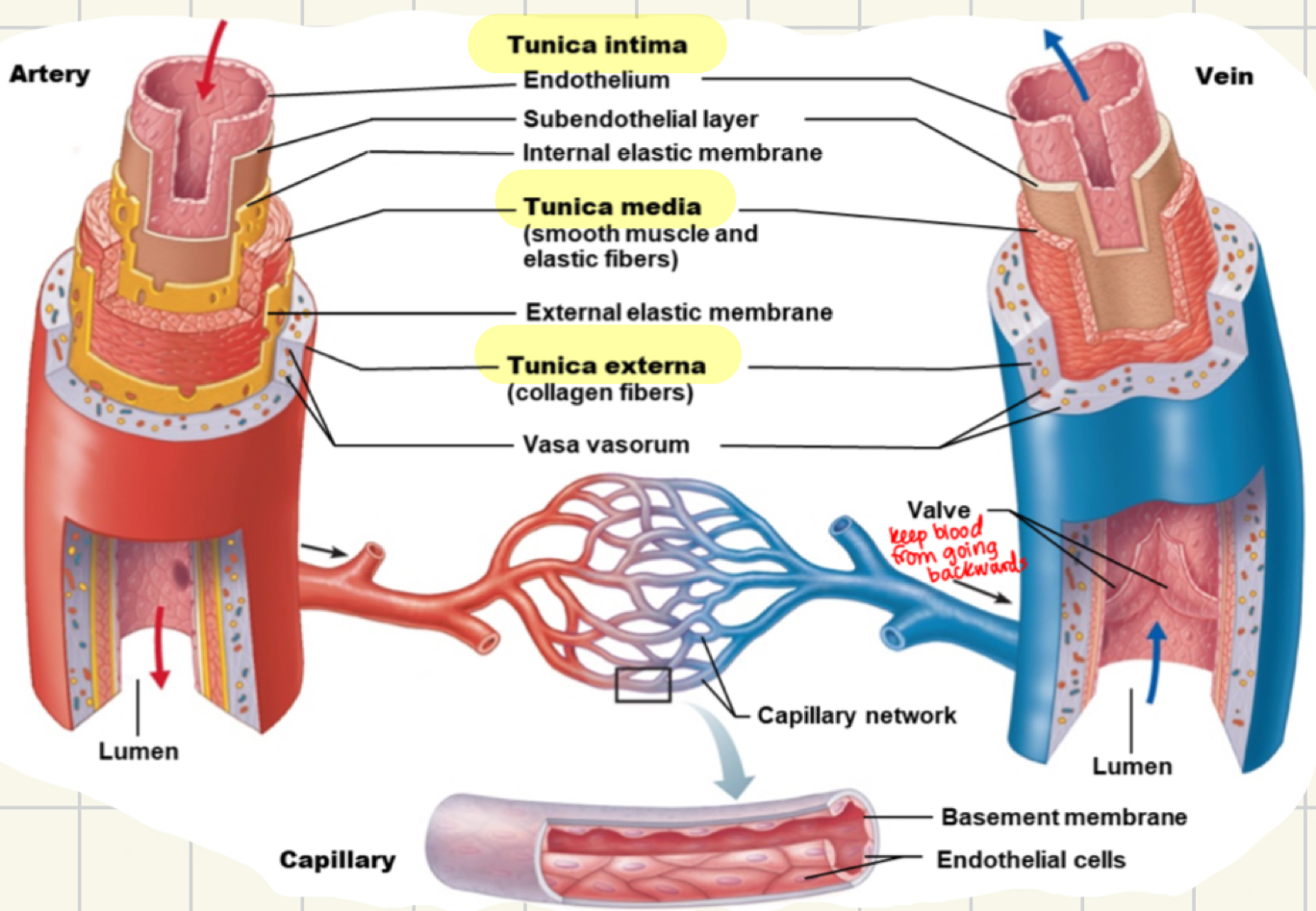
tunica intema facts
innermost layer of the blood vessel
aka endothelium
tunica media facts
smooth muscle layer of the blood vessel
middle layer
allows for open/close
contraction: vasoconstriction
relaxation: vasodilation
tunica externa facts
outermost layer of the blood vessel
CT
arteries facts
HIGH pressure
small lumens, elastin, THICK
arterioles: smallest artery
larger ones have all three tunics
diameter controlled by tissue and sympathetic nervous system
capillaries facts
smallest blood vessel
RBCs pass in a single file line
site specific
lungs: O2 enter CO2 leave
s.intestine: receive digested nutrients
endocrine glands: pick up hormones
kidneys: remove waste
what are the different types of capillaries
continuous, fenestrated, sinusoid capillaries
continuous capillaries facts
least permeable
