Physics 1B Movement and Position
1/64
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Scalar
A physical quantity that has a value/size (magnitude) and no direction.
Scalar - Example
Speed, Distance, Energy, Mass
Vector
A physical quantity that has a value/size (magnitude) AND direction.
Vector - Example
Velocity, Acceleration, Force, Displacement
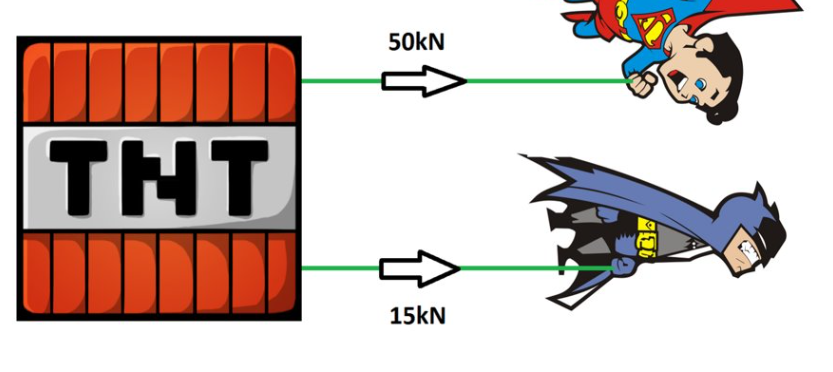
What is the resultant force?
65kN to the right
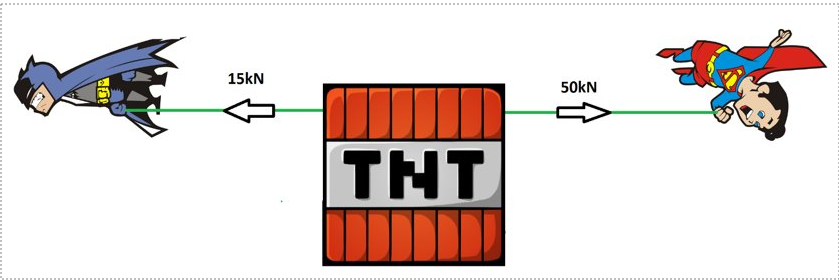
What is the resultant force?
35kN to the right
What is Newton’s first law?

Forces are measured…
in newtons (N)
If balanced forces act on an object…
they will not change the way it is moving
A force can change…
the shape of an object, or the way it’s moving
A force is…
either a push or a pull
Balanced forces…
cancel each other out
Balanced forces are the same size but…
act in opposite directions
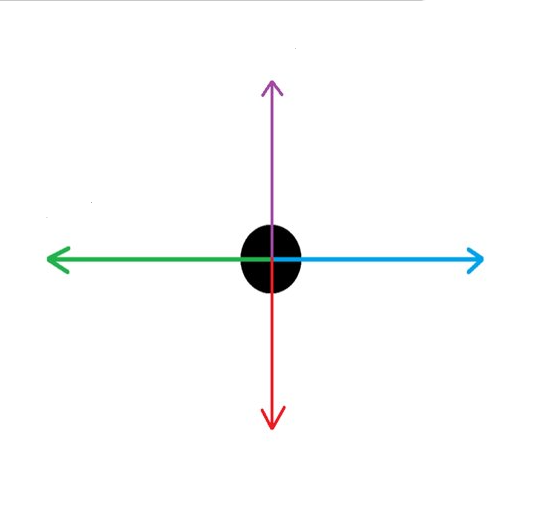
What force is the RED arrow?
