Chapter 3 - Energy, Catalysis, and Biosynthesis
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What are catabolic reactions?
Reactions that break down large molecules into smaller ones.

What are anabolic or biosynthetic reactions?
Reactions that create large molecules from small molecules.
What is metabolism?
The sum total of all chemical reactions, including catabolic and biosynthetic.
What does the First Law of Thermodynamics state?
Energy can neither be created nor destroyed, only transferred or converted.
What is kinetic energy?
The energy of motion.
What is potential energy?
Energy possessed due to position.
What does the Second Law of Thermodynamics state?
In an isolated system, the degree of disorder (entropy) can only increase.
What is entropy?
A measure of disorder in a system.
How do living cells relate to the Second Law of Thermodynamics?
Living cells must take in energy to generate order, despite increasing entropy.
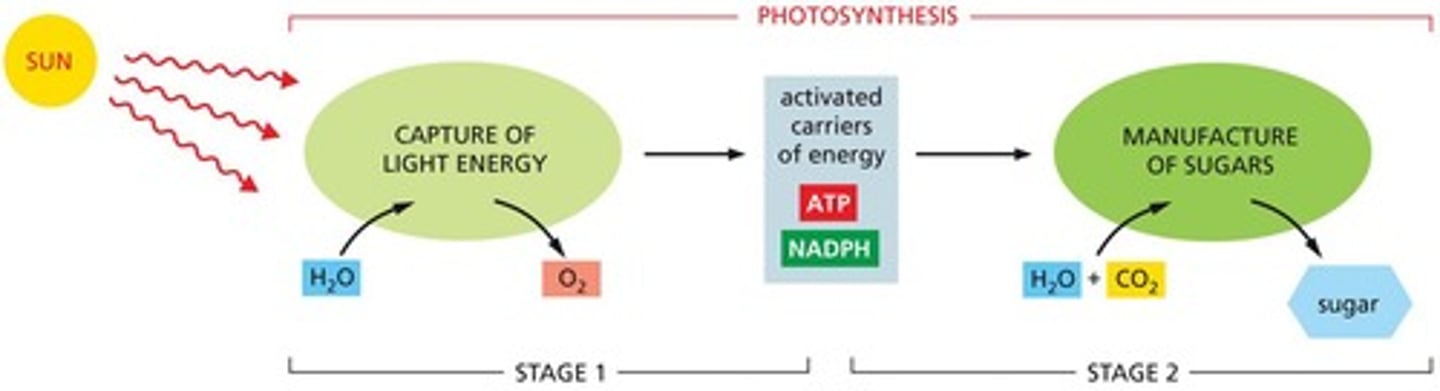
What is photosynthesis?
The process by which organisms use sunlight to synthesize organic molecules.
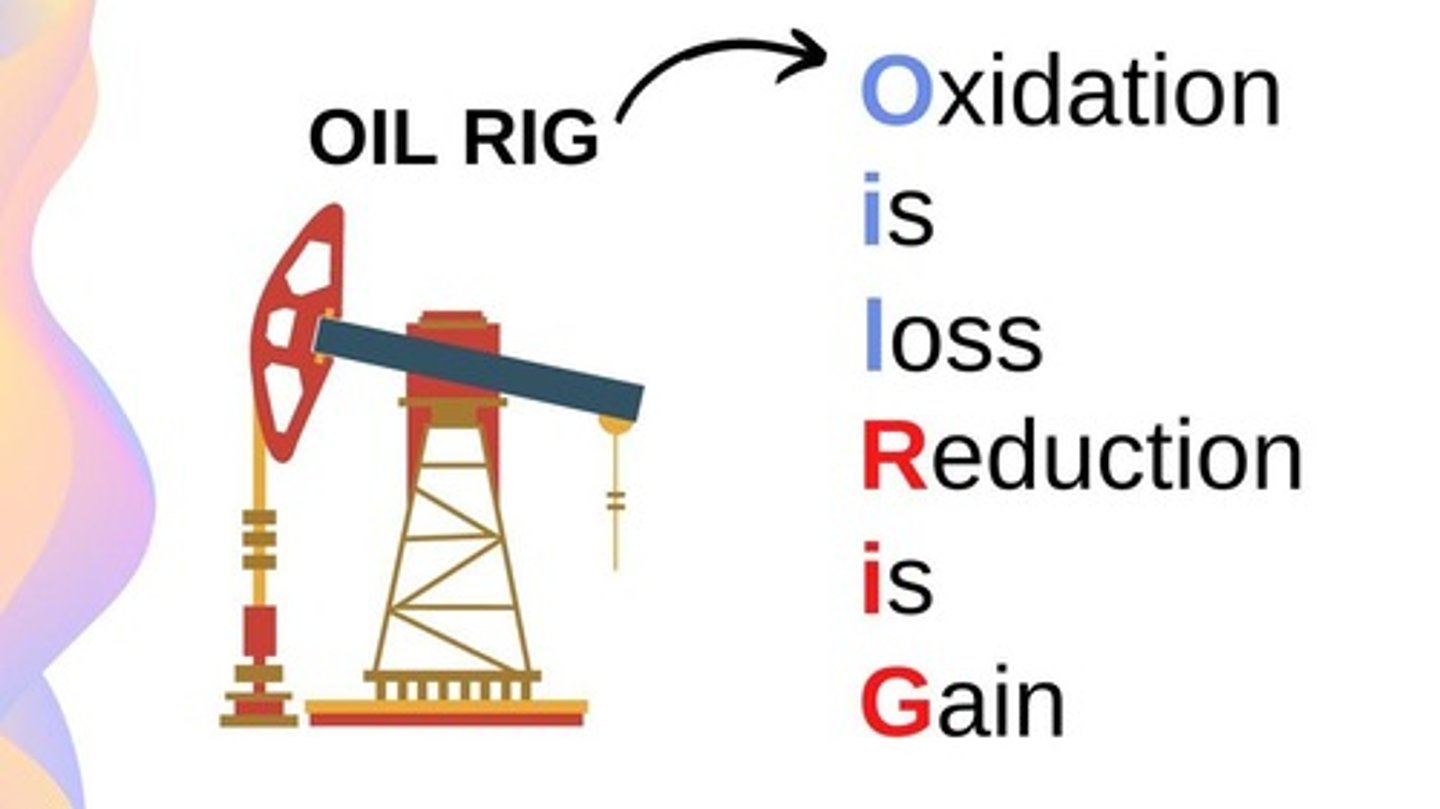
What are oxidation and reduction reactions?
Oxidation involves the transfer of electrons away from an atom, while reduction involves the addition of electrons.
What is an exergonic reaction?
A reaction that releases energy, such as glucose breaking down to CO2 and H2O.
What is an endergonic reaction?
A reaction that requires energy input, such as the formation of glucose from CO2 and H2O.
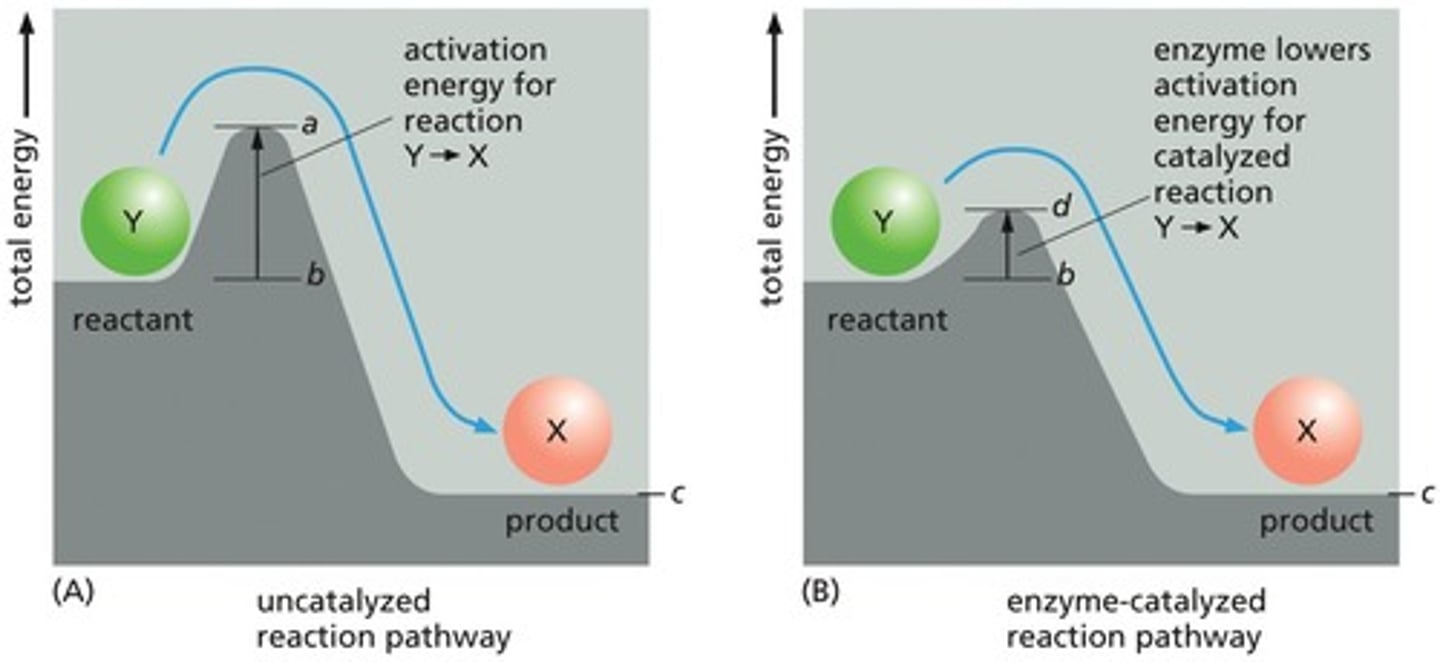
What role do enzymes play in chemical reactions?
