Radiation Effects, Dose Response, and Protection in Medical Imaging
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Protraction
Continuous dose given at lower dose rate.
Biological effects of radiation
Potential impacts on living organisms due to exposure to radiation.
Factors affecting dose response
Elements that influence the relationship between radiation dose and biological response.
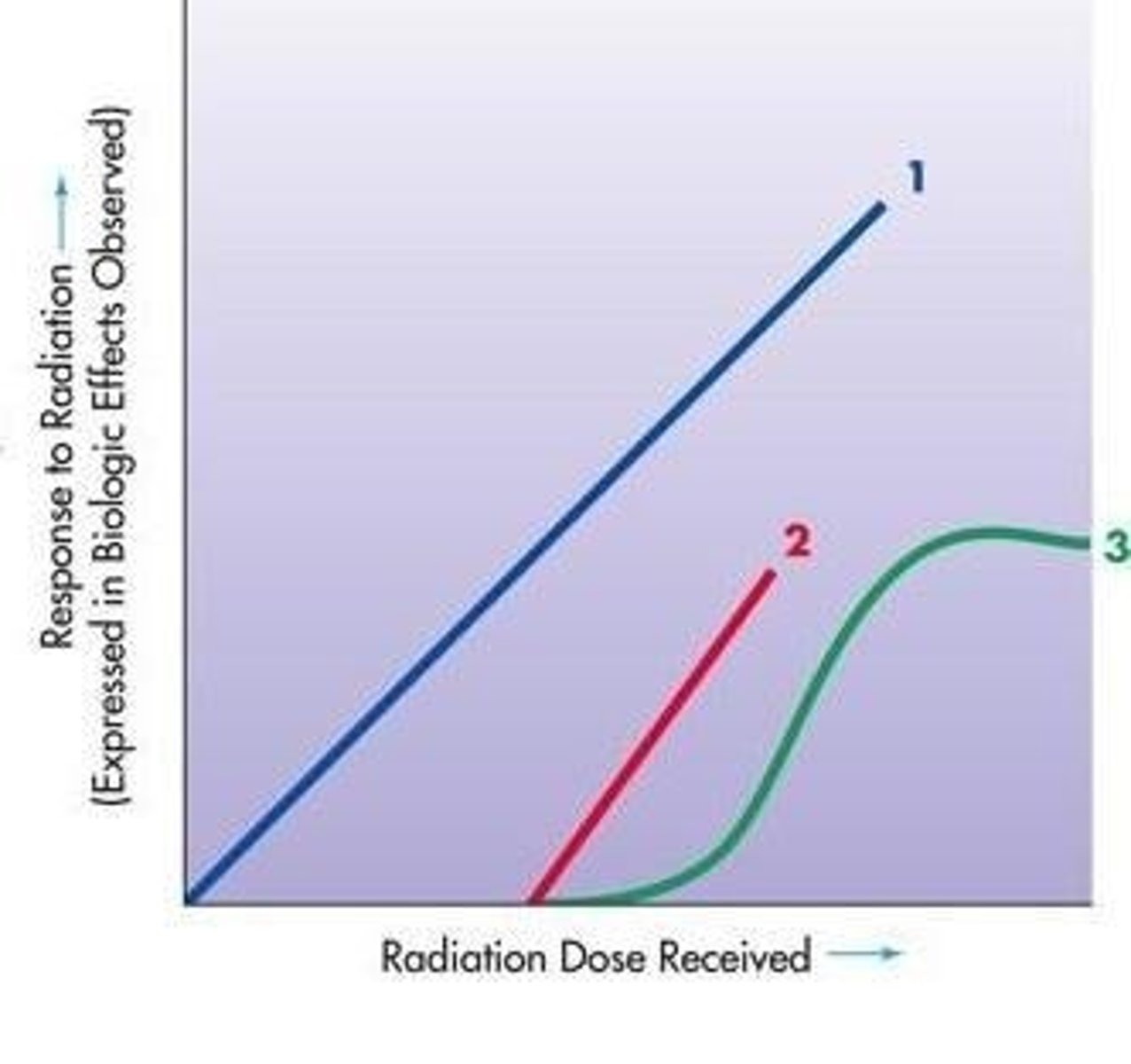
Dose response relationship
A relationship between different radiation doses and the magnitude of the observed response.
