Vertebral Column
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key vocabulary terms related to the vertebral column and associated structures discussed in the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Vertebral Column
Transmits weight of the trunk to the lower limbs, surrounds and protects the spinal cord, and supports the weight of the head. Serves as attachment sites for muscles of the neck and back as well as the ribs.
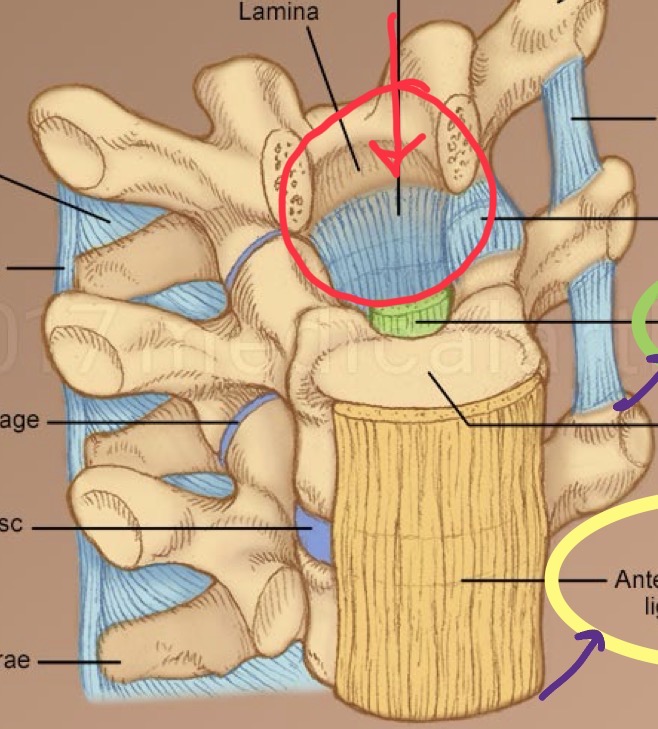
Vertebral arch
Attachment site for muscles and ligaments
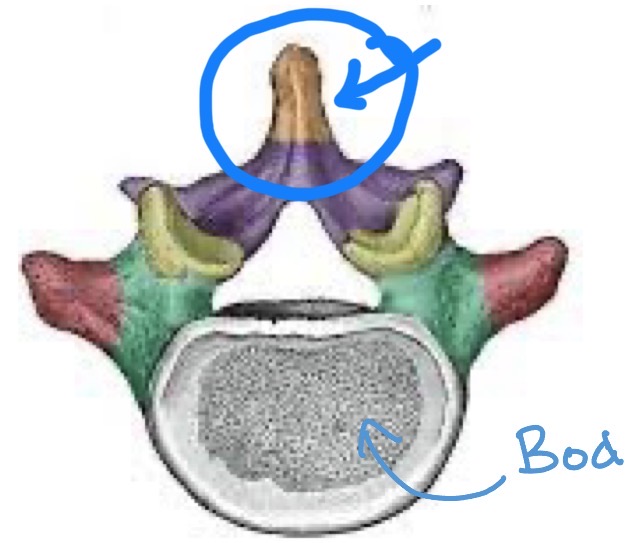
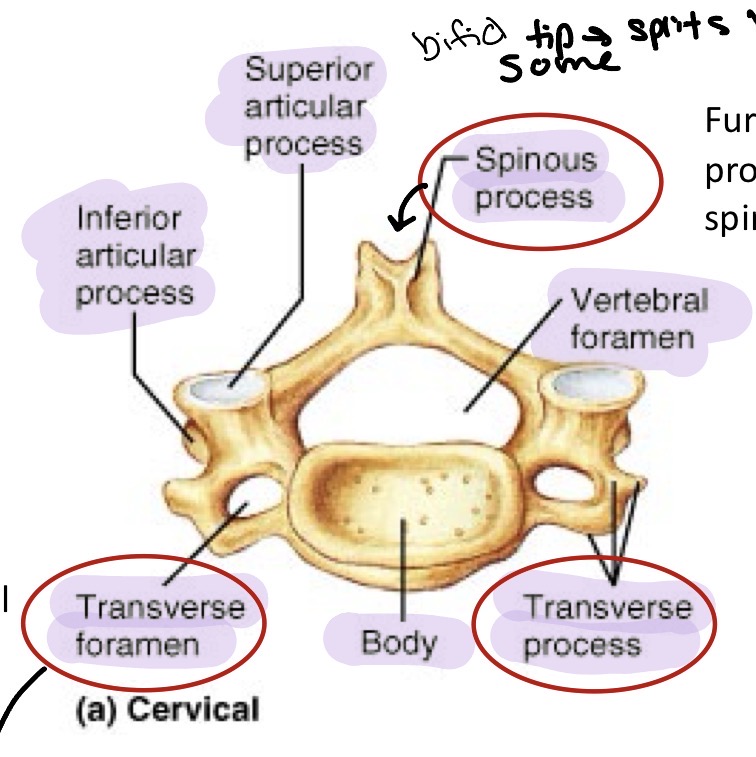
Spinous process
Each vertebrae has a single one of these centered posteriorly
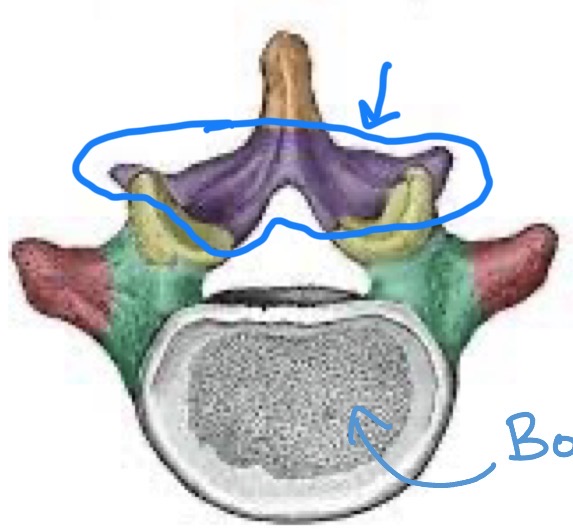
Lamina
Connect the transverse and spinous processes
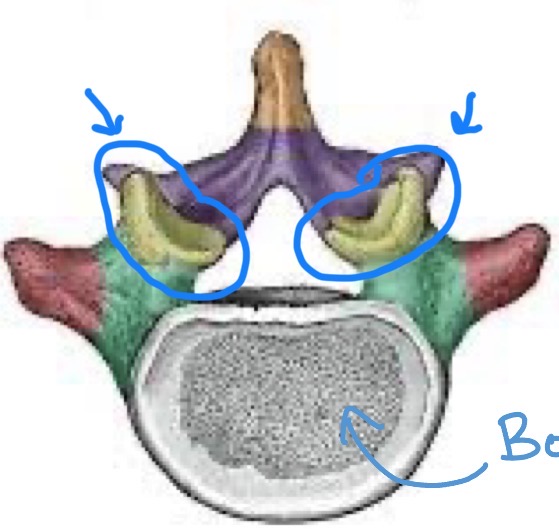
Superior articular processes
Form the joints between one vertebrate and another