Enzymes are biological catalysts that lower activation energy and speed up reactions.
What is Vmax in enzyme kinetics?
The maximum rate of reaction when the enzyme is saturated with substrate.
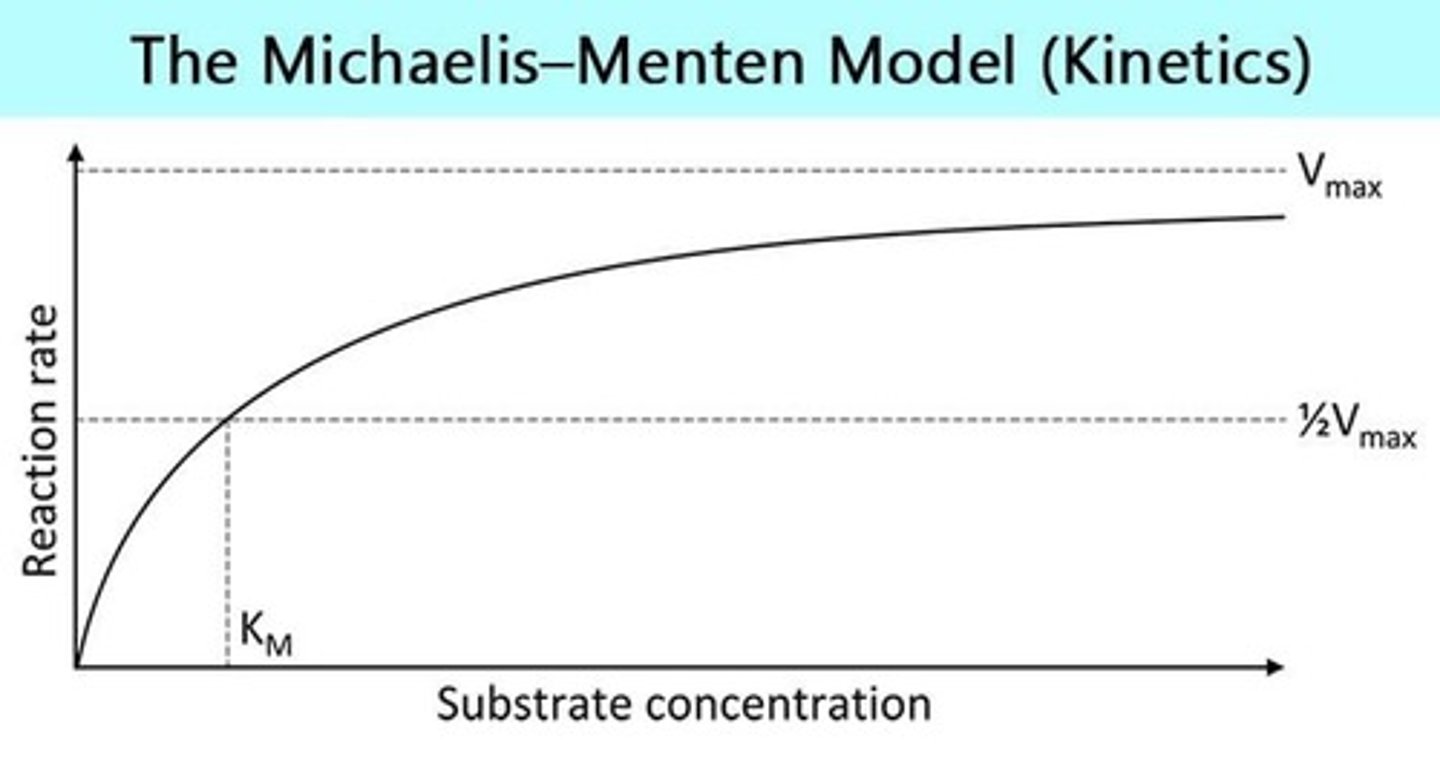
What is KM in enzyme kinetics?
