Nucleic Acids: Structure, Function, and Classification in Biology
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What are nucleic acids?
Biomolecules that create, encode, store, transmit, and express information for all living cells.
What are the two main types of nucleic acids?
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA).
What are the monomers that make up nucleic acids?
Nucleotides.
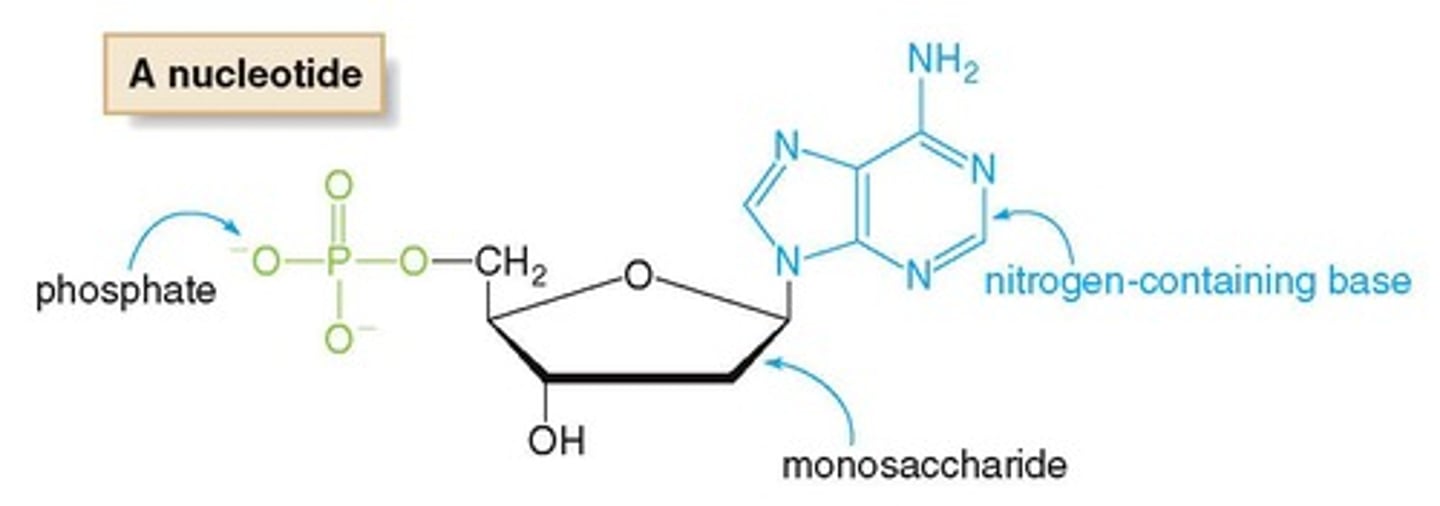
What are the three components of a nucleotide?
A nitrogen-containing base, a pentose sugar, and a phosphate group.
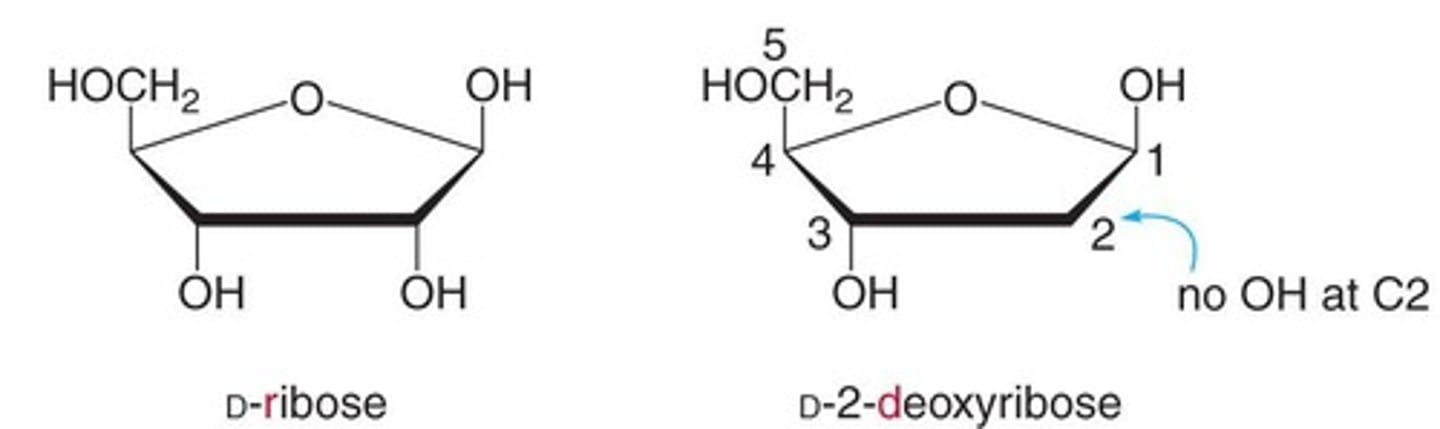
What distinguishes RNA from DNA?