most common and @ most organs
epithelial cells join by tight junctions
intercellular clefts allows little permeability
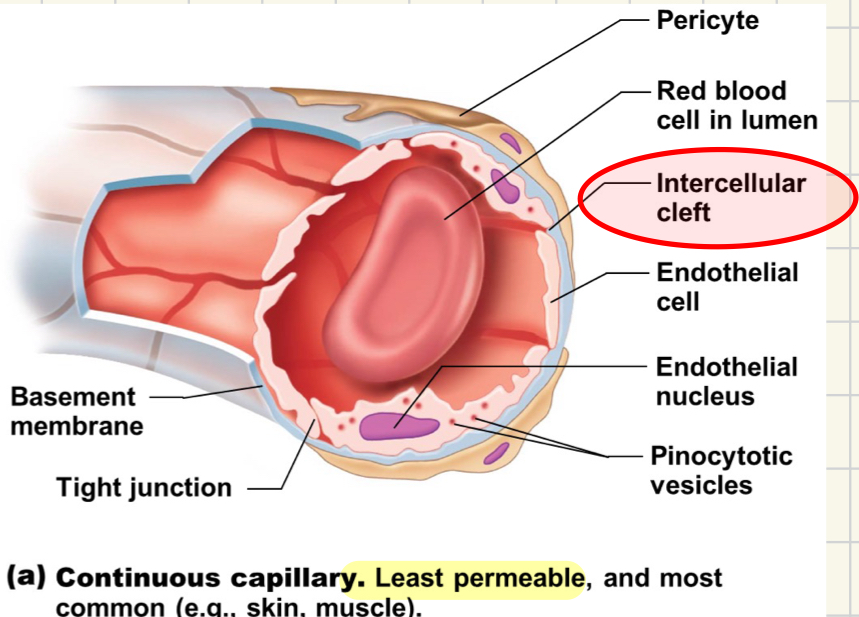
what are intercellular clefts
gaps of unjoined membranes that allow small molecules in/out
fenestrated capillary facts
medium amount of permeability
epithelial cells join by tight junctions
occurs at high rates of exchange
s.intestine, endocrine glands
fenestrations aka PORES, intercellular clefts, and pinocytotic vesicles allow permeability
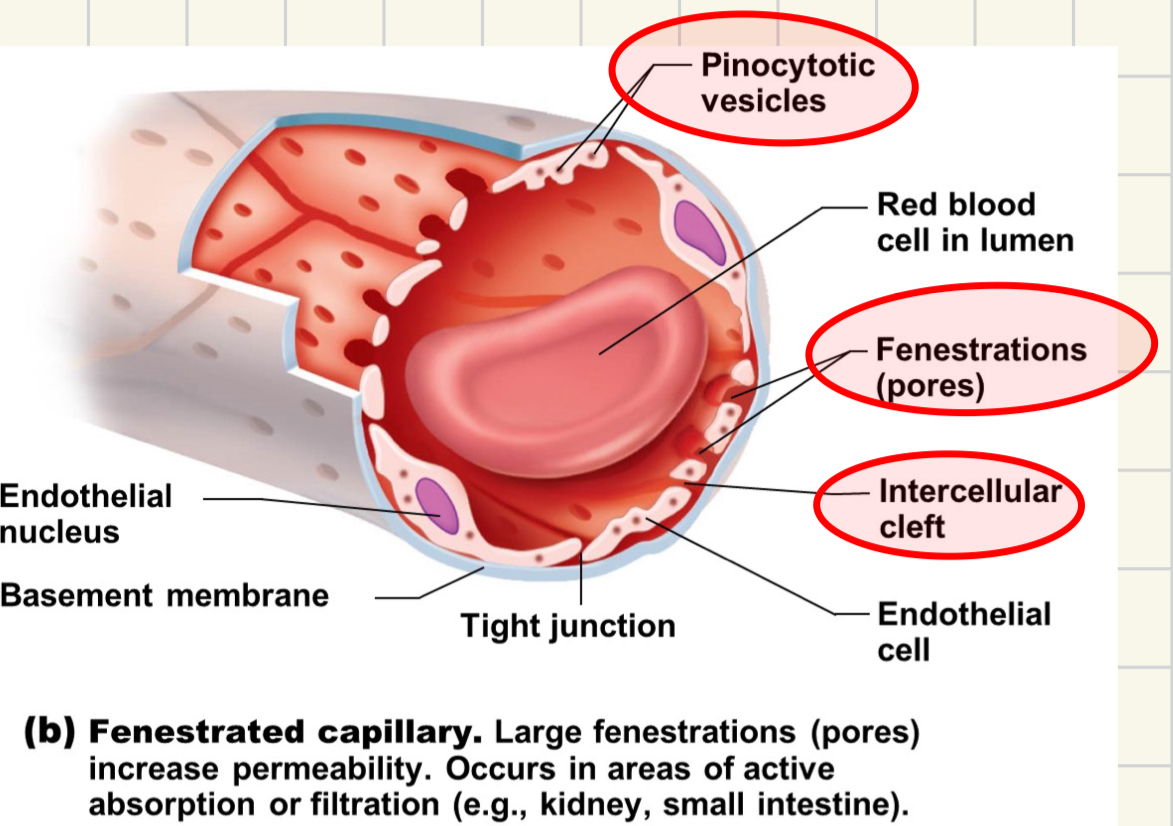
what are fenestrations?
pores
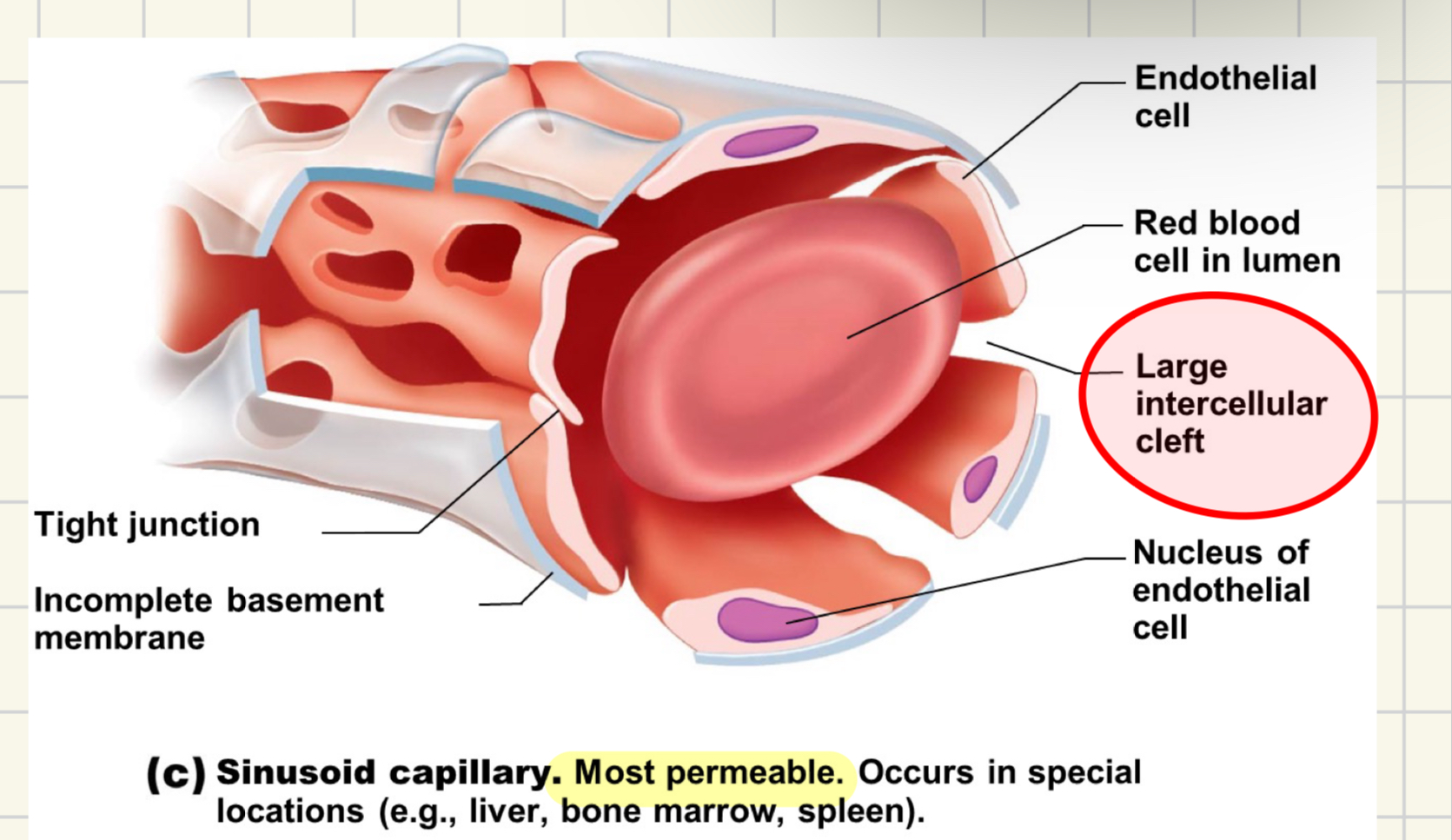
sinusoid capillaries facts
MOST PERMEABLE
wide, leaky, in some organs
liver, bone marrow, spleen
large diameter and twisted
some fenestration, WIDE intercellular clefts allow permeability
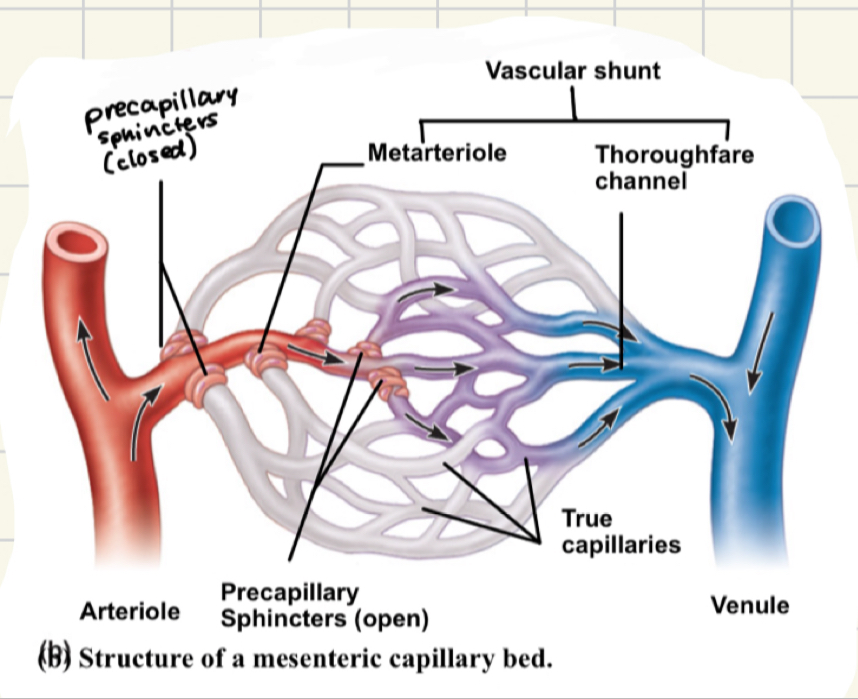
what are capillary beds?
