Vision
1/151
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
152 Terms
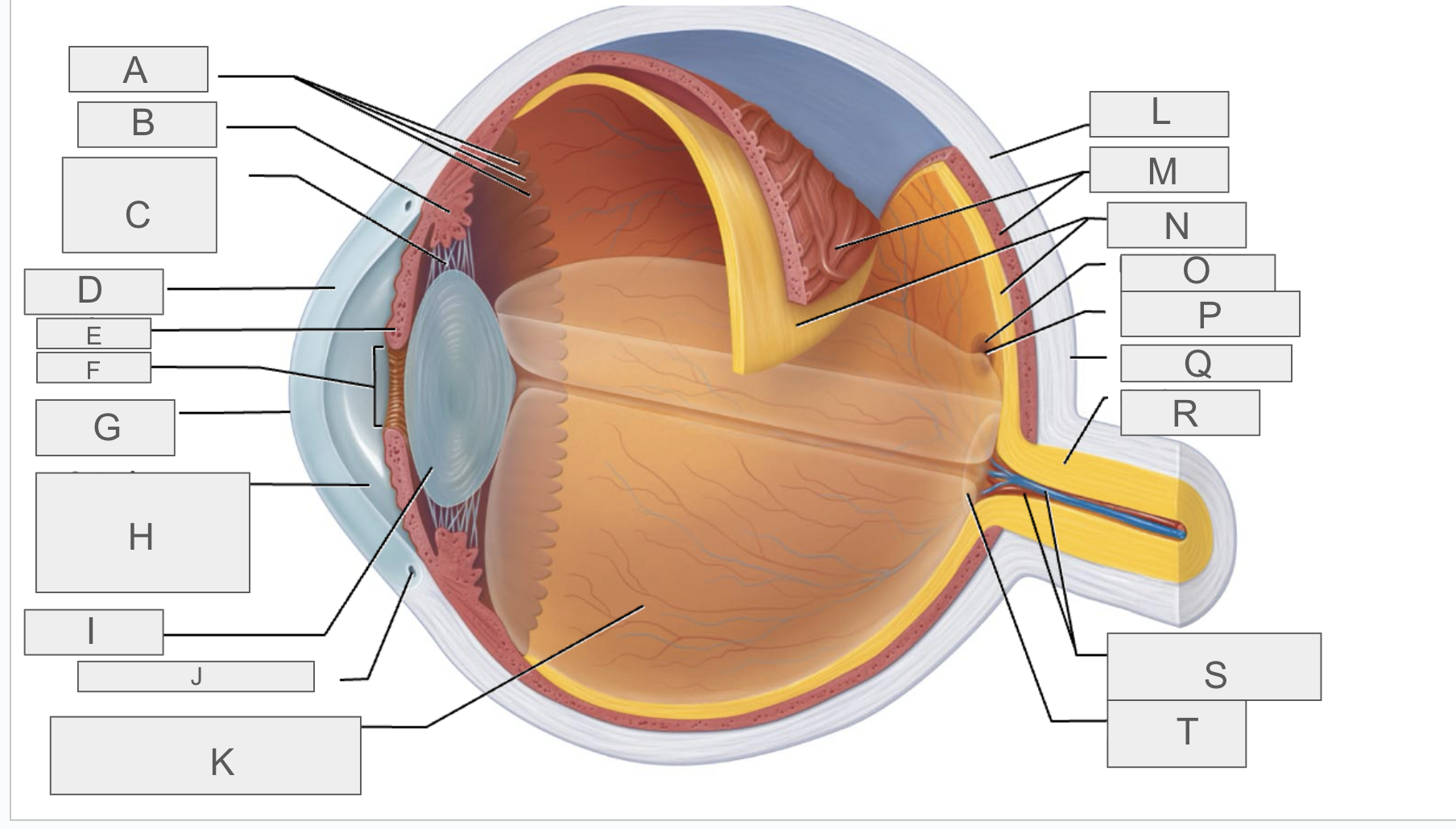
what is A?
Ora serrata
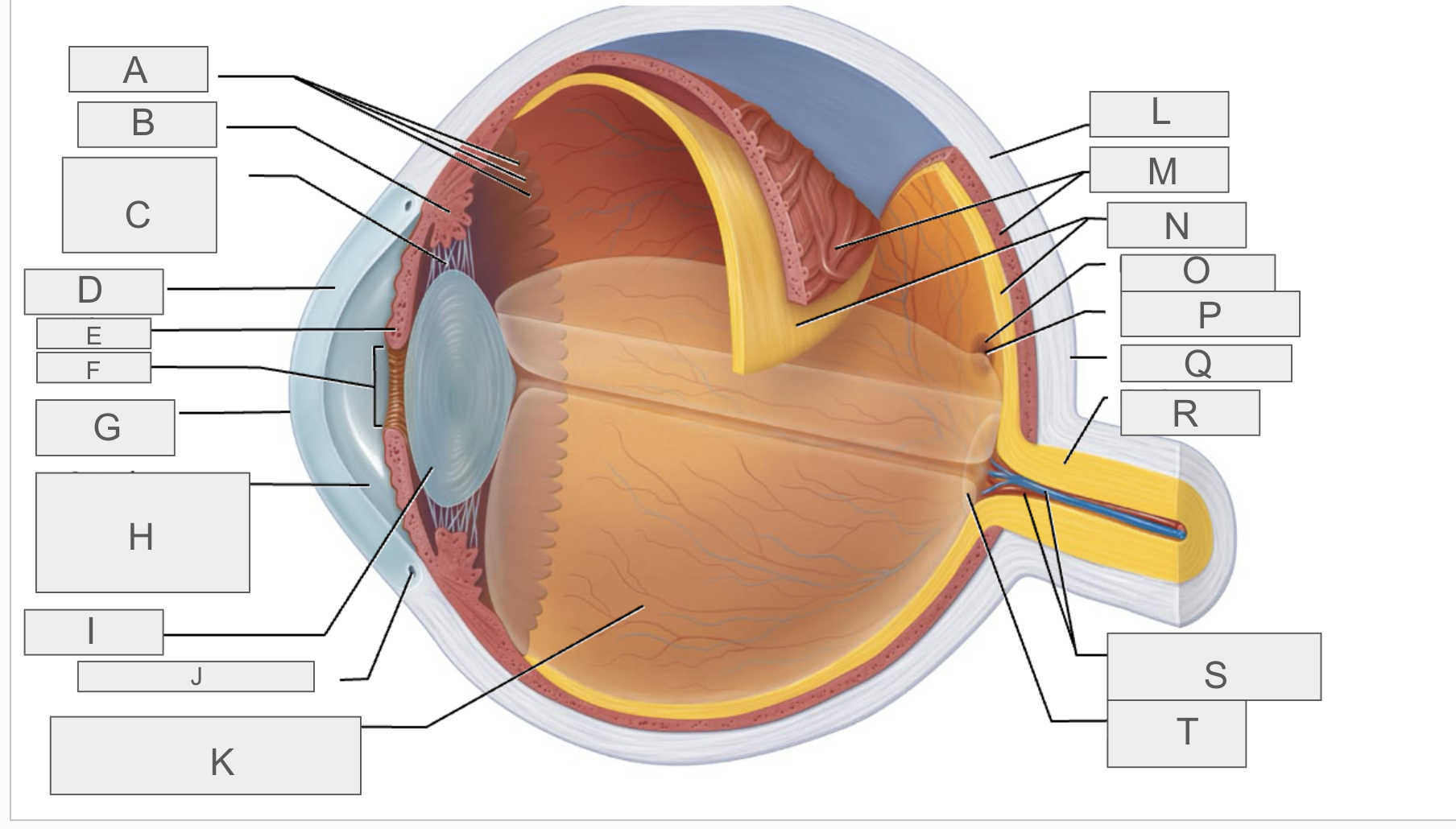
what is B?
ciliary body
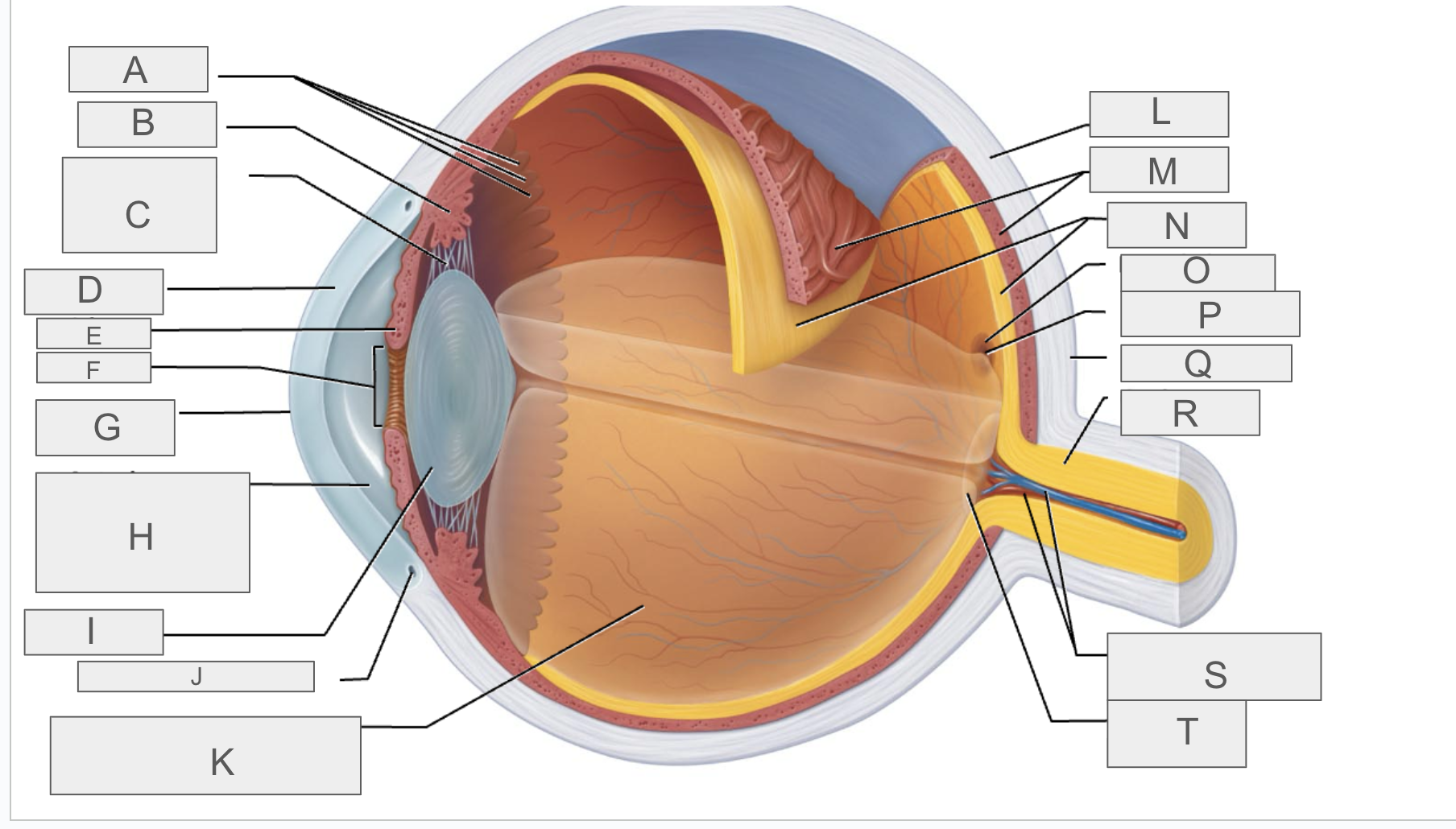
what is C?
ciliary zonule
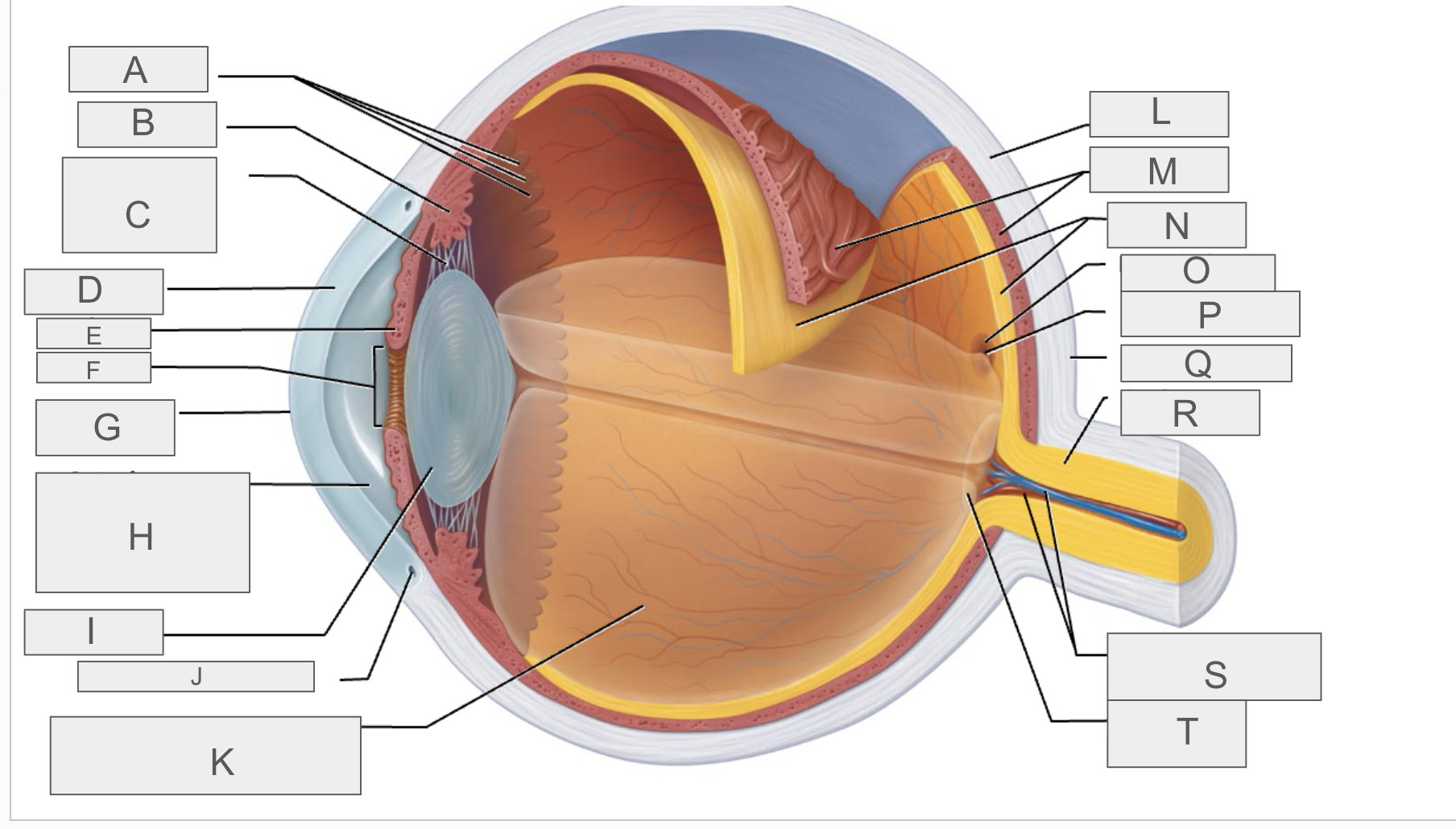
what is D?
cornea
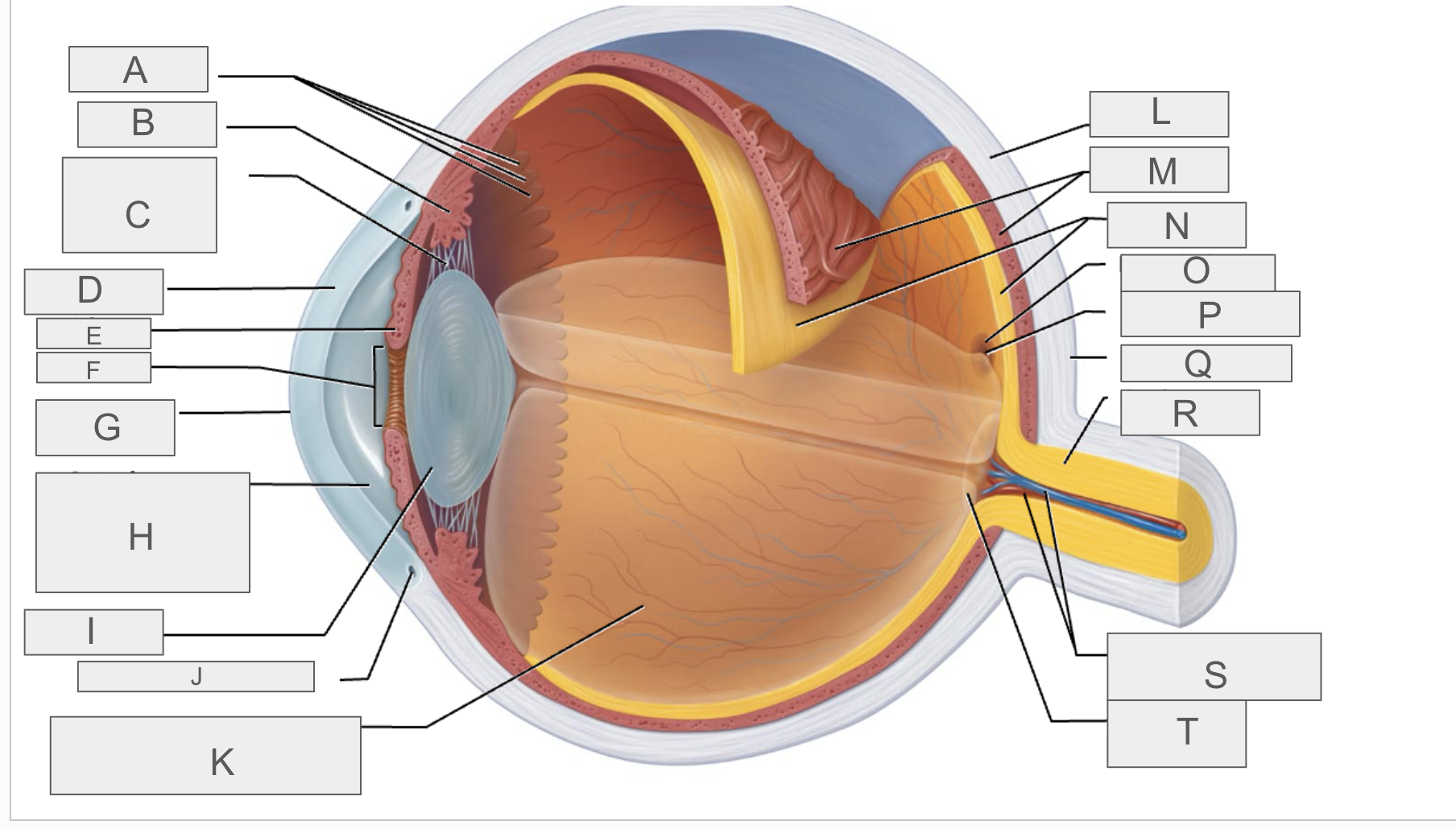
what is E?