RNA contains ribose sugar and uracil, while DNA contains deoxyribose sugar and thymine.
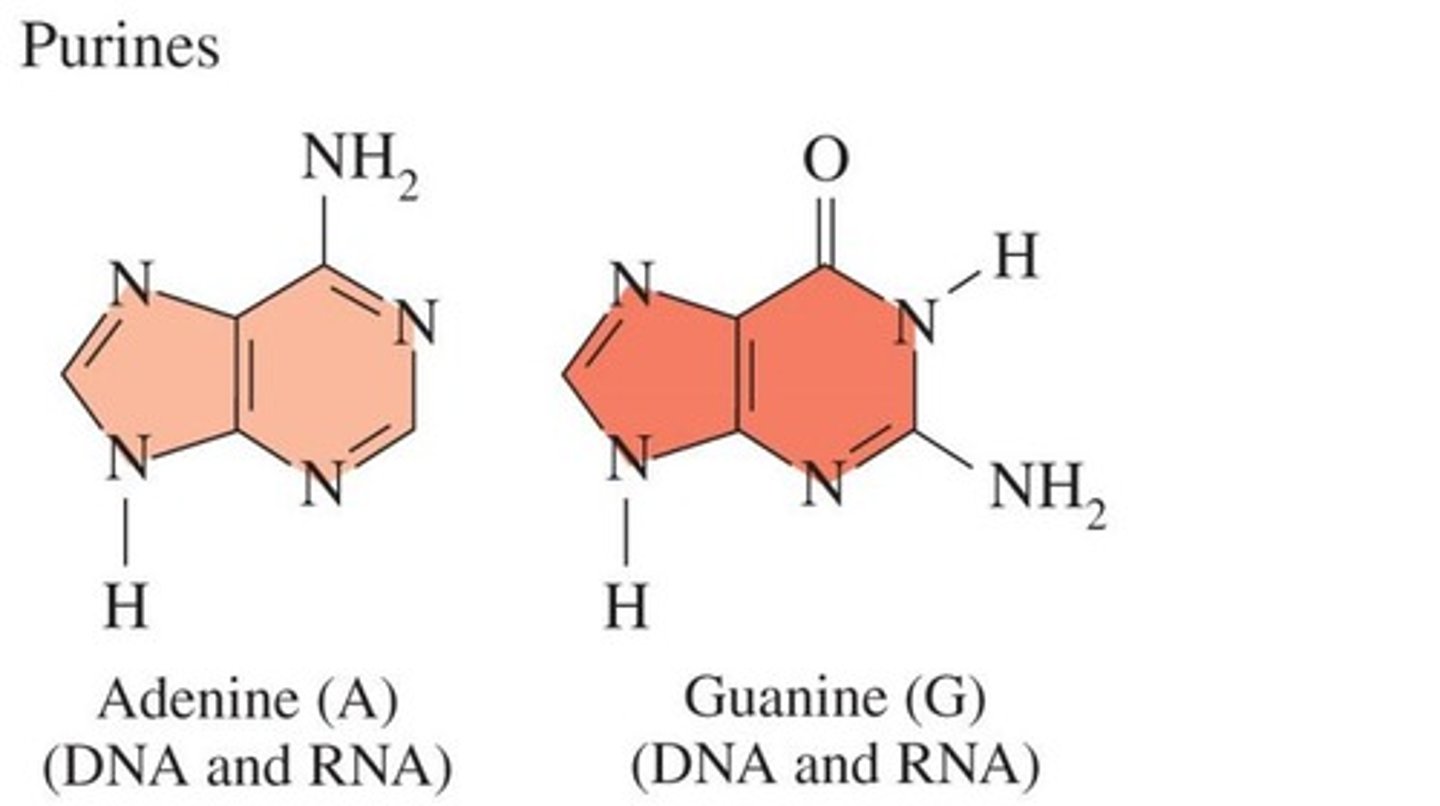
What are the nitrogenous bases found in DNA?
