Disks and I/O Devices
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
flashcards made from Disks and I/O Devices slide from week 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
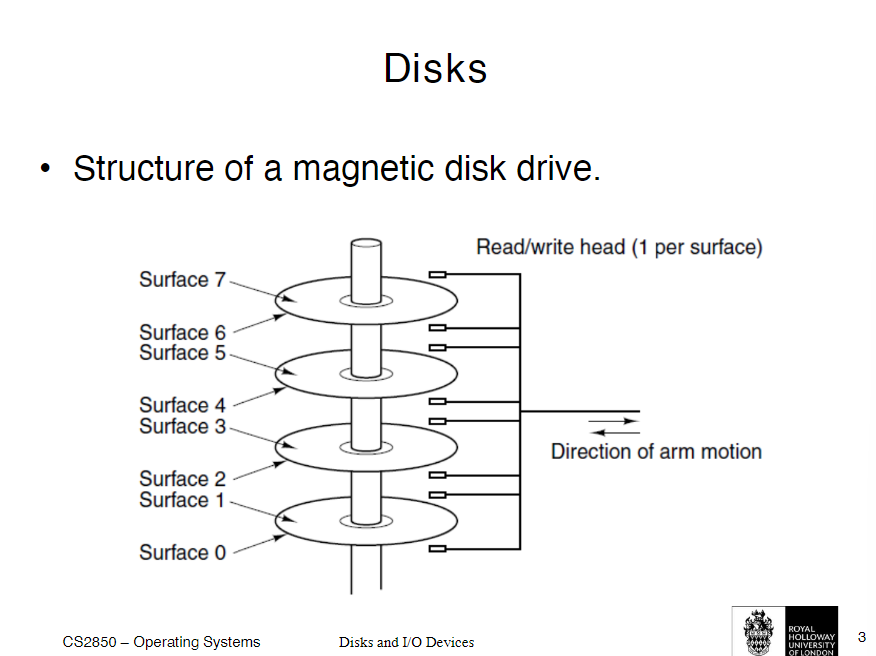
HDDs
• Magnetic disks (Hard Disk Drives – HDDs) are considerably cheaper and have more capacity than RAM
• However, they are also much slower
SSDs
• Solid State Drives (SSDs) also store large quantities of non-volatile data and have better performance, although they are more expensive
• SSDs have no moving parts and use flash memory for storage
• Hybrid drives combine SSDs and HDDs, with the former acting as cache, resulting in high speed access to data without compromising capacity
virtual memory
• Sometimes there is not enough memory to hold a program
• Virtual memory uses disk space to temporarily store information that does not fit in the existing memory
I/O devices
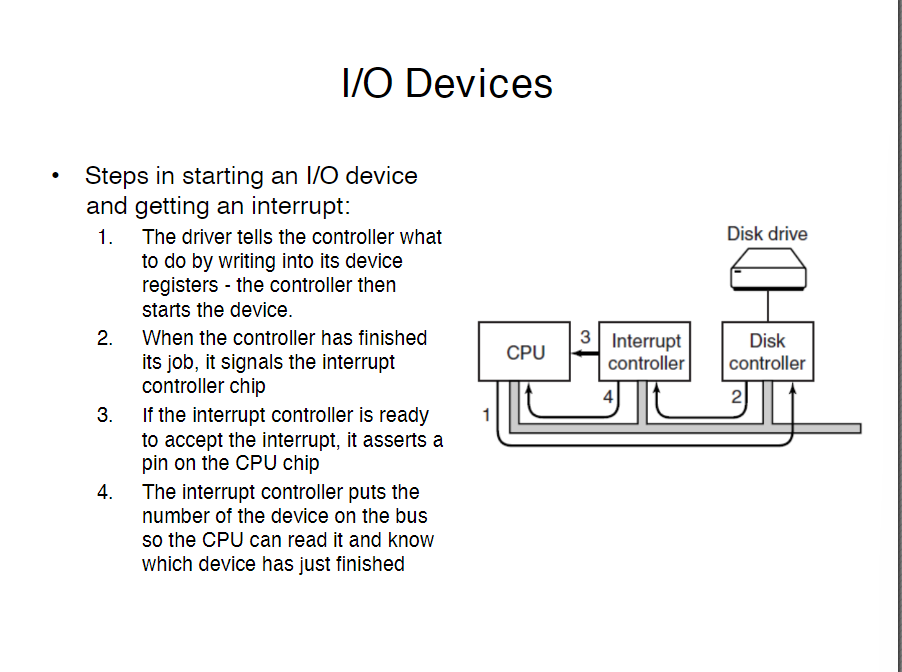
• An Input/Output (I/O) device usually consists of a controller and the device
• The controller is a hardware component that accepts commands from the operating system
– e.g. SATA disk controller
• Each controller is different, so to minimise operating system complexity, a special type of software is used: device driver
• Vendors of devices (e.g. web cam) create device drivers for each operating system they support
what is busy waiting on I/O devices and its main disadvantage?