network of capillaries running thru tissues
capillary beds facts
precapillary sphincters: smooth muscle that regulates the flow of blood to tissue
tendons and ligaments: poorly vascularized
epithelia and cartilage: avascular; receive nutrients from CT
what vessel takes blood from the capillaries back to the heart?
veins
veins facts
LOW pressure
venules: small veins, post capillary
RBCs single file line
large lumens (65% of blood in veins)
externa thicker, less elastin, thin walls
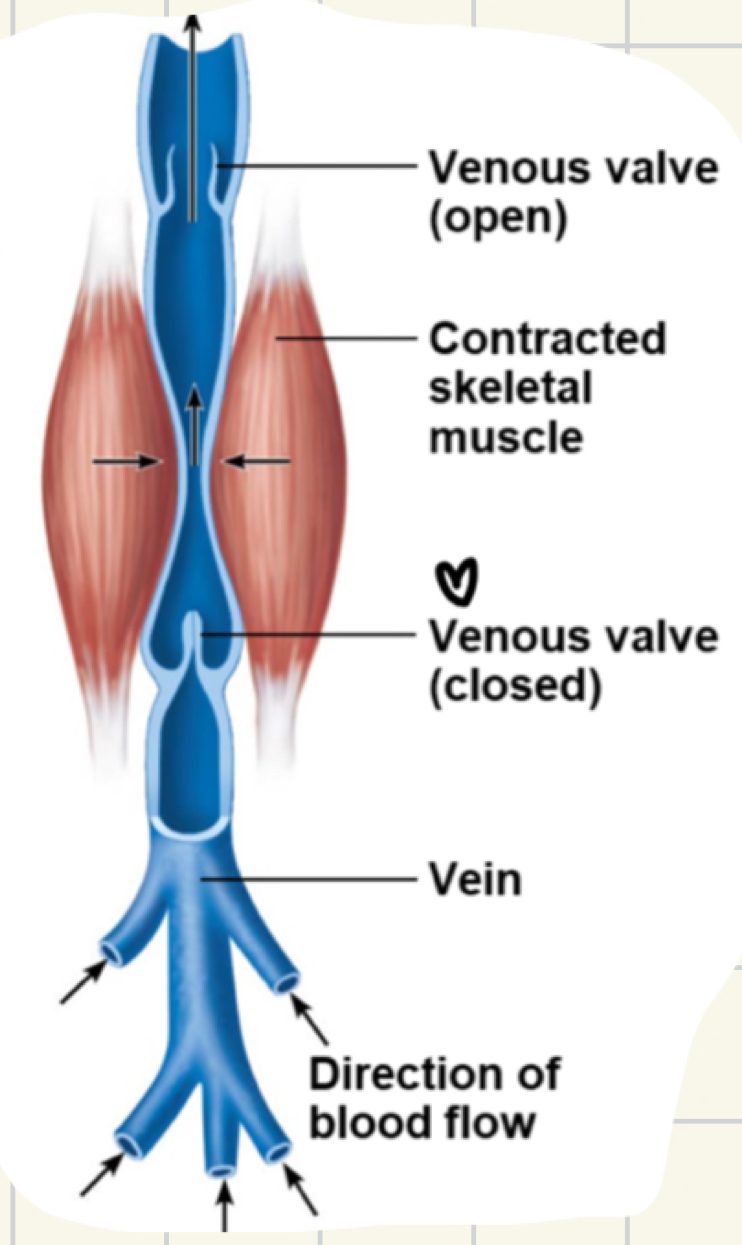
what are some mechanisms to counteract VENOUS low pressure?
valves, only in veins
prevent back flow
in limbs
skeletal muscle pump: muscles press against thin-walled veins
what is anastomosis?
vessels branching to then interconnect to nearby vessels
vascular anastomosis facts
organs receive more than one arterial source of blood
neighboring arteries form
veins anastomose way more because arteries are too thick and high pressure
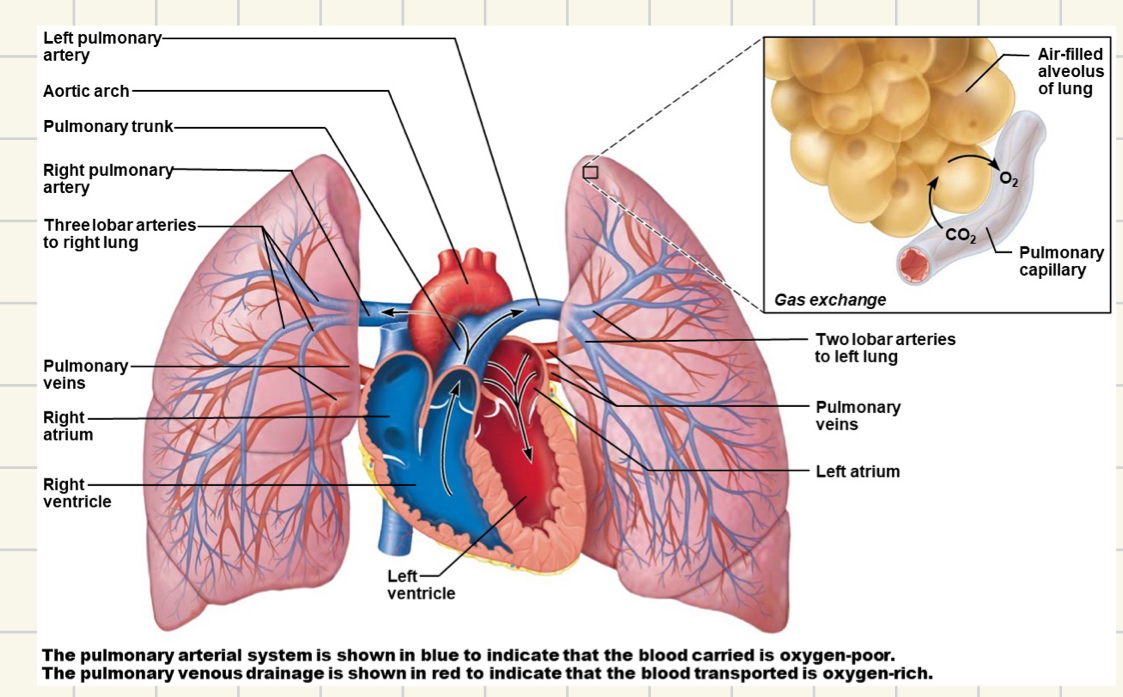
pulmonary circulation
systemic arteries facts
branch in/directly from the aorta
carries O2 blood away from heart
HIGH pressure
major arteries run deep in neck and limbs so bones and muscles protect
greater vessels that exit and enter the heart!!!