iris
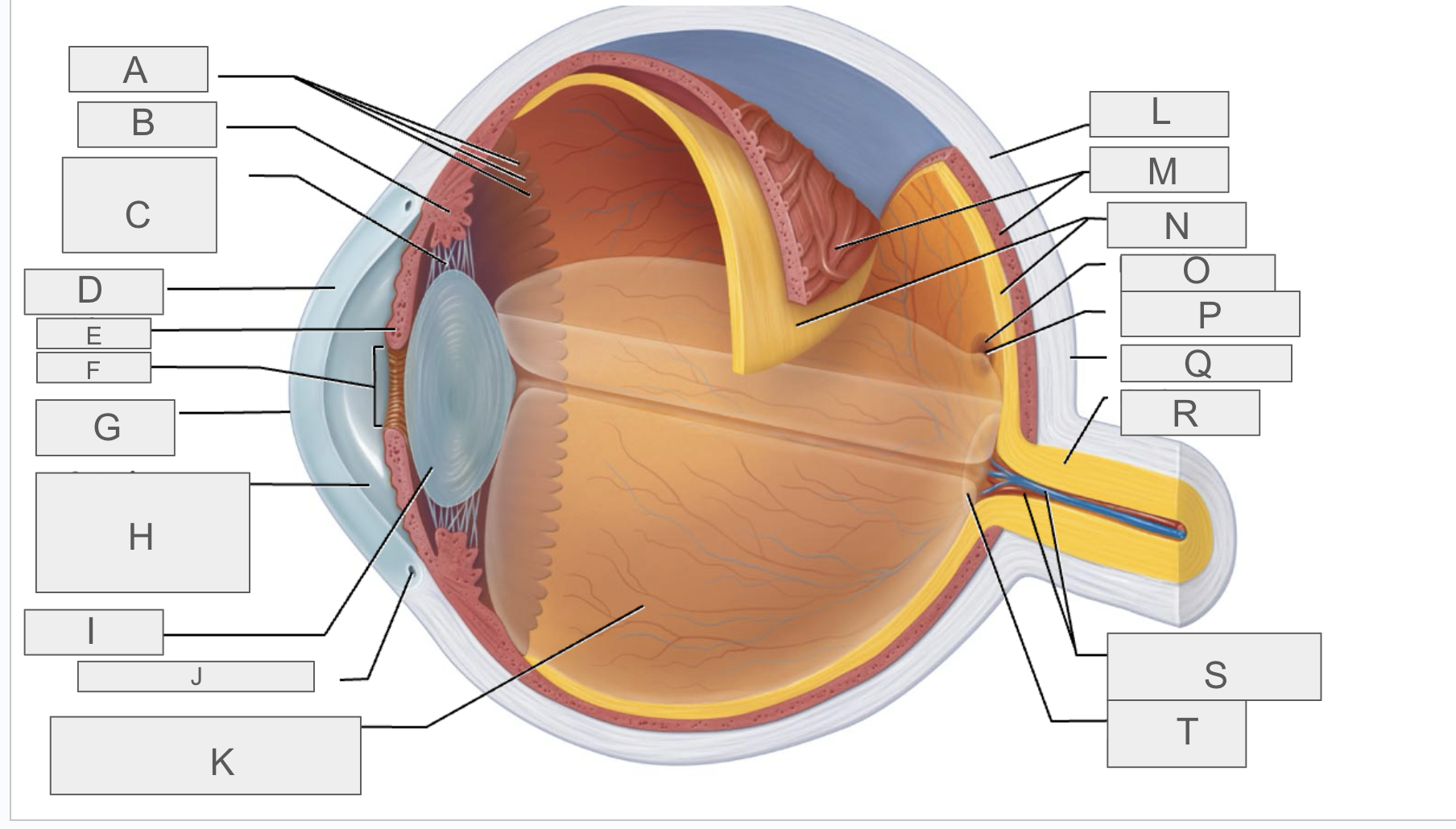
what is F?
pupil
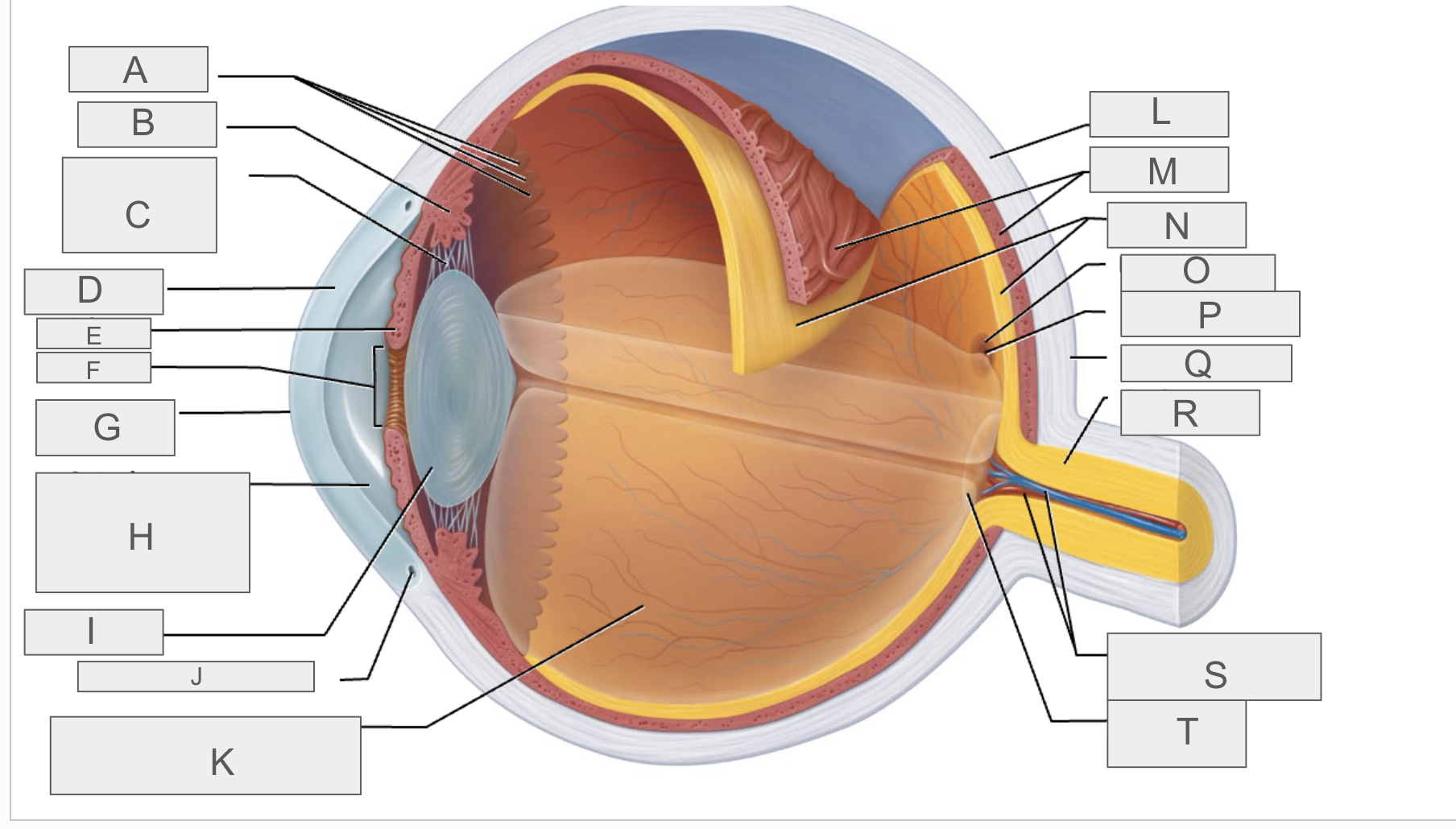
what is G?
anterior pole
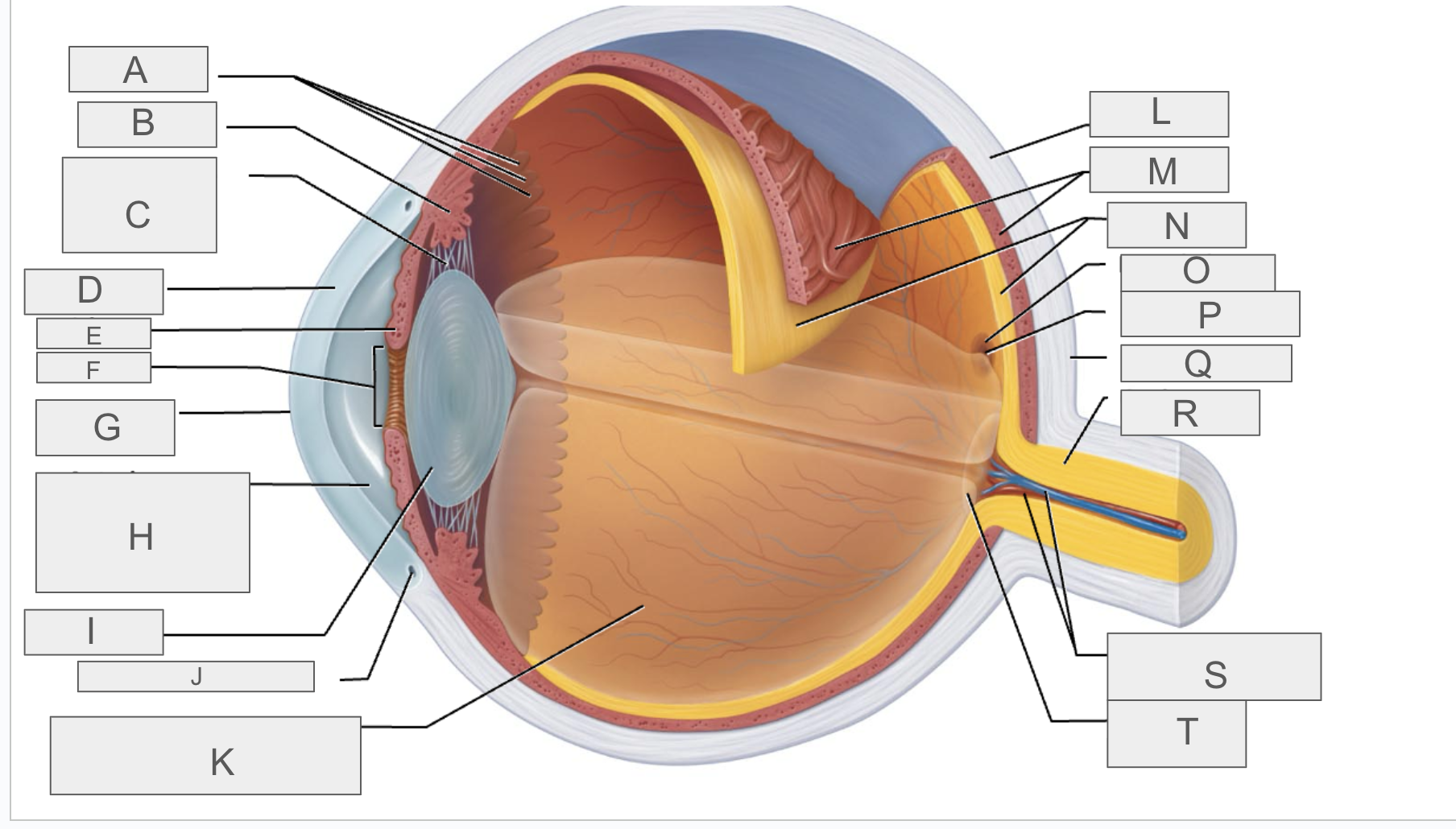
what is H?
anterior segment
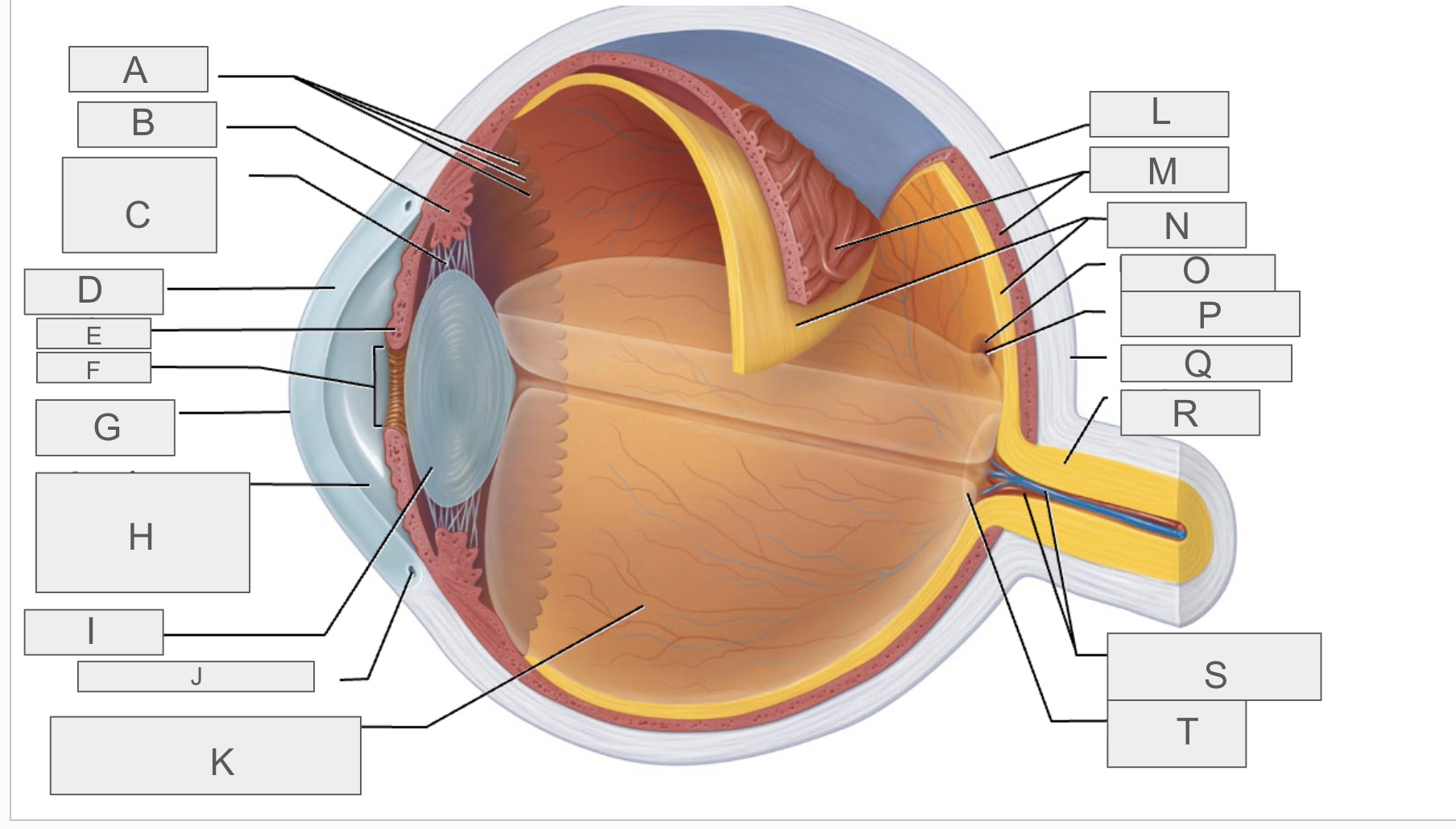
what is I?