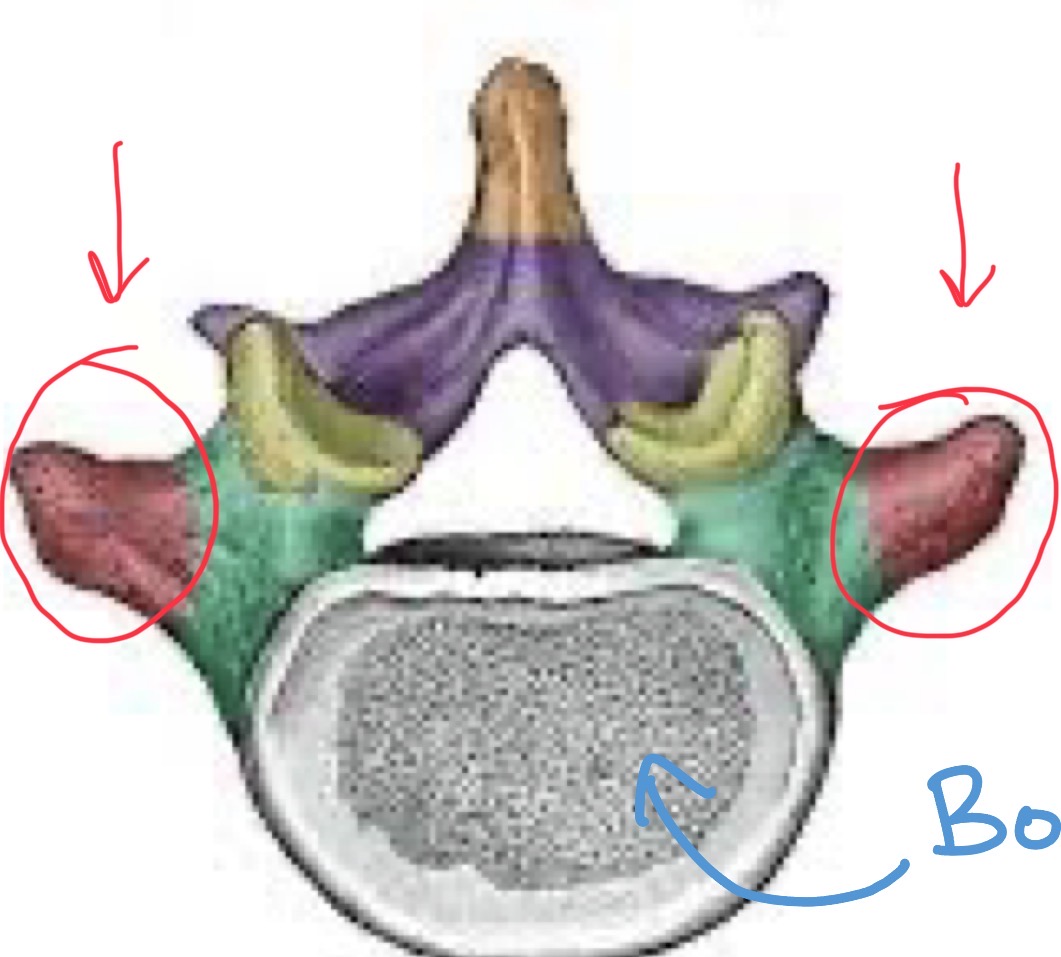
Pedicles
Connect the vertebral body to the transverse processes
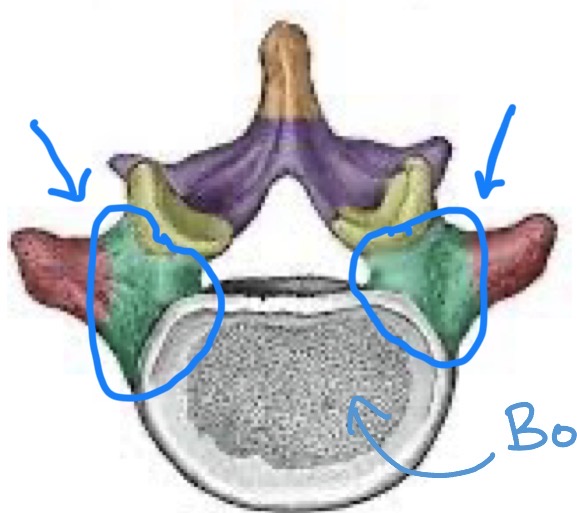
Transverse processes
Each vertebrae has two of these
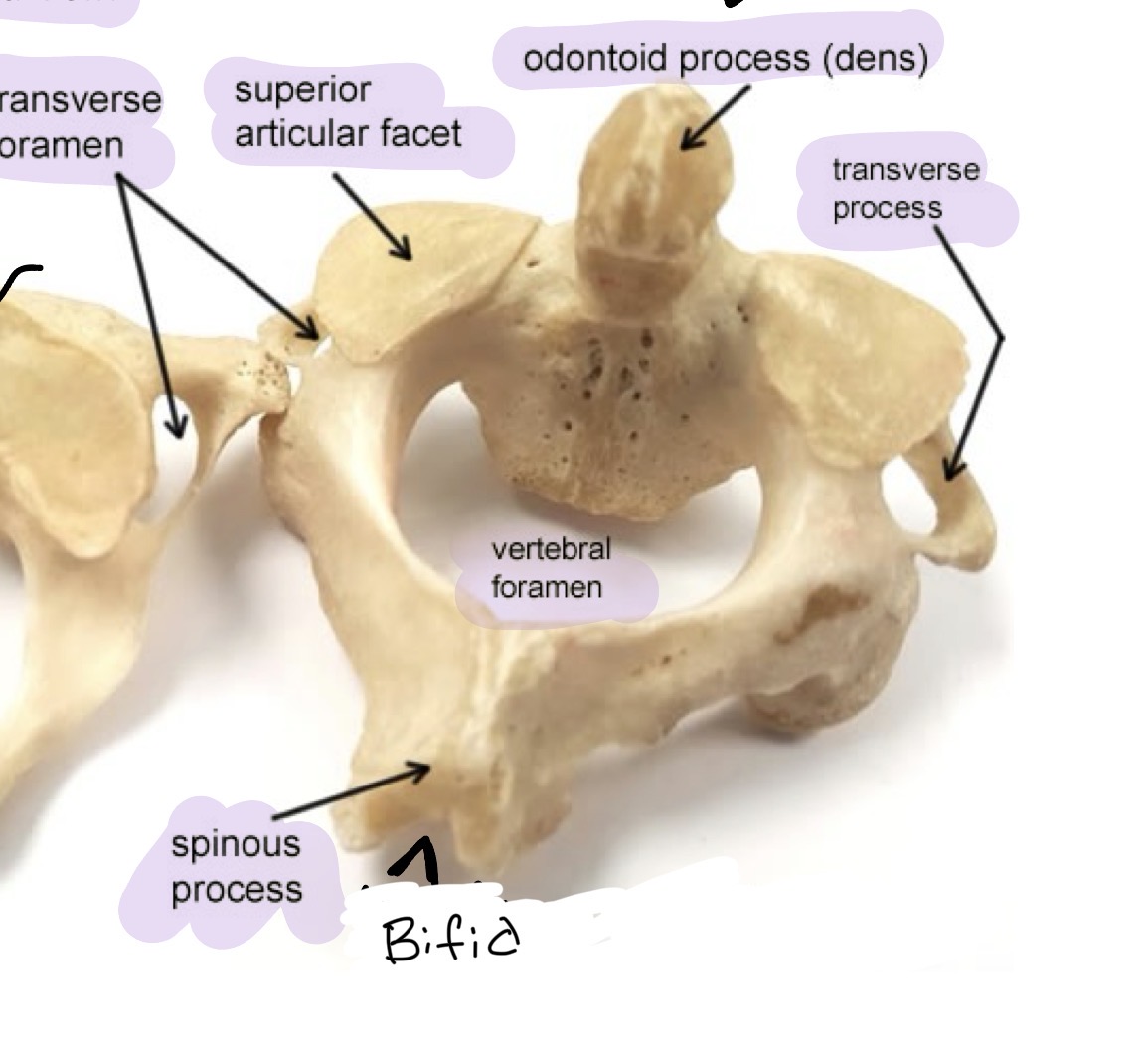
Cervical Vertebrae
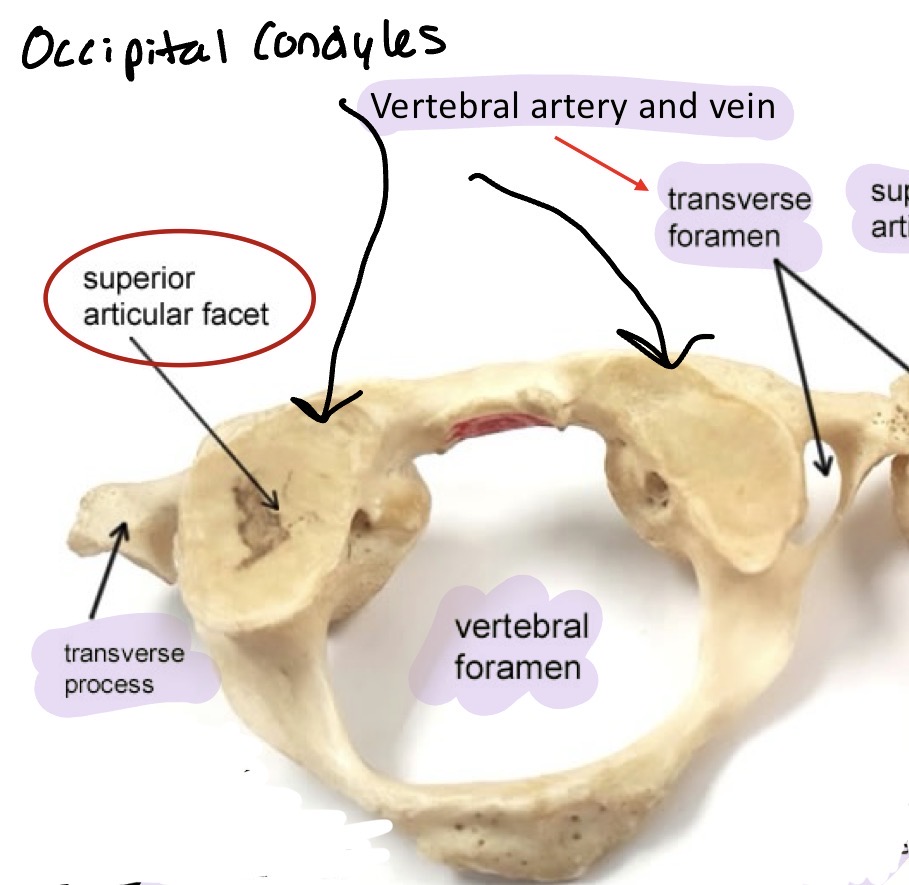
Seven vertebrae in the neck region allowing flexion, extension, lateral flexion, and rotation. C1-C7 smallest and most delicate. Has a transverse foramen and some have bifid spinous tip
Atlas C1
No vertebral body and no spinous process
Axis C2
Has odontoid process (dens) and spinous process
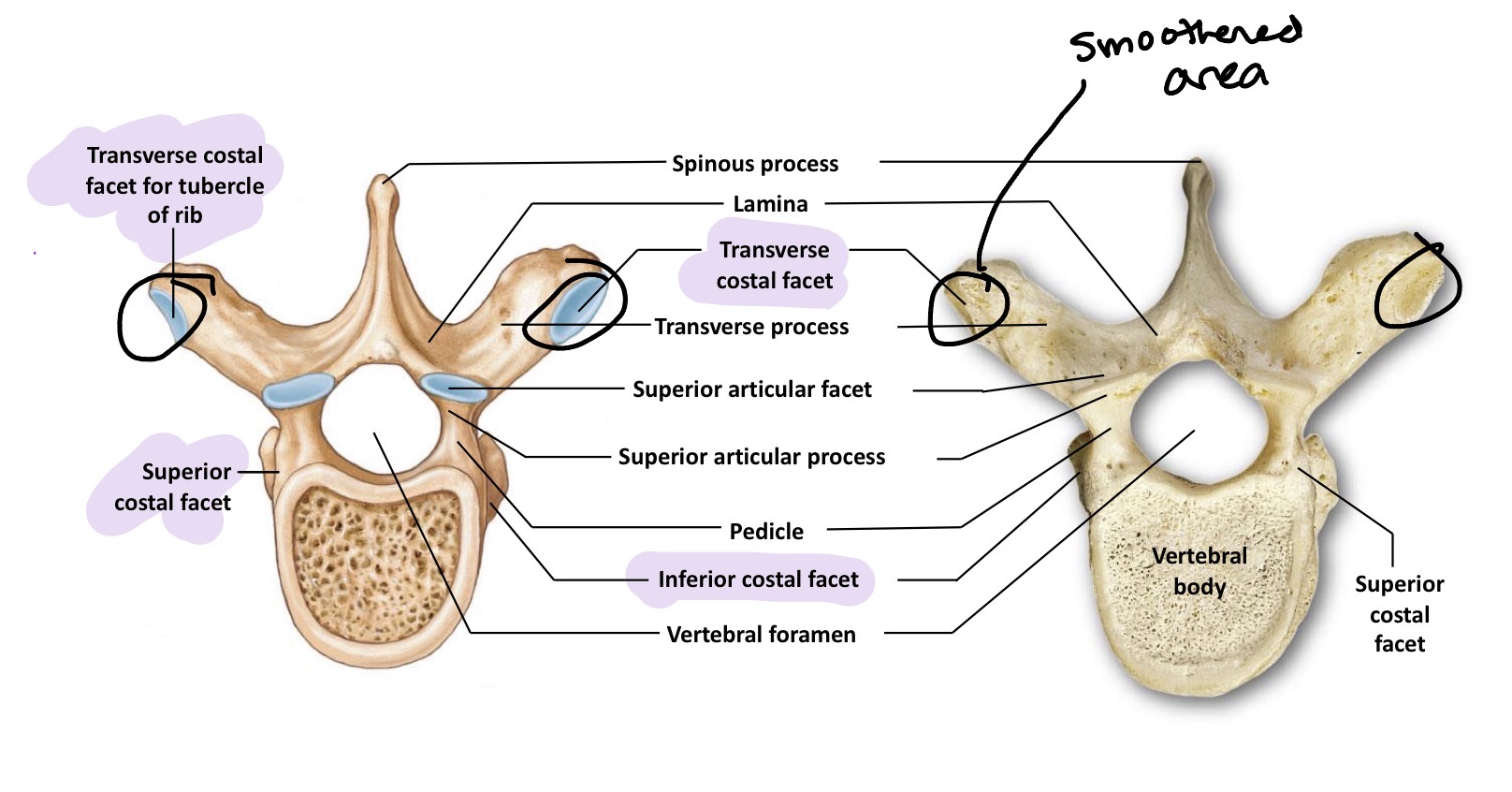
Thoracic Vertebrae
Twelve vertebrae that articulate with the ribs (rib per vertebrae ) and muscles and movement associated with respiration. Medium size and increase in size as they move down the back. They lack transverse foramina and bifid spinous processes
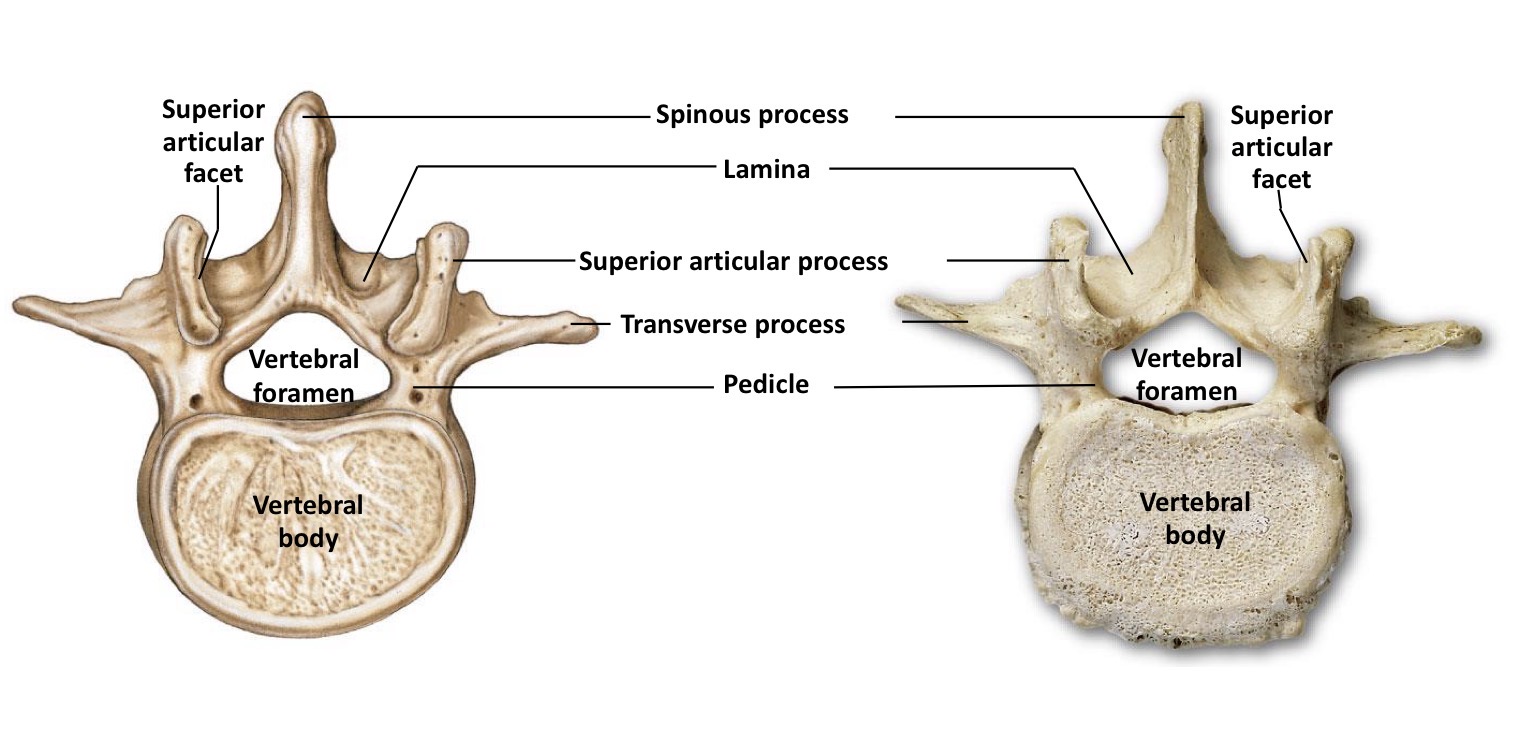
