geography pt. two
1/80
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
cartographer
they gather and create maps
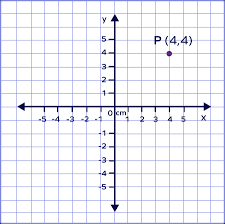
coordinates
points on a map
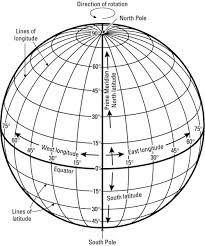
geographic grid
the internationally-recognized system of latitude and longitude used to location positions on Earth's surface
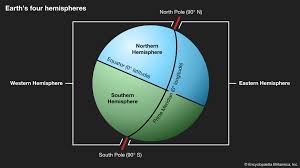
hemisphere
a half of the earth, usually as divided into northern and southern halves by the equator, or into western and eastern halves by an imaginary line passing through the poles
lines of latitude (parallels)
Lines of latitude, also called parallels, are imaginary lines that divide the Earth. They run east to west, but measure your distance north or south
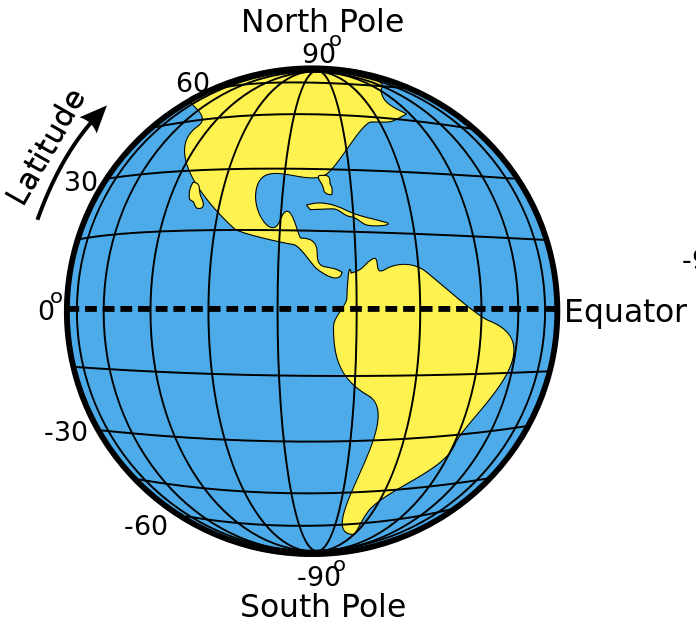
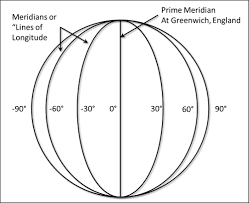
lines of longitude (meridians)
imaginary lines that divide the Earth. They run north to south from pole to pole, but they measure the distance east or west
projection (map)
the method of transferring the graticule of latitude and longitude on a plane surface
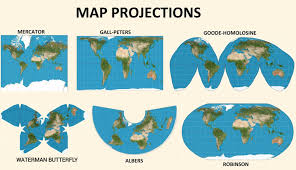
marcator projection map
cylinder shaped map, shows land and water distorted but direction is accurate
contiguous
sharing a common border; touching
robinson projection map
land shapes and locations with minimal distortion in the center of the map
arctic circle
The Arctic Circle, roughly 67° north of the Equator, defines the boundary of the Arctic waters and lands.
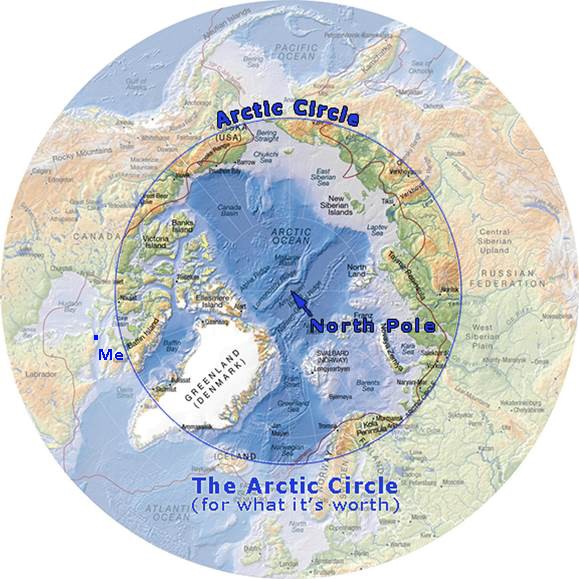
arctic region
the area within the Arctic Circle, a line of latitude about 66.5° north of the Equator
equidistant projection
shows land + water in relation to center point
polar projection
type of equidistant projection that includes one of the poles at its center
central america
the southern most region of north america
dependency
a dependent or subordinate thing, especially a country or province controlled by another.
greater antilles
Cuba, the Cayman Islands, Jamaica, Hispaniola (Haiti on the west and the Dominican Republic on the east) and Puerto Rico
lesser antilles
a group of several small Caribbean Islands that make a chain reaching from the Virgin Islands in the north to Grenada in the south
political map
a type of map that represents political divisions, or human-created boundaries, of the world, continents and major geographic regions
west indies
not a country. They are a crescent-shaped group of islands more than 2,000 miles (3,200 kilometres) long separating the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea, to the west and south, from the Atlantic Ocean, to the east and north.
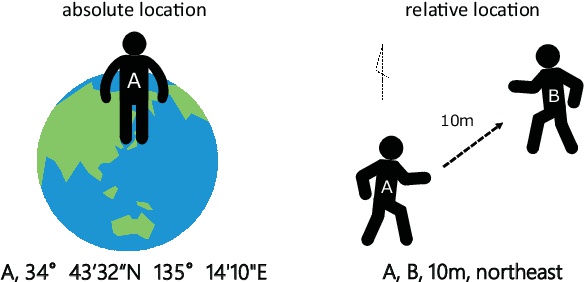
Absolute location:
description of a place using grid coordinates (latitude and longitude)
Eurasia
a landmass made up of the continents of Asia and Europe
mental map
a map that a person pictures in his or her mind
relative location
description of a place using the relation of one place to another
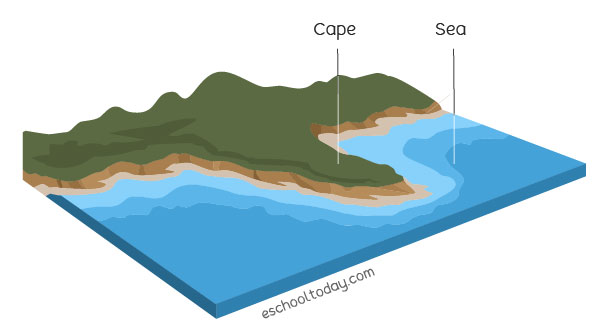
sea
a body of salt water that is part of an ocean, yet is partially enclosed by land

