PSIO 201 Practical 3
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
162 Terms
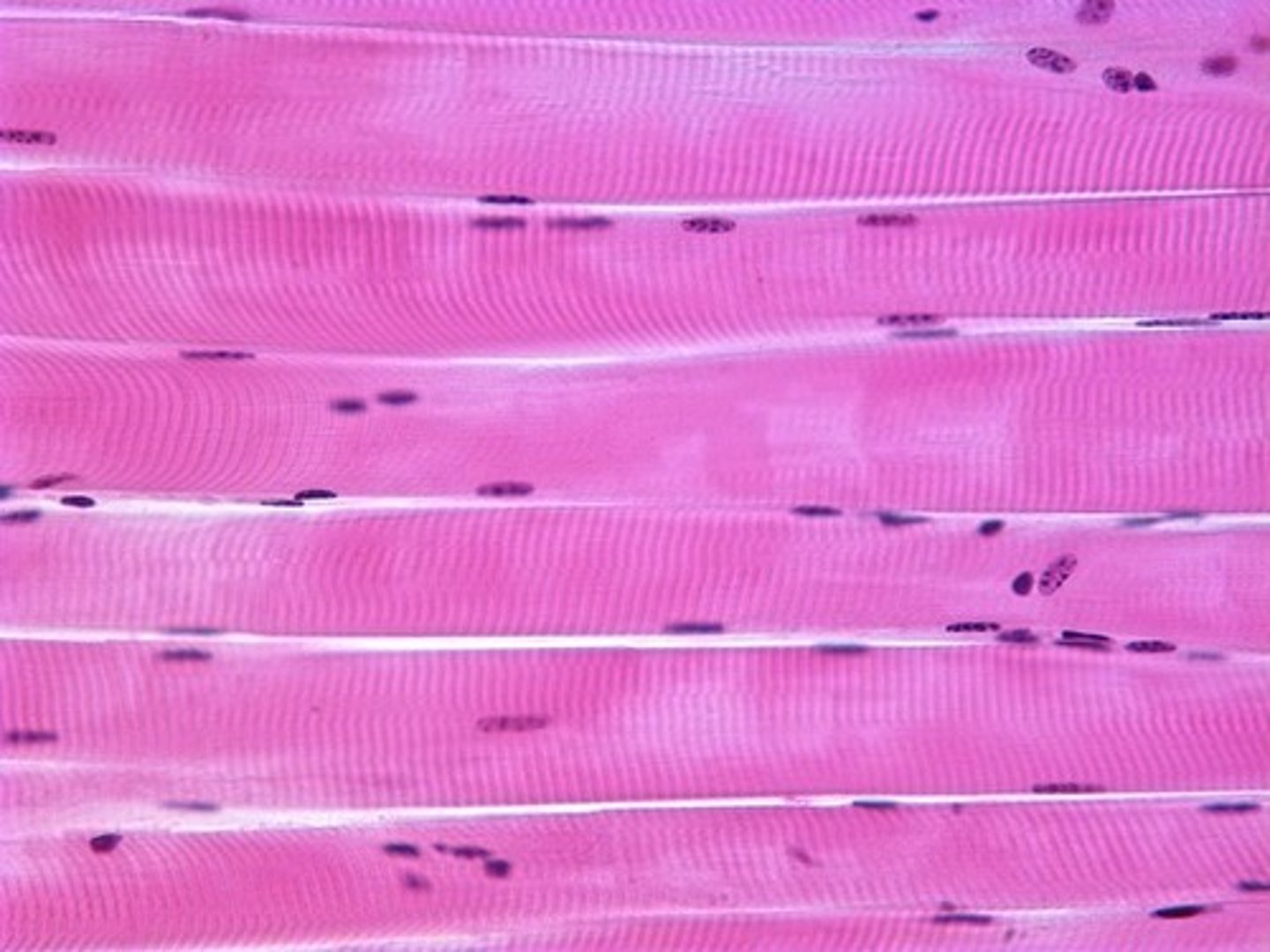
3 defining characteristics of skeletal muscle tissue
1. Cylindrical-shaped muscle fibers
2. 3-5 nuclei per muscle fiber
3. Striations due to organization of actin(thin) and myosin(thick) filaments
Z disc
Forms the boundary of each sarcomere
Connects and stabilizes thin filaments
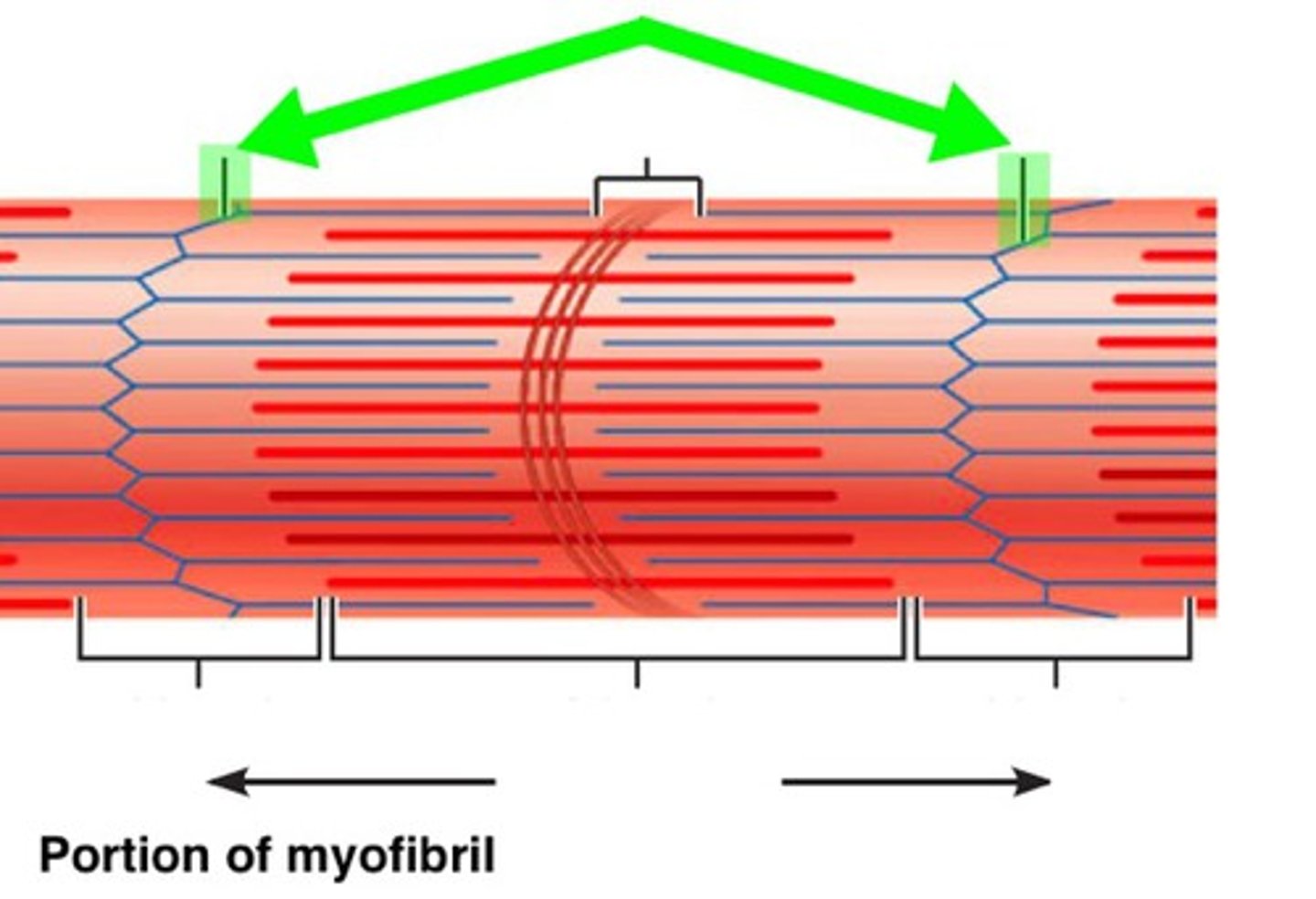
I band
Contains only actin(thin filaments)
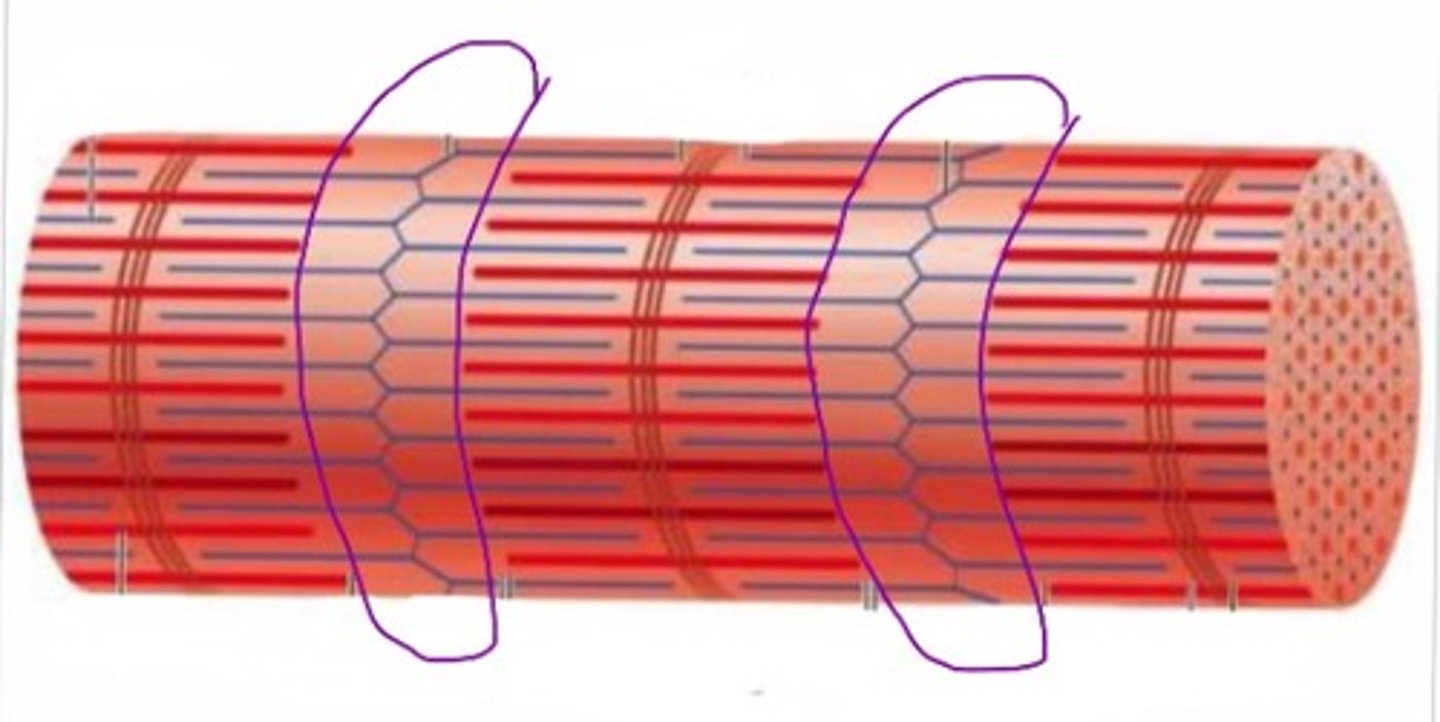
H zone
Contains only myosin(thick filaments)
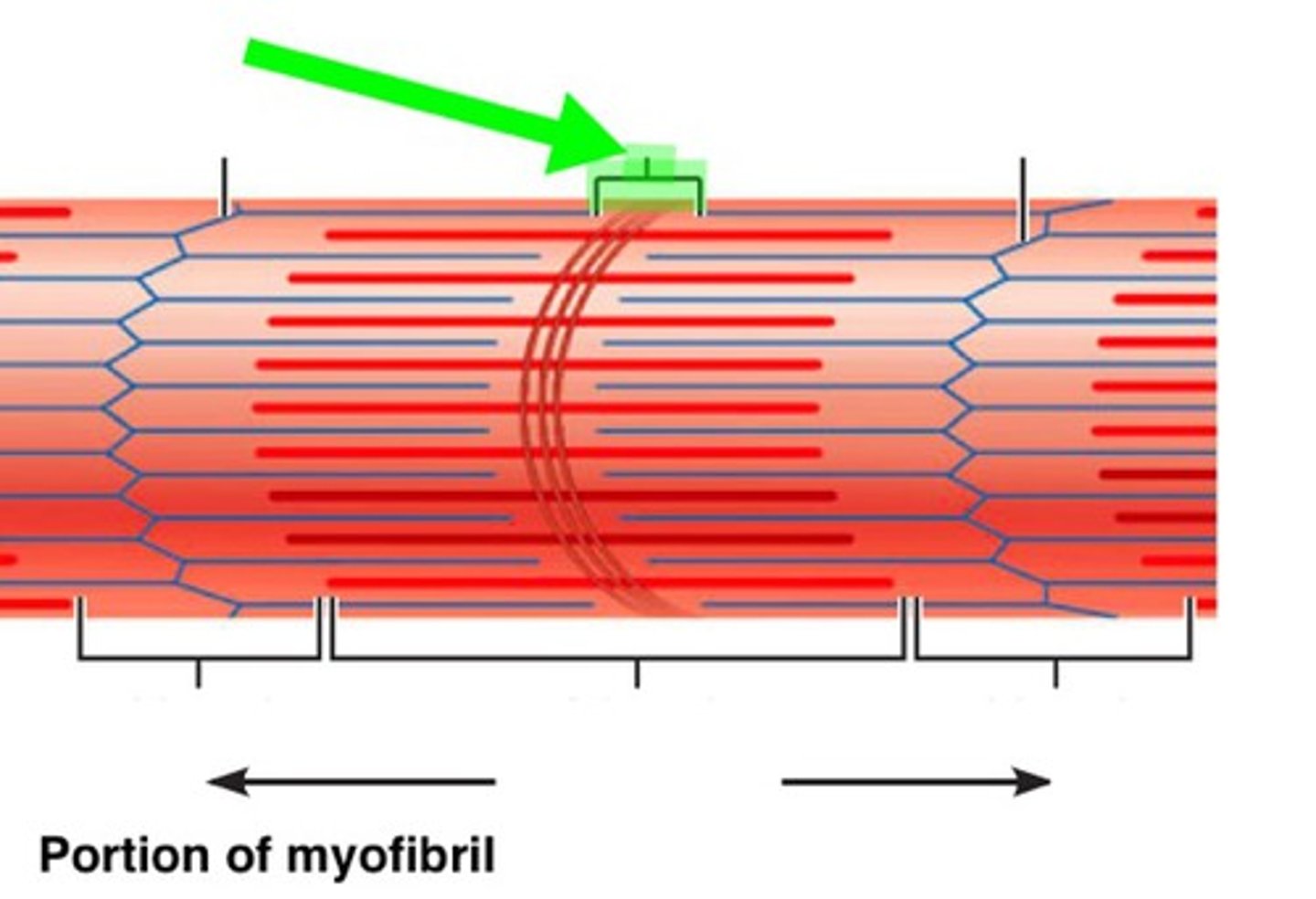
A band
Spans the entire length of thick filaments, including the zone of overlap
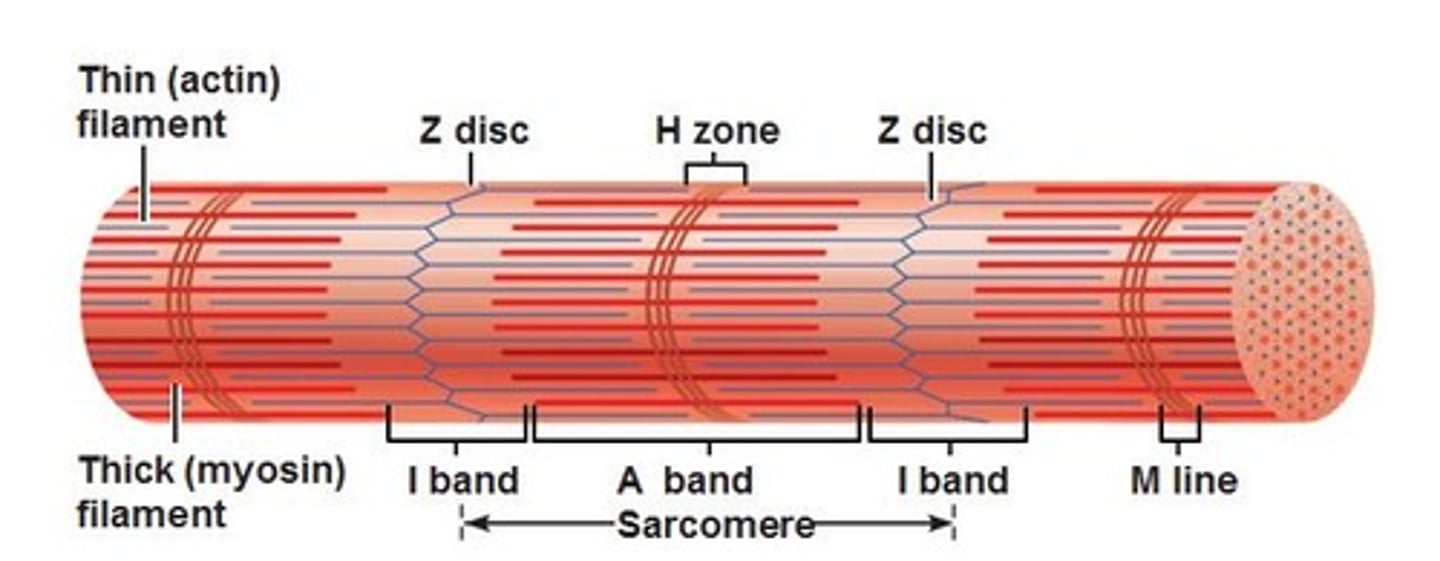
Zone of overlap
Region where thick and thin filaments overlap to produce contraction
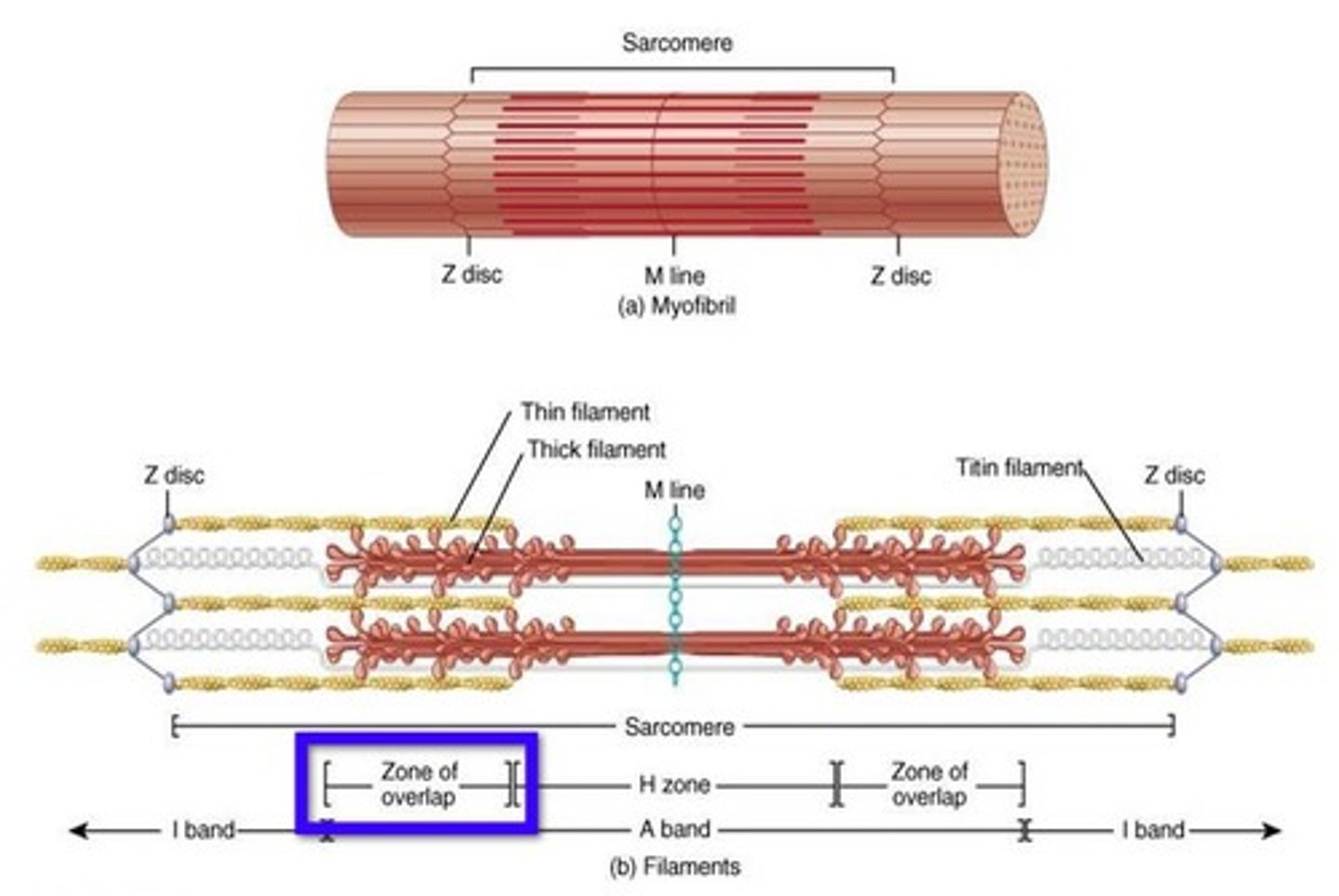
M line
Central structure that helps stabilize the thick filaments
Thin filaments are composed of
Actin, troponin, and tropomyosin
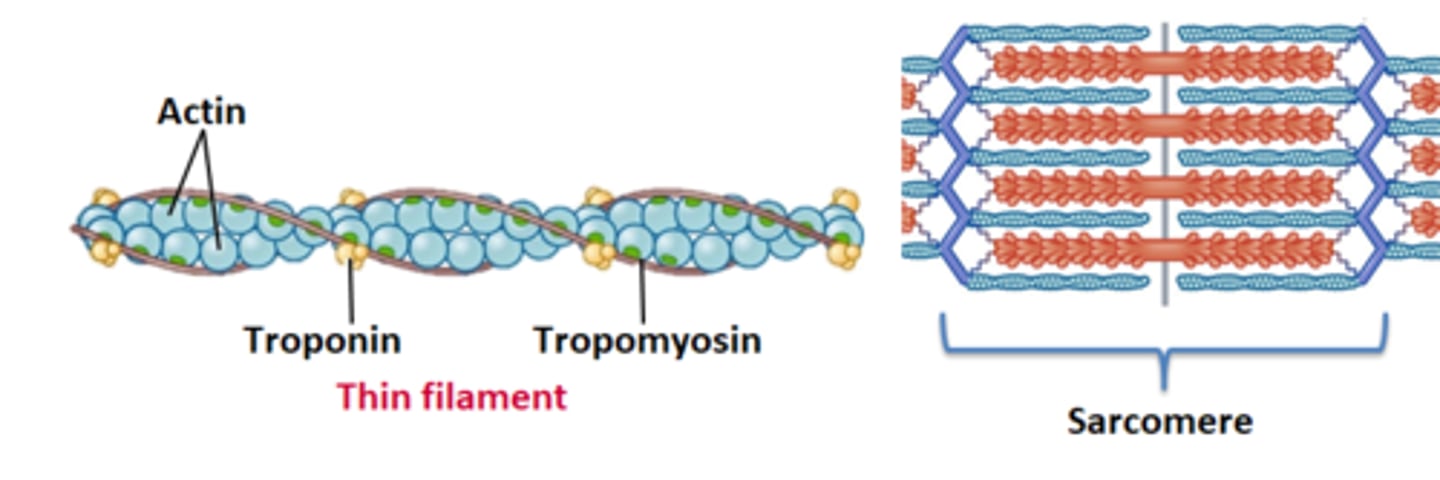
Thick filaments are composed of
Myosin
Origin
Fixed/less moveable attachment (proximal attachment point of muscle)
Insertion
More moveable attachment, moves toward the origin during contraction (distal attachment point)
Agonist
Prime mover: primary muscle that carries out a muscle action
Synergist
Muscle that assists the agonist
Antagonist
Muscle that performs the opposite action of the agonist
Opposes the initial muscle action
Fixator
Muscle that stabilizes the joint so the agonist can function efficiently
Synergist and Antagonist Principles
A muscle cannot be it's own antagonist!