Lumbar Vertebrae
The largest vertebrae that support the weight of the upper body, characterized by large bodies and lack of transverse foramina, costal facets, or bifid spinous processes
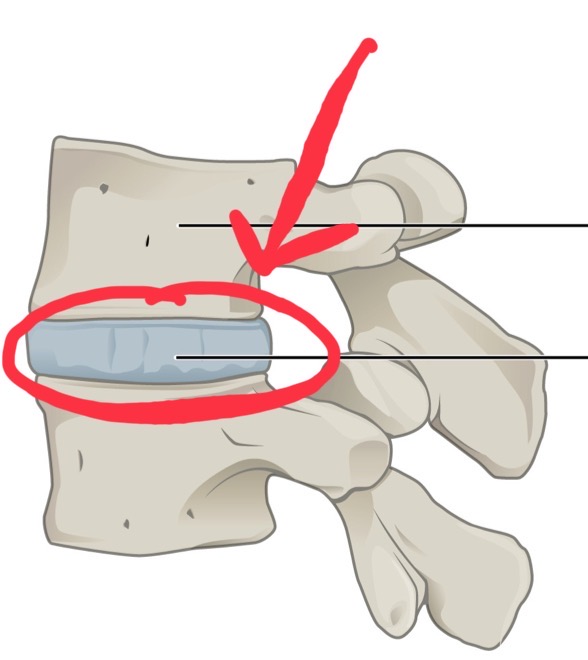
Intervertebral Disc
A fibrocartilaginous cylinder that lies between vertebrae, providing flexibility and acting as a shock absorber. There are two regions: nucleus pulposus and annulus fibrosus
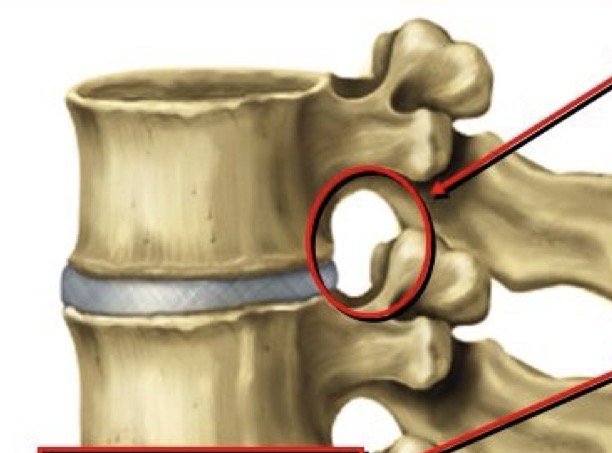
Intervertebral foramen
Formed from vertebral notches of adjacent vertebrae, and passageway for spinal nerves. Spinous process of one vertebrae and the spinous process of a vertebrae below it form this.
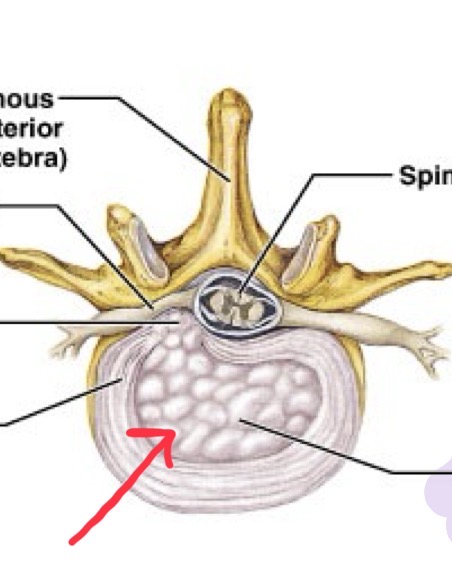
Nucleus Pulposus
The jelly-like inner core of the intervertebral disc.
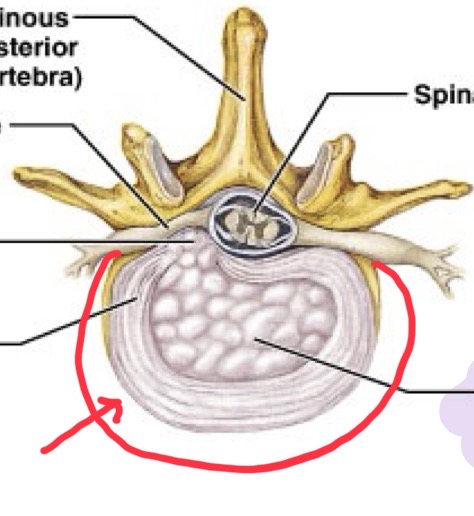
Annulus Fibrosus
The tough, collagenous outer layer surrounding the nucleus pulposus in an intervertebral disc.