map sketch
a rough drawing of a mental map
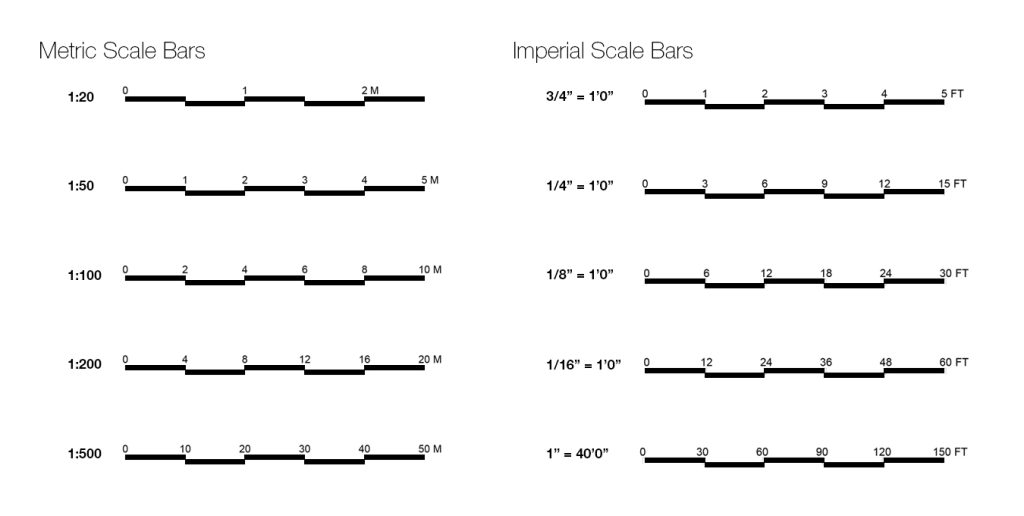
bar scale
small graphics that indicate the proportions of a map to the original geographic area and help users measure distances on maps
highway interchange
a junction where two or more highways meet, allowing vehicles to change direction or access different routes without stopping.

interstate highway
a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National Highway System in the United States
mileage
a number of miles traveled or covered used to measure distance or fuel efficiency

road map
a visual representation of roads and highways, showing routes, distances, and landmarks

U.S. Highway
a network of highways that are numbered and maintained by the state and federal governments, connecting cities and regions across the United States

air carrier airport
airport that serves planes of commercial (carry people) airlines.

cargo
all freight, except baggage, carried by an airplane including goods and merchandise

concourse
a large open area inside or in front of a public building, as in an airport or train station.

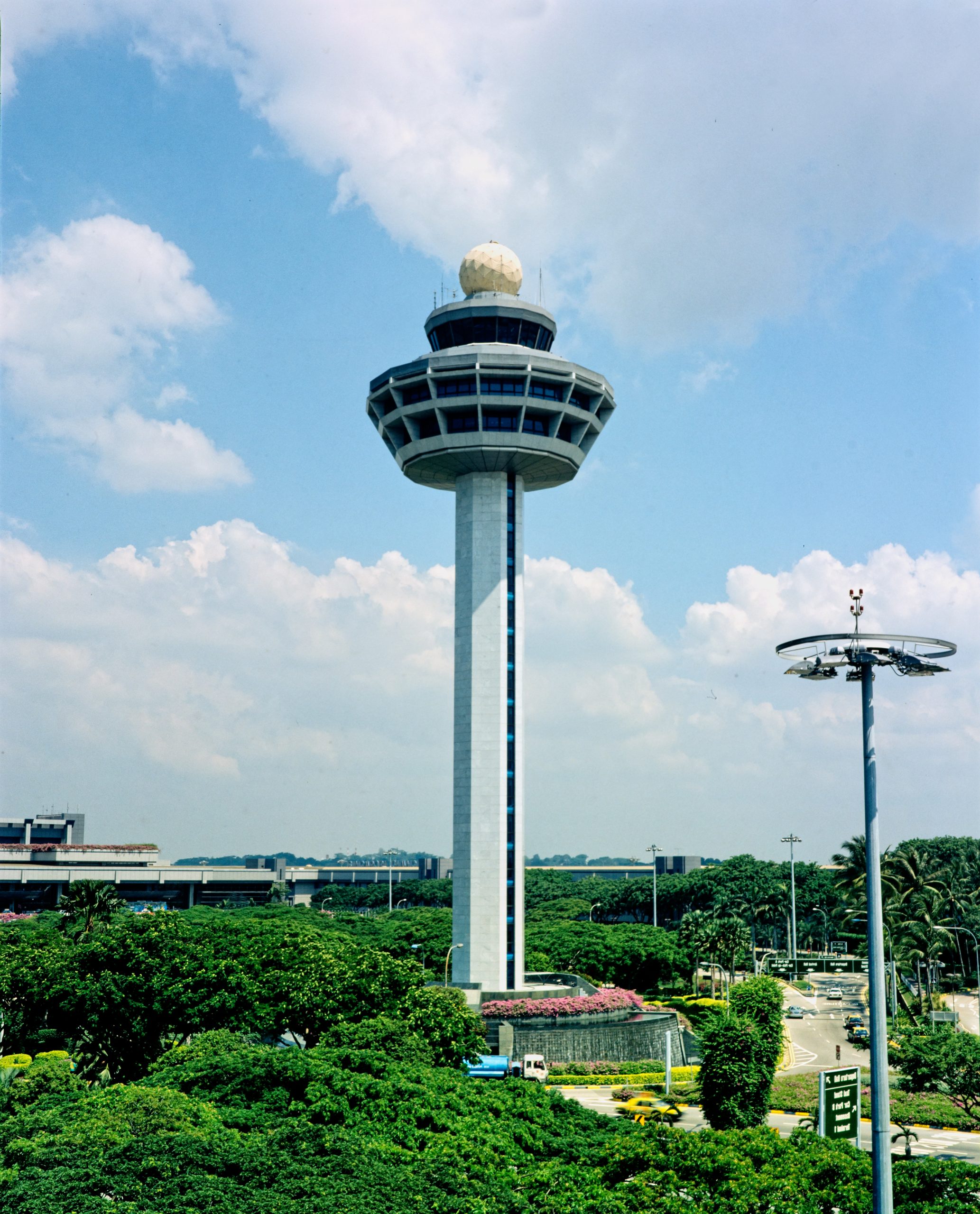
control tower
a tall building at an airport from which the movements of air and runway traffic are controlled