lens
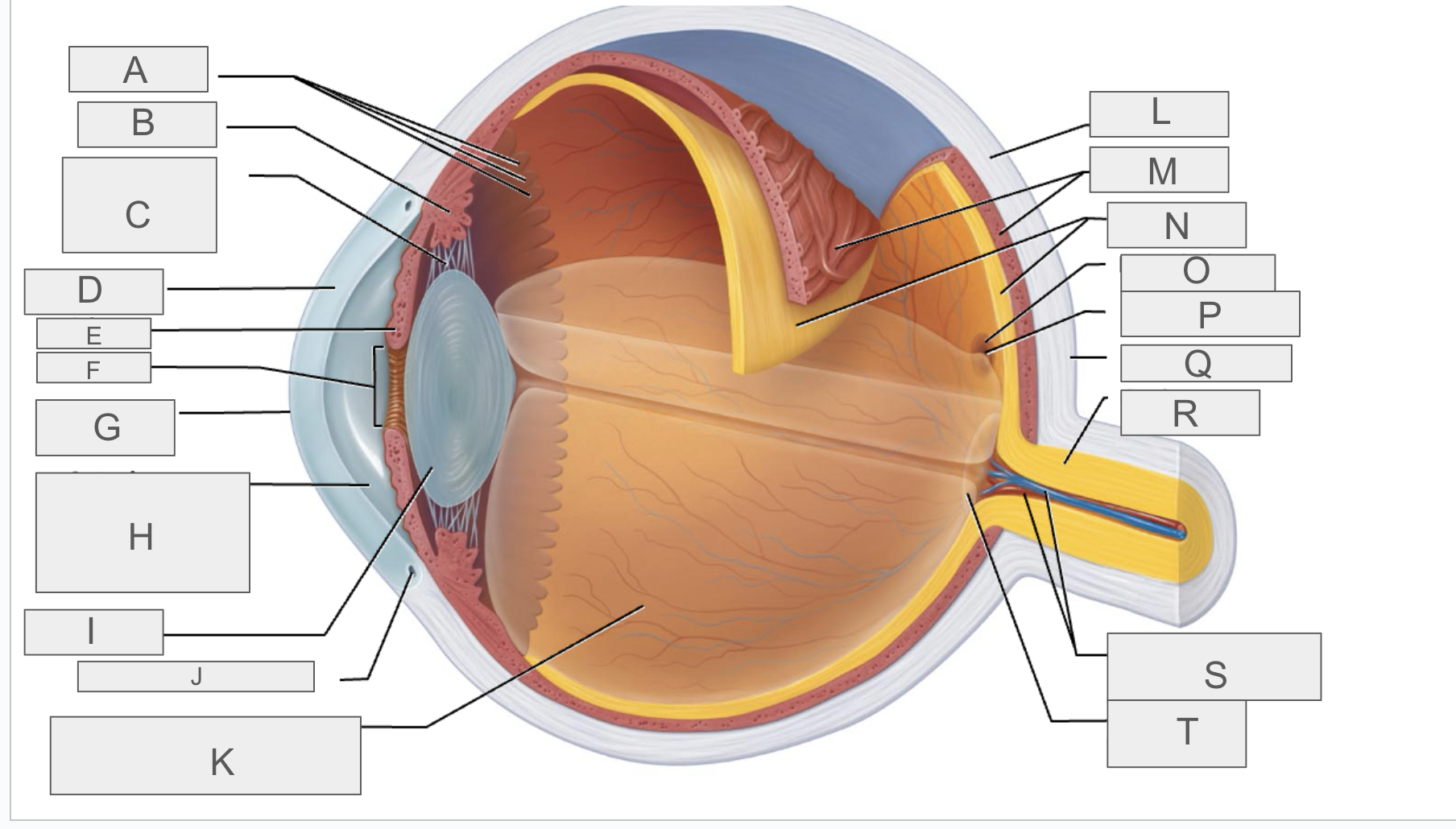
what is J?
scleral venous sinus
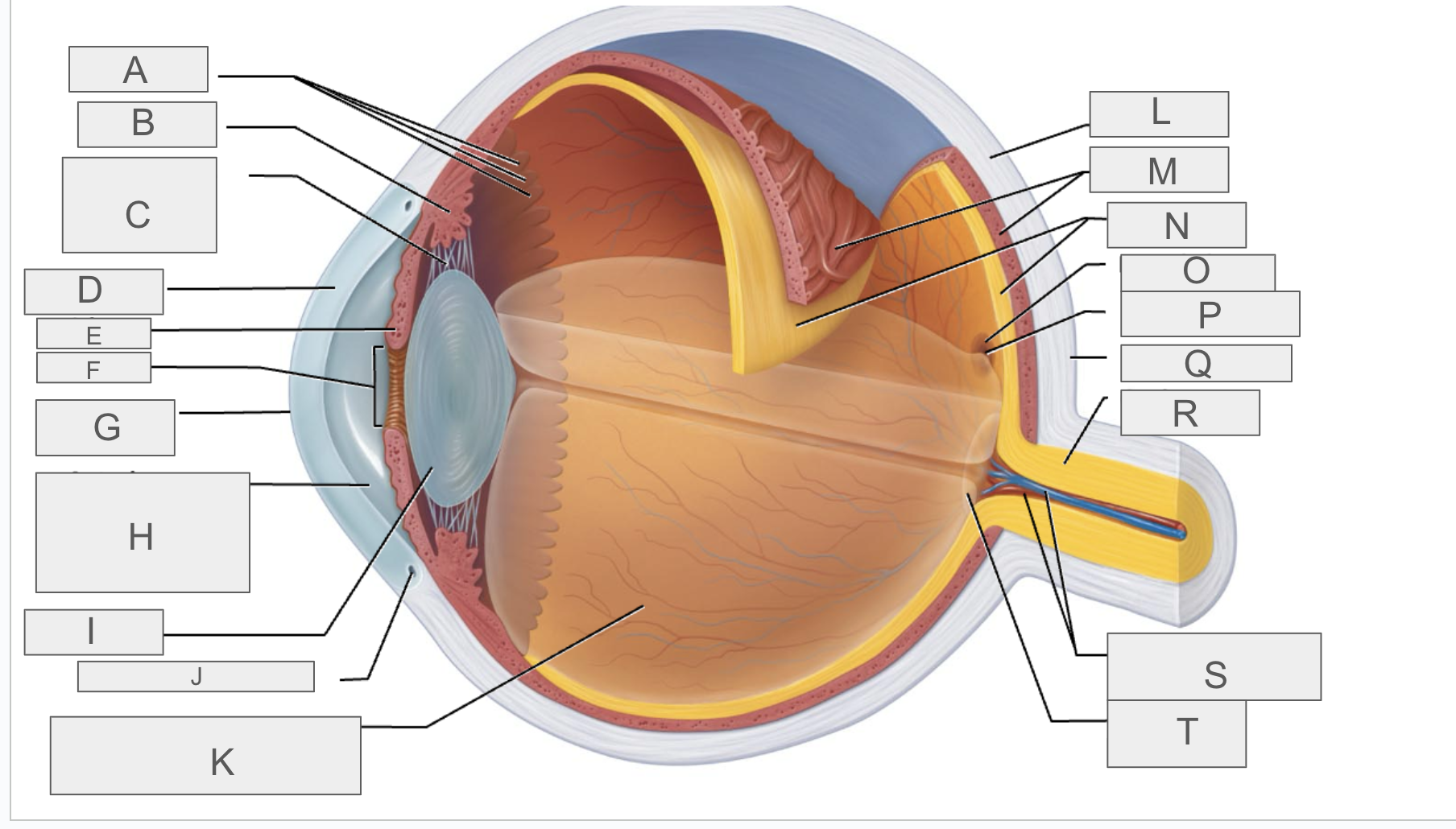
what is K?
posterior segment
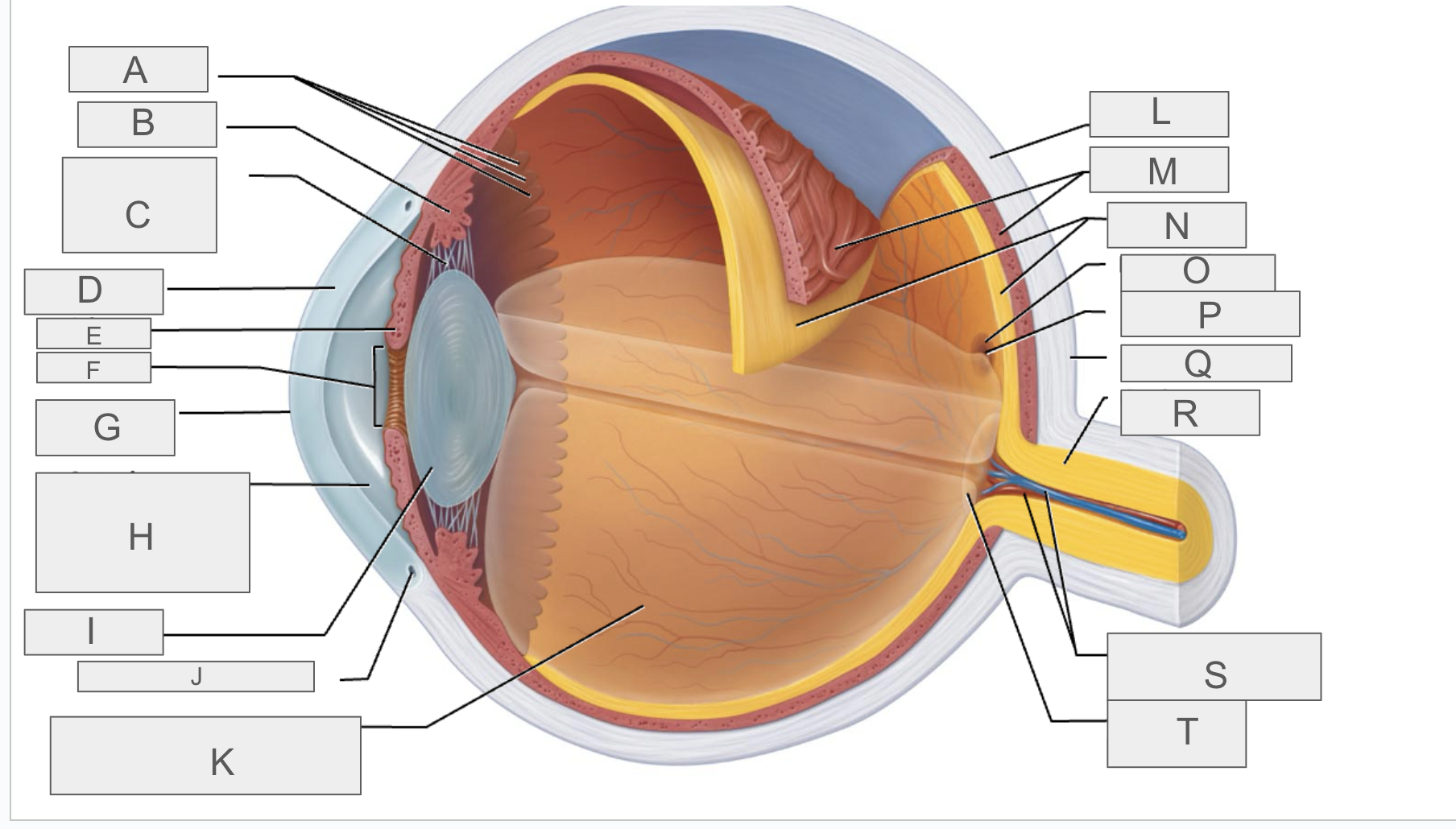
what is L?
sclera
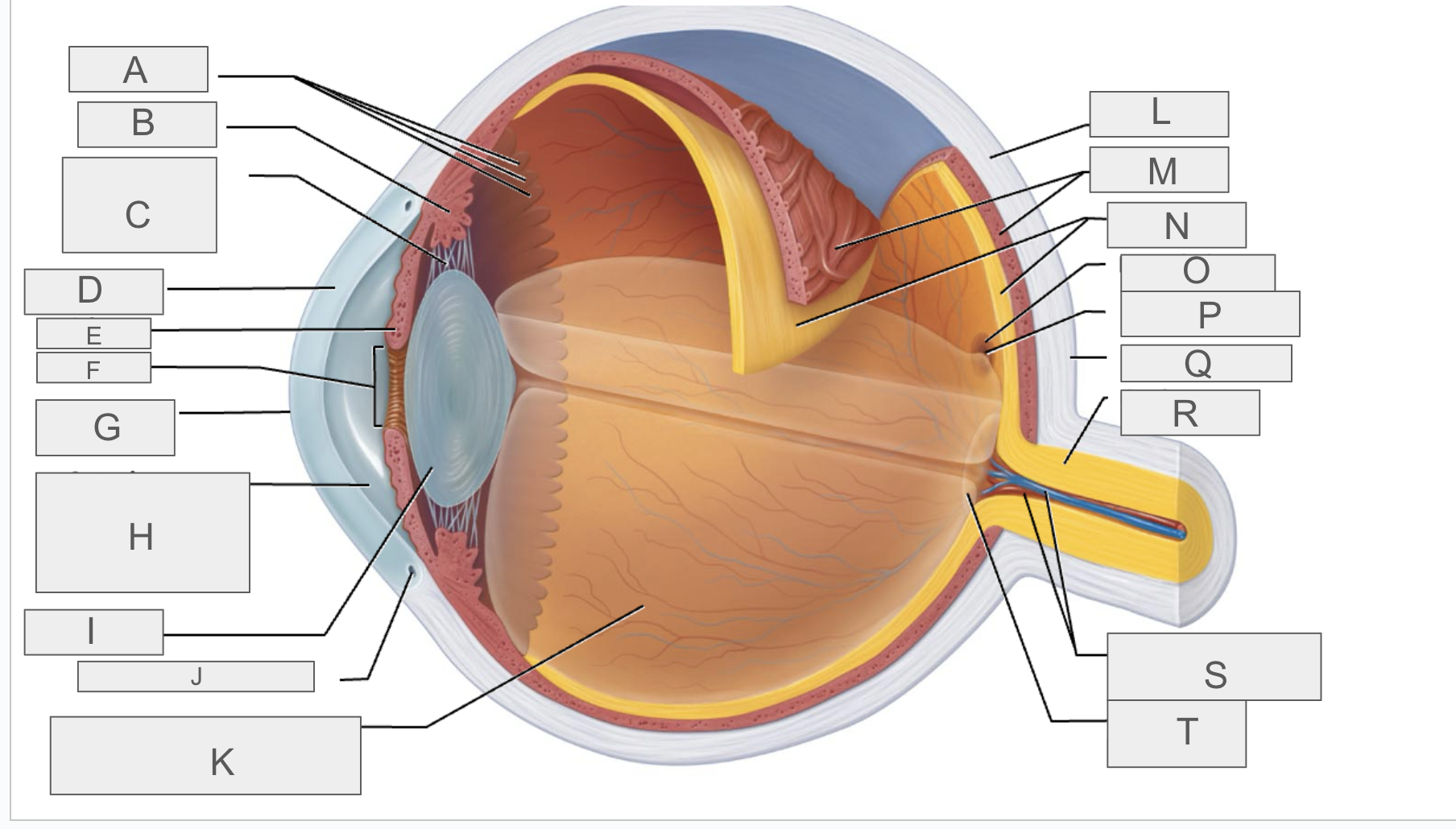
what is M?
choroid
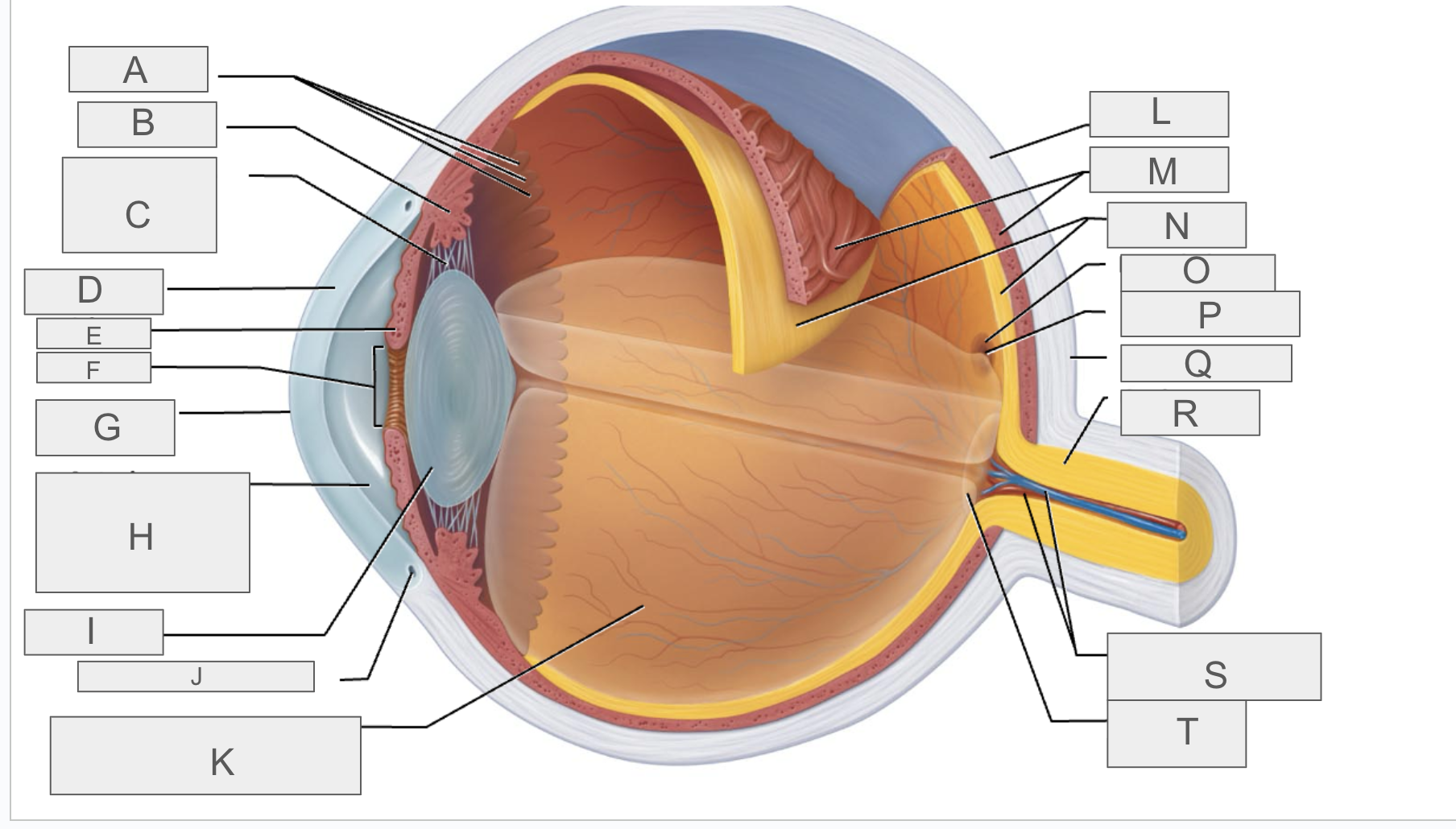
what is N?