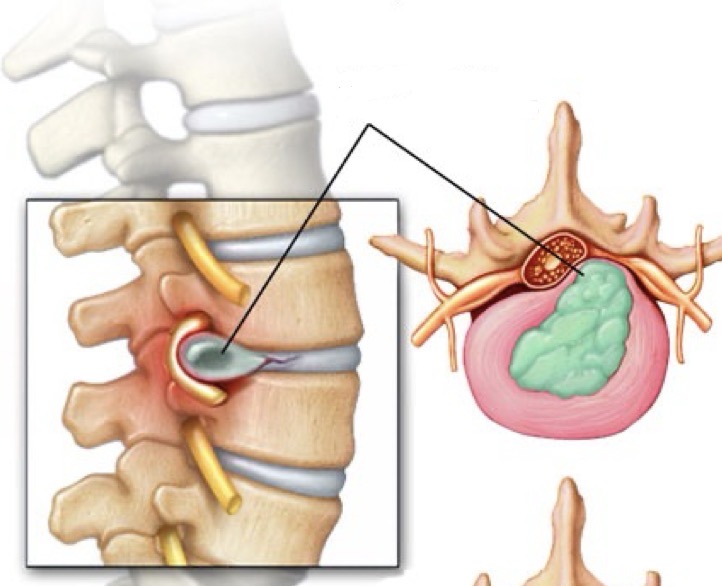
Herniated disc
Happens in the lumbar region, the nucleus pulposus ruptures, breaking the annulus fibrosus. Result and pressure on the spinal cord and pressure on the nerves.
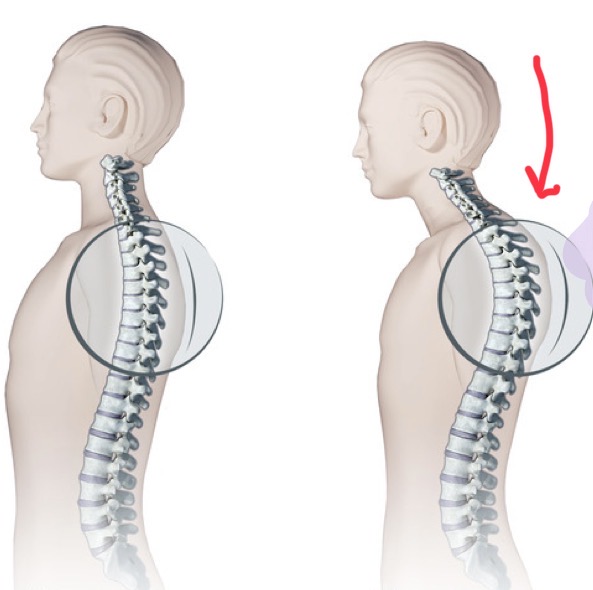
Kyphosis
An exaggerated rounding of the back, commonly known as 'hunchback'. Most often affects the thoracic region and in elderly people
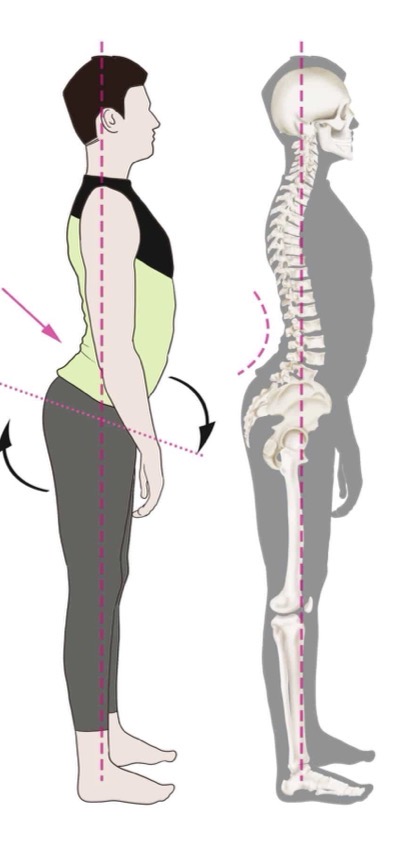
Lordosis
An excessive inward curve of the spine, often referred to as 'swayback'. Common and pregnant women.
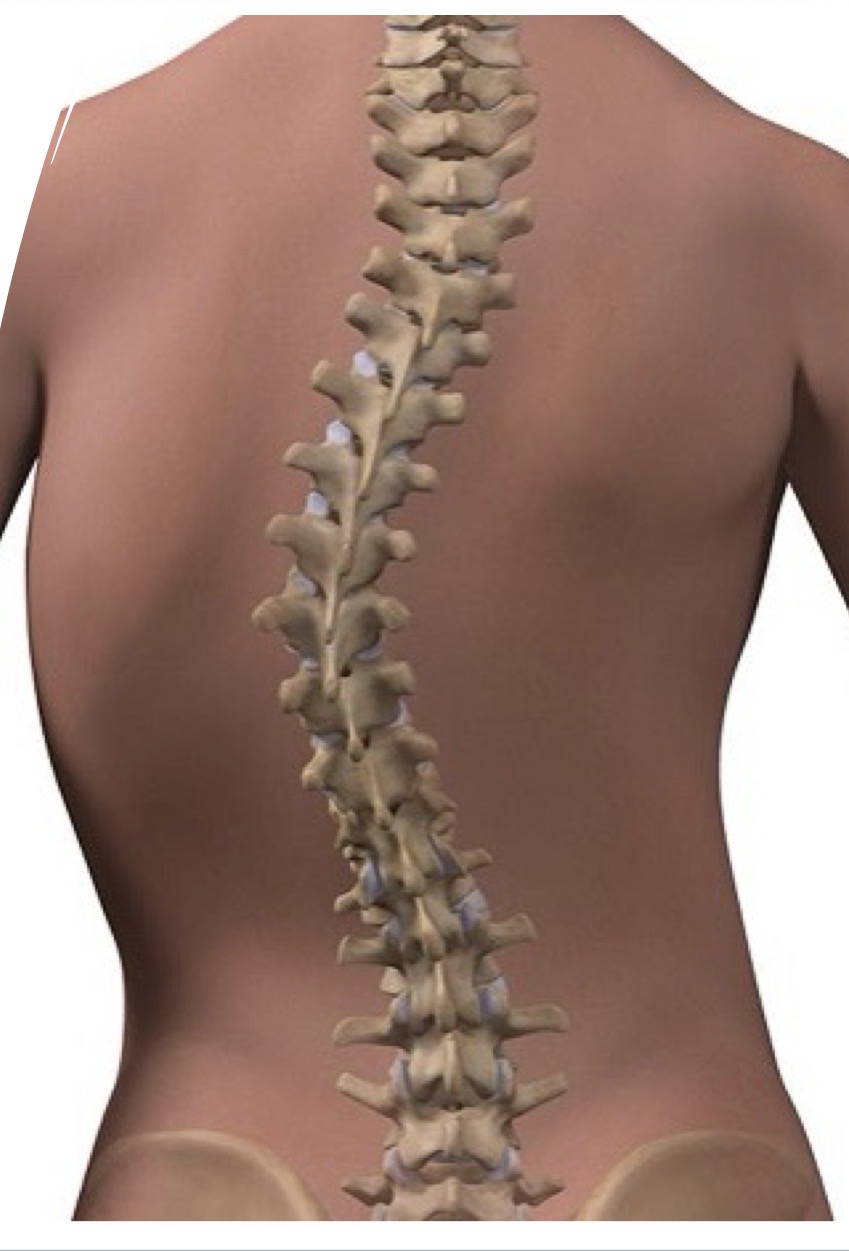
Scoliosis
A sideways curvature of the spine that often occurs during growth spurts before puberty.
Vertebral ligaments: Anterior longitudinal ligament ALL and the posterior longitudinal ligament PLL
Run the entire length of the spinal column. The ALL attaches to the front of the vertebral bodies and the PLL to the back. These ligament strength strengthen the disc to help prevent herniation.
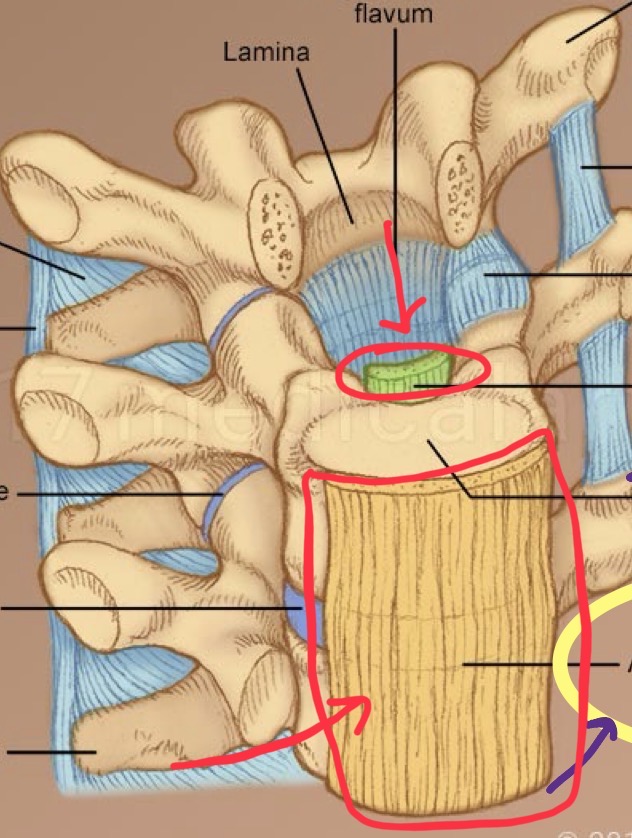
Ligamentum flavum
Extend from one vertebrate lamina to the next inside the vertebral canal. These bands serve as a covering over the spinal canal. Made from elastin fibers. .
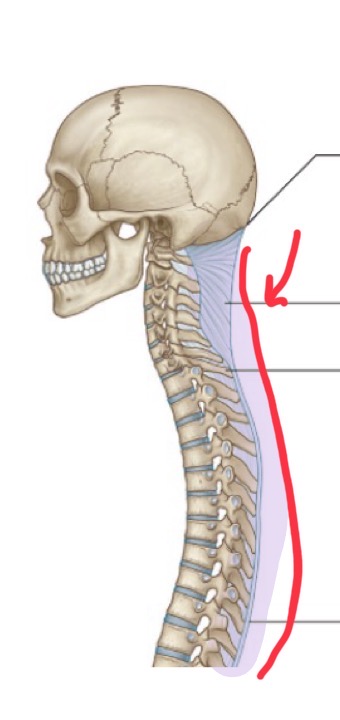
Ligamentum nuchae
Spans from the external occipital protuberance to spinous process of C7. Stabilize his massive head when running.