gate
an airport terminal entryway used for boarding or leaving an airplane

terminal
a main airport building for passenger services
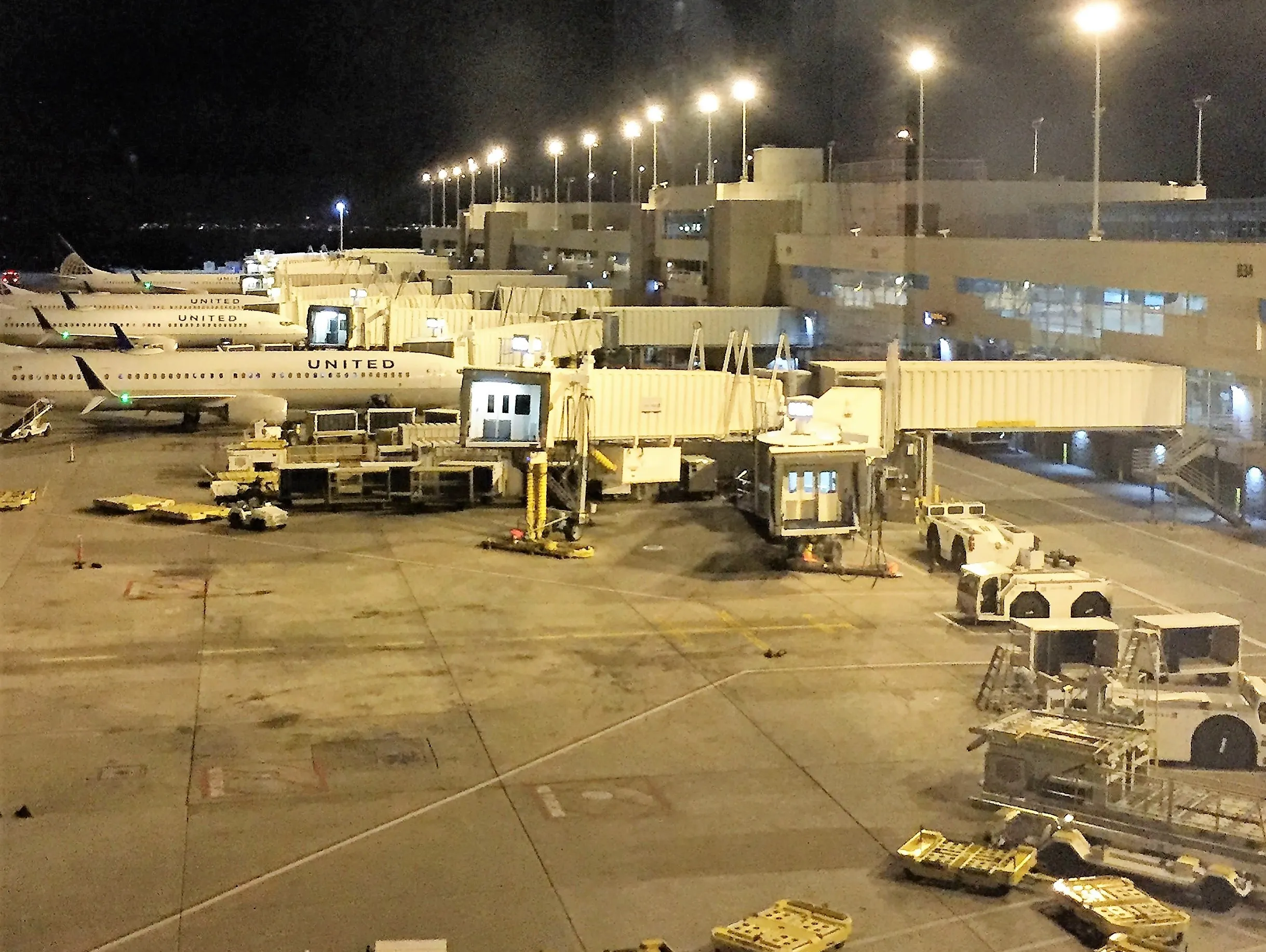