Adenine (A), Thymine (T), Guanine (G), and Cytosine (C).
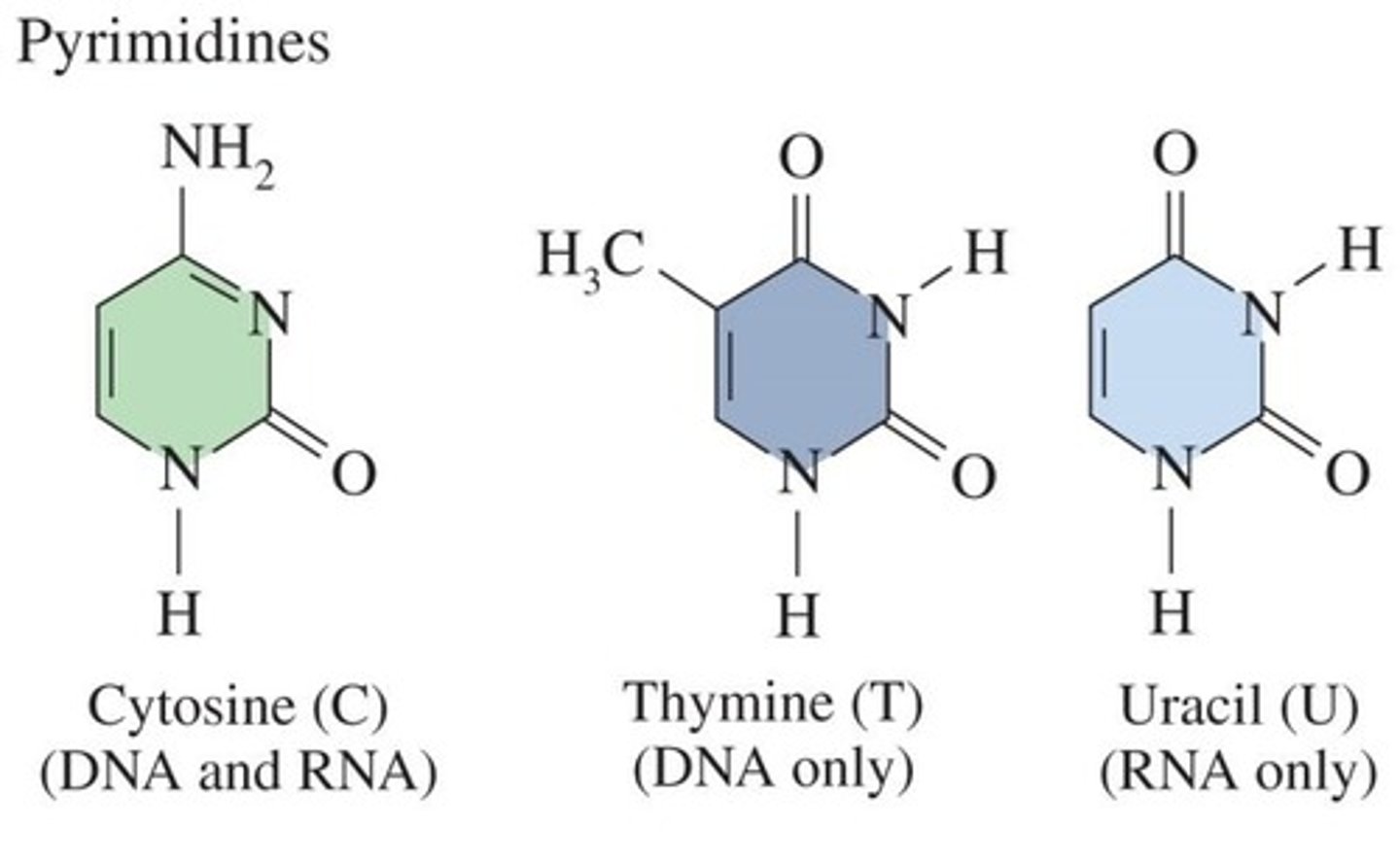
What are the nitrogenous bases found in RNA?
