3.5 - Energy Transfer in and Between Organisms
1/143
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
What is gross primary productivity?
Chemical energy store in plant biomass, in a given area / volume, in a given time
What is net primary productivity?
The chemical energy store in plant biomass after respiratory losses to the environment have been taken into account
Formula for NPP?
NPP = GPP - R
where r = respiratory losses
What can NPP be used for?
it is available for plant growth and reproduction. It is also available for other trophies levels in the ecosystem, such as herbivores and decomposers.
What is the formula for net production of consumers?
N = I - (F+R)
where I = chemical energy in ingested food
F = chemical energy lost to the environment
R = respiratory losses to the environment
In what terms can biomass be measured?
mass of carbon or dry mass of tissue per given area per given time.
How can the chemical energy in biomass be measured?
calorimetry
How are most of the sugars produced by photosynthesisers used?
to make respiratory substrates
What is solar energy from the sun called?
a constant energy source known as solar flux
Why is solar energy more intense at the equator than the poles?
due to the curvature of the earth
What percentage of solar flux is available for photosynthesis?
1%
How is the solar energy striking a green leaf divided?
4% reflected or transmitted
56% not absorbed by chlorophyll (wrong wavelength)
40% of incident solar energy left to form GPP
What enzyme catalyses the breakdown of ATP?
ATP hydrolase
What enzyme catalyses the synthesis of ATP?
ATP synthase
What is the compensation point?
when the rate of photosynthesis is equal to the rate of respiration
What is the light captured in the light dependent reaction of photosynthesis used for?
photolysis and adding Pi to ADP
What is photolysis?
The splitting of water using light energy into H+ and OH-
What is photoionisation?
When light energy 'excites' electrons in chlorophyll molecule, giving them more energy and causing them to be released.
So the electrons are carried away by an electron carrier, which is reduced. The chlorophyll is oxidised.
What is the formula for photolysis of water?
2H2O -> 4H+ + 4e- + O2
What are the products of the photolysis of water needed for?
- electrons are used to replace the electrons lost form the chlorophyll
- protons used by the proton pump
How and where is the electrochemical gradient for H+ established?
H+ are pumped across the membrane by proton pumps, causing a high conc and +ve charge in the thylakoid space, and a relatively -ve charge in the stroma.
Where does photolysis of water occur?
Thylakoid interior space
What happens to the H+ ions pumped by the proton pump?
They cross the thylakoid membrane through the ATP synthase channel proteins. This changes the structure of the enzyme which then catalyses the combination of ADP + Pi (photophosphorylation)
What are stalked granules?
ATP synthase channel proteins which form small granules on the thylakoid membrane surface
What is photophosphorylation?
It is the process of generating ATP from ADP and phosphate by means of chemiosmosis, using a proton motive force generated across the thylakoid membrane of the chloroplast or the membrane of certain prokaryotes during the light dependent reactions of photosynthesis.
What happens to the H+ and e- after PSII?
they are accepted by NADP?
How does NADP+ become reduced NADP?
They accept and hold two energy electrons along with an H+ ion.
What are coenzymes?
molecules that aid the functions of enzymes
What is the coenzyme in photosynthesis?
NADP
What is non-cyclic phosphorylation?
when electrons fall to a lower energy level and produce ATP. This ATP provides the energy for the synthesis of glucose during the calvin cycle. Basically PS2 because the electrons aren't recycled.
What are the products of the light dependent stage? They are needed for the independent stage.
Reduced NADP and ATP
What are the three stages of the light-independent reaction?
carboxylation
reduction
regeneration
Which enzyme is used in carboxylation?
rubisco
What is the 5-carbon compound that is used in carboxylation?
Ribulose Biphosphate
What is produced in carboxylation?
glycerine-3-phosphate
Describe carboxylation.
CO2 reacts with the 5-Carbon compound ribulose biphosphate (RuBP) to produce two molecules of glycerine-3-phosphate (GP). This is catalysed by the enzyme rubisco.
What is produced in the reduction stage of the light indpendent reaction?
triose phosphate
Describe the reduction stage of the light independent reaction.
The reduced NADP from the light dependent stage is used to reduce GP to triose phosphate (TP) using the energy supplied by ATP.
Describe the regeneration stage of the light independent reaction.
- NADP is reformed and goes back to the light-dependent reaction to be reduced again by accepting more protons
- Some TP molecules are converted to organic substances the plant needs, like starch, cellulose, etc.