traffic pattern
a pattern of flight around an airport for arriving and departing aircraft
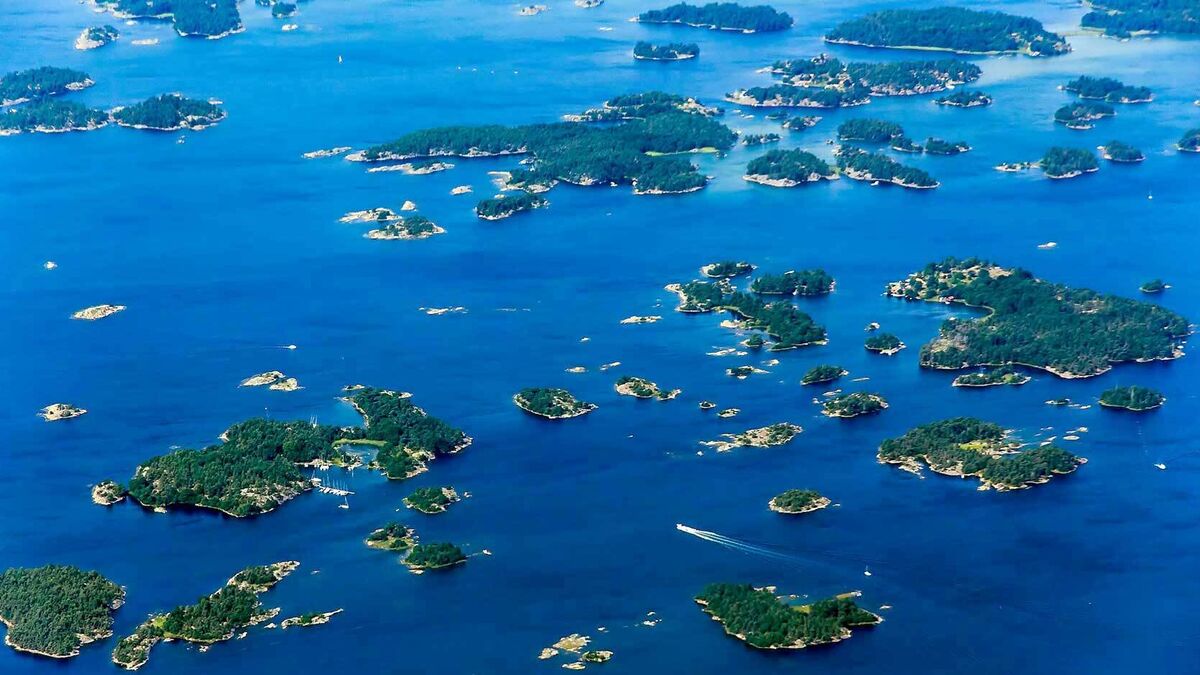
archipelago
a group of islands

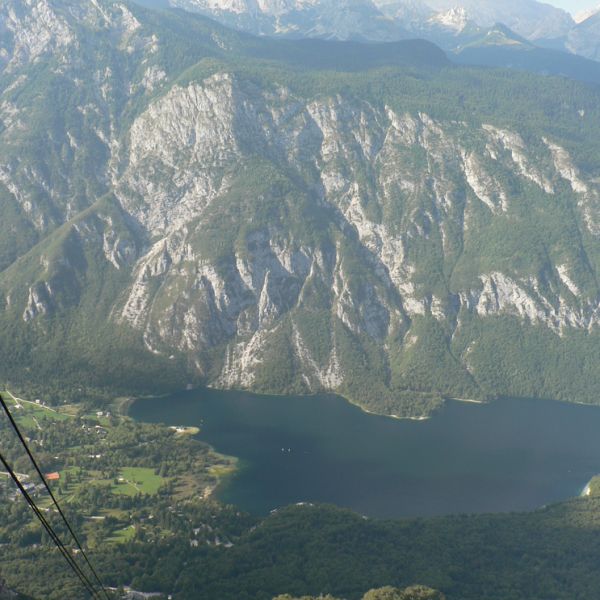
basin
a depression, or dip, in the Earth's surface

cape
a point or extension of land jutting out into water as a peninsula or as a projecting point
elevation
height above a given level, especially sea level

mountain range
a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground
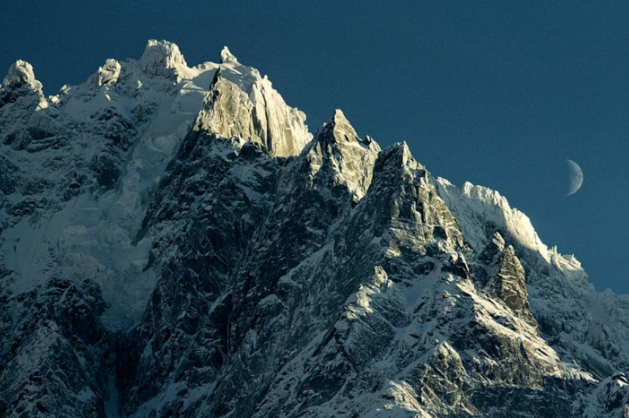

passage
a narrow channel of water that connects two larger bodies of water
physical map
a type of map that shows the physical features and sometimes elevation of a particular area or region in a two-dimensional format
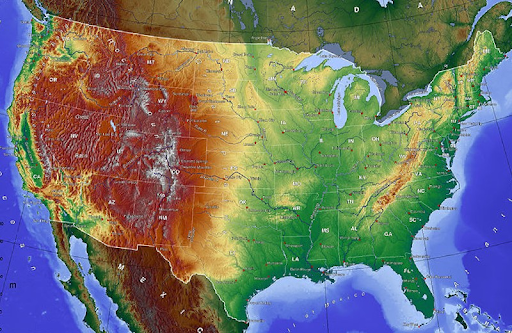
straight
a narrow waterway between two pieces of land that connects two large bodies of water

