Lecture 5 - Soft Tissue Mobilization
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
Soft Tissue Mobilization (STM)
Assessment, Treatment, and Management of soft tissue injury/pain/dysfunction
- Primarily of neuromusculoskeletal system
- Therapeutic manipulation + deformation of soft tissue
STM Goal
Affect movement either directly or indirectly
- Increase mobility/flexibility
- Reduce pain
Massage vs STM
Massage = Increase blood flow, remove metabolic waste from muscle
- Relieve physical + emotional stress
STM = Addresses soft tissue restrictions
STM Framework
1. Increase circulation
2. Deliberate microtrauma
- introduce healing cycle
3. Release of adhesions
4. Neuromodulation of pain and tone
Skin + Fascial Layers
From superficial to deep...
1. Skin
2. Superficial fascia
3. Deep fascia
4. Epimysium
5. Muscle
Skin Color Assessment
Can help identify cause of dysfunction
Red skin
Fever, allergy, infection, inflammation, heat, embarassment
- Relates to DVT, blood clots
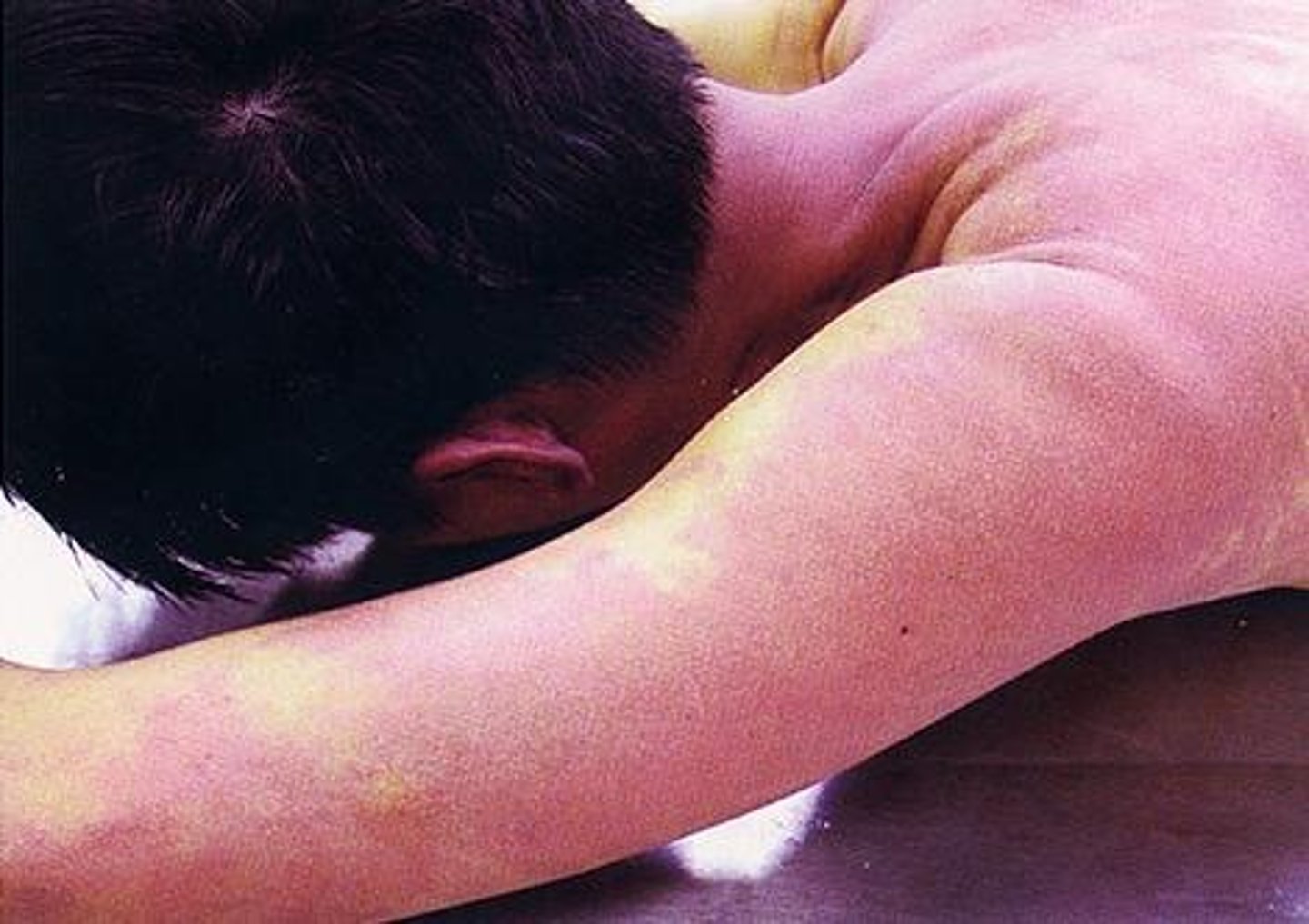
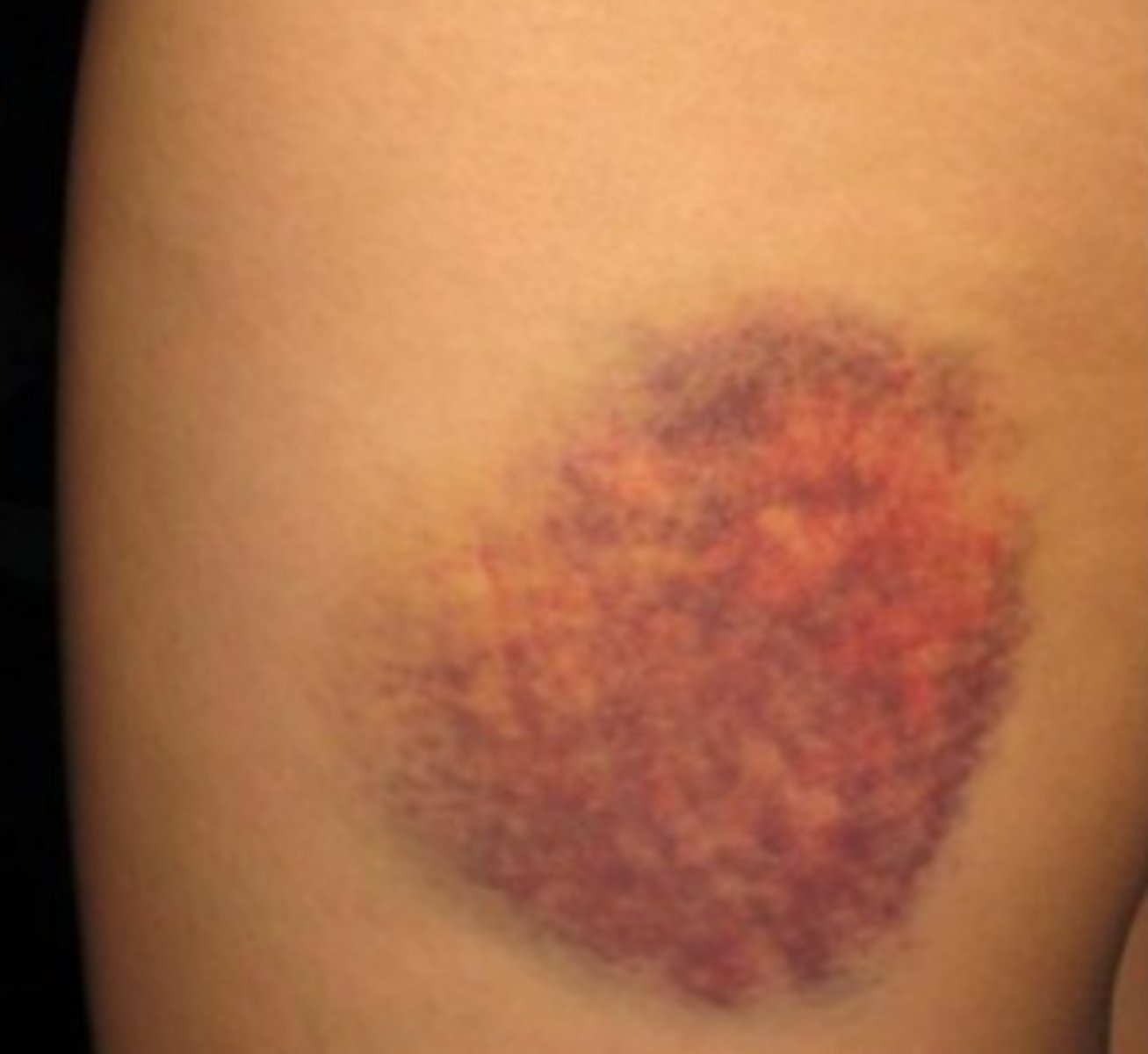
Black and Blue skin
Bruises -- Blood clots under skin
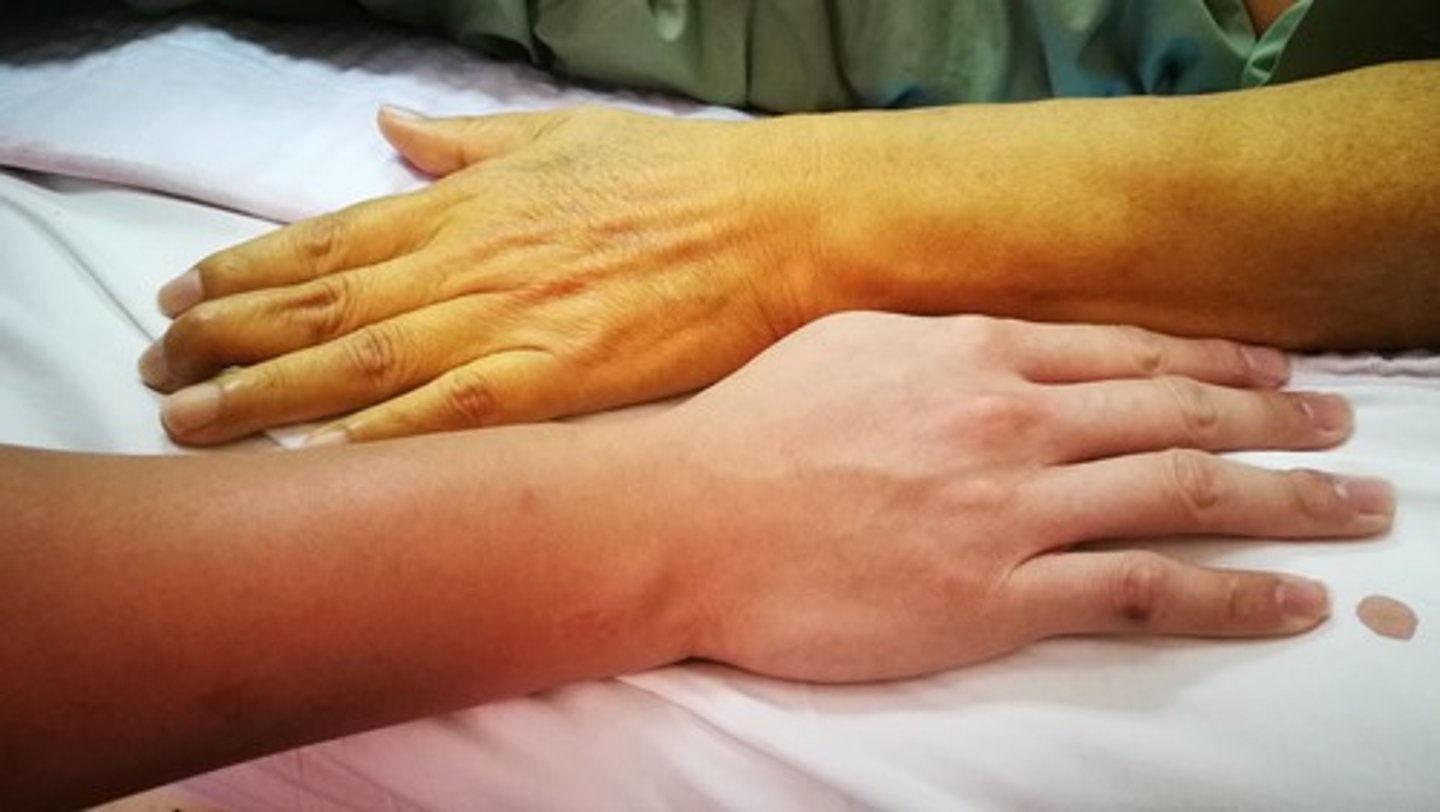
Yellowish skin
Accumulation bile pigments
- Sometimes cirrhosis
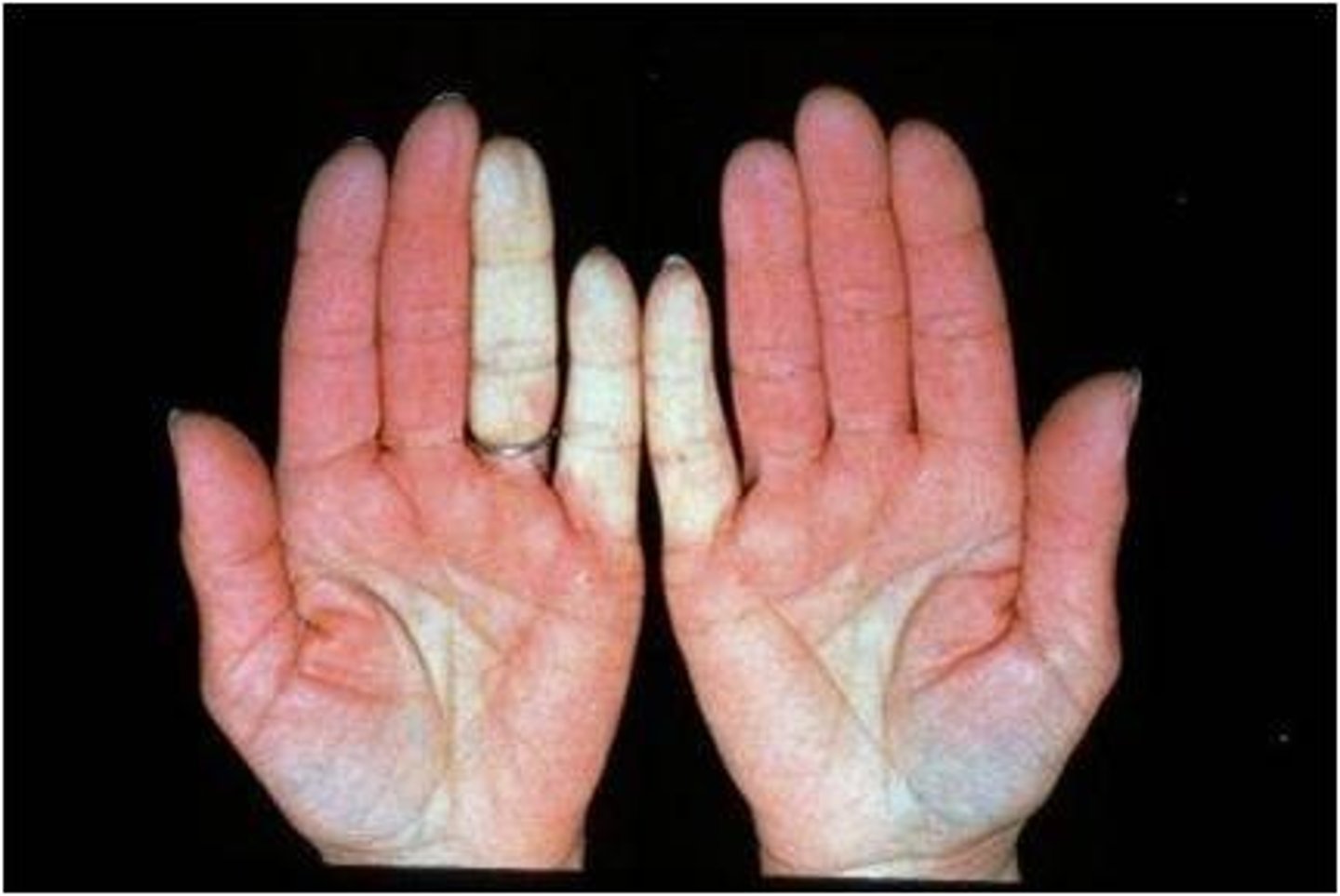
Pallor or blanching skin
- Anemia
- Emotional or physical stress
- Decreased arterial blood flow
Hypertrophic scar
Raised at site of original wound, but maintains borders
- Reddish, sometimes itchy
- Caused by too much stress on scar early on
- Body makes more scar tissue, but nowhere to go but up
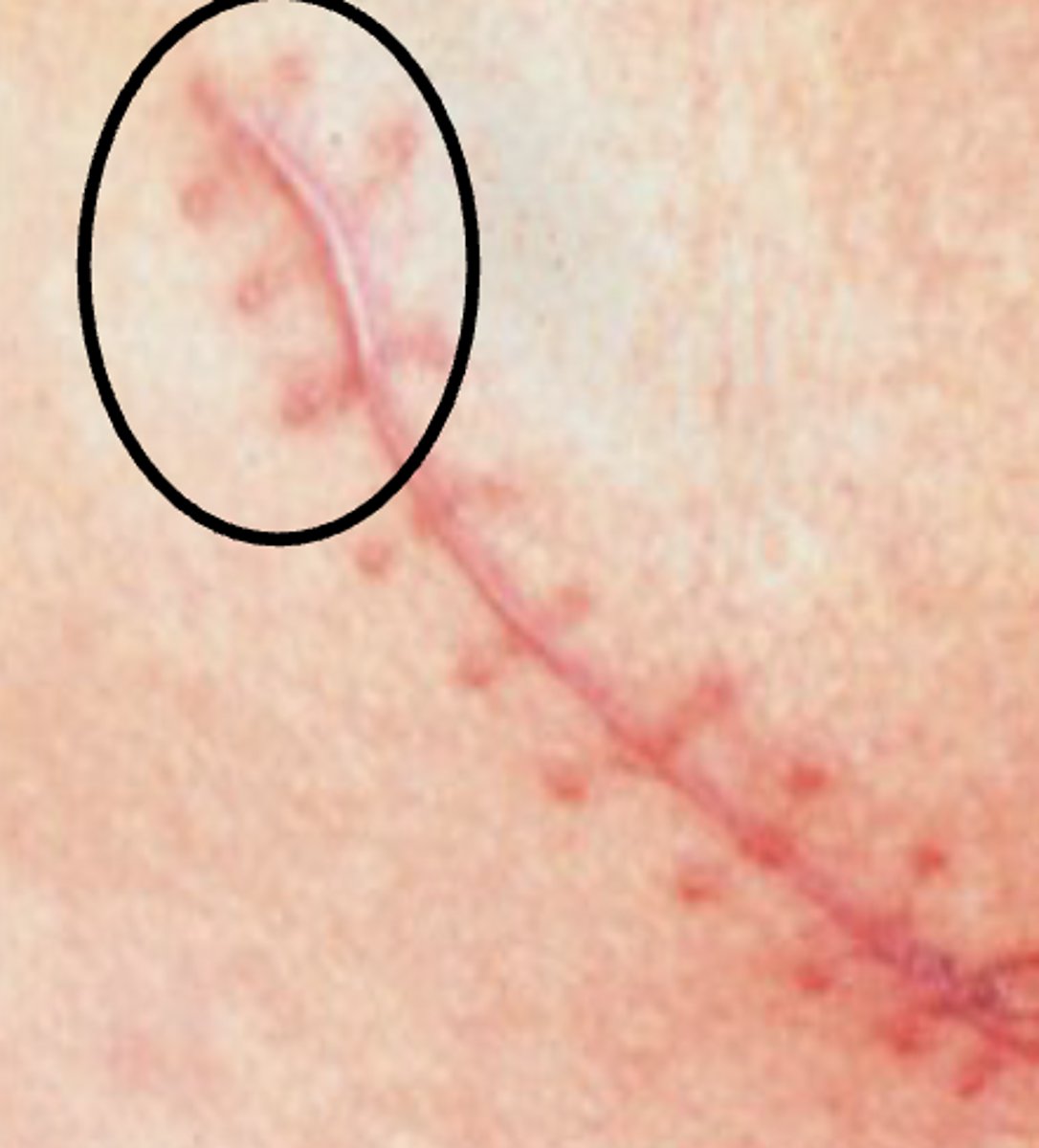
Keloid Scar
Also raised, but grow past the site of the wound
- Overtaking normal, healthy tissue
- BEYOND borders of wound!