ascending aorta
aortic arch
brachiocephalic trunk
left common carotid
left subclavian
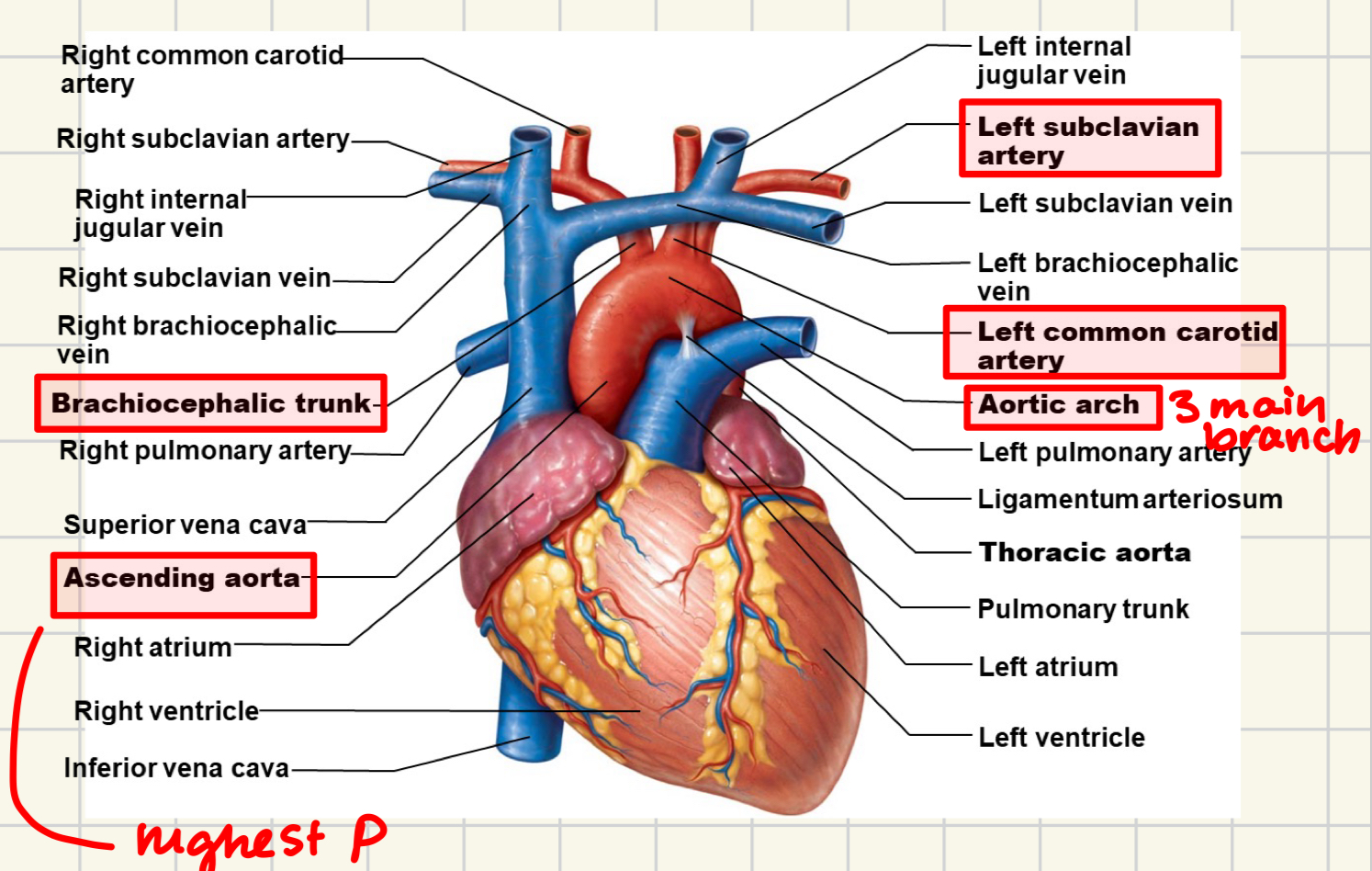
aorta facts!!!
ascending - highest pressure, from left ventricle
branches right and left coronary artery @ beginning of the arch end of ascending
arch - posterior to manubrium
branches L common carotid/cubclavian and brachiocephalic
descending → thoracic and abdominal
R/L common iliac arteries
what does “common” mean?
the first branch off of the MAIN branch
major arteries of the upper limb