Ex: posterior deltoid fibers can't be an antagonist to the anterior deltoid fibers
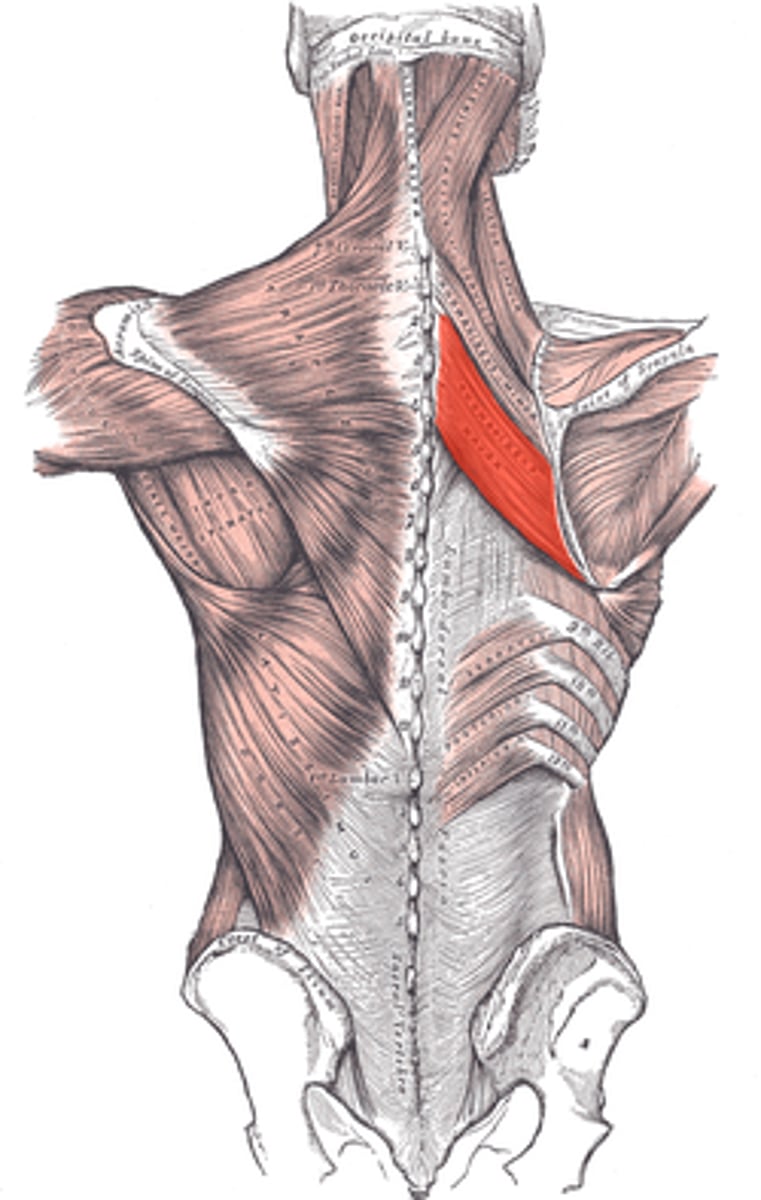
Rhomboid major
adducts/retracts, elevates and inferiorly rotates the scapula
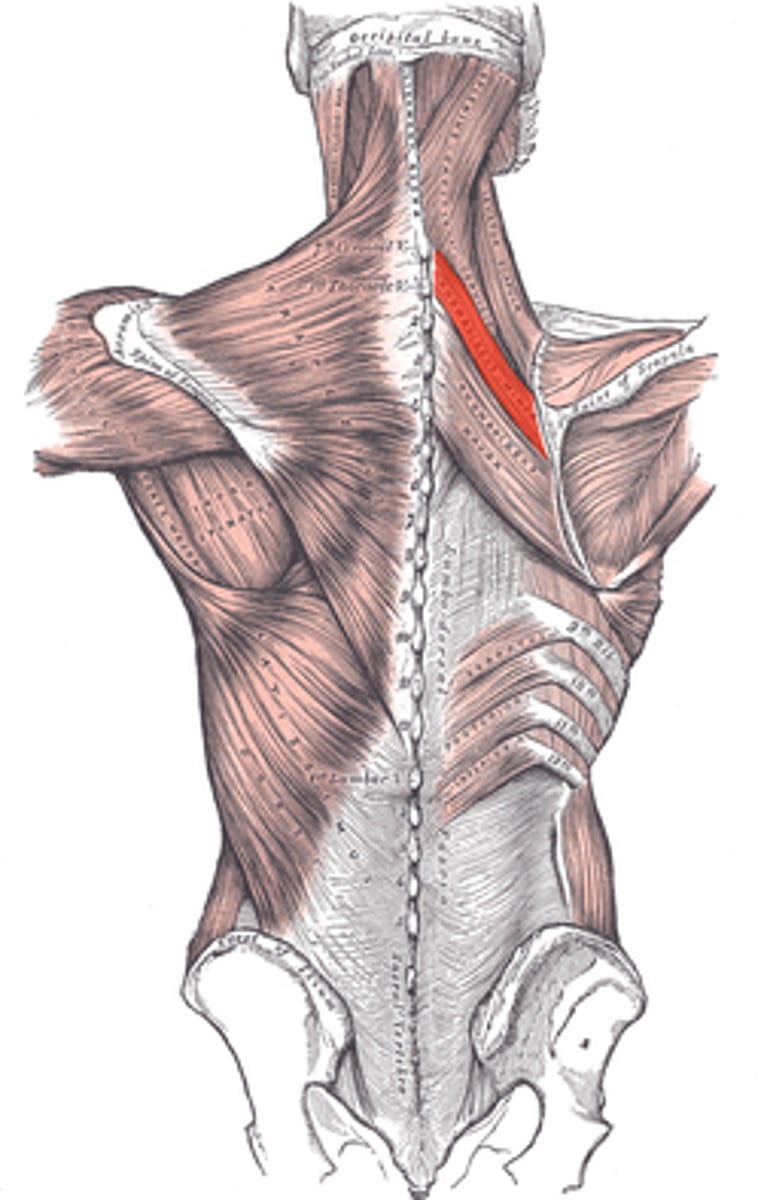
Rhomboid minor
Adducts/retracts, elevates, and inferiorly rotates the scapula
Trapezius
Superior, middle, and inferior fibers
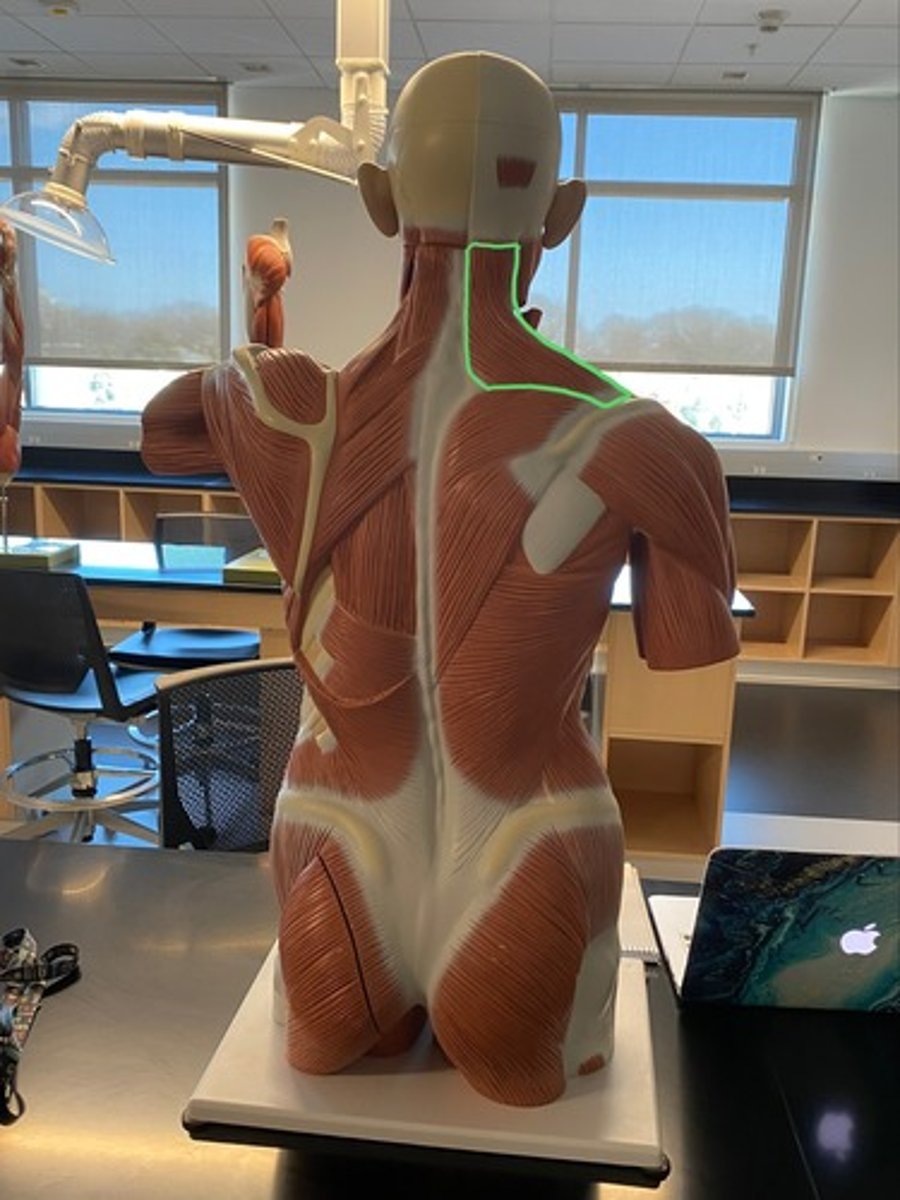
Superior trapezius fibers
Elevate the scapula and clavicle, extend the head, superiorly rotate the scapula
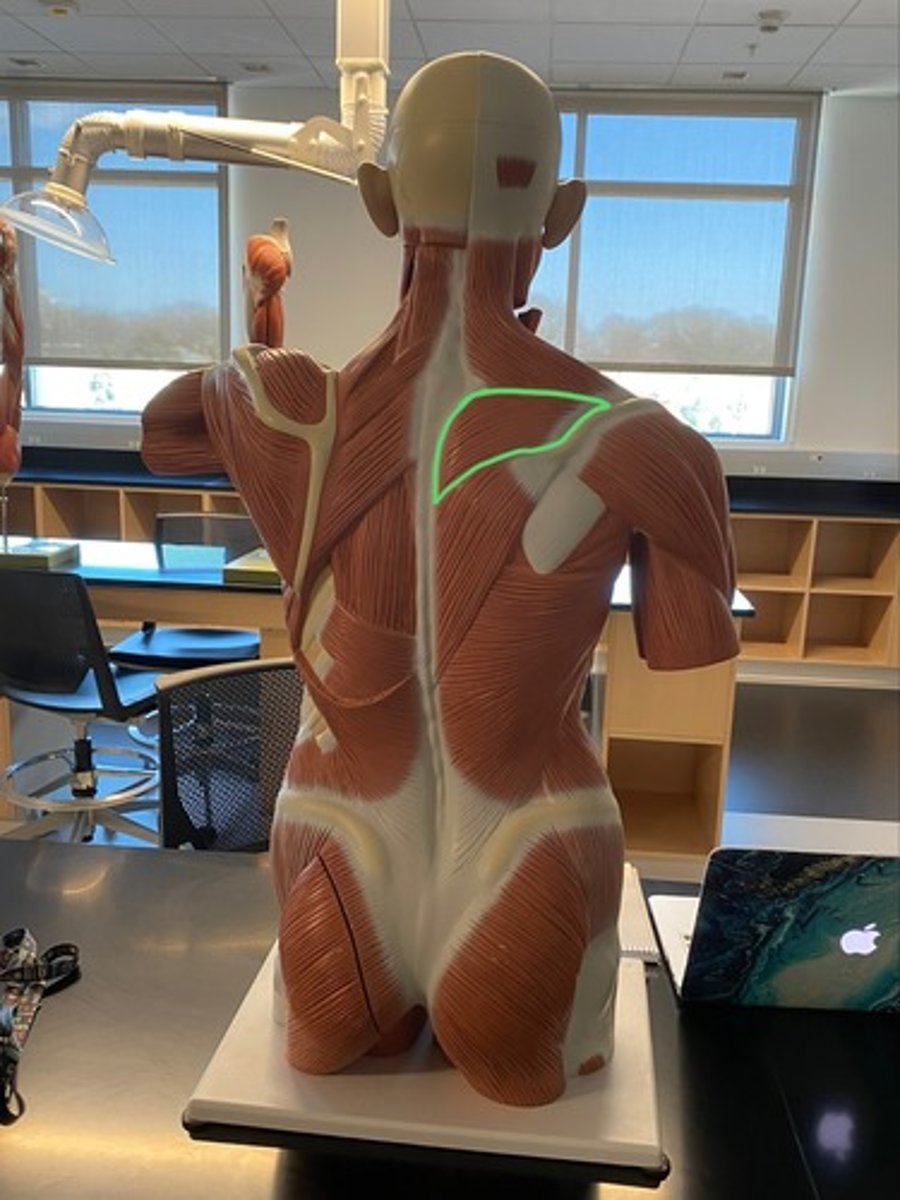
Middle trapezius fibers
Adduct/retract the scapula
Inferior Trapezius Fibers
Depress the scapula
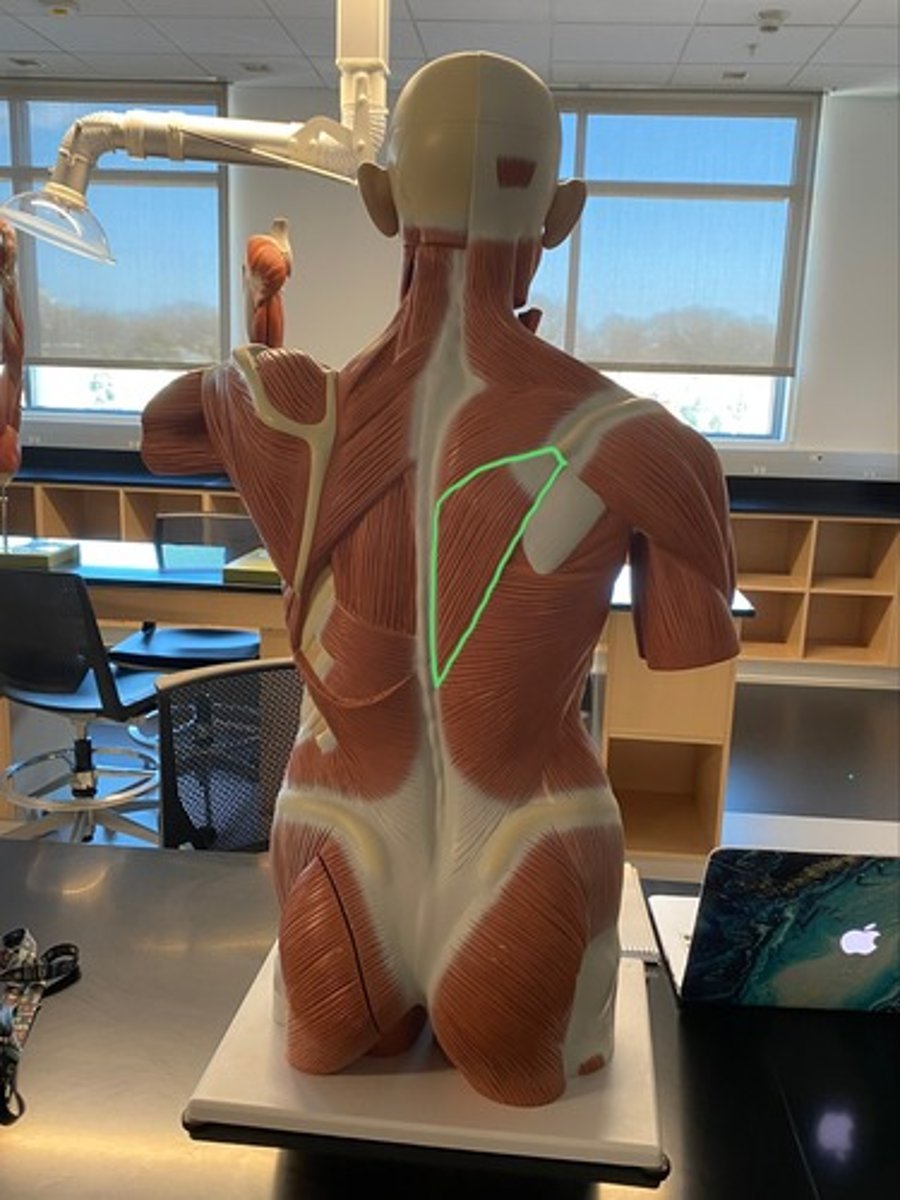
Levator scapulae
Elevates and inferiorly rotates the scapula
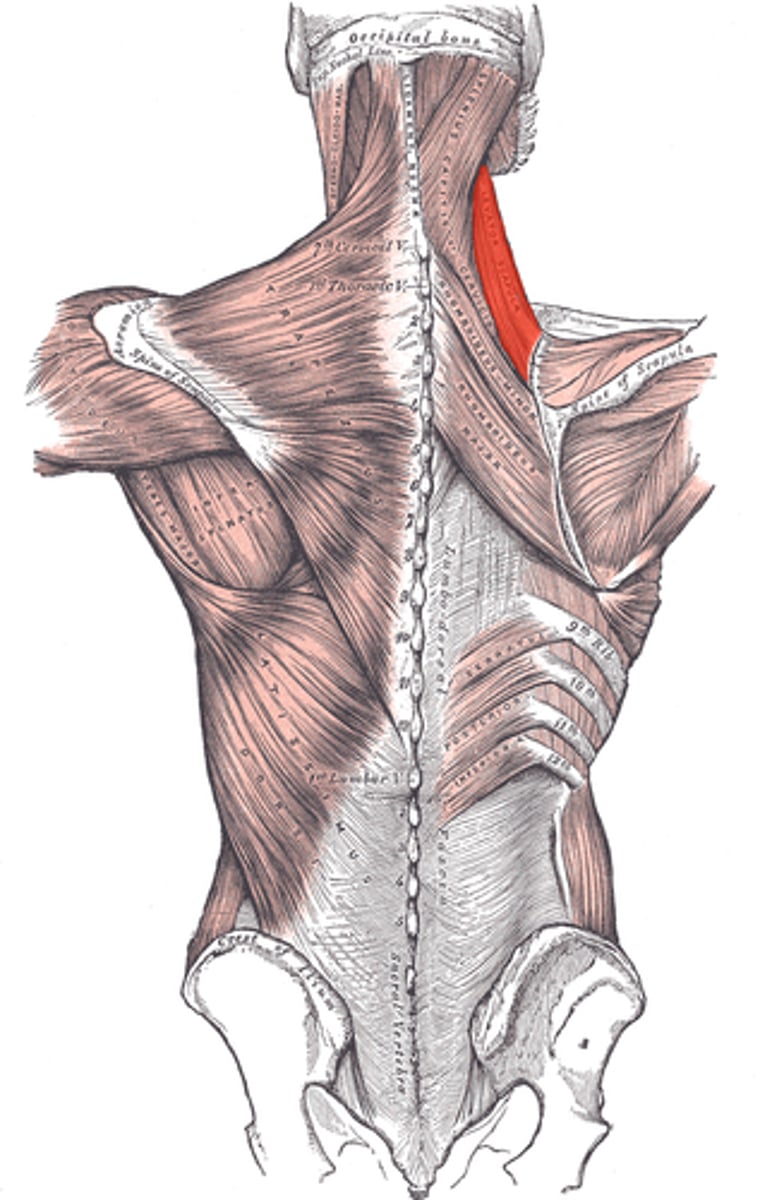
Pectoralis Minor
Depresses, abducts/protracts, and inferiorly rotates the scapula
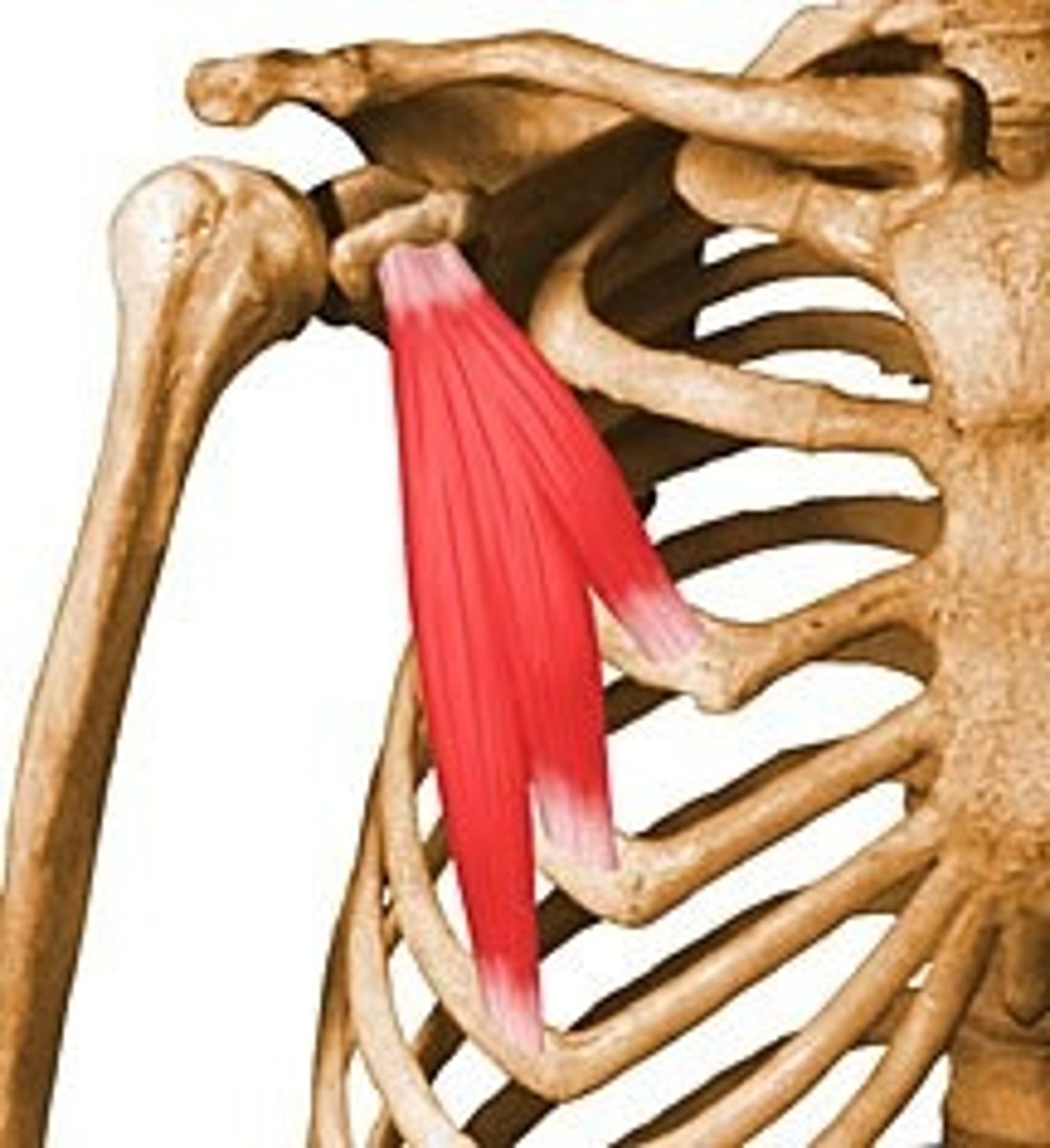
Serratus anterior
Abducts/protracts and superiorly rotates the scapula
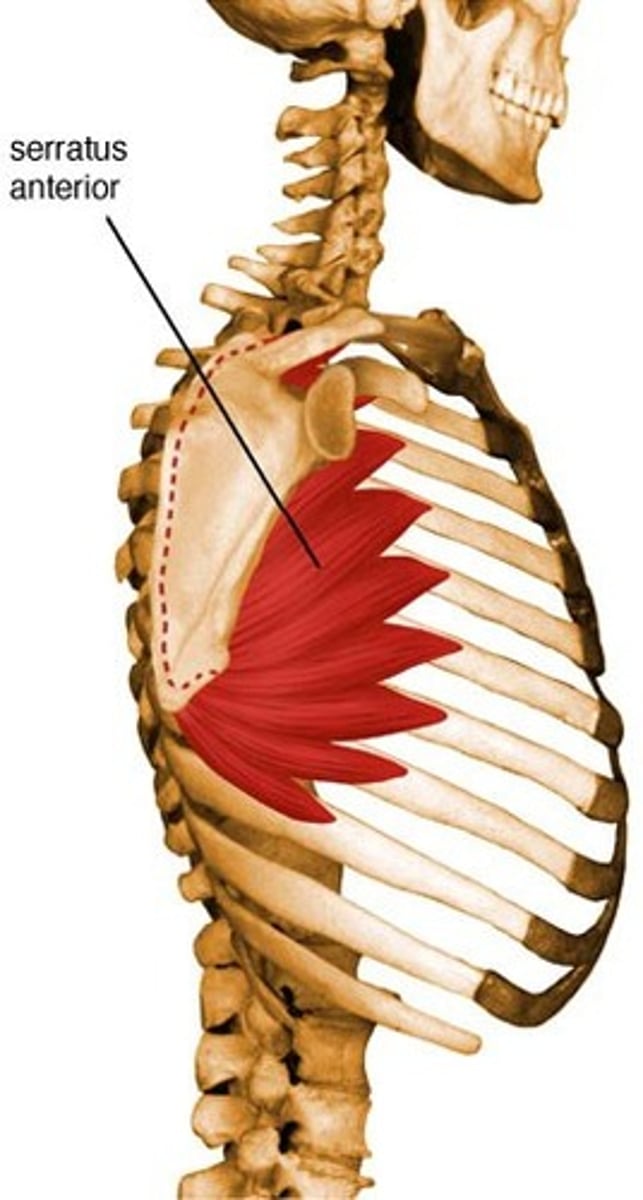
Pectoralis Major
Flexes, adducts, and medially rotates the arm
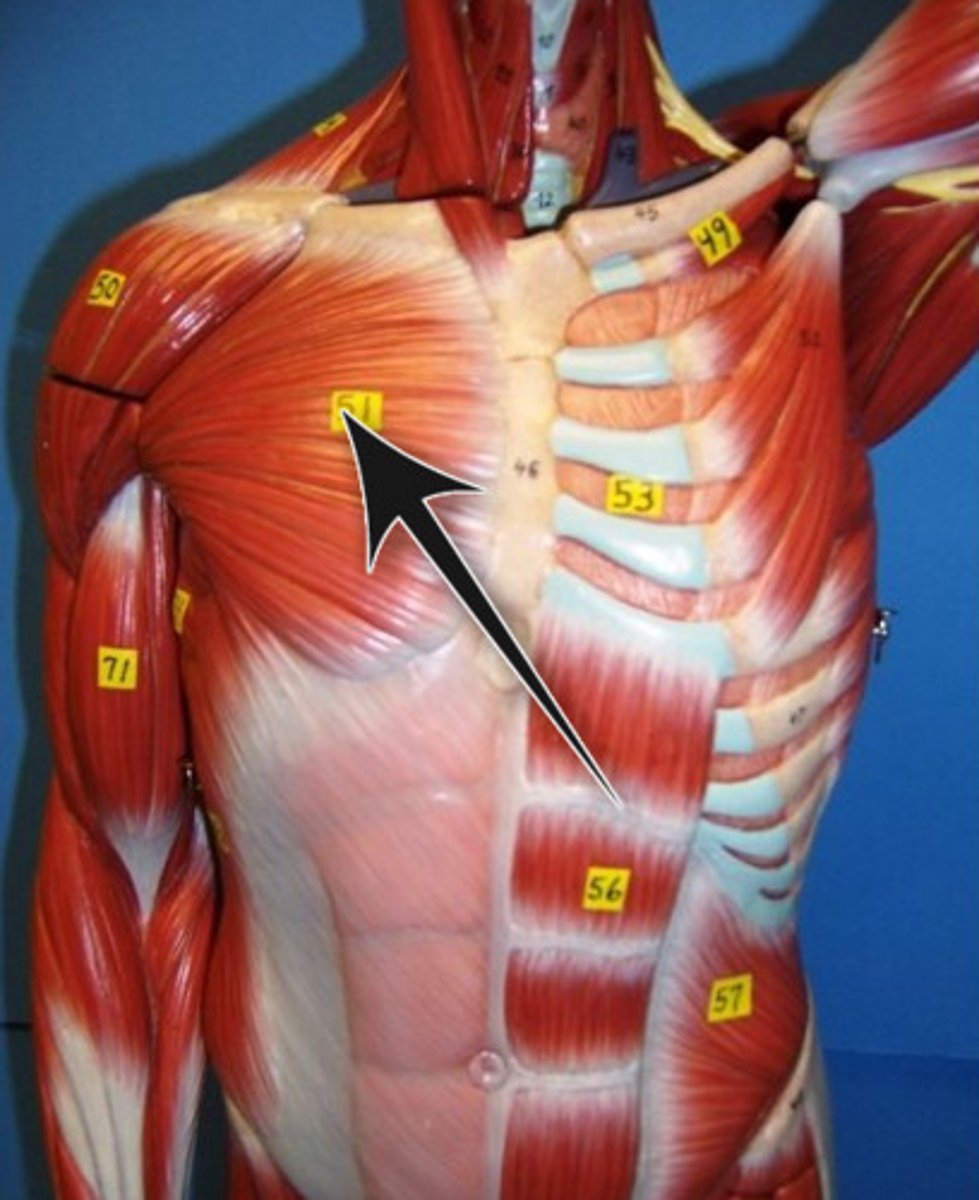