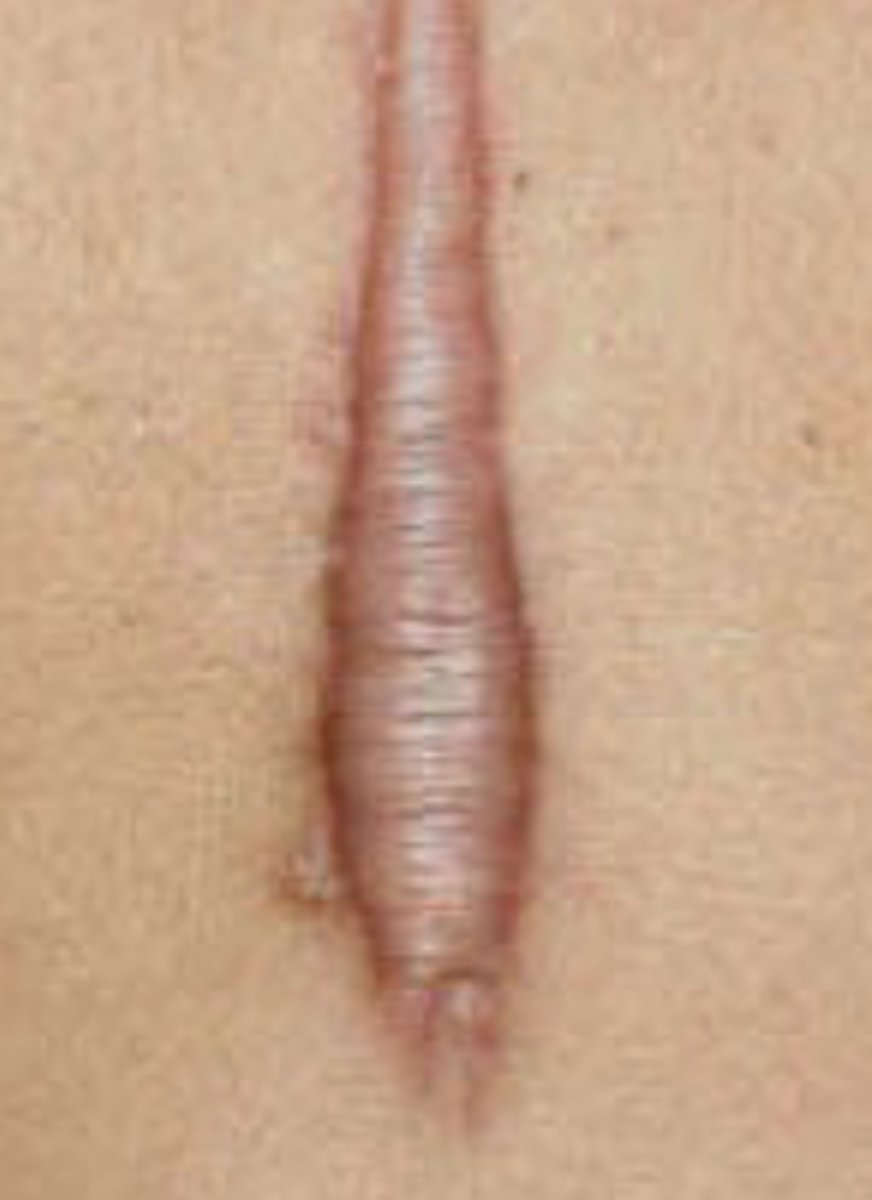
Deep cut healing time
Appropriate stress is key!
- After 2 years is typical for return to normal
- i.e. Incision after hip replacement surgery
STM and Skin
Assesses mobility, relation to underlying tissue
- Asseses scar mobility relating to superficial/deep fascial connections
Fascia
Sheet/band of connective tissue found throughout the body
Fascia characteristics
1. Interdependent layers with several depths
- Ranging from skin to bone
2. Attaches, encloses, & separates muscle/organs
3. Nerves, vessels, muscle, adj. tissue move within compartments
4. Innervated by sensory tissue
Fascia and Muscle
Fascia is ANATOMICALLY inseparable from muscle!
- Sensory receptors in fascia help signal pain
Fascial Slings
Working one part can impact another part of sling via fascia
Connective Tissue Nature
Visco-elastic!