Adenine (A), Uracil (U), Guanine (G), and Cytosine (C).
What is a nucleoside?
A nucleobase attached to a pentose sugar, without a phosphate group.
How is a nucleotide named?
By the nucleoside name followed by the number of phosphate groups, e.g., adenosine-5'-triphosphate (ATP).
What type of bond links nucleotides in nucleic acids?
Phosphodiester linkages.
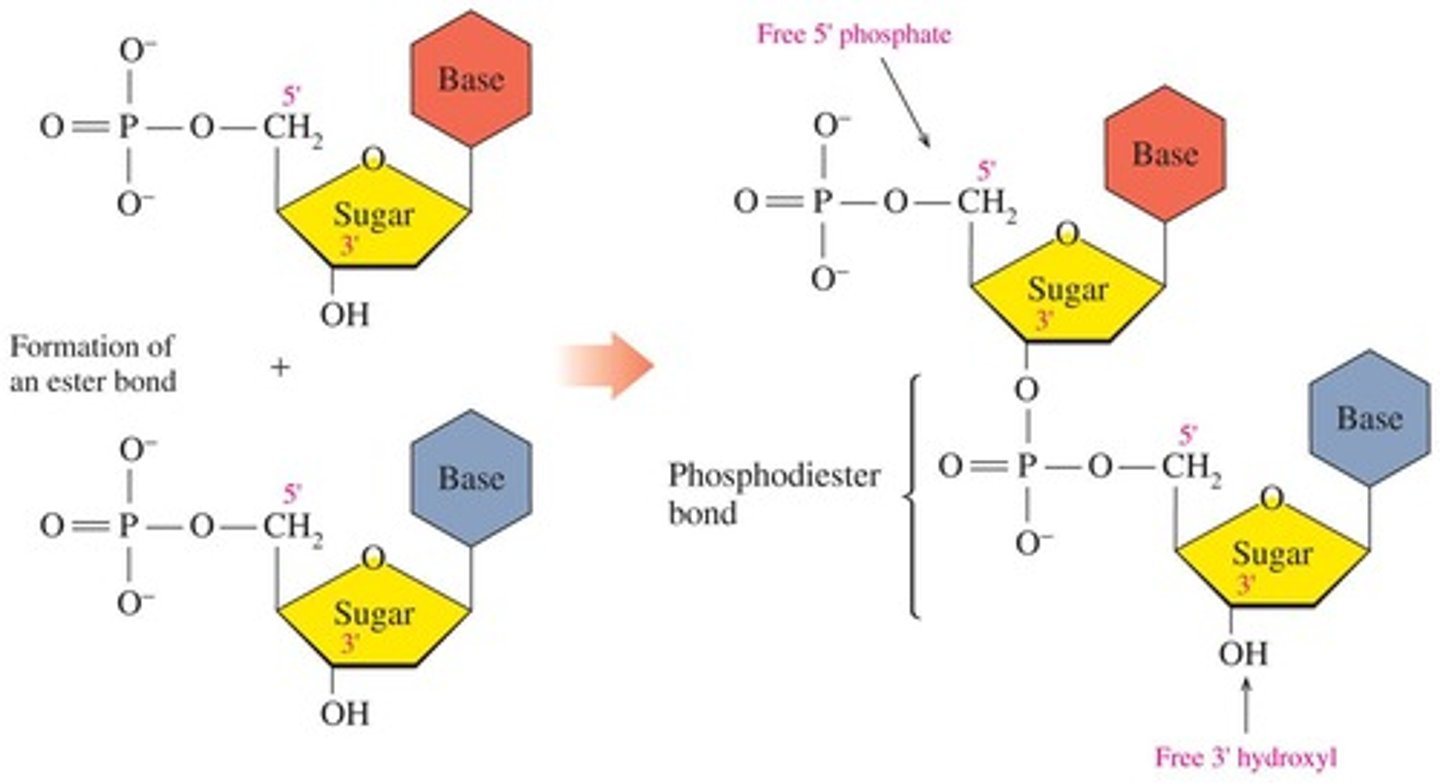
What is the primary structure of nucleic acids?