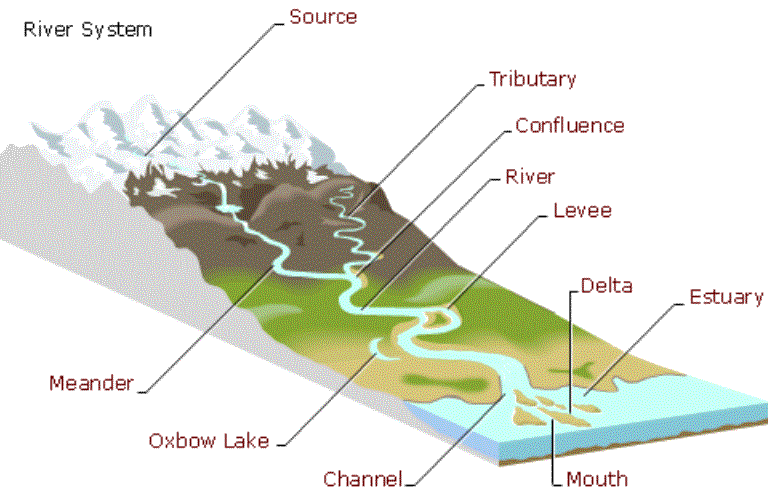
tributary
a river or stream flowing into a larger river or lake

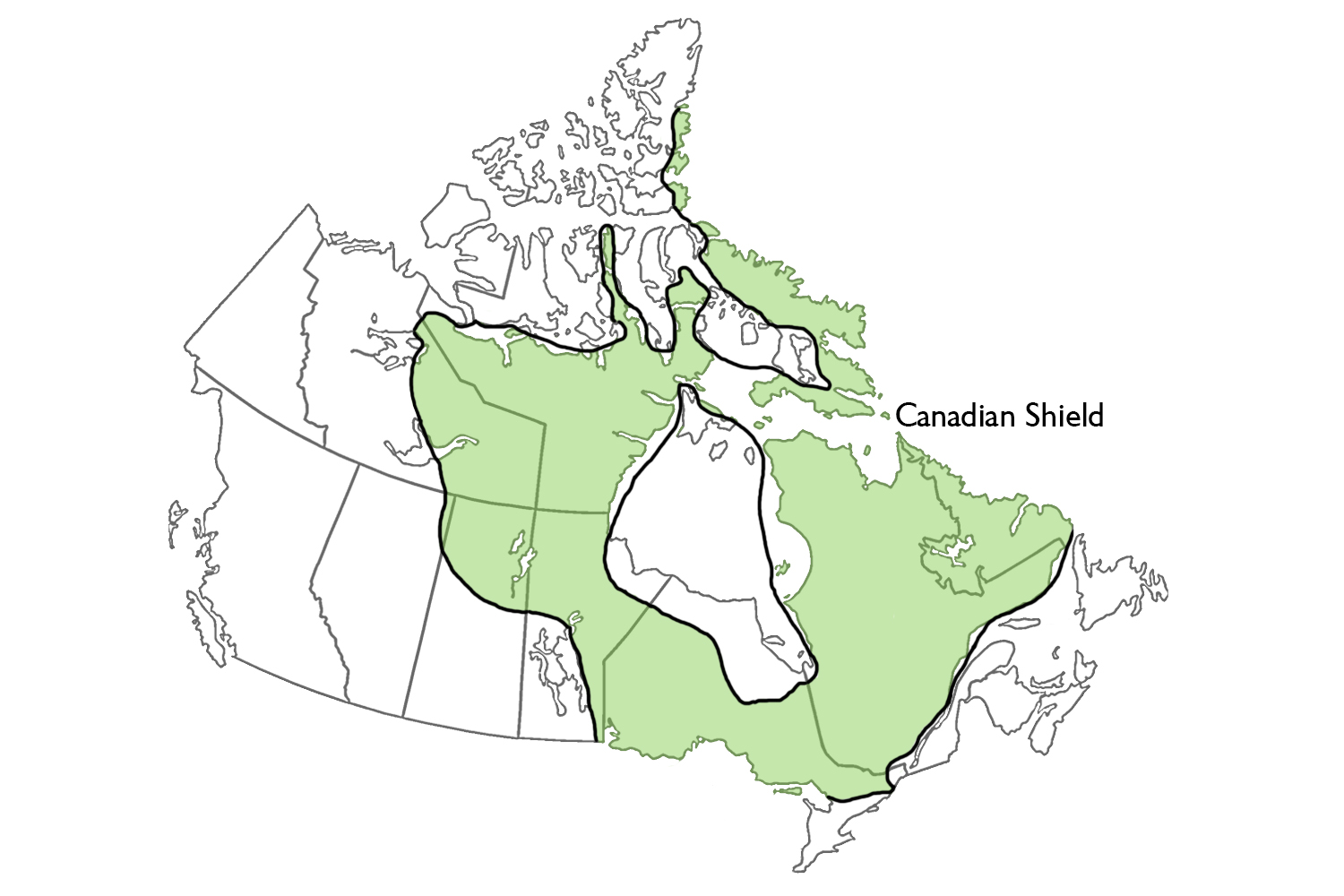
canadian shield
the exposed portion of the continental crust underlying the majority of North America
desert
a region of land that is very dry because it receives low amounts of precipitation
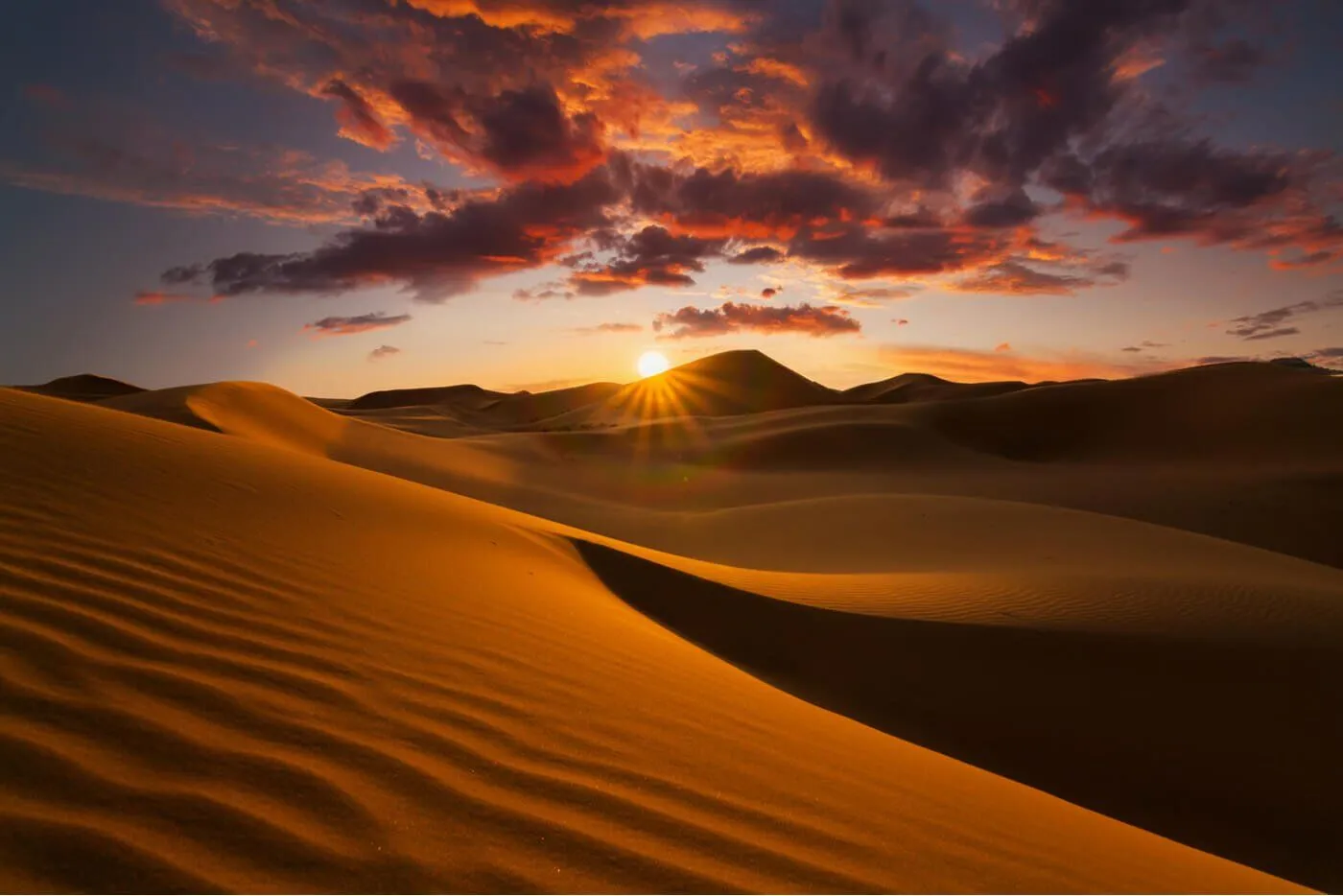