retina
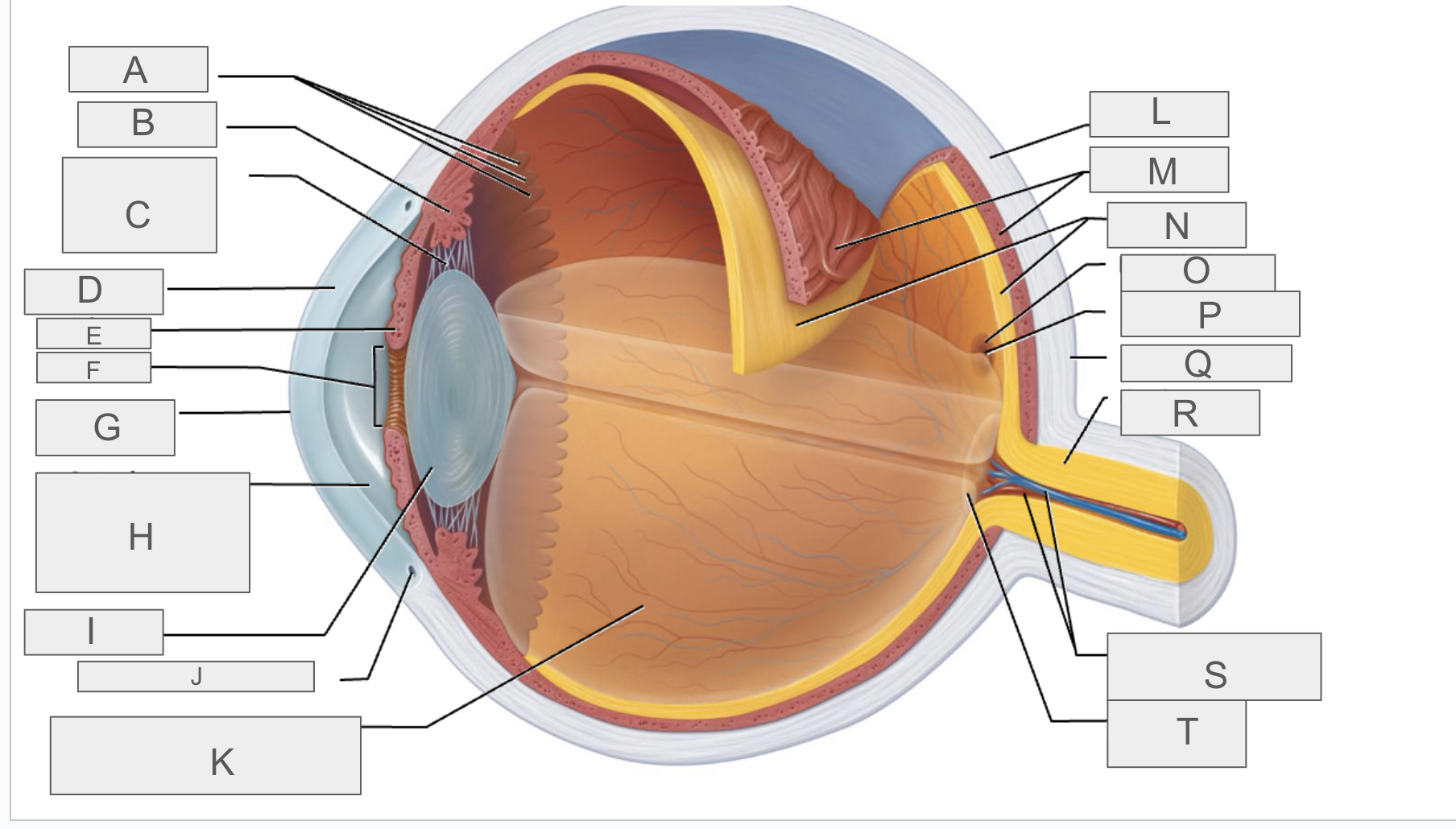
what is O?
macula lutea
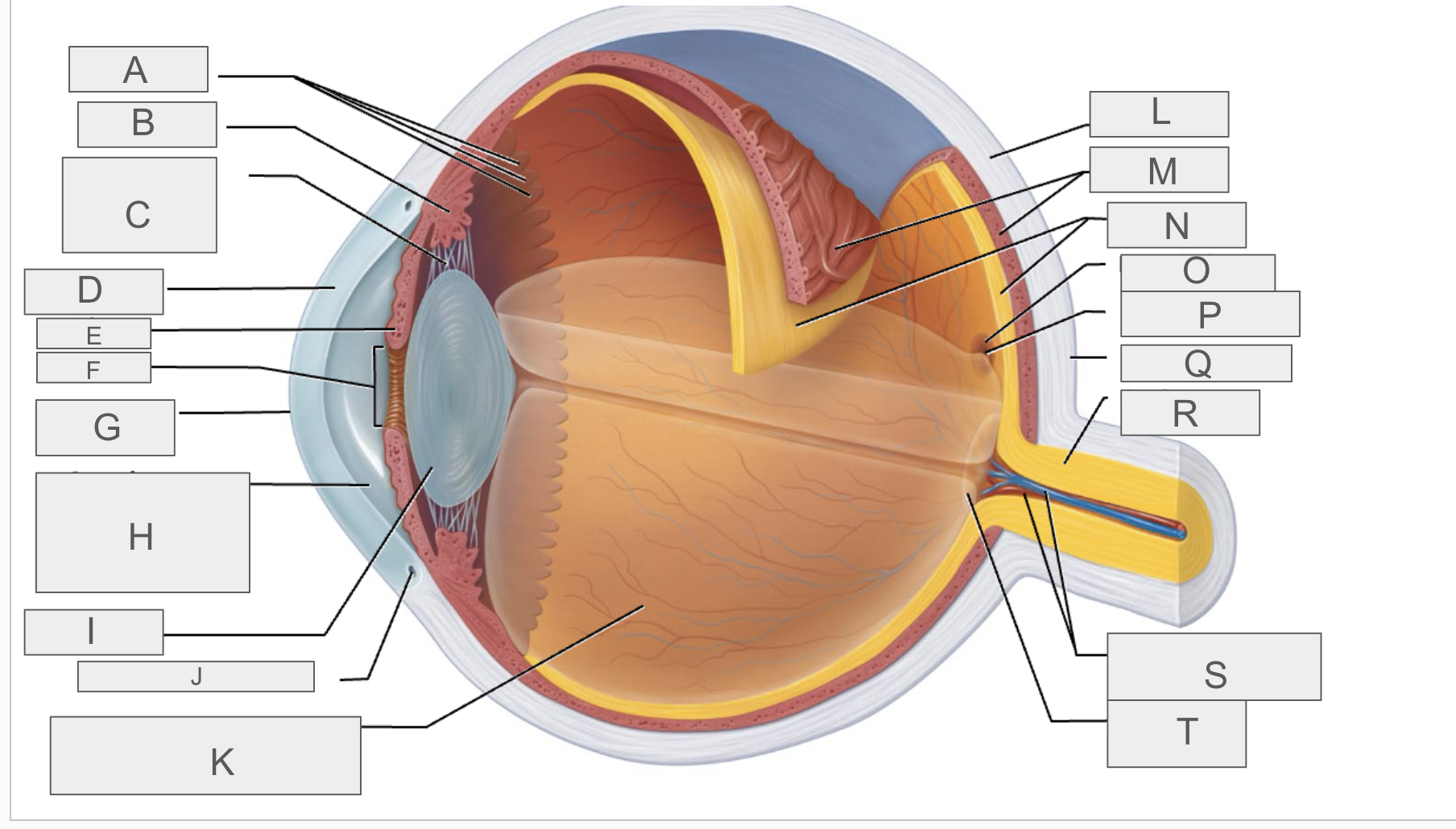
what is P?
fovea centralis
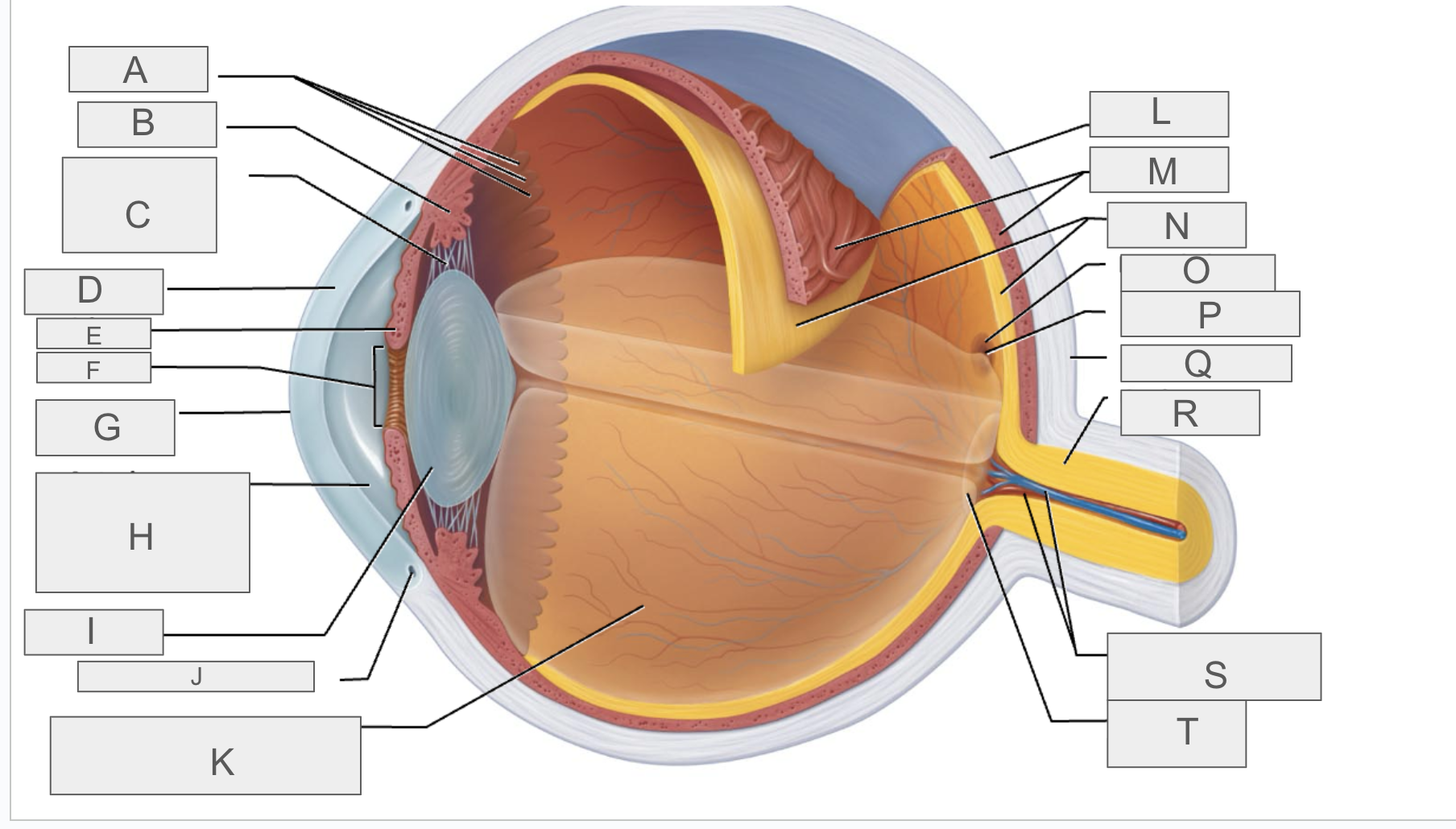
what is Q?
posterior pole
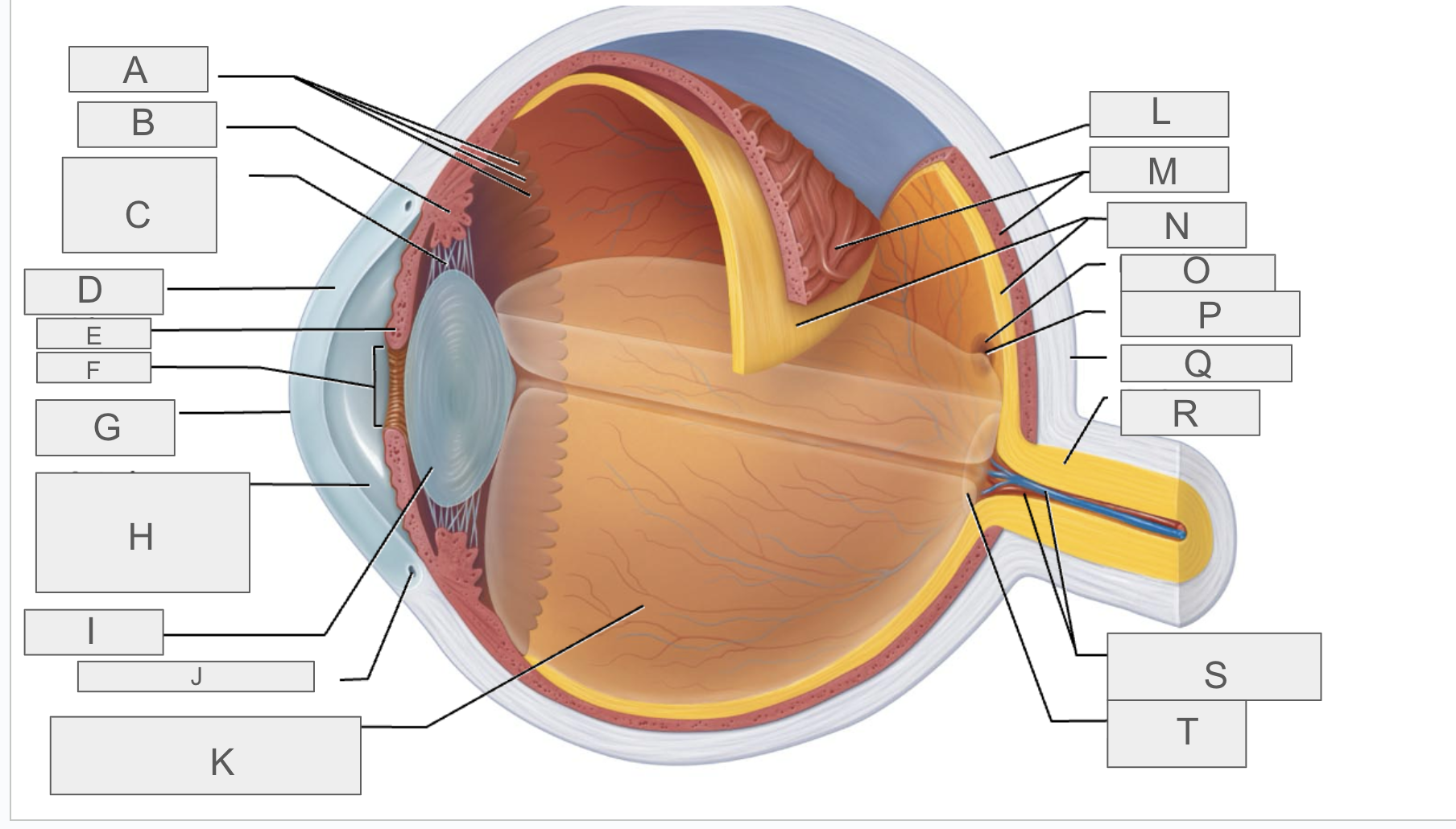
what is R?