Connective Tissue: Viscosity
If deformation of tissue is sustained/repeated, it will stay deformed
- Slow recovery to baseline
Connective Tissue: Elasticity
When lengthened, will return to its original length when force is removed
Immobilization of Connective Tissue
1. Loss of ground substance
2. Fibro-fatty infiltrates
3. Macro-adhesions
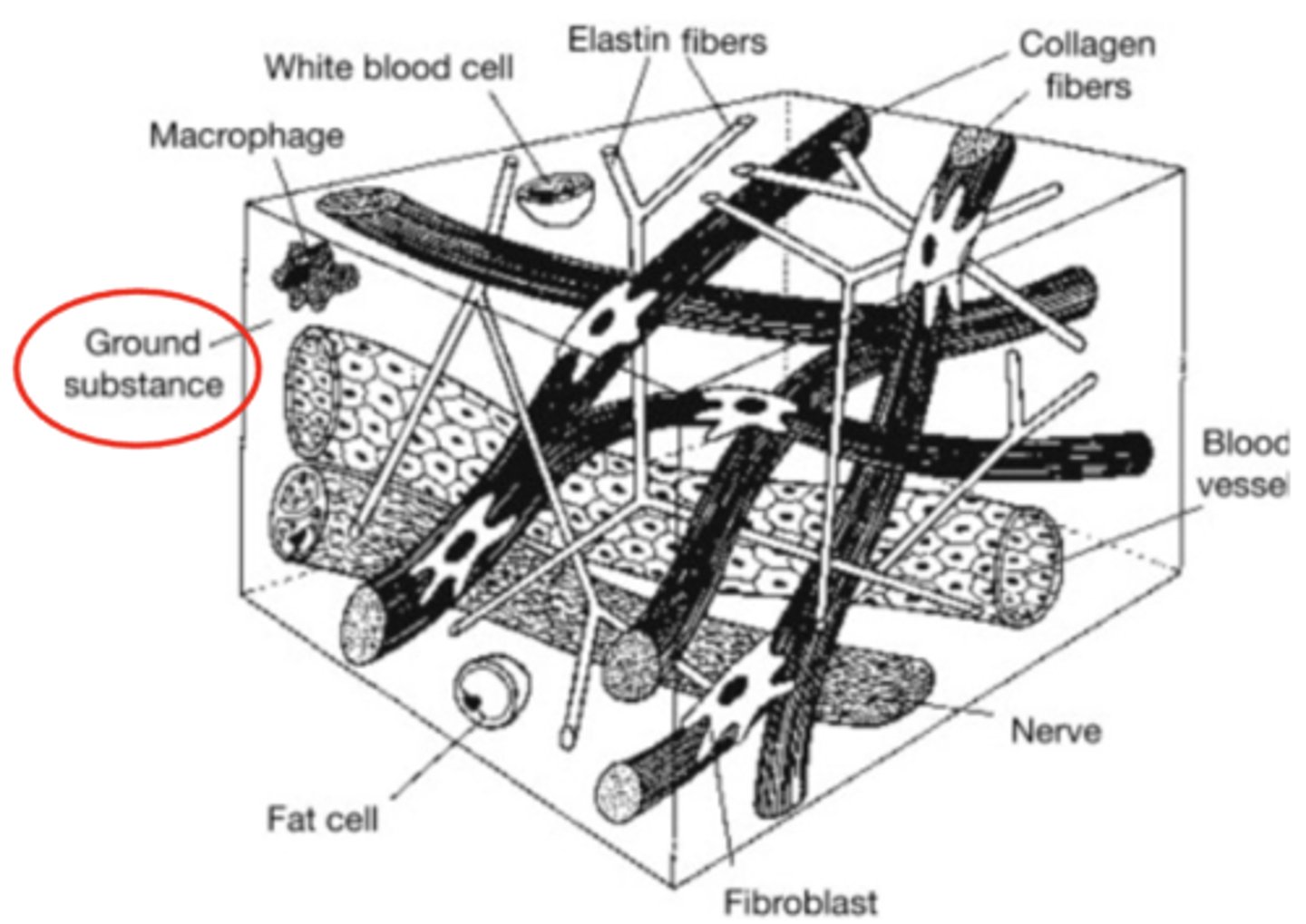
Ground Substance
Maintains space between collagen fibers
- Improves ability of tissue to move freely
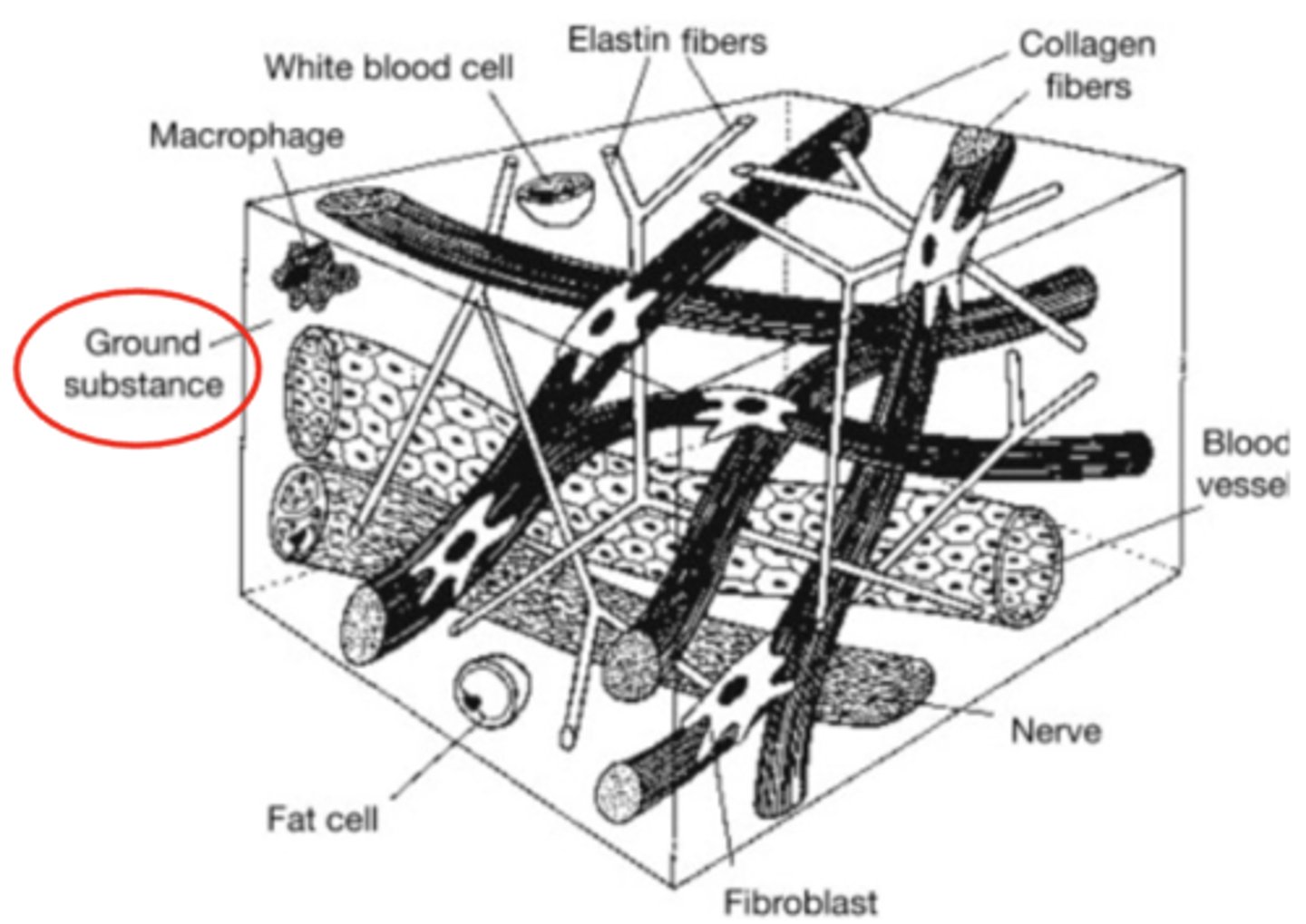
Loss of ground substance
- Decreased distance between adjacent fibers
- Increased fiber contact --> Micro-adhesions
- Random fiber orientation due to no stress from immobilization
Fibrofatty Infiltrates
Change in structure/organization of collagen in joint capsules and ligaments after 2 weeks immobilization
- Due to no stress
- Rapid degeneration with DENSE fibrofatty conn. tissue
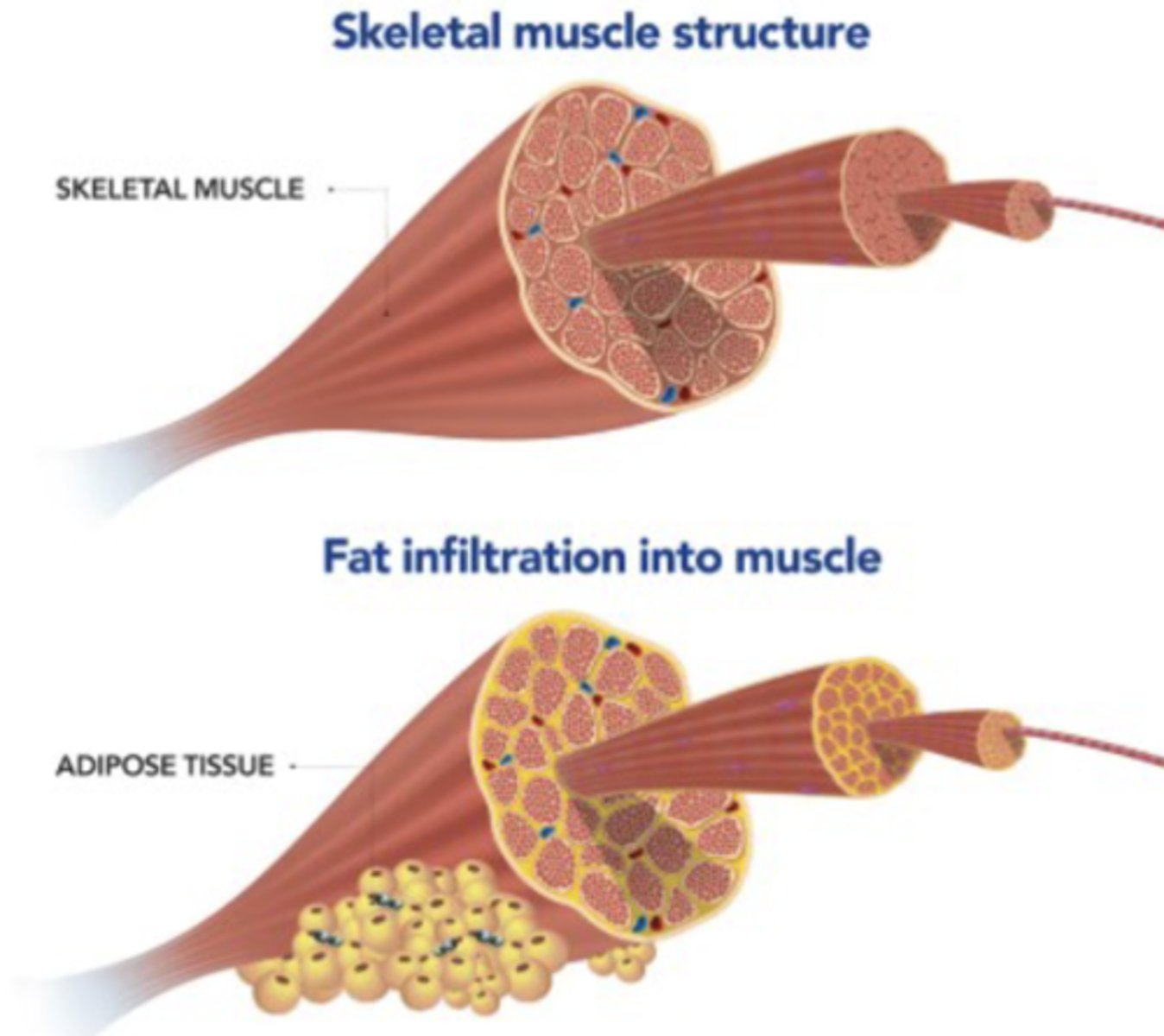
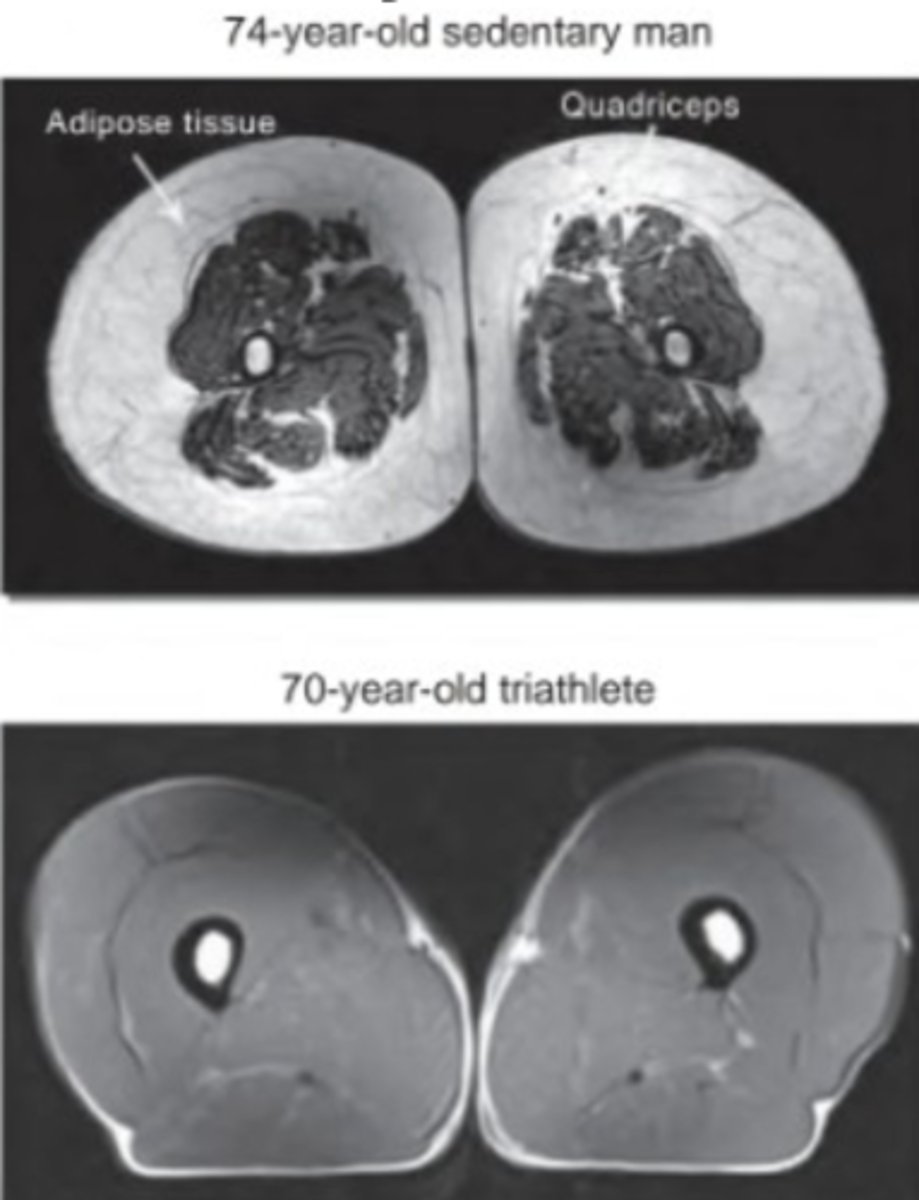
Fibrofatty infiltrates
White = Increased Fat Deposits
Macro-adhesions
Unwanted connections between neighboring tissues
- Larger fibrofatty infiltrates adhering adj. tissues together
Bonds that you DONT want to occur!
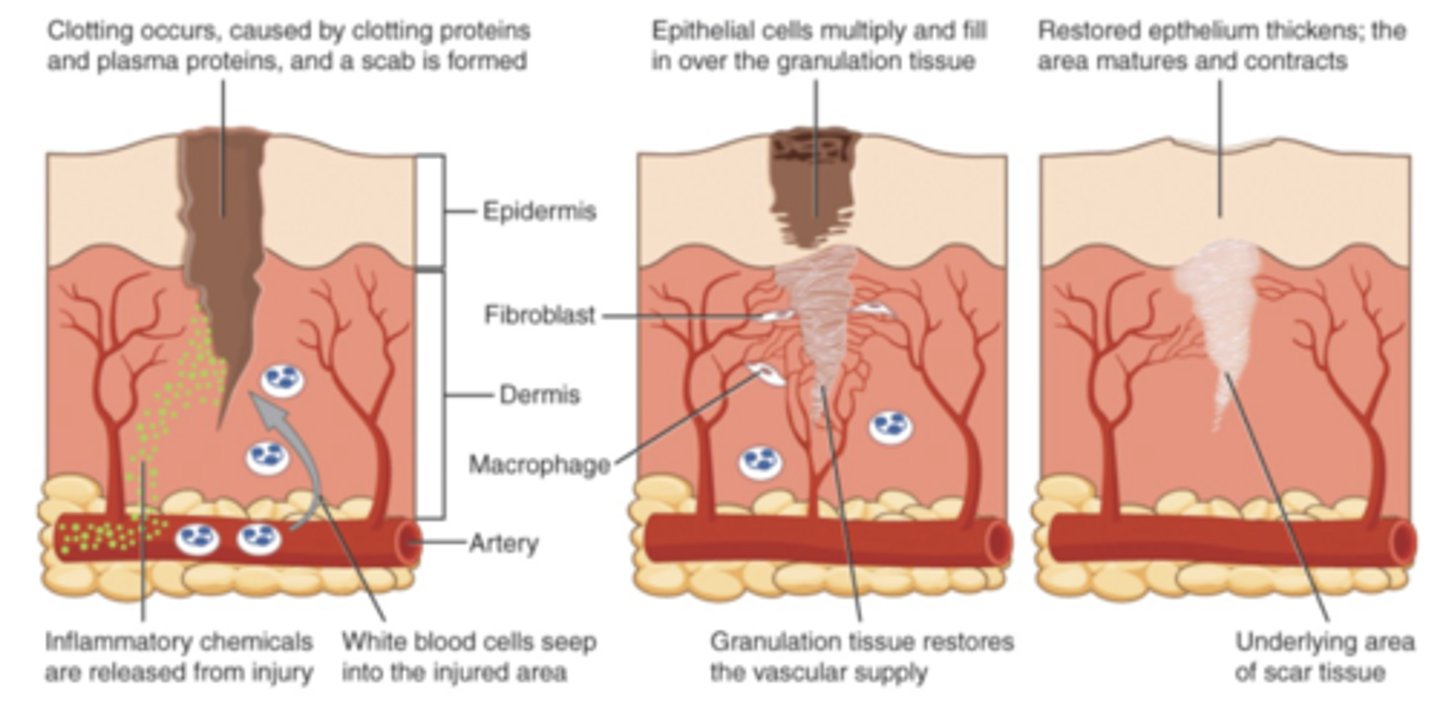