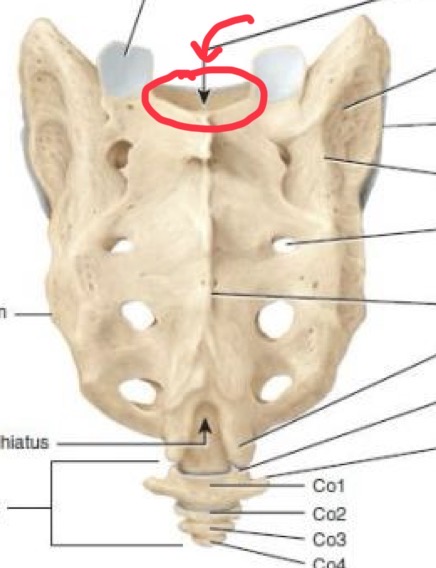
The sacrum
Collection of five fused vertebrae
Sacral canal
Sacral nerves
Superior articular process
Articulate with the fifth lumbar
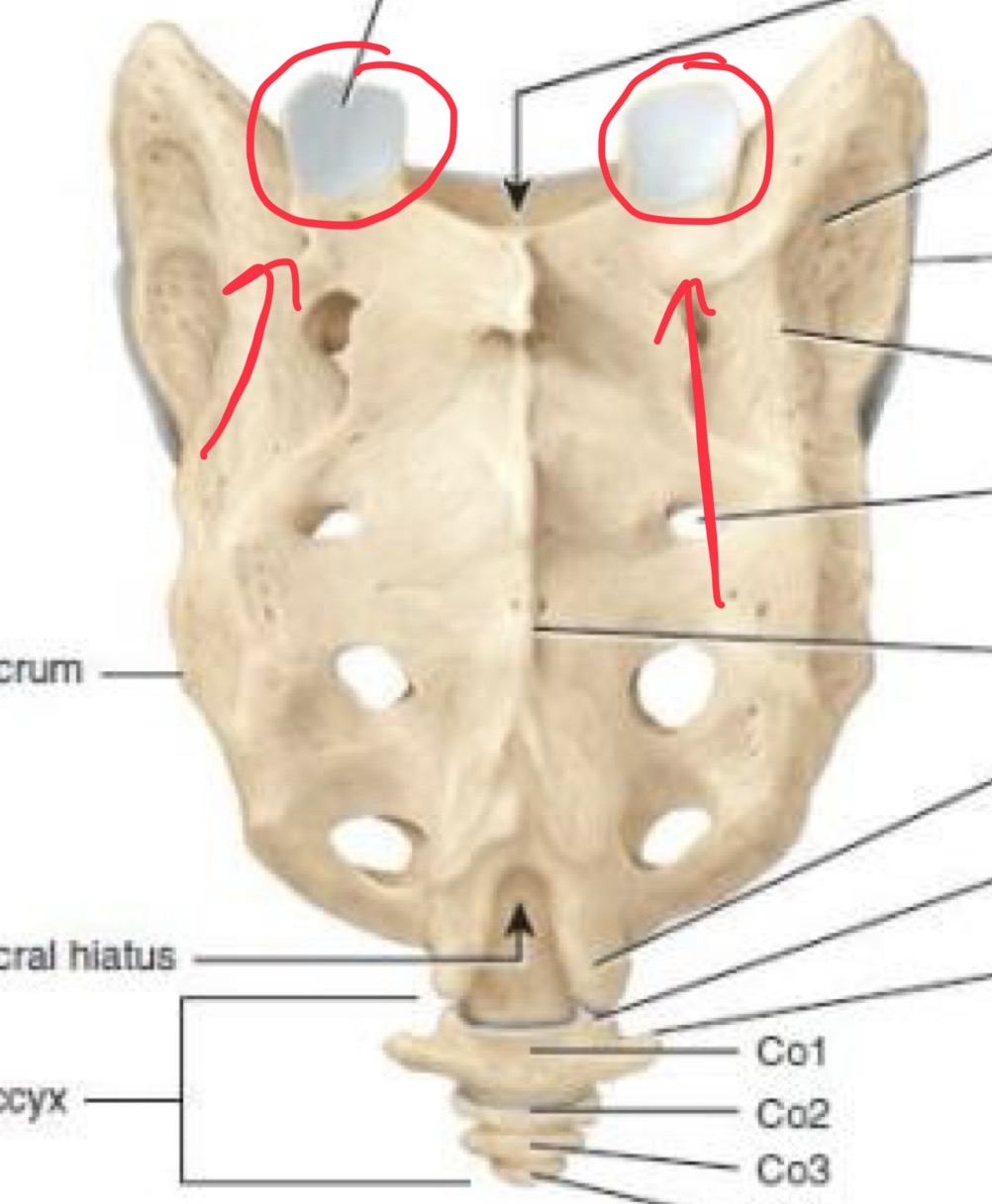
Posterior sacral foramina
Allow the sacral nerve fibers enter and leave the central canal