gulf
a portion of the ocean that penetrates land
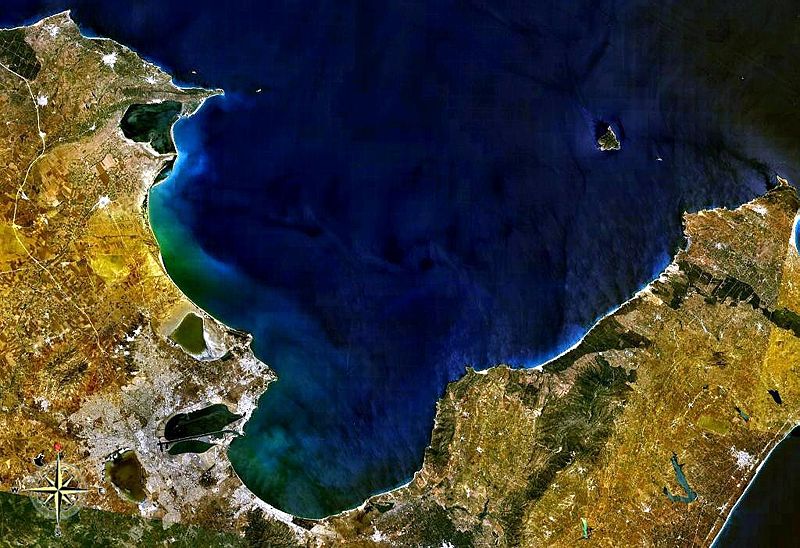