Michaelis' constant; the substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is half of Vmax.
What are competitive inhibitors?
Inhibitors that block substrate binding by competing with the substrate for the active site.
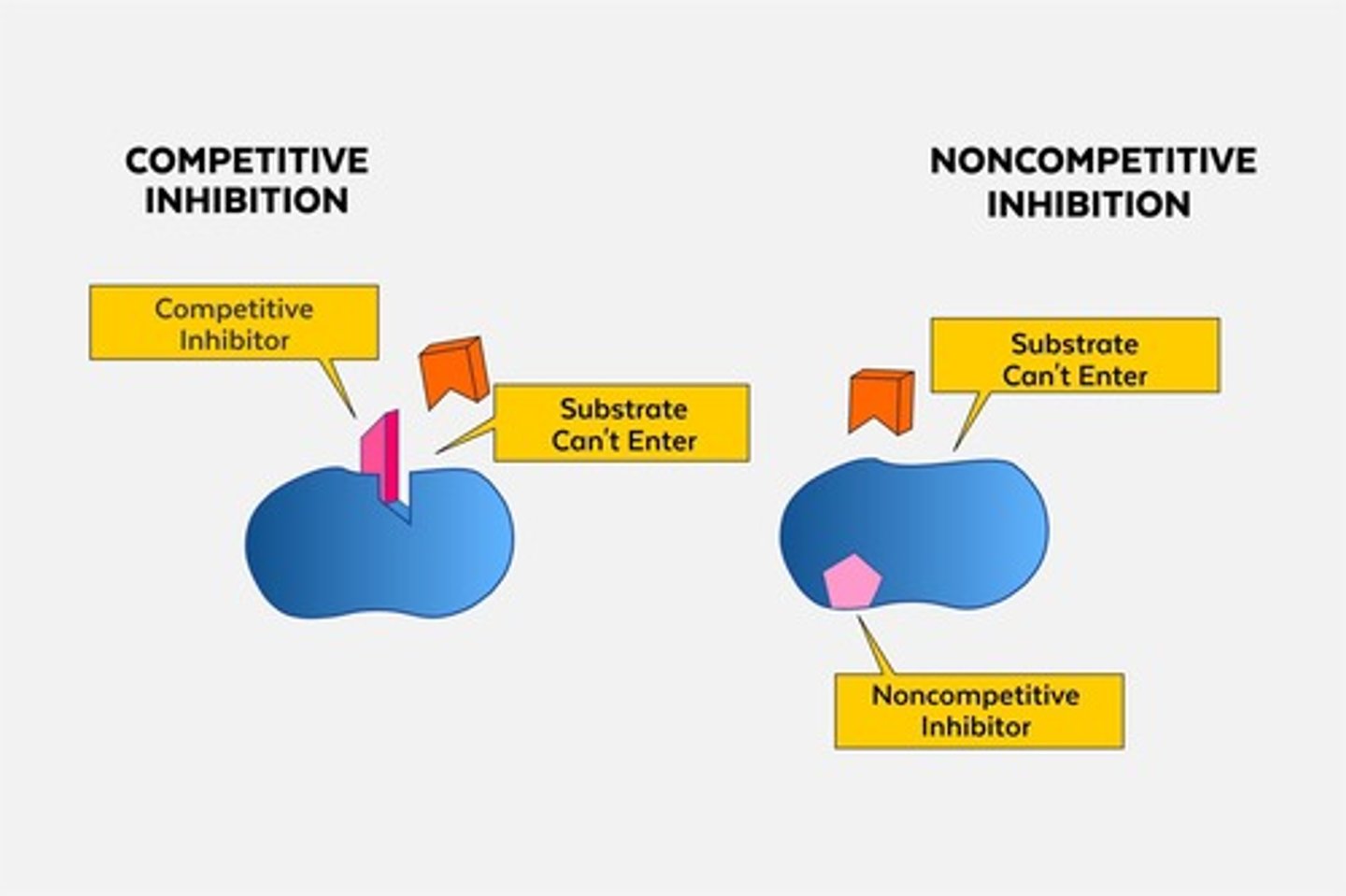
What are noncompetitive inhibitors?
Inhibitors that bind to an enzyme at a site other than the active site, causing a conformational change.
What are cofactors?
Nonprotein partners that assist enzymes, such as metal ions.
What are coenzymes?
Organic cofactors derived from vitamins that help transfer electrons between enzymes.
