Bio II Unit 1 Achieve
1/31
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
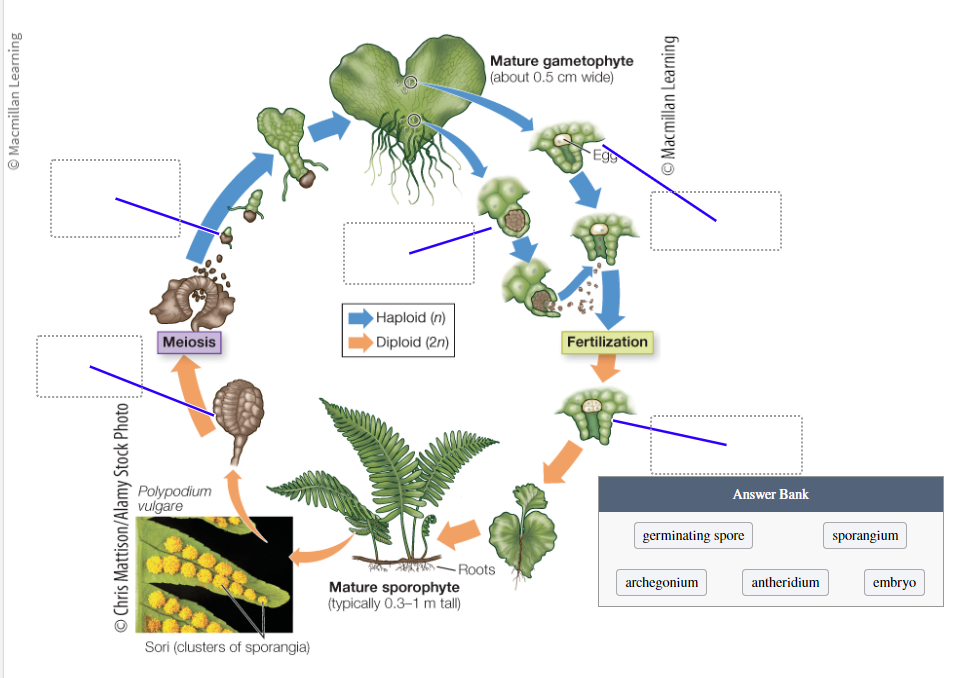
Identify stages that occur in the fern life cycle:
Archegonium
Sporangium
Germinating sore
Embryo
Antheridium
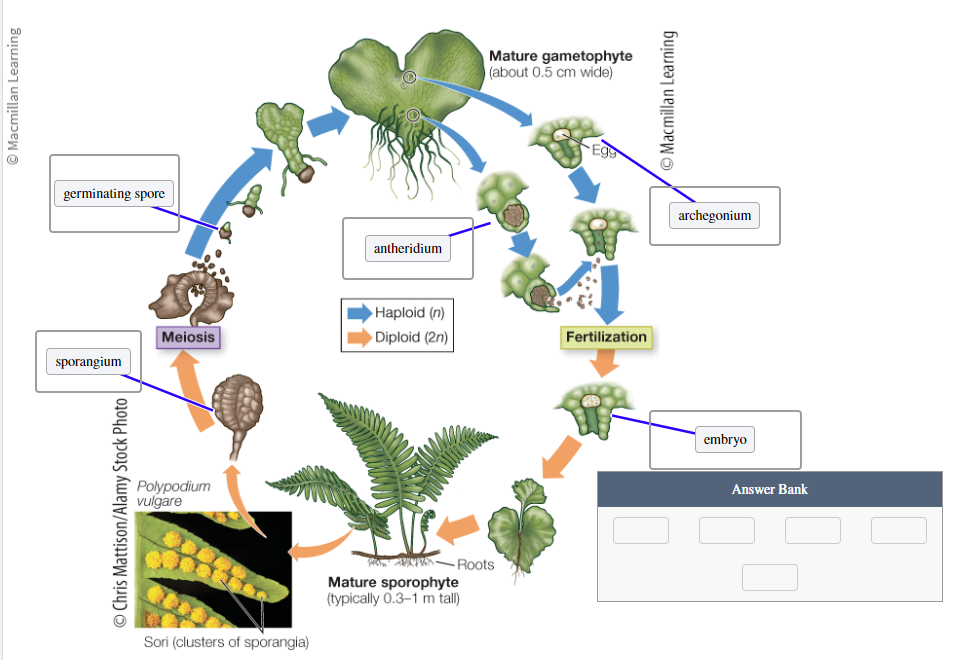