- Most TP molecules are used to regenerate ribulose biphosphate using ATP from the light-dependent reaction
Where does the light independent reaction occur?
stroma of the chloroplast
How us the chloroplast adapted for the light independent reaction??
- stroma fluid contains necessary enzymes
- stroma fluid surrounds grana so that products of the LI reaction can readily diffuse into the stroma
- contains both DNA and rubosomes so it can quickly and easily manufacture some of the proteins involved in the LI reaction
What are the four stages of aerobic respiration?
glycolysis, link reaction, krebs cycle, oxidative phosphorylation
What is glycolysis?
The splitting of the 6-carbon glucose molecule into two 3-carbon pyruvate molecules
What is the link reaction?
The 3-carbon pyruvate molecules enter into a series of reactions which lead to the formation of acetylcoenzyme A, a 2-carbon molecule
What is the Krebs cycle?
The introduction of acetylcoenzyme A into a cycle of oxidation-reduction reactions that yield some ATP and a large quantity of reduced NAD and FAD
What is oxidative phosphorylation?
the use of the electrons, associated with reduced NAD and FAD, released from the Krebs cycles to synthesise ATP with water as a by-product. The mechanism by which some of the energy of the electrons within the hydroen atoms is conserved in the formation of ATP.
What equipment would you use to measure photosynthesis?
a photosynthometer
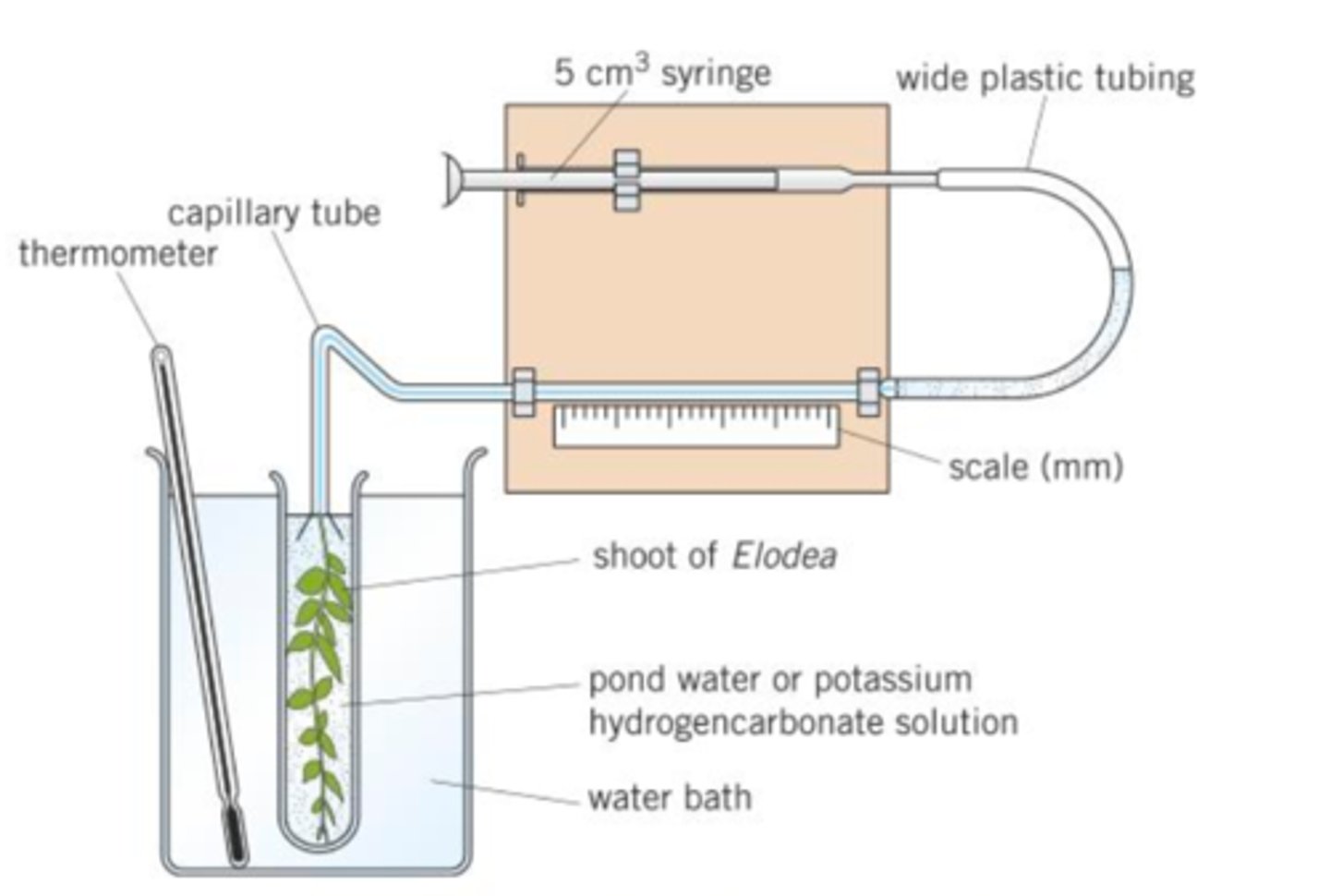
What factors does the rate of photosynthesis depend on?
