midterm (copy)
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/276
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:51 PM on 11/27/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
277 Terms
1
New cards
choosing the appropriate pipette
depends on volume youre transfering, the nature of the liquid (density, vapor, pressure, viscosity, surface tension) and the required degree of accuracy
2
New cards
Pasteur pipette
are made of glass and have a long tapered end that allows access to small soaces
3
New cards
serological pipettes
glass or plastic, available in a wide variety of sizes and are graduated which allow for transfer of specific volumes
4
New cards
transfer pipettes
made of plastic and contain volume markers which allow one to estimate volume aspirated and dispensed. only used if accuracy is not critical
5
New cards
piston driven air displacement pipettes
work horses of lab pipe tying typically used for dispensing accurate volumes less than 1 ml. has dial and specific tips.
6
New cards
volumetric pipettes
glass pipettes designed to accurately transfer a specified volume. liquid is aspirated with a suction device and dispensed by force of gravity. designed to deliver or to contain a specific volume
7
New cards
capillary pipettes
are much like volumetric pipettes but are intended for very small volumes the liquid is aspirated by capillary action and dispenses by the force of gravity may be graduated or intended for a set volume
8
New cards
we mainly use which pipettes
serological and piston driven
9
New cards
pipetting requires _____ and ____
precision and accuracy
10
New cards
accuracy
closeness of a measurement to a standard
11
New cards
Precision
closeness of individual measurements to eachother
12
New cards
range of pipette
the smaller the range the more accurate. find the smallest range for the volume you need
13
New cards
aspiration
pulling up
14
New cards
expulsion
pushing out
15
New cards
what's the key word to serological pipette
slowwww
16
New cards
serial dilution
substance in solution is diluted in a stepwise manner using a dilution factor that is constant at each step
17
New cards
why are serial dilutions prepared for experiments
things that require the use of concentration curves or trend lines and are also useful in procedures for plating cells
18
New cards
R^2 value can be used to determine how
the linear line fits the data- directly related to your accuracy
19
New cards
density of water
1 g/mL
20
New cards
in vivo
performed in a living organism- answer questions about multiple organs or organ systems
21
New cards
what makes a good model system
relatively inexpensive, easy to maintain, entire genome has been sequenced, have systems that are homologous to more complicated eukaryotic organisms including humans
22
New cards
ex vivo
scientific processes being performed on cells, tissues, or organs outside of the body
23
New cards
cell free systems
do not contain whole cells and have provided information about the roles of the proteins involved in membrane trafficking, proteins that bind to the membrane to initiate vesicle formation, and proteins responsible for cargo selection
24
New cards
in vitro model systems
cultured cells and cell free systems
25
New cards
cultured cells mimic
the activity of cells in living organisms
26
New cards
primary cells
cells that are harvested and used immediately for experimentation
27
New cards
cell line
genetically identical cells that divide indefinitely and can be cultured in the laboratory
28
New cards
HeLa cells
famous cancer cells from Henrietta Lacks
29
New cards
cultured cells have allowed scientists to
mimic the activity of cells in living organisms
30
New cards
Senesence
cells stop dividing
31
New cards
Cho cells
Chinese Hamsters Ovary Cells
32
New cards
Cho cells are ____ for many alleles
hemizygous
33
New cards
hemizygous
only one of two alleles is functional
34
New cards
basal media
provides vitamins, amino acids, fatty acids, lipids, carbs, trace elements, necessary for cell growth.
35
New cards
basal media we used
Dulbecco's Modified Eagle Medium and Hams F-12 media
36
New cards
serum
provides final concentration, vitamins, hormones, growth factors etc.
37
New cards
Serum we used
FBS (fetal bovine serum)
38
New cards
additives
penicillin/streptomycin
39
New cards
temperature
37 C
40
New cards
humidity
flask with semi-permiable membrane to allow for gas exchange- pan of water in bottom of incubator
41
New cards
carbon dioxide
5% and sodium bicarbonate buffer to help with acidity
42
New cards
Splitting
cells multiply, and have to be divided so they can continue multiplying. cho cells need to be split 2x per week
43
New cards
CHO cells morphology
grow in a monolayer, contact inhibited, polygonal shape, large centralized nucleus
44
New cards
light microscopy
visible light and lenses to create magnified lenses. requires stains. fixed cells.
45
New cards
Phase-contrast microscopy (PCM)
converts light phase shifts to changes in brightness int he image that is observed. no stains or fixation needed.
46
New cards
electron microscopy
most powerful type. uses a beam of electrons accelerated for illumination.