Deltoid
Anterior, middle, and posterior fibers
Anterior deltoid fibers
Flex and medially rotate the arm
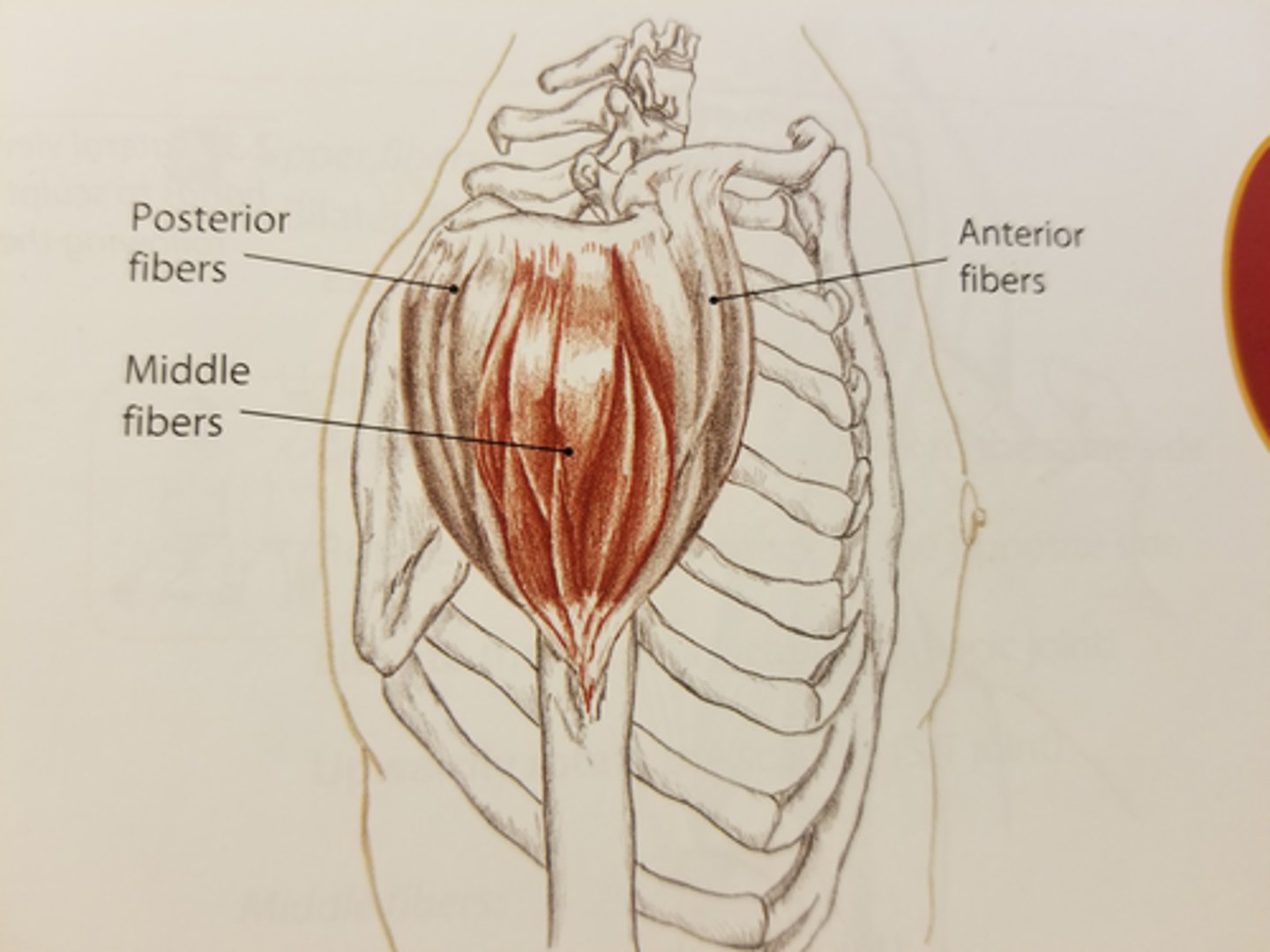
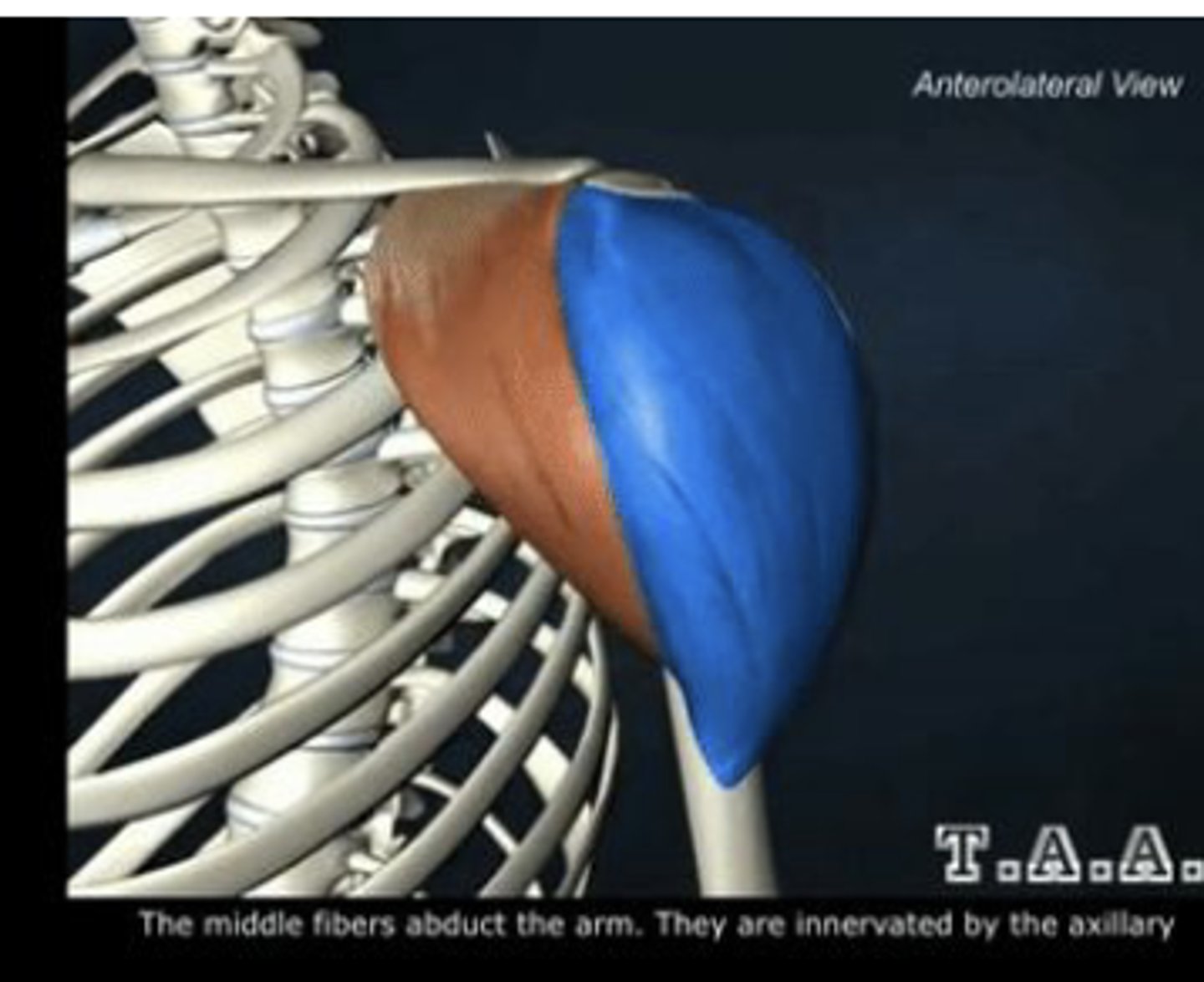
Middle deltoid fibers
Abduct the arm
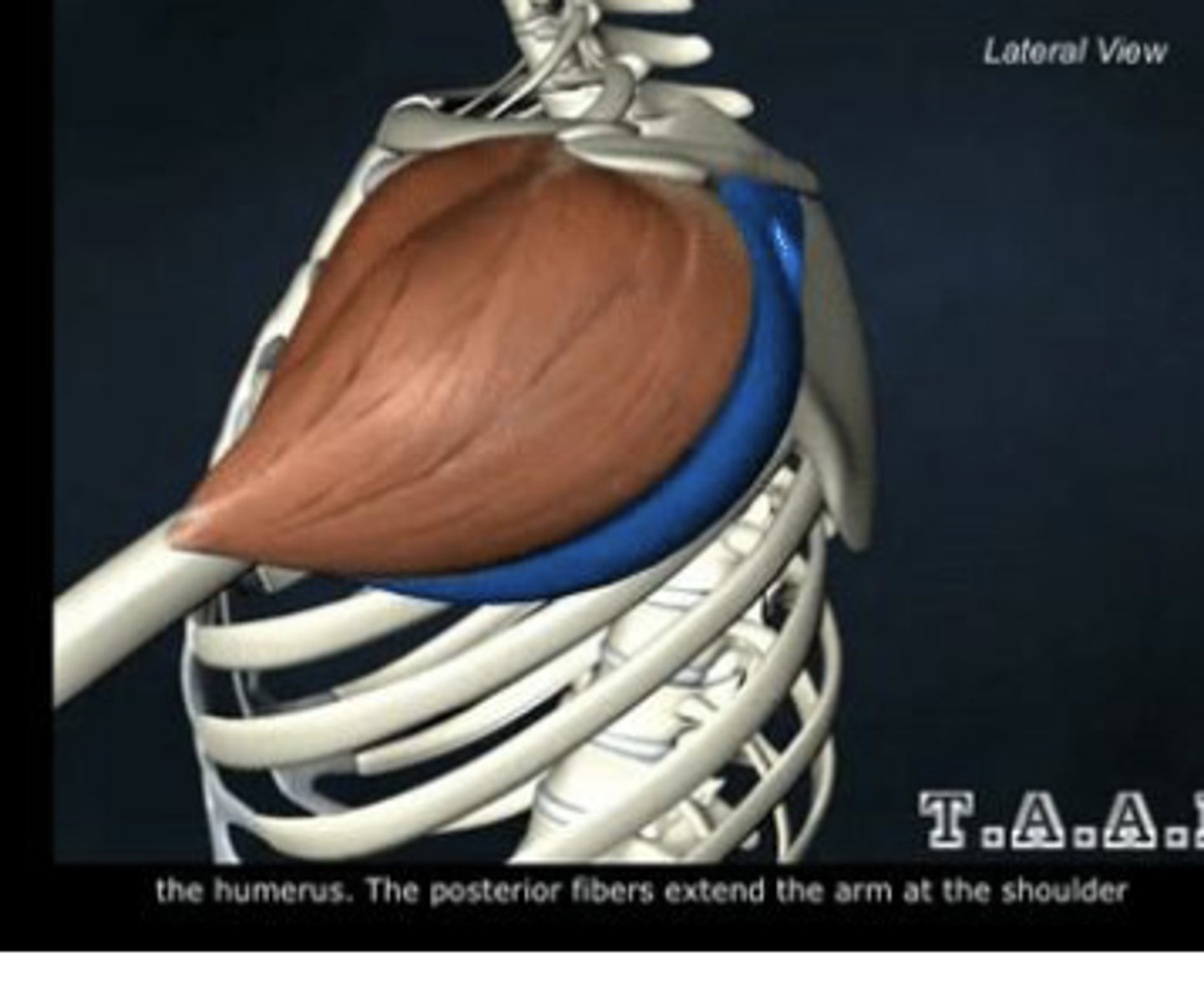
Posterior deltoid fibers
Extend and laterally rotate the arm
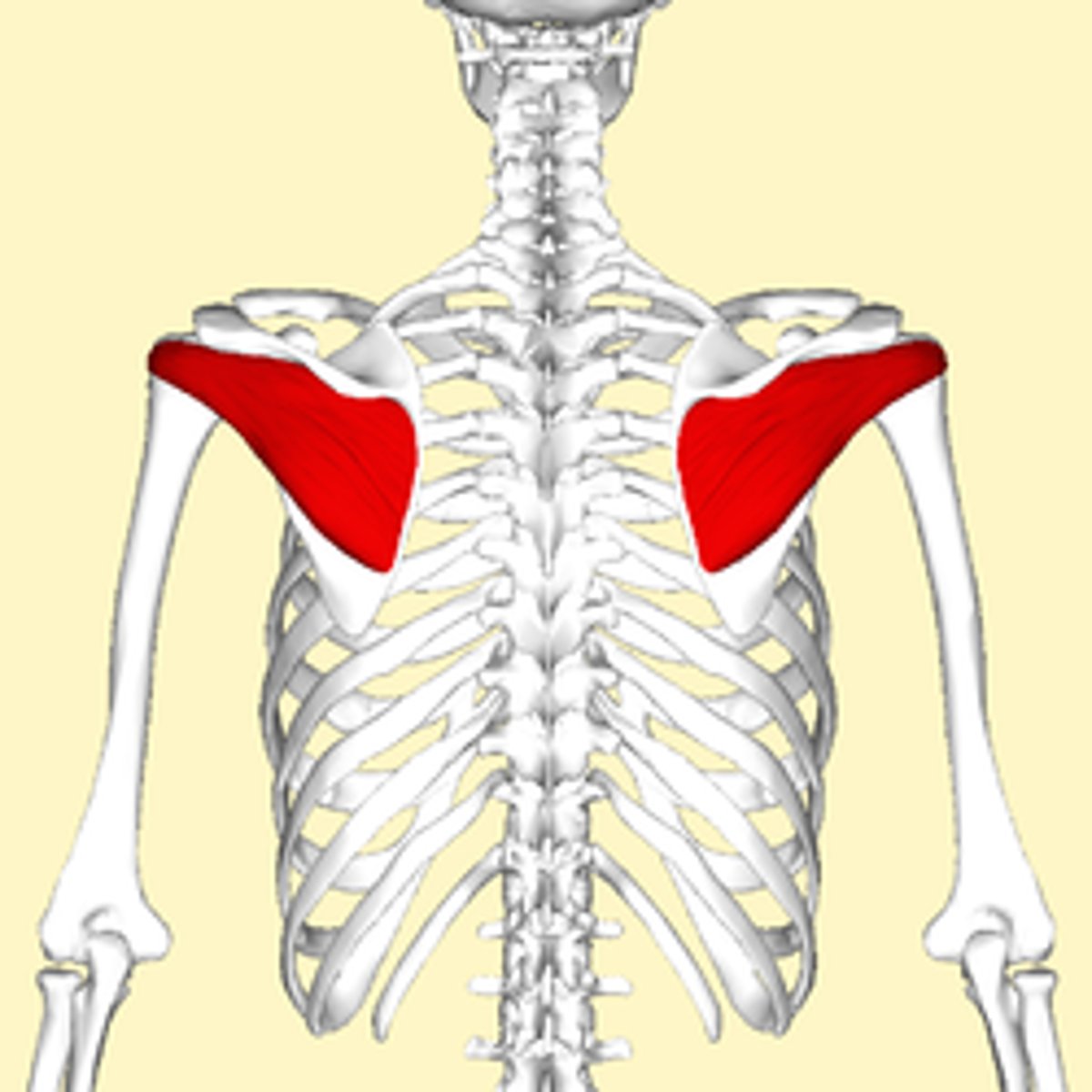
Supraspinatus
Abducts the arm
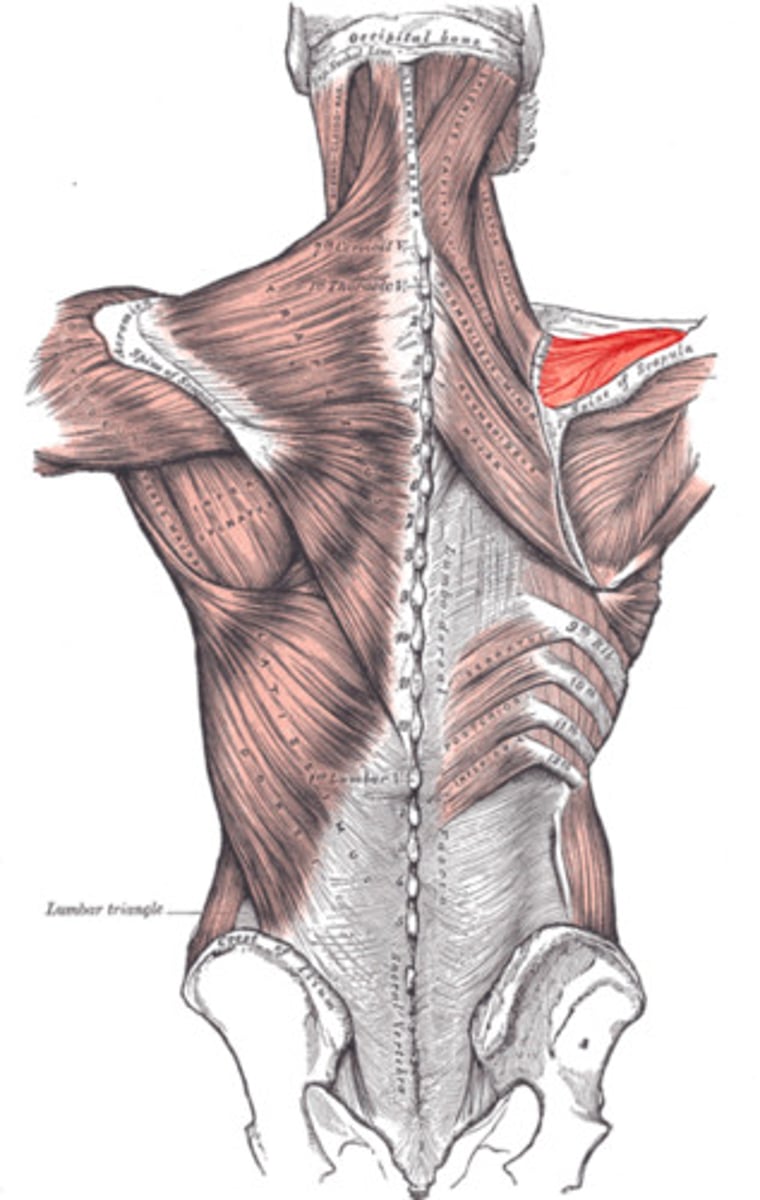
Infraspinatus
Adducts and laterally rotates the arm
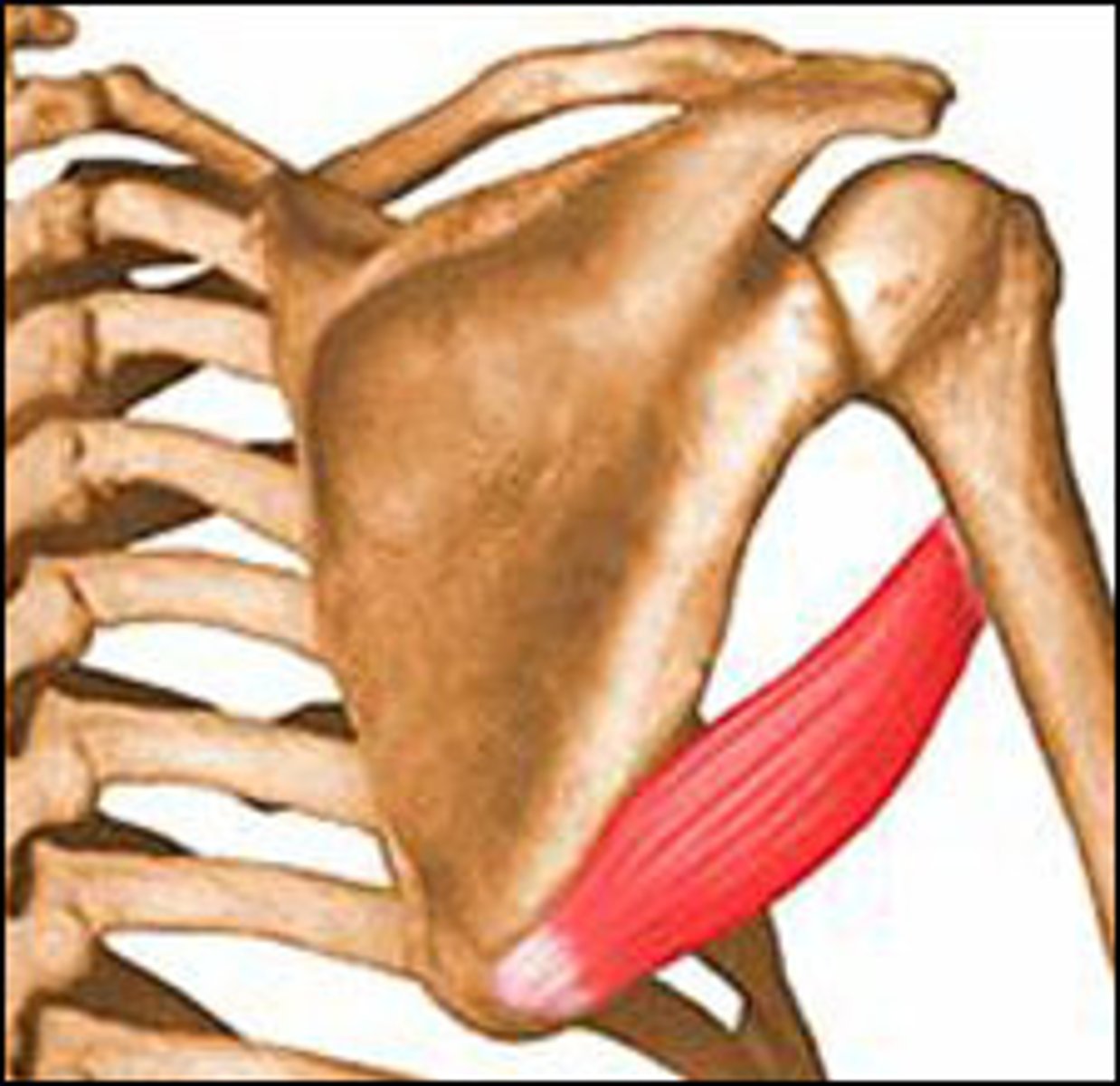
Teres major
Extends, adducts, and medially rotates the arm
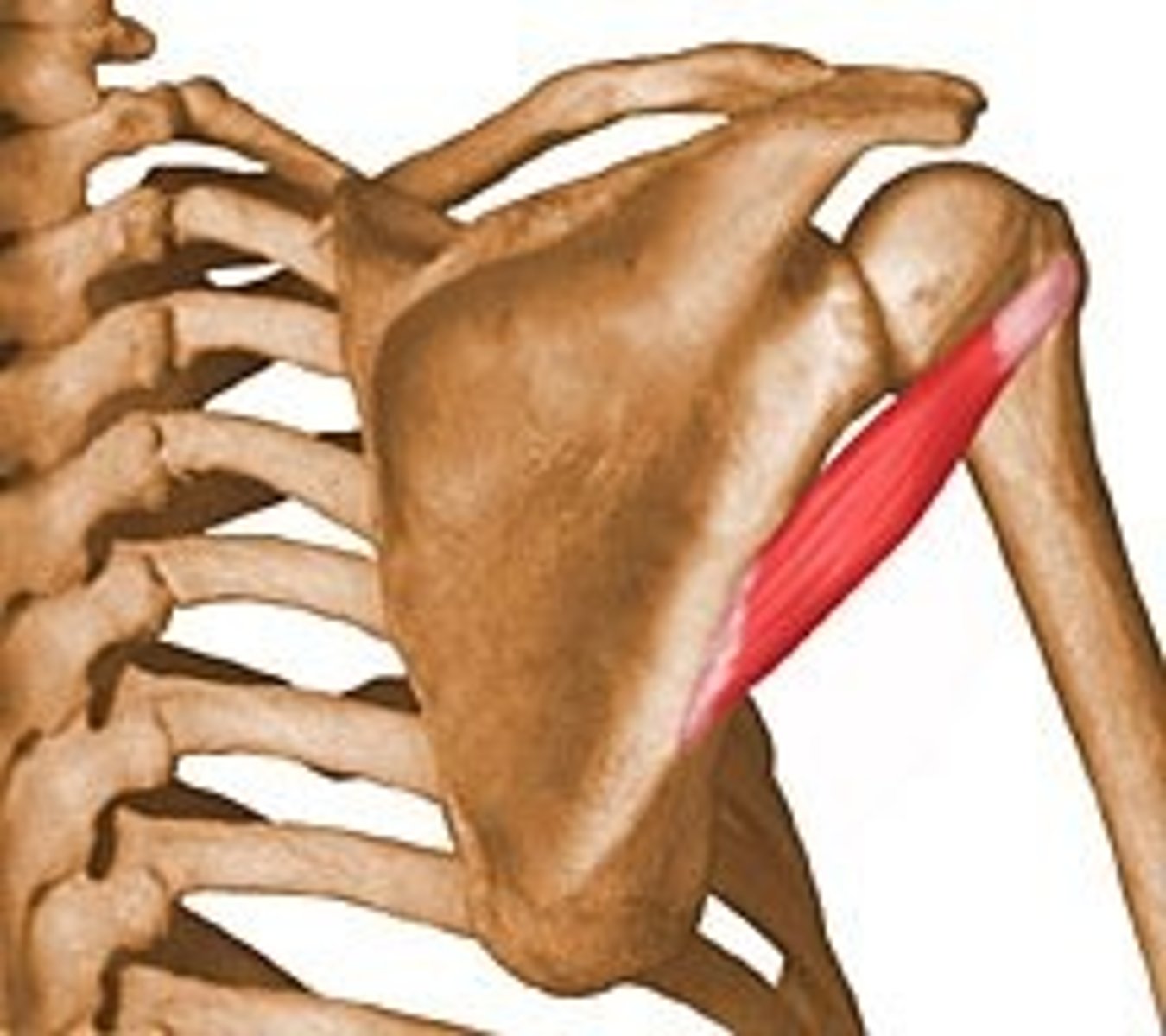
Teres minor
Extends and laterally rotates the arm
Subscapularis
Medially rotates the arm
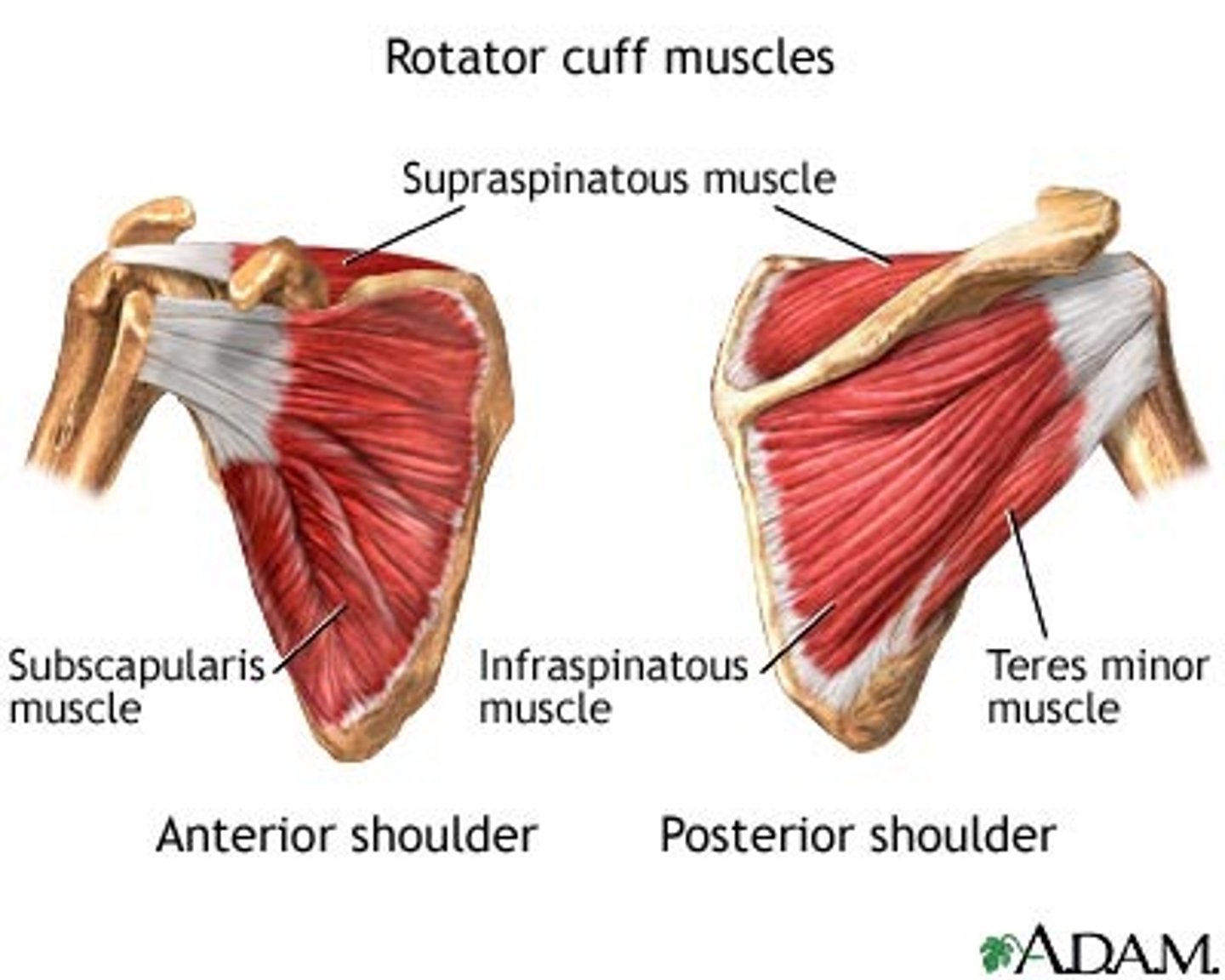
Rotator cuff muscles
SITS
Supraspinatus
Infraspinatus
Teres minor
Subscapularis
They stabilize the head of the humerus against the glenoid cavity of the scapula
Rotator cuff tear
Injury to one or more of the muscles/tendons from overuse in sports or heavy lifting
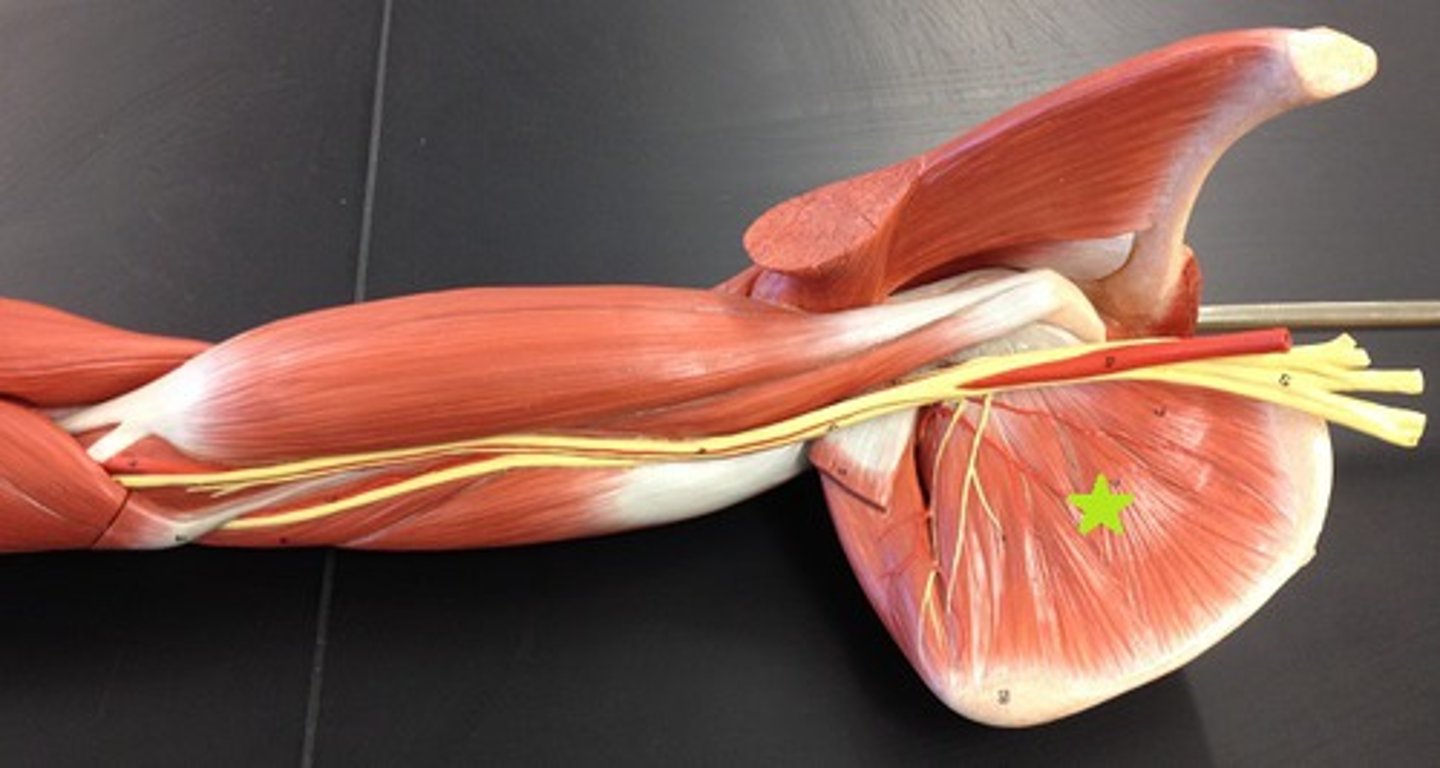
Which muscle is most commonly affected in a rotator cuff tear?