- light intensity
- availability of water
- availability of carbon dioxide
- availability of chlorophyll
- temperature
Draw a graph of LI against no. of bubbles produced per minute due to photosynthesis and label the compensation point.
(add pic from notes)
Where does glycolysis occur?
cytoplasm
Where do the link reaction and krebs cycle occur?
matrix of mitochondria
Where does the electron transport chain occur (respiration)?
membrane of the cristae
What are the four stages of glycolysis?
1) Phosphorylation of glucose to glucose phosphate
2) Splitting of phosphorylated glucose
3) Oxidation of triose phosphate
4) Production of ATP
Describe the first stage of glycolysis.
two Pi molecules are added (from the hydroglysis of ATP) to one glucose molecule, making it more reactive by phosphorylating it. this lowers the activation energy for the enzyme-controlled reactions to follow
Describe the second stage of glycolysis.
split into two molecules called triose phosphate
Describe the third stage of glycolysis
Hydrogen is removed from each of the two triose phosphate molecules and transferred to a hydrogen-carrier molecule called NAD to form reduced NAD
Describe the fourth stage of glycolysis
Enzyme-controlled reactions convert each triode phosphate into another 3-C molecule called pyruvate. In the process, two molecules of ATP are reformed.
What is the overall yield of glycolysis?
2 pyruvate, 2 ATP, 2 reduced NAD
(4 ATPs are actually produced, but 2 are used, so the net product is 2)
Why do all cells still utilise glycolysis?
because the prokaryotes that evolved glycolysis are ancestors of all modern life; life on earth first evolved without free oxygen, and glycolysis doesn't involve free oxygen
Describe the link reaction
- pyruvate oxidised to acetate. The 3-C pyruvate loses a CO2 molecule and two Hydrogens. The hydrogens are accepted by NAD to form reduced NAD.
- the 2-C acetate combines with a molecule called Coenzyme A to produce a compound called acetylcoenzyme A.
What is the formula for the link reaction?
pyruvate + NAD +CoA -> acetyl CoA + reduced NAD + CO2
How many turns of the link reaction and Krebs do you get from one glucose molecule which goes through glycolysis?
2, because 2 pyruvate molecules are produced and 1 pyruvate is needed for each turn of the cycle.
What is the yield from the link reaction and Krebs cycle for each molecule of pyruvate?
- reduced coenzymes such as NAD and FAD
- one molecule of ATP
-3CO2
Why are reduced coenzymes such as NAD and FAD important products of the Krebs cycle?
- they have the potential to provide energy to produce ATP molecules by oxidative phosphorylation
Where does the Krebs cycle occur?
mitochondrial matrix
Draw a diagram illustrating the link reaction and krebs cycle.