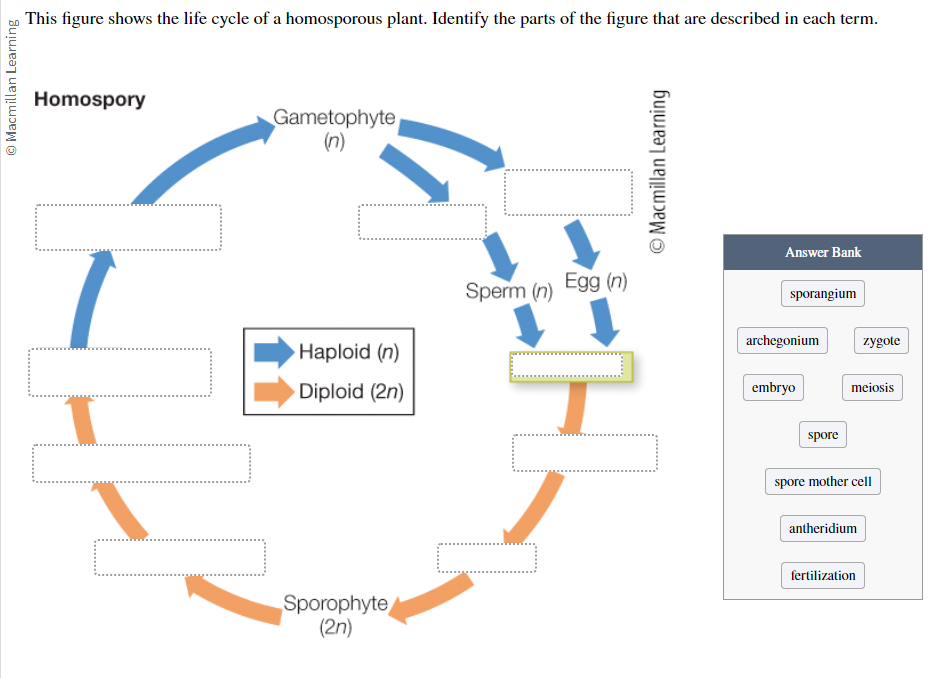
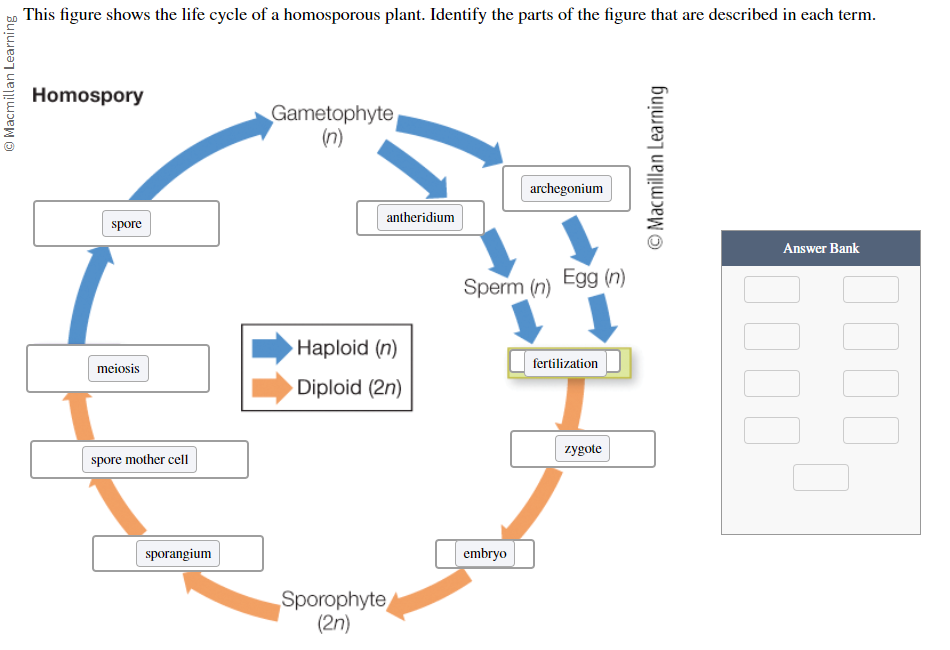
This figure shows the life cycle of a homosporous plant. Label the figure:
Sporangium
Archegonium
Zygote
Embryo
Meiosis
Spore
Spore mother cell
Antheridium
Fertilization