Normal Healing
- Local Response
- Decreased Mobility
- Linear w/ distinct end point
Local Healing Response
1. Inflammatory
2. Fibroblast formation
3. Maturation / Remodeling
Fibrotic Tissue
Fibrotic tissue formation is normal for healing process when controlled
Fibrosis
Formation of excessive fibrotic tissue
- Occurs when normal tissue is immobile
- Scarring continues to happen beyond normal timeframe
Abnormal result = Scarring after prolonged immobilization
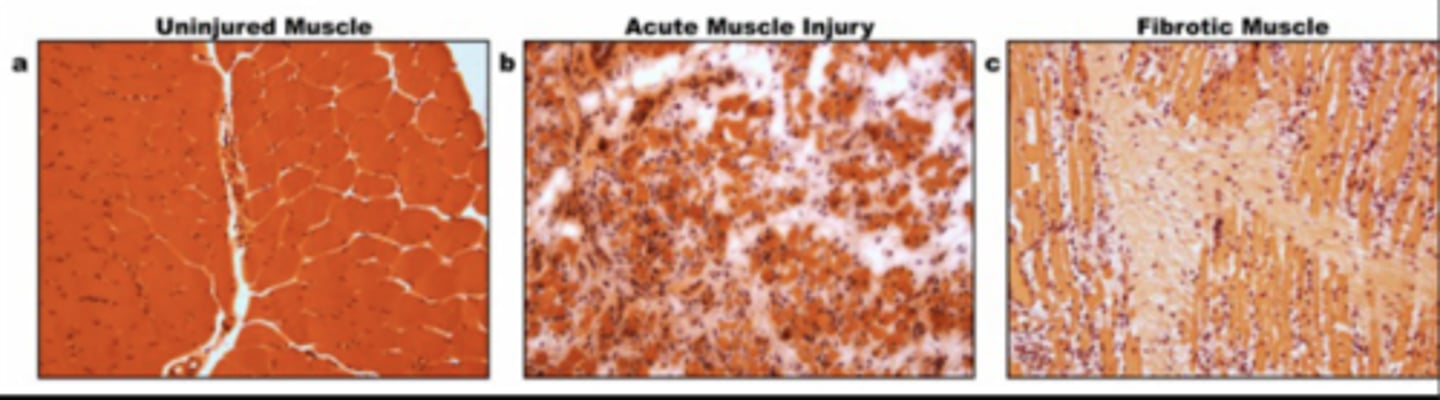
Fibrosis Characteristics
- Traumatic
- Immobilization
- Change in structure (larger area)
- Cyclic (progresses if no intervention)
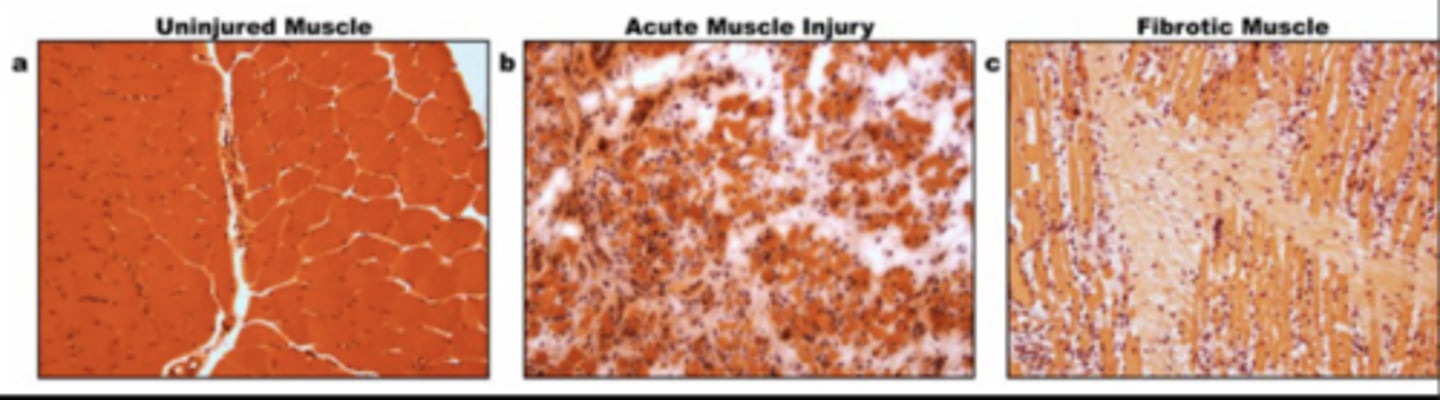
Fibrotic Tissue Characteristics
No give to it -- All force goes to joint!
- Hard & Fibrous
- Inflexible
- Less functional
- Increased joint load
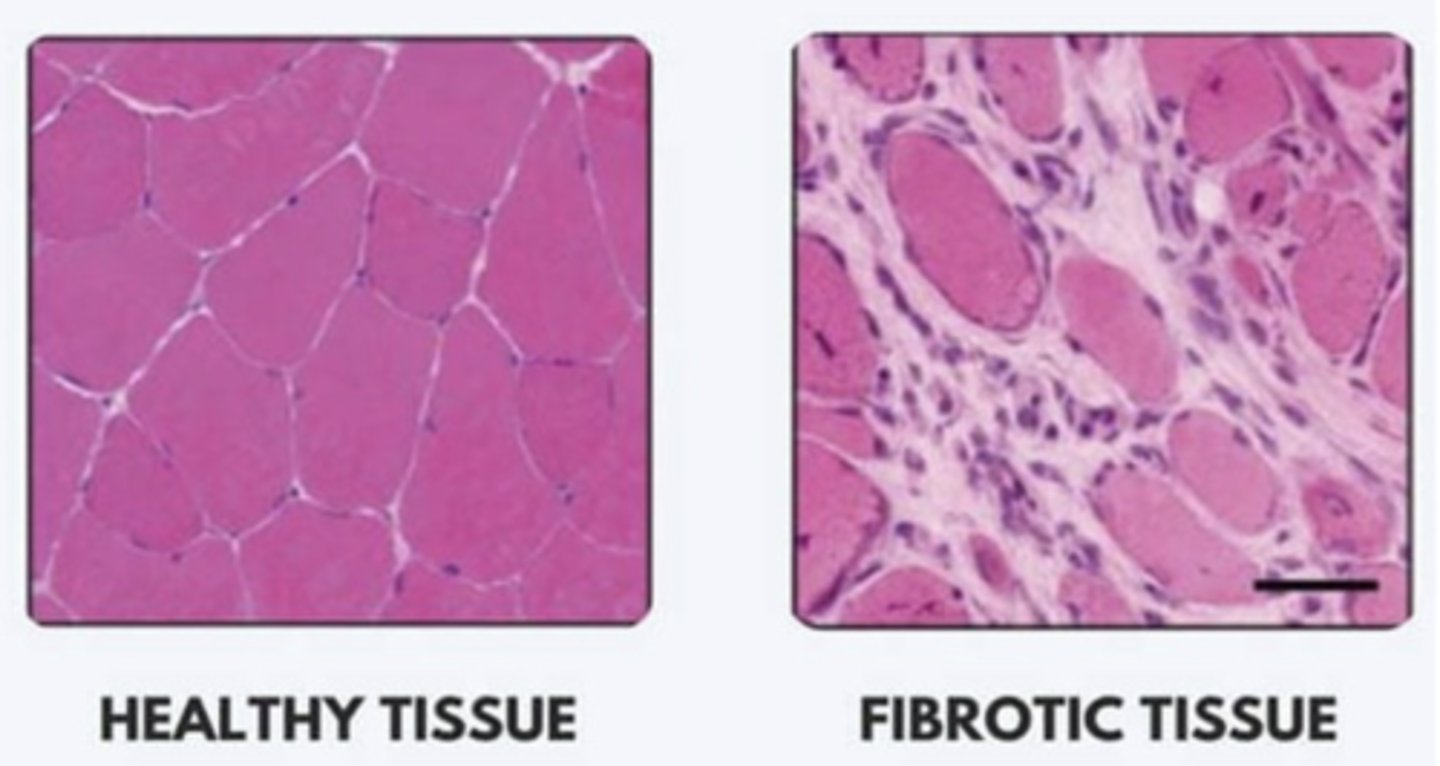
Healthy Tissue Characteristics
- Soft/Supple
- Flexible
- Highly functional
- Decreased joint load
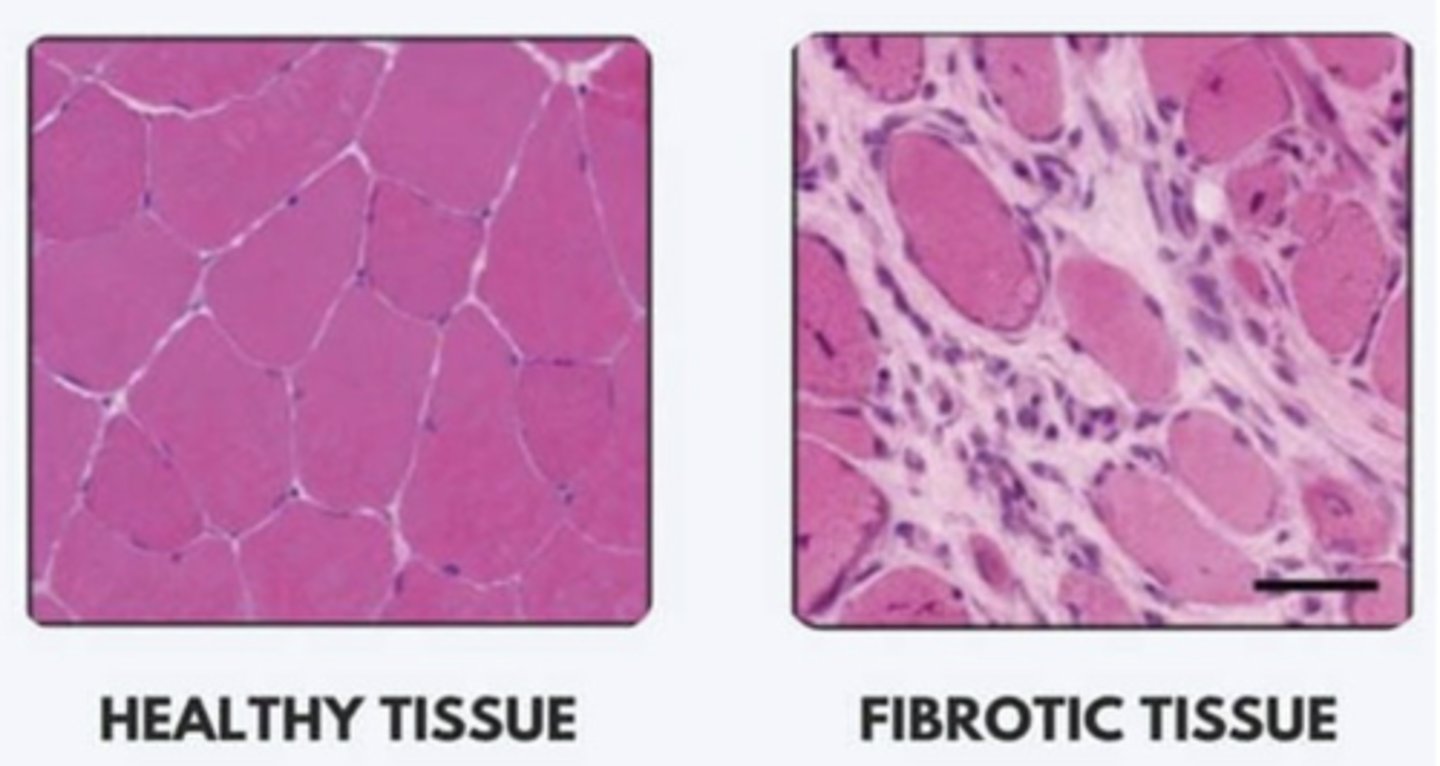
Fibrotic Tissue Treatment Goal
Decrease load of the joint
Muscle adhesion
Band of fibrous tissue that holds structures together abnormally
- Things won't move as smoothly/efficiently
- Rupture more likely for shortened muscles
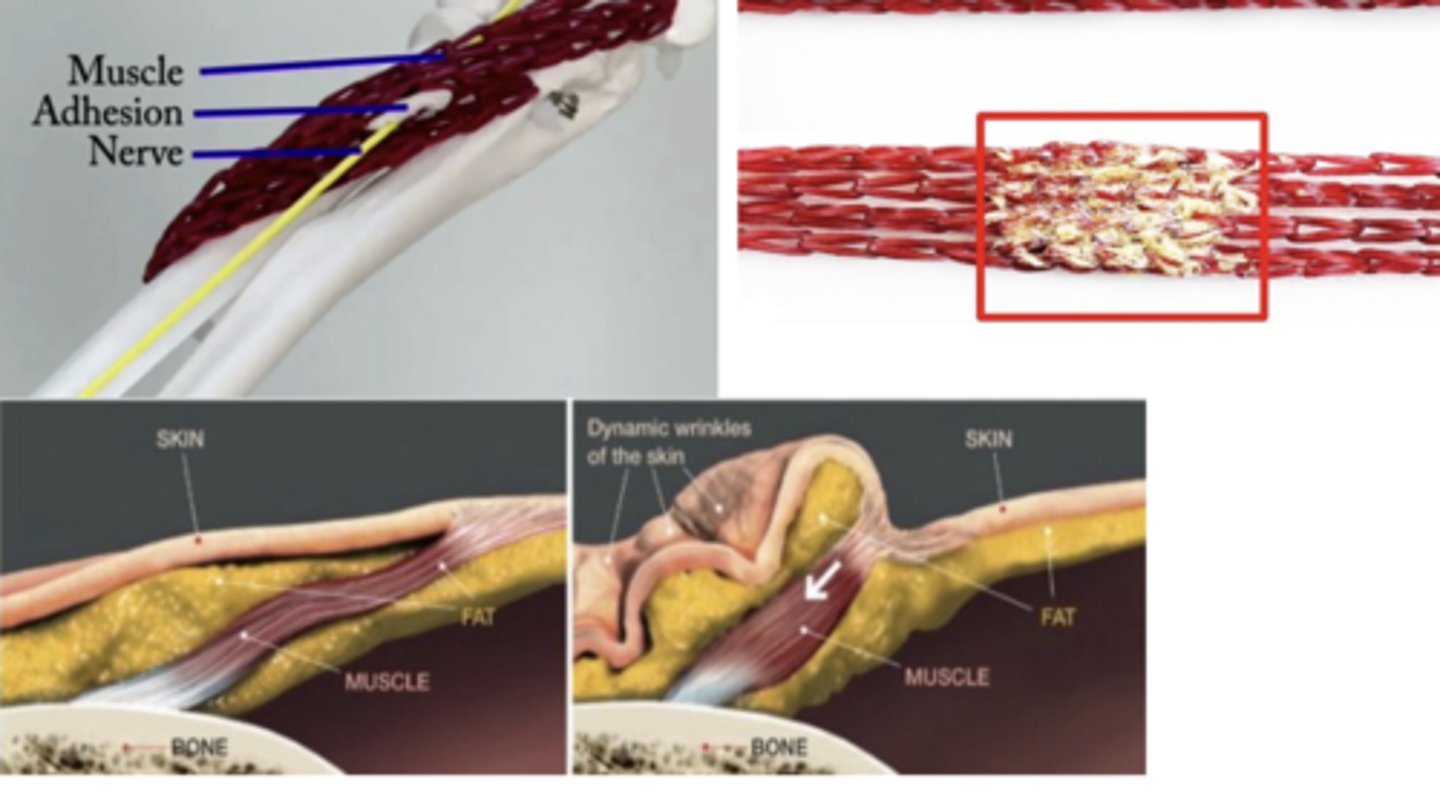