L/R subclavian arteries
axillary
brachial
radial and ulnar
internal thoracic
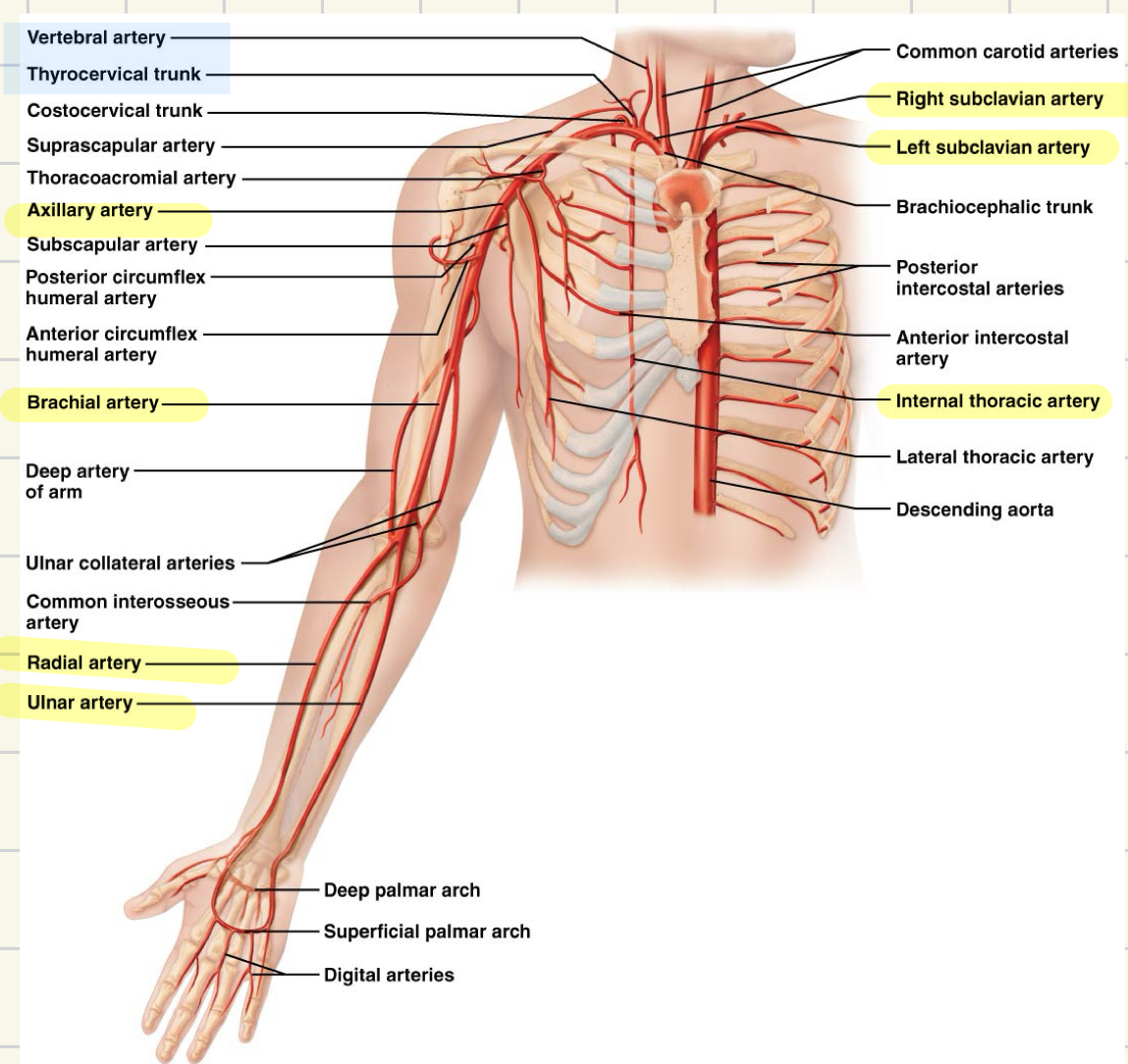
arteries of upper limb from the aortic arch
subclavian → axillary → brachial → radial and ulnar
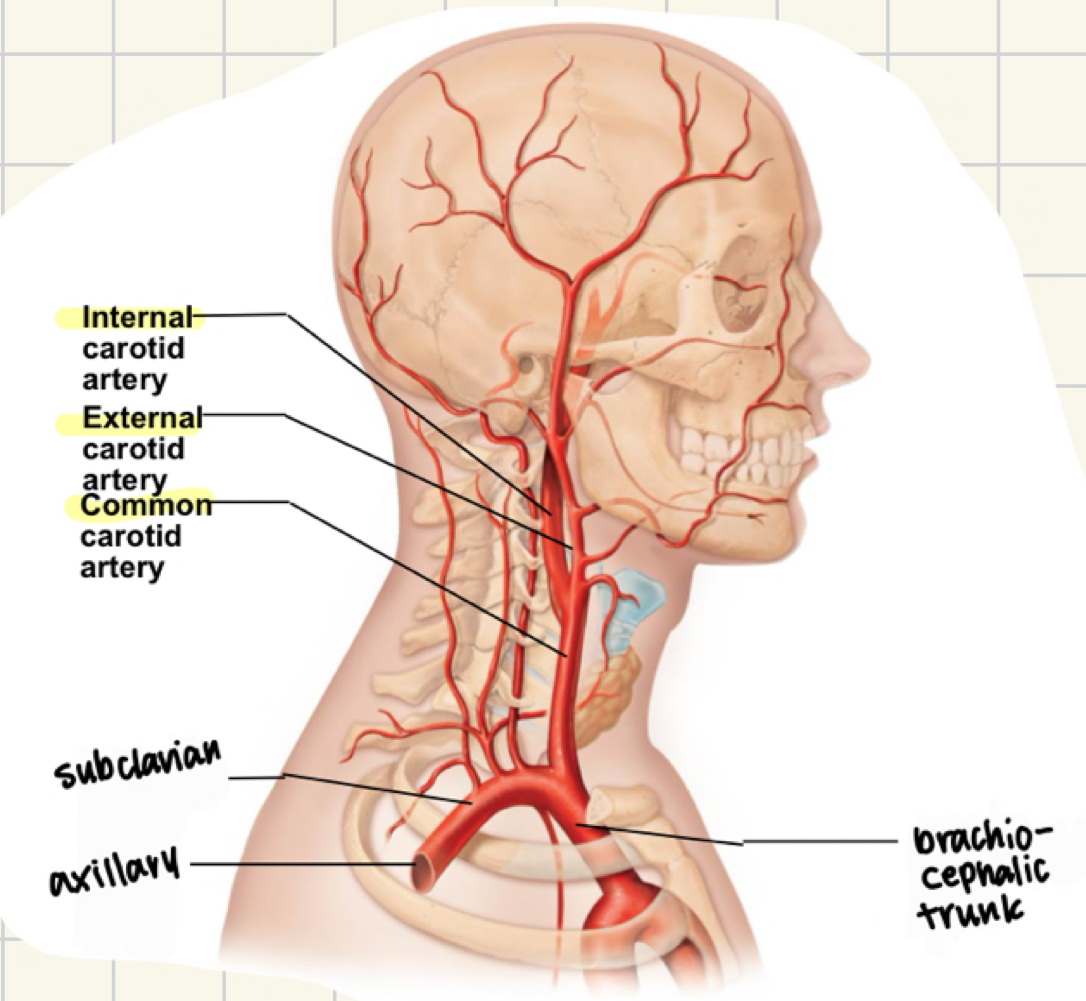
major arteries of the head
common carotid
internal carotid: to the brain
external: face and scalp
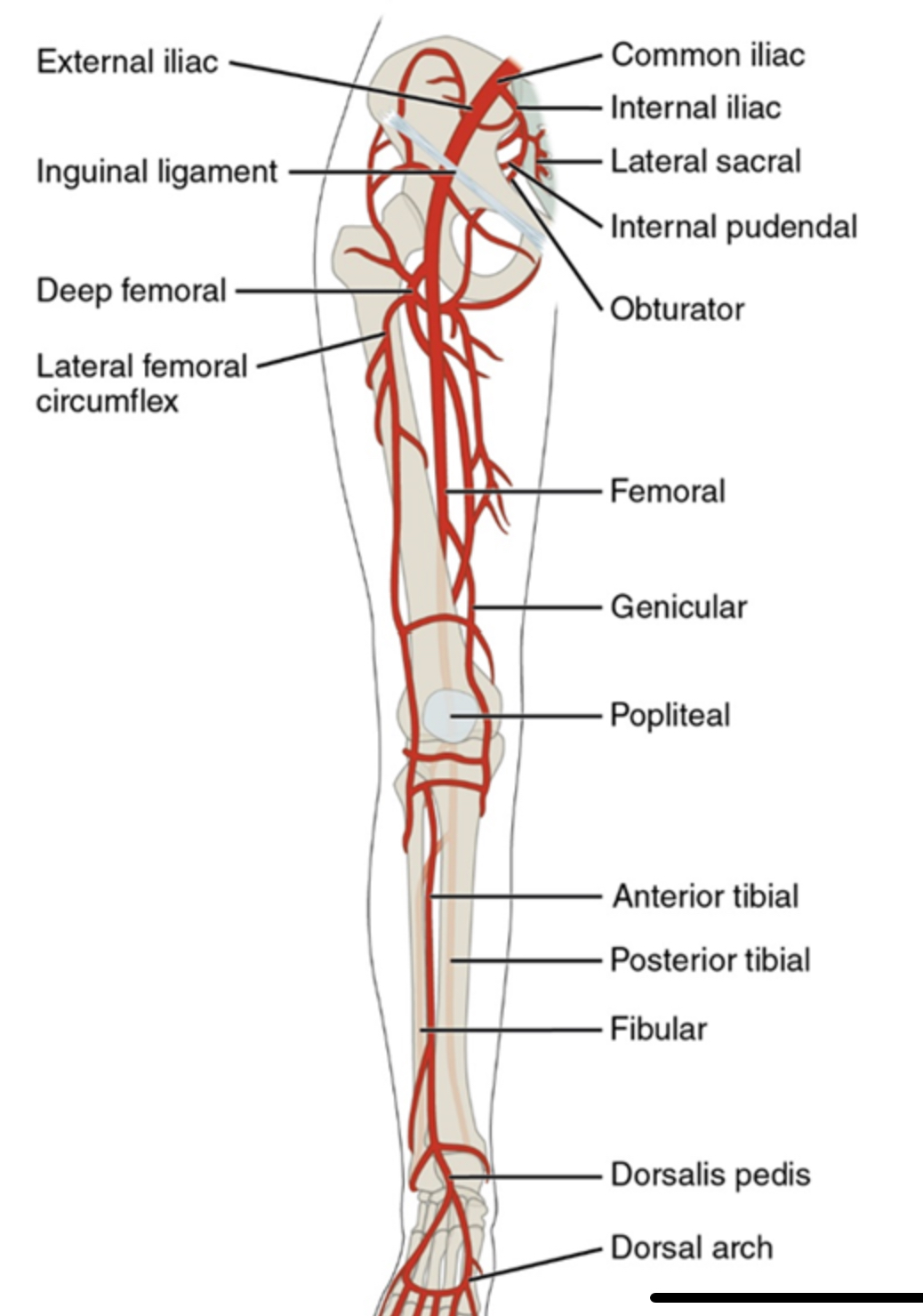
arteries of the lower limbs
from the abdominal aorta → common iliac
internal - into pelvis