Supraspinatus due to impingement under the acromion of the scapula
Symptoms of a rotator cuff tear
Shoulder pain, weakness, and difficulty with mobility(abduction and external rotation of the arm)
Treatment for a rotator cuff tear
Ice, NSAIDs, physical therapy, surgery for severe cases
Latissimus Dorsi
Adducts, extends, and medially rotates the arm
Biceps brachii
Flexes and supinates the forearm, flexes the arm
Brachialis
Flexes the forearm
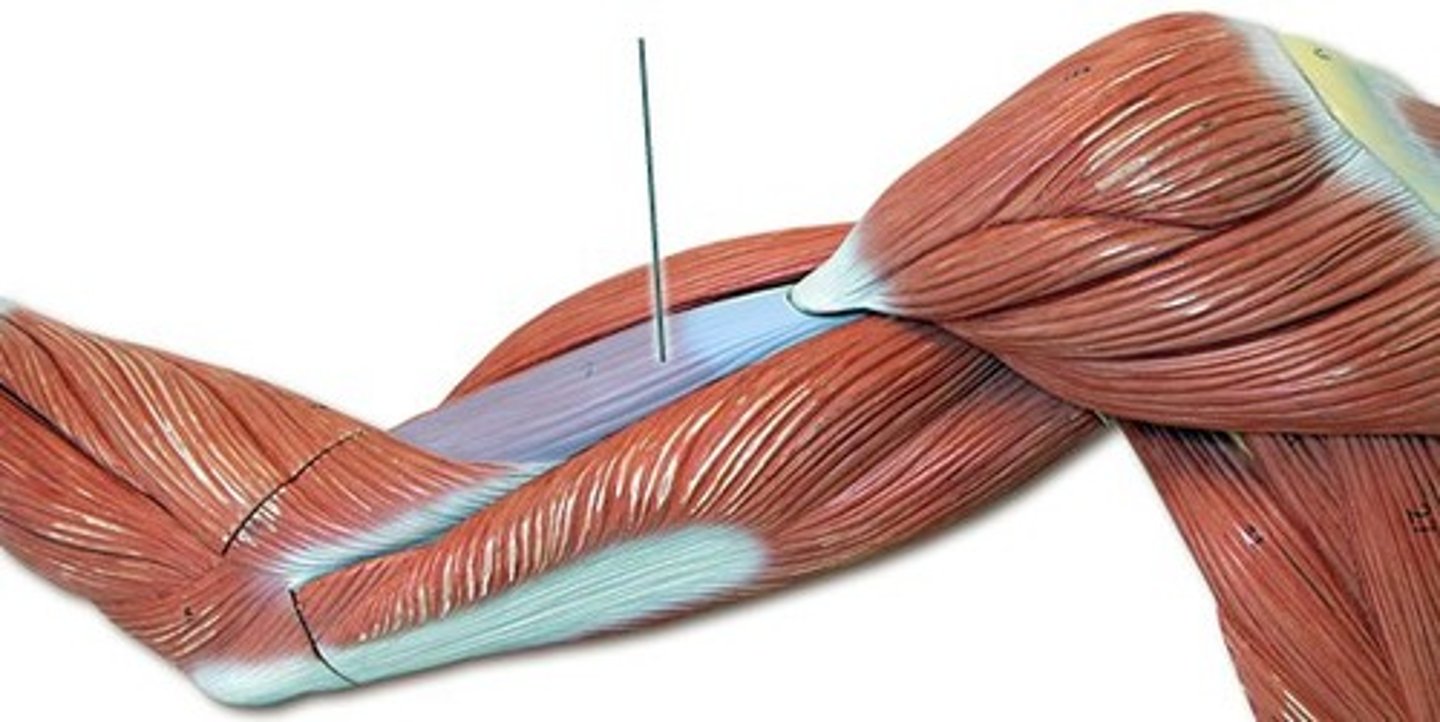
Triceps Brachii
Extends the forearm and extends the arm
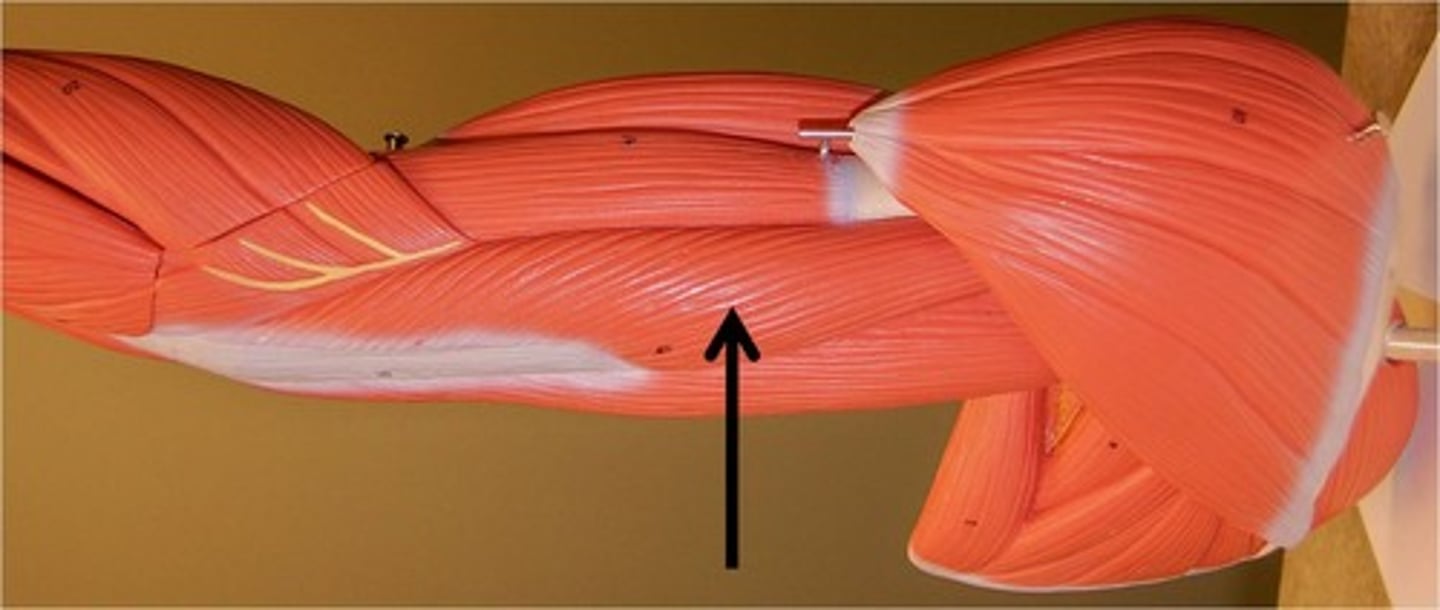
Pronator Teres
Pronates and flexes the forearm
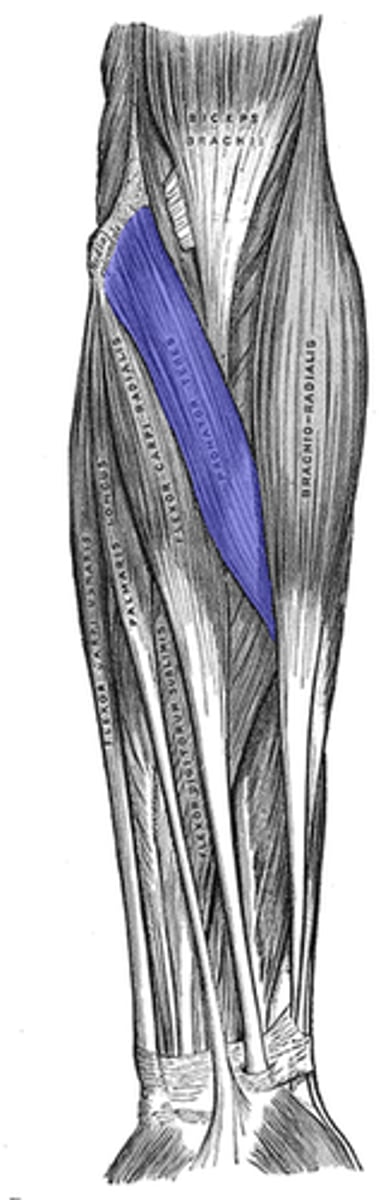
Brachioradialis
Pronates and flexes the forearm
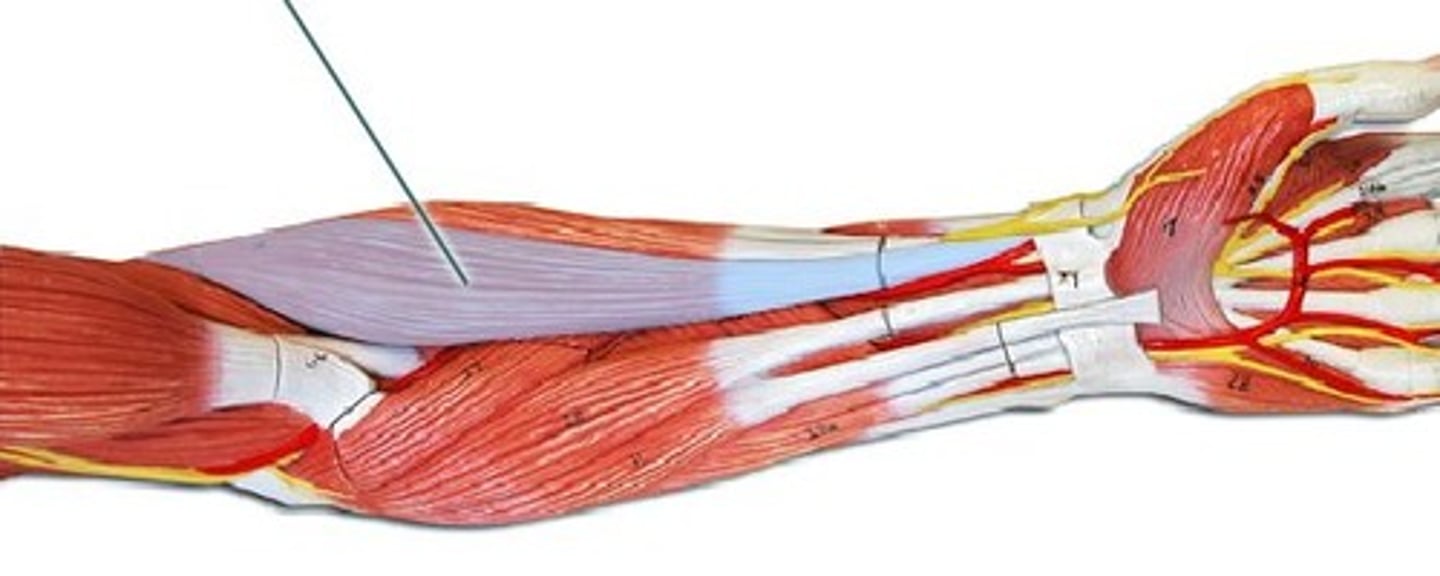
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
Flexes and adducts the hand
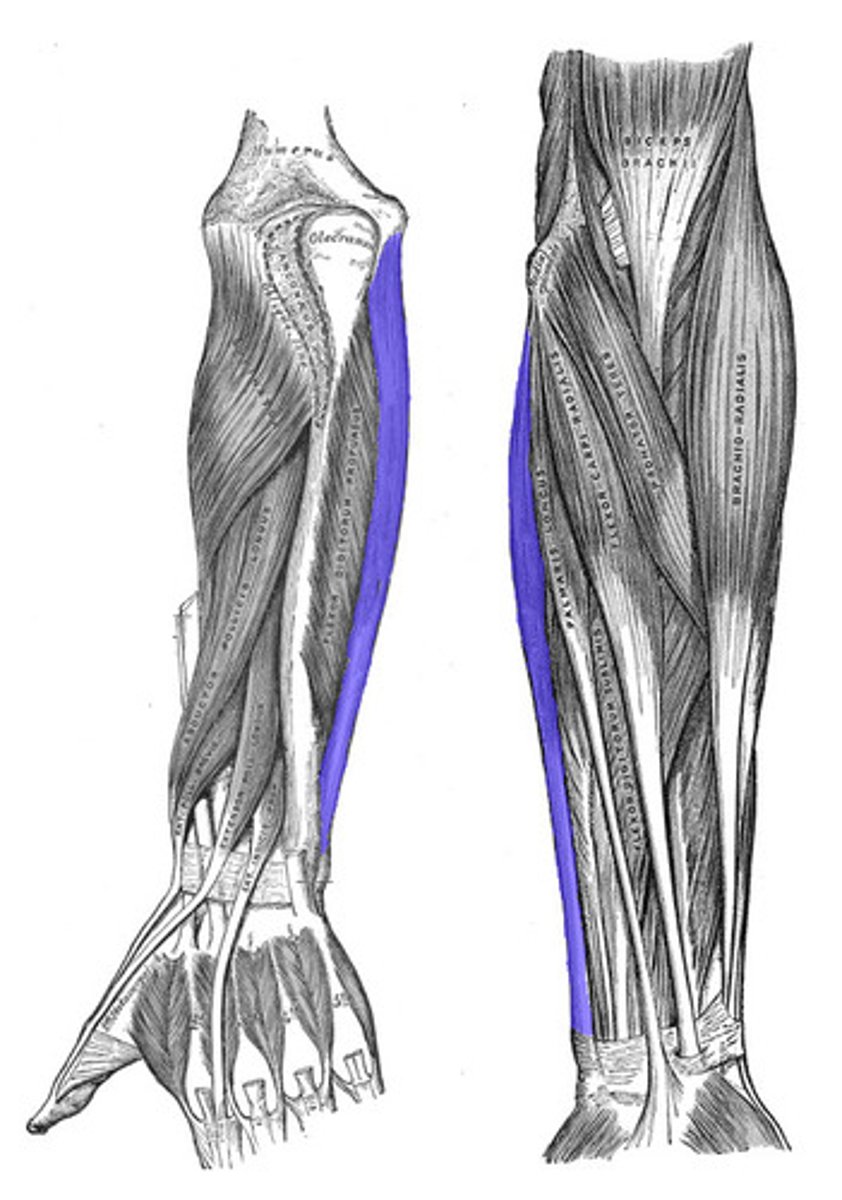
Flexor carpi radialis
Flexes and abducts the hand
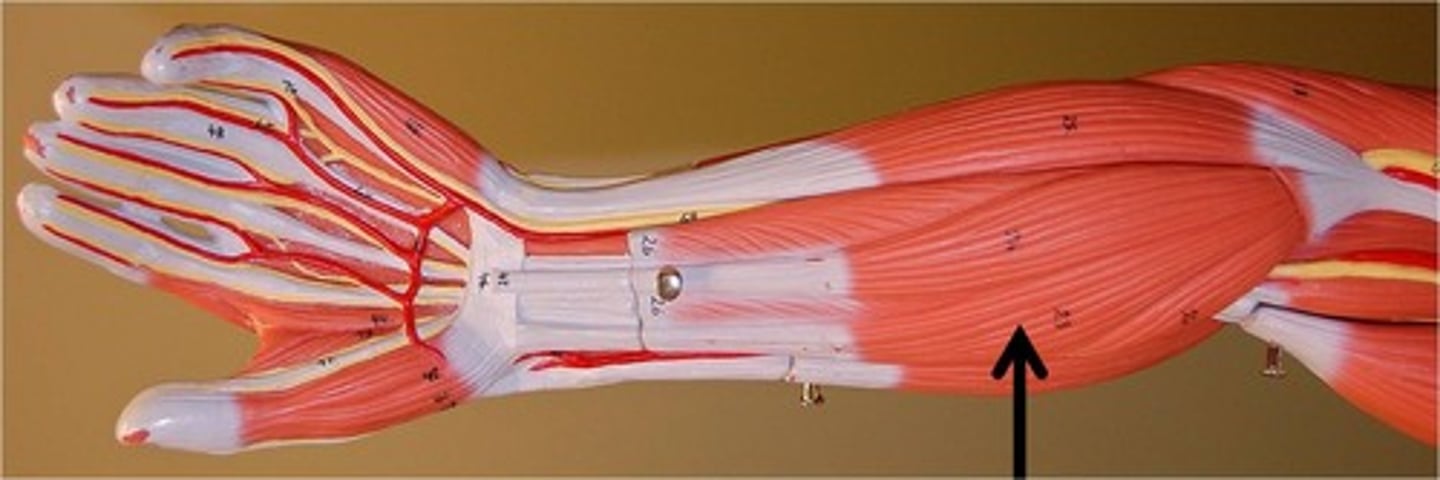
Flexor digitorum superficialis
Flexes digits II-V of the hand
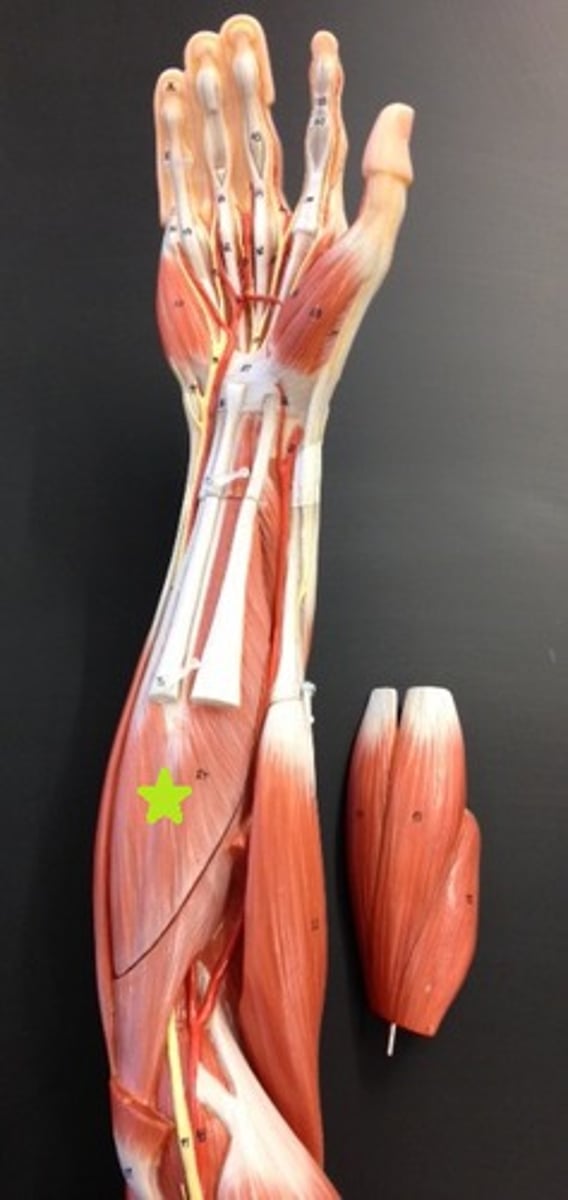
Flexor digitorum profundus
Flexes digits II-V of the hand