STM: Connective Tissue
Reducing adhesions by releasing bonds
- Early intervention = Most beneficial response
- Rarely done as sole treatment
- ROM, Flexibility, Muscle Activation
Inflammatory Process: 4 Main Elements
1. Changes in blood circulation
2. Changes in vessel wall permeability
3. WBC response
4. Release of inflammatory mediators
Inflammatory Process
1. Injury occurs
- Initial vasoconstriction for only a few seconds
- Quick sympathetic response (few seconds)
2. Vasodilation
- Increasing blood flow/plasma
3. Edema (swelling)
WBC Response to injury
1. Open wound --> Bacteria --> Increased WBCs
- WBC presence leads to inflammatory release
2. Increasing blood vessel permeability
3. Localized inflammatory response
5 Signs of inflammatory response
1. Heat
2. Redness
3. Edema (swelling)
4. Pain
5. Loss of function
Heat & Redness (inflammatory response)
Tissue cells are damaged
- Vasodilation --> Increased blood volume
- WBCs to injury site
Edema, Pain, LOF (inflammatory response)
Increased swelling + pain --> Loss of function
- Fluid leaks out of vessels into surrounding tissue (swelling)
- Pressure activates pain receptors
Stages of Healing
1. Acute - Inflammatory
2. Subacute - Repair/Healing
3. Maturation and Remodeling