What are allosteric enzymes?
Enzymes that change shape when an effector binds, affecting their activity.
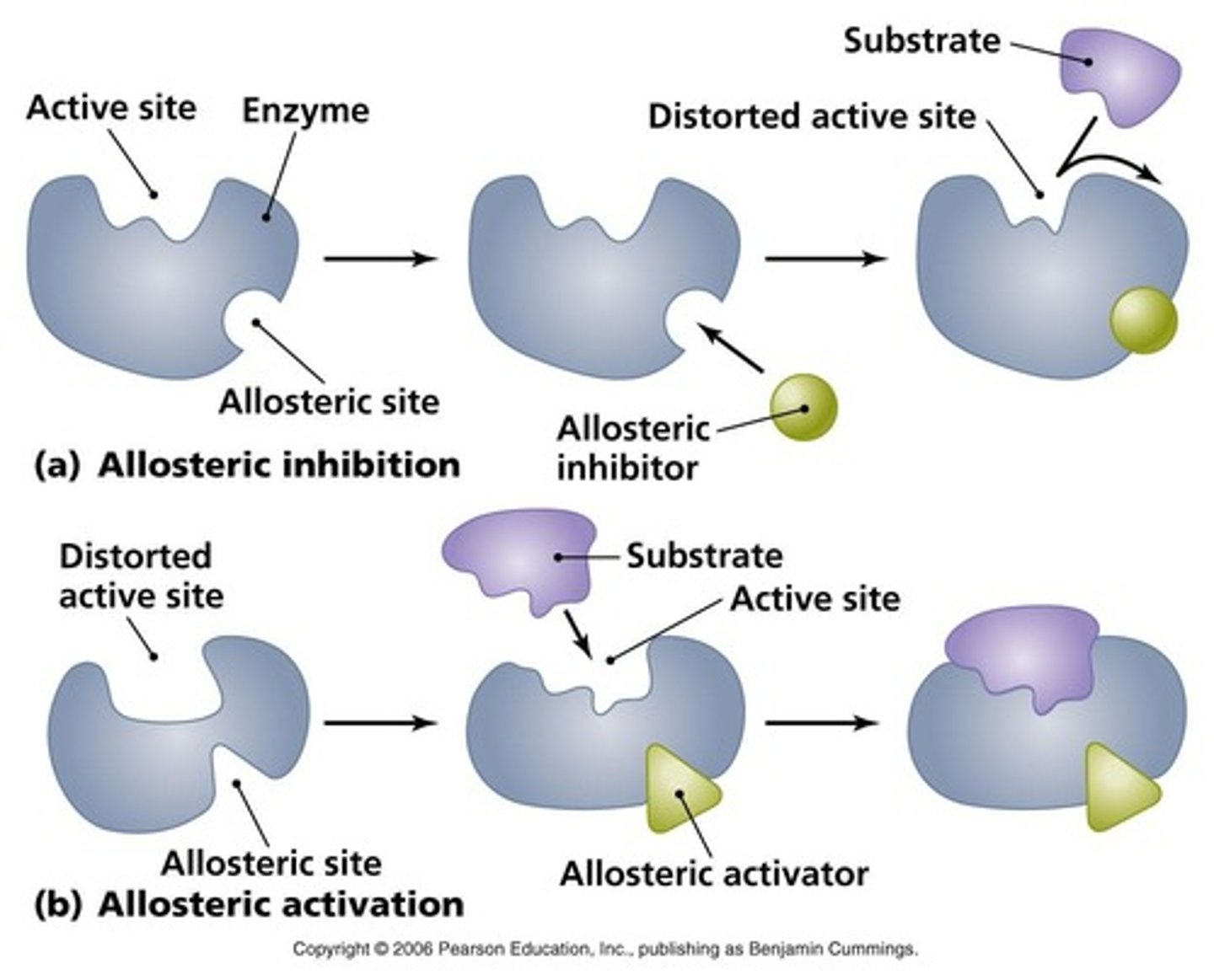
What is free energy (G) of a system?
The amount of energy available to do useful work.
What does a negative ΔG indicate?
An exergonic reaction where products have less free energy than reactants.
What does a positive ΔG indicate?
An endergonic reaction where products have more free energy than reactants.
What are activated carrier molecules?
Molecules like ATP, NADH, and NADPH that store and transfer energy needed for metabolism.
How does ATP function in cellular work?
ATP transfers a terminal phosphate to other molecules in phosphorylation reactions.
What is the significance of NADH and NADPH?
Cofactors specialized to carry high energy electrons and hydrogen atoms.