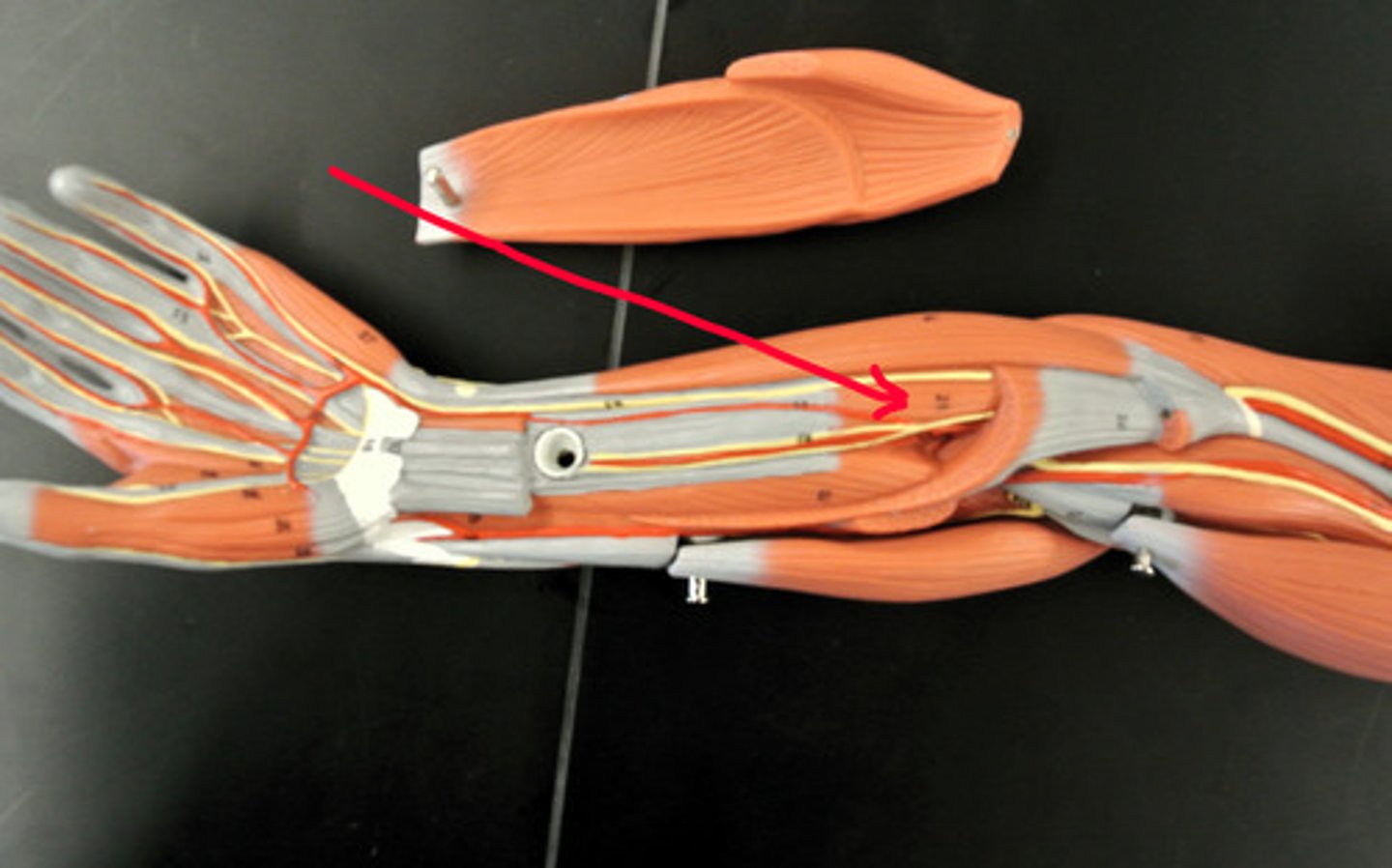
Palmaris longus
Flexes the hand
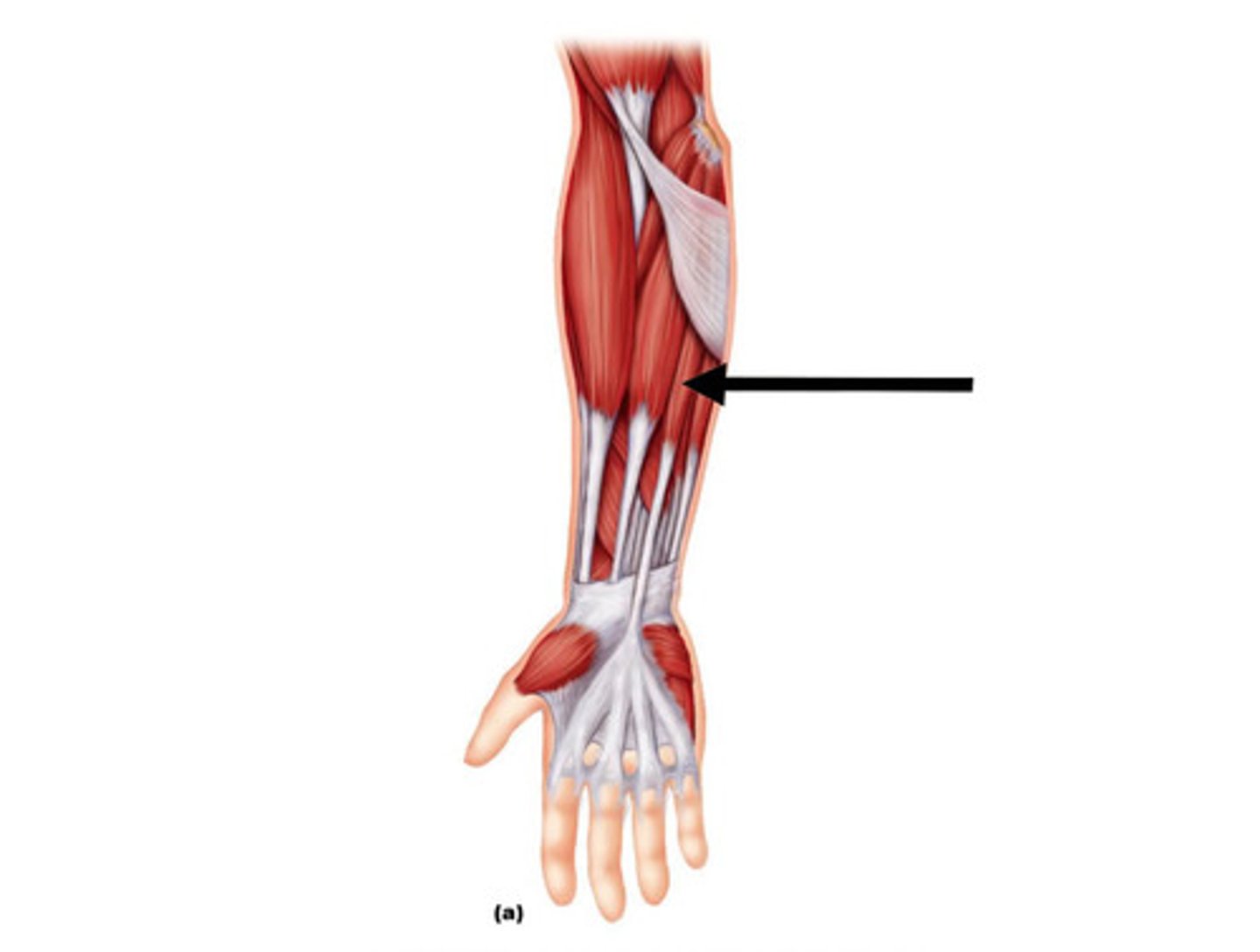
Extensor pollicis brevis
Extends the pollex(thumb)
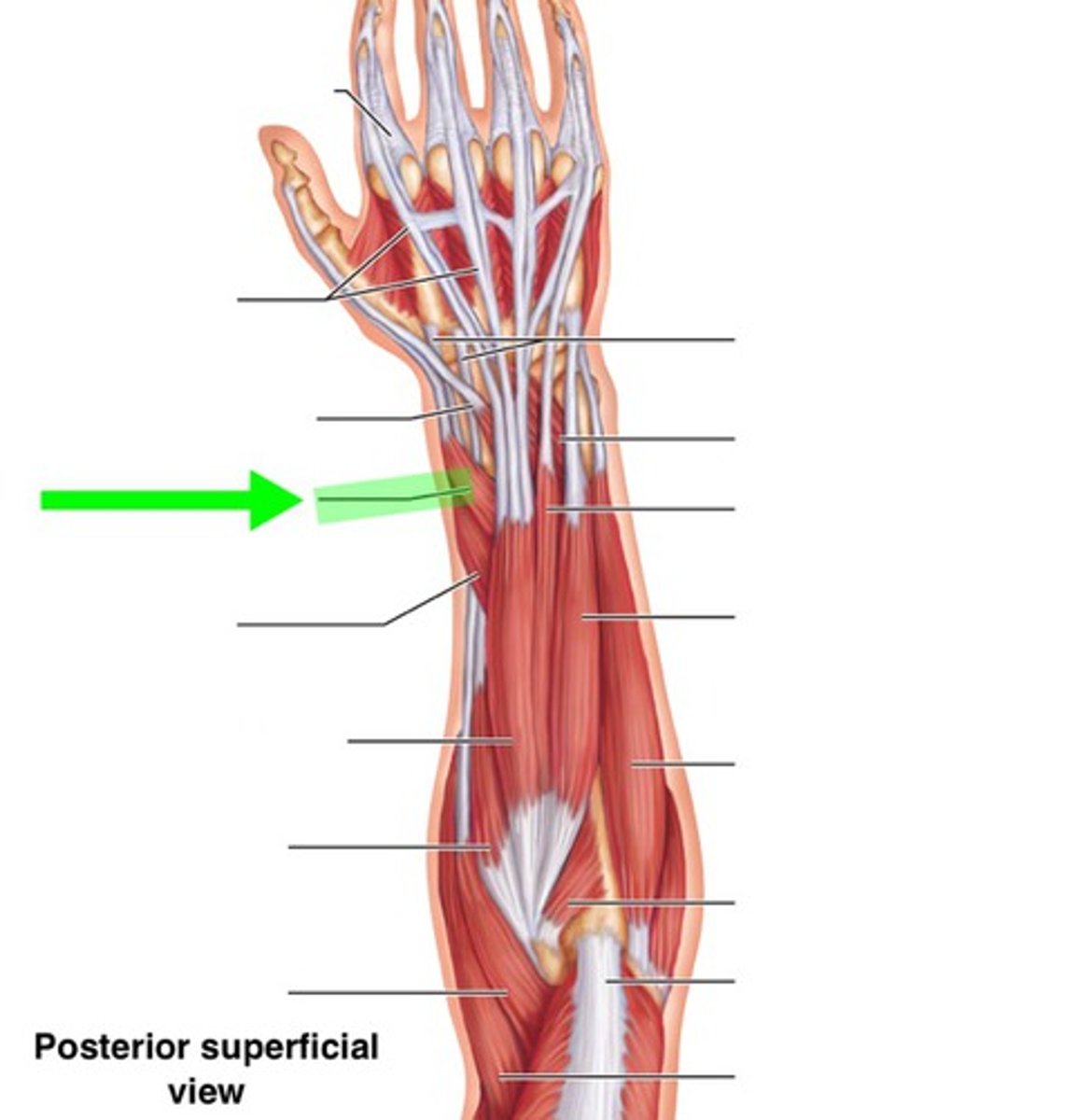
Abductor pollicis longus
Extends and abducts the pollex
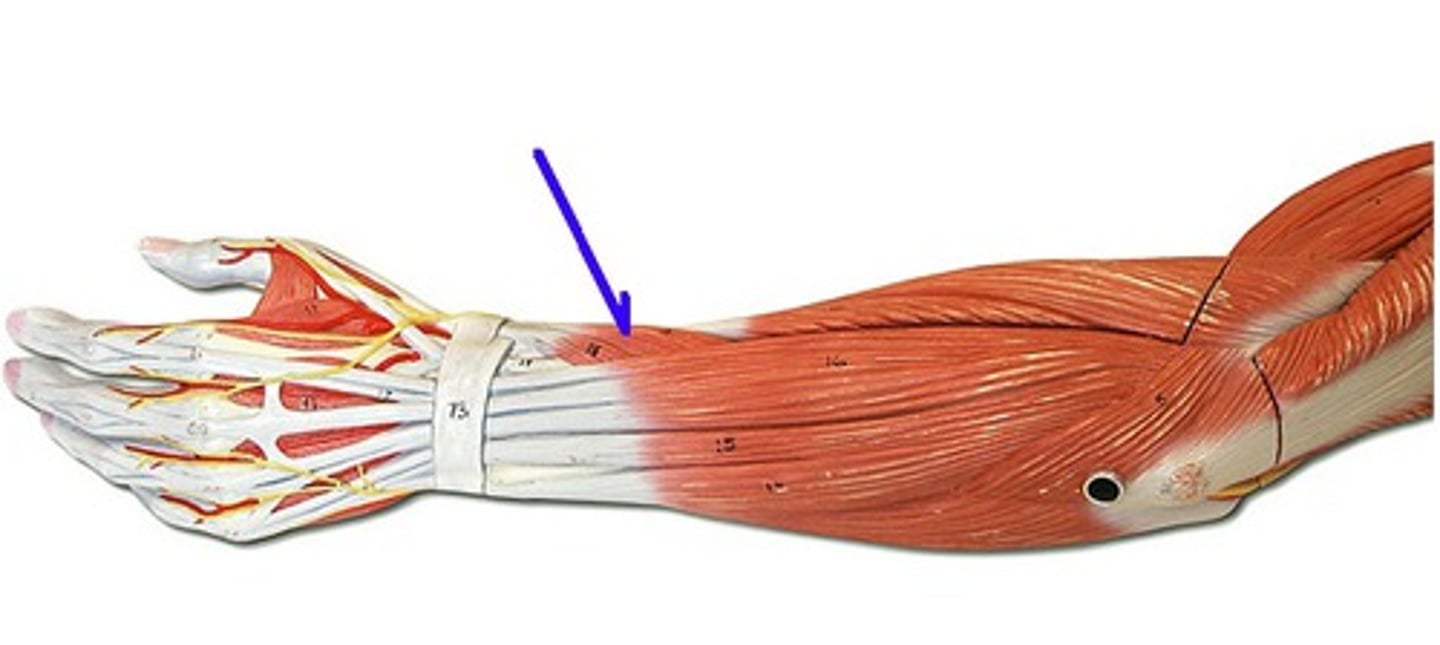
Extensor carpi radialis longus
Extends and abducts hand
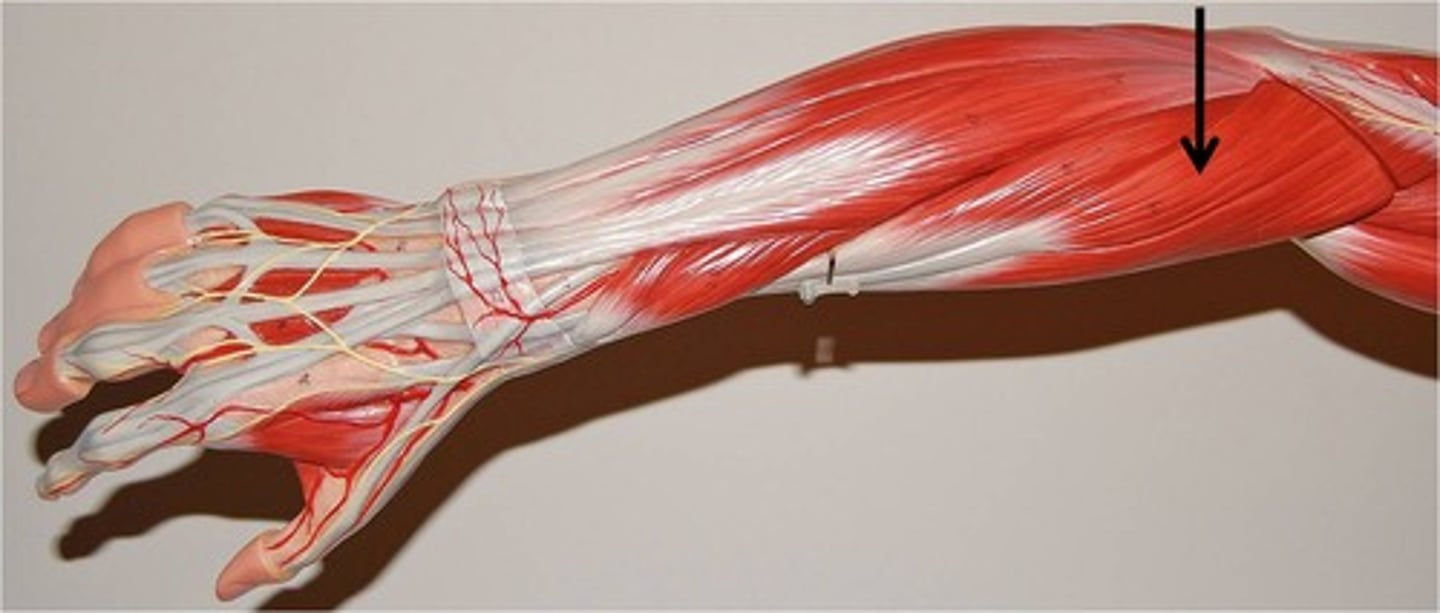
Extensor carpi radialis brevis
Extends and abducts the hand
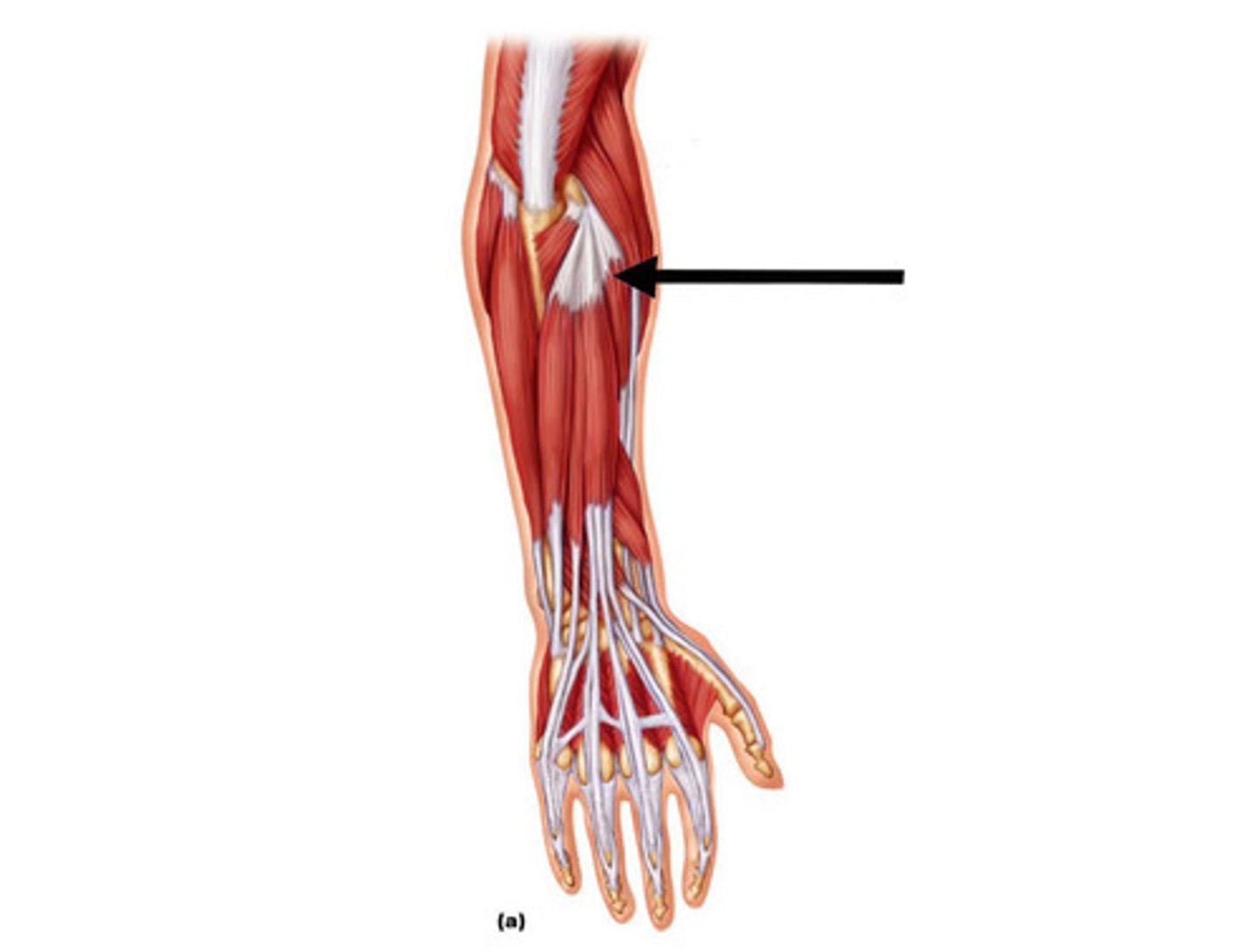
Extensor carpi ulnaris
Extends and adducts the hand
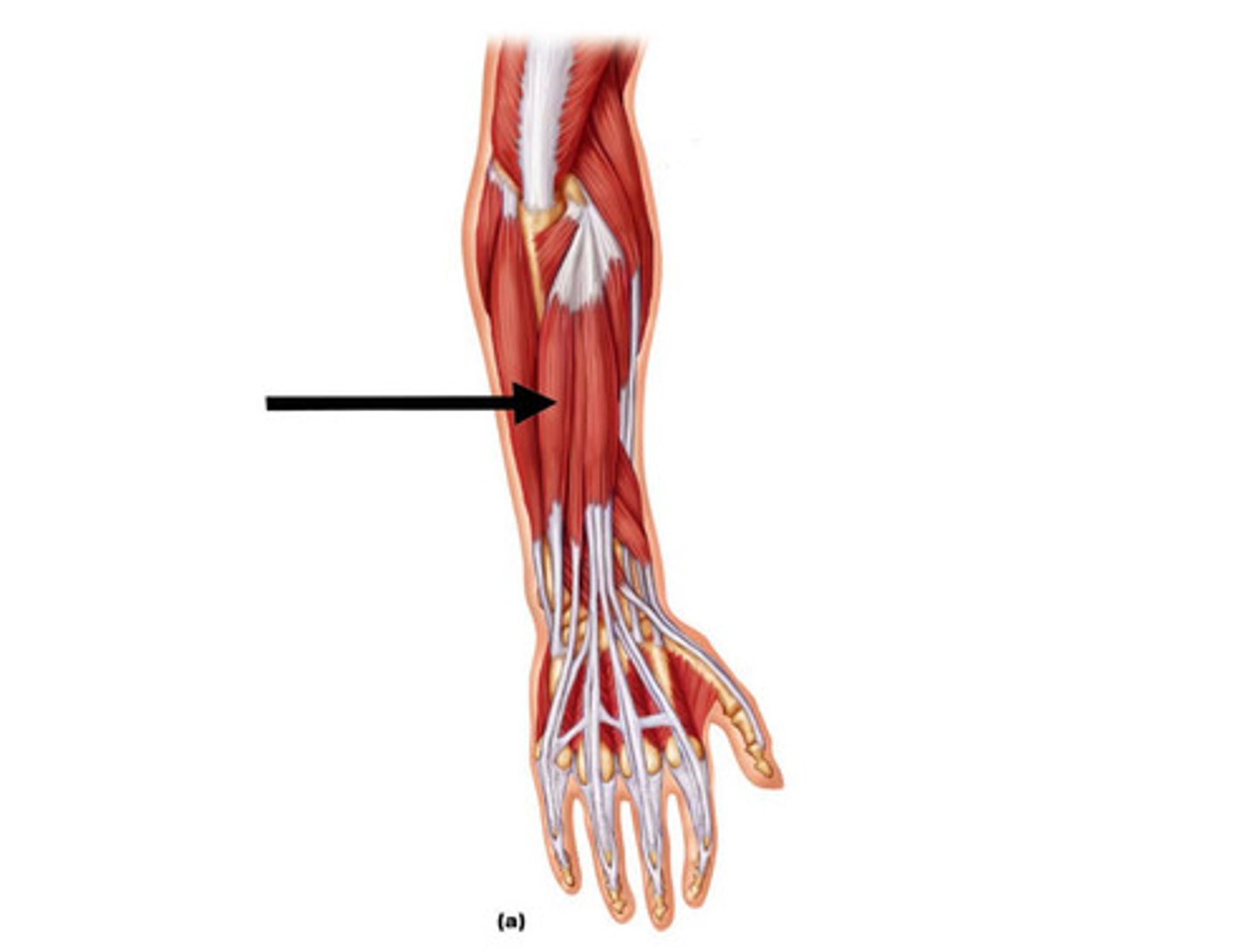
Extensor digitorum
Extends digits II-V of the hand
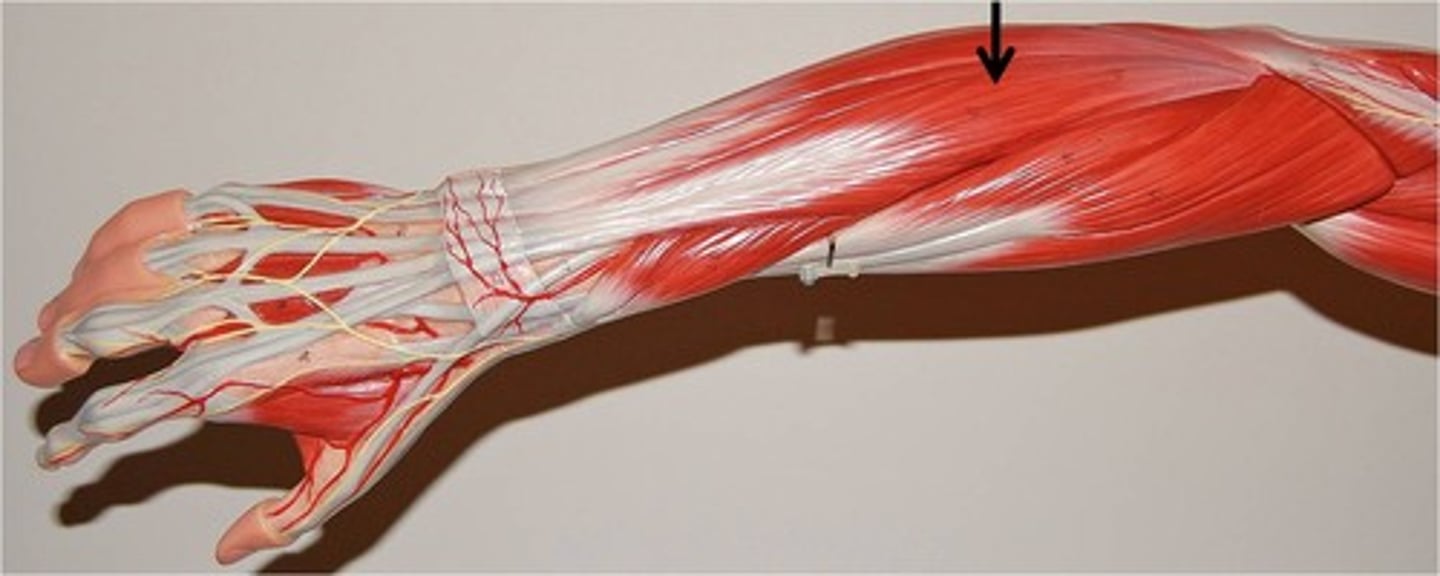
Extensor digiti minimi
Extends digit V
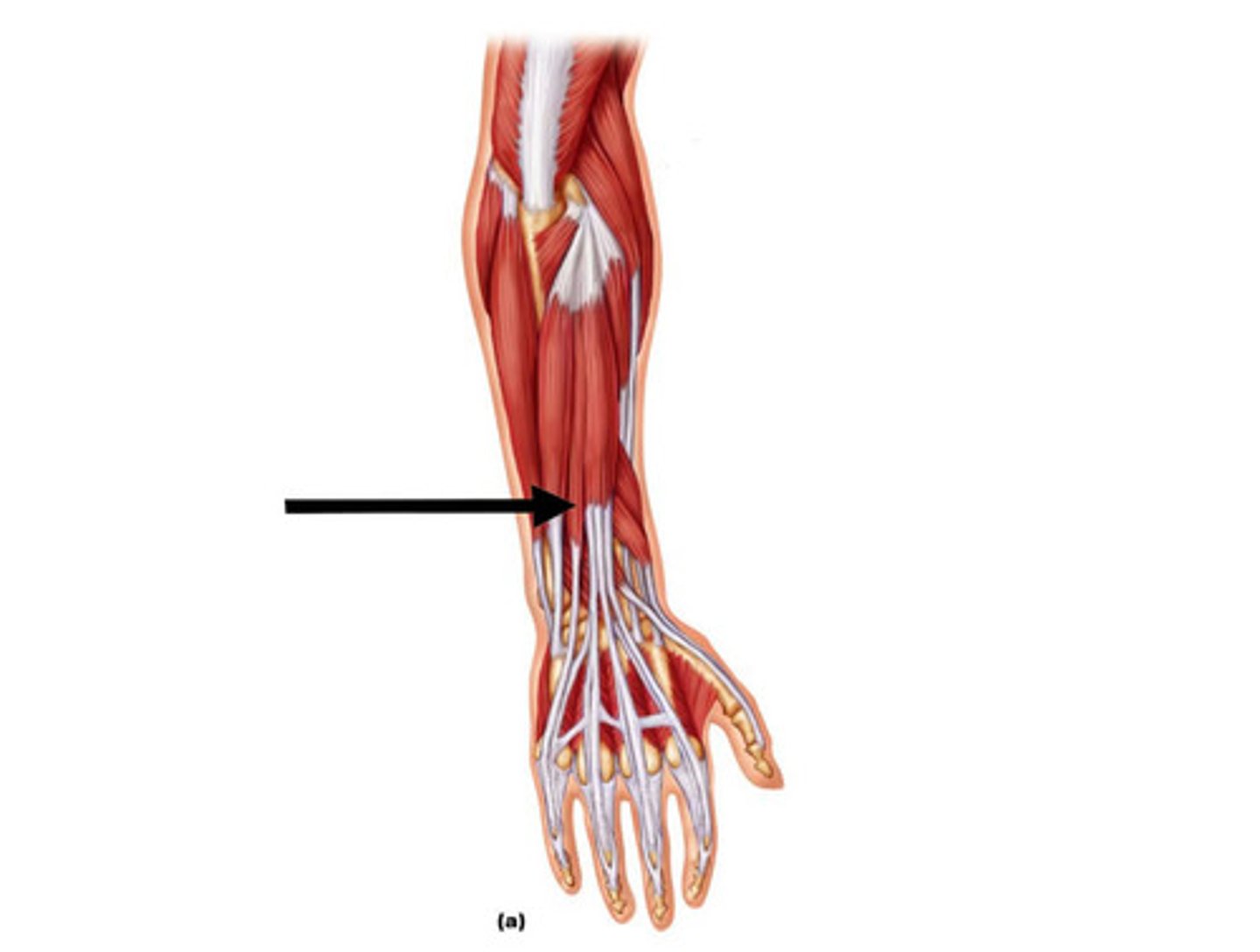
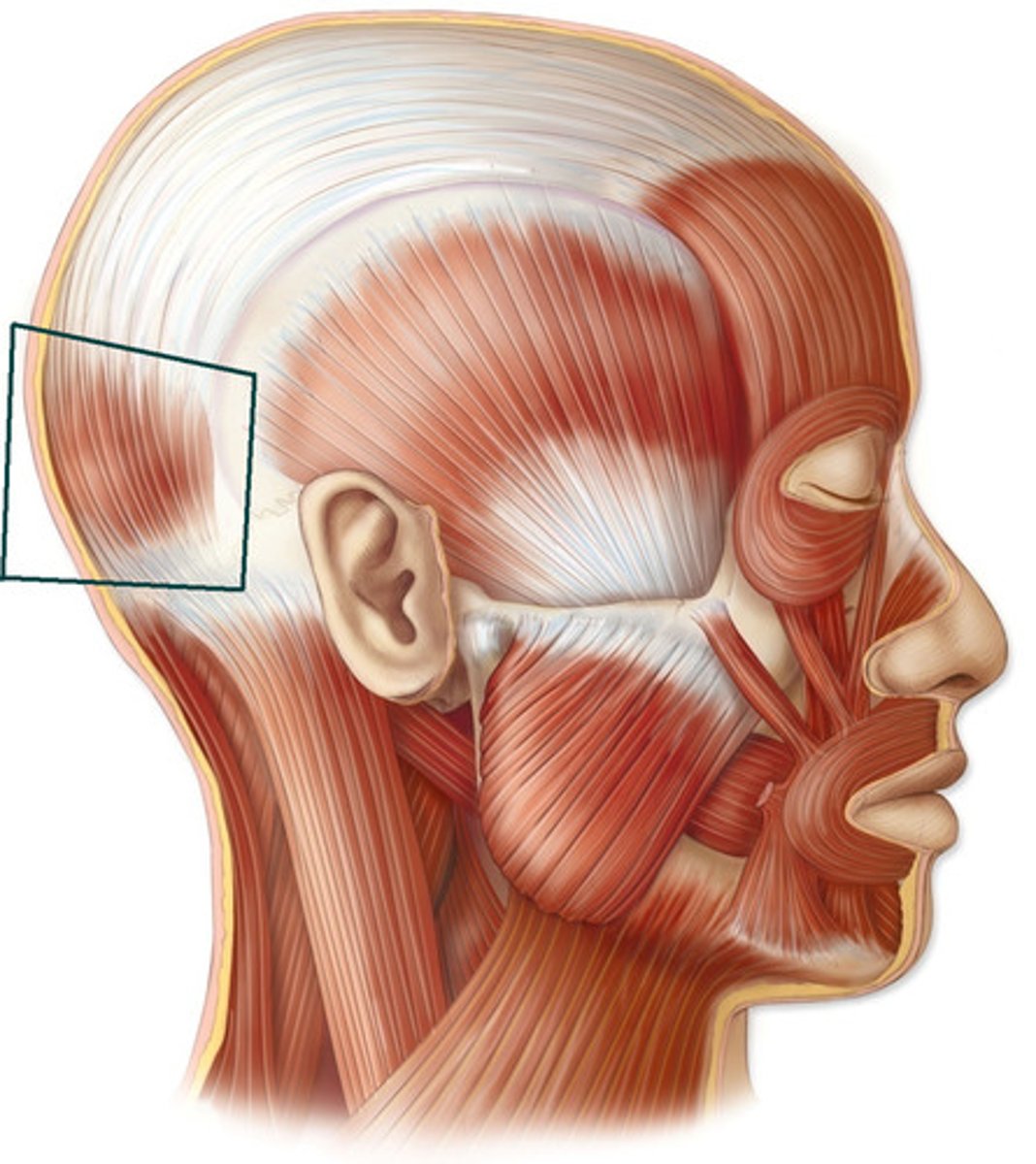
Frontalis
Elevates the eyebrows and draws the scalp anteriorly
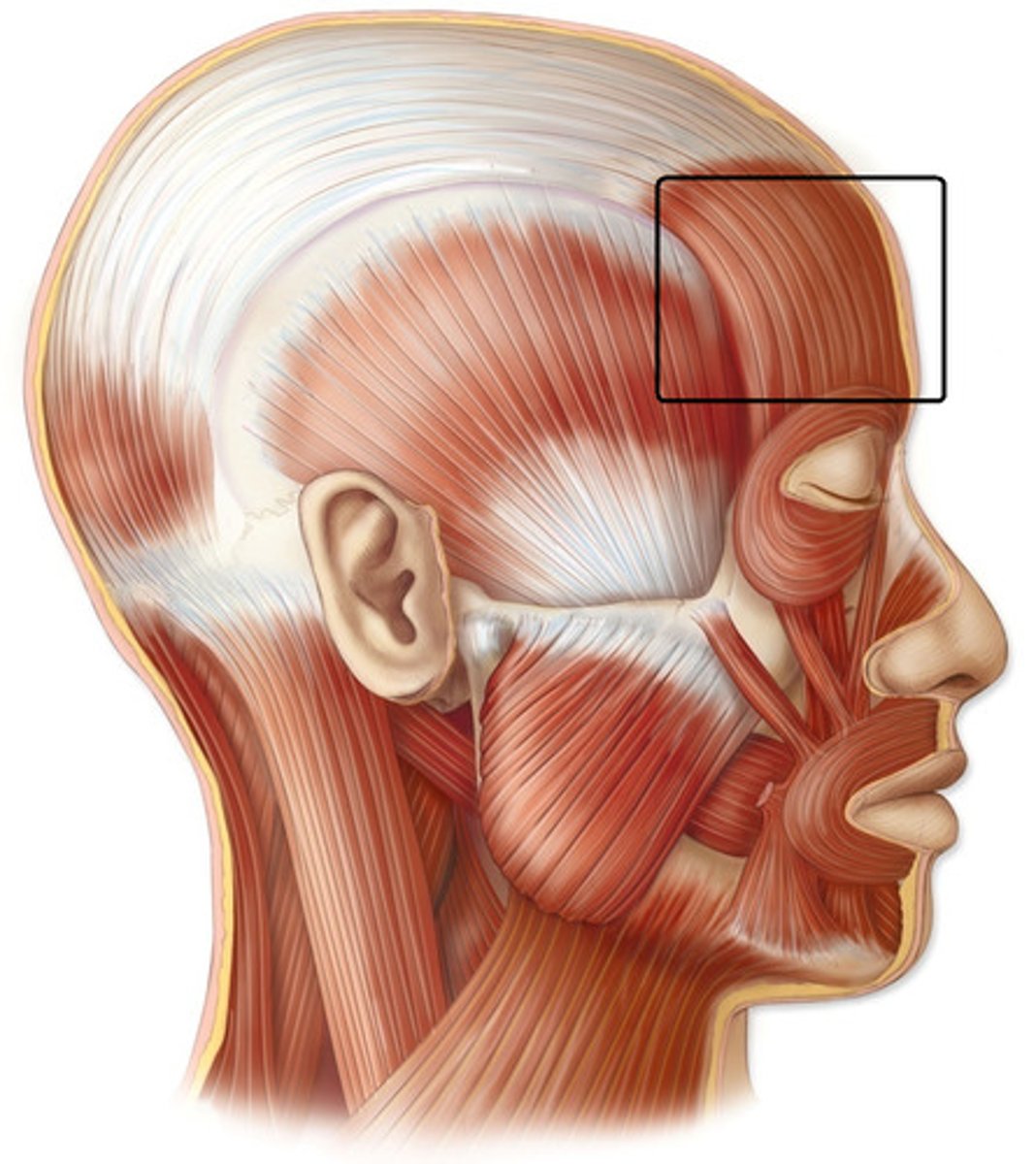
Occipitalis
Draws the scalp posteriorly
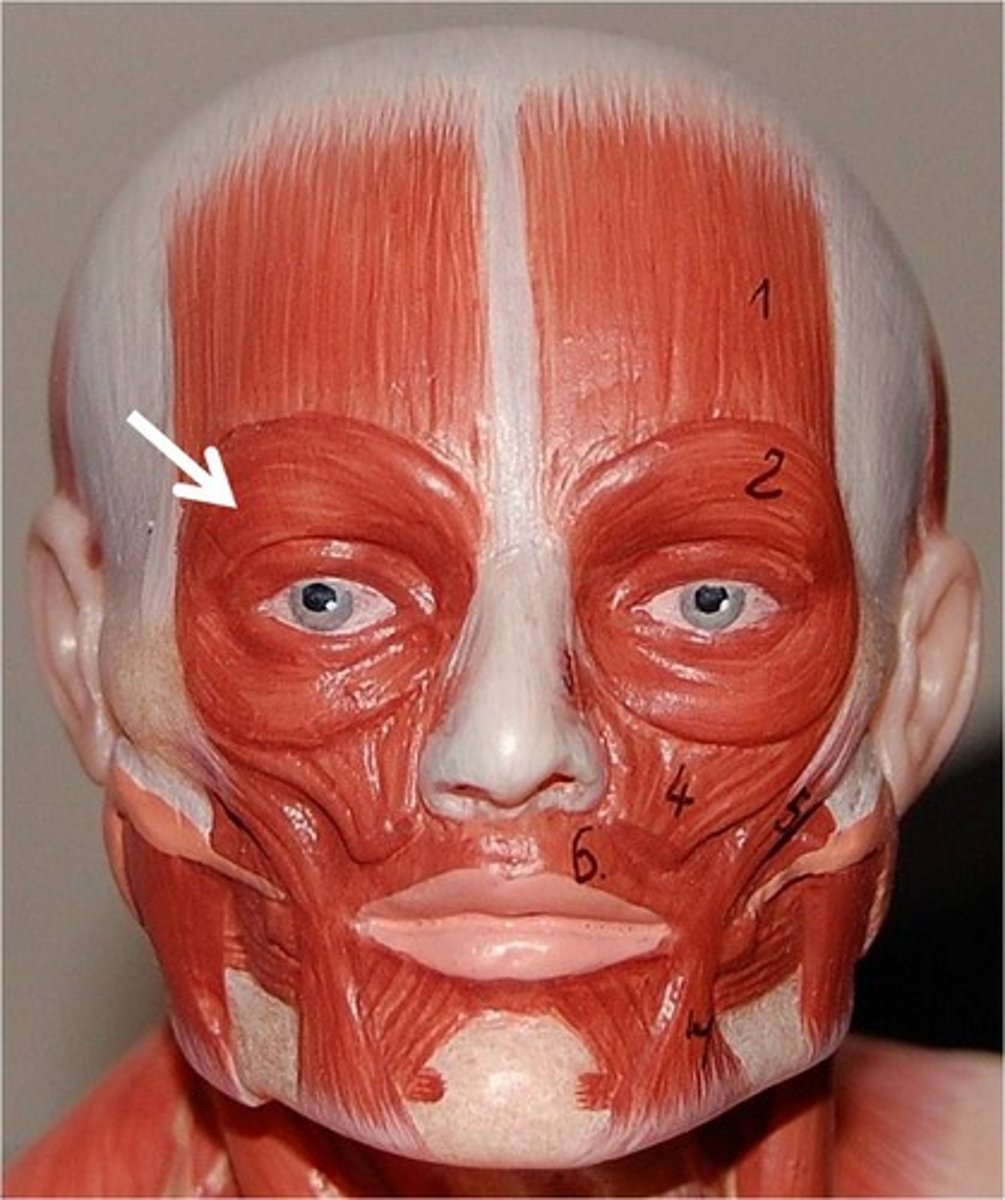
Orbicularis oculi
Closing the eyes, blinking, and squinting
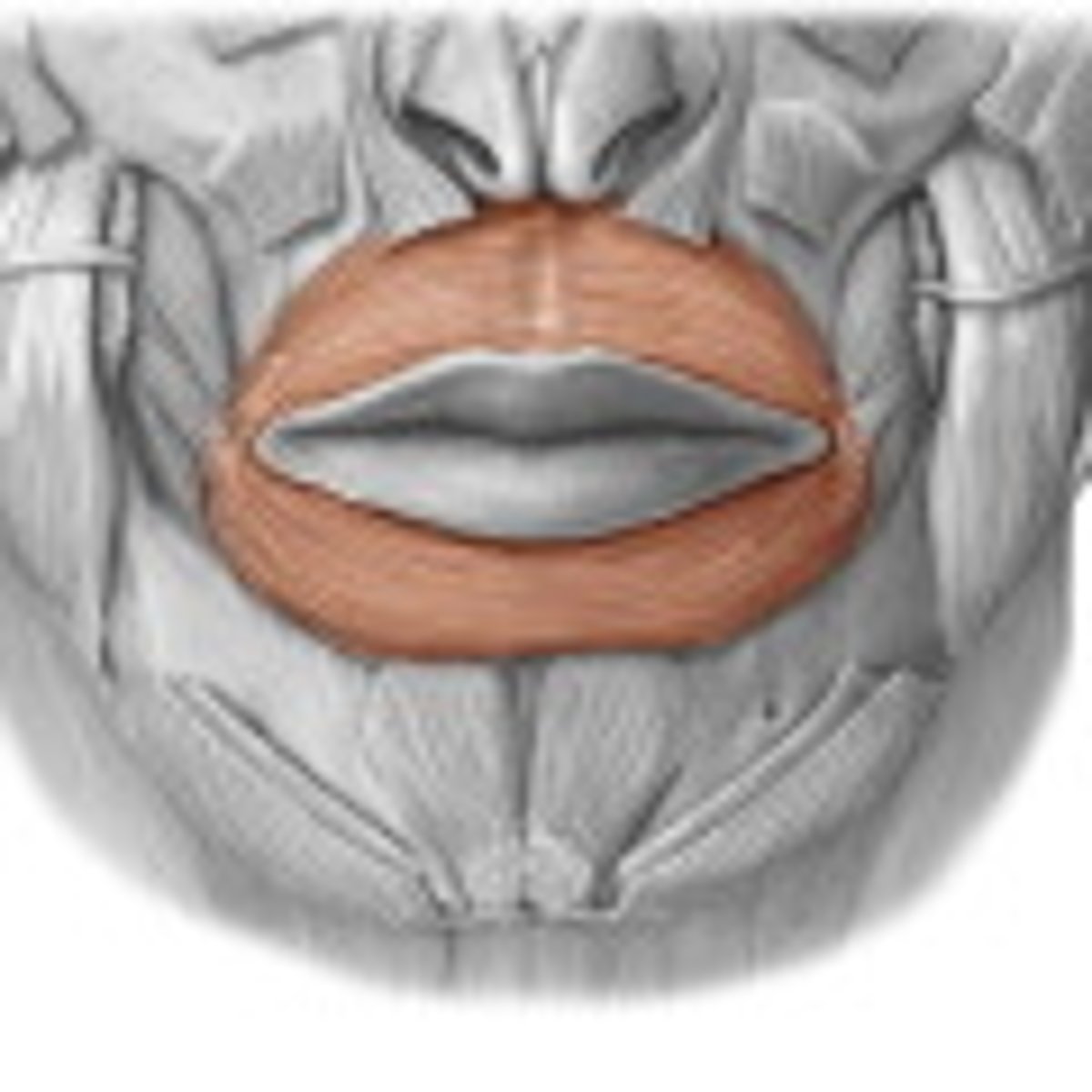
Orbicularis oris
Enables puckering and closing of the lips