A repeating sugar-phosphate backbone with a specific sequence of nitrogenous bases.
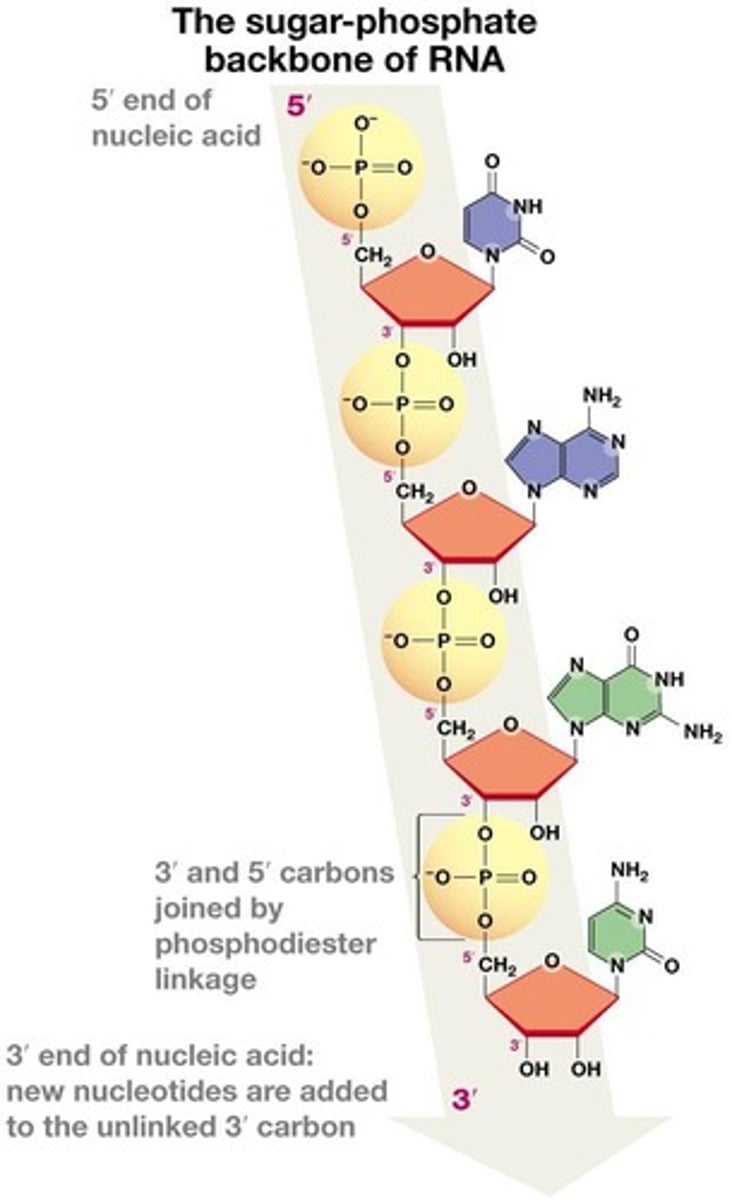
How is genetic information stored in DNA?
In the sequence of nitrogenous bases along the DNA strand.