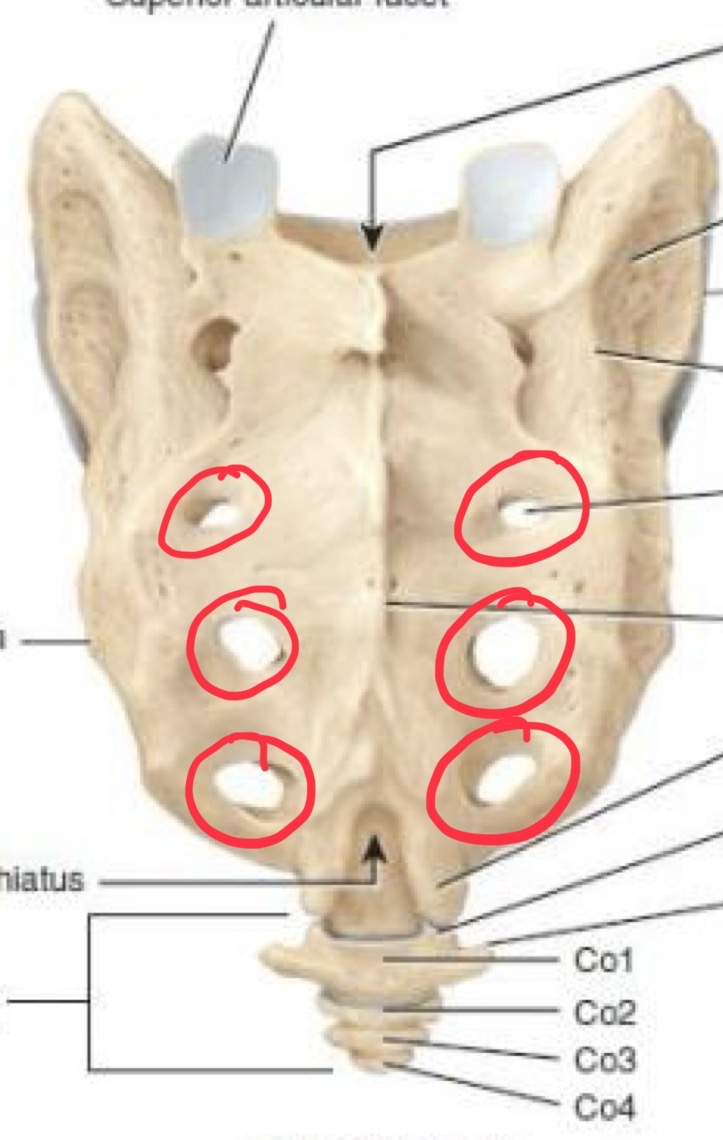
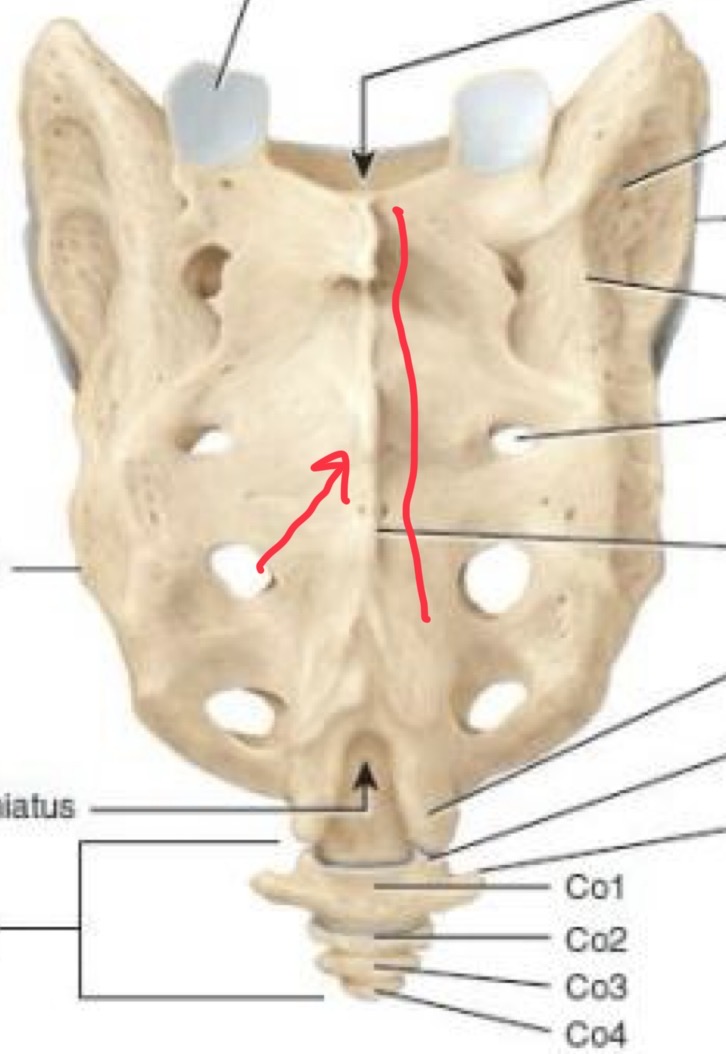
Median sacral crest
(Ridge) occurs along the midline
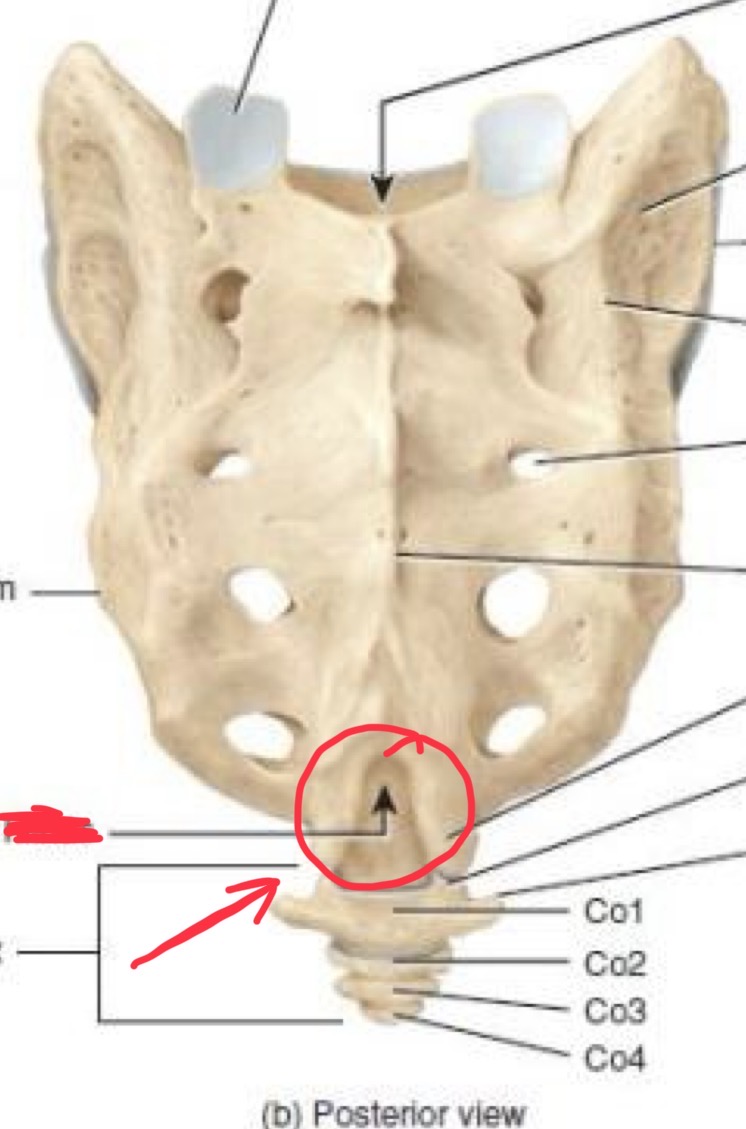
Sacred hiatus
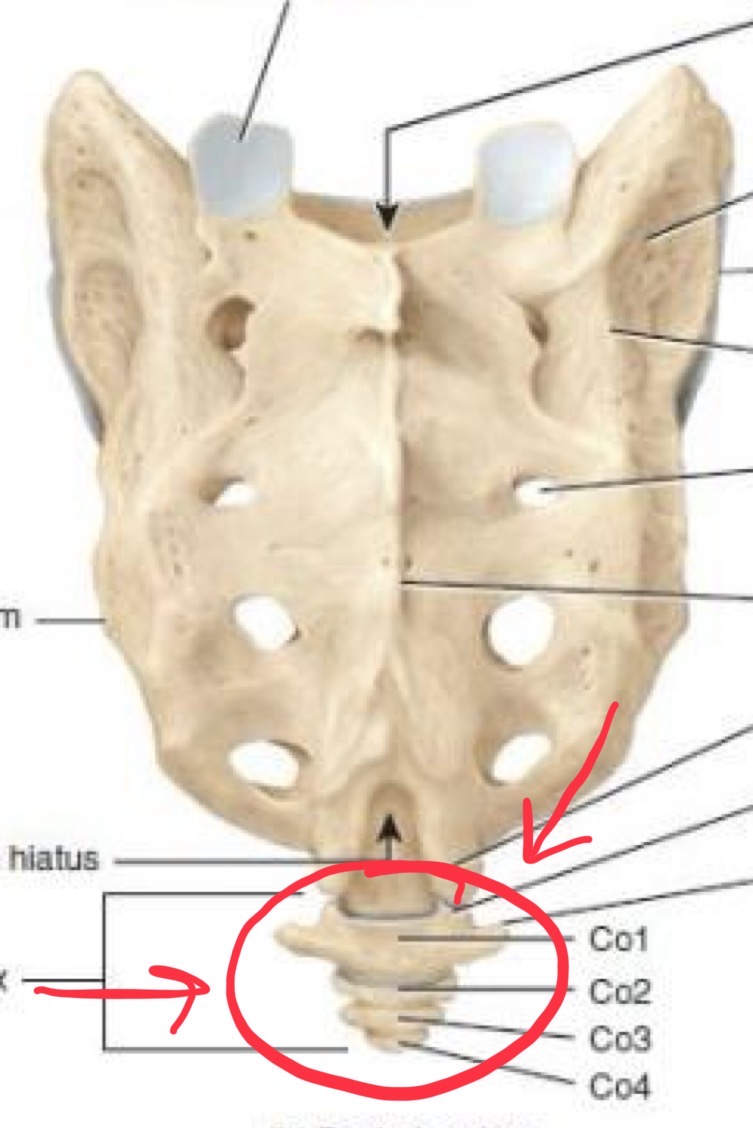
Coccyx
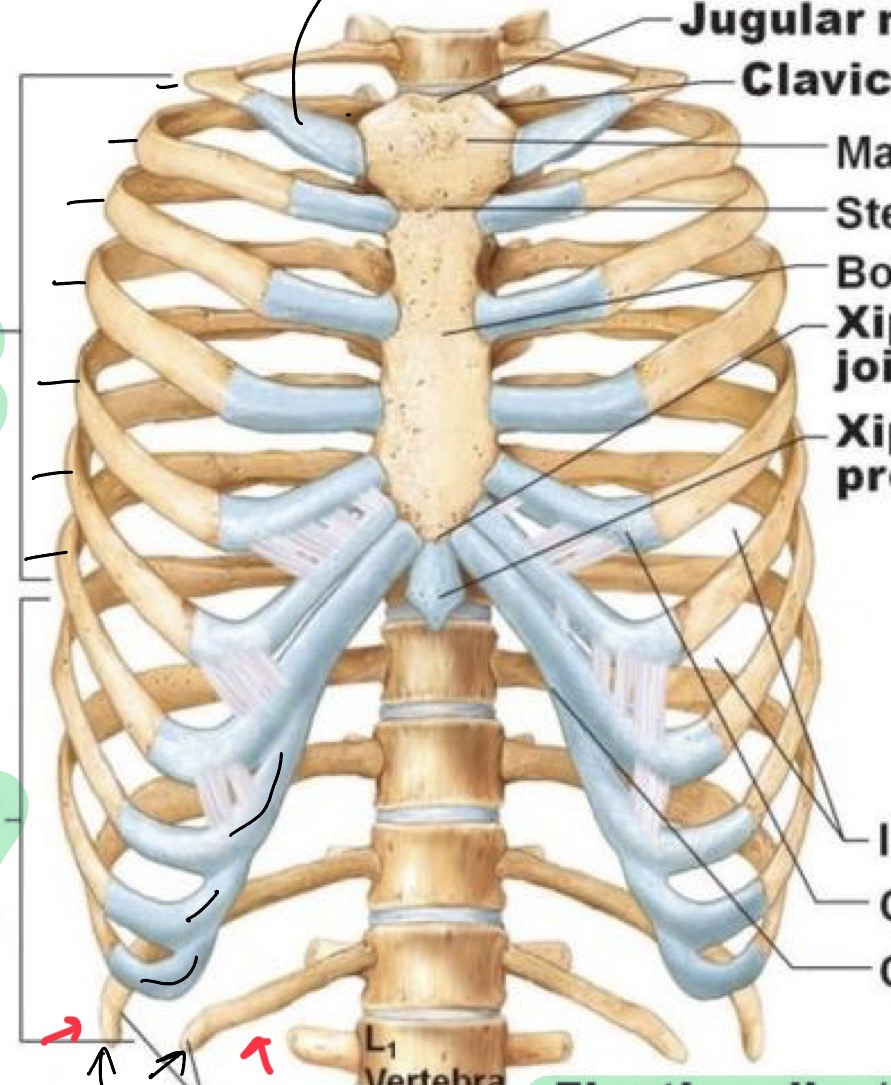
Sternum: manubrium