optic nerve
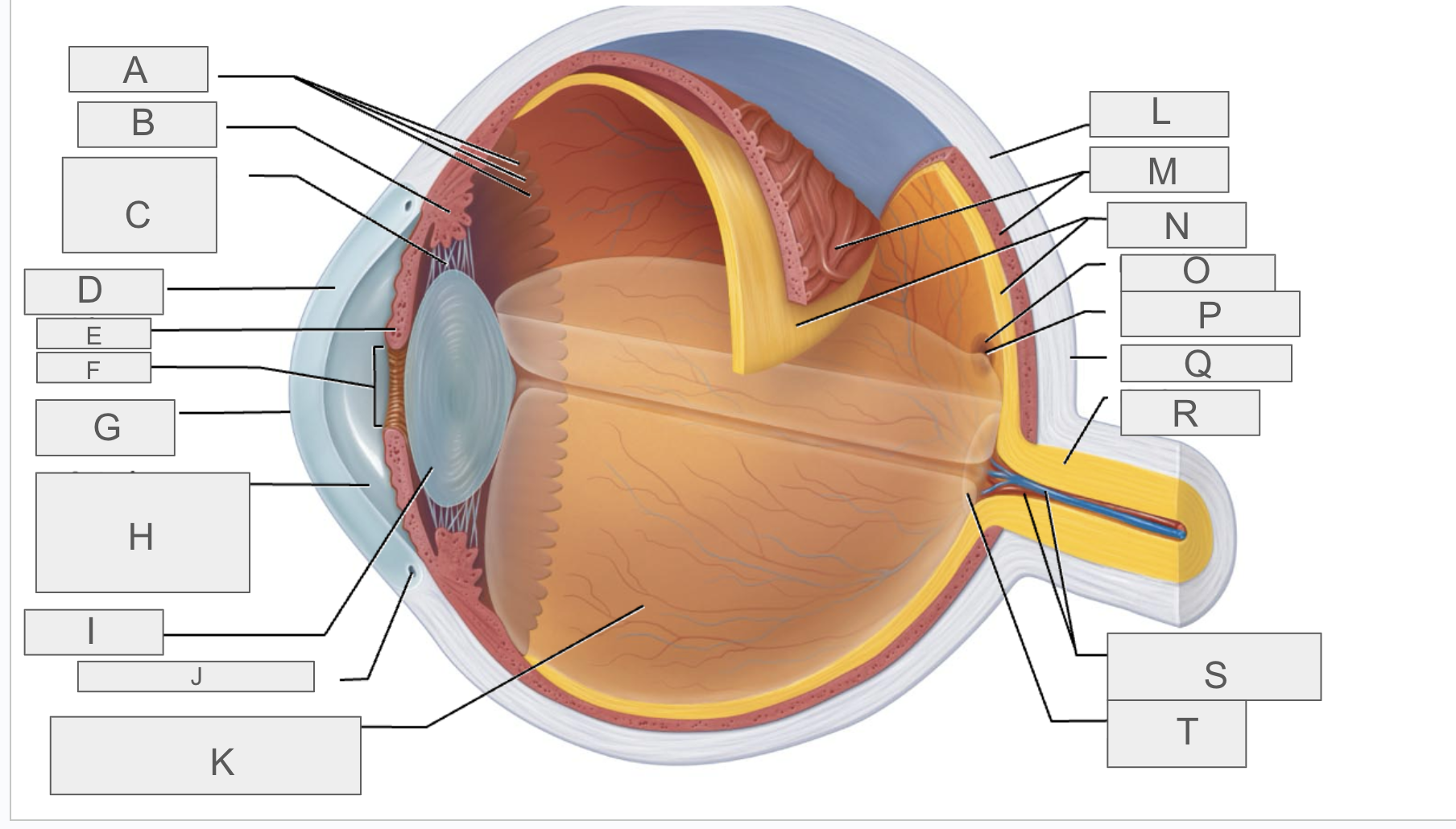
what is S?
central artery and vein of the retina
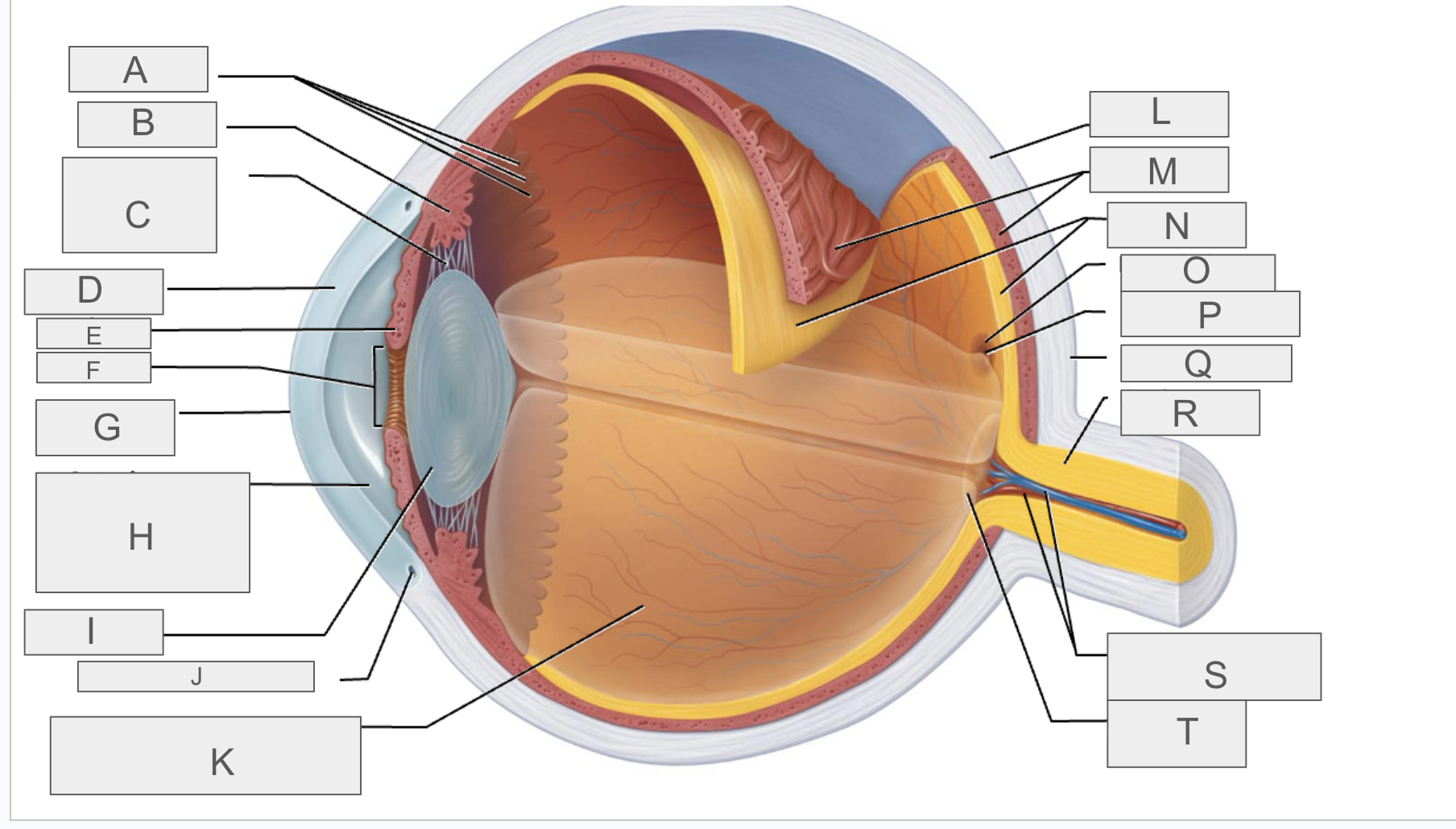
what is T?
Optic Disc (blind spot)
what are the 3 layers (tunics) of the eye?
fibrous, vascular, neural
what is the eye protected by?
a cushion of fat and bony orbit
what is the internal cavity filled with?
fluid (humors)
what separates the internal cavity of the eye into anterior and posterior segments?
lens
what makes up the fibrous layer of the eye?
sclera, cornea, scleral venous sinus
which part of the fibrous layer is in the posterior segment, made up of dense connective tissue, and avascular?
sclera
what is the function of the sclera?
protection, provide shape, sturdy anchor for extrinsic eye muscles
what part of the fibrous layer is in the anterior segment, is avascular, transparent, and made up of epithelial layers?
cornea
what is the function of the cornea?
pain reception, regeneration, and repair (mitotic)
where is the scleral venous sinus located?
the junction of the cornea and sclera
what is the function of the scleral venous sinus?
drain fluid from anterior segment of eye into blood
what makes up the vascular layer (uvea) of the eye?
ciliary body, ciliary zonule, iris, pupil, choroid
what is the part of the vascular layer that is in the posterior segment, is vascular and supports avascular structures, and contains pigment (melanocytes) to absorb light rays?
choroid
what makes up the ciliary body?
ciliary processes, ciliary muscle
what are the capillaries that secrete aqueous humor in the anterior segment of the vascular layer?
ciliary processes
what is the smooth muscle that alters the shape of the lens?
ciliary muscle
what does the ciliary muscle increase/decrease?
tension of suspensory ligaments (ciliary zonules)
what is the iris made up of?
circular and radial smooth muscle fibers
what are the two muscles in the iris?
pupillary sphincter, pupillary dilator
what part of the eye is responsible for different eye colors?
iris
when does the pupillary sphincter muscle contract?
during parasympathetic stimulation
when does the pupillary dilator muscle contract?
during sympathetic activation
what does the pupillary sphincter muscle reduce?
size of pupil, amount of light entering eye
what does the pupillary dilator muscle allow for?
increase in size and light entering eye
what is the central black hole of the eye?
pupil
what does the size of the pupil determine?
amount of light entering eye
what does the pupil change in response to?
bright/dim light, emotions
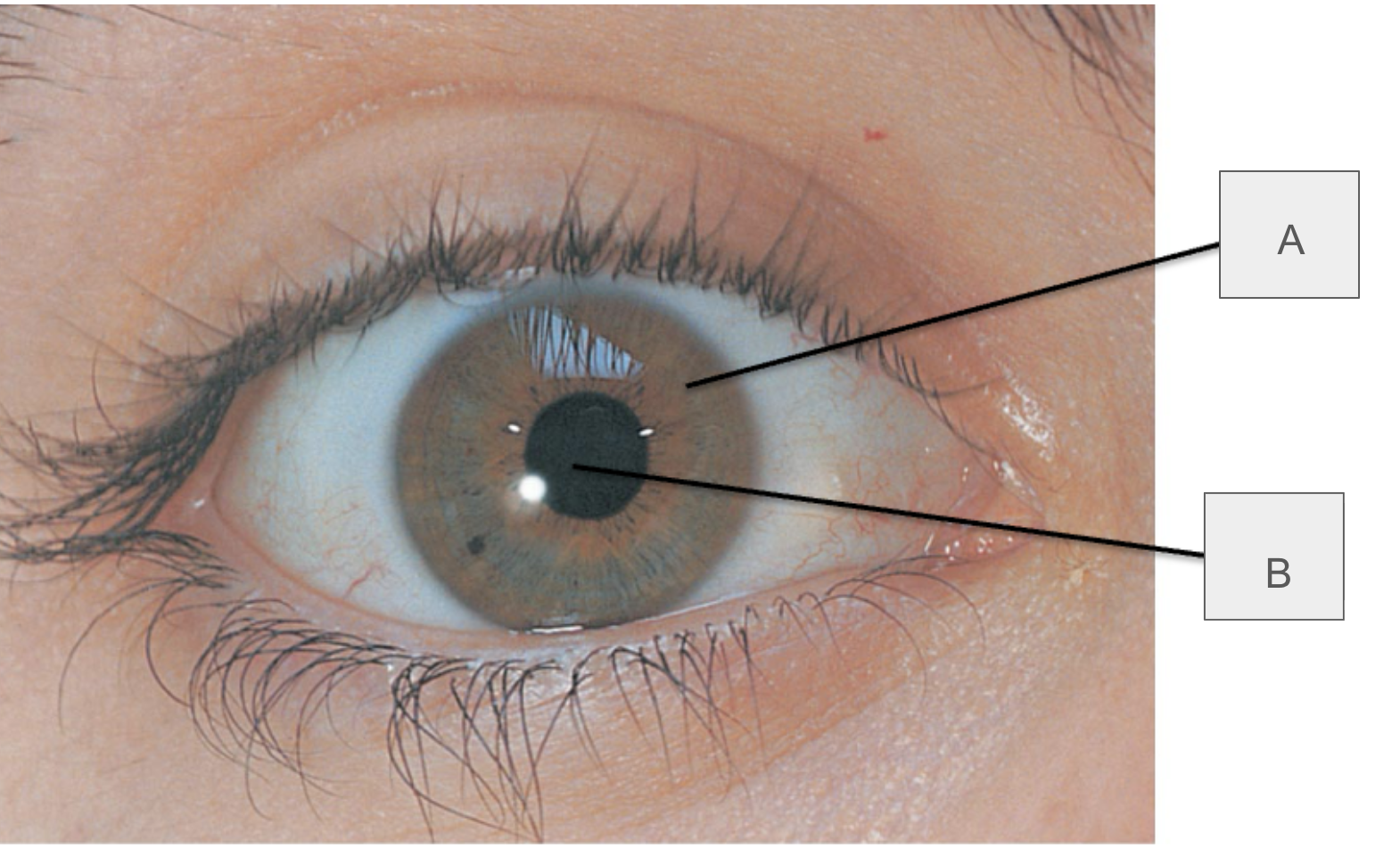
what is A?
iris
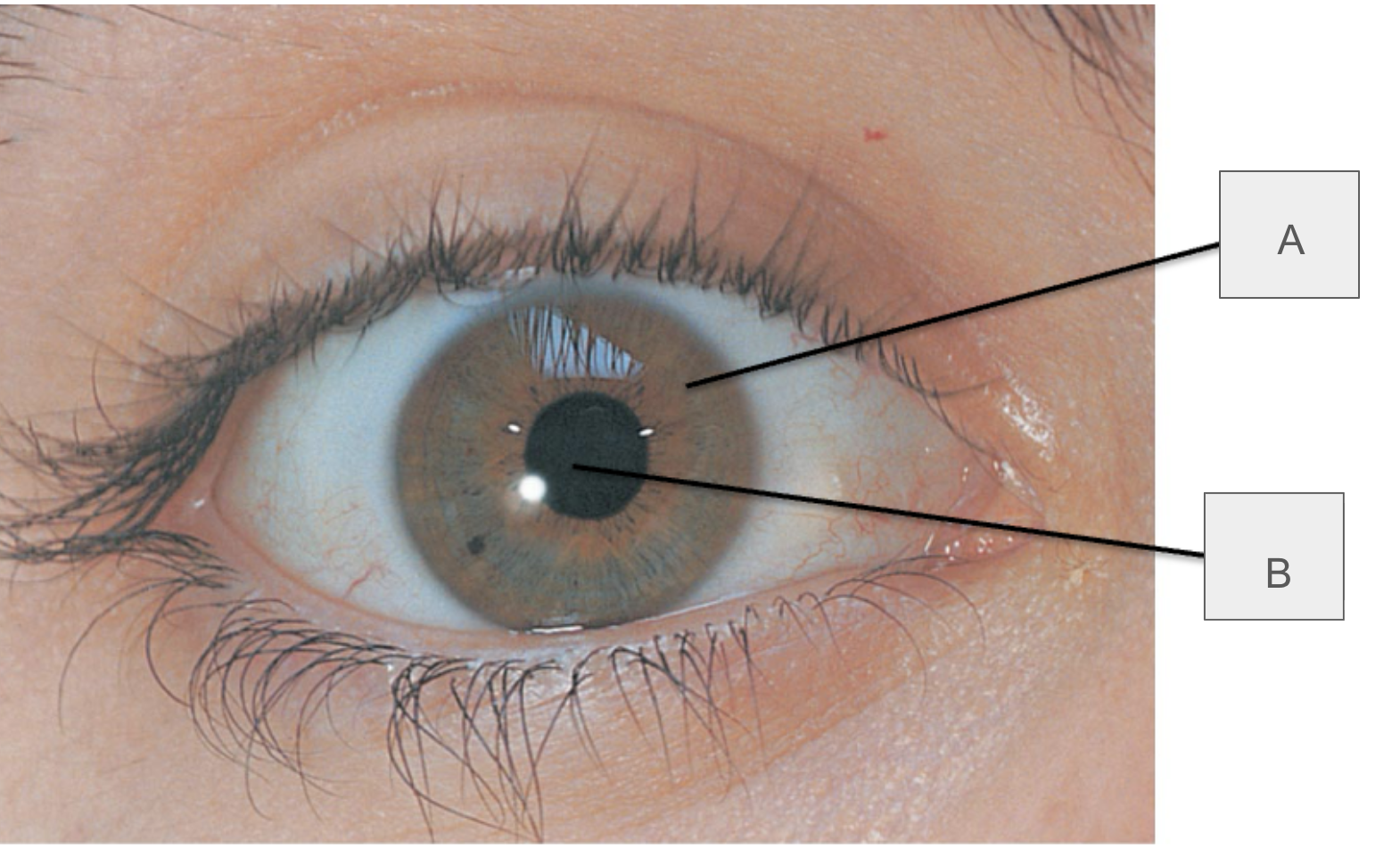
what is B?
pupil
what makes up the retinal (sensory/neural) layer?
ora serrata, retina
where is the retina located?
posterior aspect of the eyeball
what are the two layers of the retinal layer?
outer pigmented layer, inner neural layer
what part of the retinal layer absorbs light?
outer pigmented layer
what does the outer pigmented layer store?