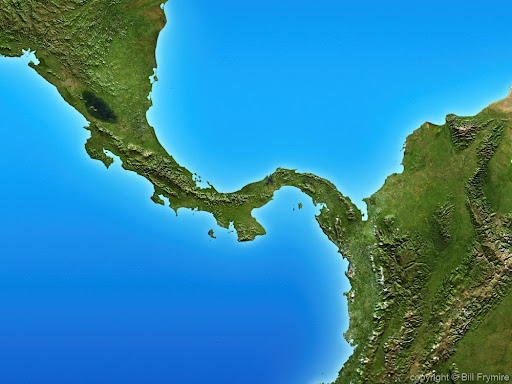
isthmus
a narrow strip of land that connects two larger landmasses and separates two bodies of water
plains
large areas of land that are mostly flat
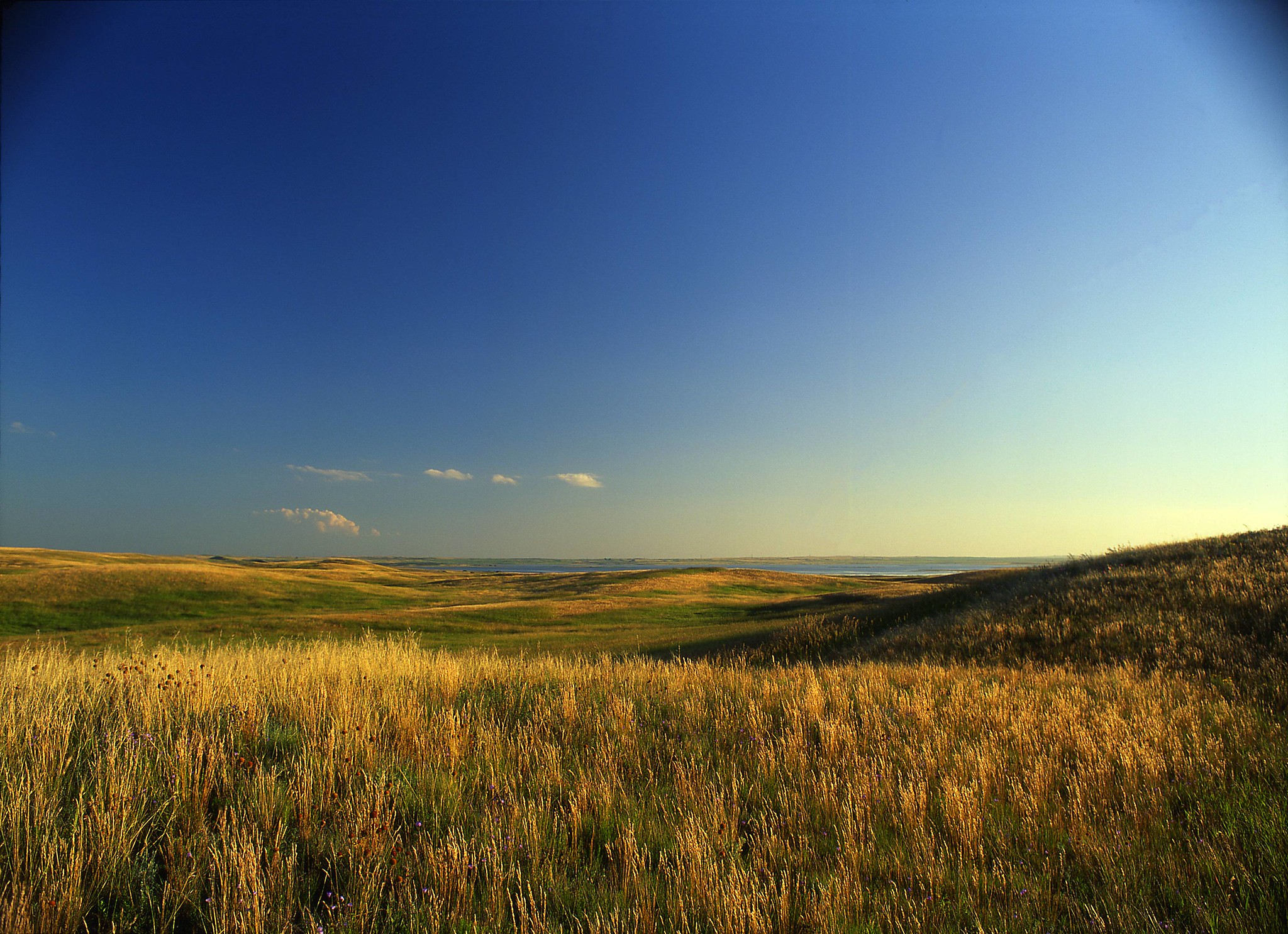

peninsula
a piece of land almost surrounded by water or projecting out into a body of water
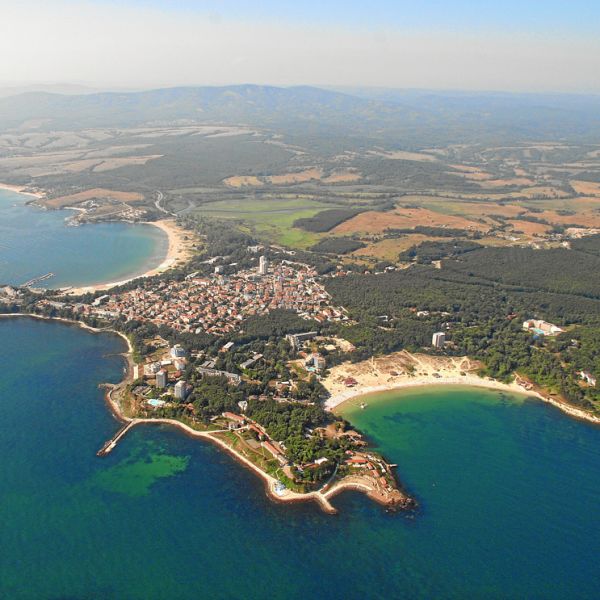