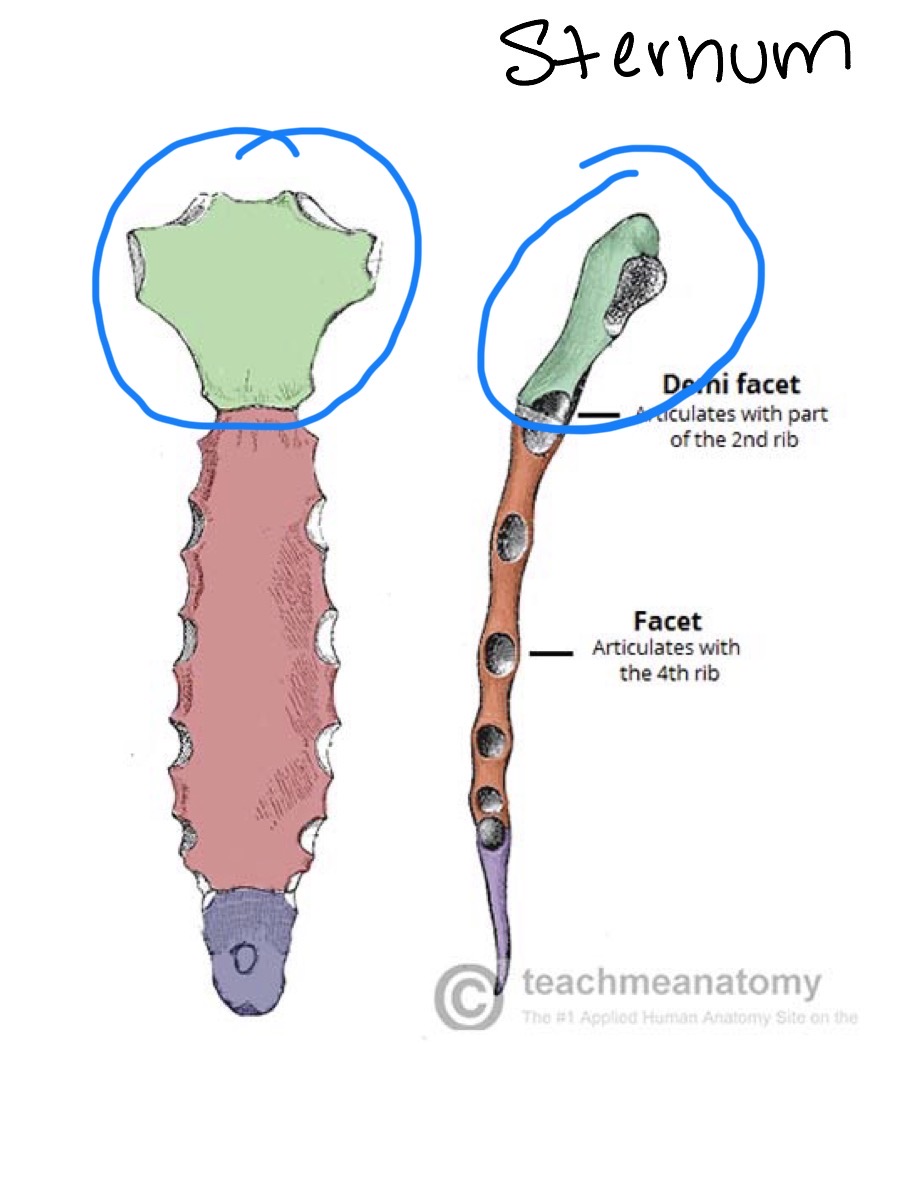
Sternum: body
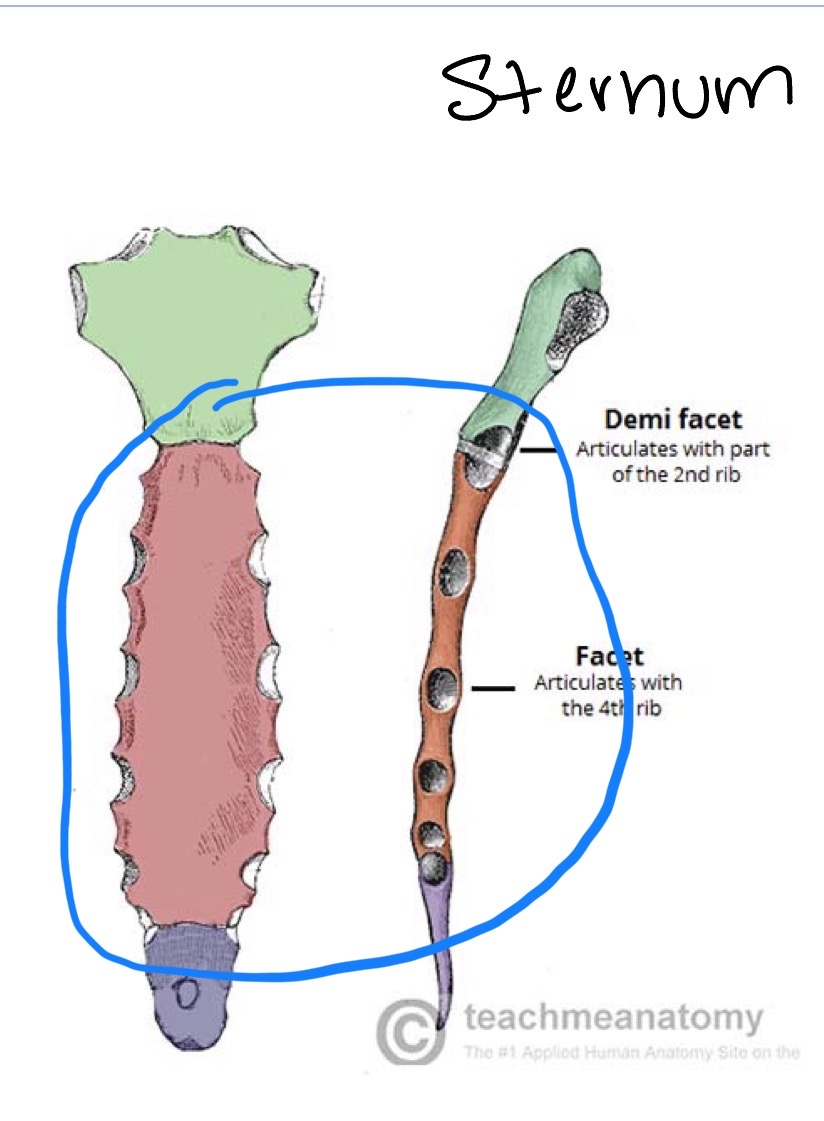
Sternum: xiphoid process
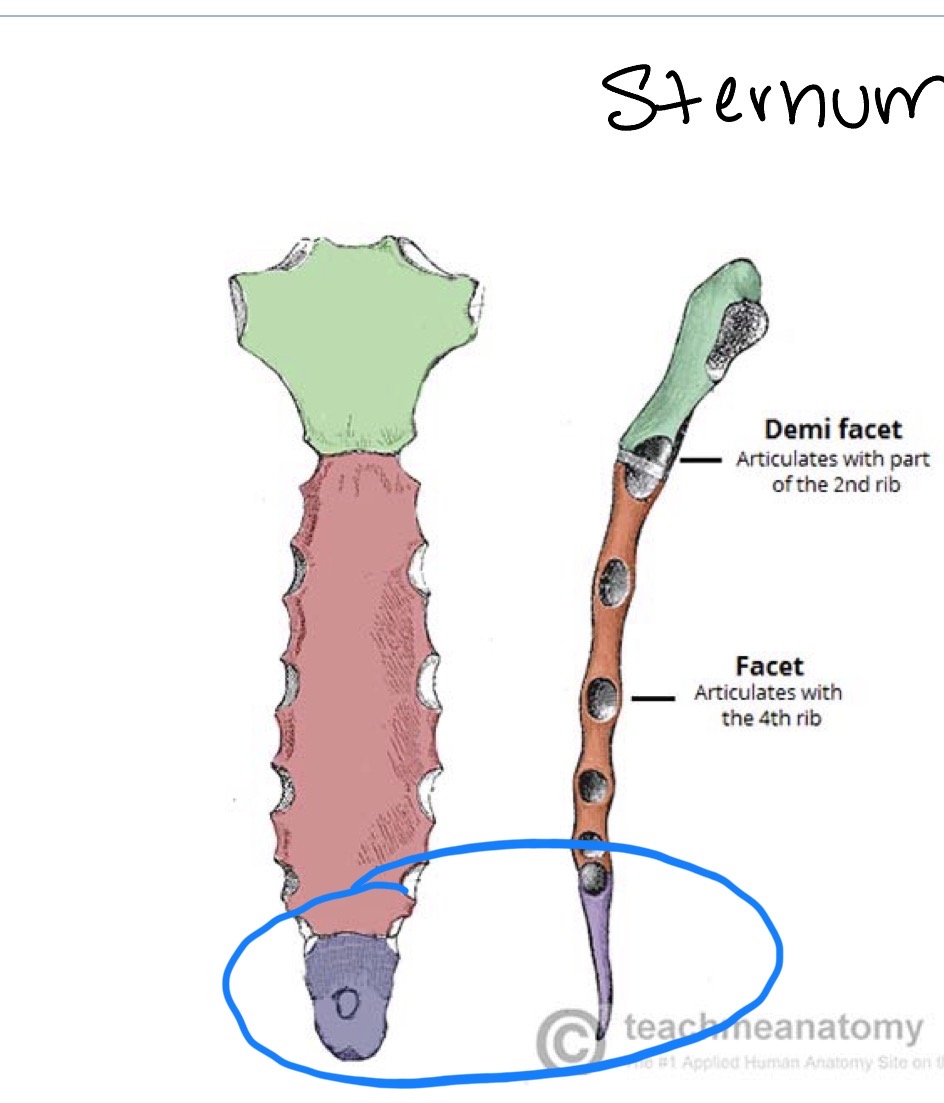
Jugular notch
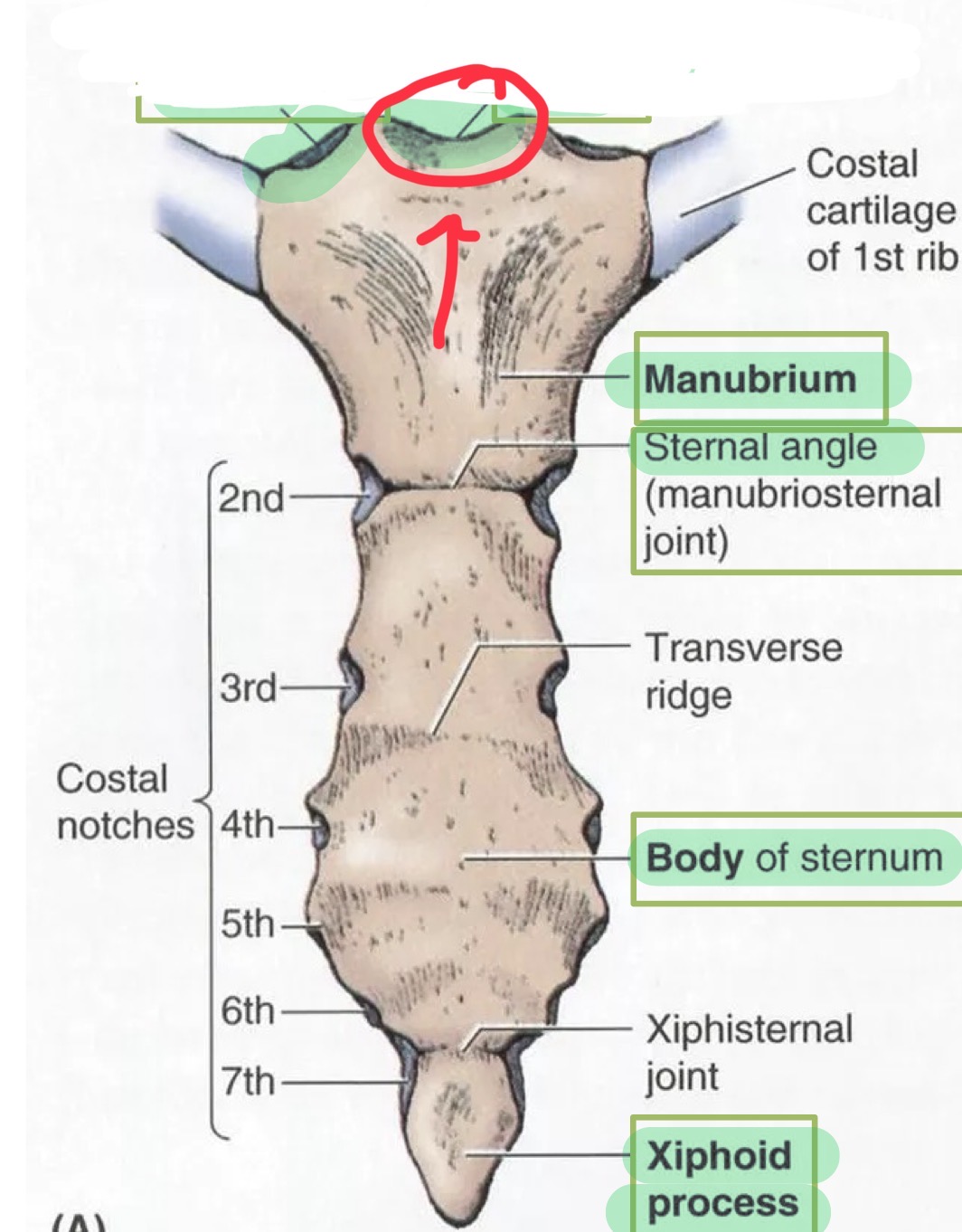
Sternal angle
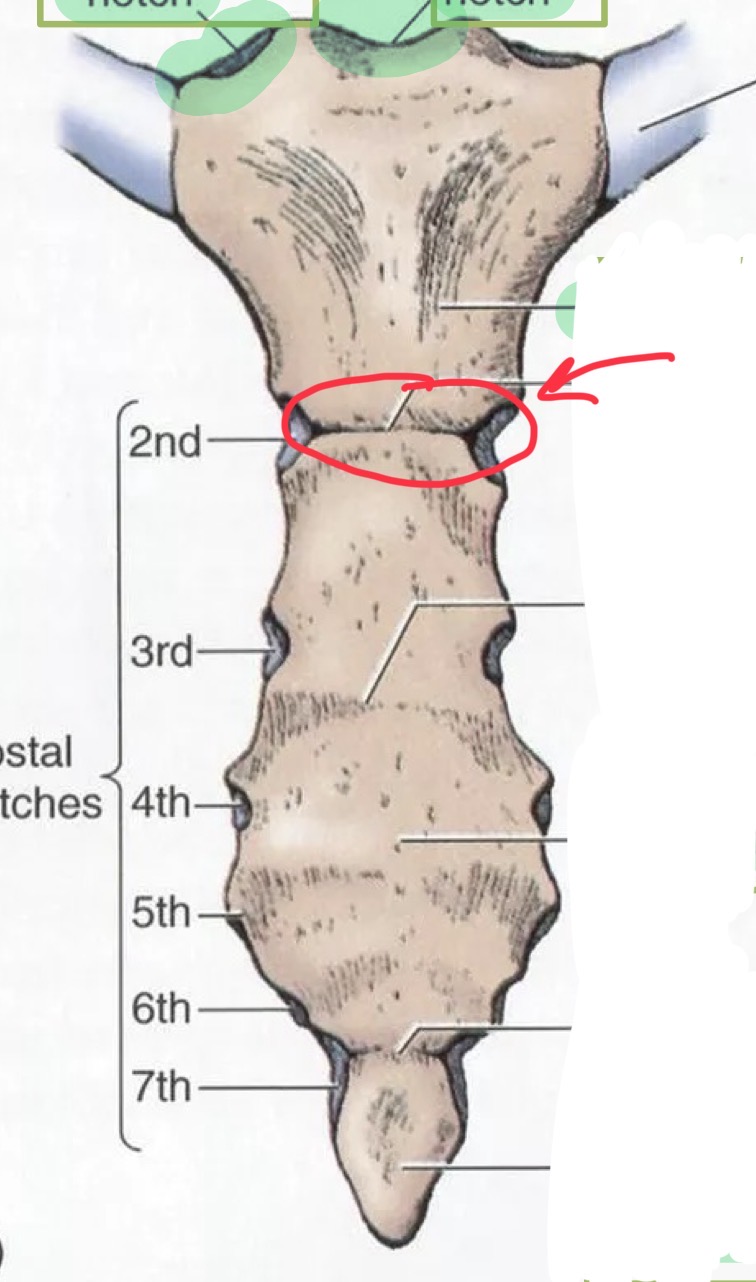
True ribs