Skin Erythema
Skin reddening; also known as a radiation burn.
Desquamation
Drying and flaking of skin.
Epilation
Hair loss that may occur anywhere on the body where radiation hits.
Hematologic Depression
Early, threshold somatic whole-body effect characterized by a decrease in circulating blood cells.
Lymphocytes
White blood cells that are most sensitive to radiation.
Thrombocytes and granulocytes
Blood cells that are moderately sensitive to radiation.
Erythrocytes
Red blood cells that are least sensitive to radiation.
Cytogenetic Effects/Chromosomal Aberrations
Early, threshold somatic effect seen at the next mitosis, with changes to cells.
Acute Radiation Syndrome
Early threshold whole body somatic effect that often results in death.

Mean survival time
Time between exposure and death, which decreases with increasing dose.
Gonadal Dysfunction
Early, threshold local tissue somatic effect causing delayed menstruation or decreased sperm count.
Temporary sterility
Short-term inability to reproduce, which can occur in either sex.
Permanent sterility
Long-term inability to reproduce, which can occur in either sex.
Threshold Doses
Specific doses at which certain effects begin to manifest.
Cataracts
Late, threshold local somatic tissue effect.
Hereditary Effects
Late, non-threshold, local tissue genetic effect.
Genetic Effects
Caused by damage to sperm or egg (one cell).
Doubling Dose
The dose that produces twice the number of genetic mutations that would normally occur.
Linear Energy Transfer (LET)
The average amount of energy transferred from ionizing radiation to tissue per unit distance.
Relative Biological Effect (RBE)
A method to compare how damaging different types of radiation are, given the same dose.
RBE of Diagnostic X-ray
1
Radiation Weighting Factor (WR)