47
New cards
Niewmann-Pick-C1
responsible for the export of lysosomal cholesterol
48
New cards
Basophillic
bluish-purple
49
New cards
acidophillic
red
50
New cards
neutrophillic
pink or neutral
51
New cards
most common acidophillic stain
eosin
52
New cards
hematoxylin
a nucelic acid binding stain which imparts a pale purple color to the cytoplasm and a darker purple color to the nucleus
53
New cards
Oil Red O
stains lipids red
54
New cards
H&E
hematoxylin and eosin- a dye combination used to stain pathology specimens
55
New cards
Masson's trichrome stain
hematoxylin, acid fuchsin, aniline blue
56
New cards
silver nitrate
stains neurons black
57
New cards
Fluoresence Microscopes do what?
view "glowing" bacteria that are tagged with fluorescent dyes
58
New cards
Hoescht 33258
fluorescent dye
59
New cards
fragmented nucleus indicates a cell that is
undergoing apoptosis
60
New cards
staining typically ____ cells
kills
61
New cards
vital stains
chemicals that can stain living cells without killing them
62
New cards
confluence
% of surface covered in cells
63
New cards
epithelial cells
skin cells that cover the outside of the body and line the internal surfaces of organs- flattened plate like cells with a hexagonal shape.
64
New cards
methylene blue
a staining dye/indicator that interacts with nucleic acid molecules and proteins, turning them to a very dark blue color. stains DNA, RNA, and other negatively charged molecules
65
New cards
when working in the hood
wash gloves and all items with isopropyl, leave door lowered, dont cross hands or go in and out excessively, never open anything outside of cabinet.
66
New cards
contaminated media turns
yellow
67
New cards
Trypsin
makes cells dissociate form plastic side of container
68
New cards
Trypan Blue
a viability stain used to differentiate dead cells (blue) from living cells (clear)
69
New cards
PBS
phosphate buffered saline- like a wash rinse for the cells to remove the media so that trypsin can work
70
New cards
media contains the anecdote for
trypsin
71
New cards
cultured cells will not be ______ for observation
stained
72
New cards
epithelial cell
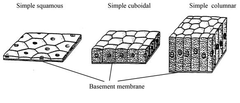
73
New cards
vessels for cell culture
flasks, culture dishes, multi well plates, chamber slides.
74
New cards
knowing surface area of vessel is important to determine
number of cells in the vessel
75
New cards
passaged
split
76
New cards
splitting cells is necessary to
maintaining the quality and phenotype of the culture
77
New cards
steps of cell splitting
disruption of cell monolayer, trituration of the cells, discarding a portion of the cell suspension resulting in the disposal of unwanted cells, and replating a small percentage of the homogenous cell suspension containing the desired number of cells
78
New cards
cell spreading/ cell seeding
making multiple vessels out of one original vessel of cells. important how many cells are transferred. that number is dependent on
- confluency required for the experiment
- doubling time of the particular cell line
- amount of time between seeding and performing the experiment.
- confluency required for the experiment
- doubling time of the particular cell line
- amount of time between seeding and performing the experiment.
79
New cards
size of our flasks
25 cm^2- polystyrene, Tissue culture treated surface
80
New cards
if the flask filter gets wet
the cells suffocate
81
New cards
Trituate
The process of mechanically mixing a material ( pipetting cells up and down to break up clumps)
82
New cards
UV light sterilizer
Utilizes UV light to kill bacteria in a dry setting
83
New cards
our cells must be split
2x per week
84
New cards
BSS
balanced salt solution ph of 7.4
85
New cards
trypsin
An enzyme that catalyses the extracellular breakdown of proteins. and stops cells ability to adhere to the surface or eachother
86
New cards
trypan blue
only appears in dead cells (cells with a compromised membrane)
87
New cards
cellometer
automatic cell counter
88
New cards
hemocytometer / advantages
Instrument used in counting blood cells- can distinguish between dead and alive cells
89
New cards
each 1mm^2 corner of a hemocytometer represents
total volume of 10^-4/cm^3
90
New cards
cells/ml =
average number of cells per square x dilution factor x conversion factor
91
New cards
pellets need to be frozen at
-80 degrees C
92
New cards
review hemocytometer cell count calculations
yay
93
New cards
H&E staining
hematoxylin and eosin
94
New cards
Hand E is most comonly used for
histology and cytology applications
95
New cards
H and E can be used to determine if a cell is
undergoing apoptosis or necrosis
96
New cards
apoptosis inducers
tunicamycin and UV light
97
New cards
cells are fixed with
formaldehyde
98
New cards
fixation
kills the cells, but preserves their morphology
99
New cards
mounting media
substance that is highly dense and has a high refractive index
100
New cards
mounting media we used
glycerol