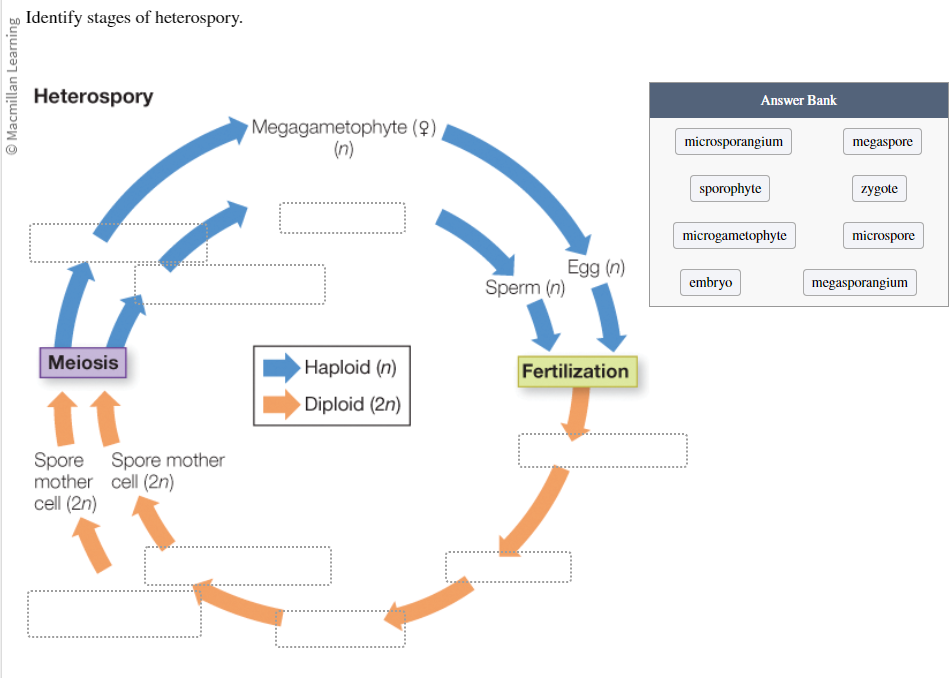
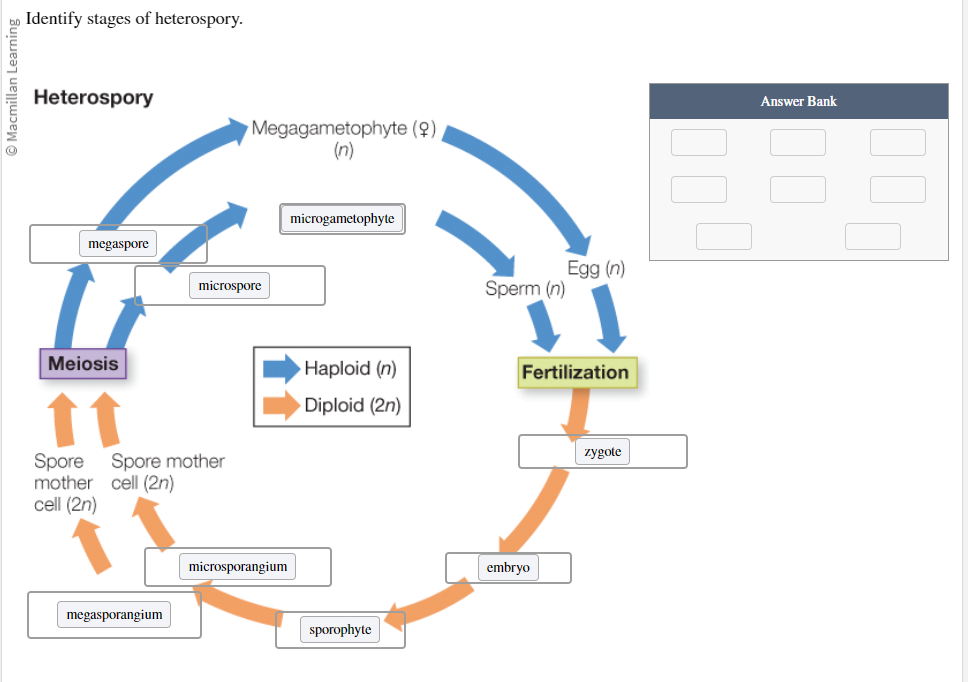
Identify the stages of heterospory:
Microsporangium
Sporophyte
Microgametophyte
Embryo
Megaspore
Zygote
Microspore
Megasporangium
Where does meiosis take place in the moss life cycle?