Specific for each radiation type and accounts for biological effectiveness.
Fractionation
Dose divided up into fractions with time in between.
Oxygen Effect
Radiation + oxygen = increase radiosensitivity.

Oxygen Enhancement Ratio (OER)
The difference in biological harm for each radiation type.
Tissue Weighting Factor (Wt)
Different body tissues have different radio-sensitivities relative to each other.
Exposure Area
Radiation has less effect when only part of the body is exposed vs. whole body.
Ionizing Radiation
Can cause excitation or ionization.
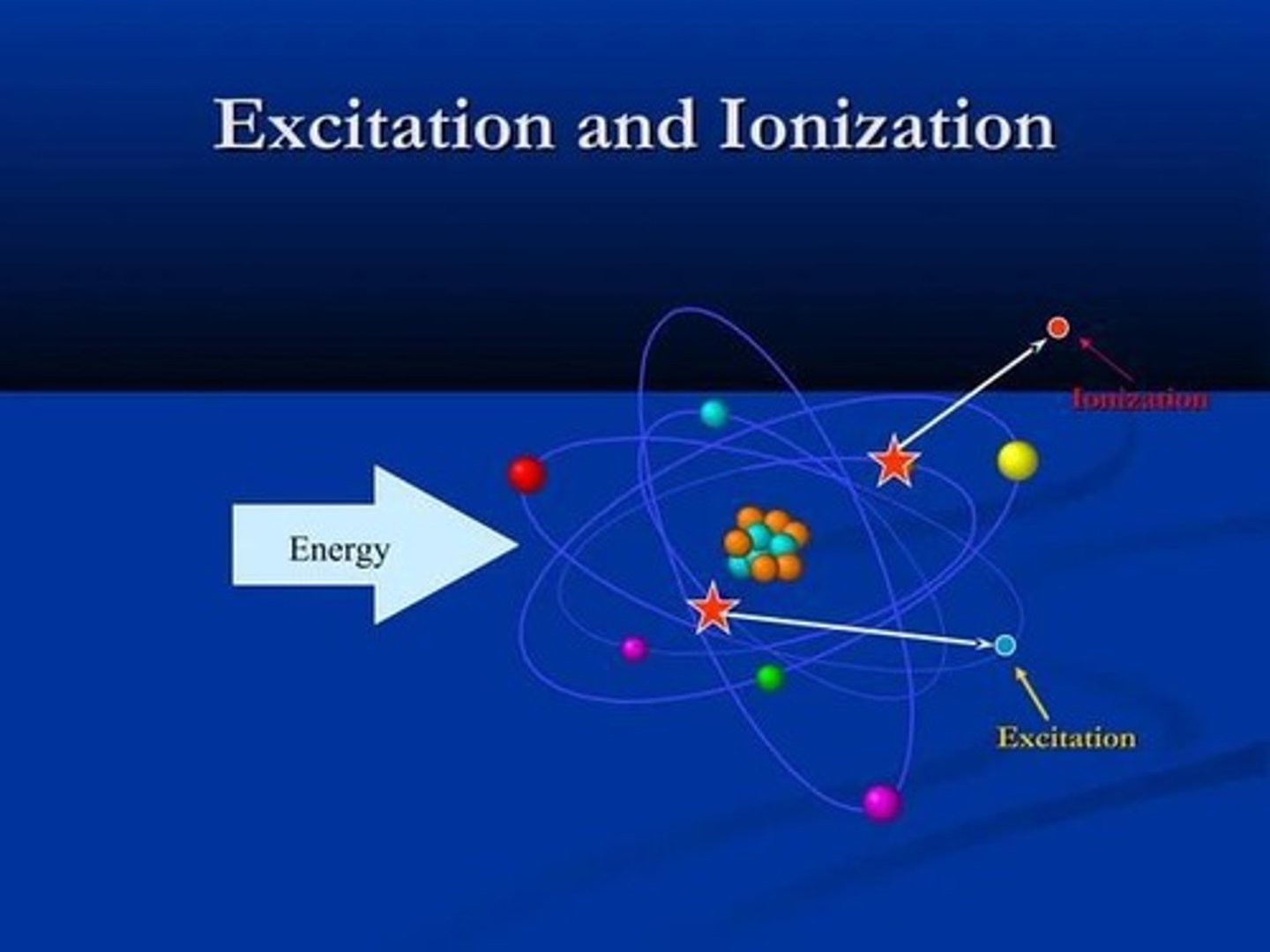
Non-Ionizing Radiation
Can cause excitation only.
Primary Radiation
Useful beam produced in x-ray tube.
Scatter Radiation
Produced in part being imaged and travels in all directions.
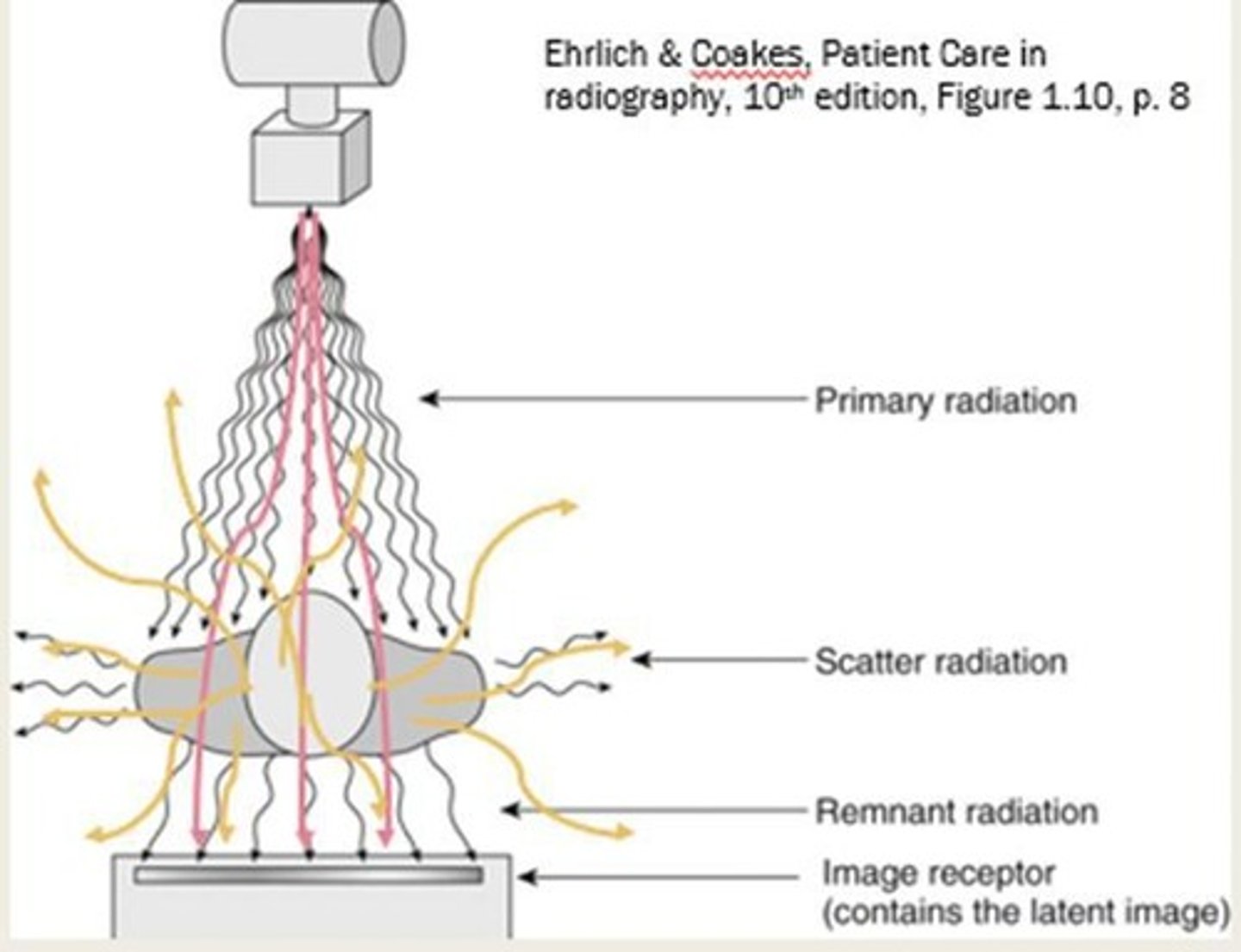
Remnant/Exit Radiation
The remainder of the x-ray beam after it passes through matter.
Radiation Hormesis
The concept that low doses of radiation may be beneficial.
Target Theory
Radiation is most harmful when it hits the critical target (DNA).
Direct and Indirect Action
The study of how ionizing radiation affects biological systems at the molecular level.
Molecular Radiobiology
Focuses on understanding the molecular mechanisms by which radiation causes damage to cells.
Cell death
One of the three principal observable effects resulting from irradiation of DNA.
Mutation
One of the three principal observable effects resulting from irradiation of DNA.
Chromosomal aberrations
One of the three principal observable effects resulting from irradiation of DNA.
Radiolysis of Water
When water interacts with radiation, water molecules dissociate into other molecular products.
Free radical
An ion or molecule that has unpaired electrons, making it highly reactive and unstable.