Vitamin A
what are the 3 zones of neurons of the retina’s inner neural layer?
photoreceptors, bipolar cells, ganglion cells
what are the two photoreceptors of the inner neural layer?
rods, cones
which photoreceptors dim light, are responsible for peripheral vision, aand do not provide sharp images?
rods
which photoreceptors are responsible for color and are only active in bright light?
cones
where are there no photoreceptor cells?
optic disc/blind spot
what do amacrine and horizontal cells do?
modify electrical signals
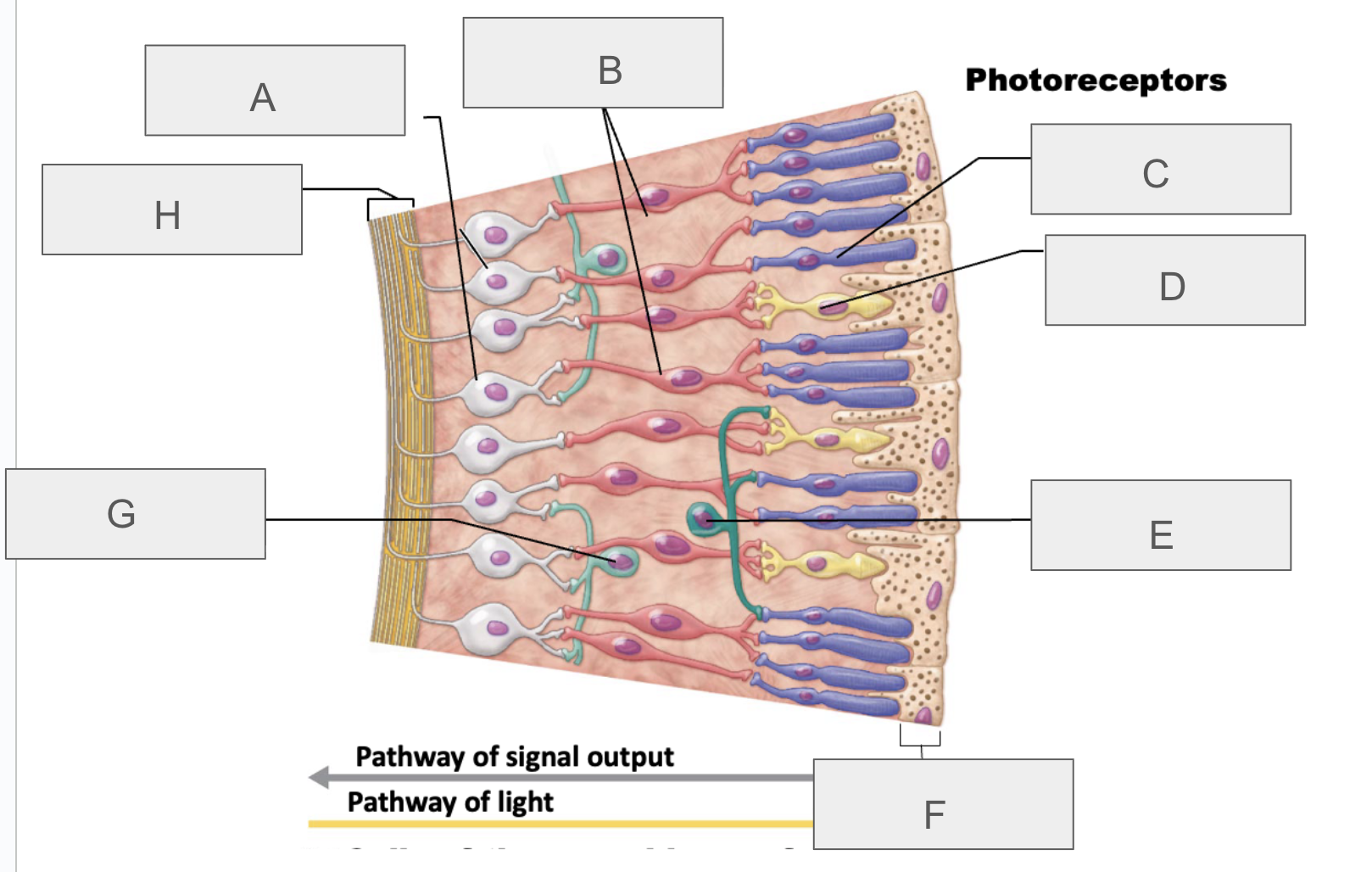
what is A?
ganglion cells
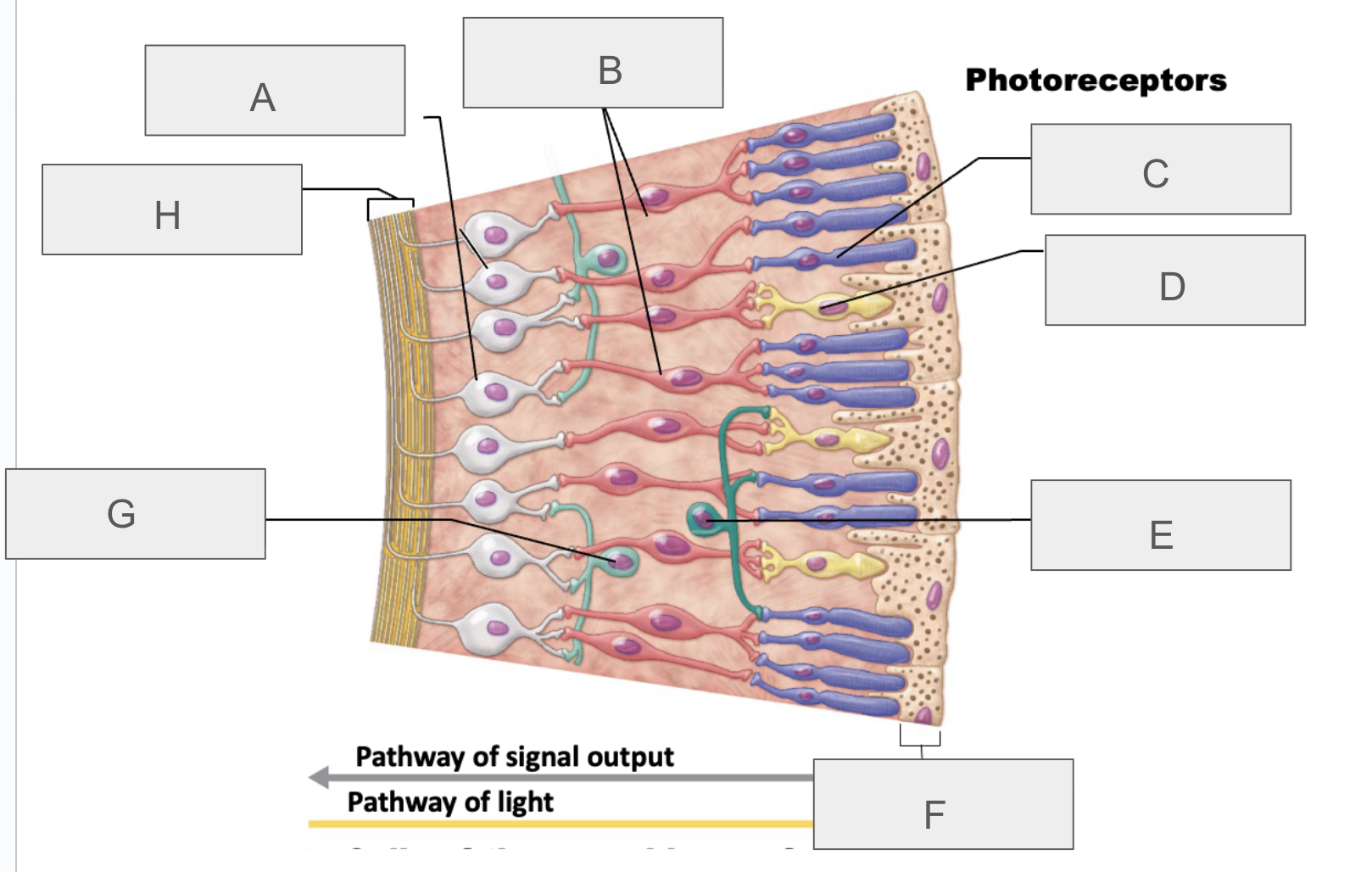
what is B?
bipolar cells
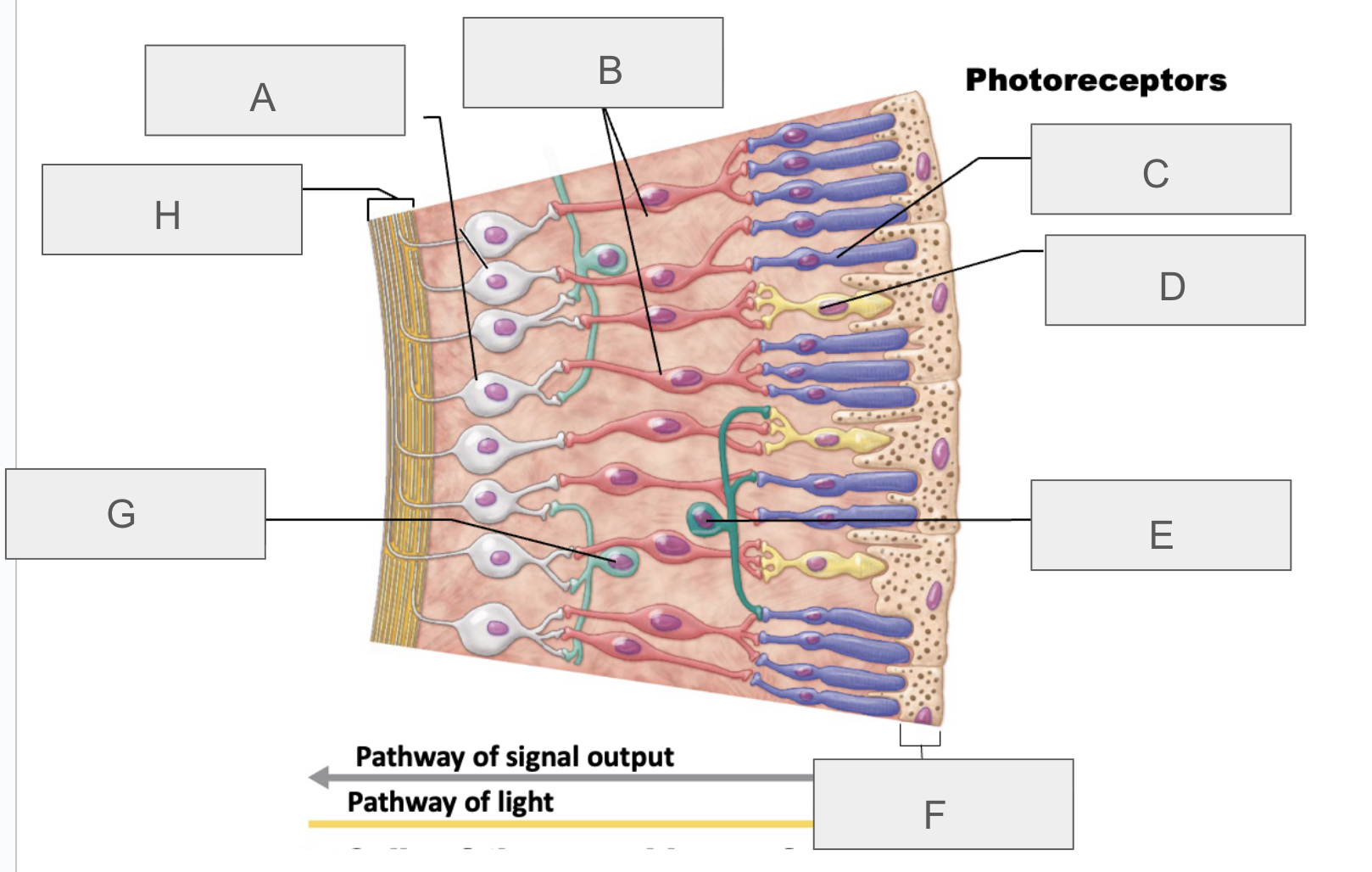
what is C?
rod
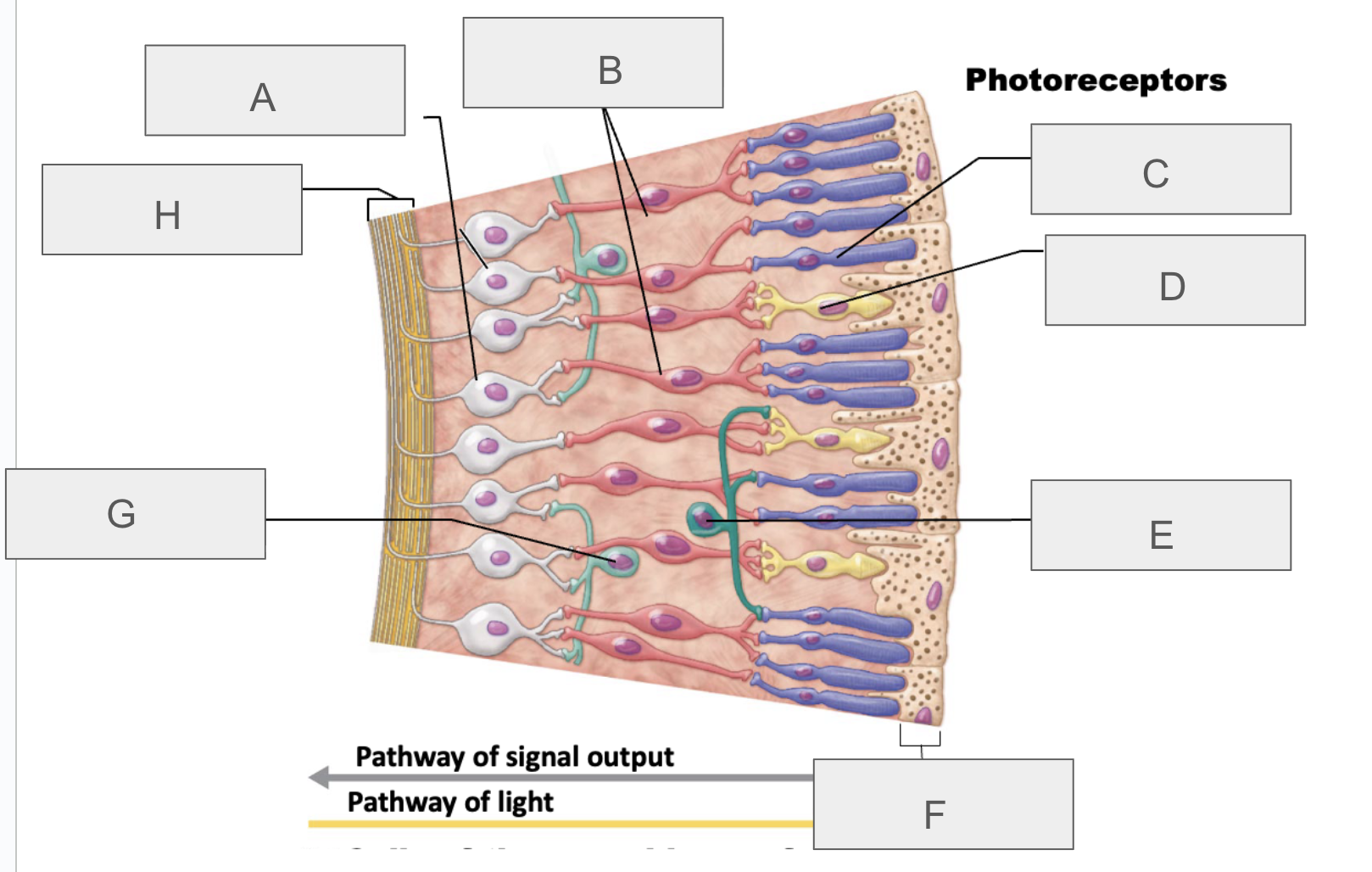
what is D?
cone
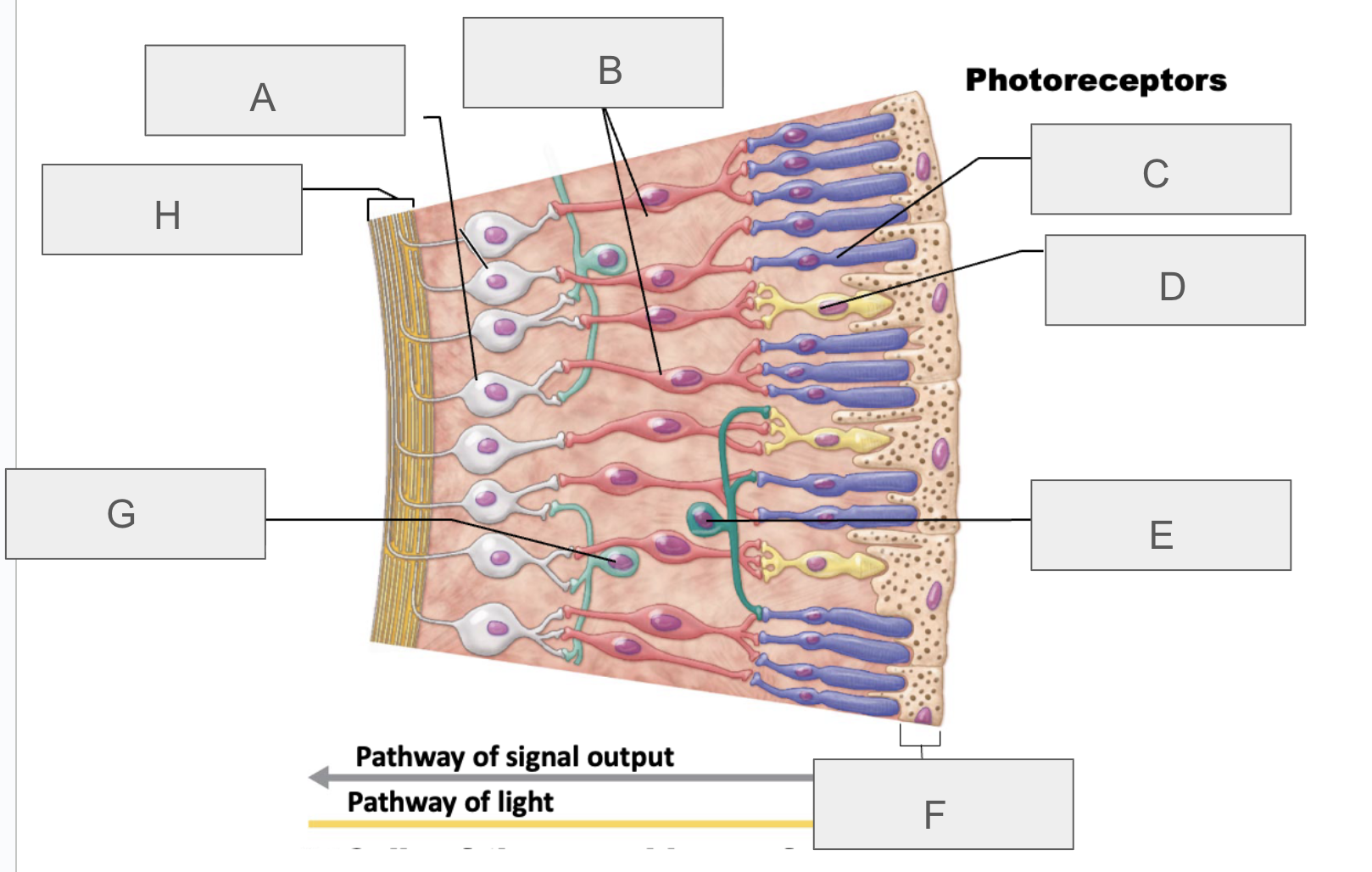
what is E?