1-7 have Hyaline Cartilage that directly connects to the sternum
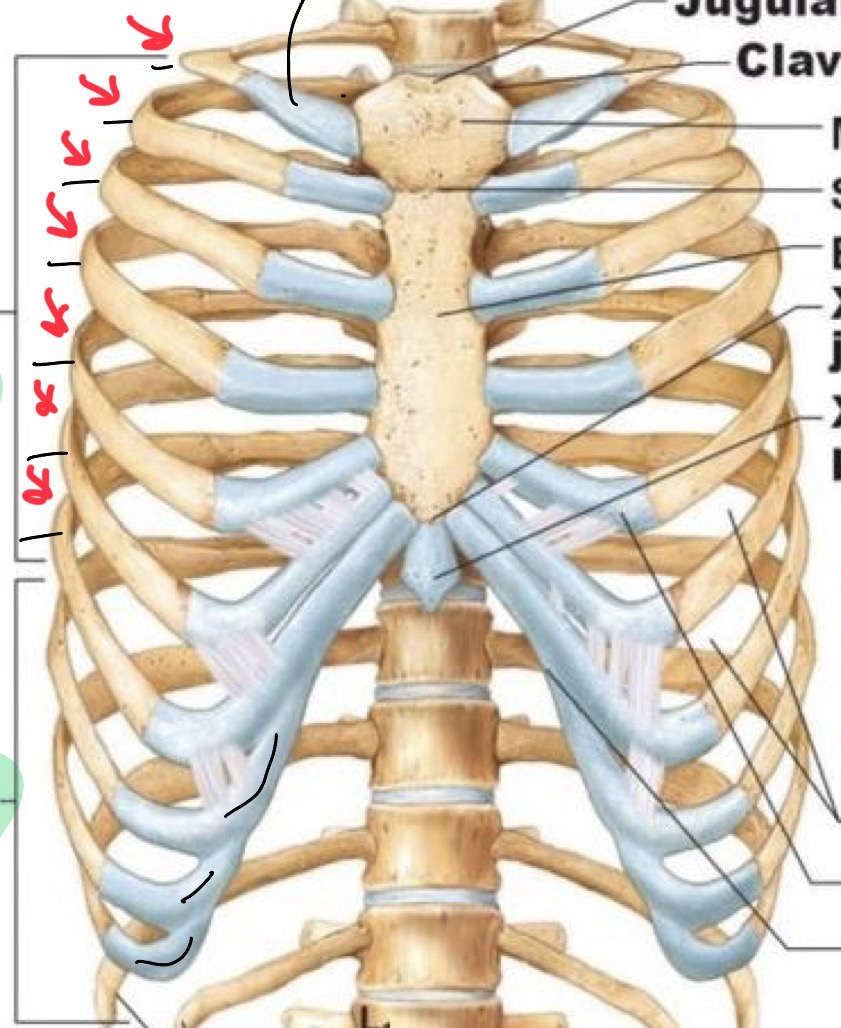
False ribs
“ hijack” onto rib seven hyaline cartilage. Indirect connection to sternum.
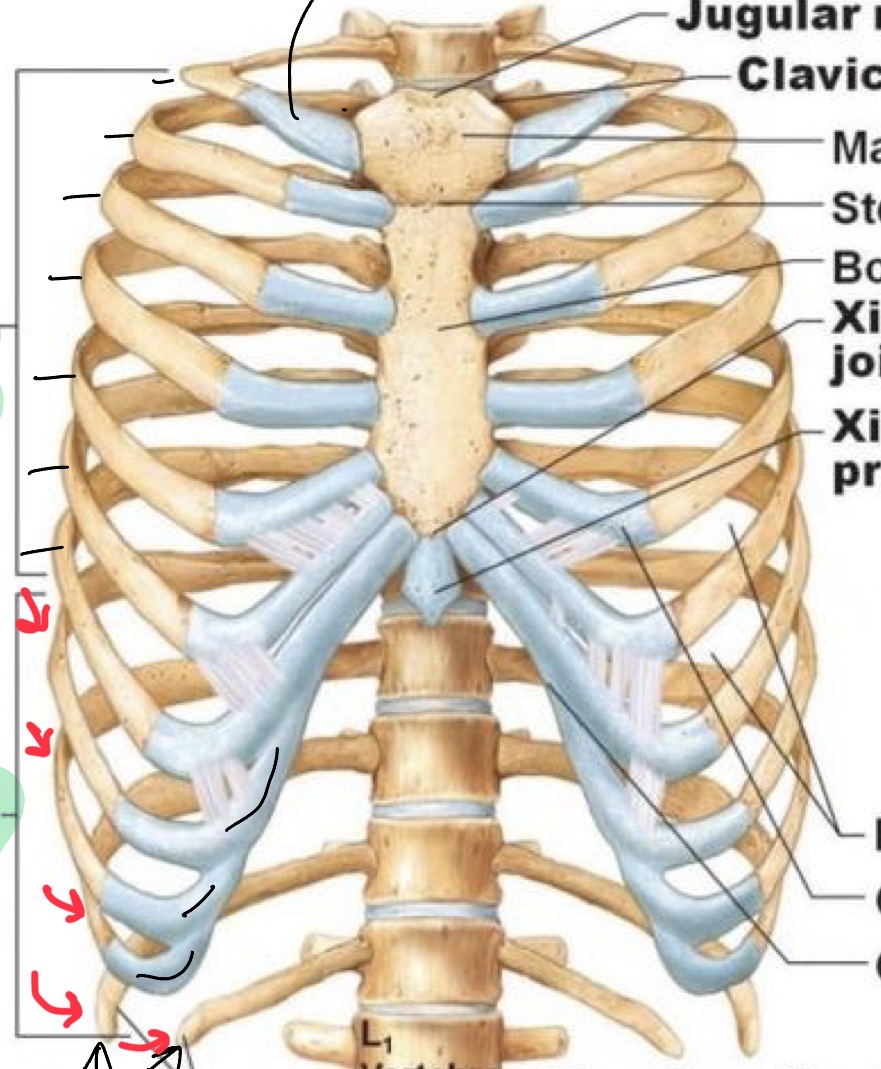
Floating ribs
11, 12, no hyaline cartilage and no connection to sternum