Acute Inflammatory Stage: Characteristics
- Vascular changes
- Inflammatory exudates
- Clot formation
- Early fibroblastic activity
Acute Inflammatory Stage: Clinical Signs
- Inflammation
- Pain BEFORE tissue resistance
Acute Inflammatory Stage: STM Intervention
Protection
- Promote healing and prevent compensatory patterns
- Passive movement in pain-free range
- STM to assist w/ inflammatory exudate absorption
- i.e. Hypertrophic scar
Subacute Inflammatory Stage: Characteristics
- Growth of capillary beds
- Collagen formation -- Granulation tissue
- Fragile, easily injured tissue
Subacute Inflammatory Stage: Clinical Signs
- Diminishing inflammation
- Pain DURING tissue resistance
- Patient in pain AT end-feel
Subacute Inflammatory Stage: STM Interventions
Controlled Motion
- Promote scar mobility
- Controlled STM of scar tissue toward injury
- Improve connections, sliding skin around scar!
Maturate/Remodeling Stage: Characteristics
- Scar remodeling
- Collagen aligns along lines of stress forces
- Improved tissue strength and organiztion
Maturate/Remodeling Stage: Clinical Signs
Absense of inflammation!
- Pain AFTER tissue resistance (overpressure)
Maturate/Remodeling Stage: STM Interventions
Return to normal function!