Zygomaticus minor
Elevating the upper lip during smiling
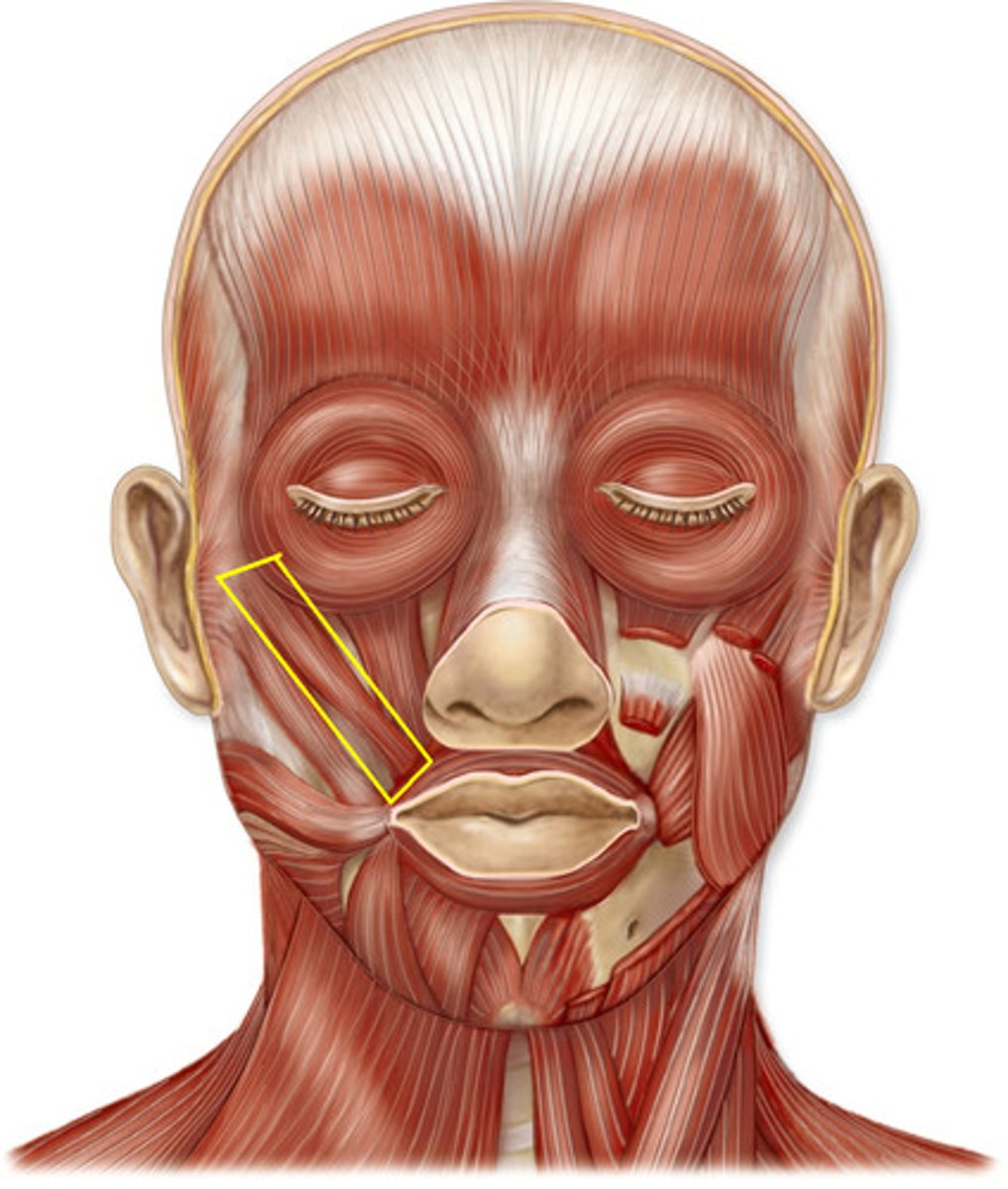
Zygomaticus major
Raising the lateral corners of your mouth upward
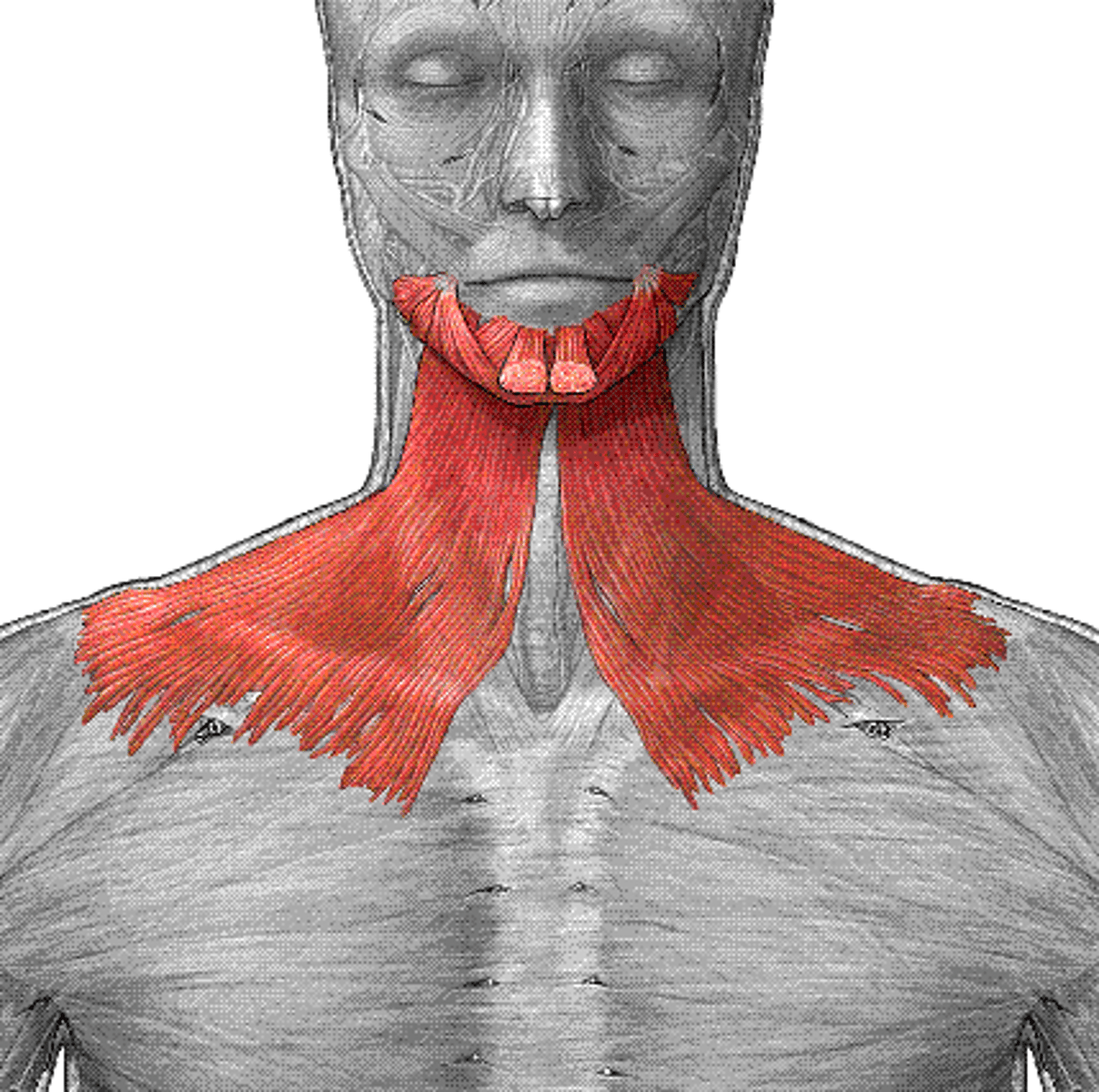
Platysma
Helps in tensing the skin of the neck, lowering the jaw, and depressing the lower lip
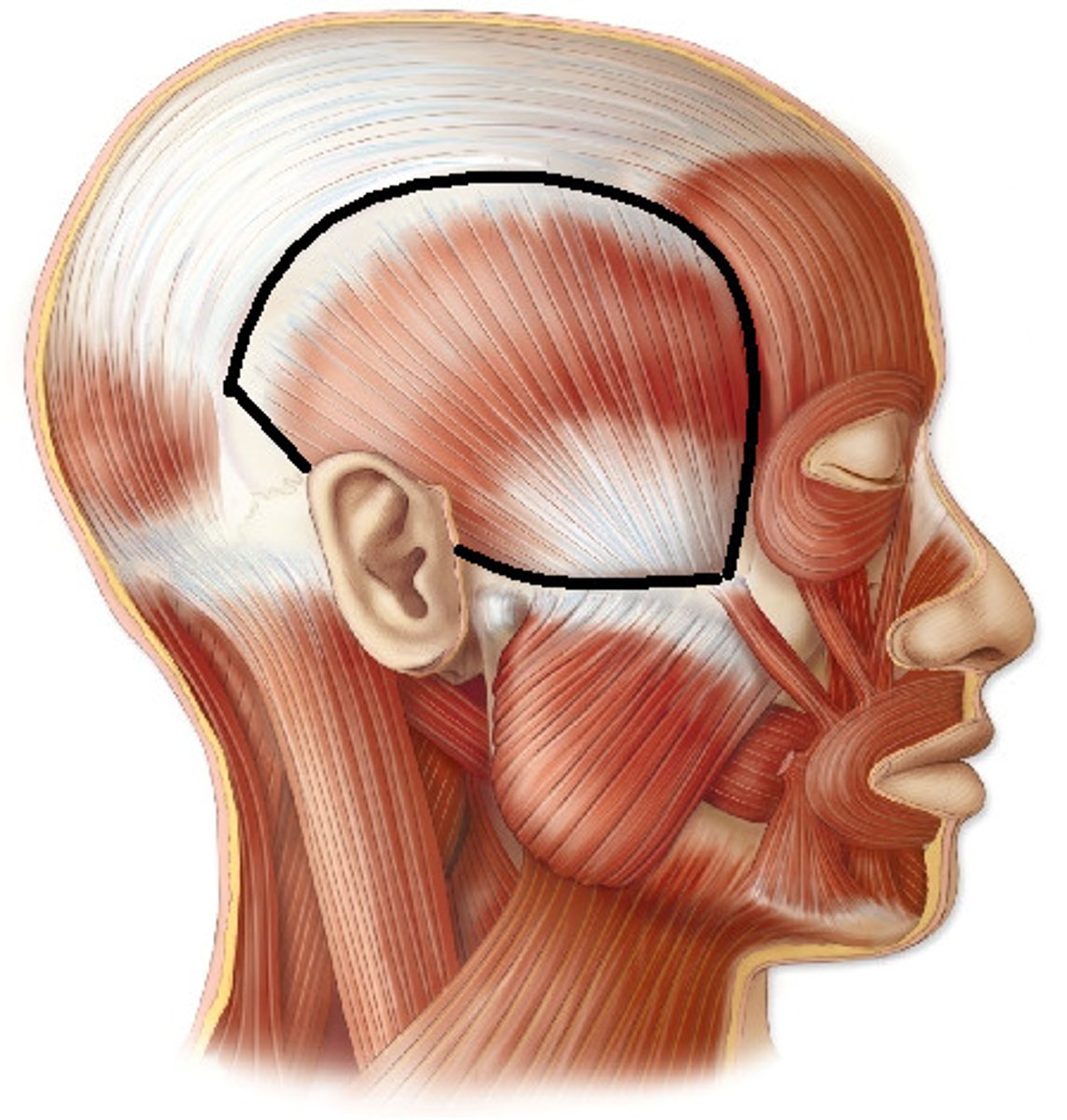
Temporalis
Aids in elevating and retracting the mandible for chewing and closing the jaw
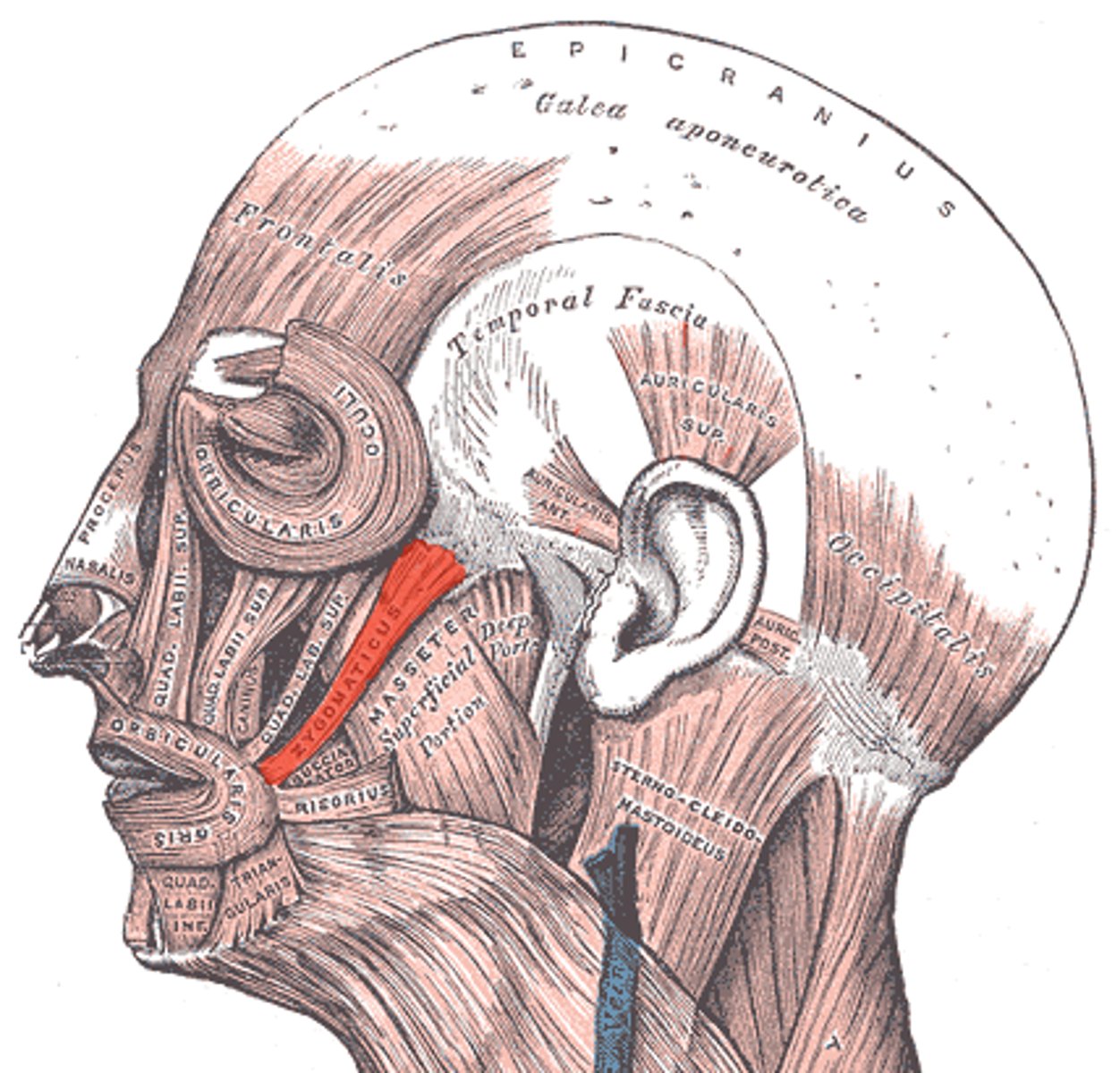
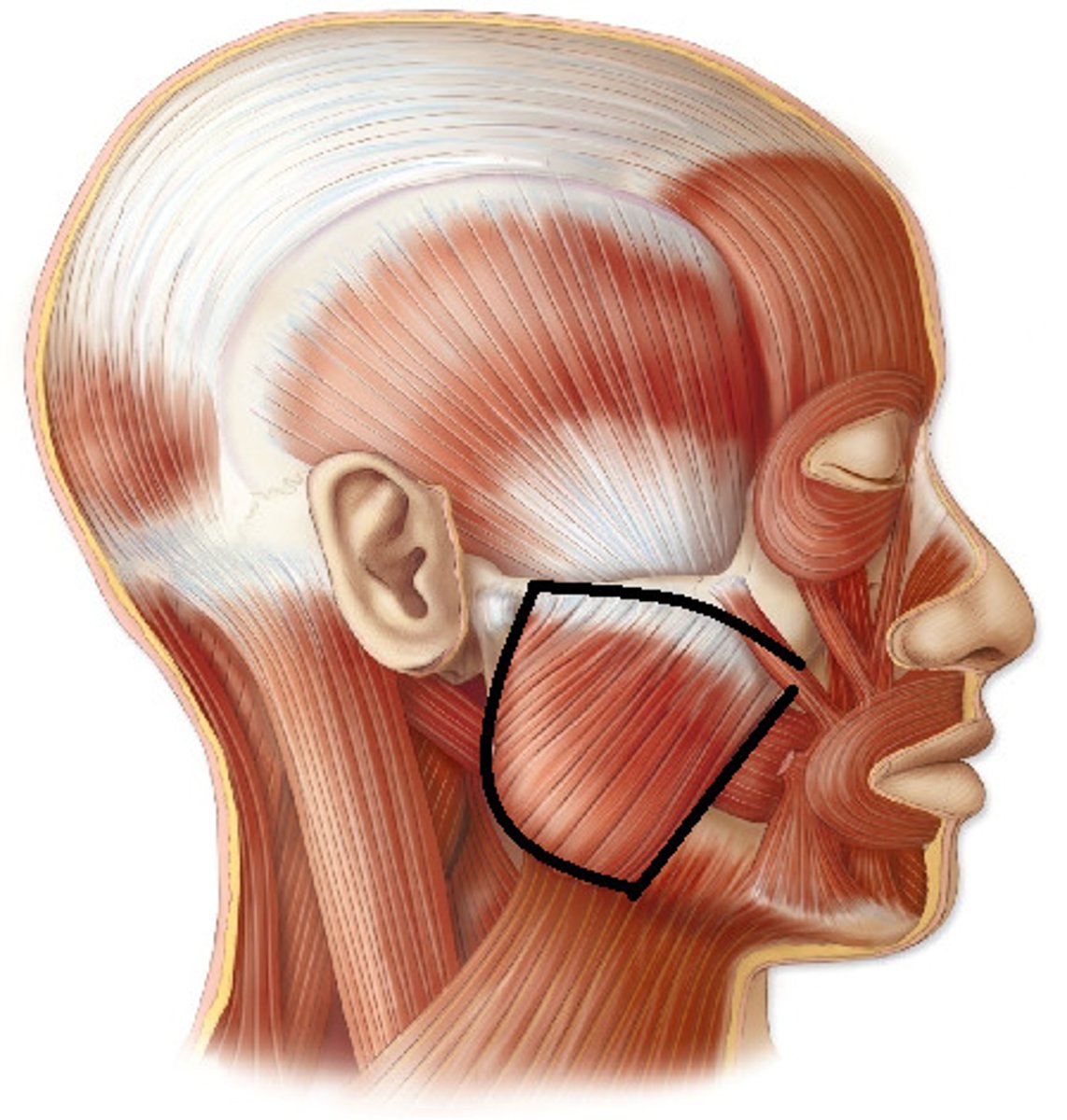
Masseter
Responsible for elevating, protracting, and retracting the mandible during chewing
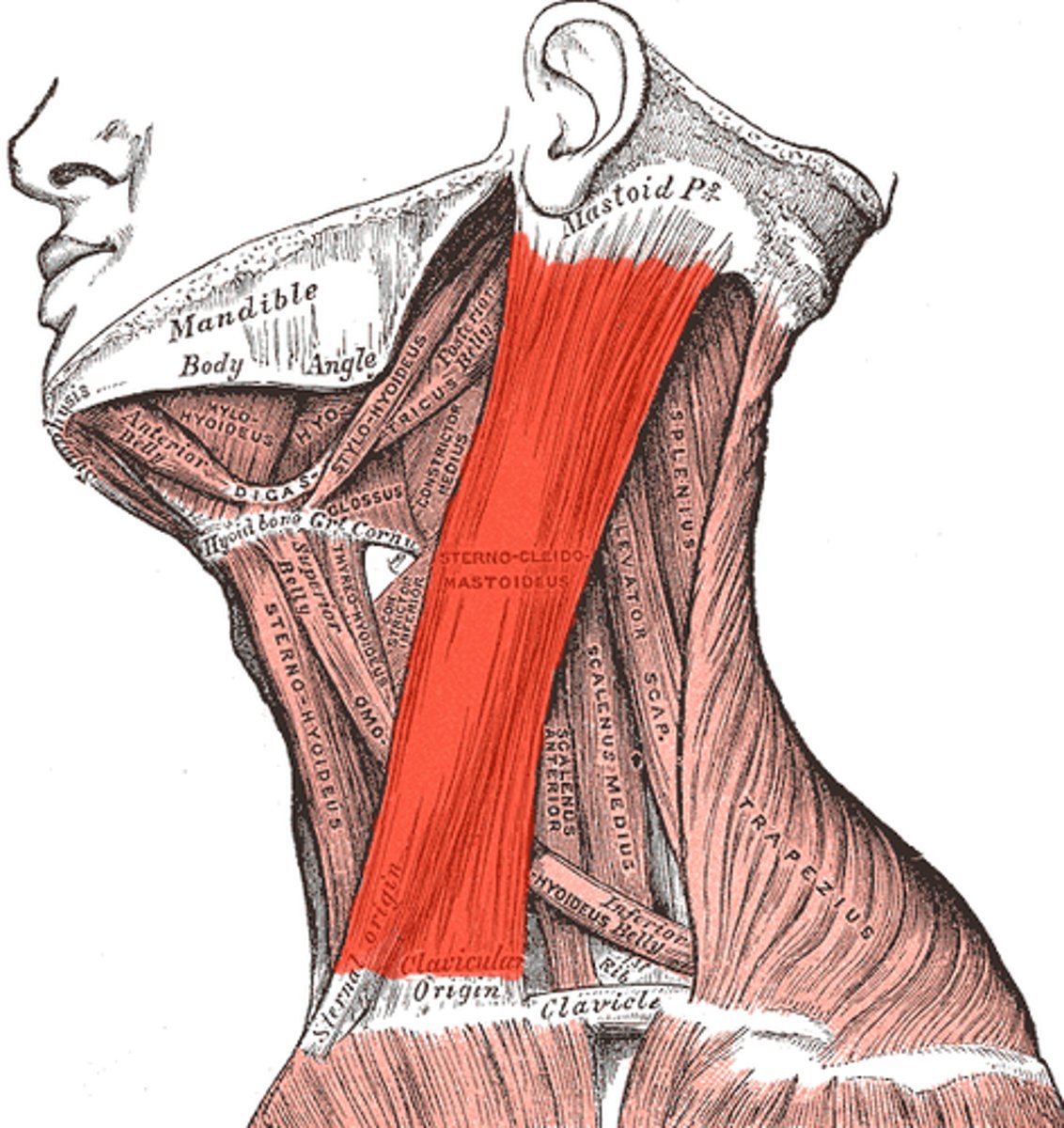
Sternocleidomastoid
Helps in rotating (1 side contracts, laterally rotating to the opposite side) and flexing the head (both contract)
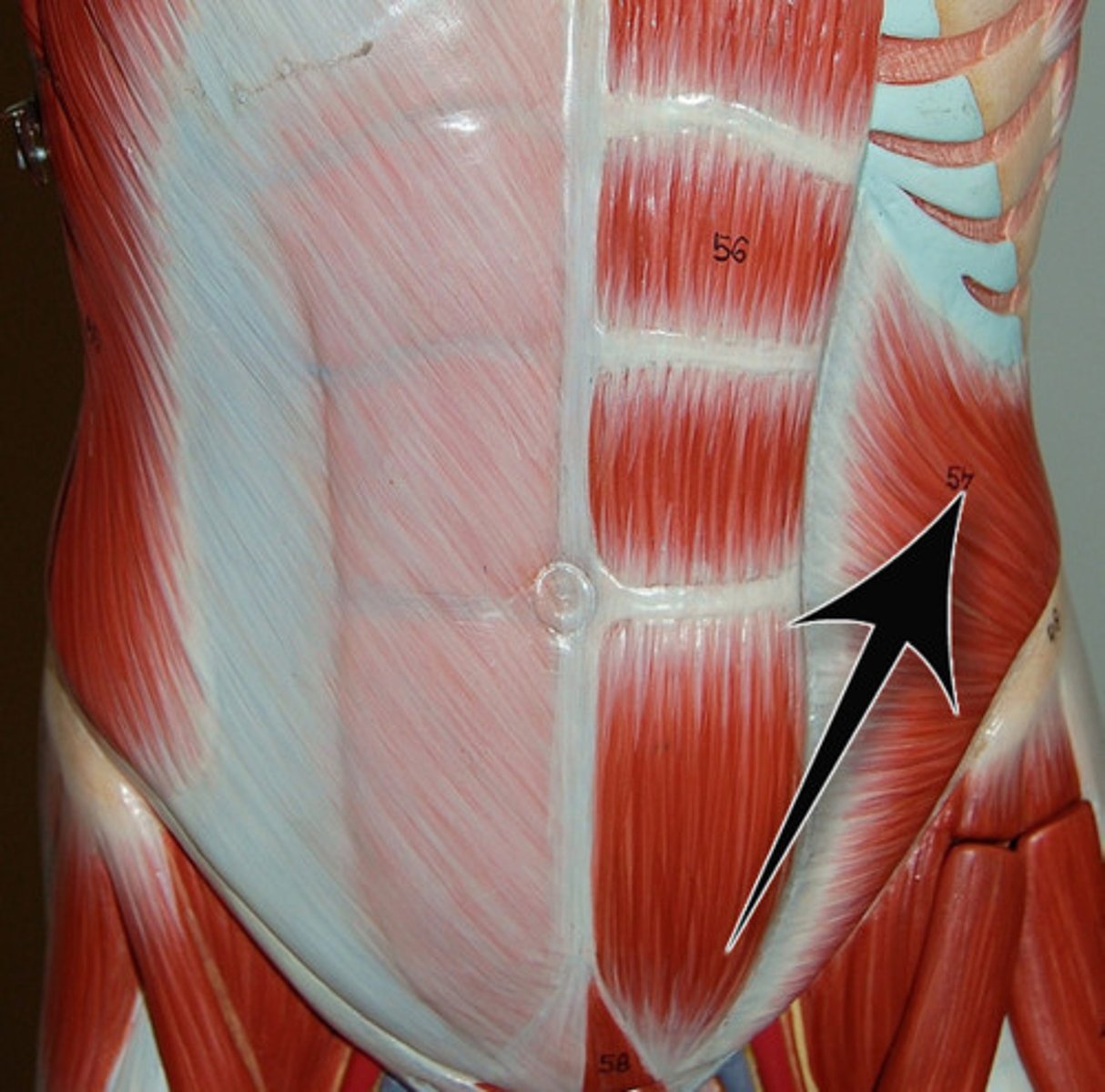
External oblique
Assist in trunk rotation and lateral flexion
Compress the abdomen
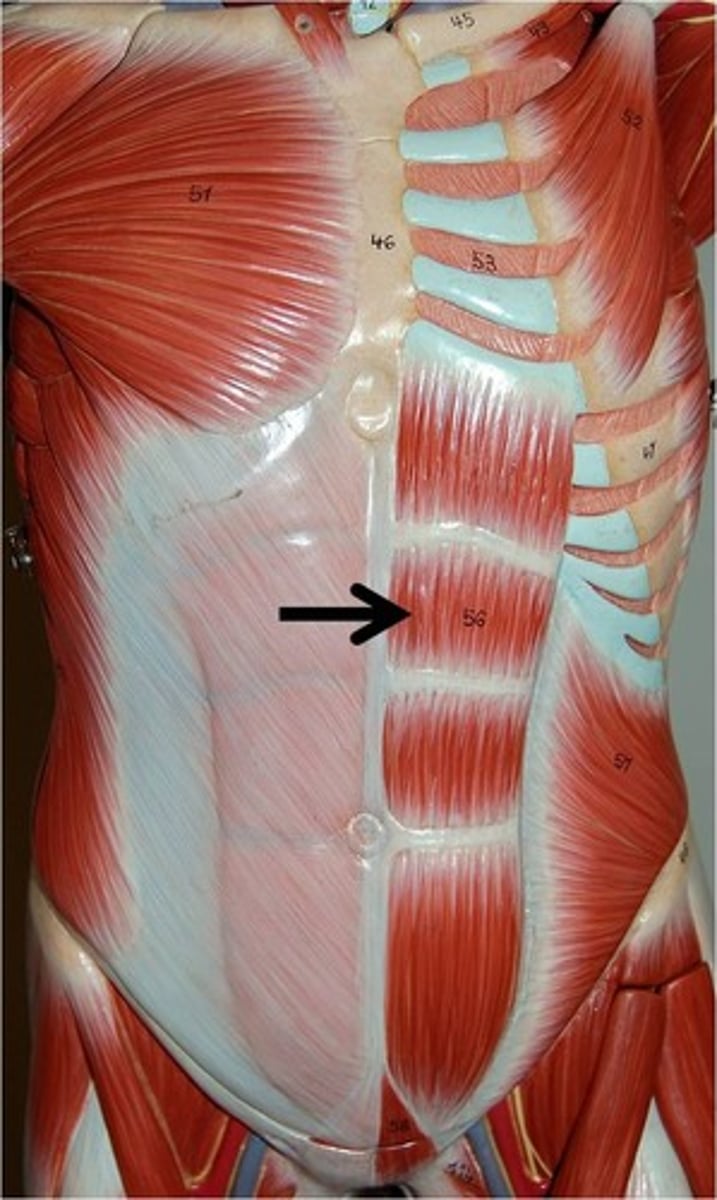
Rectus abdominis
Responsible for flexing the vertebral column and compressing the abdomen
Internal oblique
Rotate and flex the torso
Compress the abdomen
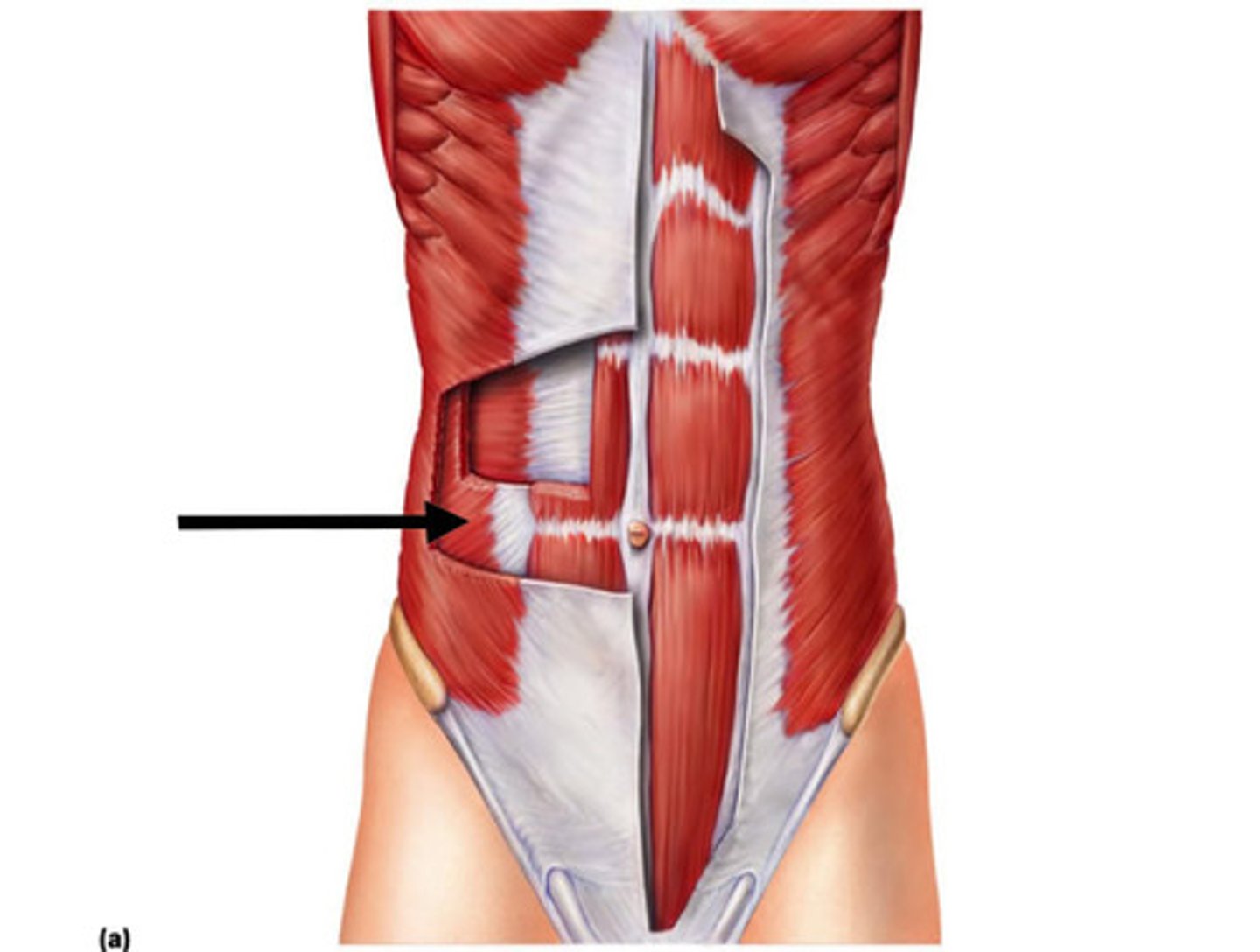
Transverse abdominis