In the spores after being released by the sporophyte
In the sporangium at the time of spore formation
In the antheridia and archegonia of the gametophyte generation
In the archegonium of the gametophyte generation
Option 2:
In the sporangium at the time of spore formation
Where does fertilization take place in the moss life cycle?
In the sporangium at the time of spore formation
In the spores after being released by the sporophyte
In the antheridium of the gametophyte generation
In the archegonium of the gametophyte generation
Option 4:
In the archegonium of the gametophyte generation
Which set of terms represents a haploid/diploid pair?
Spore/sporophyte
Gamete/gametophyte
Sperm/egg
Sporophyte/zygote
Option 1:
Spore/sporophyte
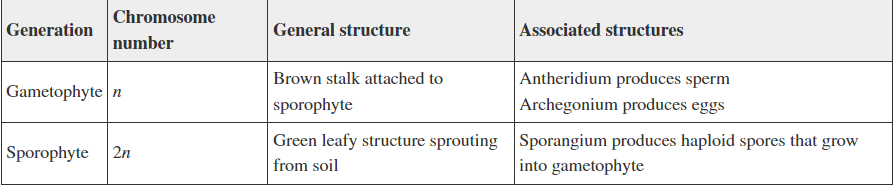
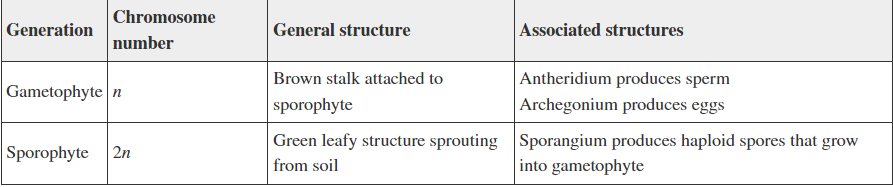
A student created this table as a study guide referring to the moss life cycle. Evaluate the accuracy of the information in the table:
The chromosome numbers are not assigned correctly
The general structures are reversed for the two generations
All information is accurate
There is an error in the information listed in the last column
Option 2:
The general structures are reversed for the two generations
What was the origin of all chloroplasts?
A single green alga
A group of green algae
A group of cyanobacteria
A single cyanobacterium
Option 4:
A single cyanobacterium
Which phrase can be used in a description of secondary endosymbiosis?
A prokaryote engulfing a eukaryote
A eukaryote engulfing a eukaryote
A prokaryote engulfing a prokaryote
A eukaryote engulfing a prokaryote
Option 2:
A eukaryote engulfing a eukaryote
What would a biologist look for in order to determine whether a chloroplast in a cell evolved as the result of primary endosymbiosis or secondary endosymbiosis?
The size of the chloroplast
The number of membranes in the chloroplast
The number of chloroplasts in a single cell
The presence of chloroplast DNA
Option 2:
The number of membranes in the chloroplast
Based on the information provided in the animation (Animation Quiz 19.1), which pair of organisms has the closest evolutionary relationship?