external → femoral → popliteal(back of knee) → anterior and postural tibial
systemic veins facts
run along the arteries, have similar names
LOW pressure
empty into the vena cava and coronary sinus (O2 poor from myocardium)
superficial and deep
TEMP CONTROL
vena cava facts
superior
head, upper limbs, thorax
anything above diaphragm
inferior
abdomen, liver, pelvis, lower limbs
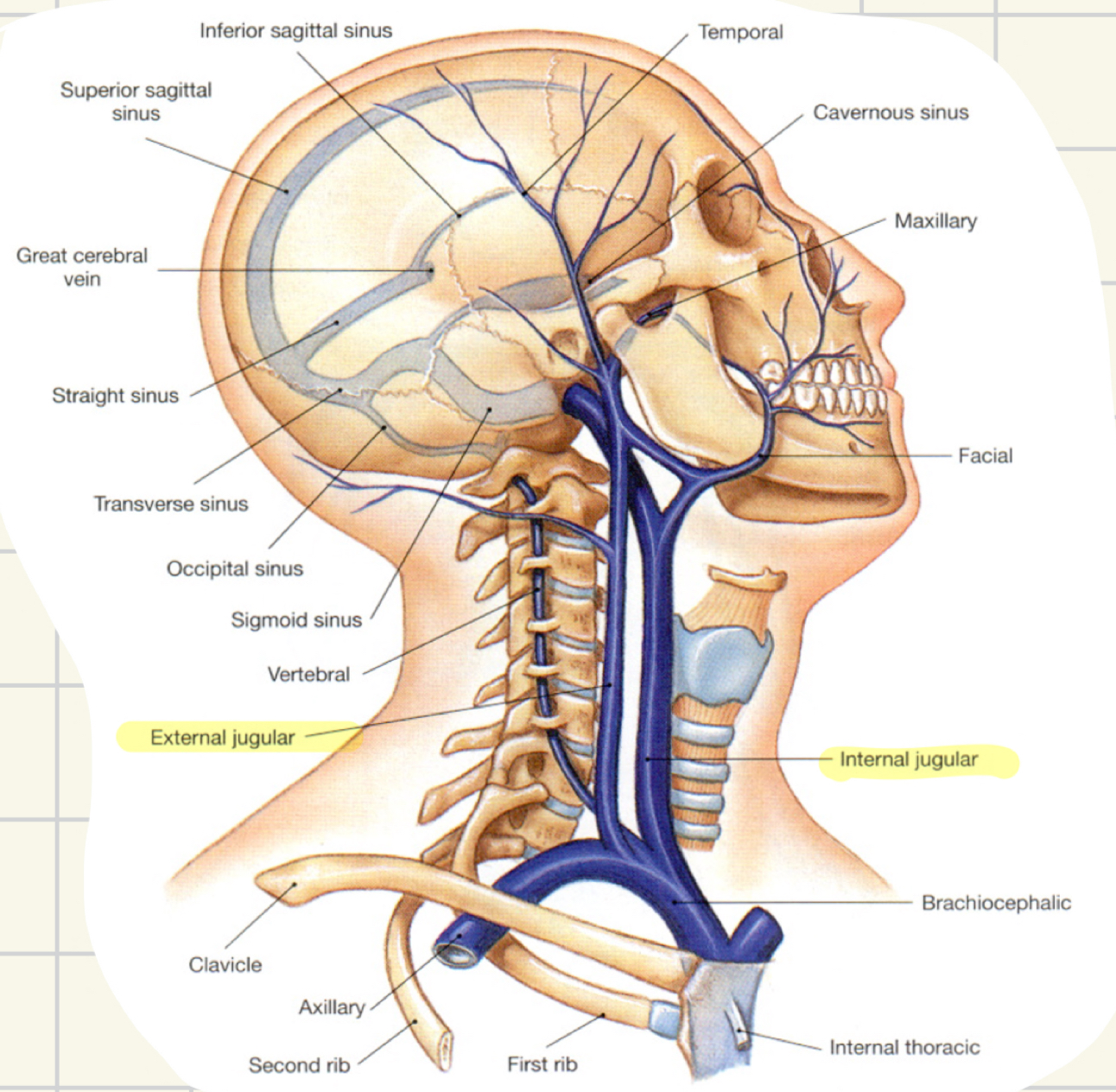
veins of the head
internal jugular: from the brain
external jugular: from the face and scalp