Tissue Radiosensitivity
The susceptibility of tissues to damage from radiation exposure.
Law of Bergonie and Tribondeau
A principle stating that radio-sensitivity increases with decreased cell maturity, decreased age of tissues or organs, increased metabolic activity, and increased proliferation rates.
Somatic Effects
Effects of radiation that affect the individual exposed, not passed to offspring.
Stochastic Effects
Effects of radiation that occur by chance and have no threshold, such as cancer.
Deterministic Effects
Effects of radiation that have a threshold and increase in severity with increased dose, such as skin burns.
Exposure
A measure of the number of ionizations in air, with units of Coulombs/Kilogram (C/kg) or Gray (Gy).
KERMA
Kinetic Energy Released in Mass, measuring the energy of ionizations in air, with units of Joules/Kilogram (J/kg) or Gray (Gy).
Air Kerma
A measure of the energy of ionizations in air, commonly used to assess scatter radiation and tube leakage.
Absorbed Dose
A measure of energy absorbed in the body, with units of Gray (Gy) or milligrays (mGy).
Equivalent Dose
Accounts for the type of radiation and its biological effect, calculated using the formula: Equivalent Dose (H) = Absorbed Dose (D) × Radiation Weighting Factor (Wᵣ).
Effective Dose
A measure used to compare biological harm based on radiation and tissue type, calculated using the formula: Effective Dose (E) = ∑(Equivalent Dose × Tissue Weighting Factor Wt).
Sievert (Sv)
The unit of measure for equivalent dose and effective dose, reflecting biological effect rather than just energy absorbed.
Milligray (mGy)
A subunit of Gray, commonly used in clinical practice to measure absorbed dose.
Still learning (27)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!