Weight
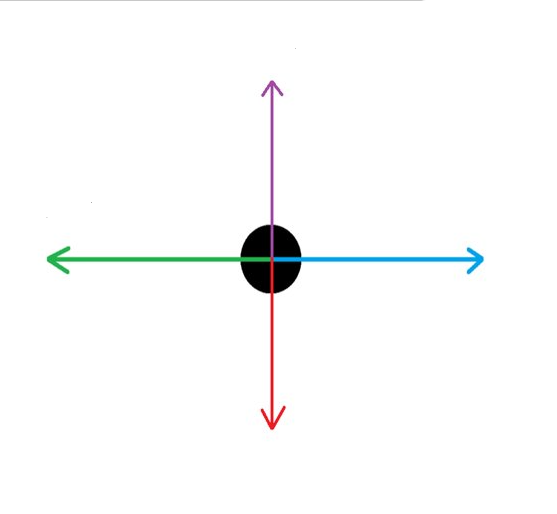
What force is the PURPLE arrow?
Reaction
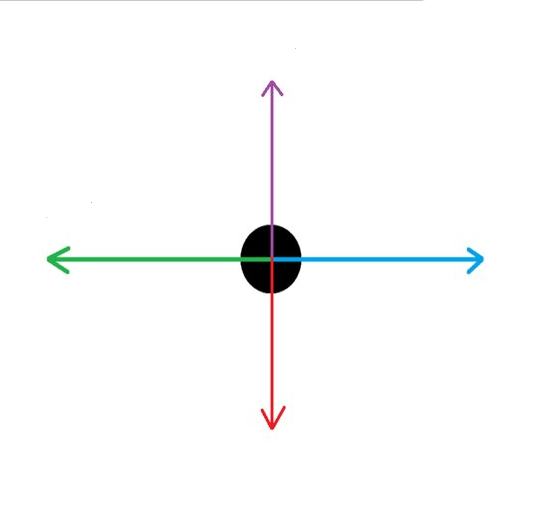
What force is the GREEN arrow?
Drag
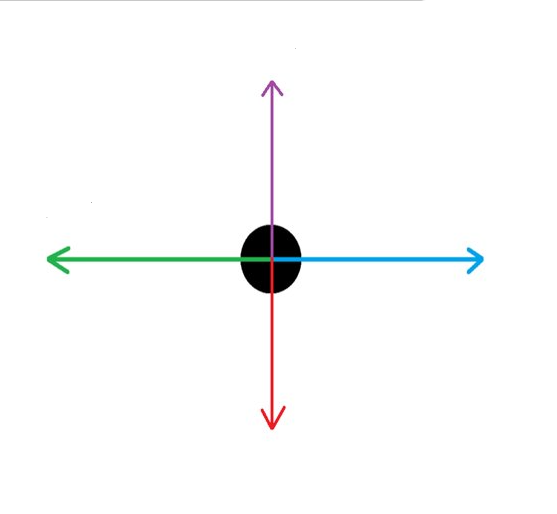
What force is the BLUE arrow?
Thrust
What is mass?
How much matter is in an object
What is the equation for Newton’s second law?
F=ma
In comparison to gravity’s acceleration, how much would you be accelerating by if you were accelerating by 1g?
10 m/s²
In comparison to gravity’s acceleration, how much would you be accelerating by if you were accelerating by 3.25g?
32.5 m/s²
In comparison to gravity’s acceleration, how much would you be accelerating by if you were accelerating by 42.1 m/s²?
4.21g
Newton’s 1st Law - At rest
An object at rest will remain at rest if the net force acting on it is zero.
Newton’s 1st law - In motion
An object in motion will continue moving at constant speed if the net force acting on it is zero.
Weight is…
A force measured in Newtons (N)
Your weight…
depends on the gravity around you
Your mass…
stays the same no matter where you are
Why would your weight be less on the Moon (compared to Earth)?
The gravitational field strength of the Moon is less than that of the Earth
Why would your mass be the same on the Moon AND the Earth
Your mass stays the same no matter where you are.
What is the relation between weight, mass and acceleration due to gravity?
Weight = mass x acceleration due to gravity
W = mg
What is Earth’s gravitational field strength?
10N/kg
If the mass of a dog is 7kg on Earth, what is the weight of the dog?