Cyanobacteria and land plants
Euglenids and red algae
Green algae and land plants
Land plants and red algae
Option 3:
Green algae and and plants
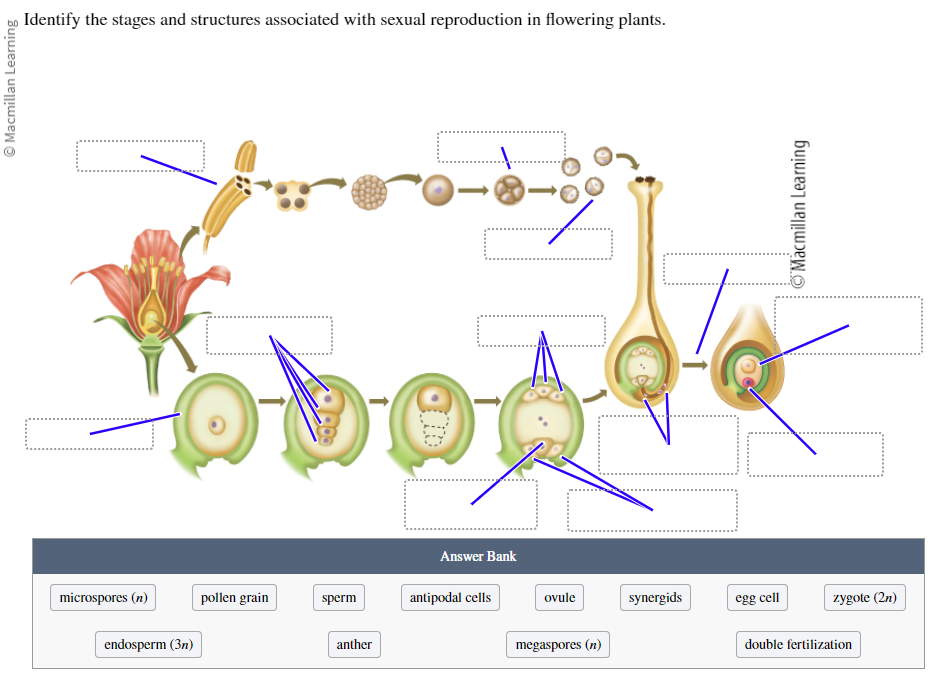
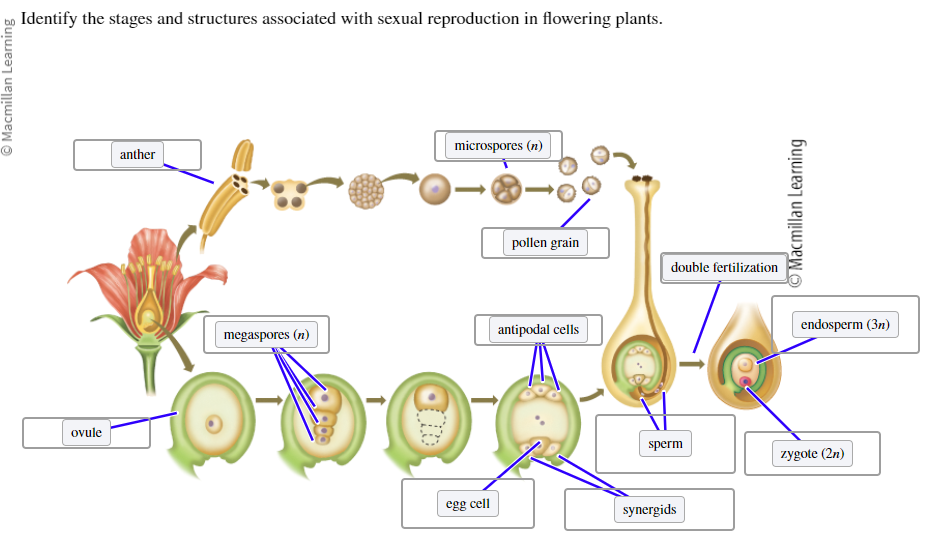
Identify the stages and structures associated with sexual reproduction in flowering plants:
Microspores (n)
Pollen grain
Sperm
Antipodal cells
Ovule
Synergids
Egg cell
Zygote (2n)
Endosperm (3n)
Anther
Megaspores (n)
Double fertilization
What structures allow water vapor to escape the leaves of a plant?
Leaf veins
Mesophyll cells
Stomata
Cell walls
Option 3: Stomata
According to the current model of fluid flow in the xylem, what creates the force that moves water from the roots to the leaves?
An increase in root pressure
Cellular pumps in leaves
Differences in water potential between roots and leaves
An increase in water tension in leaves
Option 4:
An increase in water tension in leaves
Where does the energy come from that drives water transport in plants?
ATP
Membrane pumps
Water
The sun
Option 4: The sun
Which would you expect to increase the rate of water transport in a plant?
