2 - Atomic Structure
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Go through these flashcards and then complete exam questions
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Mass number
Number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom
Atomic number
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
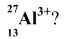
How many (i) electrons, (ii) neutrons, has the aluminium ion, (see picture)?
i) 10
ii)14
Atomic orbital
A region in space where there is a high probability of finding an electron
Isotopes
Atoms of the same element that have the same atomic number but different mass number
Relative atomic mass
The average mass of an atom of an element compared to 1/12 the mass of an atom of carbon-12
Explain why relative atomic masses are rarely whole numbers
Average of mass numbers of the isotopes of an element
The dispositive ion M2+ has 28 electrons and 34 neutrons. What is
i) the atomic number
ii) the mass number, of M?
i) 30 //
ii) 64
How did Thomson account for the fact that atoms are electrically neutral?
Plum-pudding model / Electrons embedded at random in a positive sphere
Based on the model of the atom that Thomson had proposed after his discovery of the electron, which one of the observations from Rutherford’s gold foil experiment was the most unexpected: most alpha particles passed through the foil with no deflection or very slight deflections, a small number were deflected through large angles, and a very tiny number rebounded back along their original paths, ?
Very tiny number of alpha particles rebounded
What conclusion did Rutherford reach about the structure of the atom from all of the observations in the gold foil experiments taken together?
Atom has a small nucleus / small (dense) core / atom is mostly empty space
Explain how Rutherford deduced from these observations that the nucleus is
i) positive,
ii) small and dense.
i) Repulsion (deflection) of positive alpha particles
ii) Most alpha particles undeflected - few reflected straight back
Explain why some alpha particles were deflected at large angles as they passed through the gold foil
Repelled //
when passing near the positive nucleus.
Why were some alpha particles reflected back along their original paths?
Why did this happen to only a very small number of alpha particles?
They collided with the positive nucleus //
Nucleus very small / most of atom is empty space
What are alpha particles?
Helium nuclei / He2+ / particles having two protons and two neutrons
State one piece of evidence for the existence of energy levels in atoms
Atomic (line, emission, absorption) spectra (e.g. Balmer series) / flame tests / ionisation energies / periodic table layout
State two limitations of Bohr’s atomic theory that led to its modification
Only works for hydrogen atom / wave nature of electron not included / Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle not included //
Did not explain sublevels (orbitals) / only accounted for main energy levels (shells)
Write the s, p, d electron configuration for an atom of bromine in its ground state
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p5
What is the principle of the mass spectrometer?
Positively charged ions are separated on the basis of their relative masses in a magnetic field
What are the fundamental processes, in the sequence in which they occur, involved in the operation of a mass spectrometer?
Vaporisation //
Ionisation //
Acceleration //
Separation //
Detection
{ V I A S D }
State two applications of mass spectrometry
To determine the isotopic abundance of a particular element / determine relative atomic mass / analysis of gases from a waste dump / drug detection / heavy metals in water / etc

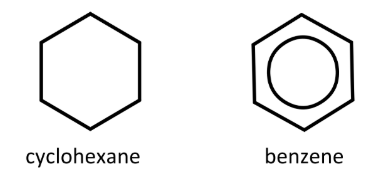
What is the average number of electrons shared between any two adjacent carbon atoms in a molecule of
i) cyclohexane,
ii) benzene?
i) 2
ii) 3
What was Dalton’s atomic theory?
Matter composed of atoms (tiny particles) //
Atoms are indivisible //
Atoms can neither be created nor destroyed //
Atoms of the same element are identical
Name the scientist whose work on cathode rays led him to identify the electron as a subatomic particle
Thomson
What is an electron?
Negatively charged subatomic particle orbiting the nucleus, located in electron cloud of atom //
mass 1/1840 amu / very small mass
Law of Conservation of Mass
Mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction
What term is used to refer to the condition of the hydrogen atom when its electron occupies the E1 level?
Ground state
What term us used for the condition of the hydrogen atom when its electron occupies any of the levels E2, E3, etc?
Excited
What causes the electron to leave E1 level?
It acquires energy / it is heated
Why does the electron not remain in any of the levels E2, E3, etc?
Higher energy state is unstable
The visible lines in the atomic emission spectrum of a sample of hydrogen are produced when electrons fall into a particular energy level. Identify this energy level.
E2 / n = 2 / second
Why might the electron in a hydrogen atom not occupy the n = 1 energy level?
Too much energy / excited / gained energy
What colour light is associated with the electron in a hydrogen atom moving from n = 3 to n = 2?
Red
Name the series of visible lines in the hydrogen emission spectrum
Balmer
How many sub-levels are associated with the n = 3 energy level
3
How many orbitals are associated with the n = 2 energy level?
4
What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy the n = 3 energy level in a multi-electron atom?
18
How does modern atomic theory describe the behaviour of electrons?
Electrons exhibit both wave //
and particle properties
Draw a labelled diagram of Thomson’s plum pudding model of the atom
Small negative particles (electrons) embedded //
in a positive sphere
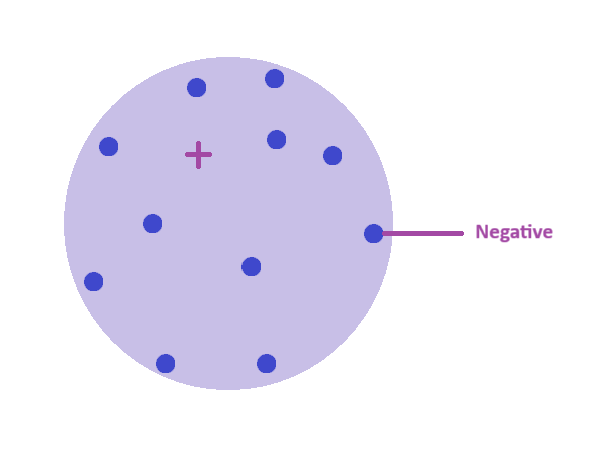
What are cathode rays?
Streams of negatively charged electrons (which travel from cathode to anode)
Give two properties of cathode rays
Negatively charged // negligible mass // straight-line motion // penetrating // cause fluorescence // move paddle wheel // high speed
Give one way of detecting the presence of cathode rays inside a vacuum tube.
Fluorescence / shadow cast by anode (cross, object) / paddle wheel rotated
What was the purpose of Millikan’s ‘oil drop’ experiments of 1908 to 1913?
Determine the size of the charge of the electron
Name one of the three scientists who shared the 1903 Nobel prize in Physics for their pioneering work on radioactivity which provided evidence for subatomic particles.
Henri Becquerel / Marie Curie / Pierre Curie
A sample of the element gallium is composed of 60.1% gallium-69 and 39.9% gallium-71.
Calculate the relative atomic mass of gallium from this information
69.798
{must show all workings, this is just the answer}
How many neutrons are there in 0.14g of carbon-14?
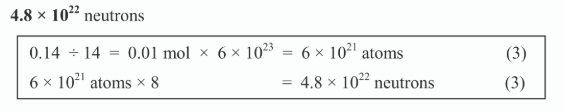
Name the scientist who measured the ratio of charge to mass of the electron, e/m
Thomson
Name the scientist who proved that electrons in an atom reside in an electron cloud surrounding a small dense positive central nucleus
Rutherford
Name the scientist who measured the charge on the electron, e
Millikan