bay
a broad inlet of the sea where the land curves inward

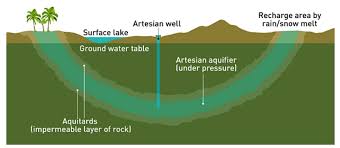
artesian basin
a source of water layered between impermeable rock
bight
a concave bend or curvature in a coastline, river or other geographical feature

coral
small marine animals. The “hard” type of coral grows with the help of algae, which gives it color and nutrients that help it form a sturdy, stony skeleton

coral reef
an underwater ecosystem characterized by reef-building corals

political map
a type of map that represents political divisions, or human-created boundaries, of the world, continents, and major geographic regions
tableland
an area containing elevated landforms characterized by a distinct, flat, nearly level, or gently undulating surface

mountain
a large natural elevation of the earth's surface rising abruptly from the surrounding level; a large steep hill

mountain peak
the pointed top of a mountain or ridge

mountain system
a line of mountains connected by high ground


butte
tall, flat-topped, steep-sided towers of rock

desert
A place that receives less than 25 centimeters (10 inches) of rain per year

dune
a mound of sand made by wind, often along a beach or desert

mesa
a flat-topped mountain or hill
oasis
an area made fertile by a source of freshwater in an otherwise dry and arid region
plateau
sand sea
mouth
The place where a river enters a lake, larger river, or the ocean

river system
a system or group of rivers so united that the water carried by the minor component streams finally unites in one body of flowing water
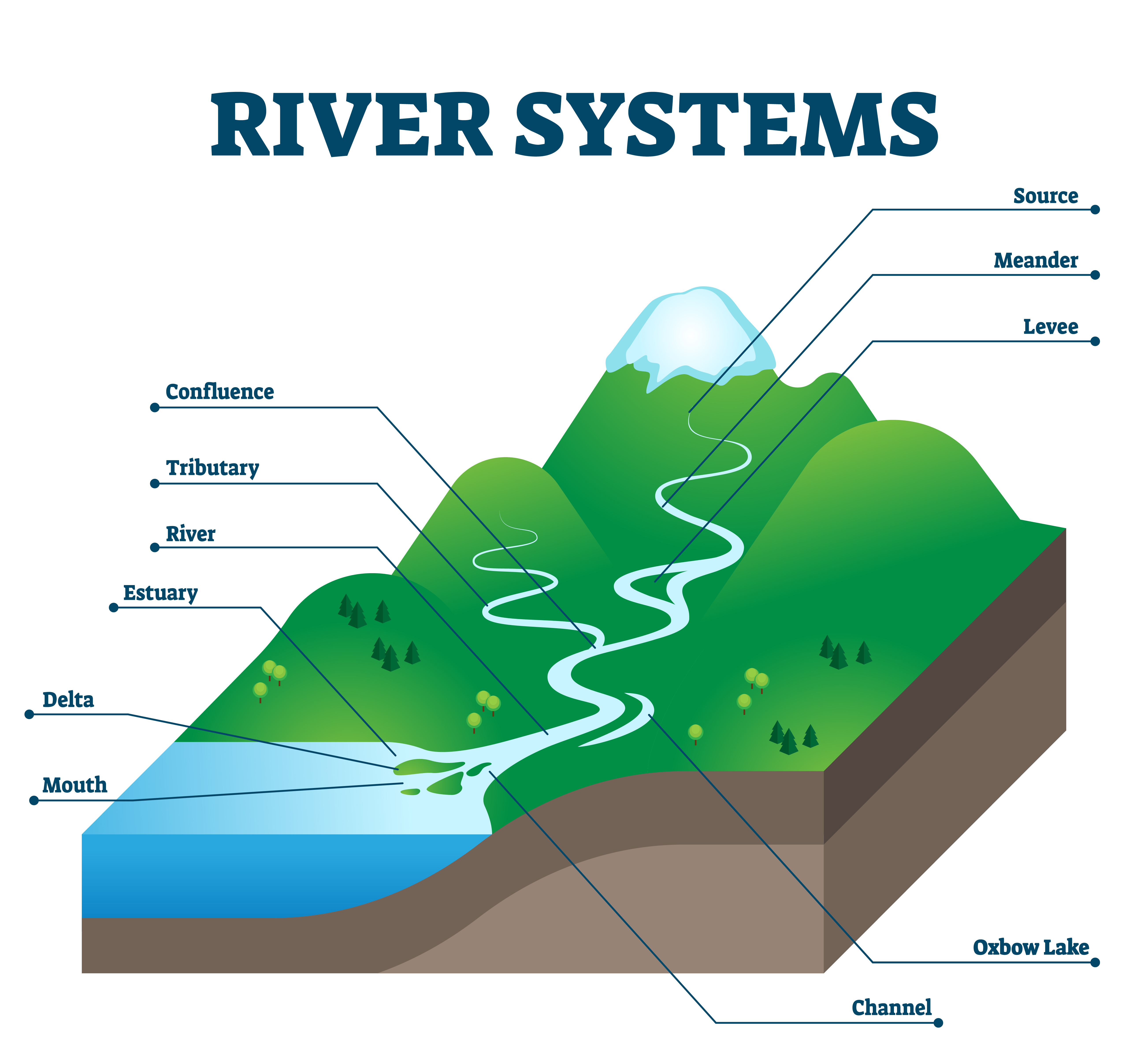
source
the place where a river begins
pacific region
Alaska, Washington, Oregon, California, and Hawaii
rocky mountain region
Colorado, Idaho, Montana, New Mexico, Utah, Wyoming
southwest region
Arizona, New Mexico, Texas, Oklahoma
north-central region
Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, North Dakota, Ohio, South Dakota, and Wisconsin
southeast region
Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, Puerto Rico, the United States Virgin Islands, and Virginia
northeast region
Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, New York, New Jersey, and Pennsylvania
dependency
a country, province, or territory controlled by a bigger, more powerful country