A rise in temperature
The removal of leaves and a seal of the excision sites
Blockage of the stomata
An increase in humidity
Option 1:
A rise in temperature
Double fertilization, which is a hallmark of angiosperm sexual reproduction, results in a
Haploid zygote and a triploid endosperm
Haploid zygote and a diploid endosperm
Diploid zygote and a triploid endosperm
Diploid zygote and a diploid endosperm
Option 3:
Diploid zygote and a triploid endosperm
Which statement correctly describes the general pattern of the alteration of generations in angiosperms:
The sporophyte generation (2n) produces spores (n) that produce gametophytes (n) that produce gametes (n) that fuse to produce a new sporophyte (2n).
The sporophyte generation (2n) produces spores (2n) that produce gametophytes (2n) that produce gametes (n) that fuse to produce a new sporophyte (2n).
The sporophyte generation (n) produces gametes (n) that produce gametophytes (2n) that produce spores (2n) that fuse to produce a new sporophyte (n).
The sporophyte generation (2n) produces gametes (n) that produce gametophytes (n) that produce spores (n) that fuse to produce a new sporophyte (2n).
Option 1:
The sporophyte generation (2n) produces spores (n) that produce gametophytes (n) that produce gametes (n) that fuse to produce a new sporophyte (2n).
Which structure is NOT a part of the sporophyte generation?
Leaf
Anther
Flower
Egg
Option 4: Egg
A biologist discovers a seed-bearing plant that has never been classified. Which feature will help him determine whether the plant is a gymnosperm or an angiosperm?
Female structure that produce an egg closed in a protective structure
A large sporophyte generation that bears the gametophyte generation in a single individual
The presence of heterospory
Male structures that produce pollen that must be transported to fuse with an egg
Option 1:
Female structure that produce an egg closed in a protective structure
Which statement about the pressure flow model of fluid flow in phloem is true?
Sucrose concentrations determine the direction of the fluid flow
Fluid always flows in a downward direction from high pressure to low pressure
Pressure is exerted on fluid in phloem by changes in water volume due to evaporation from stomata
Fluid can flow in any direction from an area of low pressure to an area of high pressure
Option 1:
Sucrose concentrations determine the direction of the fluid flow
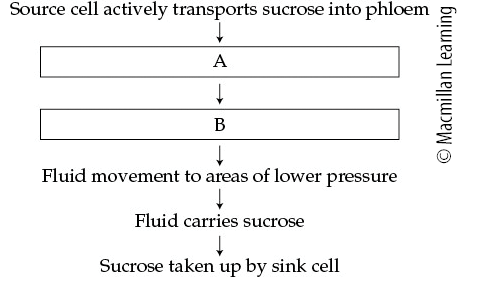
This partially completed flowchart describes the mechanism underlying fluid flow in the phloem.
A= Water movement by osmosis; B= Pressure increase
A= Water movement by active transport; B= Pressure increase
A= Water movement by osmosis; B= Pressure decrease
A= Water movement by active transport; B= Pressure increase
Option 1:
A= Water movement by osmosis; B= Pressure increase
Which are examples of source and sink cells in a plant?
Source: flower; sink: mature leaf
Source: immature leaf; sink: root
Source: mature leaf; sink: fruit
Source: flower; sink: fruit
Option 3:
Source: mature leaf; sink: fruit
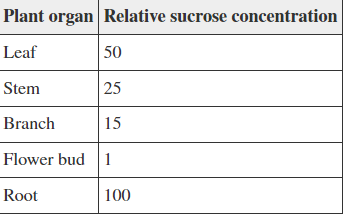
Refer to the table below.
In the spring, a plant grows from a root system that had been dormant throughout the winter. The plant produces a stem, several branches, leaves, and begins to flower. The relative concentrations of sucrose in cells of various organs of the plant are shown in the table. How would you describe the fluid pressure in the plant phloem at this time?
Highest in leaf and lowest in flower bud
Highest at the top of the plant and lowest at the bottom
Highest in root and lowest in flower bud
Highest in photosynthetic tissues and lowest in non-photosynthetic tissues
Option 3:
Highest in root and lowest in flower bud
When a plant is illuminated from one side, auxin is transported to the _____ side of the shoot, where it stimulates cells to _____, causing the shoot to bend toward the light.
light; divide
light; expand
dark; expand
dark; divide
Option 3: dark; expand
Which is the correct order of events during auxin-mediated cell elongation?