horizontal cell
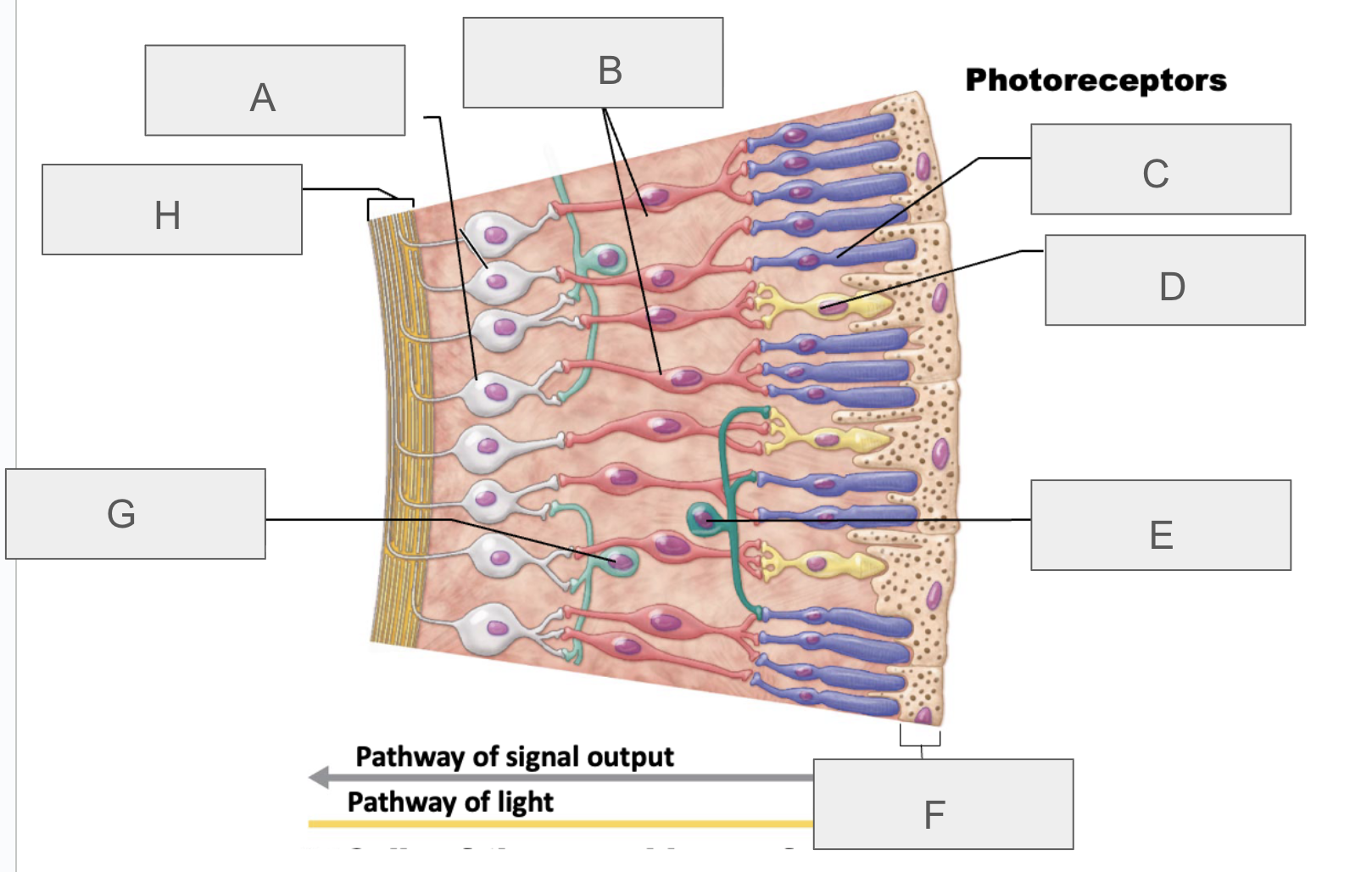
what is F?
pigmented layer of retina
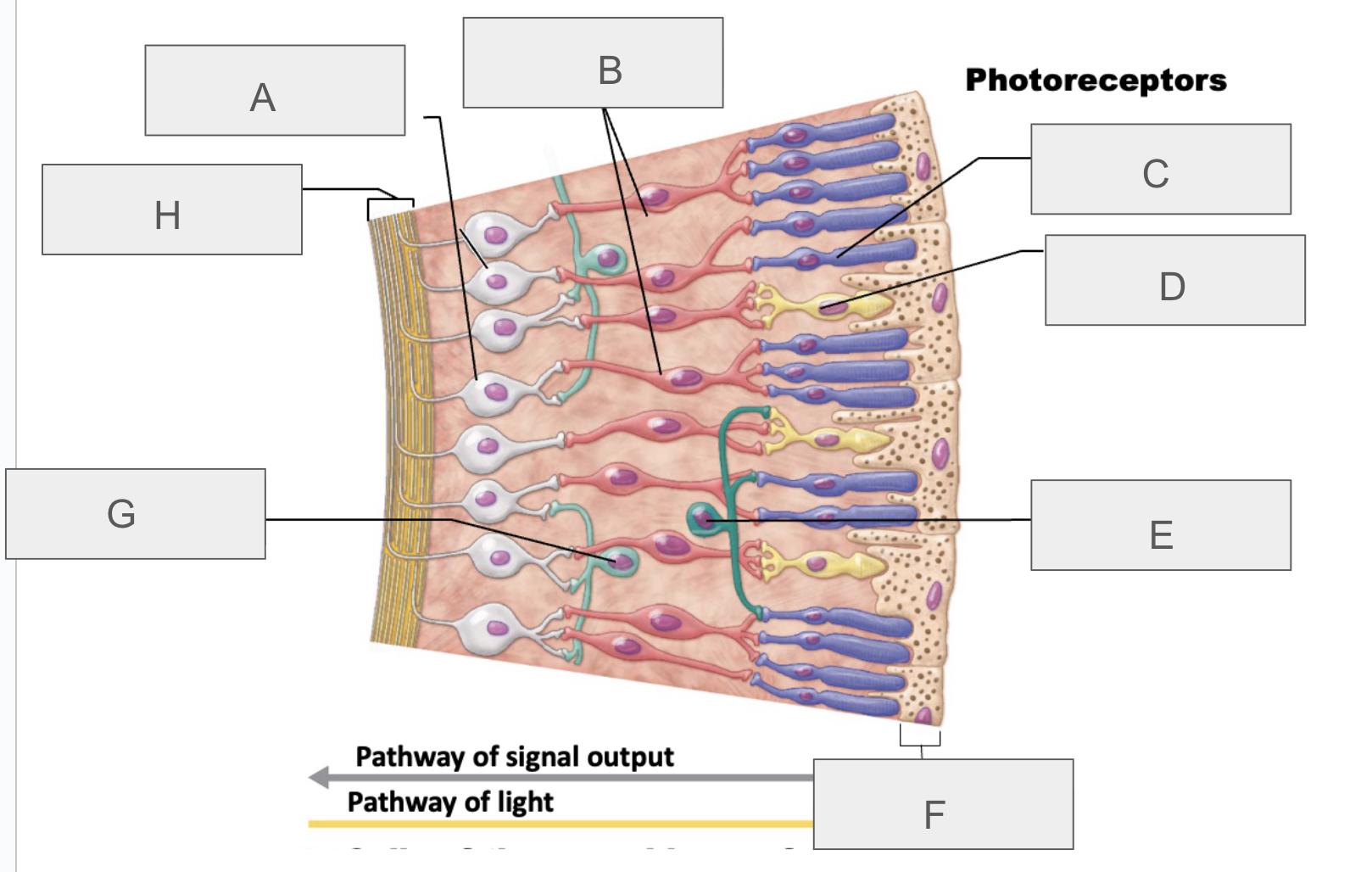
what is G?
amacrine cell
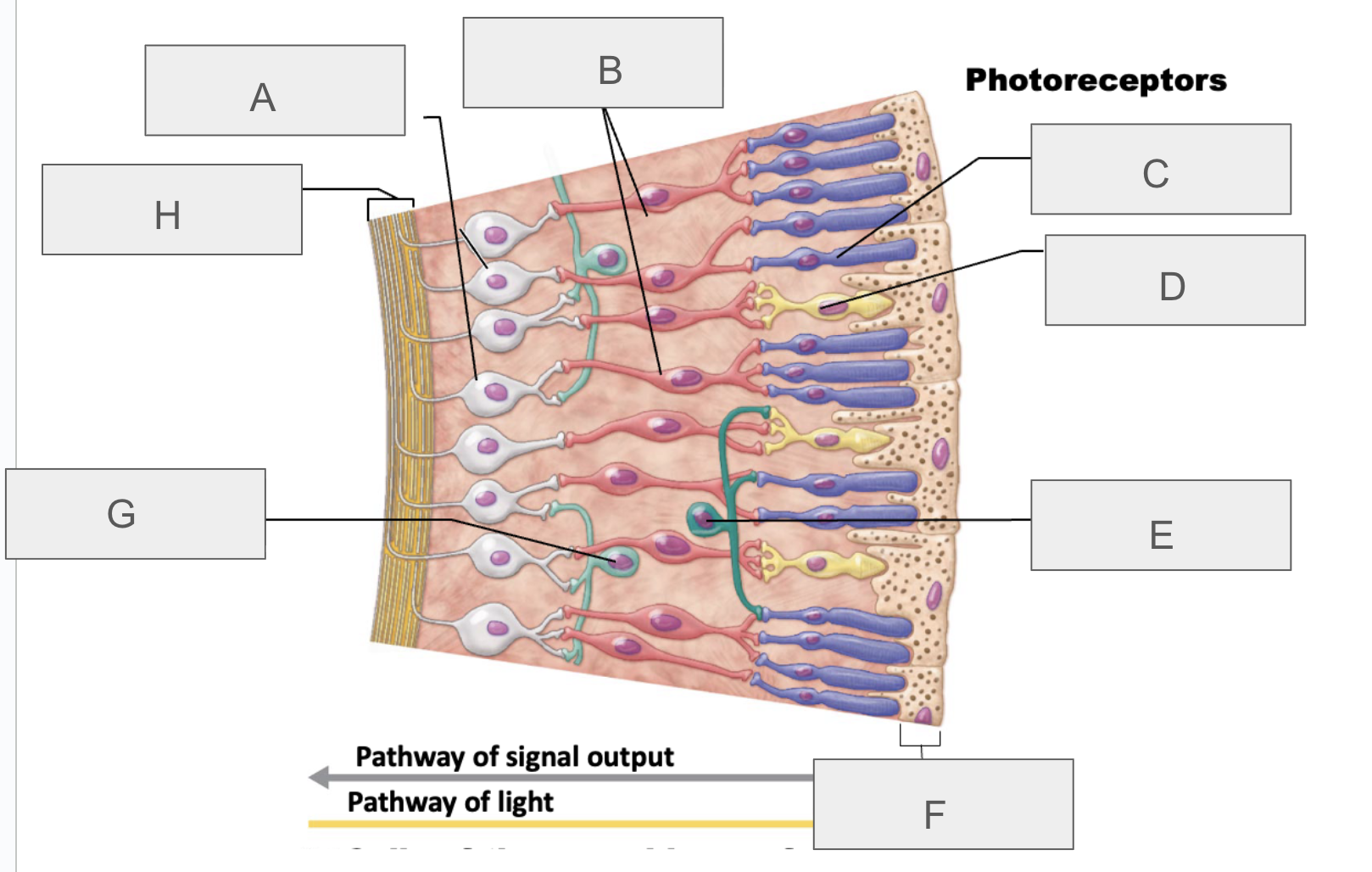
what is H?
axons of ganglion cells
where is there a high concentration of cones and high visual acuity?
macula lutea
what is the point within the macula lutea where there is only cones and highest visual acuity/focus?
fovea centralis
what leads to progressive loss of visual acuity, particularly in center of visual field, and may also cause visual distortion and changes in color perception?
macular degeneration
what is the transparent, avascular, layers of protein structure of the eye?
lens
what is the lens held in place by?
suspensory ligaments (ciliary zonules)
what does the lens separate?
anterior and posterior ligaments
why does the lense change shape?
to help focus light on retina
what is it called when the lens loses transparency due to thickening, hardening of the lens, loss of organization fibers, and becomes cloudy?
cataracts
what are causes of cataracts?
trauma, UV exposure, diabetes, aging
what does the anterior segment/cavity consist of?
2 chambers in front of lens filled with aqueous humor
what is the anterior chamber between?
cornea and iris
what is the posterior chamber between?
iris and lens
what fluid does the posterior segment contain?
vitreous humor
what fluid does the anterior segment contain?
aqueous humor
what secretes aqueous humor?
ciliary processes
what is the aqueous humor responsible for?
intraocular pressure (shape of eyeball)
what does the aqueous humor nourish?
avascular lens and cornea
what part of the eye is responsible for carrying waste away, draining via scleral venous sinus?
aqueous humor
what is the condition in which the blockage of draining increases intraocular pressure and puts pressure on retina and Optic nerve?
glaucoma
what is the gel-like substance behind the lens that holds the retina against pigmented layer?
vitreous humor
when is the vitreous humor formed?
before birth
what is the exposed surface of the cornea/sclera?
bulbar
what is the area under the upper and lower eyelids?
palpebral
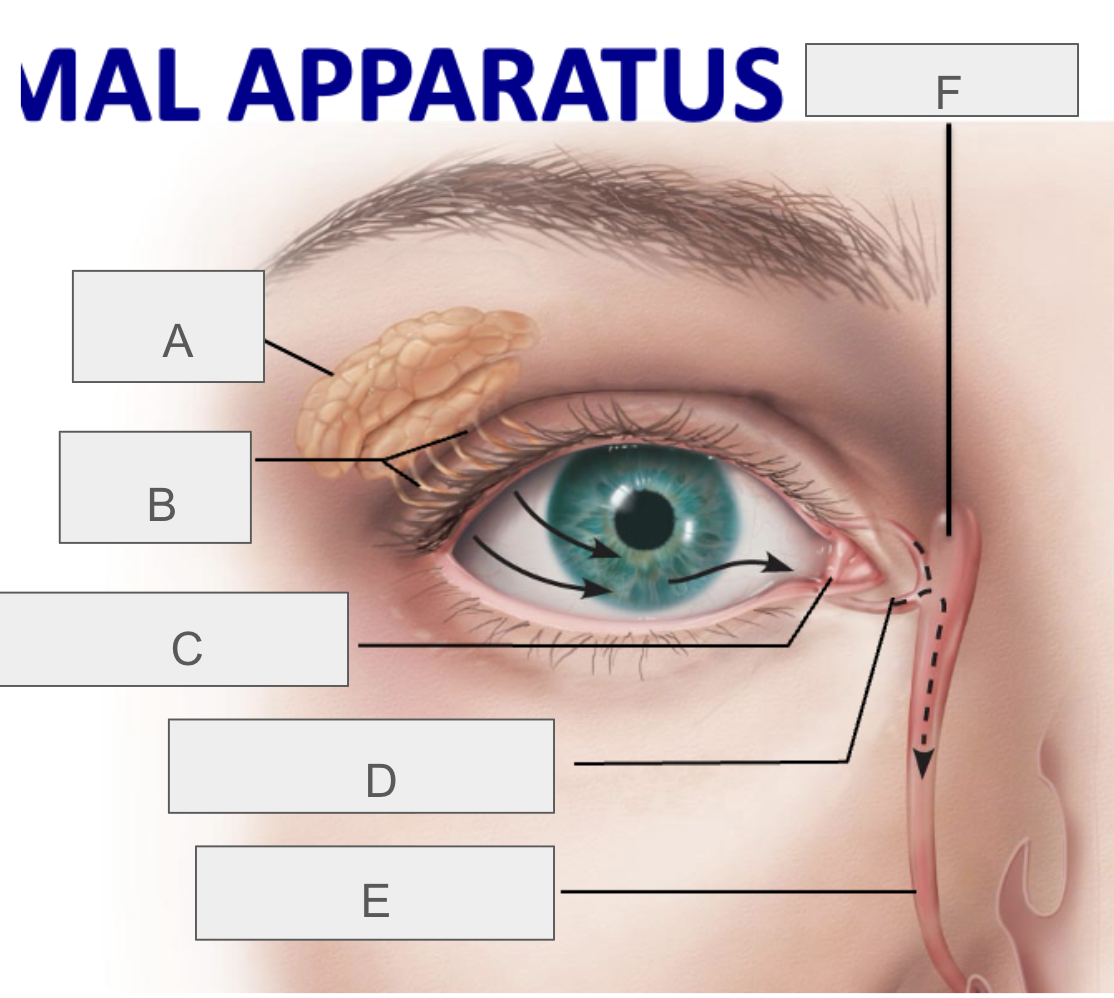
what is A?