veins of the upper limb
deep veins follow path of arteries
superficial: visible beneath skin
cephalic
basilic
median cubital
median vein (forearm)
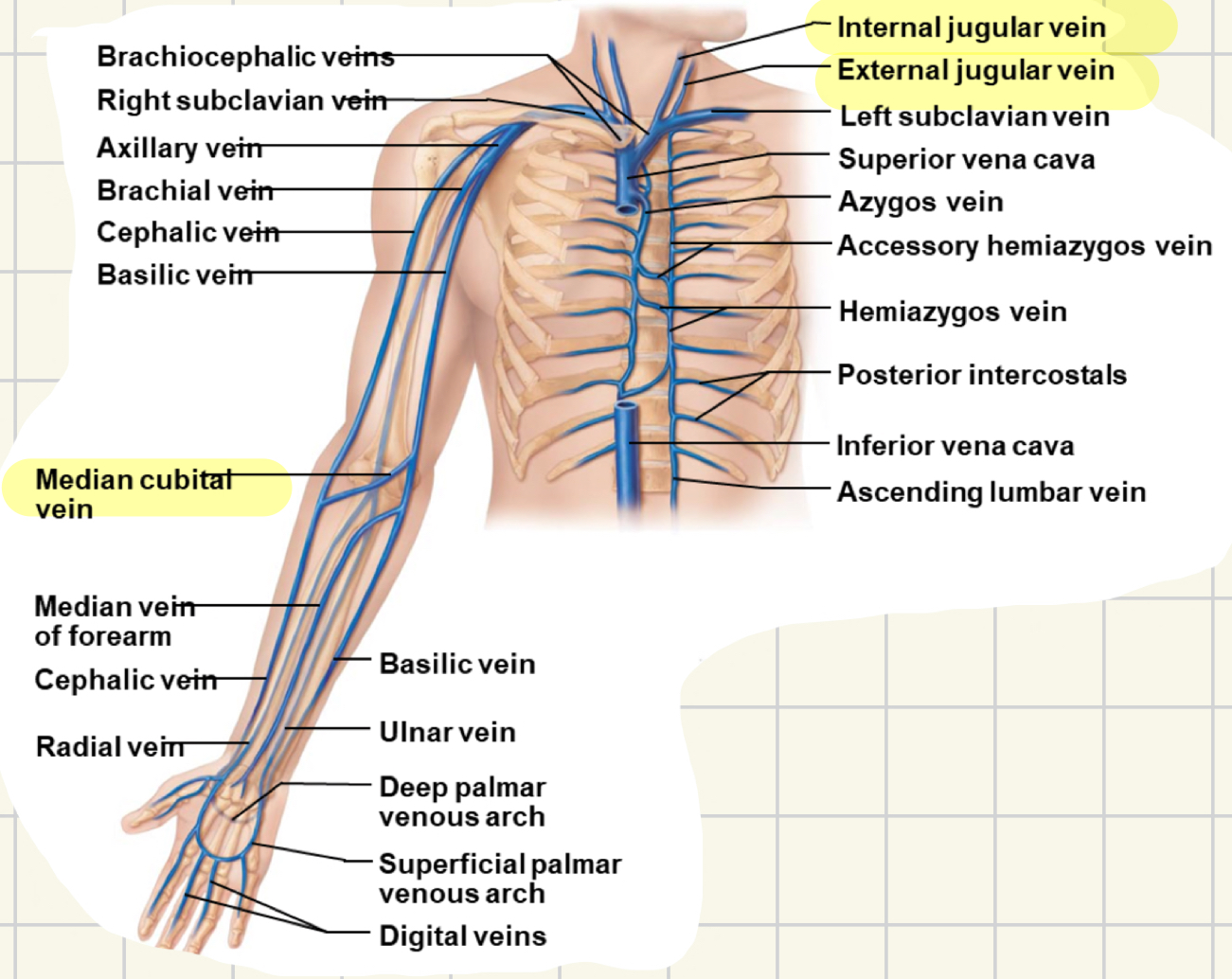
veins of the abdomen
lumbar
gonadal
renal
suprarenal
hepatic
what is the venous system with draining capillary veins in the intestine that then get filtered at the liver capillary vein?
the hepatic portal system
what does the hepatic portal system do?
takes everything you have eaten and transferred to blood to the liver to then clean and go back to the heart