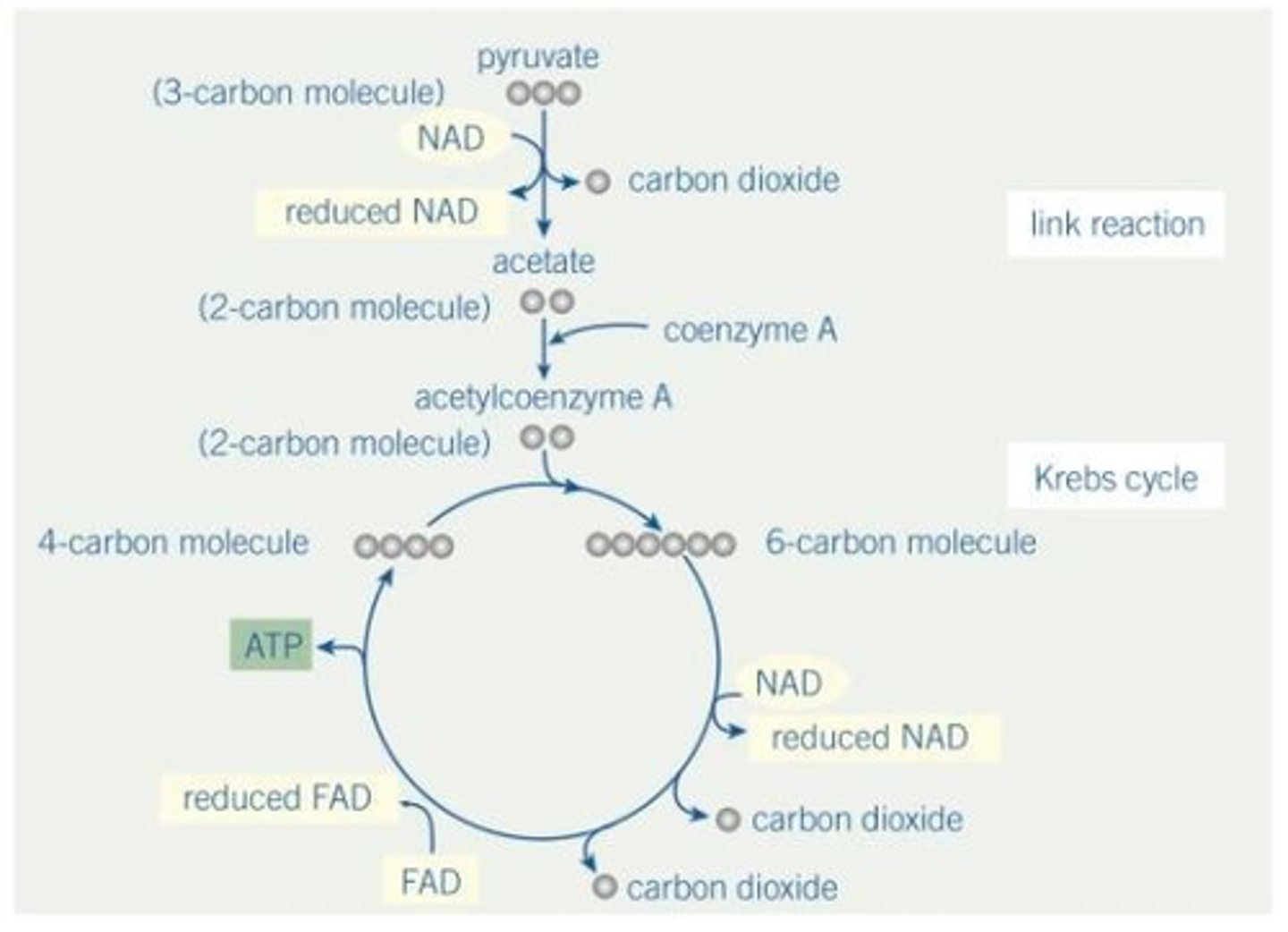
What is the significance of the Krebs cycle?
Breaks down macromolecules into smaller ones
Produces H to reduce NADH for ETC.
Produces 4-carbon molecule to combine with acetylCoA, which would otherwise accumulate.
Source of intermediate compounds used by cells in manufacture of other substances e.g. amino acids.
What is substrate-level phosphorylation?
ATP synthesis when the phosphate donor is a substrate
of glucose.
What are the products of one turn of the Krebs cycle?
3 molecules of reduced NAD, 1 molecule of FAD, 1 molecule of ATP and 2 molecules of CO2
If you add hydrogen to a molecule, is it reduced or oxidised?
reduced
Where does oxidative phosphorylation occur?
inside the cristae of the inner folded membrane
What is cytochrome?
an electron carrier
Describe the synthesis of ATP by oxidative phosphorylation.
- hydrogen atoms produced during glycolysis and krebs combine with NAD and FAD
- reduced NAD/FAD donate electrons of the hydrogen atoms they are carrying to the first molecule in the electron transfer chain
- the electrons pass along the chain of electron transfer carrier molecules in a series of oxidation-reduction reactions. As the electrons flow along the chain, the energy they release is used to actively transport protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane and into inner-membranal space
- the protons accumulate in this space before they diffuse back into the mitochondrial matrix through ATP synthase channels embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
- at the end of the chain the electrons combine with these protons and oxygen to form water. Oxygen is therefore the final acceptor of electrons in the electron transfer chain.