- Increase strength + alignment of scar tissue
- Cross-fiber friction massage
- Progressive stretching + ROM
- More aggressive, encourage motion
Analgesic Effect
Reduces pain
STM: Pain Management
Has analgesic effect
- Improves blood flow, reduces inflammation (systemic)
- Removes pressure on pain receptors
- Temporarily reduce muscle spasm
Light touch (STM)
Reduces nociceptive signaling
Acupressure points
Helps release endogenous opioids to assist with pain recovery
Median Nerve
Must elongate 20% to be functional
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Transverse carpal ligament thickens
- Lessens space for median nerve
- Impacts hand
Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome
Tibial nerve becomes compressed in tarsal tunnel
- Similar to carpal tunnel, impacts foot
Nerve adhesion (vertebrae)
- Increased ant. tilt, angled lower back
- Facet joint closed
- Scar forms where nerve adheres to tissue
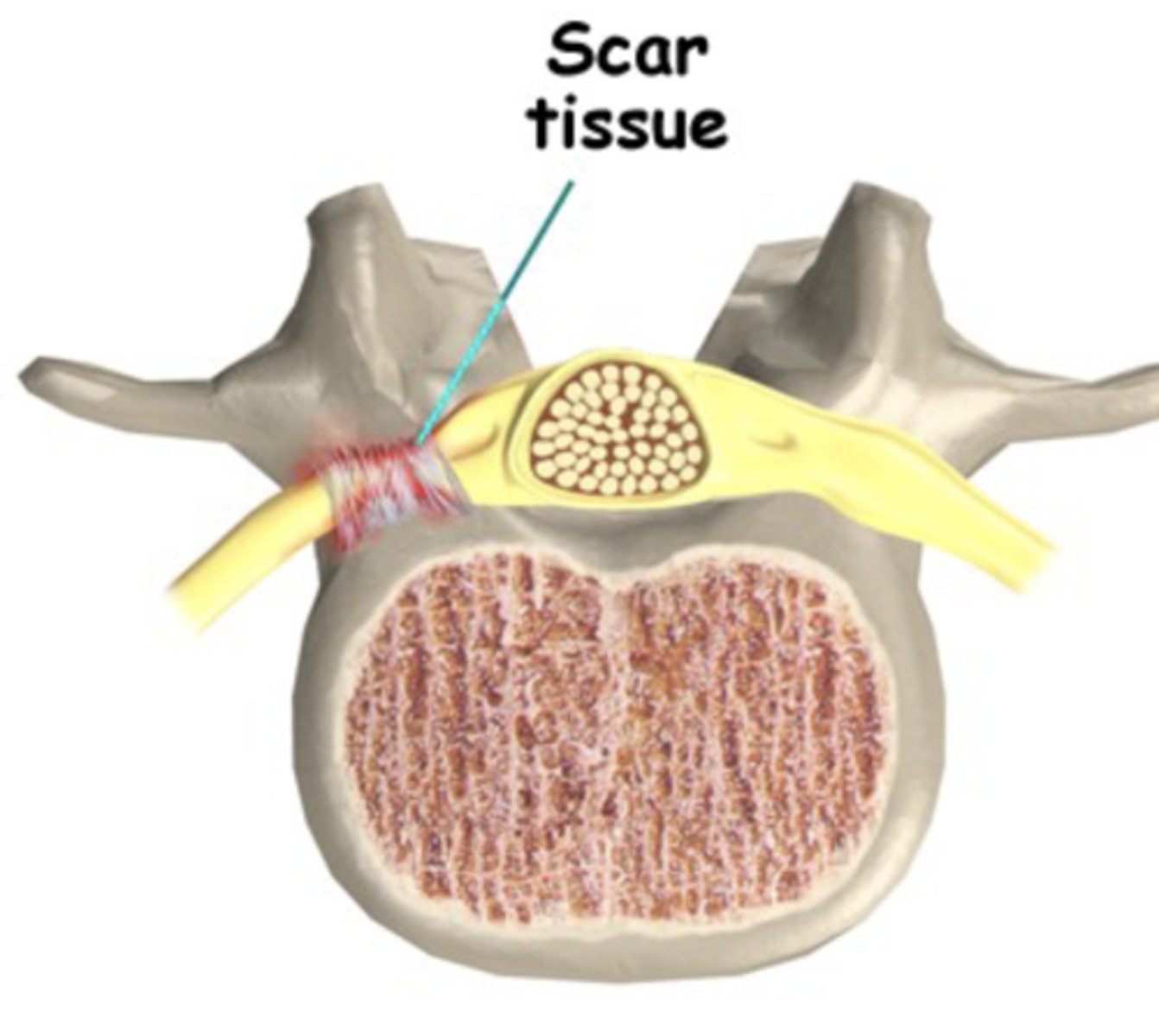
Myofascial Release (MFR)
Techniques for moving fascia + soft tissue of hypomobile areas
- Typically done from superficial to deep
- Skin shearing --> muscular deformation --> TrP release
MFR Treatment Progression
Depth:
Superficial --> Deep
Force:
Direction: Start Parallel --> Perpendicular
Intensity: Less force --> Greater force
Length of involved tissue:
Shortened --> Lengthened
- Lengthened = Less tolerable
STM Contraindications
- Malignancy
- Inflammatory skin condition
- Unstable fx
- Hemorrhage
- Localized infection
STM Precautions
- Circulatory/Cardiovascular disorders
- Abnormal sensation
- Immunocompromised
- Scar healing
Superficial Fascia/Skin Shearing: Contraindications
- Recent incision
- Burn graft
- Psoriasis
Bony Contours: Contraindications
- Osteoporosis
- Fracture
Body Mechanics
- Flexed fingers
- Force thru top hand
- Straight line
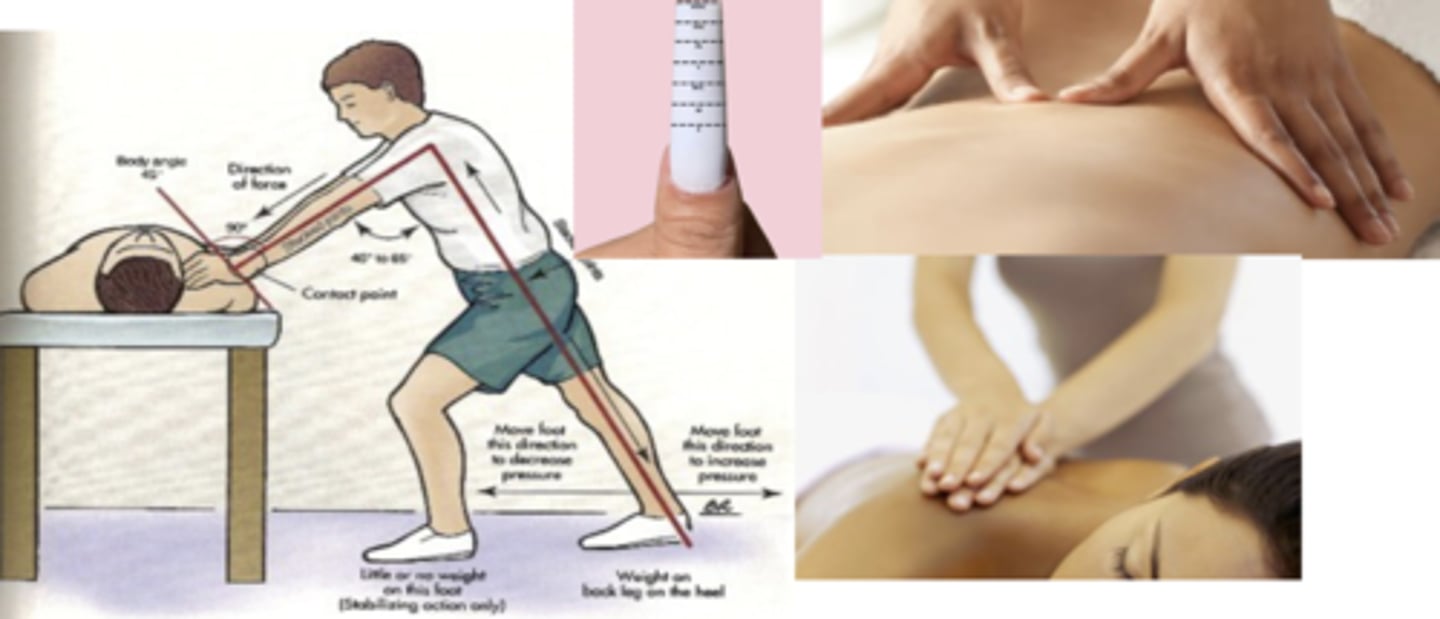
STM Clinical Application
Purposeful, supplemented with other intervention
- Patient is not here for "massage"
Layers of Palpation
1. Skin / Superficial Fascia
2. Muscle
3. Tendon
4. Ligament / Joint Capsule
5. Bone
Normal Skin Quality
Smooth & Pliable
- Hair growth sometimes present
Normal Skin Temperature
Uniform body temp
Normal Skin Consistency
Soft and very elastic
- Skin becomes firmer with more tension placed on it