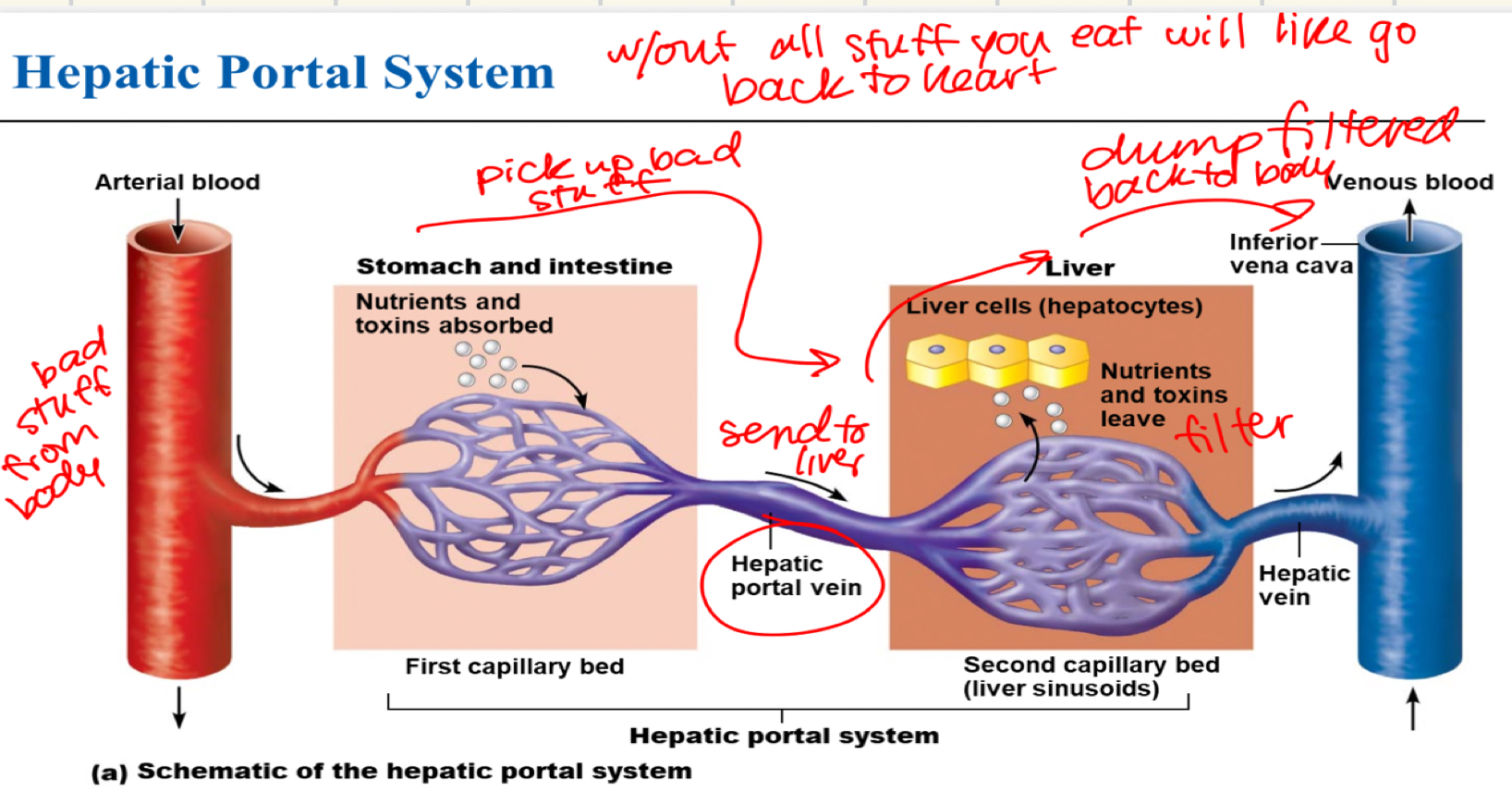
hepatic portal system facts
takes contents of the intestines to the liver to filter → systemic circulation
proteins, fats, alcohol, toxins
one way the liver FILTERS blood
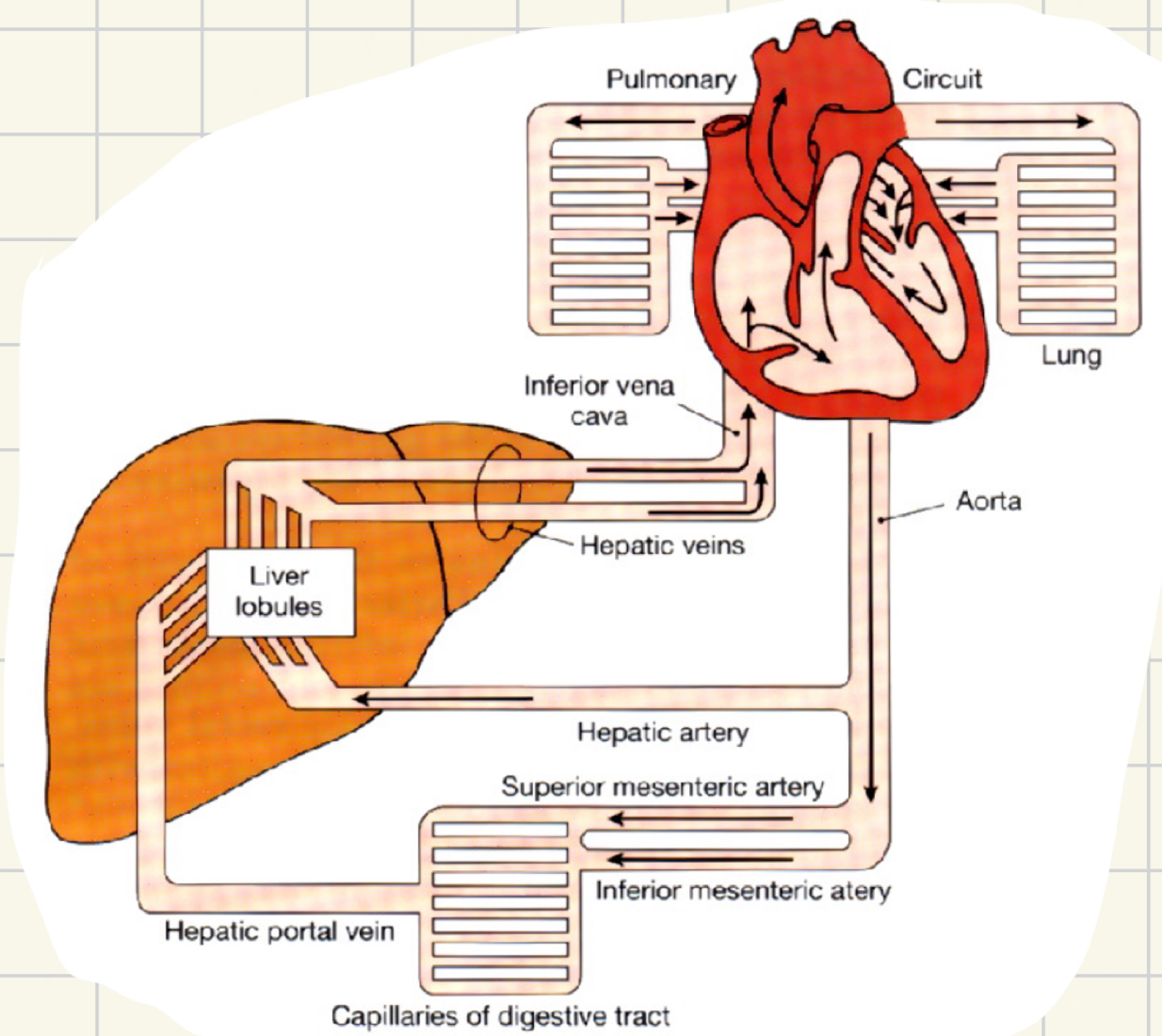
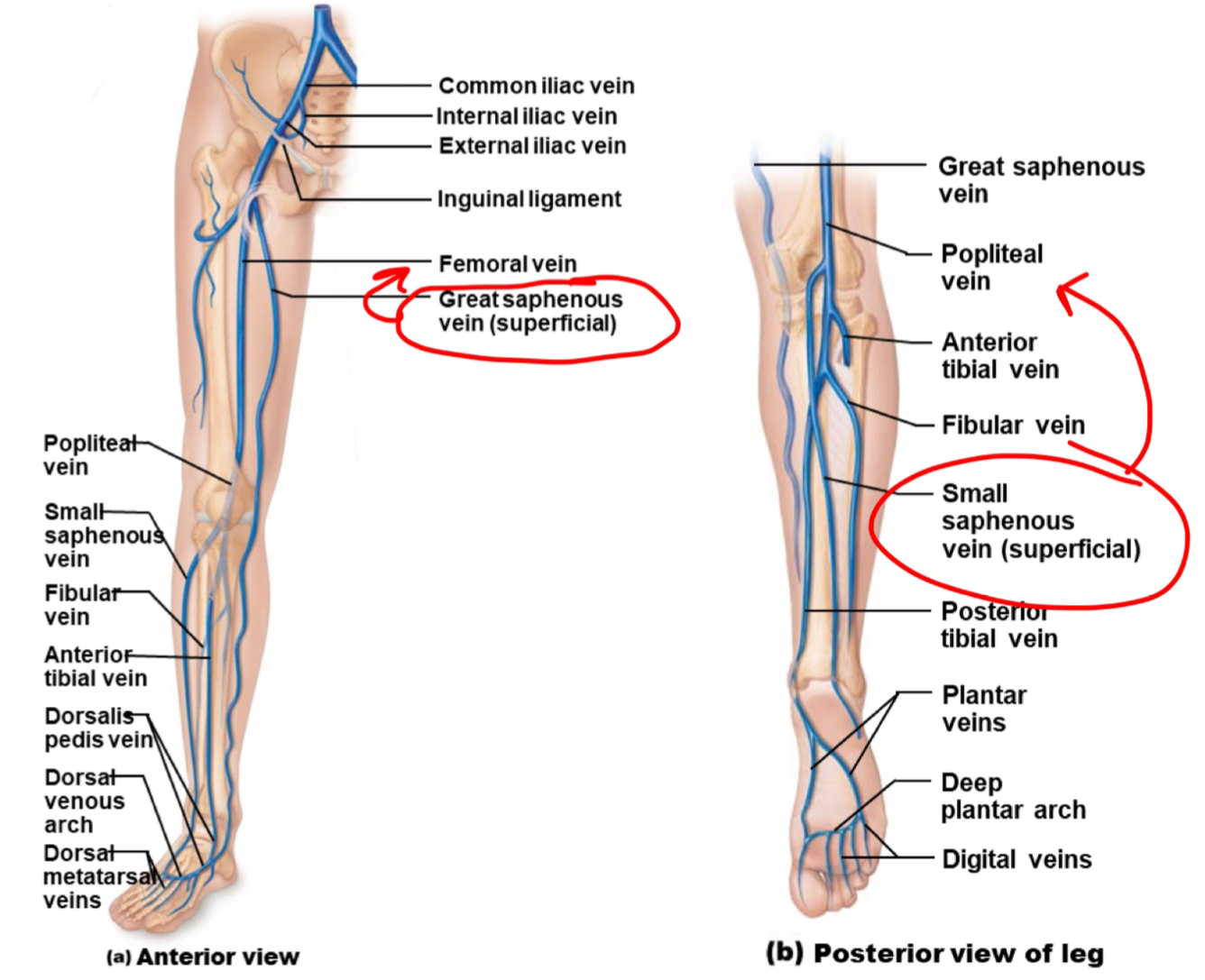
veins of the pelvis and lower limb
deep veins share name of accompanying artery
superficial
great saphenous - empties into the femoral vein
small saphenous - empties into the popliteal