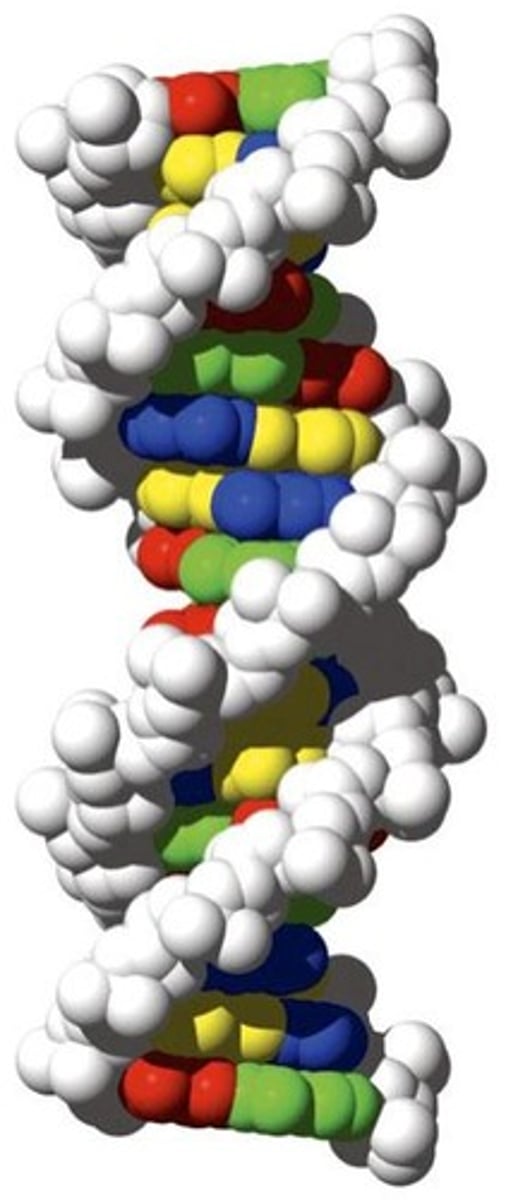
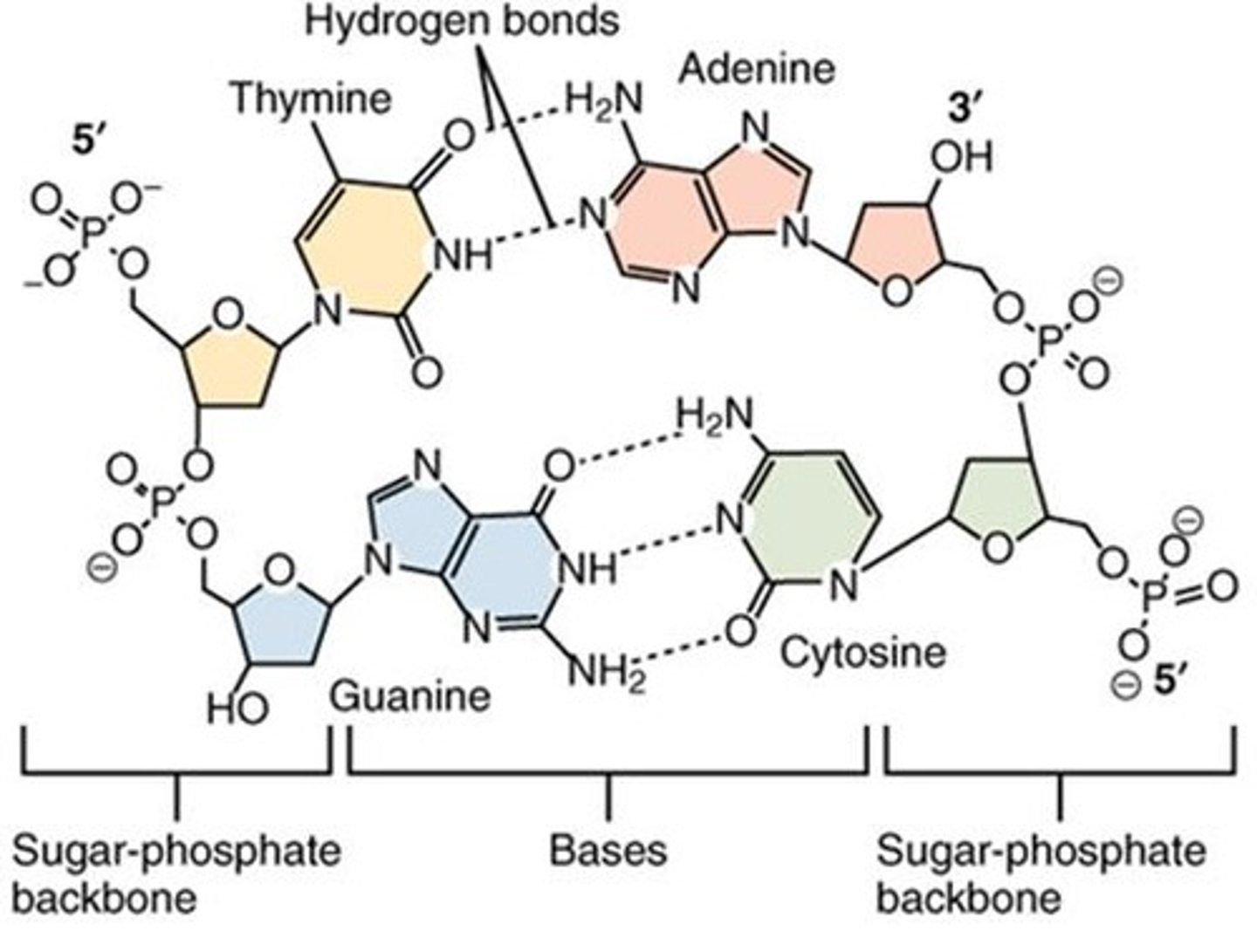
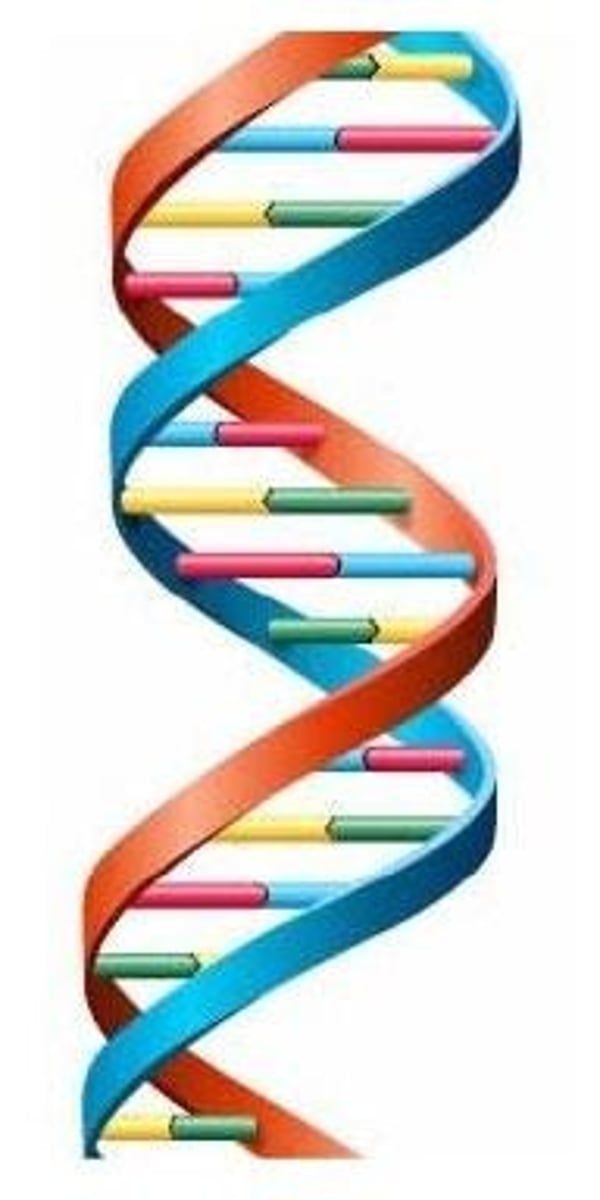
What is the structure of DNA?
A double helix formed by two antiparallel strands with complementary base pairing.
What is the complementary base pairing in DNA?
Adenine pairs with Thymine, and Guanine pairs with Cytosine.
What is the role of RNA in protein synthesis?
RNA mediates the expression of information in DNA to produce proteins.
What makes RNA less stable than DNA?
The presence of a 2′ hydroxyl (OH) group in RNA makes it more susceptible to hydrolysis.
What is a ribozyme?
An RNA molecule that can catalyze chemical reactions.
What is the cellular role of ATP?
ATP serves as the cellular energy currency.
What is the significance of the 5' and 3' ends of nucleic acids?
Nucleic acids have a free phosphate group at the 5' end and a free hydroxyl group at the 3' end.
What is the difference between DNA and RNA in terms of structure?
DNA is double-stranded, while RNA is typically single-stranded.
What is the function of coenzymes like NAD+/NADH?
They act as coenzymes for oxidoreductases in cellular reactions.
What is the role of ribonucleases (RNases)?
They degrade RNA molecules.
How many chromosomes do humans typically have?
Humans typically have 46 chromosomes.
What type of virus is the coronavirus?
It is an RNA virus.
What type of virus is the influenza virus?
RNA virus