Compresses the abdomen
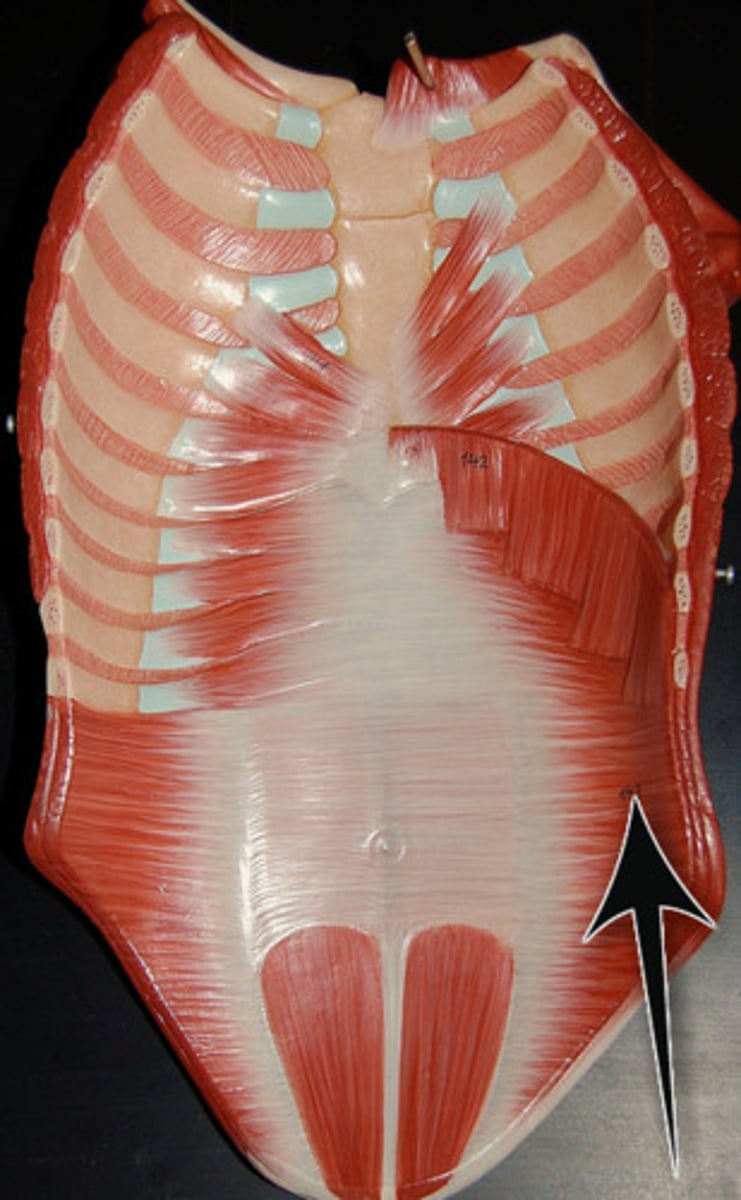
Name the abdominal muscles from deep to superficial
Transverse abdominis
Internal oblique
Rectus abdominis
External oblique
Remember the acronym TIRE
Erector spinae
3 main muscle groups:
Iliocostalis, longissimus, and spinalis
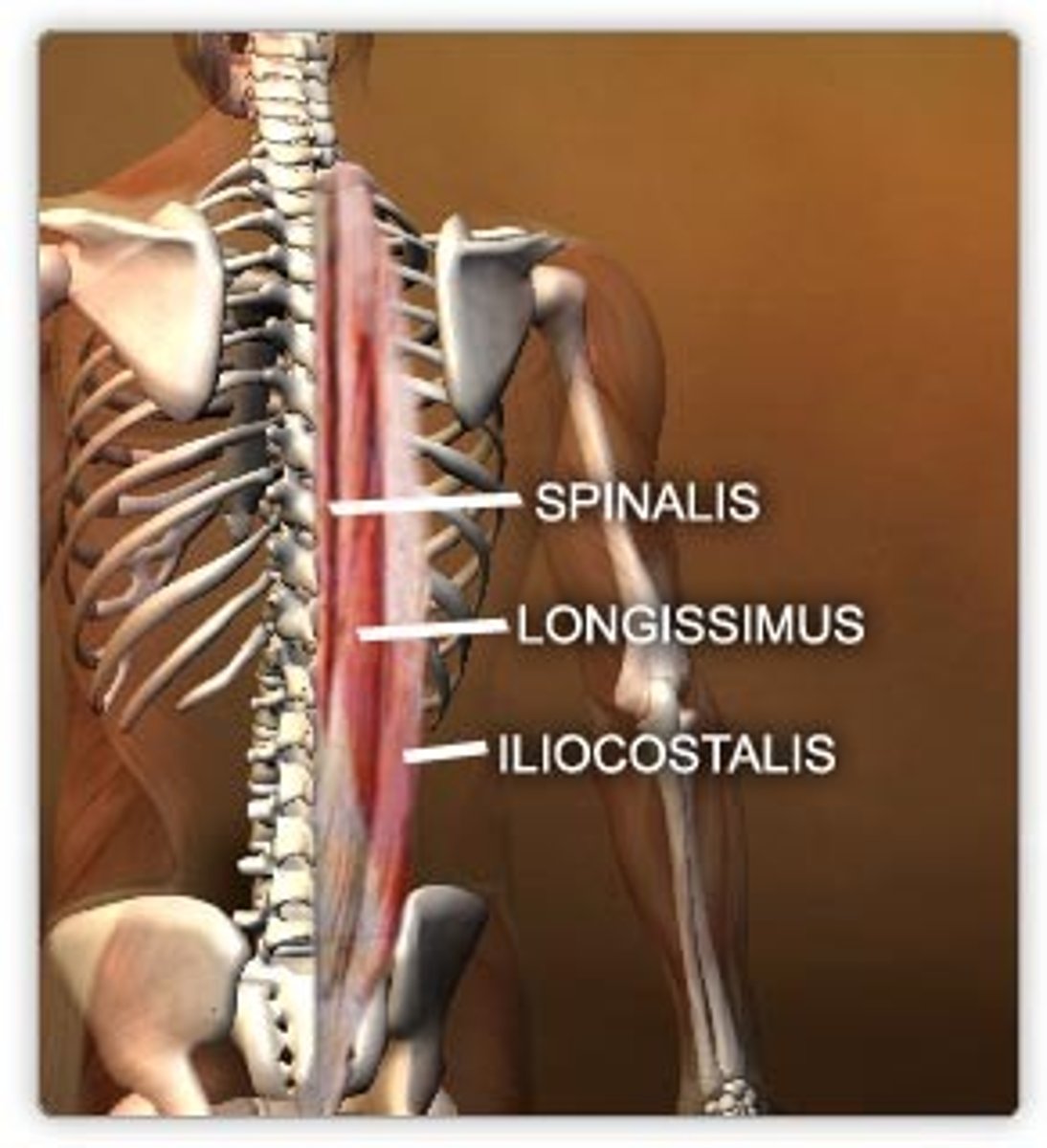
If one side of the erector spinae contract...
Result is lateral flexion and rotation of the vertebral column
If both sides of the erector spinae contract...
Result is extension of the vertebral column
Name the erector spinae muscles from lateral to medial
Iliocostalis group, Longissimus group, Spinalis group
Diaphragm
Contracts downward during inspiration
Is active during quiet(at-rest) inspiration and labored inspiration
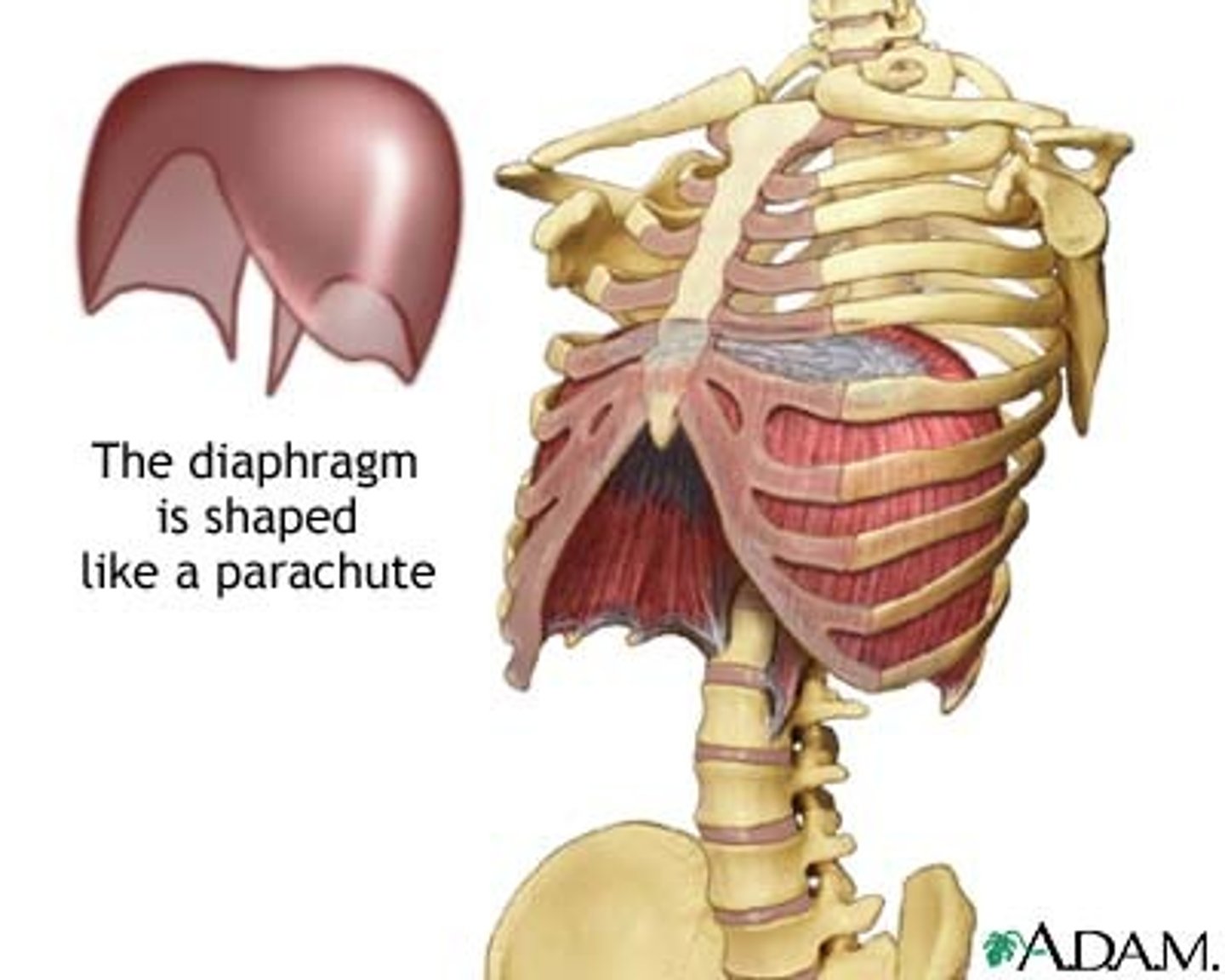
What does the diaphragm do during expiration?
Relaxes and moves superiorly, pushing air out of the thoracic cavity
External intercostals
Elevate the ribs during inspiration
Contract during quiet(at-rest) inspiration and labored inspiration
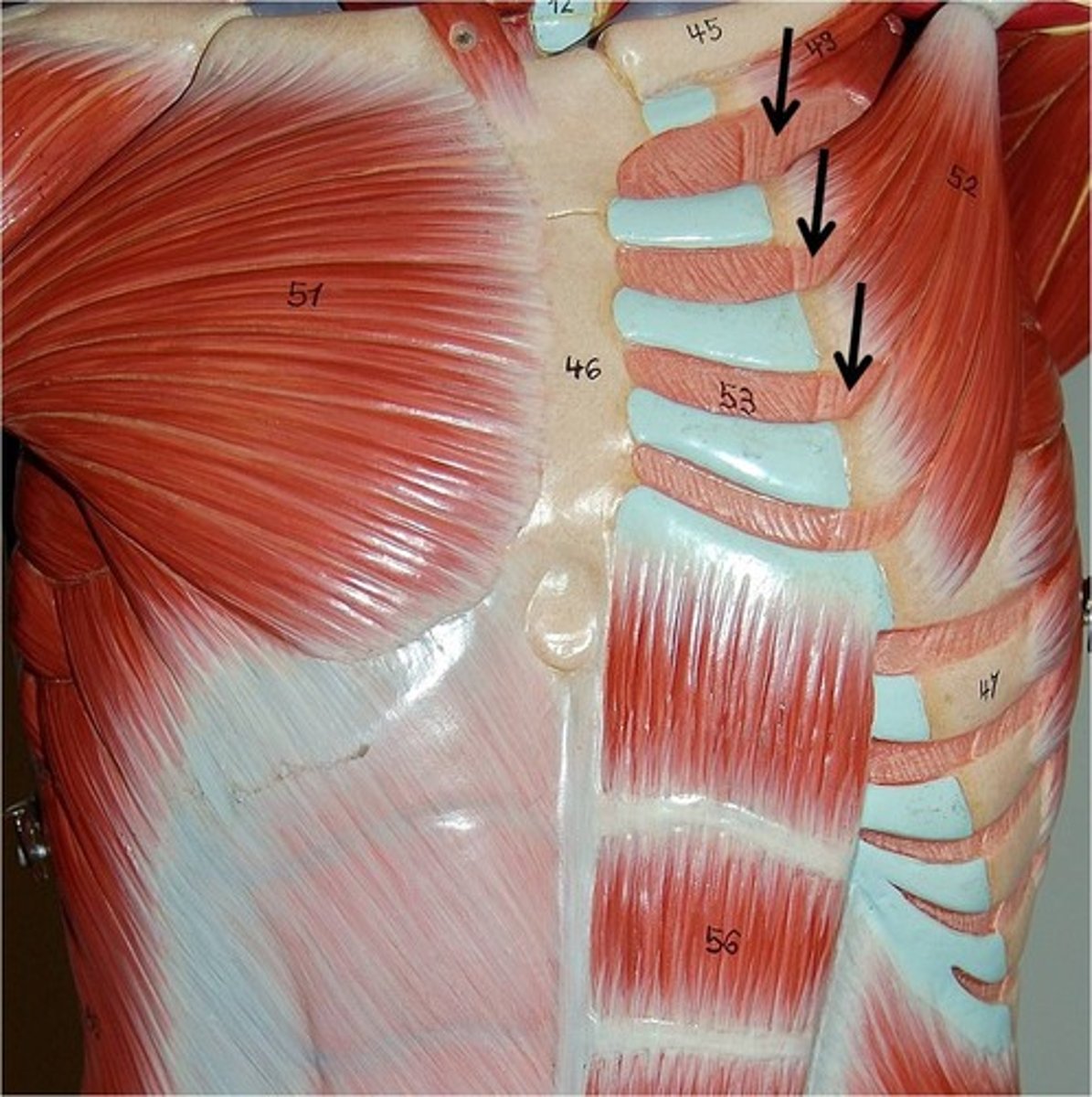
What do the external intercostals do during expiration?