Why is energy released in stages down the carrier molecules instead of one step?
the energy wouldn't all be harvested, as it would be lost as heat instead. The transfer of electrons down the gradient gradually releases energy in a more useful manner.
What happens if no oxygen is present for the electrons to go to at the end of the chain?
the electrons back up through the chain, and respiration would come to a halt; there would be a build up of reduced NAD and FAD
How many ATP molecules do you get from one molecule of reduced NAD?
3
What is the net production of ATP from respiration?
38
Why is the theoretical yield of energy greater than the actual yield in aerobic respiration?
- leakage of H ions when passing across membrane
- ATP is used in active transport of pyruvate
- ATP is used to move H ions from cytoplasm into mitochondria
Which is the only stage of respiration that can occur anaerobically?
glycolysis
What is the problem with glycolysis occuring without oxygen?
The reduced NAD cannot be oxidised to allow it to collect the Hydrogen produced in glycolysis. NAD is needed to collect the hydrogen, and the products of glycolysis (H+ and pyruvate) must be consistently removed so that glycolysis can continue.
What is the solution to replenishing NAD in glycolysis?
the pyruvate molecule from glycolysis accepts the hydrogen from the reduced NAD, hence oxidising it to produce NAD which can then be used in further glycolysis.
What is the pyruvate converted to in animals/plants/microorgansims such as yeast?
- plants and microorganisms such as yeast: pyruvate converted to ethanol and carbon dioxide
- animals: pyruvate converted to lactic acid
What is the summary equation for anaerobic respiration in plants and some microorganisms?
pyruvate + reduced NAD -> ethanol + CO2 + oxidised NAD
When is anaerobic respiration useful in animals?
in a baby mammal just after birth, or for an animal living in water where the amount of oxygen may sometimes be very low.
or in muscles during periods of strenuous exercise
What is the summary equation for anaerobic respiration in animals?
pyruvate + reduced NAD -> lactate + oxidised NAD
How is the NADH from glycolysis removed in animals when oxygen is in short supply?
each pyruvate molecule takes up the two hydrogen atoms from the reduced NAD produced in glycolysis to form lactate.
Which are the two ways energy from cellular respiration is derived?
- substrate-level phosphorylation in glycolysis
How is lactate broken down in animals?
It can be oxidised back to pyruvate or it is taken to the liver and coverted back to glycogen.
What is a sapriobiont?
an organism that feeds on dead material
What is a heterotroph?
An organism that cannot make its own food.
What is an autotroph?
An organism that makes its own food
Define productivity.
the rate at which something is produced
How to improve net productivity in agriculture?
- improving energy lost to other organisms e.g. pests
- improving energy lost to unnecessary respiration (e.g. restrict movement)
Why is simplifying food chains useful?
- if we can get rid of food chains that don't involve humans, energy losses will be reduced and productivity increased.
- pests can be removed using pest controlled (using parasites of pests or pathogens of pests, or using herbicides and insecticides)
- inter
How can pests be removed?
- using parasites of pests or pathogens of pests, or
- using herbicides and insecticides
- integrated systems can combine both of these and can be more effective than one on its own
What do we need to do to improve net productivity in agriculture?
- prevent natural climax community by removing certain plants
- use pesticides/herbicides to remove unwanted plants and animals
- protect from disease using sprays and supplements
- feed animals certain diets
- house animals in warm conditions
- prevent movement of animals as much as possible
Why do plants need to produce ATP in respiration as well as photosynthesis?
- if only photosynthesis occurred, not enough ATP would be produced.
- in the dark, no photosynthesis would occur
- some tissues cannot photosynthesise
- ATP cannot be moved from cell to cell/stored
Why are only 2 ATP produced per glucose in anaerobic respiration?
- only glycolysis occur
- so the glucose is not fully broken down.
Why is energy lost between trophic levels?
- some of the organsim is not consumed
- some parts are consumed but cannot be digested and are therefore lost in faeces
- some energy lost is excretory materials such as urine
- some energy losses occur as heart from respiration. These losses are high in mammals and birds because they have high body temperatures
Suggest suitable units for the measurement of biomass produced in a certain time.
Kg per m^2 per year