(7×10) = 70N
If the weight of scissors on Earth is 3N, what is the mass of the scissors?
(3/10) = 0.3kg = 300g
True or False - If the Earth stopped spinning we would float into space
False
True or False - Weight is measured in kg
False
True or False - There is no gravity in space because space is a vacuum
False
What are three things you must be able to do to stop quickly?
You must perceive the hazard in your path of travel.
You must react.
You must brake to a safe stop.
What are some factors that affect braking distance?
Driver’s ability/capability
Speed of the vehicle
Vehicle condition
The surface of the roadway
Hills/curvature of the road
Weight of the vehicle’s load
What is braking distance?
The distance your vehicle travels from the time you apply the brake until you stop.
Braking distance is proportional to…
x² (the square) of your speed / (speed)²
What is the distance the vehicle travels before the driver puts their foot on the brakes called?
Thinking distance.
What factors could increase the distance the vehicle travels for in this time?
Medication, Speed of vehicle, Tiredness, Awareness.
What is the relation between thinking distance, stopping distance, and braking distance?
Thinking distance = Stopping distance - Braking distance.
The braking distance is 35m for the car. If the stopping distance is 50m, how far did the car travel before the driver put their foot on the brakes?
50m - 35m = 15m
Stopping distance
The sum of thinking distance and the braking distance.
Friction
A force that the road exerts on the tyres as the car is stopping .
Thinking distance
The distance a car travels before the brakes are applied.
Braking distance
The distance a car travels whilst it is braking.
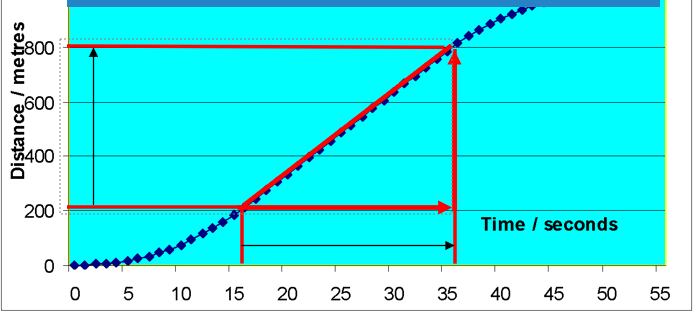
Based on the graph, what is the speed of the car
200m → 800m = 600m
15s → 35s = 20s
600m/20s = 30m/s
What is the relation between total stopping distance, thinking distance, and braking distance?
Total stopping distance = Thinking distance + braking distance
Which investigation could you carry out to measure the speed of vehicles on a road.
Measure out a known distance (preferably 100m) alongside a road.
Record the time it takes vehicles to cover the distance measured.
Use speed formula s=d/t to calculate the speeds of various different vehicles.
Measure the speed of at least 20 vehicles and then represent your data graphically.
What are some things that rely on elasticity?
Trampolines, Beds, Bungee jump, Astronaut seats.
Hooke’s law states that extension…
happens when an object increases in length.
Hooke’s law states that compression…
happens when an object decreases in length.
What is described by Hooke’s law?
The extension of an elastic object.
What does Hooke’s law state on the amount an object stretches?
The amount an object stretches is directly proportional to the amount of force applied, up to the limit of proportionality.
What is meant by the term limit of proportionality?
The point to where an object can be stretched to and able to return to its original form.
What happens if an object is stretched beyond the limit of proportionality?
The object becomes permanently deformed.
What is the relation for Hooke’s law?
Force = spring constant x extension
F = kx
What unit is the spring constant measured in?
Newtons per metre (N/m)
What is the elastic limit?
The maximum extent to which an object (spring) may be stretched without permanently changing its size or shape.
What does the gradient of a force - extension graph tell you?
The spring constant.
What is force directly proportional to?
The extension of the spring.
Non-linear extension and inelastic deformation can…
be seen above the limit of proportionality.
Linear extension and elastic deformation can…
be seen below the limit of proportionality.