Relax
Internal intercostals
Involved in labored expiration
They depress the ribs by pulling them downward
Flexion
Decreasing the angle between 2 bones
Extension
Increasing the angle between 2 bones
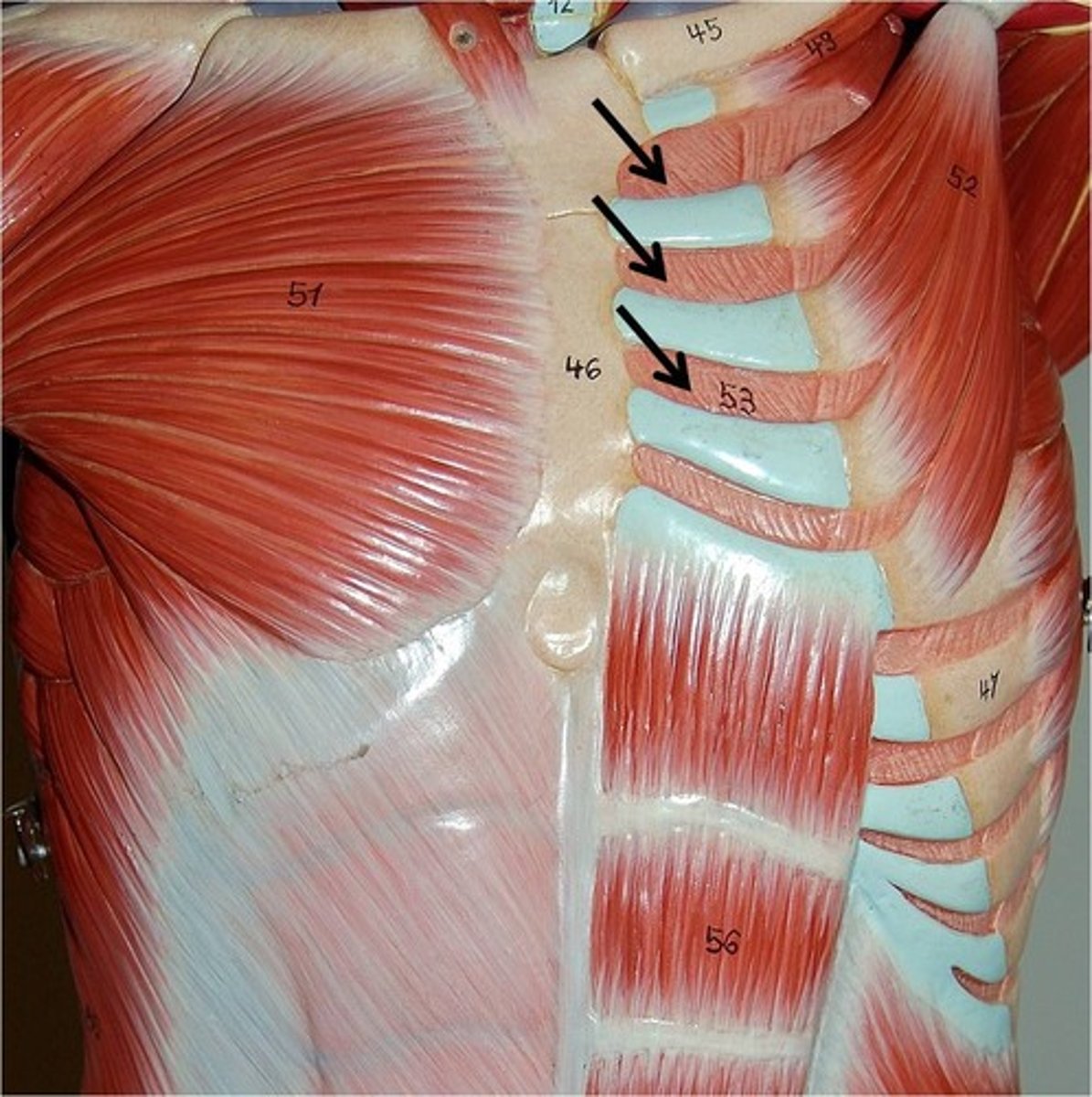
Lateral flexion
Trunk of body moves in a frontal plane laterally away from the body
Hyperextension
Joint is extended beyond it's normal range (past 180 degrees)
Abduction
Lateral movement of a body part away from the body midline
Adduction
Medial movement of a body part towards the midline
Lateral rotation
External rotation of the front of the femur or humerus away from the body's midline
Medial rotation
Internal rotation moving the front of the femur or humerus toward the midline
Supination
Forearm rotates laterally so that the palm faces anteriorly or superiorly
Pronation
Medial rotation of the forearm so the palm is directed posteriorly or inferiorly
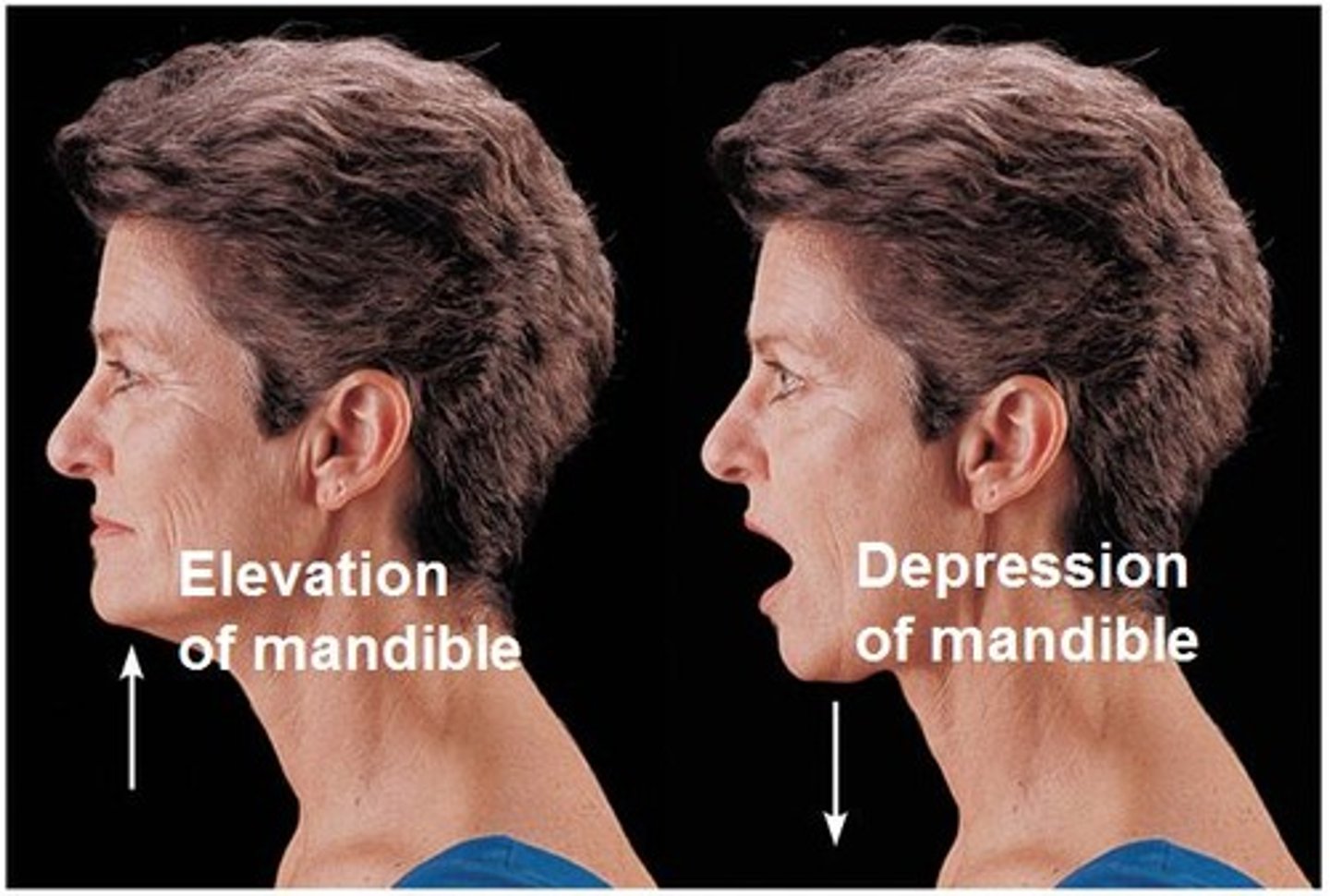
Depression
Inferior movement of a body part
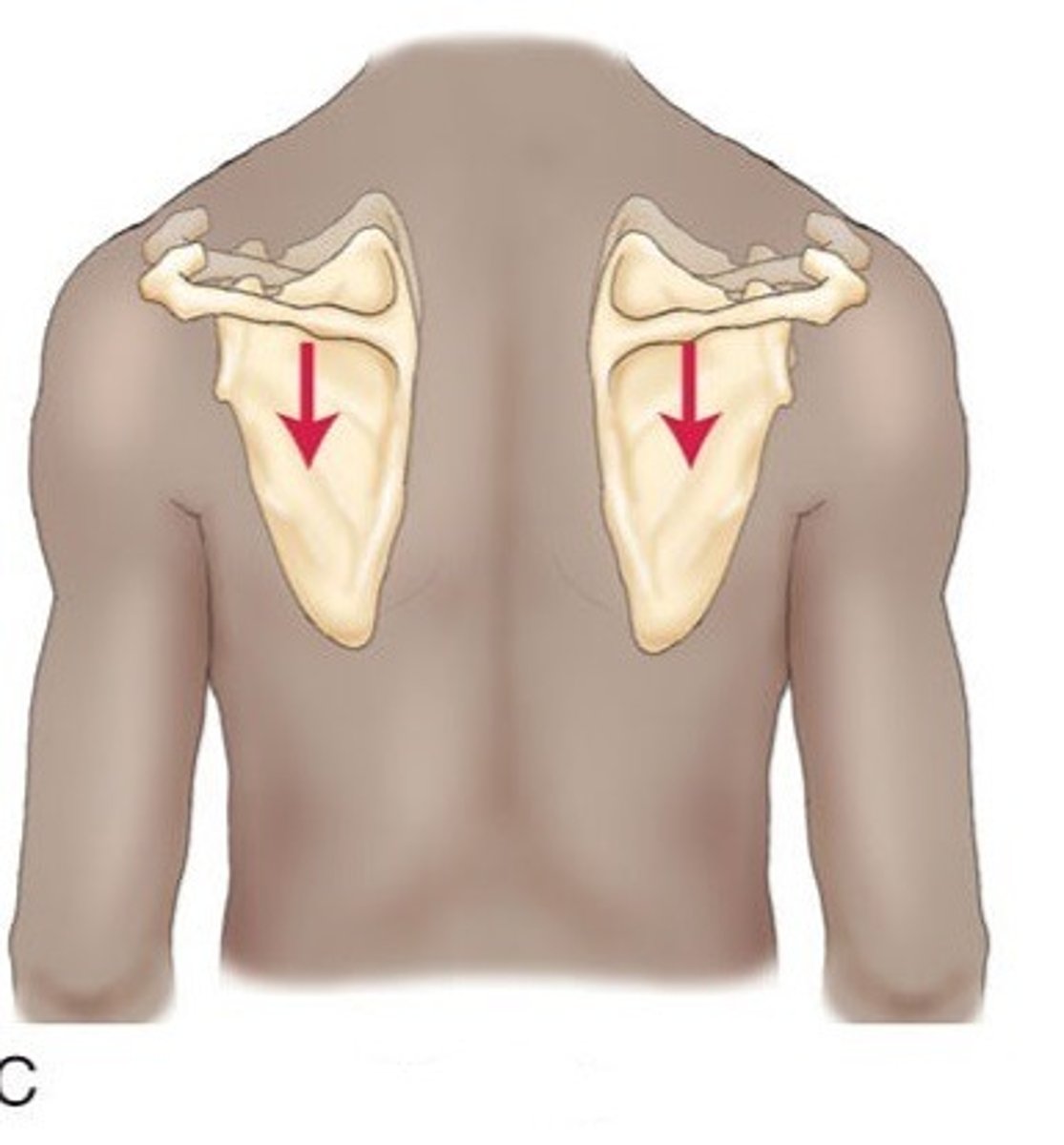
Elevation
Superior movement of a body part
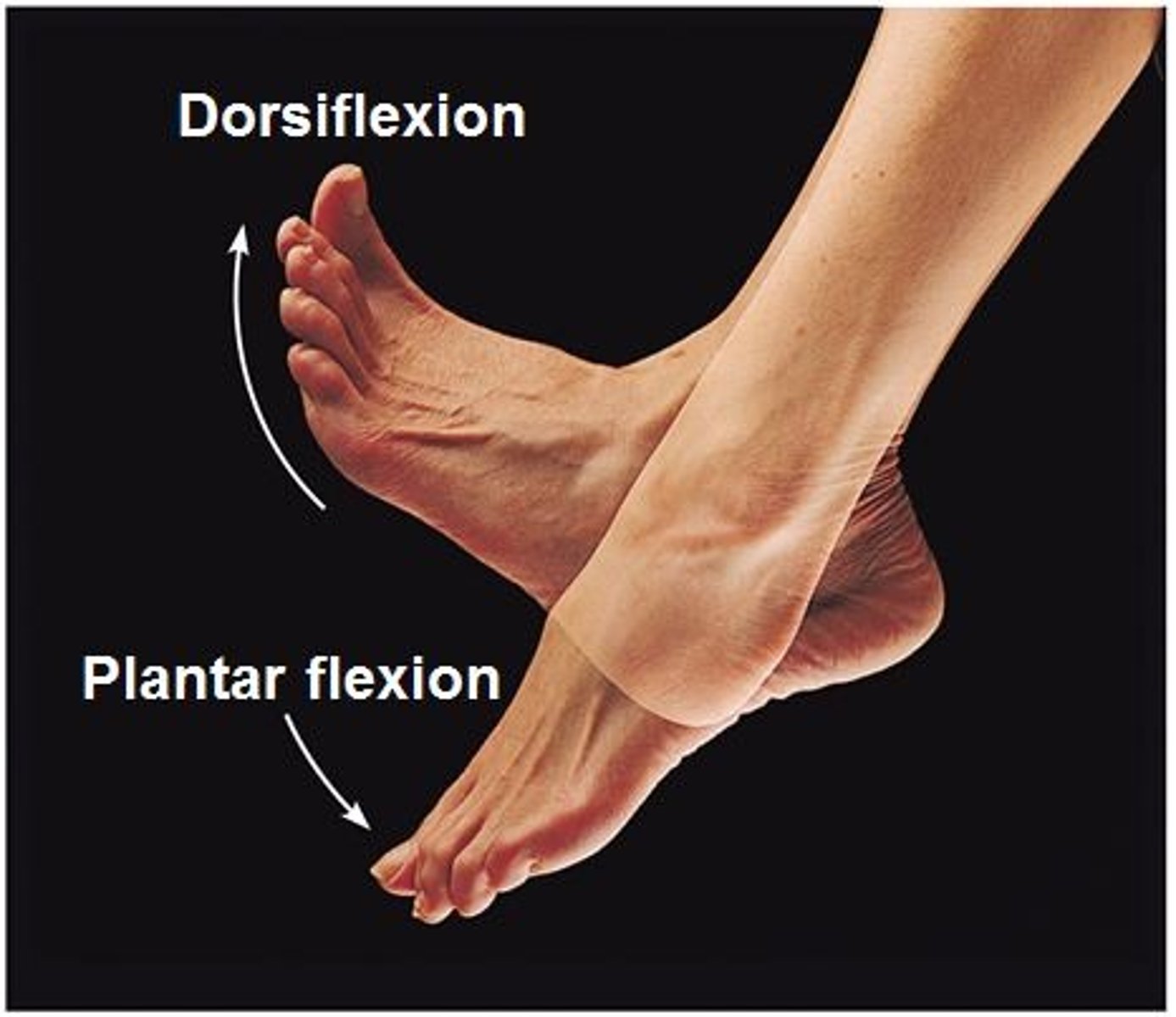
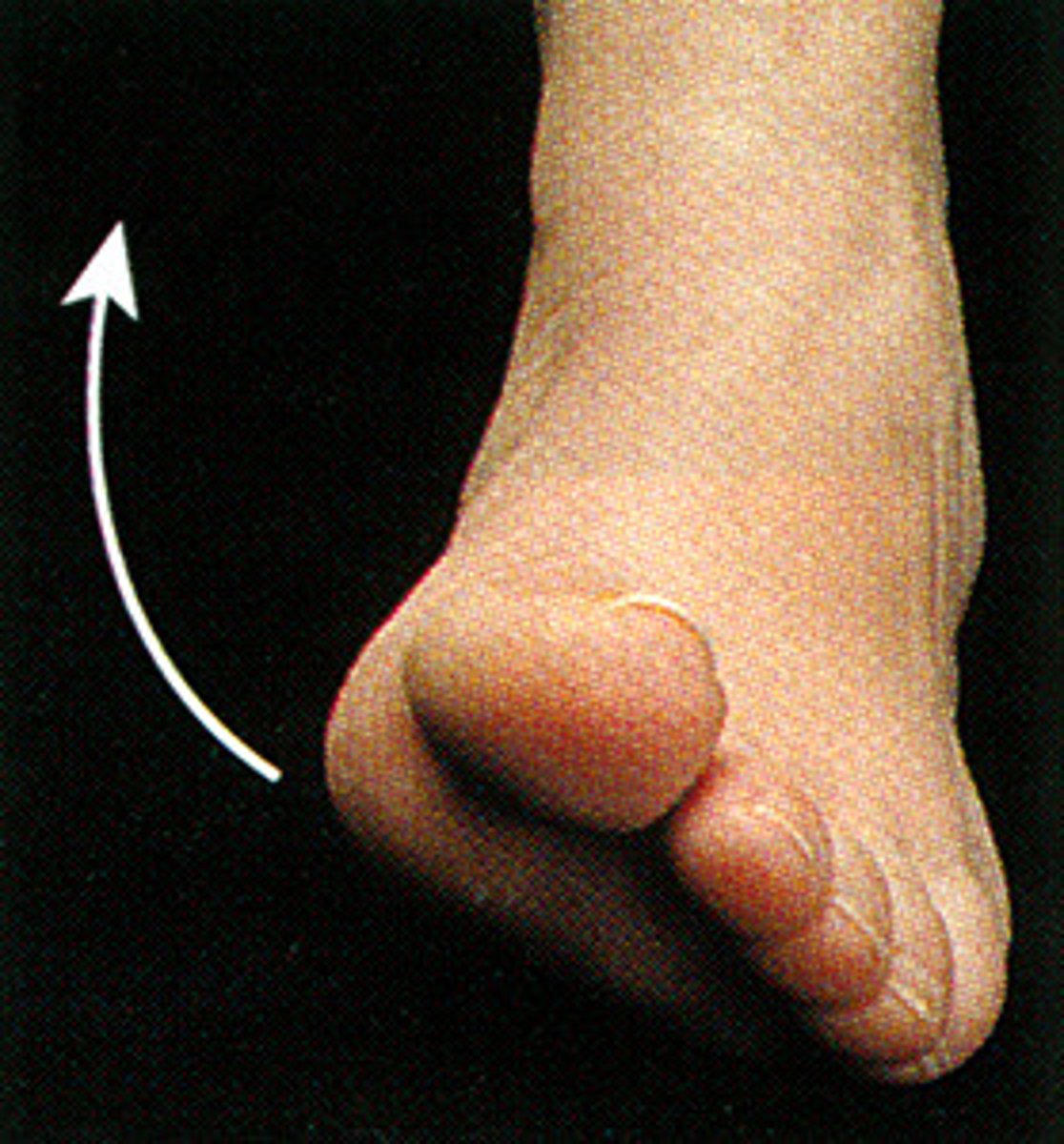
Dorsiflexion
Movement at the ankle joint where the top of the foot moves toward the leg
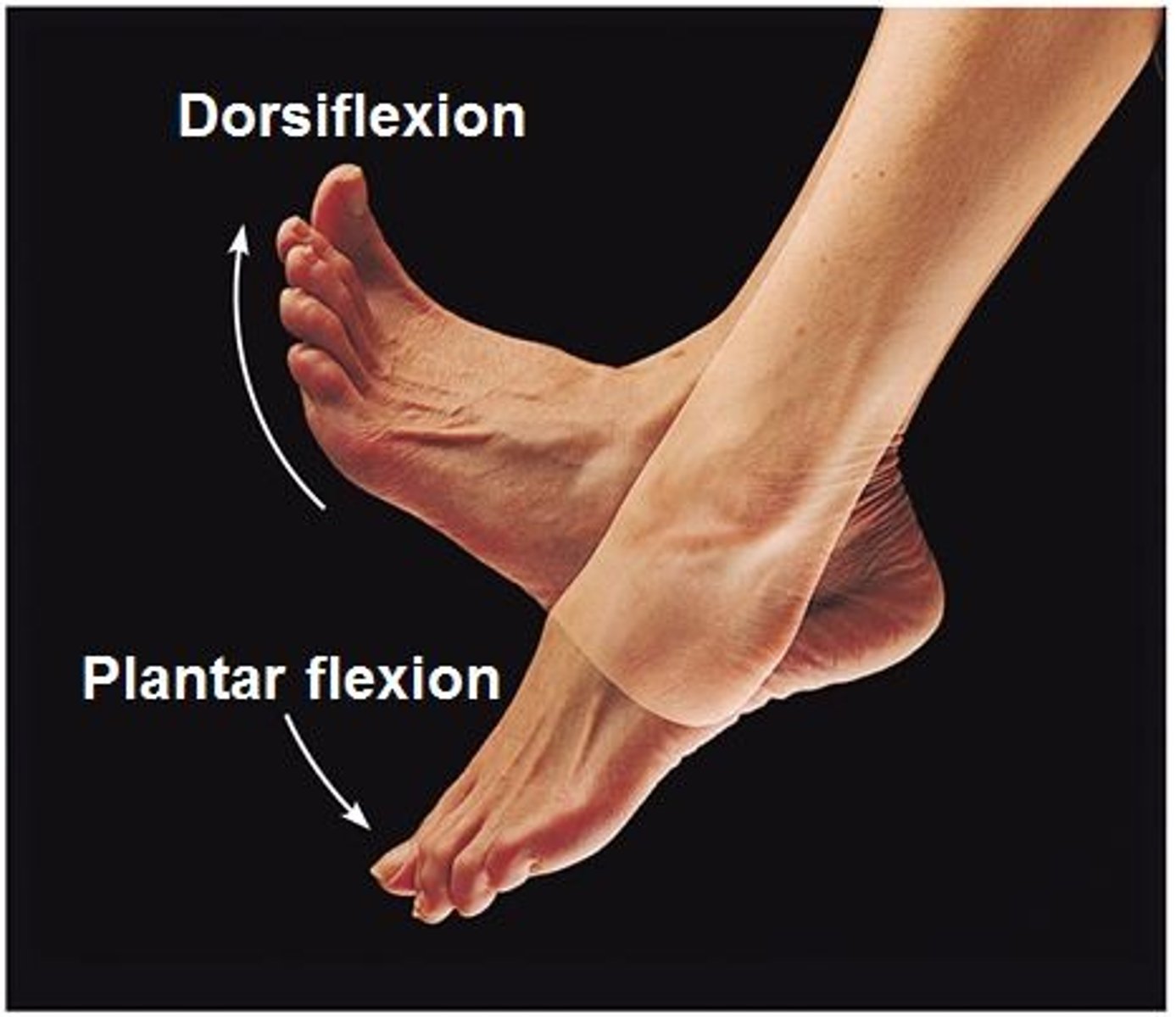
Plantar flexion
Occurs when the foot points downward, away form the leg
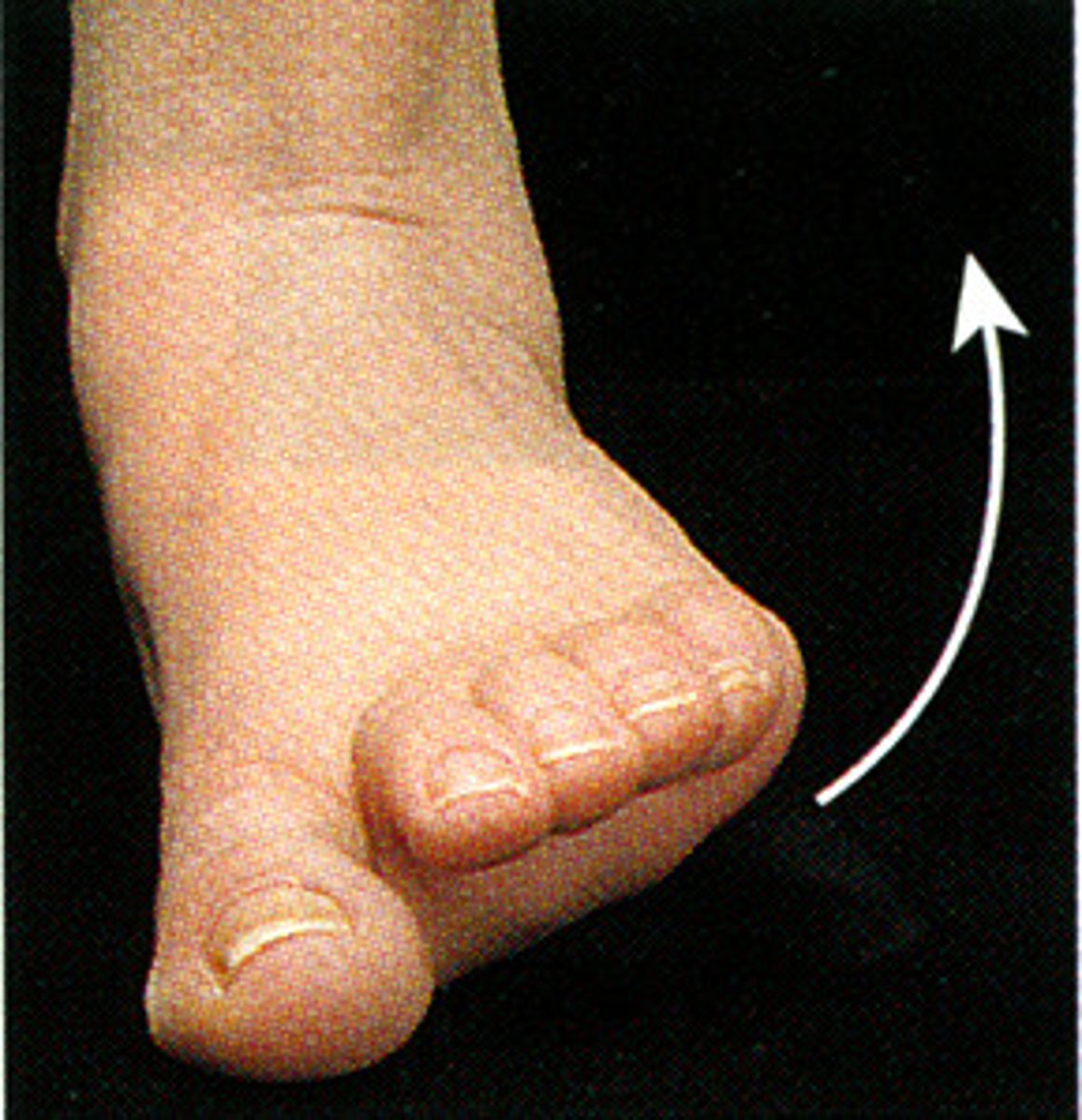
Eversion
Sole of the foot faces laterally
Inversion
Sole of the foot turns medially
Protraction
Forward movement of a body part form its anatomical position
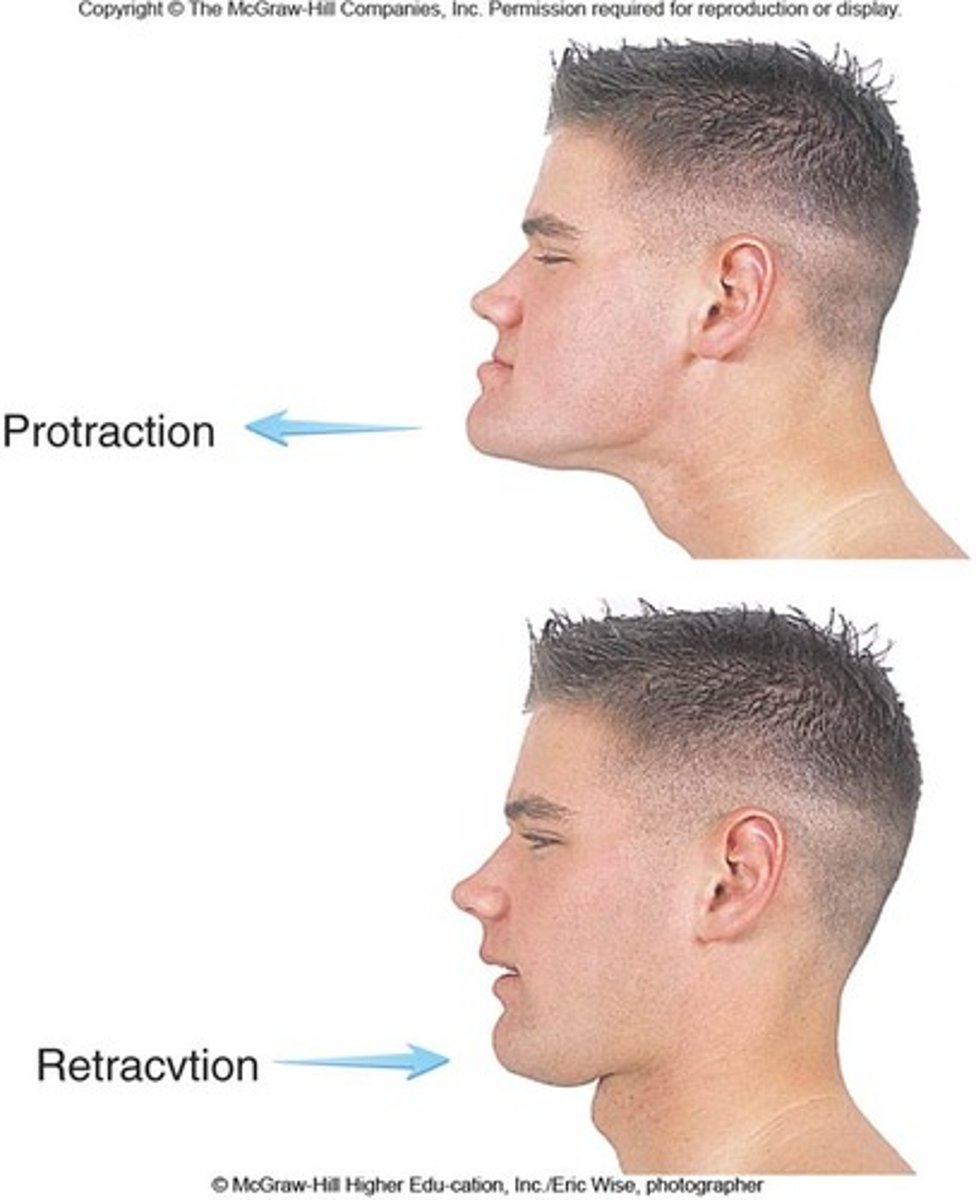
Retraction
Posterior movement of a body part, returning it to the anatomical position