• Input/Output can take place in several ways
• The simplest form is called busy waiting:
1. A program issues a system call
2. The operating system translates it to a call to the device driver
3. The driver initiates the I/O and continuously polls the device to check if it has completed the operation
4. Once that is the case, it returns any result and the operating system passes it to the original caller
• Main disadvantage:
– The CPU is tied up during the polling process
Alternative way to do I/O
• An alternative way to do I/O is for the device driver to initiate the request to the device and ask it to be notified when it finishes the operation
• Whilst the device is completing the operation, the operating system can block the original caller and do other work
• When the controller detects the end of the original operation, it generates an interrupt to signal this
What are the steps in starting in an I/O device and getting an interrupt
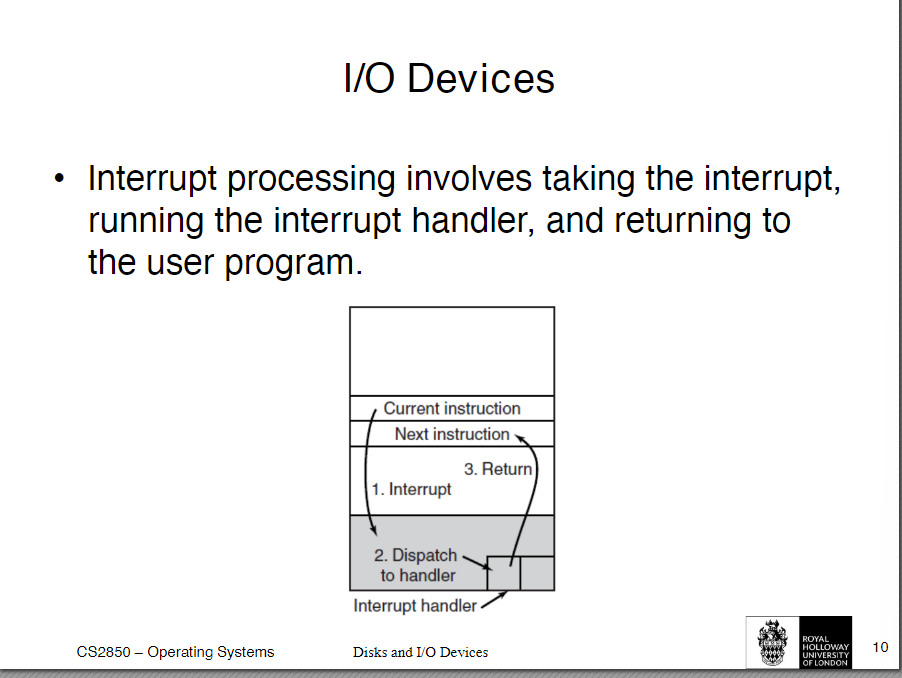
interrupt processing
Direct memory access (DMA)
• Another way for doing I/O further minimizes CPU intervention: Direct Memory Access (DMA)
• This is a chip that can get instructions from the CPU, namely the number of bytes to transfer, the direction and the memory addresses involved
• When the DMA chip completes the operation it will generate an interrupt
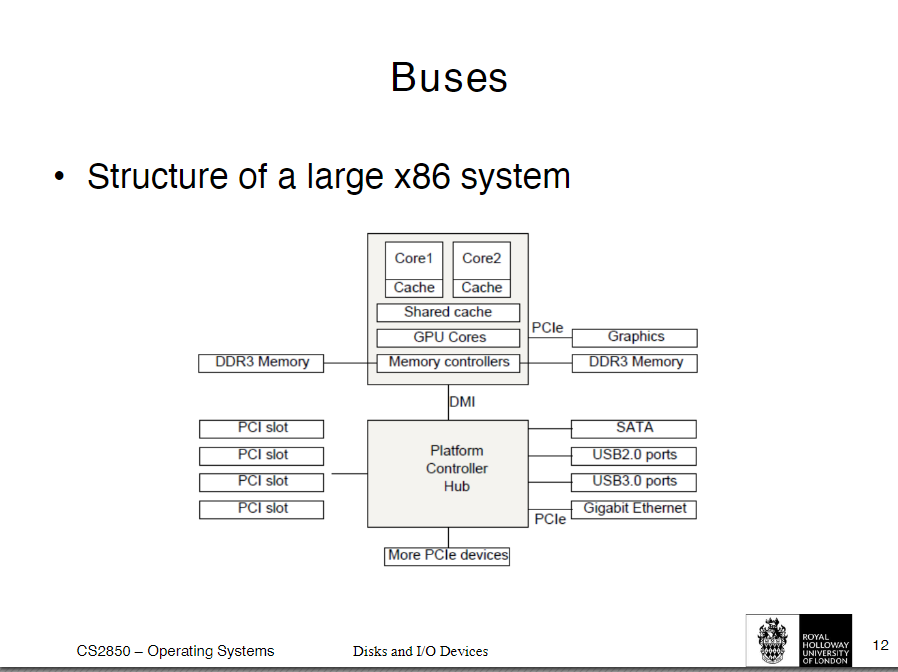
Structure of a large x86 system
PCIe is a high speed bus