Proton pump gene expression→ ATP hydrolysis→ H+ movement into cell wall→ expansin activation
Proton pump gene expression→ expansin activation→ ATP hydrolysis→ H+ movement into cell wall
expansin activation→ proton pump gene expression→ H+ movement into cell wall→ ATP hydrolysis
ATP hydrolysis→ expansin activation→ proton pump gene expression→ H+ movement into cell wall
Option 1:
Proton pump gene expression→ ATP hydrolysis→ H+ movement into cell wall→ expansin activation
A biologist isolates cells that are not actively producing auxin from a section of a plant stem. She places them in a culture dish with a growth medium that keeps the cells alive. When she adds auxin to the dish, the cells begin synthesizing more cellulose. What is an alternative that the biologist can add instead of auxin that would allow her to observe the same response?
Light
Acid
ATP
Water
Option 2: Acid
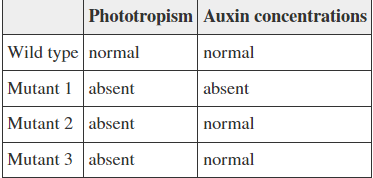
A biologist investigating the response of a particular plant species to light cues stumbles upon three mutant plant lines. Each displays a lack of normal phototropic behavior but varies in the auxin concentrations present in their growing tips. Based on the information given in the table, what could explain the behaviors of the three mutants?
1. Mutant 1 is deficient in an enzyme involved in auxin biosynthesis, whereas mutants 2 and 3 may have defective expansin and/or proton pump proteins.
2. Mutant 1 produces a defective proton pump protein, whereas mutants 2 and 3 are both deficient in an enzyme involved in auxin biosynthesis.
3. Mutant 1 is deficient in an enzyme involved in auxin biosynthesis, whereas turgor pressure changes by osmosis may be absent in mutants 2 and 3.
4. Mutant 1 produces a defective expansin enzyme, whereas mutants 2 and 3 may have defective proton pump proteins.
Option 1:
Mutant 1 is deficient in an enzyme involved in auxin biosynthesis, whereas mutants 2 and 3 may have defective expansin and/or proton pump proteins.
In systemic acquired resistance, which molecule is transported throughout the plant?
Phytoalexins
Polysaccharides
Salicylic acid
PR proteins
Option 3: Salicylic acid
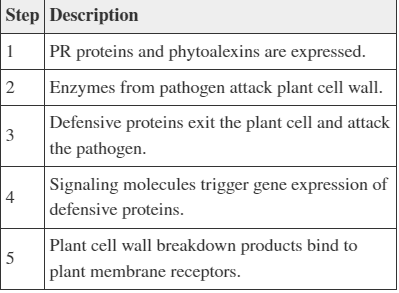
How can the steps in the table be ordered to describe a plant’s response to an invading pathogen?
1, 2, 5, 4, 3
5, 4, 3, 2, 1
4, 3, 1, 2, 5
2, 5, 4, 1, 3
Option 4:
2, 5, 4, 1, 3
Which action could help a biologist determine whether a particular plant population had been attacked by a bacterial pathogen in the recent past?
Look for elevated levels of mRNA transcripts for PR proteins in tissues of plants sampled across the population
Identify the number of genes coding for phytoalexins in the plant’s genome
Assess the numbers of plasmodesmata connecting cells in a broad sampling of plants
Determine whether any plants express membrane receptors that recognize bacterial molecules
Option 1:
Look for elevated levels of mRNA transcripts for PR proteins in tissues of plants sampled across the population
Plants of different species showed different responses to the same pathogen as summarized in this table.
Which hypothesis best explains all the observations?
Species B releases salicylic acid in a systemic response to the pathogen much earlier than species A
Species B expresses phytoalexins to enhance pathogen response much later in the course of the infection than species A
Species B is able to defend against the pathogen with a hypersensitive response, whereas species A does not mount this defense
Species B successfully blocks entry of the pathogen into its tissues, whereas species A does not block its entry
Option 3:
Species B is able to defend against the pathogen with a hypersensitive response, whereas species A does not mount this defense