lacrimal gland
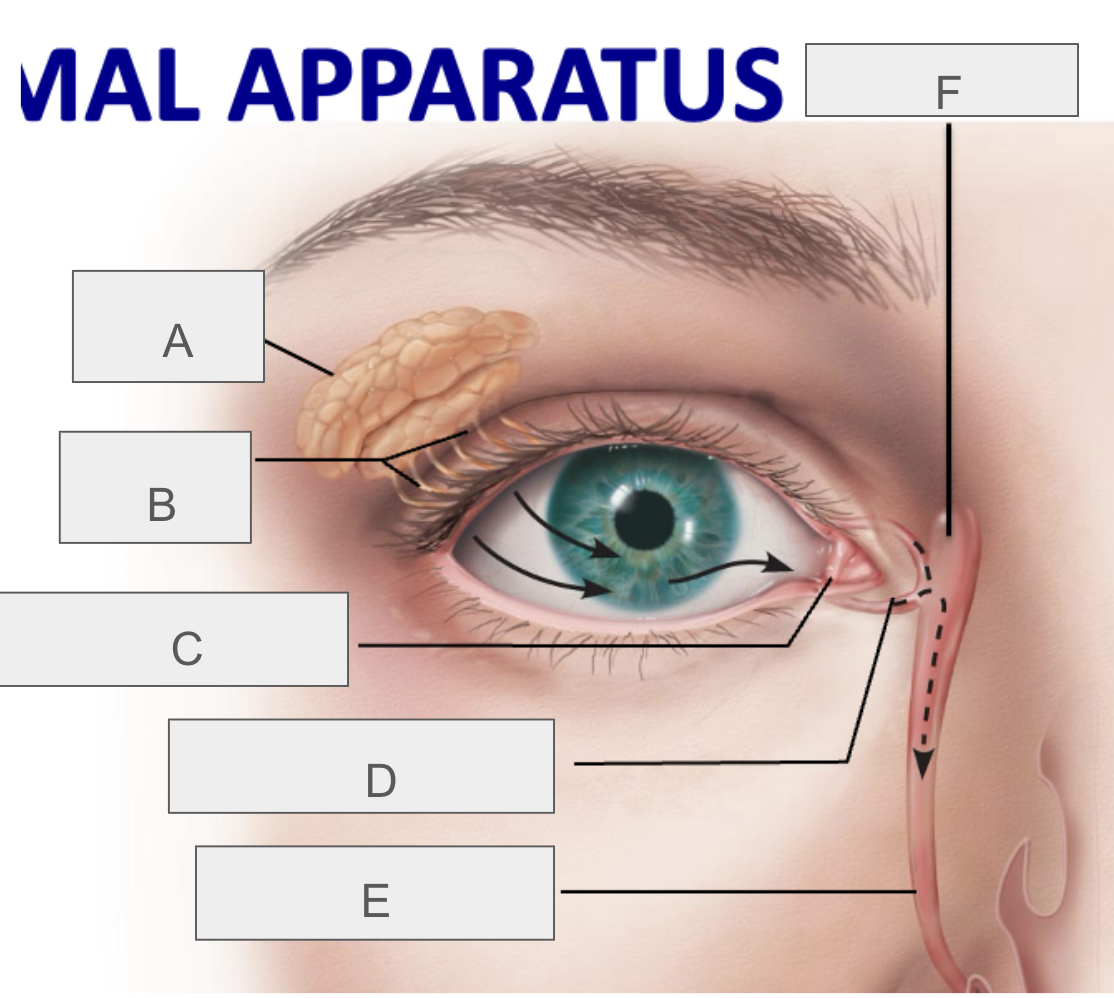
what is B?
lacrimal ducts
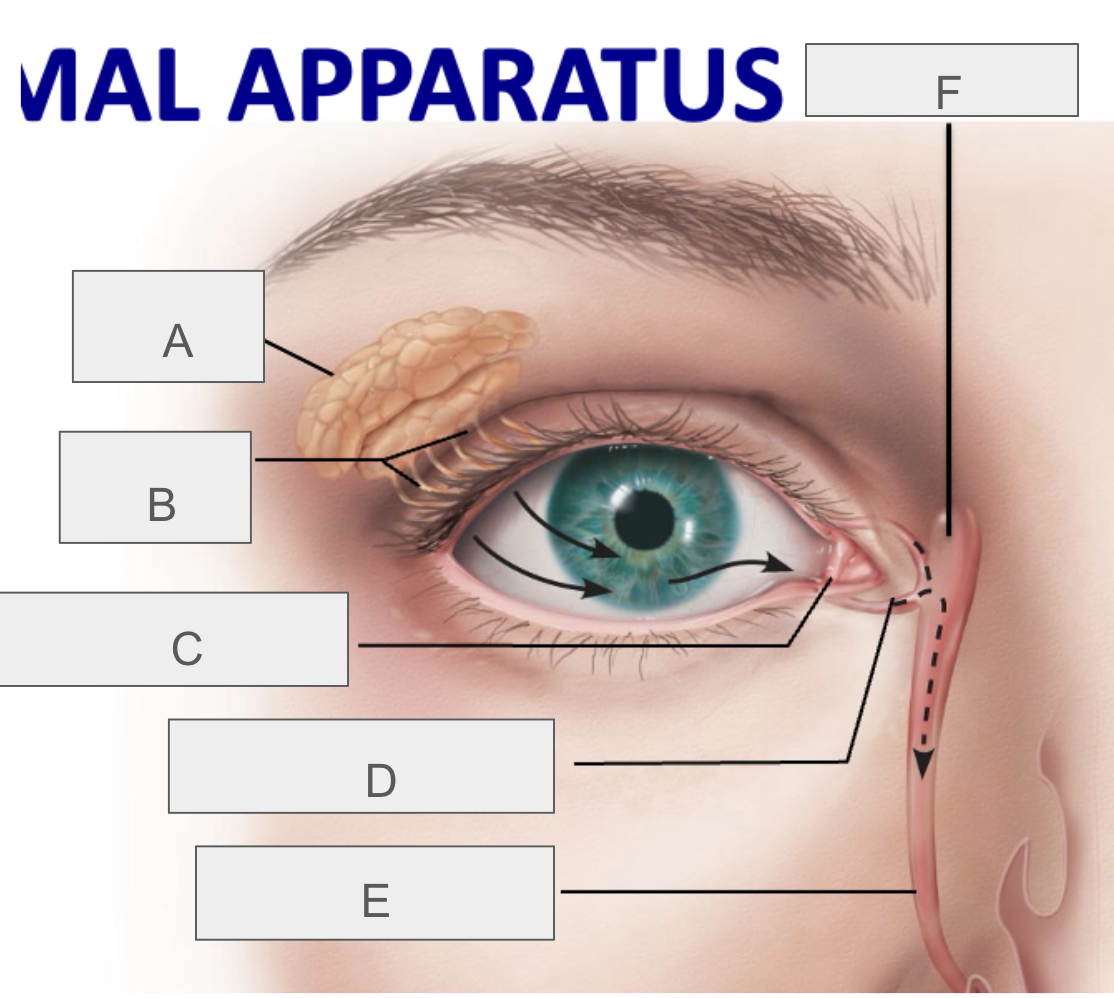
what is C?
lacrimal punctum
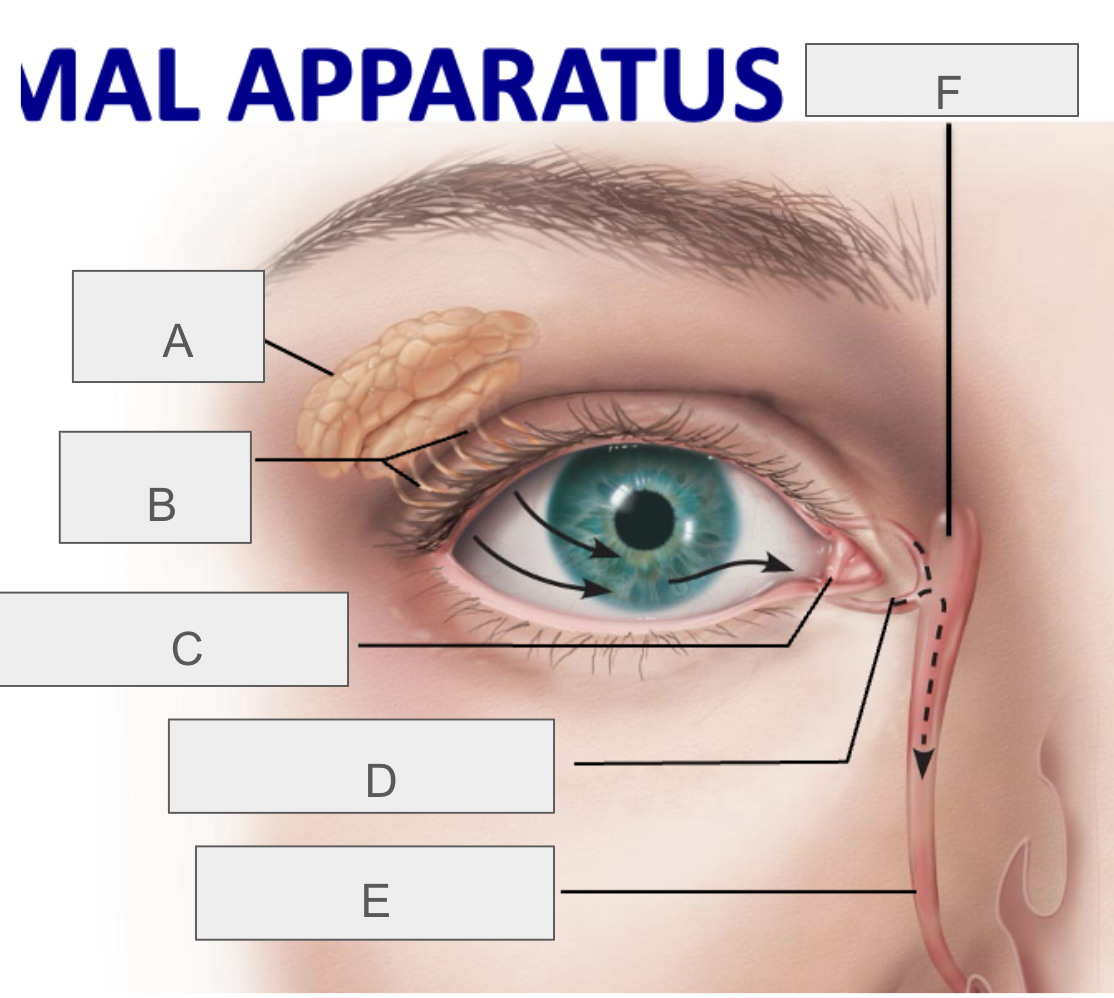
what is D?
lacrimal canaliculus
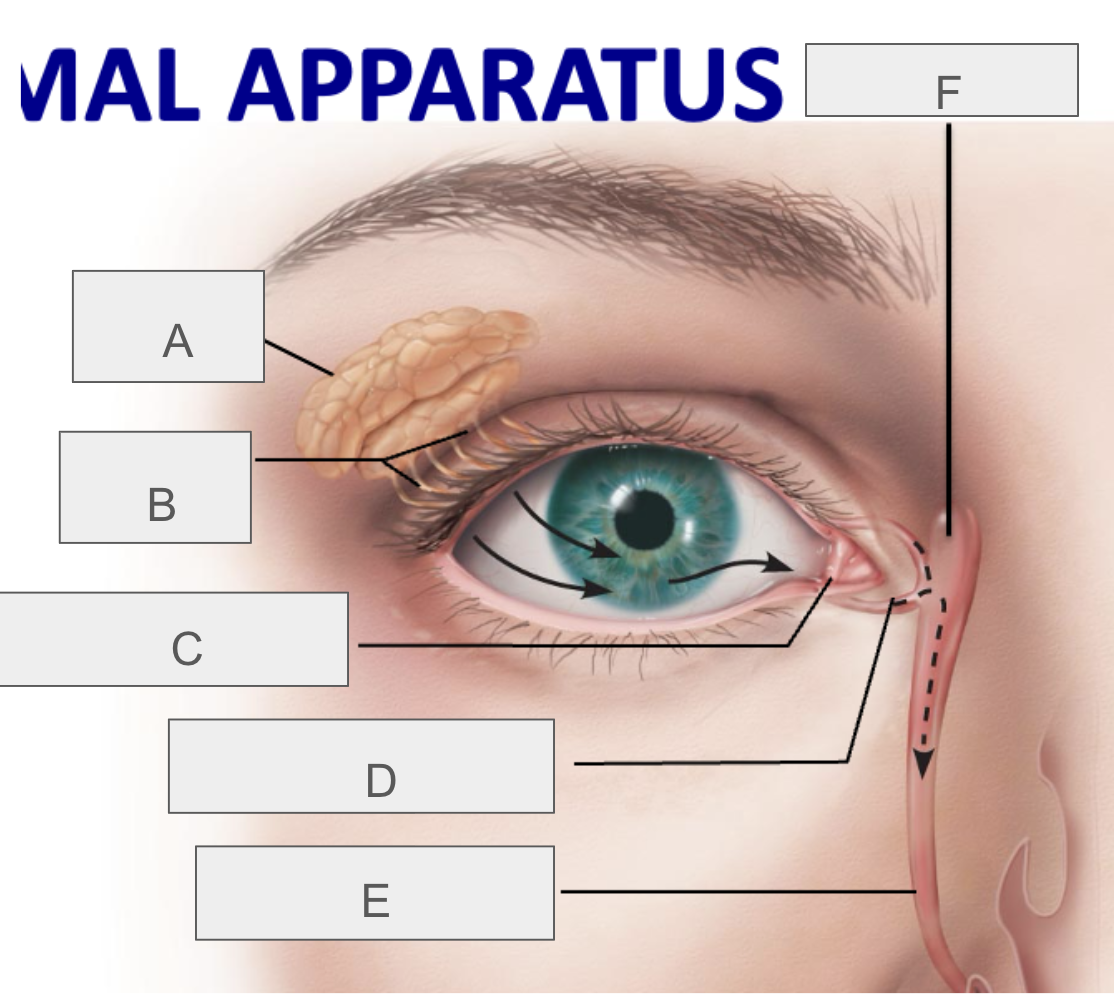
what is E?
nasolacrimal duct
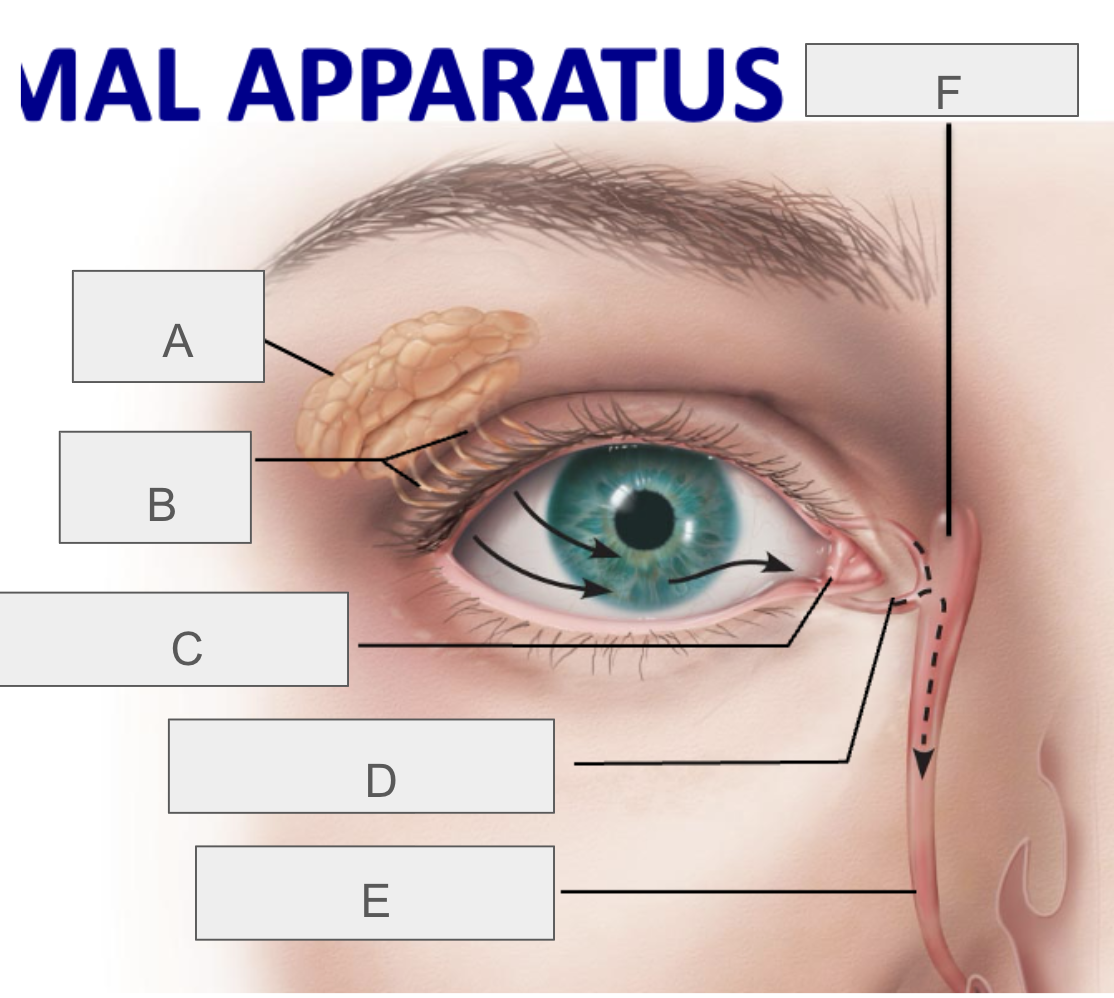
what is F?
lacrimal sac
what is the function of the lacrimal apparatus?
protect, lubricate, and clean eye
what are the extrinsic eye muscles?
lateral rectus, medial rectus, superior rectus, inferior rectus, superior oblique, inferior oblique
what do the extrinsic eye muscles do?
control eye movement